英语语言学大全
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:5.23 MB
- 文档页数:146

现代语言学术语总结Aabbreviation缩写法acculturation语言文化移入acoustic phonetics声学语言学acronym词首字母缩略词address term称谓语addresser发话人addressee受话人adjacency毗邻Adjacency Condition毗邻条件Adjacency Parameter毗邻参数Affix词缀Affixation加词缀法Affricate塞擦音Afroasiatic非亚语系agreement rule一致关系规则allophone音位变体alveolar齿龈音alveolus齿龈angular gyrus角形脑回antonymy反义现象antonym反以词apocope词尾音脱落aphasia失语症aphasic失语症患者applied linguistics应用语言学arbitrariness任意性argument论元articulatory phonetics发音语音学articulatory variable发音变项aspiration送气assimilation同化approximation近似化auditory phonetics听觉语音学Austronesian…语系BBabbling咿呀学语back-formation逆向构词法back vowel后元音Behaviorism行为主义Behaviorist learning theory行为主义学习理论Behaviorist Psychology行为主义心理学Bilabial双唇音Bilingualism双语现象Black English黑人英语Blending混合法Borrowing借用bound morpheme黏着语素brain lateralization大脑左右半球侧化branching node分叉点broad transcription宽式音标Broca’s area布罗卡区Ccaretaker speech保姆语case格Case Condition格条件case marking格标志causative verb使役动词central vowel中元音cerebral cortex大脑皮层cerebral plasticity大脑弹性channel渠道classical language古典语言clipping略写法closed class word封闭类词code代码code-switching代码切换cognate同源词co-hyponyms并列下义词coinage创新词color word色彩词combinational rule组合规则commissives承诺类communicative competence交际能力comparative reconstruction比较重建法competence语言能力complement补语complement construction补足语complementarity互补性反义现象complementary distribution互补分布complex sentence复合句componential analysis成分分析法components of meaning意义成分compound word复合词compounding复合法computational linguistics计算语言学conceptualist view意念观consonant辅音constituent成分constituent structure成分结构constraint制约construction结构content word实词context语境;上下文contextualism语境论Contrastive Analysis对比分析法conversational implicature会话含义co-operative principle合作原则coordinate sentence并列句creativity创造性critical period关键期;临界期cultural transmission文化传播Ddeclaration宣告类deep structure深层结构dental齿音derivation派生法derivational morpheme派生语素derivative派生词descriptive linguistics描写语言学design feature识别特征determiner限定词diachronic linguistics历时语言学diacritics变音符号dialect方言dialectal synonym方言同义词dichotic listening test两耳分听测试diglossia双言现象diphthong复合元音Directionalilty Parameter方位参数Directives指令类Displacement不受时空限制的特性distinctive feature区别性特征D-structure深层结构duality of structur结构二重性e double articulation结构二重性Eembedded clause子句emotive meaning表情意义entity实体epenthesis插入音Error Analysis错误分析法euphemism委婉语evaluative meaning评价意义expressives表达类Ffactive predicate叙述性谓词family tree谱系树feature symbol特征标记features of meaning意义特征finite clause定式字句finite verb定式动词formalize形式化fossilization语言僵化framework框架free morpheme自由语素fricative擦音front vowel前元音function word虚词functional shift功能性转换functor element起功能作用成分Ggender性Generative Grammar生成语法Generative Semantics生成语义学genetic predispotion基因先天条件genetic relationship亲缘关系glide滑音glottal喉音glottis声门graddabl opposites可分等级的反义词grammaticality语法性grammatical meaning语法意义Great V owel Shift元音大变位Hhard palate硬腭head核心词hemispheric dominance for language大脑半球的语言优势hierarchical structure层次结构high variety高层次变体historical comparative linguistics历史比较语言学historical linguistics历史语言学holophrastic sentence独词句homography同形homonymy同音异义;同形异义homophony同音异义hyponymy下义关系hyponym下义词Iidiolect个人语言特点illocutionary act言外形为inconsistency自相矛盾Indo-European印欧语系infinitive marker不定式标记inflection曲折变化inflectional morpheme曲折语素input输入instrumental motivation工具性学习动机intake接受integrativ emotivation介入性学习动机interference干扰interlanguage语际语internalize内在化International Phonetic Alphabet国际音标interpersonmal communication人际交际intuition语调Llabeled (unlabeled) tree diagram加标记树形图labial唇音LAD语言习得机制language acquisition语言习得language behavior语言行为language center语言中枢language faculty语言机制language family语系language perception语言感知language planning语言规划language variation语言变异larynx喉lax vowel松元音level层;平面level of language语言层次lexical category词类lexical structure词汇结构lexicology词汇学lexicon词汇linear structure线性结构linguistic competence语言能力linguistic determinism语言决定论linguistic lateralization语言侧化linguistic performance语言运用linguistic relativism语言相对论linguistic repertoire全部语言变体linguistic taboo禁忌语linguistics语言学liquid流音loan word外来词localization定位locutionary act言内行为low variety低层次变体Mmanner of articulation发音方法matrix clause主句maxim of manner方式准则maxim of quality质量准则maxim of quantity数量准则maxim of relation关联准则meaning意义meaningfulness有意义meaning relation意义关系mentalism心理主义mentalistic theory精神论message信息metathesis语音变位Middle English中世纪英语minimal pair最小对立对Modern English现代英语Monophthong单元音Morpheme词素morphlogical rule形态学规则morphology形态学mother tongue母语Move α移动α规则movement rule移位规则Nnaming theory命名论narrow transcription严式音标narrowing of meaning词义缩小nasal cavity鼻腔nasality鼻音化nasalize鼻音化natural route of development自然发展轨道negator否定词neurolinguist神经语言学家neuron神经元no-place predication空位述谓结构Oobject宾语Old English古英语one-place predication一位述谓结构optimum age最佳学习年龄oral cavity口腔overextension扩展过度overgeneralization概括过度overt thought有声思维Ppalatal腭音paralinguistic副语言学的parameter参数performance语言运用performance error语言运用错误perlocutionary act言后行为pharyngeal cavity咽腔phone音素phoneme音位phonemic contrast音位对立phonetic feature语音特征phonetics语音学phonological rule音位规则phonology音位学phrasal category词组类phrase structure rule短语结构规则pidgin洋泾浜语place of articulation发音部位plosive爆破音polysemy多义性postpone后移prepose前移postvocalic元音后的pragmatics语用学predicate谓语predication述谓结构predication analysis述谓结构分析prefix前缀presprictive (grammar)规定语法presupposition前提proposition命题prepositional content命题内容protolanguage原始语psycholinguistics心理语言学puberty青春期Qqualifying predication修饰性述谓结构RReceived Pronunciation标准发音Recursiveness循环性Reference所指语义referring expression所指名词register语域relational opposites关系反义词representation表达;呈现representatives阐述类response反应retroflex卷舌音rewrite rule重写规则rounded vowel圆唇元音SSAE标准美国英语sapir-Whorf hypothesis…假设second language acquisition第二语言习得segment切分成分semantic anomaly语义异体semantic deviation语义变异semantic broadening语义广义化semantic narrowing语义狭义化semantic shift语义演变semantics语义学semantic structure语义结构semantic triangle语义三角sense意义sequential rule序列规则setting背景;环境sexist language性别歧视语sibilant咝音simple sentence简单句Sino-Tibetan汉藏语系situational dialect语域方言sociolect社会方言sociolinguistics社会语言学soft palate软腭species-specific capacity物种特有能力specifier指示语spectrograph频谱仪speech act言语行为speech community言语社区speech variety言语变体S-structure表层结构standard language标准语stem词干stimulus刺激stop爆破音stress重音structural constituency结构成分性structural linguistics结构主义语言学subject主语subordinate predication主从述谓性结构subscript下标subvocal predication无声言语suffix后缀superordinate上坐标词suprasegmental feature超切分特征surface structure表层结构synchronic linguistics共时语言synonymy同义词syntactic ambiguity句法歧义syntactic category句法类型syntactic rule句法规则syntax句法Ttaboo word禁忌词target language目标语tautology同义反复teeth ridge齿龈隆骨telegraphic speech电报式言语tense and aspect时和体tense vowel紧元音tone音调;声调tone language声调语言topic话题;主题transfer转移Transformational-Generative Grammar转换生成语法transformational rule转换规则tree diagram树形图two-place predication双位述谓结构Uunaspirated不送气underextension扩展不足Universal Grammar普遍语法Utterance话语utterance meaning话语意义uvula小舌Vvalidity有效性variable变项velar软腭音velum软腭vernacular本地话;本国语vocal cord声带voiced浊音化的voiceless不带音的,清音的voicing带音化,浊音化vowel元音WWernicke’s area韦尼克区widening of meaning词义扩大XX-bar theory X标杆理论。


语言学术语(英—汉对照)表Glossary and IndexAabbreviation 缩写词,略语 3。
3.1Abercrombie 10.3。
2ablative 夺格,离格 4.1.1abstractness 抽象性 1。
3.2accent 重音(符)2.4。
4;2.4.5accuracy 正确性 11。
6.4accusative 宾格 4。
1。
1achievement test 成绩测试 11。
6.3acoustic phonetics 声学语音学 1。
7。
1;2.1 acquisition 习得 6.1.2acronym 缩略语 3。
3.1action process 动作过程 12。
2。
3actor 动作者 4.4.2;12。
2.3addition 添加 3.3。
2address form 称呼形式 7.2。
3addressee 受话人 1。
4;9。
4.1addresser 发话人 1。
4;9.4。
1adjective 形容词 3.1.2;4。
1。
1;5.5。
2adjunct 修饰成分;附加语 12.2.3adverb 副词 3.1。
2affix 词缀 3。
2.1affix hopping 词缀跳跃 4.3。
1affixation词缀附加法 7。
1.4affricate 塞擦音 2.4。
3;2。
4.5;2.9.1agreement 一致关系 4。
1.3airstream 气流 2alliteration 头韵 9.3。
2;9。
3。
6allomorph 词/语素变体 3.2。
4;4。
3。
1allophone 音位变体 2。
8allophonic variation 音位变体 2.8。
3allophony音位变体现象 2。
8。
3alveolar ridge 齿龈 2。
2alveolar 齿龈音 2。
4。
4;2.4。
5ambiguity 歧义 4.2。
2;4。
3.1;6.2.3;8.2。
2;8。

100个最常用的语言学术语(“欧美语言学”课)1.语言language2.语言学linguistics3.语言学家linguist;philologist4.语法grammar5.语法单位grammatical unit6.语法形式grammatical form7.语法意义grammatical meaning8.语法手段grammatical device9.语法范畴grammatical category10.元音vowel11.辅音consonant12.语文学philology13.传统语法traditional grammar14.历史比较语言学historical comparative linguistics15.转换生成语法transformational generative grammar16.结构主义语言学structural linguistics17.应用语言学applied linguistic18.方言dialect19.语言教学language teaching20.语言规划language planning21.语言政策language policy22.语言学习策略language learning strategy23.发现程序discovery procedure24.语境context;language environment25.中介语interlanguage26.音位phoneme27.音节syllable28.语素morpheme29.词法morphology30.句法syntax31.交际法communicative approach32.认知cognition33.习得acquisition34.第二语言second language35.第二语言习得second language acquisition (SLA)36.自由语素free morpheme37.黏着语素bound morpheme38.复合词compound word39.普遍语法universal grammar,UG40.词类part of speech41.直接法direct method42.认同identification43.语言能力language competence44.语言机能language faculty45.交际能力communicative competence46.人工语言artificial language47.外语foreign language48.术语terminology;technical terms49.比较comparison50.对比语言学contrastive linguistics51.词典学lexicography52.母语mother tongue;native language53.语感linguistic intuition54.语料库corpus55.句子sentence56.前缀prefix57.结构structure58.希腊语Greek59.拉丁语Latin60.梵语Sanskrit61.语音学phonetics62.词汇学lexicology;lexics63.语用学pragmatics64.语源学(词源学)etymology65.词典学lexicography66.地理语言学geographic linguistics67.儿童语言学the study of child language68.翻译学translatology69.机器翻译machine translation70.计算语言学computational linguistics71.目的语target language72.普通语言学general linguistics73.社会语言学sociolinguistics74.实验语音学experimental phonetics75.缩略语abbreviation76.统计语言学statistical linguistics77.外来词/外语词loanword;foreign words78.网络语言cyber language;language used on the Internet79.文化语言学cultural linguistics80.心理语言学psycholinguistics81.音译词transliterated word82.语言信息处理language information processing83.语言哲学philosophy of language84.自然语言natural language85.格case86.逻辑学logic;logistics87.修辞学rhetoric88.词word89.相关性relativity90.黏着agglutination91.语言类型学linguistic typology92.音位学phonology;phonemics;phonematics93.构拟reconstruction94.组合关系syntactic relations;syntagma95.聚合关系paradigmatic relations96.功能function97.变体variant98.屈折inflection99.派生derivation100.直接成分immediate constituents (IC)。

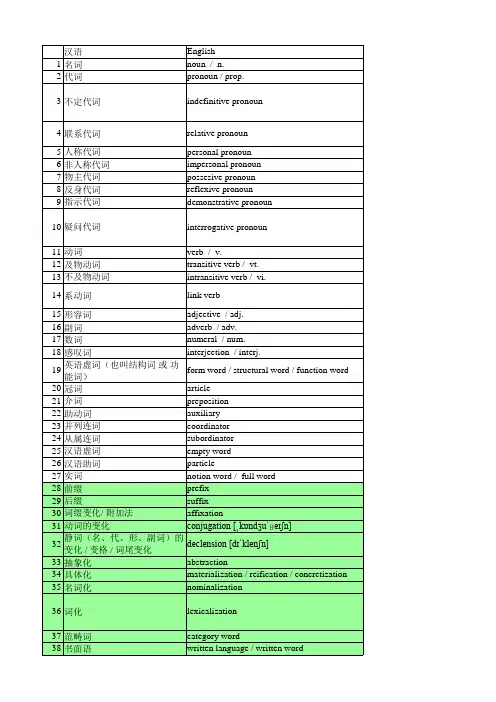
语言学词汇分类汇总语言学词汇分类汇总(按字母顺序排列)abbreviation缩写法acculturation语言文化移入acousticphonetics声学语言学acronym词首字母缩略词addressterm称谓语addresser发话人addressee受话人adjacency毗邻adjacencycondition紧邻条件adjacencyparameter紧邻参数affix词缀affixation加词缀法affricate塞擦音afro-asiatic非亚语系agreementrule一致关系规则allophone音位变体alveolar齿龈音alveolus齿龈angulargyrus角形脑回antonymy反义现象antonym夏斯利词apocope词尾音脱落aphasia失语症aphasic失语症患者appliedlinguistics应用领域语言学arbitrariness任意性argument论元articulatoryphonetics发音语音学articulatoryvariable发音变项aspiration送气assimilation同化approximation近似化auditoryphonetics听觉语音学austronesian…语系babbling咿呀学语back-formation逆向构词法backvowel后元音behaviorism行为主义behavioristlearningtheory行为主义自学理论behavioristpsychology行为主义心理学bilabial双唇音bilingualism双语现象blackenglish黑人英语blending混合法borrowing借予boundmorpheme黏着语素brainlateralization大脑左右半球侧化branchingnode锯齿点broadtranscription宽式音标broca’sarea布罗卡区caretakerspeech保姆语case格casecondition格条件casemarking格标志causativeverb使役动词centralvowel中元音cerebralcortex大脑皮层cerebralplasticity大脑弹性channel渠道classicallanguage古典语言clipping略读法closedclassword封闭类词code代码code-switching代码转换cognate同源词co-hyponyms并列下义词coinage创新词colorword色彩词concept概念conceptualistview意念观consonant辅音constituent成分constituentstructure成分结构constraint制约construction结构contentword实词context语境;上下文contextualism语境论contrastiveanalysis对比分析法conversationalimplicature会话含义co-operativeprinciple合作原则coordinatesentence并列句creativity创造性criticalperiod关键期;临界期culturaltransmission文化传播declaration宣告类deepstructure深层结构dental齿音derivation衍生法derivationalmorpheme派生语素derivative派生词descriptivelinguistics描绘语言学designfeature辨识特征determiner限定词diachroniclinguistics历时语言学diacritics变音符号dialect方言dialectalsynonym方言同义词dichoticlisteningtest两耳分听测试diglossia双言现象diphthong复合元音directionaliltyparameter方位参数directives指令类displacement不受时空限制的特性distinctivefeature区别性特征d-structure深层结构dualityofstructur结构二重性edoublearticulation结构二重性embeddedclause子句emotivemeaning表情意义entailment含义entity实体epenthesis填入音erroranalysis错误分析法euphemism直截了当语evaluativemeaning评价意义expressives表达类factivepredicate叙述性谓词familytree谱系树featuresymbol特征标记featuresofmeaning意义特征finiteclause定式字句finiteverb定式动词formalize公理化fossilization语言理性化framework框架freemorpheme民主自由语素fricative擦音frontvowel前元音functionword虚词functionalshift功能性转换functorelement起功能作用成分gender性generativegrammar分解成语法generativesemantics分解成语义学geneticpredispotion基因先天条件geneticrelationship亲缘关系glide滑音glottal 喉音glottis声门graddablopposites可分等级的反义词grammaticality语法性grammaticalmeaning语法意义greatvowelshift元音小变位hardpalate硬腭head核心词hemisphericdominancelanguage大脑半球的语言优势hierarchicalstructure层次结构highvariety高层次变体historicallinguistics历史语言学holophrasticsentence独词句homography同形homonymy同音异义;同形异义homophony同音异义hyponymy下义关系hyponym下义词idiolect个人语言特点illocutionaryact言外形为inconsistency自相矛盾indo-european印欧语系infinitivemarker不定式标记inflection曲折变化inflectionalmorpheme坎坷语素input输出instrumentalmotivation工具性学习动机intake接受integrativemotivation介入性学习动机interference干扰interlanguage语际语internalize内在化internationalphoneticalphabet国际音标labeled(unlabeled)treediagram加标记树形图labial唇音lad语言习得机制languageacquisition语言习得languagebehavior语言犯罪行为languagecenter语言中枢languagefaculty语言机制languagefamily语系languageperception语言认知languageplanning语言规划languagevariation语言变异larynx喉laxvowel松元音level层;平面leveloflanguage语言层次lexicalcategory词类lexicalstructure词汇结构lexicology词汇学lexicon词汇mannerofarticulation发音方法matrixclause主句maximofmanner方式准则maximofquality质量准则maximofquantity数量准则maximofrelation关联准则meaning 意义meaningfulness有意义meaningrelation意义关系mentalism心理主义mentalistictheory精神论message信息metathesis语音变位middleenglish中世纪英语minimalpair最小对立对modernenglish现代英语monophthong单元音morpheme词素morphlogicalrule形态学规则morphology形态学mothertongue母语moveα移动α规则movementrule移位规则namingtheory命名论narrowtranscription严式音标narrowingofmeaning词义缩小nasalcavity鼻腔nasality鼻音化nasalize鼻音化naturalrouteofdevelopment自然发展轨道negator否定词neurolinguist神经语言学家neuron神经元no-placepredication空位述谓结构object宾语oldenglish古英语one-placepredication一位述谓结构optimumage最佳自学年龄oralcavity口腔overextension拓展过度overgeneralization归纳过度overtthought有声思维palatal腭音paralinguistic副语言学的parameter参数performance语言运用performanceerror语言运用错误perlocutionaryact言后行为pharyngealcavity咽腔phone音素phoneme音位phonemiccontrast音位矛盾phoneticfeature语音特征phonetics语音学phonologicalrule音位规则phonology音位学phrasalcategory词组类phrasestructurerule短语结构规则pidgin洋泾浜语placeofarticulation发音部位plosive爆破音polysemy多义性postpone后移prepose前移postvocalic元音后的pragmatics语用学predicate谓语predication述谓结构predicationanalysis述谓结构分析prefix前缀presprictive(grammar)规定语法presupposition前提proposition命题prepositionalcontent命题内容protolanguage原始语psycholinguistics心理语言学puberty青春期qualifyingpredication润色性述谓结构receivedpronunciation标准发音recursiveness循环性reference所指语义referringexpression所指名词register语域relationalopposites关系反义词representation抒发;呈现出representatives阐述类response反应retroflex卷舌音rewriterule重写规则roundedvowel圆唇元音sae标准美国英语sapir-whorfhypothesis…假设secondlanguageacquisition第二语言习得segment切分成分semanticanomaly语义异体semanticdeviation语义变异semanticbroadening语义广义化semanticnarrowing语义狭义化semanticshift语义演变semantics语义学semanticstructure语义结构semantictriangle语义三角sense意义sequentialrule序列规则setting背景;环境sexistlanguage性别歧视语sibilant咝音simplesentence简单句sino-tibetan汉藏语系situationaldialect语域方言sociolect社会方言sociolinguistics社会语言学softpalate软腭species-specificcapacity物种特有能力structuralconstituency结构成分性structurallinguistics结构主义语言subject主语subordinatepredication主从述谓性结构subscript下标subvocalpredication无声言语suffix后缀superordinate上坐标词suprasegmentalfeature逊于切割特征surfacestructure表层结构synchroniclinguistics共时语言synonymy同义词syntacticambiguity句法歧义syntacticcategory句法类型syntacticrule句法规则syntax句法tabooword禁忌词targetlanguage目标语tautology同义反复teethridge齿龈隆骨telegraphicspeech电报式言语tenseandaspect时和体tensevowel紧元音tone音调;声调tonelanguage声调语言topic话题;主题transfer转移transformational-generativegrammar切换分解成语法transformationalrule转换规则treediagram树形图two-placepredication双位述谓结构unaspirated不声母underextension拓展严重不足universalgrammar广泛语法utterance话语utterancemeaning话语意义uvula小舌validity有效性variable变项velar软腭音velum软腭vernacular本地话;本国语vocalcord声带voiced浊音化的voiceless不拎音的,清音的voicing拎音化,浊音化vowel元音wernicke’sarea韦尼克区wideningofmeaning词义扩大x-bartheoryx标杆理论。


Chapter 1 Introduction语言学的定义:Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language.问题:How do you interpret the following definition of linguistics: Linguistics is the scientific study of language?→It is a scientific study because it is based on the systematic investigation of linguistic data, conducted with reference to some general theory of language structure.What the linguist has to do “first, then, but”:①to observe and collect language facts and generalizations are made about them.②to formulate some hypotheses about the language structure.③to check the hypotheses thus formed repeatedly against the observed facts to fully prove their validity.The study of language as a whole is often called general linguistics. (普通语言学)问题: What are the major branches of linguistics? What does each of them study?→phonetics(语音学)→the study of sounds→phonology(音位学)→study how sounds are put together and used to convey meaning→morphology(形态学)→study the way in which symbols or morphemes are arranged and combined to form words.→syntax(句法学)→the study of rules of forming sentences →semantics(语义学)→the study of meaning→pragmatics(语用学)→ the context of language use Sociolinguistics(社会语言学):The studies of all these social aspects of language and its relation with society form the core of the branch.Psycholinguistics(语言心理学):Relate the study of language to psychologyApplied linguistics(应用语言学):In a narrow sense it refers to the application of linguistic theories and principles to language teaching, especially the teaching of foreign and second languages.Some important distinctions in linguistics:①prescriptive(规定性)/descriptive(描写性)②synchronic(共时)/diachronic(历时)③speech(口语)/writing(书面语)④langue(语言)/parole(言语)(the Swiss linguist F. de Saussure ——Course in General Linguistics)⑤competence(语言能力)/performance(语言应用)(the American linguist N. Chomsky)⑥traditional grammar (传统语法)/modern linguistics(现代语言学)问题:in what basic ways does modern linguistics differ from traditional grammar?①linguistics is descriptive while traditional grammar is prescriptive.②modern linguistics regards the spoken language as primary, not the written.③modern linguistics does not force languages into a Latin-based framework.问题:Is modern linguistics mainly synchronic or diachronic? Why?In modern linguistics, a synchronic (不考虑历史演进的, 限于一时的) approach seems to enjoy priority over a diachronic (探求现象变化的, 历时的) one.Because it is believed that unless the various states of a language in different historical periods are successfully studied, it would be difficult to describe the changes that have taken place in its historical development.Synchronic descriptions are often thought of as being descriptions of language in its current existence, and most linguistic studies are of this type.问题:For what reasons does modern linguistics give priority to speech rather than to writing?From the point of view of linguistic evolution, speech is prior to writing. The writing system of any language is always “invented”by its users to record speech when the need arises. Even in today’s world there are still many languages that can only be spoken but not written. Then in everyday communication, speech plays a greater role than writing in terms of the amount of information conveyed.Spoken language reveals more true features of human speech while written language is only the “revised”record of speech. And linguists’data for investigation and analysis are mostly drawn from everyday speech, which they regarded as authentic.语言的定义:Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.Design features of language(7个识别特征)①arbitrariness 任意性(at the syntactic level)②productivity 能产性,创造性Secondary units(底层结构 sounds)③duality 双层性Primary units (上层结构 units of meaning)④displacement 不受时空限制性(handle generalization and abstraction)⑤cultural transmission 文化传递性⑥interchangeability 互换性⑦convention 约定性Functions of language:三大主要功能:The descriptive functionThe expressive functionThe social functionRoman Jacobson(6种首要因素,结构主义语言学家)①speaker addresser→emotive 感情功能②addressee→conative 意动功能③context→referential所指功能④message→poetic 诗学功能⑤contact→phatic communion交感功能⑥code→metalinguistic 元语言功能Other functions:①phatic function 问候功能②informative f. 信息功能③interrogative f. 询问功能④expressive f. 表达功能⑤evocative f. 感染功能⑥directive f. 指令功能⑦performative f. 行使(权力)功能M.A.K. Halliday①ideational②interpersonal(indicate/establish/maintain/social relationships)③textual问题:How is Saussure’s distinction between langue and parole similar to Chomsky’s distinction between competence and performance?The distinction between langue and parole was made by Saussure, langue is abstract; it is not the language people actually use. Parole is concrete; it refers to the naturally occurring language events. Langue is relatively stable; it does not change frequently, while parole varies from people to people, and from situation to situation.The distinction between competence and performance proposed by the American linguists Chomsky, competence is a deal user’s knowledge of the rules of his language, and the performance is the actual realization of this knowledge in linguisticcommunication. Imperfect performance is caused by social and psychological factors.Saussure makes this distinction in order to single out one aspect of language for serious study. In his opinion, parole is simple a mass of linguistic facts, too varied confusing for systematic investigation, and that linguistics should do is to abstract langue from parole, i.e., to discover the regularities governing the actual use of language and make them the subjects of study of linguistics.Similar to Saussure, Chomsky thinks what linguists should study is the ideal speaker’s competence, not his performance, which is too haphazard to be studied.问题:What are the main features of human language that have been specified by C. Hockett to show that it is essentially different from animal communication system?①arbitrariness 任意性(at the syntactic level)②productivity 能产性,创造性Secondary units(底层结构 sounds)③duality 双层性Primary units (上层结构 units of meaning)④displacement 不受时空限制性(handle generalization andabstraction)⑤cultural transmission 文化传递性⑥interchangeability 互换性⑦convention 约定性Chapter 2 PhonologyPhonetics: (语音学)①the study of the phonic medium of language②look at speech sounds from 3 distinct but related points of view.Ⅰstudy the sounds from the speaker’s point of view→articulatory phonetics(发音语音学)Ⅱlook at the sounds from the hearer’s point of view→auditory phonetics(听觉语音学)Ⅲstudy the way sounds travel by looking at the sound waves →acoustic phonetics(声学语音学)③study how sounds are produced, transmitted and perceived. Organs of speech:⒈three important areas①The pharyngeal cavity→the throat② the oral cavity→the mouth③ the nasal cavity→the nose⒉The pharyngeal cavity→windpipe/glottis/larynx/vocalcords⒊the oral cavity→tongue/uvula/soft palate(velum)/hard palate/teeth ridge(alveolus)/teeth/lipsInternational Phonetic Alphabet (IPA)①diacritics 附加符号②broad transcription(宽式标音)→the transcription with letter-symbols only③narrow transcription(严式标音)→the transcription withletter-symbols together withthe diacriticsClassification of English speech sounds①two broad categories of speech sounds in English: Vowels/consonants②two ways to classify the English consonants: In terms ofmanner ofarticulationIn terms of place of articulation③In terms of manner of articulation:Stops/fricatives/affricates/liquids/nasals/glides④In terms of place of articulation:Bilabial/labiodental/dental/alveolar/palatal/velar/glottal⑤Classification of English vowels⒈criteria :(monophthongs)单元音The position of the tongue in the mouth: front/central/back The openness of the mouth: close vowels/semi-closevowels/semi-openvowels/open vowels The shape of the lips: unrounded/roundedThe length of the vowels: tense/lax⒉diphthongs 双元音/ ei // ai // au // əu // ɔi // iə //εə// uə /Phonology 音韵学,语音体系Difference of phonology and phonetics:①Phonetics is interested in all the speech sounds used in allhuman languages.②Phonology aims to discover how speech sounds in a languageform patterns and how these sounds are used to convey meaning in linguistic communication.Phone(音素): A phone is a phonetic unit or segment. Phoneme(音位): It is a phonological unit; it is a unit that is of distinctive value. It is an abstract unit. It is not any particular sound, but rather it is represented or realized by a certain phone in a certain phonetic context.Allophone(音位变体): The different phones which can represent a phoneme in different phonetic environments are called the allophones of that phoneme.Phonemic contrast(音位对立)Complementary distribution(音位变体的互补分布)Minimal pairs(最小对立体):含音位的单词的全部音标Minimal set(最小对立集):is used to find the important sounds in language.Phonological Analysis(音位分析)Principle: certain sounds cause changes in the meaning of a word or phase, whereas other sounds do not.Phonetically similar sounds:描述音位关系Free variants: 音位的自由变体The difference of pronouncing a sound caused by dialect, habit, individual difference or regional differences instead of by any distribution rule.Some rules in phonology①sequential rules: 序列规则If a word begins with a / l / or a / r /, then the next sound must be a vowel.If three consonants should cluster together at the beginning of a word, the combination should obey the following three rules:The first phoneme must be / s /The second phoneme must be / p / / t / / k /The third phoneme must be / l // r // w /②assimilation rule:同化规则③deletion rule:省略规则Suprasegmental features 超音段特征≠超音段(比音位更大的语言单位)①stress(单词,句子层面):the location of stress in English distinguishes meaning.Syllable音节:A syllable nucleus (often a vowel) with optional initial and final margins (often consonants)单音节词多音节词英语单词都有重读音位学中,单词由音节构成,音节由音位构成。

Chapter 1 Introduction语言学的定义:Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language.问题:How do you interpret the following definition of linguistics: Linguistics is the scientific study of language?→It is a scientific study because it is based on the systematic investigation of linguistic data, conducted with reference to some general theory of language structure. What the linguist has to do “first, then, but”:①to observe and collect language facts and generalizations are made about them.②to formulate some hypotheses about the language structure.③to check the hypotheses thus formed repeatedly against the observed facts to fully prove their validity.The study of language as a whole is often called general linguistics. (普通语言学)问题: What are the major branches of linguistics? What does each of them study?→phonetics(语音学)→the study of sounds→phonology(音位学)→study how sounds are put together and used to convey meaning→morphology(形态学)→study the way in which symbols or morphemes are arranged and combined to form words.→syntax(句法学)→the study of rules of forming sentences→semantics(语义学)→the study of meaning→pragmatics(语用学)→ the context of language useSociolinguistics(社会语言学):The studies of all these social aspects of language and its relation with society form the core of the branch.Psycholinguistics(语言心理学):Relate the study of language to psychology Applied linguistics(应用语言学):In a narrow sense it refers to the application of linguistic theories and principles to language teaching, especially the teaching of foreign and second languages.Some important distinctions in linguistics:①prescriptive(规定性)/descriptive(描写性)②synchronic(共时)/diachronic(历时)③speech(口语)/writing(书面语)④langue(语言)/parole(言语)(the Swiss linguist F. de Saussure——Course in General Linguistics)⑤competence(语言能力)/performance(语言应用)(the American linguist N. Chomsky)⑥traditional grammar (传统语法)/modern linguistics(现代语言学)问题:in what basic ways does modern linguistics differ from traditional grammar?①linguistics is descriptive while traditional grammar is prescriptive.②modern linguistics regards the spoken language as primary, not the written.③modern linguistics does not force languages into a Latin-based framework.问题:Is modern linguistics mainly synchronic or diachronic? Why?In modern linguistics, a synchronic (不考虑历史演进的, 限于一时的) approach seems to enjoy priority over a diachronic (探求现象变化的, 历时的) one.Because it is believed that unless the various states of a language in different historical periods are successfully studied, it would be difficult to describe the changes that have taken place in its historical development.Synchronic descriptions are often thought of as being descriptions of language in its current existence, and most linguistic studies are of this type.问题:For what reasons does modern linguistics give priority to speech rather than to writing?From the point of view of linguistic evolution, speech is prior to writing. The writing system of any language is always “invented” by its users to record speech when the need arises. Even in today’s world there are still many languages that can only be spoken but not written. Then in everyday communication, speech plays a greater role than writing in terms of the amount of information conveyed.Spoken language reveals more true features of human speech while written language①phatic function 问候功能②informative f. 信息功能③interrogative f. 询问功能④expressive f. 表达功能⑤evocative f. 感染功能⑥directive f. 指令功能⑦performative f. 行使(权力)功能M.A.K. Halliday①ideational②interpersonal(indicate/establish/maintain/social relationships)③textual问题:How is Saussure’s distinction between langue and parole similar to Chomsky’s distinction between competence and performance?The distinction between langue and parole was made by Saussure, langue is abstract; it is not the language people actually use. Parole is concrete; it refers to the naturally occurring language events. Langue is relatively stable; it does not change frequently, while parole varies from people to people, and from situation to situation.The distinction between competence and performance proposed by the American linguists Chomsky, competence is a deal user’s knowledge of the rules of his language, and the performance is the actual realization of this knowledge in linguistic communication. Imperfect performance is caused by social and psychological factors. Saussure makes this distinction in order to single out one aspect of language for serious study. In his opinion, parole is simple a mass of linguistic facts, too varied confusing for systematic investigation, and that linguistics should do is to abstract langue from parole, i.e., to discover the regularities governing the actual use of language and make them the subjects of study of linguistics.Similar to Saussure, Chomsky thinks what linguists should study is the ideal speaker’s competence, not his performance, which is too haphazard to be studied.问题:What are the main features of human language that have been specified by C. Hockett②tone(词汇层面)English is not a tone languageChinese is a typical tone language:Level/the second rise/the third fall-rise/the fourth fall③intonation(句子层面)English has four basic types of intonation:The falling tone/the rising tone/the fall-rise tone/the rise-fall tone问题:What are the two major media of communication? Of the two, which one is primary and why?Speech and writingSpeechBecause from the point of view of linguistic evolution, speech is prior to writing. The writing system of any language is always “invented” by its users to record speech when the need arises. Even in today’s world there are still many languages that can only be spoken but not written. Then in everyday communication, speech plays a greater role than writing in terms of the amount of information conveyed.Spoken language reveals more true features of human speech while written language is only the “revised” record of speech. And linguists’ data for investigation and analysis are mostly drawn from everyday speech, which they regarded as authentic.问题:What is voicing and how is it caused?Vibration of the vocal cords results in a quality of speech sounds called “voicing”, which is a feature of all vowels and some consonants in English.Chapter 3 Morphology 词法形态学1 定义和知识点:①the part of the grammar that is concerned with word formation and word structure②the branch of linguistics that studies the internal structure of words, and the rules by which words are formed.③it is essentially synchronic, primarily concerned with the forms of words through the use of morpheme construct.④it overlaps with the other sub-branches as a word is a sound unit that has meaning and syntactic function.⑤four facets:Sounds (phonology)Constructions (syntax)Meanings (semantics)Forms of words2 词性分类①open class words:名、动、形、副are the content words of a language②closed class words: 连、介、冠、代are small and stable since few new wordsare added3 词素有关❶ Morpheme: 词素构成单词的最小意义单位,包括声音和意义,abstract units(任意性)❷ Morph: 形素the sound of a morpheme 声音❸ Allomorphs: 语素变体The variant forms of a morpheme4 分类morphemes① Free morpheme(自由词素): A morpheme which can be a word by itself② bound morpheme(粘着词素):A morpheme that must be attached to another one③ lexical morphemes/ derivational morphemes(派生词素,包括前后缀): They are used to derive new words, also known as derivational morphemes④ inflectional morphemes(屈折词素):词类不发生变化5 单词定义:WordA word is a unit of expression which is intuitively recognized by native speakers in both spoken and written language.A word is a basic and minimal units of a language to make sentences, which are6 lexical meaningSense and referenceSense 定义:It is concerned with the inherent meaning of a linguistic form, the collection of all its features; it is abstract and de-contextualized. (Dictionary compilers are interested in)每个单词都有它的意义(sense)Reference 定义:It means what a linguistic form refers to in the real, physical world; it deals with the relationship between the linguistic element and the non-linguistic world of experience.不是所有单词都有语义(reference)Major sense relations:❶synonymy 同义关系synonyms①dialectal synonyms 方言同义词(British English and American English)Girl------lass/lassie (Scottish dialect)Liquor-------whiskey (Irish dialect)B AAutumn fallLift elevatorLuggage baggageLorry truckPetrol gasolineFlat apartmentWindscreen windshieldTorch flashlight②stylistic synonymsWords having the same meaning may differ in style, or degree of formalityE.g. old man/daddy/dad/father/male parentStart/begin/commenceKid/child/offspringKick the bucket/pop off/die/pass away/decease③synonyms that differ in their emotive or evaluation meaningCollaborator / accomplice④collocational synonyms 短语同义词Accuse…of/charge…with/rebuke…forRotten tomatoes/addled eggs/rancid bacon/sour milk⑤semantically different synonyms语义上不同的同义词Amaze/astoundDrift/float❷polysemy 一词多义❸homonymy 同音异义①identical in sound(homophones): Rain/reign night/knight piece/peace leak/leek②identical in spelling(homographs): Bow/bow tear/tear lead/lead③identical in both sound and spelling(complete homonyms): Fast/fast scale/scale❹hyponymy 下义关系①It refers to the sense relation between a more general, more inclusive word and a more specific word.②superordinate 上坐标词③hyponyms 下义词④co-hyponyms 共同下义词E.g. Flower: rose/tulip/carnation/lily/morning gloryAnimal: dog/cat/tiger/lion/wolf/elephant/fox/bearFurniture: bed/table/desk/dresser/wardrobe/settee❺antonymy 反义关系①gradable antonyms 等级反义词②complementary antonyms 互补反义词(不能共存,非此即彼)③relational opposites 反向反义关系(相反的两个极端但可共存)7 sense relations between sentences①X is synonymous with Y.(X真,Y真;X假,Y假)②X is inconsistent with Y.(X 真,Y假;X假,Y真)③X entails Y.(X真,Y一定真;X假,Y可真可假)④X presupposes Y.(X真,Y一定真;X假,Y仍为真)⑤X is a contradiction. (X永远假)⑥X is semantically anomalous.语义破格句8 analysis of meaning❶componential analysis----a way to analyze lexical meaning(成分分析) Semantic features语义特征:The word “man” comprises the features of +HUMAN,+ADULT,+ANIMATE,+MALE❷predication analysis----a way to analyze sentence meaning(述谓结构分析)The meaning of a sentence is not to be worked out by adding up the meanings of all its constituent words.There are two aspects to sentence meaningGrammatical meaning: grammatical well-formednessThe grammaticality of a sentence is governed by the grammatical rules of the language.Semantic meaning:Whether a sentence is semantically meaningful is governed by rules called selectional restrictions(选择限制).(constraints on what lexical items can go with what others.)注意同生成学派次范畴化进行对比Predication analysis:proposed by the British linguist G. Leech.Predication: it is the abstraction of the meaning of a sentence.A predication consists of argument(s)(变元) and predicate(谓词)E.g. TOM(SMOKE)KID, APPLE(LIKE)(BE HOT)(SNOW)Argument(s)(变元)定义:。

语言学总结一、语言和语言学1、语言的区别性特征:Designoffeaturesof?language??任意性?arbitrariness?指语言符号和它代表的意义没有天然的联系??二重性?duality?指语言由两层结构组成??创造性?creativity?指语言可以被创造??移位性?displacement?指语言可以代表时间和空间上不可及的物体、时间、观点2、语言的功能(不是很重要)??????????????3????????????4??计5????????语言能力和语言运用:乔姆斯基(chomsky提出)能力:competence用语言的人的语言知识储备运用:performance真实的语言使用者在实际中的语言使用二、语音学1、语音学分支??发音语音学articulatoryphonetics研究语言的产生??声学语言学acousticphonetics研究语音的物理属性??听觉语音学auditoryphonetics研究语言怎样被感知2IPA(国际音标)是由danielJones琼斯提出的三、音位学1、最小对立体minimalpairs2、音位phoneme3?音位变体allophones4?互补分布complementarydistribution5?自由变体?freevariation6?区别特征?distinctivefeatures7?超音段特征suprasegmentalfeature??音节syllable重音stress语调tone声调intonation四形态学1?词的构成??语素morpheme自由语素freemorpheme粘着语素boundmorpheme主位与述位themeandrheme主位:谈话中已知的信息,说话者从它谈起known,述位:与说话者内容有关的内容whatthespeakerstatesabout 7????????交际力communicativeanddynamism简称CD指句子成分对交际发展所作的贡献的程度六、语义学1?利奇的意义七分法Leechandhis7typesofmeaning??概念意义conceptualmeaning字面意义??内涵意义connotativemeaning实际交往过程中所指的事物??社会意义??情感意义affectivemeaning??反射意义reflectivemeaning由一个词语联想起来的另外一种意义??搭配意义collocativemeaning??主位意义thematicmeaning通过调整信息的顺序和强调内容所表达的意义2????????指称论referentialtheory指将词的意义和他所指的食物联系起来的意义理论3????????语义三角semantictriangle奥格登和理查兹提出Symbol或form指语言要素(如词和语素),thelinguisticelements能指thought指概念concept所指reference指经验世界中的物体theobjectinthewordofexperience涵义sense语言形式的意义○合作原则:说话人和听话人为达一定的交际目的,都有一种默契,一种都遵循的原则??○四个准则fourcategoriesofmaxims数量、质量、关系、方式(manner)准则3????????后格赖斯时期的发展○关联理论:relevancetheory:交际应被看做一种表明自身说话意图的行为everyactofostensive(直接表明的)communicationcommunicatesthepresumptionofitsownoptimalrelevance○数量关系和关系原则theQ-andR-principles由霍恩LaurenceHorn提出八现代语言学理论和流派1?索绪尔Saussure瑞士语言学家,“现代语言学之父”或者“使语言学科走向现代的大师”2?布拉格学派PragueSchool??贡献:共时语言学研究,从“功能”角度看待语言,强调语言的系统性,把语言看做一种功能??突出贡献:语音学说,及其划分语音学和音位学??突出:Trubetzkoy特鲁别茨柯依:提出语音学属于言语,音位学属于语言,提出音位概念4????????伦敦学派theLundonSchool:系统语言学和功能语言学创始人:弗斯Firth.人物:弗斯受马林诺夫斯基影响。

语言学术语(英-汉对照)表Glossary and Index Aabbreviation 缩写词,略语 3.3.1Abercrombie 10.3.2ablative 夺格,离格 4.1.1abstractness 抽象性 1.3.2accent 重音(符)2.4.4;2.4.5accuracy 正确性 11.6.4accusative 宾格 4.1.1achievement test 成绩测试 11.6.3acoustic phonetics 声学语音学 1.7.1;2.1 acquisition 习得 6.1.2acronym 缩略语 3.3.1action process 动作过程 12.2.3actor 动作者 4.4.2;12.2.3addition 添加 3.3.2address form 称呼形式 7.2.3addressee 受话人 1.4;9.4.1addresser 发话人 1.4;9.4.1adjective 形容词 3.1.2;4.1.1;5.5.2adjunct 修饰成分;附加语 12.2.3adverb 副词 3.1.2affix 词缀 3.2.1affix hopping 词缀跳跃 4.3.1affixation词缀附加法 7.1.4affricate 塞擦音 2.4.3;2.4.5;2.9.1 agreement 一致关系 4.1.3airstream 气流 2alliteration 头韵 9.3.2;9.3.6allomorph 词/语素变体 3.2.4;4.3.1allophone 音位变体 2.8allophonic variation 音位变体 2.8.3allophony音位变体现象 2.8.3alveolar ridge 齿龈 2.2alveolar 齿龈音 2.4.4;2.4.5ambiguity 歧义 4.2.2;4.3.1;6.2.3;8.2.2;8.3.2 ambiguous歧义的 5.5.2;6.3American descriptive linguistics 美国描写语言学 12.3 American English 美式英语 10.3.5American Indian languages 美国印第安族诸语言 12.3 American structuralism 美国结构主义10.3.2;12.3 analogical creation 类推造字 3.3.1anapest 抑抑扬格 9.3.3anaphor 前指替代 4.3.3anaphoric reference 前指照应 4.3.2Anderson 6.3.1Animal communication system 动物交际系统 1.2;1.3 animate 有生命的 4.2.1annotation 注解 10.3.4;10.3.5antecedent 先行词;前在词 4.3.2anthropological 人类学的 12.3.1anthropological linguistics 人类语言学 1.8.3;7.1.1 anticipatory coarticulation 逆化协同发音 2.6.1 antonomasia 换称;代类名 7.1.4antonym 反义词 5.4antonymy 反义(关系) 5.3.2appellative 称谓性4.4.2applied linguistics 应用语言学11applied sociolinguistics 应用社会语言学7.2.4 appropriacy 适宜性11.6.4appropriateness 适宜性;得体性11.2.5approximant 无摩擦延续音2.4.3;2.4.5Apte 7;7.2.1aptitude test 素质测试11.6.2Arabic 阿拉伯语3.3.1;4.4.1arbitrariness 任意性1.3.1;12argument 中项;中词;主目4.3.3;5.5.2article 冠词3.1.2;4.1.1;4.2.1articulation 发音2.6articulator 发音器官2.4.2;2.4.3articulatory phonetics 发音语音学1.7.1;2.1 artificial speech 人工言语10aspect 体4.1.2aspirated 吐气;送气2.6.2;2.8.2assimilation 同化2.9.1;3.2.4;3.3.2;6.2.4associative 联想 4.2.1associative meaning 联想意义 5.3assonance 准压韵;半谐音9.3.2;9.3.6Atkinson, A.M. 2.1attributive 属性;修饰语;定语 4.2.2;12.2.3 auditory phonetics 听觉语音学 1.7.1;2.1Austin, John Langshaw 8.1;8.1.2authentic input 真实投入 11.4.2authorial style 权威风格 9.4.3authoring program 编程 10.1.3autonomy 自主性 1.8auxiliary 助词 3.1.2;12.4.3auxiliary verb 助动词 3.1.2;12.2.3Bbabbling stage 婴儿语阶段 12.4.1back-formation 逆构词法 3.3.1Bally, Charles 9.1Bar-Hillel 10.2.1Barnhart & Barnhart 7.1.4base component 基础部分 4.3.2;12.4。
语言学术语大全专业英语词汇在英语的学习中,词汇量的积累无疑是很重要的,语言学方面的英语单词你知道多少呢,下面是店铺整理的一些语言学术语,希望对大家有帮助。
语言学术语:语言学导论animal cry theory/bow-wow theory模声说anthropology人类学Applied linguistics应用语言学Bilateral opposition双边对立checked syllable成阻音节closed syllable闭音节Constant opposition恒定对立Contetualism语境论Conversational implicature会话含义Deictics指示词descriptive linguistics描写语言学dialectology方言学ding-dong theory/nativistic theory本能论Discourse analysis话语分析empirical linguistics经验语言学Equipollent opposition均等对立general linguistics普通语言学Graded opposition渐次对立grammar语法学historical linguistics历史语言学Isolated opposition孤立对立lexicology词汇学Meaning potential意义潜势Metalanguage原语言morphology形态学morphotactics语素结构学/形态配列学morphs形素Mutilateral opposition多边对立Neutralizable opposition可中立对立Nominalism唯名学派open syllable开音节Phatic communion寒暄交谈phonology音系学pooh-pooh theory感叹说Prague school布拉格学派Presupposition预设Private opposition表缺对立Proportional opposition部分对立Psychosomatics身学rank 等级level层次signified所指signifier能指sing-song theory唱歌说Speech acts言语行为stylistics文体学sub-structure低层结构super-structure上层结构syntactic categories句法范畴syntactic classes句法类别序列syntax句法学Systemic-functional grammar系统功能语法ta-ta theory模仿说theoretical linguistics理论语言学yo-he-ho theory劳动喊声说语言学术语:语音Active articulator积极发音器官Adam’s apple喉结Alveolar ride齿龈隆骨Anticipatory assimilation先行同化Apico-alveolar舌尖齿龈音Approximant [j,w]无摩擦延续音back舌后部Bilateral consonant双边辅音blade舌叶/舌面Breath state呼吸状态Broad transcription宽式标音center舌中部Central approximant中央无摩擦延续音Centring diphthong央二合元音Click/ingressive吸气音Closed state封闭状态Closing diphthong闭二合元音Coalescent assimilation融合同化Contiguous assimilation临近同化Contrastive stress对比重音Devoicing清音化Diacritic mark附加符号Diphthongization二合元音化Diphthong二合元音Dorso-alveolar舌背齿龈音Dorso-palatal舌背腭音dorsum舌背Dorsum舌背Ejective呼气音Epenthesis插音Etymology词源Free variant自由变体Free variation自由变异front舌前部Glottal stop喉塞音glottalic airstream mechanism喉气流机制Glottalised stop喉塞音Immovable speech organ不能动发音器官Impossive内爆破音initiator启动部分Interdental齿间音Intonation contour语调升降曲线Intonology语调学Juxtapostional assimilation邻接同化Labal-velar唇化软腭音laryngealization喉化音laryngeals喉音Lateral approximant边无摩擦延续音Lateral边音Lexical stress词汇重音Lexical tone词汇声调Maximal onset principle最大节首辅音原则Monophthongization单元音化Monosyllabic word多音节词Movable speech organ能动发音器官Multilevel phonology多层次音系学Narrow diphthong窄二合元音Narrow transcription窄式标音Non-lateral非边音Non-segmental非音段Nuclear tone核心声调Orthoepy正音法Orthography正字法Palato-alveolar后齿龈音Palato-alveolar腭齿龈音Partial assimilation部分同化Passive articulator消极发音器官pharynx喉/咽腔Phonetic similarity语音相似性Plurisegmental复音段Polysyllabic word单音节次Post-dental后齿音Post-palatal后腭音Pre-palatal前腭音Primary stress主重音Progressive assimilation顺同化pulmonic airstream mechanism肺气流机制Pure vowel纯元音Reciprocal assimilation互相同化Regressive assimilation逆同化Resonant共鸣音rolled consonant滚辅音root舌跟Secondary stress次重音Segmental phonemes音段音位Segmental phonology音段音系学Sentence stress句子重音Stress group重音群Suprasegmental超音段Synthetic language综合型语言tip舌尖Tone units声调单Tonetics声调学top舌顶trachea/windpipe气管Trill [r]颤音trilled consonant颤辅音Triphthong三合元音Unilateral consonant单边辅音velaric airstream mechanism腭气流机制Velarization软腭音化vocal cords声带vocal tract声腔Voice state带音状态Voiced consonant浊辅音Voiced sound浊音Voiceless consonant请辅音Voiceless sound清音Voicing浊音化Weak stress弱重音Whisper state耳语状态Wide diphthong宽二合元音Word stress词重音。
第一章Invitation to Linguistics1.Definition of language:Language is a system of vocal (and written) symbols with meaning attached that is used forhuman communication of thoughts and feelings.2.Design features of language(语言的普遍特征):①.Arbitrariness 任意性:The forms of linguistic signs generally bear no natural relationship to the meanings they carry②.Duality 二重性:Human language has two levels of structures: the primary meaningful level of morphemes, words, phrases, sentences and the secondary meaningless level of sounds. The units of the primary level are composed of elements of the secondary level, and each of the two levels has its own principles of organization.③.Creativity 创造性:Language is resourceful because of its duality and recursiveness.④.Displacement移位性:Human languages enable their users to symbolize objects, events and concepts which are not present in time and space at the moment of communication.3.Functions of language1)Informative function2)Interpersonal function人际功能3)Performative (行为) function4)Emotive function5)Phatic (寒暄) function6)Recreational function7)Metalingual function(元语言功能)指用语言去说明或解释语言的功能4.Main branches of linguistics:Main branches of linguistics (microlinguistics微观) and interdisciplinary(跨领域、跨学科)fields of linguistics (macrolinguistics宏观)1) Main branches of linguistics:(1) Phonetics发音学,语音学;(2) Phonology;(音位学、语音体系)(3) Morphology 词法/ Lexicology词汇学;(4) Syntax句法;(5) Semantics语义学(6) Pragmatics语用学:研究特定情境中的特定话语,在不同的语言交际环境中如何理解和运用语言支。
第一章、绪论Introduction1、语言学的主要分支是什么。
每个分支的研究对象是什么?Linguistics mainly involves the following branches:General linguistics, which is the study of language as a whole and which deals with the basic concepts, theories, descriptions, models and methods applicablein any linguistic studyPhonetics, which studies the sounds that are used in linguistic communicationPhonology,which studies how sounds are put together and used in communicationMorphology, which studies the way in which morphemes are arranged to form wordsSyntax, which studies how morphemes and words are combined to form sentencesSemantics, which is the study of meaning in language.Pragmatics, which is the study of meaning not in isolation, but in context of useSociolinguistics, which is the study of language with reference to societyPsycholinguistics, which is the study of language with reference to the workings of mind.Applied linguistics, which is concerned about the application of linguistic findings in linguistic studies; In a narrow sense, applied linguistics refers to the application of linguistic principles and theories to language teaching and learning, especially the teaching of foreign and second languages.Other related branches are anthropological linguistics, neurological inguistics, mathematical linguistics, and computational linguistics.2、现代语言学Modern linguistics与传统语法Traditional grammar 有什么区别?Traditional grammar is prescriptive; it is based on "high "(religious, literary) written language. It sets models for language users to follow. But Modern linguistics is descriptive; its investigations are based on authentic, and mainly spoken language data. It is supposed to be scientific and objective and the task of linguists is supposed to describe the language people actually use, whether it is "correct" or not.3、什么叫共时研究?什么叫历时研究?The description of a language at some point in time is a Synchronic study (共时研究); the description of a language as it changes through time is a diachronic study(历时研究). A synchronic study of language describes a language as it is at some particular point in rime, while a diachronic study of language is a historical study; it studies the historical development of language over a period of time.4、人类语言的甄别性特征是什么?1) Arbitrariness 。
★Haliday—child language. Macrofunctions: ideational, interpersonal, textual.★what are major branches of linguistics? what does each study?Phonetics----the study of the phonic medium of language, it’s concerned with all the sounds that occur in the world’s languages.Phonology---the study of sounds systems—the inventory of distinctive sounds that occur in a language and the patterns into which they fall.Morphology---It’s a branch of a grammar which studies the internal structure of words and the rules by which words are formed.Syntax-------it's a subfield of linguistics that studies the sentence structure of a language. Semantics---It’s simply defined as the study of meaning in abstraction.Pragmatics---the study of meaning in context of words. The study of how speakers of a language use sentences to effect successful communication.Sociolinguistics—the study of language with reference to society.Psycholinguistics---the study of language with reference to the working of the mind. Applied linguistics---the application of linguistic principles and theories to language teaching and learning.Chapter2 Phonology★three branches of phonetics:①Articulatory —describes the way our speech organs work to produce the speech sounds and how they differ. ②Auditory-–studies the physical properties of speech sounds, reaches the important conclusion that phonetic identity is only a theoretical ideal. ③Acoustic-–studies the physical properties of speech sounds ,the way sound travel from the speaker to the hearer.★Organs of Speech : Pharyngeal cavity–咽腔Oral cavity–口腔greatest source of modification of air stream found here Nasal cavity–鼻腔★Broad transcription: The transcription of speech sounds with letter symbols only. (leaf /l/) ★Narrow transcription: The transcription of speech sound with letters symbols and the diacritics.(dark /l/~)★Phonetics and Phonology区别: are concerned with the same aspect of language- the speech sounds. ①Phonetics: it is interested in all the speech sounds used in all human languages; phonetic features they possess; how they can be classified, etc. ②Phonology: it aims to discover how speech sounds in a language form patterns and how these sounds are used to convey meaning in linguistic communication.★rules in Phonology:①Sequential rules: Rules that govern the combination of sounds in a particular language. ②Assimilation rules: The assimilation rule assimilates one sound to another by’ copying ’a feature of a sequential phoneme, thus making the two phones similar.③Deletion rule: It’s a phonological rule which tells us when a sound is to be deleted although its orthographically represented.★Suprasegmental超切分特征: The phonemic features that occur above the level of the segment are called suprasegmental features. the main suprasegmental features include stress ,intonation and tone.(intonation: when pitch, stress and sound lenth are tied to the sentence rather than the word in isolation. //tone: Tone are pitch variations, which are caused by the differing rates of vibration of the vocal cords. Tone is a suprasegmental feature.)Chapter3 Morphology★open class words: new words can be added to these classes regularly. Such as nouns, verbs,adjectives and adverbs. Such as Beatnik. Closed class words:conjunctions, prepositions, articles and pronouns consist of the grammatical or functional words. The number of such words is small and stable since few new words are added.Chapter4 Syntax★determine a word’s category:①meaning. Word categories often bear some relationship with its meaning. The meaning associated with nouns and verbs can be elaborated in various ways. The property or attribute of the entities denoted by nouns can be elaborated by adjectives.(pretty lady, attribute the property “pretty”to the lady.) ②inflection. Words of different categories take different inflections. Such nouns as boy and desk take the plural affix -s. Verbs such as work and help take past tense affix -ed and progressive affix -ing. ③distribution. That is what type of elements can co-occur with a certain word. For example, the girl and a card ④小结A word's distributional facts together with information about its meaning and inflectional capabilities help identify its syntactic category.★phrase包括: head, specifier, complement. ①The word round which phrase is formed is termed head. ②The words on the left side of the heads are said to function as specifiers. Specifiers have both special semantic and syntactic roles: Semantically, they help make more precise the meaning of the head. Syntactically, they typically make a phrase boundary. ③The words on the right side of the heads are complements. Complements are themselves phrases and provide information about entities and locations whose existence is implied by the meaning of the head. They are attached to the right of the head in English.★phrase structure rule: The special type of grammatical mechanism that regulates the arrangement of elements that make up a phrase is called a phrase structure rule.★XP rule: In all phrases, the specifier is attached at the top level to the left of the head while the complement is attached to the right. These similarities can be summarized as an XP rule, in which X stands for the head N,V,A or P. (XP-----> (specifier) X (complement))★coordination rule:Some structures are formed by joining two or more elements of the same type with the help of a conjunction such as and or or. Such phenomenon is known as coordination. Such structure are called coordination structure. (Four important properties:①There is no limit on the number of coordinated categories that can appear prior to the conjunction. ②A category at any level (a head or an entire XP) can be coordinated. ③Coordinated categories must be of the same type. ④The category type of the coordinate phrase is identical to the category type of the elements being conjoined.) Coordination Rule: X------ > X *Con X)★deep structure and surface structure: There are two levels of syntactic structure. The first, formed by the XP rule in accordance with the head's subcategorization properties, is called deep structure (or D-structure). //The second, corresponding to the final syntactic form of the sentence which results from appropriate transformations, is called surface structure (or S-structure).Chapter 5 Semantics★The naming theory: (Greek scholar Plato) According to this theory, the linguistic forms or symbols, in other words, the words used in a language are taken to be labels of the objects they stand for, so words are just names or labels for things.★The conceptualist view: It holds that there is no direct link between a linguistic form and what it refers to; rather ,in the interpretation of meaning they are linked through themediation of concepts in the mind.★Contextualism: (J.R. Firth) people should be studied in terms of situation, use, context—elements closely linked with language behaviour. It’s based on the presumption that one can derive meaning from or reduce meaning to observable contexts. two kinds of context: the situational and the linguistic context. {A) the situational context: Every utterance occurs in a particular situation, the main components of which include, the speaker and the hearer, the actions they are performing, the various objects and events existent in the situation.-----The seal could not be found. B) the linguistic context: co-text, is concerned with the probability of a word’s co-occurrence or collocation with another word, which forms part of the “meaning” of the word, and also with the part of text that precedes and follows a particular utterance.-----black coffer& black hair.}★Sense refers to the inherent meaning of a linguistic form, which is the collection of all the features of the linguistic form, it’s abstract and de-contextualized. //Reference is what a linguistic form refers to in the real, physical world, it is a matter of relationship between the form and reality. //关系: ①Linguistic forms, having the same sense, may have different reference in different situations. ②Linguistic forms with the same reference may differ in sense.-----morning star= evening star. ③Linguistic forms may have sense, but have no reference in the real world.------dragon, ghost.★Hyponymy:It refers to the sense relation between a more general, more inclusive word and a more specific word. the word which is more general in meaning is called superordinate, and the more specific words are called its hyponyms.★X entails Y: entailment: the relationship between two sentences where the truth of one is inferred from the truth of the other. E.g. Cindy killed the dog entails the dog is dead. (X :John married a blond heiress. Y: John married a blond.)★componential analysis: an approach to analyze the lexical meaning into a set of meaning components or semantic features. For example, boy may be shown as [+human] [+male] [-adult]. semantic features:The smallest units of meaning in a word, which may be described as a combination of semantic components. For example, woman has the semantic features [+human] [-male] [+adult]. //Advantages: by specifying the semantic features of certain word, it will be possible to show how these words are related in meaning.★Predication Analysis:①The meaning of a sentence is not the sum total of the meanings of all its components, that is, the meaning of a sentence is not to be worked out by adding up all the meanings of its constituent words. E.g: The dog bit the man. & The man bit the dog.②There are two aspects to sentence meaning: grammatical meaning and semantic meaning. Grammaticality: grammatical (well-formedness); Semantically meaningful: selectional restrictions. (selectional restriction: Whether a sentence is semantically meaningful is governed by the rules called selectional restrictions, i.e. constraints on what lexical items can go with what others.)……(consist of predicate and argument)Chapter 6 pragmatics★Context(John Firth): The notion of context is essential to the pragmatic study of language, it’s generally considered as constituted by the knowledge shared by the speaker and the hearer. ★Speech act theory(John Austin)★Searle’s Classification of Speech Acts: 1 representatives: Stating or describing, saying what the speaker believes to be true. 2 directives: Trying to get the hearer to do something. 3commisives: Committing the speaker himself to some future course of action. 4 expressives: Expressing feelings or attitude towards an existing state. 5 declaration: Bring about immediate changes by saying something. ///Conclusion: All the acts that belong to the same category share the same purpose but differ in their strength or force.★cooperative Principle(CP): Proposed by Paul Grice, the principle that the participants must first of all be willing to cooperate in making conversation, otherwise, it would be impossible to carry on the talk.★Historical linguistics: a branch of linguistics, is mainly concerned with both the description and explanation of language changes that occurred over time.★semantic broadening: when the meaning of a word becomes broader, it may include all the meanings it used to mean, and then more. Such as holiday, which originally meant holy day, but it means any day which we don’t have to work.★semantic narrowing: semantic change has narrowed the meaning of some words. such as deer(any animal—a particular kind of animal)★semantic shif t: a lexical item may undergo a shift in meaning is the third kind of semantic change.★sociolinguistics: is the sub-field of linguistic that studies the relation between language and society, between the uses of language and the social structures in which the users of language live.★Inter-relationship between language and society:A) language is used not only to communicate meaning, but also establish and maintain social relationships. B) Users of the same language in a sense all speak differently, due to their social backgrounds. C) Language, especially the structure of its lexicon, reflects both the physical and the social environments of a society. E.g. there is only one word in English for snow, and there are several in Eskimo.D) Language is related to the structure if the society in which it is used, therefore, judgments concerning the correctness and purity of linguistic varieties are social rather than linguistic.E.g. the use of postvocalic [r] in England and in New Y ork city.★speech community: the social group that is singled out for any special study.★speech variety: refers to any distinguishable form of speech used by a speaker or a group of speakers. i.e. regional dialects, sociolects, registers★Register: in a restricted sense, refers to the variety of language related to one’s occupation. In a broader sense, the type of language which is selected as appropriate to the type of situation is a register. {A) Field of discourse---- topic: the purpose and subject matter of the communicative behavior.---- why/ what---vocabulary, phonological, grammatical features B) Tenor of discourse---- role: participants and in what relationship they stand to each other. ---- formality/ technicality of the language we use. C) Mode of discourse ---- means of communication.-----how ( speaking or writing).}★degree of formality: intimate; casual; consultative; formal; frozen★culture: A)In a broad sense: Culture means the total way of life of a people, including the patterns of belief, customs, objects, institutions, techniques, and language that characterizes the life of the human community. B) In a narrow sense: Culture may refer to a local or specific practice, beliefs or customs, which can be mostly found in folk culture, enterprise culture or food culture etc.★The relationship between language and culture:①language as an integral part of human being permeates his thinking and way of viewing the world. It both expresses and embodies cultural reality. ②reflects and affects a culture’s way of thinking and helps perpetuate and change the culture and its influence, which also facilitates the development of this language at the same time. ③language is a part of culture.★Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis: A belief that the way people view the world is determined wholly or partly by their structure of their native language.------interdependence of language and thought….(there are two interpretations: a strong version and a weak one. The strong version believes that language patterns determine people’s thinking and behavior. The weak one holds that the former influences the later.)★Greetings and terms of address:A) People in different countries choose the proper greetings to greet different people they meet on different occasions. B) The terms of address can be different in different countries. C) Chinese people will also extend kinship terms and indicate people’s influential st atus.★cultural overlap: The situation between two societies due to some similarities in the natural environment and psychology of human being★cultural diffusion: Through communication, some elements of culture A enter culture B and become part of culture B, thus bringing about cultural diffusion.★linguistics imperialism: it is a kind of kind of linguicism which can be defined as the promulgation of global ideologies through the world-wide expansion of one language.★language acquisition: It refers to the child’s acquisition of his mother tongue, i.e. how the child comes to understand and speak the language of his community. (the behaviourist, the innatist{ LAD= Language Acquisition Device}, the interactionist view{motherese, child directed speech, caretaker talk}★under-extension: Use a word with less than its usual range of denotation. E.g, baby uses animal to refer to cat, but denies the bird belongs to an animal.★over-extension:Extension of the meaning of a word beyond its usual domain of application by young children. E.g, baby uses apple for all fruit.★Atypical Development:hearing impairment, mental retardation, autism, stuttering, aphasia, dyslexia, dysgraphia.★second language acquisition: It refers to the systematic study of how one person acquires a second language subsequent to his native language.★Connection between first language acquisition and second language acquisition: ①Theoretically----The new findings and advances in fist language acquisition especially in learning theories and learning process are illuminating in understanding second language acquisition. ②Practically------The techniques used to collect and analyze data in first language acquisition also provide insights and perspectives in the study of second language acquisition. ③second language acquisition is different from first language acquisition and the second language learners generally fail to attain native-like competence. ★interlanguage: A type of language produced by second and foreign language learners, who are in the process of learning a language, and this type of language usually contains wrong expressions. It is also called learner language.-- its main feature is fossilization.★overgeneralization: The use of previously available strategies in new situations, in which they are unacceptable. E.g: Jane suggested me to give up smoking (×).★cross-association: some words are similar in meaning as well as spelling and pronunciation. This internal interference is called cross-association. E.g. The apricot is too sour to eat it(×). ★Individual Differences:①Language aptitude ②motivation(instrumental motivation; integrative motivation; resultative motivation; intrinsic motivation pleasure from learning.)③learning strategie (cognitive strategies; metacognitive strategies; affect/ social strategies)④Age of Acquisition. ⑤Personality★Neurolinguistics: is the study of language disorders and the relationship between the brain and language. It includes research into how the structure of the brain influences language learning, how and in which parts of the brain language is stored, and how damage to the brain affects the ability to use language.★Aphasia refers to a number of acquired language disorder due to the cerebral lesions caused by vascular problems, a tumor, an accident and so on.★psycholinguistics is the study of psychological states and mental activity associated with the use of language. It concerns the representation of language in the mind, the planning, production, perception and comprehension of speech, and language acquisition.front central backClose (high) i:I u:uSemi-close (middle)eз:。
英语语言学专业术语英语语言学是研究英语语言的起源、发展、结构和使用的学科。
以下是常见的英语语言学专业术语及其解释。
1. Phonetics(音系学):研究语音的学科。
主要研究语音发音过程,包括语音的组成、发音方式和特点等。
2. Phonology(音韵学):研究语音在语言中的功能和规律的学科。
主要研究语音在不同语境下的变化规律和相互关系,包括音素、音位和音系等。
3. Morphology(形态学):研究语言中单词的形态和构成的学科。
主要研究单词的基本单位和构成规律,包括词根、词缀和词类等。
4. Syntax(句法学):研究句子结构和句子组成的学科。
主要研究句子的构成和排列方式,包括短语、从句和主谓结构等。
5. Semantics(语义学):研究语言意义的学科。
主要研究语言符号和意义之间的关系,包括单词、短语和句子的意义等。
6. Pragmatics(语用学):研究语言使用的学科。
主要研究语言与社会文化环境的关系,包括语境、语用规则和交际意图等。
7. Discourse analysis(话语分析):研究语篇结构和语篇功能的学科。
主要研究语言在话语交际中的组织和作用,包括话语行为、话语结构和话语分析方法等。
8. Sociolinguistics(社会语言学):研究语言和社会文化因素之间的关系和影响的学科。
主要研究不同社会群体、文化背景和地理区域中语言使用的差异和变化,包括方言、语言变体和语言政策等。
9. Psycholinguistics(心理语言学):研究语言和心理过程之间的关系的学科。
主要研究语言理解、语言产生和语言习得等心理过程,包括语音知觉、语法处理和语言记忆等。
以上是英语语言学常见的专业术语及其解释,希望能够帮助你更好地了解英语语言学。