一般现在时(完整版)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:66.00 KB
- 文档页数:9

一般现在时定义与讲解一般现在时:表示经常性的事情,经常性的动作或一般性事实。
时间状语:often经常, usually通常, always总是, every每个(day,morning 等), sometimes有时,at…,在几点钟只有在第三人称单数用动词的“三单变化”,其他用动词的原形,三单变化:1多数在动词后+s 如:play- plays like-lkes(1)直接在动词词尾加-sask-asks, work-works ,get-gets ,stay-stays(2)以字母s、x、ch, sh或0结尾的动词,在诃尾直接加-es。
watch--watches wish-wishes fix--fixesdo—does go--goes pass--passes3)以“辅音字母加-y结尾的动词,要先变y为i再加-estry-tries study-studies cry-cries fly-flies2不规则变化:be-- is are have –has二、一般现在时用法1.表示经常性,习惯性,永久性的动作或存在的状态,通常与副词 sometimes, often, usually, always, every day (year, month), once (twice, three times)a day等时间状语连用。
They usually go to school by bike.I take the medicine three times a day.She helps her mother once a week.There are 50 students in my class.2.表示客观真理,科学原理,自然现象,等客观事实或格言,谚语等The sun rises in the east and sets in the west every dayThe man who has never been to the great wall s not a real man.(不到长城非好汉)Tomorrow is Tuesday.三、一般现在时的句子转换(1)当句子中有be(is、am、are)动词或情态动词时,则把be动词或情态动词( can、could等等)提到主语的前面变成疑问句,在be动词或情态动词后面加not变成否定句,例:①陈述句: She is a student疑问句→ Is she a student?否定句→ She is not a student②陈述句: I can swim疑问句→ Can you swim否定句→ I can not swin(2)当句子中即没有be动词,也没有情态动词时,则在主语前加助动词do(you,以及复数)does(单数 she he,it)变成句;在主语后谓语动词前加助动词don’t(I,you,以及复数) doesn(单数she,he,it)变成否定句,助动词后的动词要变成动词原形。

初中语法一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时四种时态的区别名称定义时间动词形式时间词always、sometimes、usually、1、动词原形often、every表示经常性或习2、第三人称单一般现在时平时、经常惯性的动作数morning、动词后-s/esevery week、twice a week等等now、rightnow、表示此时此刻或at theam/is/are+动词现在进行时现阶段正在进行正在进行ingmoment、的动作look、listen等in the future、1、will/shall+动next词原形表示将来发生的week/month、一般将来时即将、计划2、am/is/are事tomorrow、+going to+动词in two weeks原形等等ago、yesterday、表示过去某一时1、V-ed(规则last week/候或某一段时间过去(与现动词)一般过去时night、所发生的事情或在无关的)2、不规则动词just now、存在的状态变化once upon atime等注意:1、一般现在时——第三人称单数的动词变化规则:1)大多数动词在词尾加“S”如:stop-______; make-______read-______; play-______2)以辅音字母加“y”结尾的,要先将“y”变为“i”,然后在加“es”如:fly-______;carry-______study-______; worry-______3)以“s, x, ch, sh”结尾的,在词尾加“es”如:teach-______;watch-______4)以“o”结尾的动词,加“es”如:go-______do-______2、现在进行时——动词ing形式的变化规则1.一般动词直接在词尾+ing例:read→______(读)talk→______(交谈)sing→______(唱歌)2.以不发音e结尾的动词,先去e再加ing例:like→______喜欢write→______写skate→______(滑冰)3.以重读闭音节结尾且末尾只有一个辅音字母的动词,双写末尾字母,再加ing例:stop→______(停止)get→______(得到)4.少数几个以ie结尾的动词,变ie为f再加ing。

一般现在时(完整版)一、单项选择一般现在时1.— Do you like the skirt?— It _______ soft.A.is feeling B.feltC.feels D.is felt【答案】C【解析】【详解】考查时态。
句意:你喜欢这件裙子吗?——它摸起来很柔软。
此处feel是连系动词,无被动语态,结合语境可知下文描述的是客观性的动作,故用一般现在时态。
主语it表示单数第三人称含义,故谓语动词用单数。
选C。
2.The Small Goose Pagoda in Xi’an, one of the 22 Silk Road relics located in China, _______ back in 707 during the Tang Dynasty.A.dated B.was datedC.dates D.is dating【答案】C【解析】试题分析:考查动词短语和时态。
短语date back to追溯到....;从....开始有;该句型没有被动语态,也没有进行时。
通常都使用一般现在时表示从现在时间某一事物能够追溯到的时期。
故C项正确。
【名师点睛】当分词做状语的时候,要特别考虑主被动关系以及时间的先后关系。
如果构成分词的动词与句子的主语构成主动关系,就使用现在分词做状语;当二者构成被动关系,使用过去分词做状语。
如果分词的动作发生在谓语动词之前,就使用分词的完成式。
如果分词与句子的主语没有关系,可以使用状语从句或者独立主格结构。
考点:考查动词短语和时态3.---We’d better leave now.---No hurry. The train ______ at 10 o’clock.A.has left B.leftC.leaves D.would leave【答案】C【解析】试题分析:考查时态。
本句中使用一般现在时代替将来时,表示按照时间表的安排将要发生的事情。
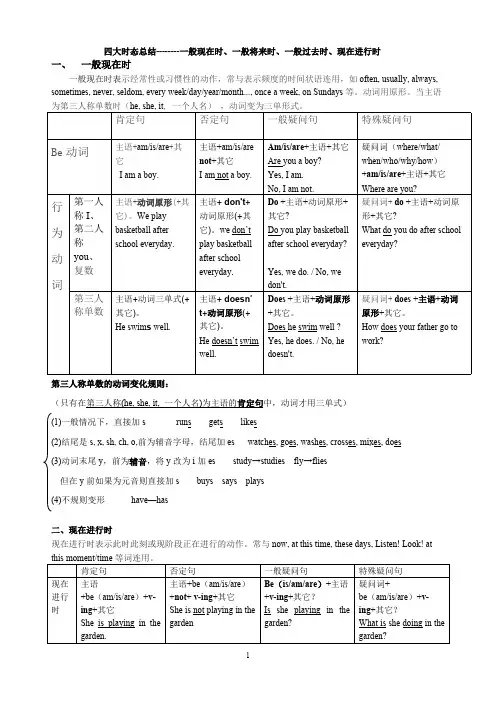
四大时态总结--------一般现在时、一般将来时、一般过去时、现在进行时一、一般现在时一般现在时表示经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用,如often, usually, always, sometimes, never, seldom, every week/day/year/month..., once a week, on Sundays等。
动词用原形。
当主语为第三人称单数时(he, she, it, 一个人名),动词变为三单形式。
肯定句否定句一般疑问句特殊疑问句Be动词主语+am/is/are+其它I am a boy.主语+am/is/arenot+其它I am not a boy.Am/is/are+主语+其它Are you a boy?Yes, I am.No, I am not.疑问词(where/what/when/who/why/how)+am/is/are+主语+其它Where are you?第一人称I、第二人称you、复数主语+动词原形(+其它)。
We playbasketball afterschool everyday.主语+ don't+动词原形(+其它)。
we don’tplay basketballafter schooleveryday.Do +主语+动词原形+其它?Do you play basketballafter school everyday?Yes, we do. / No, wedon't.疑问词+do +主语+动词原形+其它?What do you do after schooleveryday?行为动词第三人称单数主语+动词三单式(+其它)。
He swim s well.主语+ doesn’t+动词原形(+其它)。
He doesn’t swimwell.Does +主语+动词原形+其它。
Does he swim well ?Yes, he does. / No, hedoesn't.疑问词+ does +主语+动词原形+其它。





(完整版)一般现在时一般过去时现在进行时过去进行时归纳总结一般现在时一般过去时现在进行时过去进行时1. 一般现在时(1)一般现在时的构成动词一般用原形,若主语为单数第三人称,则动词加词尾-s或-es,具体变化规则如下(与名词的单数变复数规则大致一样):1.一般情况下由动词后加-s构成。
如:work→works 工作read→reads 读look→looks 看come→comes 来live→lives 居住listen→listens 听2.以s, x, z, sh, ch 以及字母o结构的动词,后加-es。
如:guess→guesses 猜mix→mixes 混和go→goes 去finish→finishes 完成catch→catches 抓住3.以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,应将y改为i 再加-es。
如:fly→flies 飞行study→studies 学习carry→carries 带,扛一般现在时主要用动词的原形表示,如果主语是第三人称单数,则在动词原形式后加—s 或—es 。
如:Tom often helps his parents do housework at home.汤姆在家经常邦助父母做家务。
Sometimes Lucy washes her clothes herself.有时候露西亲自洗她的衣服。
(2)一般现在时的用法1)表示经常性或习惯性的动作或存在的状态。
与often , always ,usually , sometimes , once a week , every day 等表示频度的副词或时间状词连用。
如:I often go to school by bike. 我经常骑自行车去上学。
2) 表示客观事实或普遍真理。
如:The earth goes around the sun .地球绕着太阳转。
3)在时间、条件等状语从句中,用现在时表示将来。
如:If it rains tomorrow, we won’t go to the park.如果明天下雨,我们就不去公园了。


一般现在时(完整版)一、单项选择一般现在时1.---Alan seems a lot taller than when I last saw him.---He . He’s grown a foot since you saw him in Shanghai.A.is B.will beC.has been D.was【答案】A【解析】试题分析:考查时态。
第二人的回答He _____.是紧随上句,所以时态和第一句的seems保持一致即:一般现在时。
句意:—Alan比我当初看见他的时候似乎高了一点。
—,确实,自从你上次在上海见到他又长高了一英尺。
故选.A考点:考查时态2.Mr. Black, as well as the professor who________ from Beijing University, ________ to attend our school meeting.A.come; is B.comes; are C.comes; is D.come; are【答案】C【解析】考查主谓一致。
第一个空处主语为定语从句中的who,指代单数名词professor,谓语用单数。
第二个空处主语为Mr. Black,为单数,谓语用单数。
故选C。
3.---We’d better leave now.---No hurry. The train ______ at 10 o’clock.A.has left B.leftC.leaves D.would leave【答案】C【解析】试题分析:考查时态。
本句中使用一般现在时代替将来时,表示按照时间表的安排将要发生的事情。
句意:—我们最好现在就走。
—不着急,火车10点才离开。
故C 正确。
考点:考查时态4.Paul could be a very attractive boy but he ______ to his behaviour.A.paid no attention B.were paying no attentionC.pays no attention D.had paid no attention【答案】C【解析】试题分析:考查动词短语。
四种时态的比较.不规则动词过去式:原形过去式原形过去式原形过去式原形过去式sweep swept teach taught have had go went keep kept think thought do did find found sleep slept buy bought eat ate say said feel felt drink drank is/am was take took read read give gave are were mean meantput put sing sang drive drove meet met cut cut begin began speak spoke make made let let ring rang write wrote see saw fly flew run ran ride rode come came draw drew sit sat hear heard tell toldgrow grew learn learned/learntget got know knew一、用动词的适当形式填空1. My parents _______ (come) from Shandong.2. Sam _______(not like) playing computer games.3. The beautiful girl _______(wear) glasses.4. The Zhang family _______(live) in a flat in Nanjing.5. My father likes _______(read) newspapers after work.6. What _______her classmates _______(call) her teacher?7. _______ you _______(love) each other in your family?8. _______(be) your cousin very clever at maths?9. She is good at dancing. She ________ (sing) very well, too.11. Amy ________(take) her dog for a walk every afternoon.12. Mr. Li ________(not teach) us maths this term. (学期)13. Mr. Chen ________(not like) tea. He ________(enjoy) drinking coffee.14. ________ your father often ________(play) tennis ?No, he loves ________(read) newspapers.15. Everyone in our class ________(like) P.E. a lot.16. Who else ________(want) to come to Millie’s party? I ________.17. Many of them ________(work) hard at their lessons. They _____ (be) cl ever at them.18. What _______ Mary _______(have) for breakfast ?She _______(have) an egg and a glass of milk.19. Our school ________(be) a big nice school. And our teacher ______(be ) a good teacher.20. Simon and Daniel ________(be) American.二、句型转换。
一般现在时基本用法介绍集团标准化办公室:[VV986T-J682P28-JP266L8-68PNN]一般现在时基本用法介绍一般现在时的功能1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。
如:The sky is blue.天空是蓝色的。
2.表示经常性或习惯性的动作。
如:I get up at six every day.我每天六点起床。
3.表示客观现实。
如:The earth goes around the sun.地球绕着太阳转。
一般现在时的构成1. be动词:主语+be(am,is,are)+其它。
如:I am a boy.我是一个男孩。
2.行为动词:主语+行为动词(+其它)。
如:We study English.我们学习英语。
当主语为第三人称单数(he, she,it)时,要在动词后加"-s"或"-es"。
如:Mary likes Chinese.玛丽喜欢汉语。
一般现在时的变化1. be动词的变化。
否定句:主语+ be + not +其它。
如:He isnot a worker.他不是工人。
一般疑问句:Be +主语+其它。
如:-Are you a student -Yes. I am. / No, I'm not.特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句。
如:Where is my bike?2.行为动词的变化。
否定句:主语+ don't( doesn't ) +动词原形(+其它)。
如:I don't like bread. 当主语为第三人称单数时,要用doesn't构成否定句。
如:He doesn't often play.一般疑问句:Do( Does ) +主语+动词原形+其它。
如:- Do you often play football - Yes, I do. / No, I don't.当主语为第三人称单数时,要用does构成一般疑问句。
一般现在时定义:一般现在时:表示通常性、规律性、习惯性的状态或者动作(有时间规律发生的事件)的一种时间状态。
句子结构当主语是第三人称单数时:肯定句:主语+动词的第三人称单数+其他否定句:主语+doesn't+动词原形+其他一般疑问句:Does+主语+动词原形+其他肯定回答:Yes,主语+does否定回答:No,主语+doesn't特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句当主语不是第三人称单数时:肯定句:主语+动词原形+其他否定句:主语+don't+动词原形+其他一般疑问句:Do+主语+动词原形+其他肯定回答:Yes,主语+do否定回答:No,主语+don't要注意,句式结构错则全局都错。
变化规律具体运用1.表示经常的或习惯性的动作,常与表示频率的时间状语连用。
时间状语: always, usually,regularly,everymorning/night/evening/day/week/year,often,sometimes,occasionally ,from time to time,twice a week,rarely,seldom,once a month, hardly, ever,never.e.g. I leave home for school at 7:00 every morning.2.表示主语具备的性格、能力、特征和状态。
e.g. I don't want so much.Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well.比较:Now I put the sugar in the cup.I am doing my homework now.3.表示客观事实和普遍真理。
e.g The earth moves around the sun.Shanghai lies in the east of China.4.在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,常用一般现在时代替将来时。
一般现在时一般现在时基本用法介绍【No. 1】一般现在时的功能1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。
如:The sky is blue.天空是蓝色的。
2.表示经常性或习惯性的动作。
如:I get up at six every day.我每天六点起床。
3客观真理,客观存在,科学事实如:The earth goes around the sun.地球绕着太阳转。
4.表示格言或警句中。
如:Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。
一般现在时的构成1. be动词:主语+be(am,is,are)+其它。
如:I am a boy.我是一个男孩。
2.行为动词:主语+行为动词(+其它)。
如:We study English.我们学习英语。
当主语为第三人称单数(he, she,it)时,要在动词后加"-s"或"-es"。
如:Mary likes Chinese.玛丽喜欢汉语。
【No.2】一般现在时的变化1. be动词的变化。
否定句:主语+ be + not +其它。
如:He is not a worker.他不是工人。
一般疑问句:Be +主语+其它。
如:-Are you a student? -Yes. I am. / No, I'm not.特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句。
如:Where is my bike?2.行为动词的变化。
否定句:主语+ don't( doesn't ) +动词原形(+其它)。
如:I don't like bread.当主语为第三人称单数时,要用doesn't构成否定句。
如:He doesn't often play.一般疑问句:Do( Does ) +主语+动词原形+其它。
如:- Do you often play football? - Yes, I do. / No, I don't.当主语为第三人称单数时,要用does构成一般疑问句。