unit5-语法
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.46 MB
- 文档页数:32

译林新版英语七上Unit 5语法解析Unit 5 A healthy lifestyle!一、语法解析可数名词及不可数名词* 定义:名词的数指数量,即“多少”。
单数:表示“一”;复数:表示“多于一”* 名词可数性:可数名词和不可数名词* 可数名词单数变复数规则1.一般情况直接加s如:star --stars; book -- books等2. 以字母s,x,sh,ch等结尾词直接加es如:bus -- buses; watch -- watches等3.以字母f或fe结尾的词将f或fe变为v再加es如:leaf -- leaves; knife -- knives等4. 以辅音字母加y结尾的词变y为i再加es如:baby -- babies; city -- cities等5.以元音字母加y结尾的词直接加s如:toy -- toys; monkey -- monkeys等6. 以es, se, ze, ge等结尾的词直接加s如:face -- faces; orange -- oranges等7. 以辅音字母加o结尾的词若表示有生命力则加es如:tomato -- tomatoes; hero -- heroes等若表示无生命力则加s如:photo --photos等8. 不规则变化改a为e型:man -- men; woman -- women改oo为ee型:tooth -- teeth; foot -- feet在词尾加-ren:child -- children单复数形式相同:sheep; deer; Chinese; Japanese常用复数形式或只有复数形式:noodles; glasses; trousers; thanks; clothes; chopsticks; people等其他特殊形式:mouse -- mice; 老鼠;mouse -- mouses鼠标注意:1. 有些以f或ef结尾的词直接加s变成复数:如:roof -- roofs; chief -- chiefs等2. 由man和woman 构成的合成词,其复数形式需前后都变复数:如:man doctor -- men doctors; woman teacher -- women teachers等3. 名词作定语修饰另一个名词时,通常只变后一个名词:如:boy student ---boy students;apple tree -- apple trees等* 不可数名词的量化:通常不可数名词没有复数形式,不能用a/an修饰,且不能用数词直接修饰。


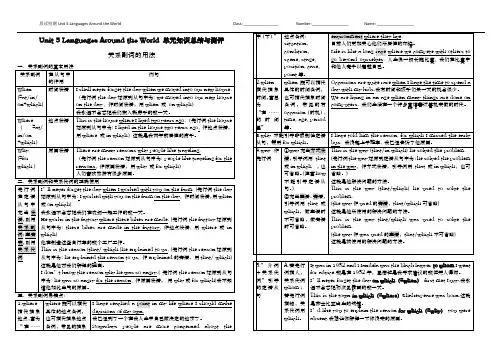
Unit 5 Do you want to watch a game show?一、单词用法1.mind(sb/sb.'s)doing sth.介意(某人)做某事2.can't stand(doing)sth.无法忍受(做)某事hope+that从句希望……expect+that从句预计……8. Sth. + happen(s) to sb.某人发生了某事。
Sb. + happen(s) to do sth.某人碰巧做某事。
二、知识点汇总1.三种方式询问对...的评价(1) What ...think of/about+sb./sth./doing(2)How...like...?(3)How...feel about...?2.mind n.主意;头脑mind vt.介意,在意(多用于否定和疑问句中)mind doing 介意做某事mind+sb/sb's+doing 介意某人做...3.can't stand doing 不能忍受做某事4. educational adj.教育的;有教育意义的education n.教育5.Planplan to do=make a plan to do 计划做某事make a plan for 为......制定计划6.news 一则消息 a piece of news7.find out“查出”,强调经过一番了解和查询,弄明白某一情况。
find“找到,发现”指偶然或意外地发现,着重指找到的结果。
8.discussiondiscussion n. have a discussion about sb/sthdiscuss v.讨论discuss sth with sb9.happen 发生、出现sth+happens/happened to sb"某人发生了某事”(常指不好的事)sb.happens/happened to do sth “某人碰巧做某事”happen 指偶然发生或突发事件的发生;take place 指按计划或事先安排的发生10.expect to do...期待/期望做什么expect sb to do 期待/期望某人做某事hope:指对愿望实现有一定信心的希望.hope to do 不能用hope sb to do11.meaningless adj.无意义的meaningful adj.有意义的meaning(s)n.意思mean(s)v.意味着,意思是12.Jenjoyable令人愉悦11Scared15.famous adj.著名的;出名的作为...而出名be famous as...因...而出名be famous for对...而言出名be famous to...16.such as 诸如...;像;比如...1 prep.超过more thanover prep. 在......的正上方over adj.完了的,结束的下课。

人教版八年级下册英语Unit5知识点总结一、语法知识点A部分知识点1.过去进行时❶ 去进行时的构成及用法过去进行时由“助动词(was/were)+动词-ing”构成,表示在过去某一时刻或某一时间段正在进行的动作。
这一特定的过去时间除有上下文暗示以外,一般用过去的时间状语来表示。
如:then, at that time, at this time yesterday, at 10:00 yesterday morning, all right以及when/while从句等。
❶ 表示过去时间点正在进行的动作。
此时常伴明确的过去时间点等。
eg:She was reading a book at this time yesterday.昨天这个时候她正在看书。
(过去时间点正在进行的动作)I was watching TV then. 那时我正在看电视。
(过去时间点正在进行的动作)❶ 表示过去的某个阶段持续的动作。
eg:She was watching TV when the phone rang.(过去一段时间内持续的动作)她正在看电视,这时电话铃响了。
❶ 表示这一阶段反复发生的动作,带有褒贬感情色彩。
此时常伴有频度副词always等。
eg:The girl was always changing her mind.(过去反复发生的动作,带有感情色彩)这个女孩老是改变主意。
❶ 表示过去动作延迟到以后发生,即用过去进行表过去将来,此类动词是一些位置的变化的词。
eg:He told me that he was going soon.(过去进行表将来)他告诉我他很快就要走了。
❶ 过去进行时的一般疑问句句型:Be(Was/Were)+主语+现在分词+其他?肯定回答:Yes,主语+be(was/were).否定回答:No,主语+be(was/were) not.eg:--Were you cooking at that time? 那时,你在做饭吗?--Yes, I were.是的。

Unit 5语法知识及练习一、被动语态(一)语态:英语的语态是通过动词形式的变化表现出来的。
英语中有两种语态:主动语态和被动语态。
主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者。
Many people speak Chinese. 谓语:speak的动作是由主语many people来执行的。
被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者,即行为动作的对象。
例如:Chinese is spoken by many people. 主语English是动词speak的承受者。
(二)被动语态的构成被动语态由“助动词be+及物动词的过去分词”构成。
人称、数和时态的变化是通过be的变化表现出来的。
现以speak为例说明被动语态在各种时态中的构成。
一般现在时:am/is/are+spoken 一般过去时:was/were+spoken一般将来时:will/shall be+spoken 现在进行时:am/is/are being+spoken过去进行时:was/were being+spoken现在完成时:have/has been+spoken(三)被动语态的用法(1)不知道或没有必要说明动作的执行者是谁。
例如:Some new computers were stolen last night.一些新电脑在昨晚被盗了。
(2)强调动作的承受者,而不强调动作的执行者。
例如:This book was written by him.这本书是他写的。
Your homework must be finished on time.你们的家庭作业必须及时完成。
(四)主动语态变被动语态的方法(1)把主动语态的宾语变为被动语态的主语。
(2)把谓语变成被动结构(be+过去分词)(根据被动语态句子里的主语的人称和数,以及原来主动语态句子中动词的时态来决定be的形式)。
(3)把主动语态中的主语放在介词by之后作宾语,将主格改为宾格。
例如:All the people laughed at him. →He was laughed at by all people.They make the bikes in the factory. → The bikes are made by them in the factory.He cut down a tree. → A tree was cut down by him.(五)含有情态动词的被动语态含有情态动词的主动句变成被动句时,由“情态动词+be+过去分词”构成We can repair this watch in two days.→This watch can be repaired in two days.They should do it at once.→It should be done at once.(六)特殊情况1.He made the boy work for two hours yesterday.→The boy was made to work by him for two hours yesterday.2.Jack gave Peter a Christmas present just now.→(1)A Christmas present was given to Peter by Jack just now.→(2)Peter was given a Christmas present by Jack just now.1. silk in Suzhou?A.Is;producedB. Are;producedC. Does;produceD. Do;produce2. I don’t understand why more girls to do housework thanboys in today’s society.A.askedB. were askedC. are askedD. ask3.The river after the heavy rain.A. has been raisedB. has been risenC. has raisedD. has risen4.—The T-shirt feels soft.—Yes. It cotton.A.is made ofB. is made inC. is made byD. is made into5. how busy he is,he is always ready to help others.A. Pay attention toB. No matterC. According toD. Thanks to解析:1. 本题主语silk与动词produce之间存在被动关系,因此应用被动语态,排除C、D两项;silk作“丝绸”讲是不可数名词,因此谓语动词用单数,排除B项。

人教版九年级全一册英语Unit5单元语法知识点总结本单元重点短语的具体用法1. be made of:表示某物由某种材料制成,且制成后原材料仍可辨认。
例如:- This table is made of wood. 这张桌子是由木头制成的。
2. be made from:与“be made of”意思相近,但强调制成的物品已经看不出原材料。
例如:- Paper is made from wood. 纸是由木头制成的。
3. be known for:意为“因……而闻名”。
例如:- This city is known for its beautiful beaches. 这座城市以其美丽的海滩而闻名。
4. be used for:表示某物被用于某种目的。
例如:- This tool is used for cutting wood. 这个工具是用来砍木头的。
5. no matter:“不论;无论”,引导让步状语从句。
例如:- No matter what happens, I will always support you. 无论发生什么,我都会一直支持你。
6. be covered with:表示被某种东西覆盖。
例如:- The ground is covered with snow. 地面被雪覆盖了。
7. as far as I know:“据我所知”,常用在句首。
例如:- As far as I know, she is a very kind person. 据我所知,她是一个非常善良的人。
8. by hand:“用手”,强调手工制作。
例如:- These cookies were made by hand. 这些饼干是手工制作的。
9. be good for:“对……有益”,例如:- Exercising is good for your health. 锻炼对你的健康有好处。
10. on the last Friday of each month:“在每个月的最后一个星期五”,例如:- The meeting is always held on the last Friday of each month. 会议总是在每个月的最后一个星期五举行。

Unit 5 What do they do?语法梳理:一般现在时的陈述句精讲精练(含答案)一般现在时表示经常性或习惯性的动作或表示现在的特征或状态,也可表示客观事实或普遍真理。
一、第三人称单数的具体情况总结我们已经了解当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词要相应地使用第三人称单数形式。
那么如何判定主语是否是第三人称单数呢?具体有以下分类:1.人称代词he, she, it作主语。
2.单个的人名、地名或称呼作主语。
例如:My sister works here.我的姐姐/妹妹在这里工作。
3.可数名词单数或“this/that/the/a等+可数名词单数”作主语。
例如:This boy looks happy. 这个男孩看上去很高兴。
The rabbit jumps high.这只兔子跳得高。
4.不定代词someone, somebody, nobody, everything, something等以及指示代词this和that作主语。
例如:Someone talks in class.有人在课堂上说话。
5.不可数名词作主语。
例如:The soup is too hot. 汤太烫了。
6.数字或者字母作主语。
例如:Thirteen and seven is twenty.十三加七等于二十。
7.特殊疑问句中,what,who等疑问代词作主语。
例如:Who lives here? 谁住在这儿?What makes you happy? 什么让你高兴?二、一般现在时的肯定句基本结构为“主语+动词原形/动词第三人称单数形式+其他.”。
例如:He likes swimming. 他喜欢游泳。
I go to school every day.我每天去上学。
This giraffe is so tall.这只长颈鹿是如此的高。
Miss Li teaches English. 李老师教英语。
三、一般现在时的否定句1.含有be动词的句子,改为否定句时,在be动词后加not,句中如有some则改为any。

一、过去进行时态1.概念:过去进行时表示在过去某一时刻或某一段时间内正在进行的动作。
这一特定的过去时间,除了有上下文暗示以外,一般带有具体的过去时间,如:this time yesterday,at 9:00 yesterday morning等;或以when,while 引导的时间状语来表示。
2.构成:过去进行时的基本结构为:主语+ was/were + v.ing + 其它成分。
否定形式是在be后加not;一般疑问句是将be提前。
下面以work为例,将其肯定式,否定式和疑问式及简略答语表述如下肯定式与否定式:I/He/She/It was working. I/He/She/It was not working.We/You/They were working. We/You/They were not working.疑问式与简略答语:—Was I working?—Yes,you were./No,you were not.—Were you working?—Yes,I was./No,I was not.—Was he/she/it working?—Yes,he/she/it was./No,he/she/it was not.—Were you/we/they working?—Yes,we/you/they were./No,we/you/they were not. was not常缩写为wasn't;were not常缩写为weren't。
过去进行时与一般过去时的用法区别:过去进行时表示过去正在进行或发生的动作,强调动作的持续性,动作可能尚未完成;而一般过去时则多强调动作的发生或已完成。
例句:Mary was writing a letter to her father last night.玛丽昨晚一直在给她爸爸写信。
(强调写信过程的延续性,但信不一定写完了。

人教版八年级下册英语Unit 5单元语法知识点总结本单元重点短语的具体用法1. make sure:确信;确认。
例如:Make sure you lock the door before you leave.(在你离开之前,确保锁好门。
)2. beat against...:拍打……。
例如:The waves were beating against the shore.(波浪拍打着海岸。
)3. fall asleep:进入梦乡;睡着。
例如:I fell asleep while watching TV.(我看电视时睡着了。
)4. die down:逐渐变弱;逐渐消失。
例如:The fire died down after the firefighters arrived.(消防员到达后,火逐渐熄灭了。
)5. wake up:醒来。
例如:I usually wake up at 7 o'clock in the morning.(我通常早上7 点醒来。
)6. in a mess:一团糟。
例如:The room is in a mess.(房间一团糟。
)7. break...apart:使……分离。
例如:The police had to break the door apart to enter the room.(警察不得不破门而入进入房间。
)8. in times of difficulty:在困难的时候。
例如:We should help each other in times of difficulty.(在困难的时候,我们应该互相帮助。
)9. at the time of:当……时候。
例如:At the time of the accident, I was sleeping.(在事故发生时,我正在睡觉。
)10. go off:(闹钟)发出响声。
例如:The alarm went off at 6 o'clock.(闹钟在6 点钟响了。

高中英语必修三Unit 5语法汇总一、过去将来时1.过去将来时表示从过去某一时间来看将要发生的动作或存在的状态,常用在宾语从句中。
一般由“would/should+动词原形”构成。
*She hoped thatthey would meet again someday.她希望将来有一天他们能再见面。
*I rang up to tellmy father that I should leave for London.我打电话告诉我父亲我要去伦敦。
2.was/were goingto+动词原形:表示过去将要发生或很有可能发生的动作,常用于口语中,表示预言、意图或者打算等。
*He was going tostart work the following week.他打算下星期开始工作。
*—Alice, whydidn’t you come yesterday?——爱丽丝,你昨天为什么没来呀?—I was going to,but I had an unexpected visitor.——我打算去的,但我家来了个不速之客。
3.start, go,come, leave, see, meet等动词的过去进行时: 表示就过去某一时刻而言即将发生的动作。
*She was cominglater.她随后就来。
*I had just put onmy overcoat and was leaving to visit a friend of mine.我刚穿上外套要去看我的一个朋友。
4.was/were aboutto do: 常用来表示即将发生的动作,“刚要/正要做……”。
注意该结构不与任何时间状语连用。
*I felt thatsomething terrible was about to happen.我感到某种可怕的事情即将发生。
*We were about togo there when it began to rain.我们刚打算去那儿,这时天下起了雨。
人教版(三起)-五上-Unit5-重点语法知识集结知识元重点语法:There be句型知识讲解There be句型一、含义There be句型是英语中常用句型,意思是“有”,表示“人或事物的存在”或“某地有某物”。
there在此结构中是引导词,已经没有副词“在那里”的含义。
二、句型结构There be(is/are)+某物/某人+在某地,即:There be+sth./sb.+sw.意为“在某地有某人或某物”例如:(1)There is a schoolbag in the classroom.(2)There are some students in the classroom.∙∙三、考点聚焦1.1.be动词的确定,遵循“单数is,复数are”原则。
对于不可数名词,看作是一个整体,默认为单数。
例如:(1)There is a ball under the chair.(2)There are two boys.(3)There is some water in the bottle.2.be动词的确定,当物体不止一种的时候,be动词的确定遵循“就近原则”,即单数在前用is;复数在前用are。
例如:(1)There is a teacher and two students in the classroom.(2)There are two students and a teacher in the classroom.3.there be“有”与have“有”的区别。
there be句型表达的是“在某个地方存在某人、某物等”,具有客观性;have则表示“某人拥有某物”,具有主观性。
例如:(1)There are some books in the bag.(2)I have some books in my bag.例题精讲重点语法:There be句型例1.Write the right form of“be”.1.There________many monkeys in the mountain.2.There_______a beautiful garden in our school.3.There_________some water in the glass.4._________there any maps on the wall?5.There__________some trees near the house.6.There_________some apple juice in the glass.例2.We moved________a new house.A.on B.for C.into例3.—________is your house?—It’s near the nature park.A.Where B.What C.How例4.There are________in it.A.a ball B.some waterC.lots of plants当堂练习单选题练习1.There__________a chair and two desks in the room.A.is B.areC.be练习2.There are________flowers.A.a B.manyC.any单句填空练习1.Finish the sentences1.在Ann的课桌里有一本新书。
姓名_______________ 上课时间__________________Unit 5 语法:动词不定式动词不定式作宾语1.构成基本形式:to+动词原形;有时可以不用to,to是不定式符号,本身无词义。
否定形式:not+(+to)动词原形2.句法功能:不定式可以作主语,表语,宾语,宾补,定语,状语,也就是除谓语动词之外的任何成分。
3.本单元重点是不定式宾语。
(1)只能接to do作宾语的动词:三个希望两答应:hope,wish,want,agree,promise。
两个要求莫拒绝:demand,ask,refuse。
设法学会做决定:manage,learn,decide。
不要假装做选择:pretend,choose。
还有would like,like,plan,expect等表示命令、打算或希望的。
(2)在find,think等后跟不定式作宾语时,常用it代替,而真正的宾语放在后面。
I find it easy to read English every day。
(3)常见的一些不带to的不定式:Why not do…,why don’t you do…,had better(not)do…,would rather do…,could/would/will you please(not)…。
I would rather stay at home。
(4)只能作某些动词的宾语,不能作介词的宾语。
(5)不定式常和疑问词what,which,when,where,how连用,相当于一个宾语从句。
He didn’t know where to go。
(6)有些动词后面跟动词不定式时,应将不定式符号to省去。
常见的动词有let,make,feel,help,watch,hear等感官动词和使役动词。
这是动词不定式作宾补。
一感(feel)、二听(hear,listen to)、三让(let,make,have)、四看(look at,see,watch,notice)。