人教版高中英语必修一全套教案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:207.55 KB
- 文档页数:26

人教版高中英语必修1教案5篇人教版高中英语必修1教案篇1Where’s your pen pal from?一、单元教材分析本单元的中心话题是pen pals。
主要语言功能项目是talk about countries, cities and languages。
语法结构为 Where…from; Where…live and whatlanguage…speak。
先以Activity1复习语言与国家的配对练习入手,Activity2a, 2b一个综合的听力训练来展示学生的听力能力,并以听力内容为基础,通过人教版高中英语必修1教案篇2教学目标知识与技能(1)熟练掌握下列词汇:rules, arrive, late, hall, dinning hall, listen, , fight, sorry outside,wear, important, bring, uniform, quiet(2)熟练掌握下列短语:dining hall, arrive late for school, (be) on time, listen to music break the rules, in class, be/ keep quiet, a lot of, bring …to…,weara hat, have to, music players(3)掌握下列句型:1. Dont eat in class.2. You must be on time.3. Eat in the dining hall.4. 正确使用情态动词can, can’t——Can we wear a hat in school?——Yes, we can./No, we can’t.5. 能正确使用have to 和 must 谈论规章制度We must be on time/ We also have to be quiet in the library. 教学重难点重点:1) 肯定祈使句是省略掉主语的原形动词开头;2) 否定祈使句则是在肯定祈使句前加上“don’t”。

Module I Unit 1 FriendshipTeaching PlanI. Teaching aims:1. Ability Goals:① Listening: gain useful information and clear views from the listening material;② Speaking: express one’s attitude or views about friends and friendship in appropriate words.③ Reading: let Ss summarize the main idea④ Writing: write a letter about how to make friends2. Knowledge Goals:① Talk about friends and friendsh ip; how to BE friends; how to gain friendship② Use the following expression:so do I / neither do II think it is a good ideaAll rightYes,but…③ to get the Ss to master direct speech and indirect speech④ vocabulary and phrases: upset, calm, concern, careless, loose, cheat, list, share, German, series, outdoors, crazy, purpose, thunder, entirely, power, trust, suffer, teenager, advice, quiz, editor, communicate, situation, add up, calm down, have got to, be concerned about, walk the dog, go through, hide away, set down, a series of, on purpose, so as to, face to face, according to, get along with, fall in love with, join in, be upset about, for once3. Emotion Goals:① To arise Ss’ interest in learning English;② To encourage Ss to take part in the act ivities and make Ss confident;③ To develop the ability to cooperate and communicate with others.4. Strategy Goals:① To develop Ss’ cognitive strategy: making notes when listening carefully;② To develop and improve Ss’ communicative strategies.5. Culture Goals:To enable the Ss to come to know different opinions about making friends from different countries.6. Reality Goals:① To make Ss respect each other and friendship② To make them get well with one another in society7. Teaching Time:Seven Periods.II. Teaching steps:Period 1 Warming up Step 1. warming up1. Ss listen to an English song AULD LANG SYNE.2. Brainstorming: let Ss say some words about friendship:careful, warm-hearted, honest, friendly, brave, humorous, funny, smart, kind, open-minded, responsible….3. To let Ss make a correct choice about their questions that they meet in warming up.Step 2. practice speaking1. Ss talk about their old friends in Junior Middle School, talk about their appearance, personality, hobbies, etc.2. Self-introduction or work in pairs3. Ss can ask some questions about life or learning.Step 3. Make new friends1. Ss go around and ask their new friends some information and fill in the following form name age/hobbies/favorite sports, books …2. Report to the class: who will probably be your friend why.Step 4. Do a surveySs do the survey in the text on P1Step 5. Listening and talkingDo Workbook on P41 (Talking). While Ss listen to the material, ask them to take notes about the speaker’s views of making friends.When Ss make their conversation, ask them to try to use the following expressions.I am afraid not exactly I agree I think that is a good idea of course not.Step 6. DiscussionDivide Ss four in one group and each group choose a topic to discuss. There are four topics.Topic 1: Why do you need friends? Make a list of reasons why friends are important to you.Topic 2: There is a saying “to have a good friend, you need to be a good friend.” What do you think of the saying and how can you be a good friend?Topic 3: Does a friend always have to be a person? What else can be your friend? Why?Topic 4: List some qualities of a person who does not make friend easily.Step 7. Summary1. Ask Ss themselves to summarize what is friendship and what is the most important in making friends.2. T shows more information about friendship and a poem about friendship.What is friendship?I want to find the answer to the questionWhat is friendship?When it rains, I think friendship is a small umbrella.It can give me a piece of clear sky.When I’m crying, I think friendship is a white handkerchief.It can wipe my tears dry.When I am sad, I think friendship is a warm word.It can bring me happiness again.When I am in trouble, I think friendship is a strong hand.It can help me escape my troubles.When I sit in a quiet place, I think friendship is a very wonderfulfeeling.It can’t be pulled and torn, because it is in everyone’s heart.It is there from the beginning to the end of our lives.3. Tell Ss: make new friends and keep the old; one is silver and the other is gold.Step 8. EvaluationSs finish the following evaluation form. Standard: A, B, CContents 自评他评1. I’m active in talking with others.2. I’m active i n cooperating with others.3. I can express myself fluently, accurately and appropriately.4. I know more about friendship after the lesson…5. Do you think you need to improve yourself in some ways? Which ways?Homework:1. Look up the new words and expressions in warm-up and pre-reading in a dictionary.2. Write a short passage about your best friend.Period 2 Reading Step 1. Warming upActivity 1: Suppose you have to stay indoors to hide yourself for a whole year. You can never go outdoors, otherwise you will be killed. You have no telephone, computer, or TV at home.How would you feel?What would you do?Four students a group discuss with each other for 2 minutes.Activity 2: Play a short part of the moviesStep 2. PredictingStudents read the title of the passage and observe the pictures and the outline of it to guess:Who is Anne’s best friend?What will happen in the passage?Step 3. SkimmingStudents skim the passage in 2 minutes to get the main idea:Who is Anne’s best friend?When did the story happen?Step 4. ScanningStudents work in pairs to find the information required below:Anne in World War ⅡStep 5. Intensive readingStudents work in groups of four to discuss the following open questions:1. Why did the windows stay closed?2. How did Anne feel?3. What do you think of Anne?4. Guess the meanings of “spellbound”, “ hold me entirely in their power” from the discourse(语篇,上下文).5. Which sentences attract you in the passage?Step 6. ActivityFour students a group to discuss the situation:Suppose you four have to hide yourselves for 3 months. During the three months, you will be offered the basic food, water and clothes. Your group can take 5 things with you.What will you take? Why?How will you spend the 3 months?How will you treat each other and make friends?Step 7. AssignmentTask 1. Surf the internet to find Anne’s Diary and read some of it. Print out a piece of the diary and write down your feelings after reading it on the page. We will share the pieces and your feelings with the whole class.Task 2.Ex 2.3 on Page3Period 3 Words and expressionsStep 1. Warming upCheck the Ss’ assignment: task 2Step 2. Language points:1. add (v.)1). To put together with something else so as to increase the number, size, importance, etc.增加,添加Please add something to what I’ve said, John.2). To join numbers, amount, etc so as to find the total 相加Add up these figures for me, please.add to something: to increase 增加The bad whether added to our difficultiesadd up to总计、加起来共是Having a big breakfast adds up to 112add…to…把…加到…Please add the names to your list2. Cheat v.1). To act in a dishonest way in order to win 欺骗;作弊2). (of, out of) to take from (someone) in a dishonest way 骗取The boss has cheated out of his money1). an act of cheating 作弊行为2). one who cheats 骗子3. Go through1).To examine carefully 仔细阅读或研究I went through the students’ papers last night.2).To experience 经历,遭受They went through the terrible earthquake at night4. Crazy (adj.)1). mad, foolish 疯狂的,愚蠢的It’s crazy to go out in such hot weather.2). wildly excited; very interested 狂热的,着迷的She is crazy about music5. Lonely (adj.) unhappy because of being alone or without friends 孤独的He has been very lonely since his wife left him.Lonely/alonealone1). without or separated from others单独的She lives alone.2). only 仅仅,只有。

高一英语必修一教案(优秀5篇)高一英语教案人教版篇一教学准备教学目标Teaching aims:1) Get the students to master some important words, phrases and sentence patterns.2) Enable the students to use the language points by themselves.教学重难点Teaching important points:Master the usages of “more than , come up, over, be based on, present, a/ the number of”Teaching difficult points:present: v adj教学工具课件教学过程1 Do you know that there is more than one kind of English?more than one不止一个eg:More than one girl in this school holds such a view.more than one后跟___________,作主语时,谓语动词要用______。
more than1). more than +num(数词) :overShe showed the visitors around themuseum,__________________________________________________________________________(其建造花了3年多时间) 2)more than +n: not onlyMusic is more than just a sound--- it’s a way of thin king.3) more than +adj/v : very听到这个消息我很高兴。

人教版必修一英语教案【篇一:人教版高中英语必修1~5精品教案】目录人教版高中英语必修1精品教案---2 人教版高中英语必修2精品教案---87 人教版高中英语必修3精品教案---171 人教版高中英语必修4精品教案---241 人教版高中英语必修5精品教案---308人教版高中英语必修1精品教案人教版高中英语必修1精品教案unit 1 friendshipwarming up, pre-reading and readingreading ―anne‘s best friend‖1. teaching objectives:1) to develop the students‘ reading ability, learn to use some reading strategies such as guessing, key sentences, skimming and so on;2). to get the students to realize the importance of friends and friendship, and to tell true friends from false friends;3). to grasp some useful words and expressions in this passage, such as on purpose, be crazy about etc.;4). to learn the writing style of this passage.2. teaching method: task-based teaching3. teaching procedures:1. please enjoy three pieces of music and find out what they are about.2. does a friend always have to be a person? what else can be your friend?3. what do you know about the world war ii?4. background introductionstep 2 fast reading1. who is anne?who/what was anne‘s best friend?when and where did the story happen?1. answer the following questions:ade her diary her best friend?what is an ordinary diary like according to anne? what about her diary?why was she so crazy about things to do with nature?why did she stay awake on purpose until very late one evening?why didn‘t she dare open the window when the moon was too bright?how do you understand the expressions ―spellbound‖and ―held me entirely in their powder‖?2. reading to summarise the main idea of each paragraph.skim the text and summarise the main idea of each paragraph in one sentence.four students a group to discuss the situation:suppose you four have to hide yourselves for 3 months. during the three months, you will be offered the basic food, water and clothes. your group can take 5 things with you.what will you take? why?how will you spend the 3 months?how will you treat each other and make friends ?step 6. homework1. review the important words, phrases and difficult sentences in the text and make sentences using the words given by the teacher.2. finish ex.1-3 on p4.unit 1 friendshipvocabulary and useful expressionslearning about languageteaching aims:1. to discover and learn to use some words and expressions.2. to enable students to rewrite sentences using direct or indirect speech3. to learn more information about anne.4. to cultivate the spirit of cooperation, self-teaching and self-exploring.teaching procedures:step 1 revision1. review something about ―anne‘s best friend‖ by using some true-or-false sentences1) a friend would laugh at you. f2) anne lived in amsterdam in the netherlands during world war ii. t3) she and her family hid away for one year before they were discovered. f5) she was fond of nature. t2. collect the sentences students think wonderful or difficult to understand.sample sentences1) she and her family hid away for nearly twenty-five months before they were discovered.2) i wonder if it‘s because i haven‘t been able to be outdoors for so long that i‘ve grown so crazy about everything to dowith nature.3) there was a time when a deep blue sky, the song of the birds, moonlight and flowers could never have kept me spellbound.4) the dark, rainy evening ,the wind, the thundering clouds held me entirely in their power.5) it was the first time in a year and a half that i‘d seen the night face to face.step 2 language points1. grow crazy about sth.对…狂热,痴迷be crazy about …eg. my cousin grows crazy about computer games.2. go through1). to examine carefully 仔细阅读或研究i went through the students‘ papers last night.2). to experience 经历,遭受或忍受you really don‘t know what we went through while working on this project.3.stay v. to continue to be in a particular state or situatioin系动词,表是状态。

新课标人教版高中英语必修一全部教学案一、教学目标1. 通过研究本单元的教学内容,帮助学生掌握必修一中的英语知识和技能。
2. 培养学生的英语听、说、读、写的综合能力。
3. 培养学生的团队合作意识和自主研究能力。
二、教学内容教学内容包括以下几个方面:1. 语法:复和巩固现在时态、过去时态、将来时态等基本语法知识。
2. 词汇:通过阅读和听力练,掌握本单元中的重点词汇和短语。
3. 阅读:通过阅读文本和相关的阅读理解题目,培养学生的阅读理解能力。
4. 听力:通过听对话和听文章练,提高学生的听力能力和听觉理解能力。
5. 口语:通过各种口语练,提高学生的口语表达能力。
三、教学方法1. 任务型教学法:通过让学生完成一系列任务,激发学生的研究兴趣,加强学生的实际运用能力。
2. 合作研究法:引导学生在小组内进行合作研究,促进学生之间的互动和交流。
3. 归纳法:通过教师引导和学生参与,将教学内容进行总结和归纳,提高学生的研究效果。
四、教学步骤1. 导入:通过引入生活例子或相关资料,唤起学生对新学知识的兴趣。
2. 语法讲解:教师通过讲解和示范,介绍本单元的语法知识。
3. 词汇研究:通过词汇游戏和词汇练,帮助学生记忆和掌握本单元的重点词汇。
4. 阅读训练:教师通过指导学生阅读文本和做阅读理解题目,提高学生的阅读理解能力。
5. 听力训练:教师播放相关听力材料,学生进行听力训练和听觉理解练。
6. 口语练:教师引导学生进行口语练,提高学生的口语表达能力。
7. 总结归纳:教师对本节课的教学内容进行总结和归纳。
8. 作业布置:教师布置相应的作业,巩固学生对本节课的研究。
五、教学评价1. 教师根据学生的课堂表现、作业完成情况和考试成绩等,进行教学评价。
2. 学生之间进行互评,促进学生之间的交流和研究成长。
六、教学资源1. 教材:新课标人教版高中英语必修一教材。
2. 多媒体设备:投影仪、电脑、音响设备等。
3. 课外资料:相关的练册、参考书和教育软件等。

人教版高中英语必修一全册教案设计人教版高中英语必修一全册名师教案设计Unit One FriendshipTeaching goals语言知识1.to talk about friends and friendship, and interpersonal relationship2.to practise expressing attitudes, agreement and disagreement, and certainty3.to master some sentences about giving advice4.to learn to use the Direct Speech and Indirect Speech(1): statements and questions5.to learn about communication skills语言技能和学习策略1.to develop listening skills by doing exercises in listening task2.to develop speaking skills by finishing the speaking task and other activities likediscussion and oral practice3.to develop reading skills through the reading materials in this unit4.to learn to write a letter of advice文化意识1.to know about friend and the real meaning of friend2.to learn how to get along with others情感态度1.to arouse the interest in learning English2.to learn to express their feeling of friends and friendshipTeaching key points:1.how to improve students’ speaking and cooperating abilities2.learn to use the Direct Speech and Indirect Speech(1):statements and questions3.master some words and expressionsTeaching difficult points:1.train the students’ speaking, listening, reading and writing abilities2.how to improve students’ cooperating abilitiesTeaching methods:Student-focus approach and task-based approachLearning methods:Cooperative studyTeaching aids:Computer词汇教学:1. survey n. 调查;测验;测量;检查;鉴定They were pleased with their wild survey of his work.他们广泛审查了他的工作,很满意。
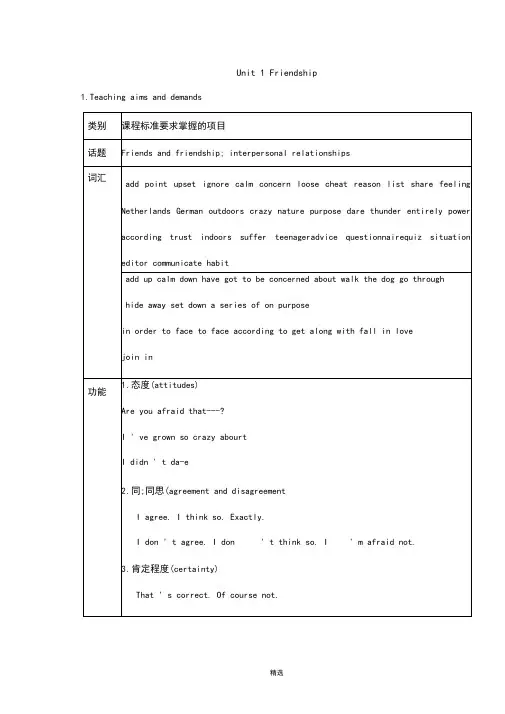
Unit 1 Friendship 1.Teaching aims and demands语法直接引语和间接引语(1):陈述句和疑问句陈述句“I don ' want to set down a series of facts in a diary.Said Anne.-- Anne said that shedidn ' Want to set down a series of facts in a diary.一般疑问句He asked Are you leaving tonigh?”---He asked us whether we were leaving that night.特殊疑问句“ When did you go to b edast nigh?” fathe said to Anne.---Father asked Anne when she went to bed the night before.1)Suggested teaching notes2). Analyses of the teaching contentsThis unit is about friendship, and nearly all the teaching materials center on it.Warming up---The questionnaire leads students to think and talk about friendship, get to know the problems between friends and seek solutions, which makes preparations forthe further teaching in topics, background and vocabulary.Pre-reading---The questions prompt students to think critically about friends and friendship in reality, alerting them to the fact that besides people, a diary can be afriend, too.Reading--- The diary by the Jewish girl Anne gave a glimpse of her life during her family ' s shelter in Amsterdam from the GermanNazis ’ lkliing in world war 2. she treats the diary as her best friend, and init revealsher longing for a normal life and close contact with nature, which helpsher get through the days.Comprehending---It helps students further understand the text by doing multiple choices, questions and answers, and matching.Learning about language---It teaches the important expressionsand structures andgrammar: direct and indirect speeches.Using language---The two letters, listening, questionnaire design, letter writing and fun writing prepares students to further talk about friendship, especiallythe problems with misunderstanding, and unfriendliness, thusstrengthening students ’ abilities to practice language, discover, and solveproblems.Summing up---It summarizes the whole contents of this unit from the aspects of topics, vocabulary and grammar.Learning tip--- This part encourages students to form the habit of writing a diary.Integrating skills--- The text introduces the way Hawaiians express friendship, to get students to realize the cultural differences in the values of friendship in additionits importance in all cultures.3)Making of the teaching planThis unit centers on friends and friendship, exploring different types of friendshipwith particular attention to that one can develop with oneself, i.e., the comfort andsupport one seeks from an imaginary friend. Students are expected to come to be trulyaware of the qualities and conducts that make a good friend, display and develop the ability to cope with misunderstanding, conflicts and problems related to friendship, and give advice on it. The concept that even an ordinary thing can be a friend should break down the traditional belief in the interpersonal nature of friendship. Also, the comparison of similarities dissimilarities in friendship comprehension between the East and the West leads students to know better the values of friendship in Westerns eyes. All in all, this unit promises to unveil the true essence of friendship and helps students to lead a more friendly and harmonious life. Thus, based on the theme, contents and teaching objectives, the whole teaching procedures can fall into five periods as follows:4)Teaching plans for each periodPeriod 1 Warming-up and Speaking1.Teaching objectives:1)Target languageI (don ' t) think ...... I (don ' t) think so. I (don ' t) agree.I believe ............. That ' s correct. In my opinion, ••2)Ability goalsa.Describe your friends in Englishb.Figure out the problems between friends and then find different ways to solve theproblems.3)Learning ability goalsa.To encourage students to think and talk about friends and friendship by using somephrases and structures.b.To learn to solve problems that may occur between friends.c.To cultivate the students to form the good habit of learning English in Senior MiddleSchool.2.Teaching important points:e the given adjectives and sentence structures to describe one of your friends.b.Learn to evaluate friends and friendship.3.Teaching difficult points:a.Work together with partners and describe one of your good friends.b.Discuss with partners and find out ways to solve the problems.4.Teaching methodsa.Task-based teaching and learningb.Cooperative learningc.Discussion5.Teaching aids:CAI6.Teaching procedures and ways:Step 1 Lead-in and Warming-upBefore the lesson, the teacher can arousethe students ’interests by showing a video of Auld Lang Syne.At the beginning of the first class, we can get the students to talk about their summer holidays. The students can talk freely as they like.1.How did you spend your summer holidays? How did you feel? What did you do inyour summer holidays? What did you do in your spare time?2.What do you think of our new school? Do you like it? Could you say somethingabout it?3.Do you like making friends? How do get in touch with your friends? Do you havemany friends? Where are they now? Do you have any old friends in our school?Have you made any new friends in our class?Step 2 Think it over1.Give a brief description of one of your friends. The following phrases and structuresmay be helpful:His/Her name is .........He /She is ....... years old.He / She likes ....... and dislikes .......He /She enjoys ......... and hates .....He /She is very kind/friendly/ ...When /Where we got to know each other.2.What types of friendship do you have?Pleasetick them out. Then fill in the blanks.girl friends boy friends pen friendslong -distance friends friends of the same agee-friends (friends over the internet) friends across generations unusual friends like animals, books ...1). _____is /are most important to you.2). You spend most of your free time with .3). You will share your secrets with .4). When in trouble, you will first turn to .Step 3 Make a survey1. List some qualities of a good friend or your ideal friend. Have the students get into groups of four to find out what each has listed.Tell your partner your standards of good friends by using the following structure:I think a good friend should (not) be ...In my opinion, a good friend is someone who ...1.Have a member of each group report on what their lists have in common and list them on theboard.2.Ask the class whether or not they agree with all the qualities listed.3.Then have the students do the survey in the textbook.4.Have the students score their survey according to the scoring sheet on page 8.5.The teacher ask some students how many points they got for the survey and assesstheir values of friendship:★4~7 points: You are not a good friend. You either neglect your friendor just do what he/she wants you to do. You should think more about what a good friend needsto do.★8~12 points: You are a good friend but you sometimeslet your friendship become too important, or you fail to show enough concern for your friend feelings. Try to strike a balance between your friend ' needs and your own responsibilities.★13+ points: You are an excellent friend who recognizes that to be a good friend you need balance your needs and your friend ' s. Well done.(You may also show your students the results above and let themselves self-reflect upon their own values of friendship)Step 4 Talking and sharing (work in pairs)1.If your best friend does something wrong, what will you do?Try to use the following phrases:I (don ' t) think ...... I (don ' t) think so.I (don ' t) agree. I believe ............That ' s correct. In my opinion, ........2.A British newspaper once offered a prize for the best definition(义)of a friend. If youwere the editor, choose the best one from the following entries保目),and explain why.One who understands my silence.A friend in need is a friend indeed.Friends are just the people who share your happiness and sorrow. When you look at your watch at 4 am, but still know you can call them and wake them up, and they still want to talk to you, that friendship. To' have a friend, you need to be a good friend.Step 5 Group work (output)The teacher can give each group one of these questions below to talk about. Then let the class sharetheir ideas. It ' better to stimulate the students to expresstheir own opinions about these questions.1.Do you think it is a good idea to borrow money from your friend?Why and Why not?2.What factors may cause the breakdown of a good friendship?3.What can be your unusual friend besides human beings? And why?Step 6 Homework1.Write down a short passage about your ideas /the factors/your unusual friends.2.Prepare for the new lesson.Period 2 Reading Anne ’ s Best Friend1.Teaching objectives:1)To develop the students r’ eading ability, learn to use some reading strategies such asguessing, key sentences, skimming and so on;2). To get the students to realize the importance of friends and friendship, and to telltrue friends from false friends;3). To grasp some useful words and expressions in this passage, such as on purpose, be crazyabout etc.;4). To learn the writing style of this passage.2.Teaching method: Task-based teaching3). Teaching procedure:Step 1.Pre-reading1.Please enjoy three pieces of music and find out what they are about.2..Why do you think friends are important to you?3.What do you think a good friend should be like? List the good qualities a good friendshould have.4.Have you ever considered making friends with animals, plants or even an object?Why or why not?Step 2.Reading1.Try to guess what Anne ’ s friend is and what the passage is about by reading the titleand having a quick at the pictures in this passage without reading it.2.Skimming the first two paragraphs to confirm your guessing.1)What was Anne ’ s best friend? Why did she make friends with it?2)Did she have any other true friends then? Why?3)What is the difference between Anne ’ s diary and those of most people?4)Do you keep a diary? What do you think most people set down in their diaries?5)We are going to read one of Anne ’ s diaries .but before reading ,can you tell me what the diary is about with the help of one key sentence in the 2nd paragraph?3.Reading of Anne ’ s diaryHow she felt in the hiding placeTwo examples to show her feelings thenStep 3.Post-reading1.What would you miss most if you went into hiding like Anne and her family? Giveyour reasons.2.Group workWork in groups to decide what you would do if your family were going to be killedjust because they did something the Emperor did not like.Where would you plan to hide?How would you arrange to get food given to you every day?What would you do to pass the time?3.Discovering useful words and expressionsComplete the following sentences, using words and expressions from Reading1)She has grown ________ about computer games.2)Was it an accident or did David do it on ___ ?3)From the beginning ,Paul made it clear that he would be ____ (完全地)incontrol.4)He used to work ______ even in the middle of winter.5)Just the _____ of more food made her feel sick.6)You had better have a ________ talk with him.7)Born in a poor family, the manager _______ lots of hardships in his childhood.8)A diary is often kept to _____ what happenins people ’ s daily lives.Step 4.Talking about friends and friendship1.T here are many proverbs about friends and friendship. Choose the one you agree with and explain why, then choose one you disagree with and explain why.A friend in need is a friend indeed.Friends are like wine; the older, the better.A friend to all is a friend to none.The same man cannot be both friend and flatterer僦奉承者).False friends are worse than open enemies.Walking with a friend in the dark is better than walking alone in the light.2.W e have talked about friends and friendship today, can you write one or two sentences to express your understanding of friends and friendship.Step 5.Homework:1.I nterview a high school student, a businessman, a police officer and a housewife to findout their opinions about friends and friendship. Write a report to share itwith the whole class.2.Describe one of your best friends following the writing style of this passage.Ending: Let ’ s sing this song about friends togetherPeriod 3 Grammar1..Teaching objectivesLearn to use direct speech and indirect speech2.Teaching important pointSummarize the rules of Direct Speech and Indirect Speech.3.Teaching difficult pointLearn about the special cases in which the tenses shouldn ed. ’ t be chang4.Teaching methodsDiscussing, summarizing and practicing.5.Teaching proceduresStep1 Lead inT: In the last lesson, we learned Anne Frank ’ s story. She is telling herstories to twher friends—you and Tom. Tom has something wrong with his ears, so you have to repeat Anne ’ s sentences, using indirect speech. Sometimes you explain Tom sentences to Anne.“I have to stay in the hiding place." said Anne. —Anne said she had to stay in the hiding place.“ Do you feel sad when you are not able to go outdoors? ” Tom asked Anne.Tom asked Anne if/whether she felt sad when she was not able to go outdoors.I don ’ t want to set down a series of facts in a diary, said Anne.Anne said that she didn ’ t want to set down a series of facts in a diary.“What do you call your diary?” Tom asked. —Tom asked what she called her diary.Ss go on this topic by themselves.Step 2 GrammarT: Now let ’ s look at these sentences again. If we want to change Direct Speech into Indirect Speech, what should be changed?Ss discuss by themselves.Ss: sentence structures, tenses, pronouns, adverbials of time and place and verbs should be changed.T: Quite right. Look at the form on the screen. These are the rules.直接引语变成间接引语时,要注意以下几点:人称变化、时态变化、宾语从句要用陈述句语序。

人教版高中英语必修1教案教案标题:人教版高中英语必修1教案教学目标:1. 通过本单元的学习,学生能够掌握必修1单元中的词汇、句型和语法知识。
2. 培养学生的听、说、读、写的能力,提高他们的英语综合运用能力。
3. 培养学生的自主学习和合作学习能力,激发他们对英语学习的兴趣。
教学重点:1. 学习并掌握本单元的词汇和句型。
2. 进行听力和口语训练,提高学生的听说能力。
3. 进行阅读和写作训练,提高学生的阅读和写作能力。
教学难点:1. 学习并掌握本单元的语法知识。
2. 进行听力和口语训练,提高学生的听说能力。
3. 进行阅读和写作训练,提高学生的阅读和写作能力。
教学准备:1. 教材:人教版高中英语必修1教材。
2. 多媒体设备:投影仪、电脑等。
3. 教具:单词卡片、图片等。
教学过程:Step 1:导入新课(5分钟)通过引入一幅有关本单元话题的图片或一个与话题相关的问题,引起学生的兴趣,激发他们的学习欲望。
Step 2:词汇和句型学习(15分钟)1. 呈现本单元的重点词汇和句型,通过图片、单词卡片等多种方式进行词汇和句型的学习。
2. 利用课堂互动,让学生进行词汇和句型的操练和运用。
Step 3:听力和口语训练(20分钟)1. 播放相关听力材料,要求学生仔细听,并回答相关问题。
2. 分组进行口语训练,让学生运用所学词汇和句型进行对话练习。
Step 4:阅读和写作训练(20分钟)1. 学生阅读本单元的相关文章,理解文章内容,并回答相关问题。
2. 学生根据所学内容,完成相关写作任务,如写一篇关于旅行的短文。
Step 5:语法知识学习(15分钟)1. 呈现本单元的语法知识,通过示例和练习的方式进行讲解。
2. 让学生进行语法知识的操练和运用。
Step 6:课堂小结和作业布置(5分钟)对本节课的学习内容进行小结,并布置相关的课后作业,如完成课后习题或写一篇关于旅行的短文。
教学反思:通过本节课的教学,学生能够在听、说、读、写各方面得到全面的训练,提高他们的英语综合运用能力。

2024年高中英语新课标人教版精彩教案必修一一、教学内容本节课选自2024年高中英语新课标人教版必修一,第三章“English Around the World”,具体内容包括:3.1 Introductionto Different English Accents,3.2 Understanding British English and American English,3.3 The Influence of English on Global Communication。
二、教学目标1. 了解世界各地的英语口音,提高学生的英语听力水平。
2. 掌握英式英语和美式英语的基本差异,提高学生的英语表达能力。
3. 认识到英语在全球交流中的重要性,激发学生学习英语的兴趣。
三、教学难点与重点1. 教学难点:英式英语和美式英语的发音差异,以及英语在全球交流中的作用。
2. 教学重点:培养学生对不同英语口音的辨识能力,提高学生的英语沟通能力。
四、教具与学具准备1. 教具:录音机、投影仪、PPT、视频资料。
2. 学具:教材、笔记本、字典。
五、教学过程1. 导入:播放一段关于世界各地英语口音的视频,引导学生关注英语的多样性。
2. 新课内容展示:通过PPT展示英式英语和美式英语的基本差异,讲解英语在全球交流中的重要性。
3. 实践情景引入:分组让学生模仿不同英语口音,进行角色扮演,提高学生的听说能力。
4. 例题讲解:讲解教材中的典型例题,引导学生掌握英式英语和美式英语的发音规律。
5. 随堂练习:让学生进行英式英语和美式英语的发音对比练习,提高辨识能力。
六、板书设计1. English Around the World2. 内容:Different English AccentsBritish English vs American EnglishThe Influence of English on Global Communication七、作业设计1. 作业题目:(1)听录音,分辨出英式英语和美式英语,并记录下来。

Unit 1 Friendship I.单元教学目标II.目标语言III. 教材分析和教材重组1. 教材分析本单元以Friend和Friendship为话题,旨在通过单元教学使学生通过讨论什么是好朋友,什么是真正的友谊,如何交友和保持友谊等问题,使学生树立正确的交友观。
并针对日常交友过程中经常遇到的实际问题,指导学生发表自己的见解和看法,通过进一步讨论提供有效的解决方案。
并能就此以编辑的身份写出指导信,对相关谚语写出观点明确、论证有力的短文。
1.1 Warming Up以调查问卷的形式,通过对学生在日常交友过程中所遇到的五个问题,展开调查,使学生对是否擅长交友做出评价,激发学生对本单元的中心话题产生兴趣;同时也使教师本单元的授课更具有针对性,从而有效地帮助学生树立正确的交友观。
1.2 Pre-Reading通过四个问题引导学生讨论交友的重要性以及自己心目中好朋友的概念和标准,并使学生认识到不仅人与人,人与物(如日记)也可以成为好朋友。
继续探究并树立正确交友观,并为阅读作好了准备。
1.3 Reading讲述第二次世界大战的纳粹统治时期,犹太人Anne一家过着滇沛流漓,与世隔绝的生活。
Anne在孤独中只能以日记Kitty 为友,倾诉衷肠,伴其渡过两年的逃亡生涯。
控诉了纳粹党的残暴统治给犹太人民带来了深重的灾难,并以日记的形式表达了以主人公Anne为代表的全世界人民憎恨战争渴望和平的共同心愿。
学生学习了新的词汇、句型,提高了阅读水平。
文中选用了主人公的一篇日记,使学生进一步感受到了挚友的可贵,对主人公内心世界的描写有了更深刻的理解。
1.4 Comprehension 设计了三种题型。
其中前两个是考查学生对READING文章细节内容的理解,最后一题是开放性问题,学生可以在更深入理解主人公内心世界的基础上各抒己见,使学生养成勤于思考勇于探究的良好的学习习惯,现时也培养了学生的想象力,进一步提高了阅读水平。

人教版新课标高中英语必修1全套教案(62页)部门: xxx时间: xxx制作人:xxx整理范文,仅供参考,勿作商业用途Unit 1 Friendship(1)课题:Friendship教材分析与学生分析:本单元的中心话题是“友谊”,几乎所有的内容都是围绕这一中心话题展开的。
Warming Up部分以调查问卷的形式引导学生了解日常生活中朋友之间发生的真实问题以及解决这些问题的方法;Pre-Reading 部分的几个问题启发学生对“友谊”和“朋友”进行思考,使学生明确不仅人与人之间可以做朋友,日记也可以成为人们的朋友;Reading部分Anne’sBest Friend以日记形式讲述了犹太女孩安妮的故事;Comprehending部分通过连句、多项选择和问答形式帮助学生对课文内容、细节进行更深入的理解;Using about Language 部分教案本课重点词汇和重点语法工程。
b5E2RGbCAP (3> 课时安排:The first period: Speaking: Warming Up and Pre-Readingp1EanqFDPwThe second period: ReadingThe third period: GrammarThe forth Period:ListeningThe fifth period: Writing(4>教案目标:知识与技能:Talk about friends and friendship; Practise talkingabout agreement and disagreement, giving advice and makingdecisions; Use direct speech and indirect speech; Learn to writean essay to express and support an opinion.DXDiTa9E3d过程与方法:本单元在读前阶段就提出问题,让学生思考是不是只有人与人之间才能交朋友,然后在阅读中通过安妮的日记向学生说明我们也可以与动物及无生命的日记交朋友。
2024年人教版高一英语必修一教案一、教学目标知识与技能:学生能够掌握本单元的核心词汇和短语,并能够在上下文中准确运用。
学生能够理解和运用本单元所学的重点语法结构,如现在完成时、直接引语和间接引语等。
学生能够读懂本单元的课文,并理解其中的主要内容和深层含义。
过程与方法:培养学生通过上下文推测词义的能力。
引导学生通过小组讨论和合作学习,提高解决问题的能力。
鼓励学生通过写作练习,巩固和拓展所学知识。
情感、态度和价值观:激发学生对英语学习的兴趣和热情。
培养学生的跨文化意识和国际视野。
引导学生形成积极向上的学习态度和人生观。
二、教学重点和难点教学重点:核心词汇和短语的掌握。
重点语法结构的理解和运用。
课文内容的理解和分析。
教学难点:现在完成时态的正确使用。
直接引语和间接引语的转换。
英语阅读理解的深入分析。
三、教学过程导入新课:通过展示与课文内容相关的图片或视频,激发学生的学习兴趣。
提问学生关于图片或视频的问题,引导学生用英语进行回答,为新课做铺垫。
简要介绍本课的学习目标和重点,让学生明确学习任务。
词汇学习:呈现本课的重点词汇和短语,通过例句让学生理解其含义和用法。
组织学生进行词汇记忆游戏或竞赛,巩固所学词汇。
引导学生通过上下文推测词义,提高词汇运用能力。
语法讲解与练习:详细讲解本课的重点语法结构,如现在完成时、直接引语和间接引语等。
通过例句和练习让学生熟悉语法规则,并能够在实际语境中运用。
组织学生进行小组讨论,解决语法练习中的疑难问题。
课文学习:让学生快速阅读课文,了解大意。
分段讲解课文,解释重点和难点句子。
组织学生讨论课文内容,提炼中心思想,理解作者的观点和态度。
综合运用:设计一些综合性的练习,如完形填空、阅读理解等,检验学生对本课内容的掌握情况。
鼓励学生用英语复述课文,提高他们的口头表达能力。
组织学生编写与本课主题相关的短文或对话,培养他们的写作能力。
四、教学方法和手段教学方法:采用任务型教学法,让学生在完成任务的过程中主动学习和探索。
人教版高中英语必修1全册教案一、教学目标本教案旨在帮助学生达到以下教学目标:1. 掌握必修1全册的英语单词、词组和句型;2. 培养学生的听、说、读、写的综合语言能力;3. 培养学生的跨学科研究能力,通过阅读、听力和讨论提高学生的综合素养;4. 培养学生的研究策略,教会他们如何有效地研究和使用英语。
二、教学内容本教案包括必修1全册的以下内容:1. 单元一:Greeting and Introduction2. 单元二:Time and Daily Routines3. 单元三:Hobbies and Leisure Activities4. 单元四:School Life5. 单元五:Family and Relationships6. 单元六:Travel and Holidays每个单元的教学内容包括听、说、读、写的综合练,以及文化背景和研究策略的介绍。
三、教学方法本教案采用以下教学方法:1. 任务型教学:通过给学生一些具体任务,培养他们自主研究和合作研究的能力;2. 情境教学:将研究内容置于真实的生活情境中,帮助学生理解和使用英语;3. 多媒体教学:结合多媒体资源,提供丰富的听力、口语和阅读材料,激发学生的研究兴趣;4. 提问引导:通过提问引导学生思考和表达,激发他们的研究动力;5. 小组合作:鼓励学生进行小组讨论、合作研究,提高他们的沟通和合作能力。
四、教学评估本教案将通过以下方式进行教学评估:1. 课堂表现:观察学生在课堂上的参与程度、口语表达能力等;2. 书面作业:布置书面作业,检查学生对教学内容的理解和掌握程度;3. 小组项目:布置小组项目,评估学生的合作能力和综合运用能力;4. 课堂测验:定期进行课堂测验,测试学生的听力、阅读和写作能力。
五、教学资源本教案所需的教学资源包括:1. 教科书:人教版高中英语必修1全册;2. 多媒体资源:包括录音、视频和网络资源;3. 手机、平板电脑等电子设备:用于学生查阅和使用研究资源。
人教版高中英语必修全册教案-新人教版高中英语必修一教案Unit 1 Women of achievement1.Target languagea. achieve, achievement, condition, welfare, institute, connection, campaign, organization, entertainment, inspire, support, devote ... tob. Watching a family of chimps wake up is our first activity of the day. P2 Everybody sits and waits while the animals in the group begin to wake up and move. P2But the evening makes it all worthwhile. P2... we see them go to sleep together in their nest for the night. P22.Ability goalsa. Learn Warming Up, and know how to tell the great women and the famous women.b. Learn the way to describe a person from what the person did, what she/he looks like and so on.3.Learning ability goalsTeach Ss how to describe a person.Teaching important pointsa. By reading A protector of African wildlife, students can learn from Jane Goodall in at least two aspects:b. Ask students to answer these questions:1) What made her a great success?2) What should we learn from Jane Goodall?Teaching difficult pointsLet everyone believe that all of us can become Jane Goodall.Teaching methodsInspiration, Questioning and Discussion.Teaching aidsA computer, a projector and a recorder.The first period readingProceduresStep I. Warming upWarming up by describingGood morning, class. Today we are going to read about A PROTECTOR OF AFRICAN WILDLIFE. But first, I’d like to know if you have ever heard of women like Elizabeth Fry,Soong Chingling, Jane Goodall, Jody Williams, Joan of Arc and Lin Qiaozhi. Now turn to page 1, look at the photos, read the captions and describe to your neighbor the women in focus. Who is she? What is she? What did she do to benefit the world?Warming up by discussingHi, every one. How did you spend your winter vacation? Did you read any books? Did you read any women of achievement? What makes a woman of achievement? Now in pairs discuss the women on page one. Which of these women do you think is a great woman? Give reasons for your choice.Warming up by reading aloud and translatingNice to see you back at school, boys and girls. As you have all prepared lessons before class I shall ask six of you at random to read aloud and translate the captions under the photos on page one. Zhao Yanfei, would you try reading aloud and translating the first caption?Well done! Next let’s have Ju Xiaohong do the second one.Step II. Pre-reading1.Looking and sayingWork in pairs. Look at the photos and the title A PROTECTOR OF AFRICAN WILDLIFE and predict the contents of the text. Whenyou are ready, join another pair and compare your predictions and the clues that helped you to make the predictions.(Key: From the photos and title I guess that the text tells about a woman scientist who is working in Africa to protect the wildlife there. She studies a family of chimps, delivers a speech on their behaviour, arguing for them to be left in the wild and protected. )2.Talking and sharingWork in groups of four. Tell your group mates what you know about wildlife protection. Then the group leader is to stand up and share your group idea with the class.(Key: I am from Group 3. We think that Jane is a woman of achievement. For she has helped people understand how much chimps behave like humans. Because of her we know that it is better for the animals to be left in the wild or in the special places set up for them. )Step III. Reading1.Reading aloud to the recordingNow please listen and read aloud to the recording of the text A PROTECTOR OF AFRICAN WILDLIFE. Pay attention to the pronunciation of each word and the pauses within each sentence.I will play the tape twice and you shall read aloud twice, too.2.Reading and underliningNext you are to read and underline all the useful expressions or collocations in the passage. Copy them to your notebook after class as homework.3.Reading to identify the topic sentence of each paragraphSkim the text and identify the topic sentence of each paragraph. You may find it either at the beginning, the middle or the end of the paragraph.(Key: 1st paragraph: Our group are all going to visit the chimps in the forest. 2nd paragraph: Nobody before has fully understood chimp behaviour. 3rd paragraph: For forty years Jane Goodall has been helping the rest of the world understand and respect the life of these animals.)4.Reading and transferring informationRead the text again to complete the table, which list what Jane does to protect African wildlife.What does Jane do?5.Reading and understanding difficult sentencesAs you have read the text times, you can surely tell which sentences are difficult to understand. Now put your questions concerning the difficult points to me the teacher. Step IV. Closing downClosing down by doing exercisesTo end the lesson you are to do the comprehending exercises No. 1 and 2. 2. Closing down by having a discussionDo you agree with Jane’s ideas? Why or why not?(Key: I agree with Jane’s idea, because leaving the animals in the wild is the only good way to protect them. The animals belong to the forest, just as we belong to the civilized world. ) What do you think is the best way to protect wildlife?(Key: I think the best way is to understand and respect the life of animals. Setting up special places where they can live safely is important and effective)Closing down by retelling the story of Jane GoodallI shall write some key words and expressions on the board. You are to retell the story of Jane Goodall according to thesewords.(Key: visit the chimps, watch the chimps, understand chimp behaviour, argue for…, set up special places)The second period Learning about LanguageAimsTo help students learn about subject-verb agreement.To help students discover and learn to use some useful words and expressions.To help students discover and learn to use some useful structures.ProceduresStepI. Warming upWarming up by discovering useful words and expressionsTurn to page 4 and do exercises No. 1, 2 ,3 and 4 first. Check your answers against your classmates’.Step II. Learning about grammar1.Reading and thinkingTurn to page 2 and read with me the text of A PROTECTOR OF AFRICAN WILDLIFE. As you read on, pay attention to the forms of sentence predicates and the subject-verb agreement shown in the sentences.(For reference: Our group a re…, Watching a family of chimps is…, Nobody before hasfully understood…)2.Doing exercises No. 1 and 2 on page 5Turn to page 5. Look at the two sentences: Our group are all going to visit the chimps in the forest. And Our group includes six boys and five girls. Have you noticed any difference between them? Yes. If the word “group ”refers to different members, use a plural verb. If the word “group”is considered as a whole, usea singular verb. Now fill in the blanks with the proper form of the given verbs in brackets on page 5. And then go on to do Exercise No. 2 on the same page, that is, fill in the correct verb form in the letter.Step III. Ready used materials for Subject-verb agreementWe all know these meanings of "agree," but when we talk about subject-verbagreement, we're talking about something different: matching subjects andverbs according to number. That is, when you have a singular subject, youhave to match it with a singular verb form: The boy plays. When you have aplural subject, you must have a plural verb form: The boys play.In short, simple sentences, you should have no problem with agreement.You can hear the problem: The boys plays. When it's wrong , it just sounds。
Unit 1 friendship1.Teaching aims and demands2.Suggested teaching notes1). Analyses of the teaching contentsThis unit is about friendship, and nearly all the teaching materials center on it.Warming up---The questionnaire leads students to think and talk about friendship, get to know the problems between friendsand seek solutions, which makes preparations for thefurther teaching in topics, background and vocabulary. Pre-reading---The questions prompt students to think critically aboutfriends and friendship in reality, alerting them to the factthat besides people, a diary can be a friend, too. Reading--- The diary by theJewish girl Anne gave a glimpse of her life during her family’s shelter in Amsterdam from the GermanNazis’killing in world war . she treats the diary as her bestfriend, and in it reveals her longing for a normal life and closecontact with nature, which helps her get through the days. Comprehending---It helps students further understand the text by doingmultiple choices, questions and answers, andmatching.Learning about language---It teaches the important expressions andstructures and grammar: direct and indirectspeeches.Using language---The two letters, listening, questionnaire design, letterwriting and fun writing prepares students to furthertalk about friendship, especially the problems withmisunderstanding, and unfriendliness, thusstrengthening students’ abilities to practicelanguage, discover, and solve problems.Summing up---It summarizes the whole contents of this unit from theaspects of topics, vocabulary and grammar.Learning tip--- This part encourages students to form the habit of writinga diary.Integrating skills--- The text introduces the way Hawaiians expressfriendship, to get students to realize the culturaldifferences in the values of friendship in additionits importance in all cultures.2) Making of the teaching planThis unit centers on friends and friendship, exploring different types of friendship with particular attention to that one can develop with oneself,i.e., the comfort and support one seeks from an imaginary friend. Students are expected to come to be truly aware of the qualities and conducts that make a good friend, display and develop the ability to cope with misunderstanding, conflicts and problems related to friendship, and give advice on it. The concept that even an ordinary thing can be a friend should break down the traditional belief in theinterpersonal nature of friendship. Also, the comparison of similarities dissimilarities in friendship comprehension between the East and the West leads students to know better the values of friendship in Westerns’eyes. All in all, this unit promises to unveil the true essence of friendship and helps students to lead a more friendly and harmonious life. Thus, based on the theme, contents and teaching objectives, the whole3. Teaching plans for each periodPeriod 1 Warming-up and Speaking1. Teaching objectives:1) Target languageI (don’t) think…… I (don’t) think so. I (don’t) agree.I be lieve……That’s correct. In my opinion, ……2) Ability goalsa.Describe your friends in Englishb.Figure out the problems between friends and then find differentways to solve the problems.3)Learning ability goalsa.To encourage students to think and talk about friends andfriendship by using some phrases and structures.b.To learn to solve problems that may occur between friends.c. To cultivate the students to form the good habit of learning Englishin Senior Middle School.2. Teaching important points:e the given adjectives and sentence structures to describeone of your friends.b.Learn to evaluate friends and friendship.3. Teaching difficult points:a.Work together with partners and describe one of your goodfriends.b.Discuss with partners and find out ways to solve the problems.4. Teaching methodsa.Task-based teaching and learningb.Cooperative learningc.Discussion5. Teaching aids:CAI6. Teaching procedures and ways:Step 1 Lead-in and Warming-upBefore the lesson, the teacher can arouse the students’ interests by showing a video of Auld Lang Syne .At the beginning of the first class, we can get the students to talk about their summer holidays. The students can talk freely as they like.1.How did you spend your summer holidays? How did youfeel? What did you do in your summer holidays? What didyou do in your spare time?2.What do you think of our new school? Do you like it? Couldyou say something about it?3.Do you like making friends? How do get in touch with yourfriends? Do you have many friends? Where are they now?Do you have any old friends in our school? Have you madeany new friends in our class?Step 2 Think it over1. Give a brief description of one of your friends. The followingphrases and structures may be helpful:His/Her name is ……He /She is …… years old.He /She likes …… and dislikes ……He /She enjoys …… and hates……He /She is very kind/friendly/……When /Where we got to know each other.2. What types of friendship do you have? Please tick them out.Then fill in the blanks.girl friends boy friends pen friendslong -distance friends friends of the same agee-friends (friends over the internet) friends across generationsunusual friends like animals, books……1).______ is /are most important to you.2). You spend most of your free time with ____.3). You will share your secrets with _____.4). When in trouble, you will first turn to _____.Step 3 Make a survey1. List some qualities of a good friend or your ideal friend. Have the students get into groups of four to find out what each has listed.Tell your partner your standards of good friends by using the following structure:I think a good friend should (not) be……In my opinion, a good friend is someone who……1.Have a member of each group report on what their lists have incommon and list them on the board.2.Ask the class whether or not they agree with all the qualities listed.3.Then have the students do the survey in the textbook.4.Have the students score their survey according to the scoring sheeton page 8.5.The teacher ask some students how many points they got for thesurvey and assess their values of friendship:★4~7 points: You are not a good friend. You either neglect your friend’s needs or just do what he/she wants you to do. You sho uld think more about what a good friend needs to do.★8~12 points: You are a good friend but you sometimes let your friendship become too important, or you fail to show enough concern for your friend’s needs and feelings. Try to strike a balance between y our friend’s needs and your own responsibilities.★ 13+ points: You are an excellent friend who recognizes that to be a good friend you need balance your needs and your friend’s. Well done. (You may also show your students the results above and let themselves self-reflect upon their own values of friendship)Step 4 Talking and sharing( work in pairs)1. If your best friend does something wrong, what will you do?Try to use the following phrases:I (don’t) think…… I (don’t) think so.I (don’t) agree. I believe……That’s correct. In my opinion, ……2. What is a friend?A British newspaper once offered a prize for the best definition(定义) of a friend. If you were the editior, choose the best one from the following entries(条目), and explain why.One who understands my silence.A friend in need is a friend indeed.Friends are just the people who share your happiness and sorrow. When you look at your watch at 4 am, but still know you can callthem and wake them up, and they’ll still want to talk to you ,that’s friendship.To have a friend, you need to be a good friend.Step 5 Group work (output)The teacher can give each group one of these questions below to talk about. Then let the class share their ideas. It’s better to stimulate the students to express their own opinions about these questions.1.Do you think it is a good idea to borrow money from your friend?Why and Why not?2. What factors may cause the breakdown of a good friendship?3.What can be your special friend besides human beings? And why?Step 6 homework1.Write down a short passage about your ideas /the factors/yourunusual friends.2.Prepare for the new lesson.Period 2 Reading “Anne’s Best F riend”1. Teaching objectives:1) To develop the students’ reading ability, learn to use some reading strategies such as guessing, key sentences, skimming and so on;2). To get the students to realize the importance of friends and friendship, and to tell true friends from false friends;3). To grasp some useful words and expressions in this passage, such as on purpose, be crazy about etc.;4). To learn the writing style of this passage.2. Teaching method: Task-based teaching3). Teaching procedure:Step 1.Pre-reading1. Please enjoy three pieces of music and find out what they are about.2 .Why do you think friends are important to you?3. What do you think a good friend should be like? List the good qualities a good friend should have .4. Have you ever considered making friends with animals, plants or even an object? Why or why not?Step 2.Reading1. Try to guess what Anne’s friend is and what the passage is about by reading the title and having a quick at the pictures in this passage without reading it.2. Skimming the first two paragraphs to confirm your guessing.1) What was Anne’s best friend? Why did she make friends with it?2) Did she have any other true friends then? Why?3) What is the difference between Anne’s diary and those of most people?4) Do you keep a diary? What do you think most people set down in their diaries?5) We are going to read one of Anne’s diaries .but before reading ,can you tell me what the diary is about with the help of one key sentence in the 2nd paragraph?3. Reading of Anne’s diaryHow she felt in the hiding placeTwo examples to show her feelings thenStep 3.Post-reading1.What would you miss most if you went into hiding like Anne and her family? Give your reasons.2.Group workWork in groups to decide what you would do if your family were going to be killed just because they did something the Emperor did not like.Where would you plan to hide?How would you arrange to get food given to you every day?What would you do to pass the time?------3. Discovering useful words and expressionsComplete the following sentences, using words and expressions from Reading1) She has grown _______ about computer games.2) Was it an accident or did David do it on _______?3) From the beginning ,Paul made it clear that he would be ______ (完全地)in control.4) He used to work _______ even in the middle of winter.5) Just the _______ of more food made her feel sick.6) You had better have a _________ talk with him.7) Born in a poor family, the manager _________ lots of hardships in his childhood.8) A diary is often kept to ________ what happens in people’s daily lives.Step 4.Talking about friends and friendship1.There are many proverbs about friends and friendship. Choose the one you agree with and explain why, then choose one you disagree with and explain why.A friend in need is a friend indeed.Friends are like wine; the older, the better.A friend to all is a friend to none.The same man cannot be both friend and flatterer(阿谀奉承者).False friends are worse than open enemies.Walking with a friend in the dark is better than walking alone in the light.2. We have talked about friends and friendship today, can you write one or two sentences to express your understanding of friends and friendship.Step 5.Homework:1. Interview a high school student, a businessman, a police officer and a housewife to find out their opinions about friends and friendship. Write areport to share it with the whole class.2. Describe one of your best friends following the writing style of this passage.Ending: Let’s s ing this song about friends togetherPeriod3 GrammarDirect & Indirect SpeechI Statements & Questions1.Teaching objectivesLearn to use direct speech and indirect speech2. Teaching important pointSummarize the rules of Direct Speech and Indirect Speech.3. Teaching difficult pointLearn about the special cases in which the tenses shouldn’t be changed.4. Teaching methodsDiscussing, summarizing and practicing.5. Teaching proceduresStep1 Lead inT:Good morning, class. In the last lesson, we learn ed Anne’s story. Now she is telling her stories to two of her friends—you and Tom. Tom has something wrong with his ears,so you have to repeat Anne’s sentences, Sometimes you need to explain Tom’s sentences to the class. Look at the blackboard.“I have to stay in the hiding place.” said Anne.→T:What did Anne say ?As we know , Tom has something wrong with his ears,so you have to repeat Anne’s sentence.Ok,first of all, let’s translate the sentence into Chinese.安妮说:“我不得不呆在躲藏处。
Unit 2 English Around the WorldI Teaching aims1.Knowledge aim2.Master the words and phrases and get a view of the road to modern English.3.Ability aim4.Train students’ reading skill.5.Emotion aim6.Let students know more about English and inspire students to study English hard. IITeaching important pointsThe understanding and comprehension of the passage.III Teaching difficult pointHow to get to master the useful words and expressions.How to improve students’ ability to read an article.IV Teaching ProceduresV Teaching TimeSeven Periods.Period 1 Warming up and ReadingStep1. Warming up1. Lead in: Show Ss a map of the world, and ask them the following questions:1) How many languages are there in the world?2) How many English-speaking counties are there in the world?3) How are you ever heard some differences between American English and BritishEnglish?Step2. Reading(1)SkimmingRead the passage quickly and find out the answers of the questions in comprehension.(2)ScanningThe cause Cultures communicate with one another Time Things that happenedBetween AD450 and 1150Based on German1150 to 1500 Less like German; more like FrenchIn the 1600’sShakespeare broadened the vocabulary A bigchanged in EnglishLater British people broughtEnglish to Australia(3)Listen to the tape and tell the meaning of each paragraph.1. Para1: Brief introduction of the change in English.2. Para.2: An example of different kinds of English.3. Para3: The development of English.Para4: English spoken in some other countries.(4)Post readingStep3. DiscussionSome people say that Chinese is a much more elegant language, so it is more important for us to master it and it is not so necessary to master foreign language. Do you agree with this opinion and why?Period 2 Language pointsLanguage points:1. Do you know that there is more than one kind of English in the world?你知道世界上英语的种类并不止一种吗?more than one +名词单数,后面的谓语动词用单数例如:More than one student wants to go to swim.2.In some important ways they are very different form one another.在某些重要的方面,它们彼此有些差异。
Unit 2 English Around the WorldI Teaching aims1.Knowledge aim2.Master the words and phrases and get a view of the road to modern English.3.Ability aim4.Train students’ reading skill.5.Emotion aim6.Let students know more about English and inspire students to study English hard. IITeaching important pointsThe understanding and comprehension of the passage.III Teaching difficult pointHow to get to master the useful words and expressions.How to improve students’ ability to read an article.IV Teaching ProceduresV Teaching TimeSeven Periods.Period 1 Warming up and ReadingStep1. Warming up1. Lead in: Show Ss a map of the world, and ask them the following questions:1) How many languages are there in the world?2) How many English-speaking counties are there in the world?3) How are you ever heard some differences between American English and BritishEnglish?Step2. Reading(1)SkimmingRead the passage quickly and find out the answers of the questions in comprehension.(2)Scanning(3)Listen to the tape and tell the meaning of each paragraph.1. Para1: Brief introduction of the change in English.2. Para.2: An example of different kinds of English.3. Para3: The development of English.Para4: English spoken in some other countries.(4)Post readingStep3. DiscussionSome people say that Chinese is a much more elegant language, so it is more important for us to master it and it is not so necessary to master foreign language. Do you agree with this opinion and why?Period 2 Language pointsLanguage points:1. Do you know that there is more than one kind of English in the world?你知道世界上英语的种类并不止一种吗?more than one +名词单数,后面的谓语动词用单数例如:More than one student wants to go to swim.2.In some important ways they are very different form one another.在某些重要的方面,它们彼此有些差异。
(1)in…way(s)/by…means 在……方面We should solve this problem in a different way.=We should solve this problem by a different way.(2)one another/each other 彼此,相互之间We should communicate with one another/each other.我们应该相互交流。
We send card to one another/each other every year.我们每年都相互寄卡片。
3.They include Canadian, British, American and India English.include 包含、包括The price includes dinner, beds and breakfast.including(prep) included(adj)The bill came to $450,including tax.The bill came to $450, tax included.contain 包含,容纳contain指某物容纳在比其更大的东西之内The basket contains a variety of fruits.这篮子装有各种水果。
include指包括作为整体的一个部分或要素The tour includes a visit to Paris这旅程包括游览巴黎。
4. English plays an important role as a first or second language.plays a/an … role/part 扮演……的作用、角色Monitor plays an important role in managing a class.班长在班级管理中起着重要的作用。
5. Nearly all of them live in England.他们几乎全部都住在英格兰。
almost与nearly①两者都可以修饰all, every, always等词,都可以用于否定句中。
②在very, pretty, not后用nearly, 不用almost。
例如:I’m not near ly ready.③在any, no, none, never前用almost, 不用nearly。
例如:I almost never see her.练一练:用nearly或almost填空(1). He said ______ nothing interesting.(2).______ 1000 people were here.(3).There is not ________enough boo for the whole class.解析(1)与nothing连用,所以填almost(2).与具体数字连用,用nearly(3).被not修饰时,用nearly6. Native English speakers can understand each other even if they don’t speak the same kind of English. 把英语作为母语的人相互之间可以交流,即使他们说的不是同一种英语。
even if /even though即使,引导让步状语从句Even though/if he had got a good job, he still wants to look for a better one.即使他找到了一份好的工作,他还想找更好的。
7.Would you please come up to my flat for a visit?来我的公寓坐坐怎么样?come up 上来,走近,被提出,发芽Strangers came up to him and asked how much his books are.陌生人走到他面前,问他课本值多少钱。
The problem came up in the meeting.问题在会议中被提出来了。
8. Actually, it was based on German than present day English.事实上,那时候的英语更象德语,而不是今天的英语。
(1)actually/in fact/as a matter of fact 事实上,实际上(2)base on/upon… 以、、、为基础This movie is based on facts.(3)present (adj) 目前的、现在的You should look clearly the present situation.9. It became closer to the language you are learning now.它和我们现在学的英语更加接近。
close to相近,靠近,几乎Our house is close to the bus stop.close(adv) 位置上接近closely(adv) 抽象关系上的密切Come close to me.I looked into the matter closely.10. Shakespeare made use of a wider vocabulary than ever before.莎士比亚使用了比以前更为广泛的词汇量。
make (good/full/no…) use of 使用We could make good use of our resources.Every minute should be made good use of.11. India has a very large number of English speakers.印度有很多的人讲英语。
a number of 大量的(其后谓语动词用复数)A number of people have came.the number of……的数目(其后谓语动词用单数)The number of homeless people has increased.只能修饰可数名词的:a large/ great/ good number of,a good/ great many, dozens of,scores of, quite a few只能修饰不可数名词的:a great deal of, a large amount of,quite a little, a large sum of既可修饰可数也可修饰不可数名词的:plenty of, a lot of, lots of,a large quantity of12. Only time will tell. 时间会证明一切。