核电厂系统与设备复习资料
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:825.38 KB
- 文档页数:13

核电厂系统及设备讲义一、核电厂概述核电厂是利用核裂变或核聚变能产生电能的设施。
核电厂通常由核反应堆、发电机、冷却系统、辅助设备等组成。
二、核反应堆核反应堆是核电厂的核心设备,它是进行核裂变或核聚变反应的地方。
核反应堆通常采用压水堆、沸水堆等不同类型。
核反应堆的安全运行是核电厂的关键。
三、发电机核电厂的发电机是将核反应堆产生的热能转化为电能的装置。
发电机通过转动产生电能,供给电网使用。
四、冷却系统核电厂的冷却系统用于散热,避免核反应堆过热。
冷却系统通常采用水冷却或气冷却的方式。
五、安全系统核电厂的安全系统包括应急关闭系统、防护系统等。
这些系统是核电厂保障安全运行的关键。
六、辅助设备核电厂的辅助设备包括控制系统、监测设备、燃料装置等。
这些设备为核电厂的正常运行提供支持。
七、废物处理系统核电厂产生的废物处理是核电厂运行的重要环节。
废物处理系统包括核废料处理设施、废水处理设施等。
以上就是核电厂系统及设备的简要介绍,核电厂作为清洁能源的重要组成部分,在全球范围内发挥着重要作用。
随着技术的不断发展,核电厂的安全性和效率将得到进一步提升。
八、安全防护设施核电厂的安全防护设施是保障核反应堆安全运行的重要一环。
其中包括核反应堆容器、保护壳和防辐射屏障等。
这些设施能够有效隔离放射性物质,确保辐射对周围环境和人员的影响得到最小化。
九、辐射监测系统核电厂使用辐射监测系统对反应堆周围环境和工作人员进行实时监测,以确保辐射水平在安全范围内。
这些监测系统包括气体采样装置、人员穿戴的辐射监测仪器等,能够及时警报,保障人员和环境的安全。
十、应急预案核电厂拥有完善的应急预案,对各种可能的事故和突发状况进行了充分的预案和演练。
一旦发生紧急情况,核电厂能够迅速启动应急预案,以及时有效地应对和解决问题。
十一、燃料处理系统核电厂的燃料处理系统负责燃料元件的储存、运输和辐射监测。
燃料元件是核反应堆的关键部件,核电厂需要对其进行精心管理和维护,以确保核反应堆的正常运行。
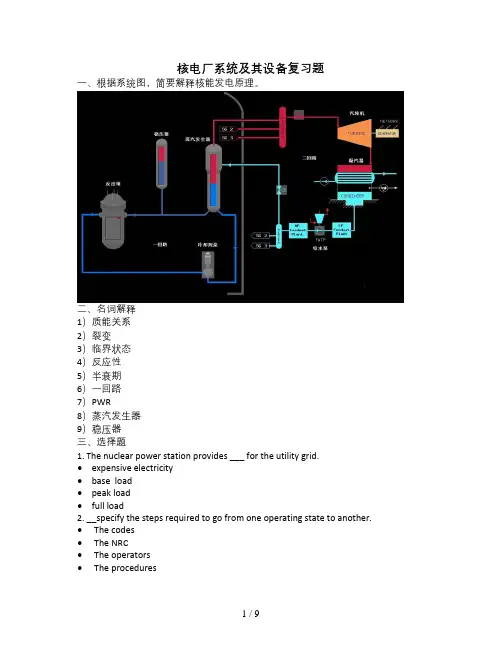
核电厂系统及其设备复习题一、根据系统图,简要解释核能发电原理。
二、名词解释1)质能关系2)裂变3)临界状态4)反应性5)半衰期6)一回路7)PWR8)蒸汽发生器9)稳压器三、选择题1. T he nuclear power station provides ___ for the utility grid. •expensive electricity•base load•peak load•full load2. __specify the steps required to go from one operating state to another. •The codes•The NRC•The operators•The procedures3. When large decrease in turbine load the steam from the steam generators is sent to the__.•steam condenser•atmosphere•steam dump system•heat exchanger4. An excess of coolant inventory can result in a___.•power increase•temperature increase•reactor trip•turbine trip5. Following the coastdown of the coolant pumps, the core residual heat will be removed by___.•condensers•natural circulation•boiling heat transfer•emergency power6. The operation of a nuclear plant is ___than operating a modern fossil fuel power station.•easier•more difficult•rather•more complex7. The heat is transferred by the reactor coolant from the core to the___. •cecondary loop•outlet nozzles•steam generators•pressurizer8. The fuel rod provides___to the escape of fission products.•two barriers•three barriers•seals• a barrier9.The CEA guide tubes are made of__.•stainless steel•ceramic•zircaloy•B4C10. The helium inside the fuel cladding improves the ____.•characteristic•gap heat conductivity•gap heat convection•clad strain11. The CEA guide tubes are arranged___.•in the fuel assembly•around the fuel assembly•in the center of fuel assembly•outside the fuel assembly12. The coolant can ___through the guide tubes.•not flow•be•flow•pass13. There ___ steam generator(s) in each primary loop.•is one•are two•are there•is no14. At the top of the tube bundle shroud, ___ are mounted.•eggcrates•steam-water separators•plates•baffles15. There ___ in the system 80+ steam generator.•is one feedwater inlet•are two feedwater inlets•are three feedwater inlets•are many feedwater inlets16. The flywheel on the motor is to provide___.•energy•water•coastdown flow•torque17. The temperature of the water in the seal assembly is maintained within acceptable limits by___.•water•oil•steam•water and oil18. In accordance with the coolant temperature program,the average reactor coolant temperature is ____ when steam demand is increased.•constant•fall•raised•high19. In pressurized water reactors water is used as___.•moderator•coolant•both a and b•neither a nor b20. The thermal efficiency of PWRs is___.•more than 40%•about 30%•less than 10%•about 70%21. The space between the reactor vessel and the core barrel is the ___.•fuel rods•control rods•downcomer•plenum22. The ECCS is provided to___.•cool the core•control reactivity•control volume•drive pump23. There are___ successive barriers in PWR to prevent radioactivity escape.•two•three•four•five24. The containment enclose the_____.•reactor•reactor and pressurizer•primary system and secondary system•entire primary system25. From the text the safest nuclear power plant may be a __.•expensive one•cheap one•big one•small one26. Following a decrease in turbine load, the water pressure and temperature in the reactor__.•will increase•increase•decrease•will be unchanged27. A temperature decrease of reactor vessel water results in an___. •insertion of control rods•power decease•power increase•increase of reactivity28. Loss of power is a ___.•upset condition•abnormal increase•reactor trip•reactor shutdown accident29. Inadvertent auxiliary spray will result in____.•temperature decrease•power decrease•pressure decrease•abnormal condition30. The long-term control of core reactivity means adjustment of____. •control rods•boric acid•power output•coolant31. The burnable absorber rod assembly provides the capability of high absorber strength__.•in all its life•at the beginning of refueling•at the end of refueling cycle•during operation32. The fuel assemblies used in a reactor are__.•similar•different•three types•same33. In the fuel rod the spring is set on the___.•pellet column•spacer disc•end cap•top34. The CEA guide tubes are welded to the___.•spacer grids•lower end fittings•control rods•end cap35. The fuel spacer grids are made of__.•stiff arches•springs•plates•zircaloy strips36. After long time radiation the boron carbide will___.•decrease in mass•be swelling•increase in mass•be dissipated37. The economizer increases the cold leg side ___ before coolant leaving the steam generator.•flow rate•temperature•temperature difference•relative flow38. The water from the steam separators flows down into the ___.•economizer•shroud•bundle•evaporator section39. In the downcomer the water is___.•saturated•boiling•very cold•subcooled40. The pump is connected with the motor by a___.•diaphragm•tube•coupling•casing41. ___ pressurizer heaters are connected to proportional controllers.• A few•The remaining•Most of the•Many42. The fluid from economizer section is ___.•two-phase flow•boiling water•subcooled water•saturated water43. The amount of heat that has been converted in steam turbine is ___ that removed in condenser.•more than•less than•same as•similar to44. The hot primary fluid exchanges its heat with the secondary fluid in the__. •pressurizer•condenser•header•steam generators45. Residual heat-removal system remove the decay heat from the core___. •during plant operation•after plant shutdown•during start-up•during transient condition46. The ___ is connected to the spent fuel pond by transfer canal. •containment•pressure vessel•pipe•reactor cavity47. One of the important factors influencing containment design is __.•the size•the pressure inside•LOCA•economic48. A sodium hydroxide additive is provided to reduce__.•the iodine concentration•the pressure•the radioactivity•vapor四、解释如下蒸发流程图,阐述作用和工作原理。

核电厂系统及设备知识反应堆是核电厂的核心设备,用于进行核裂变反应,产生大量热能。
反应堆一般由燃料组件、反应堆压力容器、反应控制系统等组成。
燃料组件是含有放射性核燃料的结构部件,可以产生裂变反应;反应堆压力容器是储存反应堆冷却剂的金属容器,保证核反应的正常进行;反应控制系统用于控制核反应的速率和安全性。
蒸汽发生器是连接反应堆和蒸汽涡轮发电机组的重要设备。
它通过将反应堆冷却剂的热能转移给水,使水蒸发成为高温高压的蒸汽,用于驱动蒸汽涡轮发电机组发电。
蒸汽涡轮发电机组是核电厂的主要发电设备,它将高温高压的蒸汽能量转化为电能。
核电厂的冷却系统用于冷却反应堆和蒸汽发生器,防止核反应过热和爆炸。
冷却系统通常包括主冷却循环、辅助冷却循环和应急冷却系统等。
核电厂的控制系统是对核反应堆进行监控和控制的设备,保证核反应的安全、稳定和高效进行。
此外,核电厂还有辅助设备包括供应水系统、通风系统、废物处理系统等,用于保障核电厂的运行和安全。
总的来说,核电厂的系统和设备是一个密不可分的系统,各部分设备协同工作,确保核反应的安全、高效进行,并将热能转化为电能。
核电厂是人类利用核能进行能源开发的重要手段之一。
尽管核能的利用被一些人质疑其安全性,但是通过严格的安全管理和监控,以及先进的技术和设备,核电厂在为人类提供清洁、高效的能源的同时,也保证了可靠性和安全性。
接下来我们将更加深入地了解核电厂的系统和设备知识。
反应堆是核电厂的核心部件,是核能转变为热能的场所,其内部包含着燃料组件,用以控制和维持反应中子的自持和增殖。
燃料组件一般是由铀或钚等元素的化合物构成,包装在金属或陶瓷的包壳中。
反应堆压力容器则是容纳反应堆冷却剂的主要设备,其壁厚、材料及焊缝质量等都受到严格的监控。
反应堆控制系统则是用于监控和控制核反应的速率和安全性的设备,包括各种传感器、控制棒和自动系统,确保核反应能够达到预期的状态。
蒸汽发生器连接在反应堆之后,通过将反应堆冷却剂的热能转移给水,使水蒸发生成高温高压的蒸汽。

注:本资料主要针对《核电厂系统及设备》臧希年编著第2版清华大学出版社2011年7月;笔者根据所学知识及综合一些其它资料汇编而成,分为课后习题解答与复习提纲两部分;本资料仅供读者作些参考,由于笔者知识有限,有些知识难免存在一些偏差,请批评指正。
2014年2月16日星期日第一部分:课后习题参考答案(2、3、4、5、7、8)第二章压水堆核电厂1.从电能生产的观点看,压水堆核电厂有哪些部分?各自有什么作用?答:从电能生产的角度看,压水堆核电厂分为核岛与常规岛,核岛利用核能生产蒸汽,常规岛利用蒸汽生产电能。
2.从热力循环的观点看,压水堆核电厂由几个回路组成?各自的作用是什么?答:压水堆核电厂主要由反应堆冷却剂系统(简称一回路),蒸汽和动力转换系统(又称二回路),循环水系统组成。
一回路生产蒸汽,二回路与三回路将蒸汽的热能转换为推动核汽轮机组转动的机械能。
3.核电厂的厂址须满足什么要求?答:应考虑三个方面①核电厂的本身特性。
核反应堆是一个强大的放射源,核电厂的热功率决定了反应堆内的放射性的总储量,在相同的运行条件下,堆内放射的总量与功率成正比。
②厂址的自然条件与技术要求。
应尽可能地避免或减少自然灾害(如地震,洪水,及灾难性气象条件)造成的后果,并应利于排出的放射性物质在环境中稀释③辐射安全要求。
⑴辐射安全应符合国家环境保护,辐射防护等法规和标准的要求⑵将核电厂设置在非居民区⑶考虑厂址周围的人口密度和分布。
4.核电厂主要有哪些厂房?核电厂主要有反应堆厂房(即安全壳),燃料厂房,核辅助厂房,汽轮机厂房和控制厂房。
5.解释名词:多道屏障,纵深防御,单一故障准则多道屏障:在所有情况下保证绝对控制过量放射性物质对外释放,核电厂设置了三道屏障,只有这三道屏障全部被破坏才会释放大量的放射性物质。
纵深防御:将安全有关的所有事项置于多重防御之下,在一道屏障失效后还有另一道屏障来弥补。
单一故障准则:当系统中某一部件不能执行其预定功能安全功能时,并不影响整个系统功能的执行。





核电厂系统及设备知识概述核电厂是一种利用核能发电的设施,它包含了一系列的系统和设备,每个系统和设备都发挥着重要的作用。
本文将介绍核电厂的主要系统和设备,并解释它们的功能和工作原理。
主要系统1.反应堆系统2.蒸汽发生器系统3.蒸汽涡轮机系统4.发电机系统5.控制和保护系统6.辅助系统下面将对每个系统进行详细介绍。
1. 反应堆系统反应堆系统是核电厂的核心组成部分。
它包括核反应堆、燃料组件、冷却剂循环系统和反应堆容器等。
核反应堆是核能发电的关键元素,它通过控制核反应过程来产生热能。
燃料组件是反应堆内用于核反应的燃料,通常使用铀或钚等放射性物质。
冷却剂循环系统用于将冷却剂(如轻水或重水)循环传递到反应堆中,从而控制反应堆的温度。
2. 蒸汽发生器系统蒸汽发生器系统使用反应堆中产生的热能将水转化为蒸汽。
蒸汽发生器是其中的关键设备,它通过将热能传递给水来产生高温高压的蒸汽。
蒸汽发生器中的水一般以自然循环或强制循环方式进行传热。
3. 蒸汽涡轮机系统蒸汽涡轮机系统利用蒸汽的能量驱动涡轮机的转动,从而产生机械能。
涡轮机通常由高压涡轮、中压涡轮和低压涡轮组成,每个涡轮对应一个级别的蒸汽。
这些涡轮通过轴传递机械能给发电机。
4. 发电机系统发电机系统将涡轮机传递过来的机械能转化为电能。
发电机是核电厂中非常重要的设备,它通过利用电磁感应原理将机械能转化为电能。
5. 控制和保护系统控制和保护系统对核电厂的运行和安全起着重要作用。
它包括控制设备、保护设备和监测设备等。
控制设备用于控制核反应堆和其他系统的运行,保护设备用于检测和响应发生异常情况,监测设备用于监测核电厂的运行状态和参数。
6. 辅助系统辅助系统是核电厂的辅助设备,它们为主要系统提供支持和保障。
常见的辅助系统包括给水系统、消防系统、氢气系统、冷却水系统等。
设备知识除了核电厂的主要系统,还有一些关键设备需要了解。
1.控制棒2.轻水堆3.反应堆压力容器4.冷却塔5.辐射防护设备控制棒是用于控制和调节核反应堆的关键设备,它可以通过插入或提取来控制核反应堆中的核反应过程。

核电厂系统与设备一回路复习题绪论1、简述压水堆核电站基本组成及工作原理?基本组成:以压水堆为热源的核电站。
主要由核岛(NI)、常规岛(CI)、电站配套设施(BOP)三大部分组成。
工作原理:(一)工作过程:核电厂用的燃料是铀235。
用铀制成的核燃料在“反应堆”的设备内发生裂变而产生大量热能,再用处于高压力下的水(冷却剂)把热能带出,在蒸汽发生器内产生蒸汽,蒸汽推动汽轮机带着发电机一起旋转,电就源源不断地产生出来,并通过电网送到四面八方。
一回路冷却剂循环:反应堆蒸汽发生器冷却剂泵反应堆二回路工质循环:蒸汽发生器汽轮机凝汽器凝、给水泵蒸汽发生器(二)压水堆核电站将核能转变为电能的过程,分为四步,在四个主要设备中实现的。
1、反应堆:将核能转变为热能(高温高压水作慢化剂和冷却剂);2、蒸汽发生器:将一回路高温高压水中的热量传递给二回路的给水,使其变为饱和蒸汽,在此只进行热量交换,不进行能量的转变;3、汽轮机:将饱和蒸汽的热能转变为高速旋转的机械能。
4、发电机:将汽轮机传来的机械能转变为电能。
能量传递过程为:裂变能→热能→传递→机械能→电能。
2、厂房及房间的识别符号如何定义?(P 3-5)厂房的识别定义:厂房的识别一般用3个符号来表示。
第一个符号为数字,表示机组识别,即该厂房是属于那个机组的,或两个机组共用的,还是不属于任何机组,而是属于工地系统的,第二、三个符号为两个英文字母,其中第一个字母表示厂房,第二个字母表示该厂房之区域。
房间的识别定义:房间的识别一般用三个数字符号来表示,第一个数字表示楼层,第二、三个数字表示房号。
3、设备的识别符号如何定义?设备识别用9个符号来表示。
这9个符号又分为两个大组,前4个符号为功能组符号,表示该设备属于哪台机组,哪个系统。
后5个符号为设备组符号,表示是什么设备及设备的编号。
(L—字母,N—数字)I-第一章1、压水型反应堆由哪几大部分组成?反应堆由堆芯、压力容器、堆内构件和控制棒驱动机构等四部分组成。

核电站系统与设备复习资料一回路部分:1、了解压水堆核电厂的基本组成、工作原理、安全设计、环境保护,熟悉我国各主要核电站的堆型、功率、发展战略等。
基本组成:核岛(NI)、常规岛(CI)、电站配套设施(BOP)工作原理:一回路冷却剂循环:反应堆→蒸汽发生器→冷却剂泵→反应堆二回路工质循环:蒸汽发生器→汽轮机→凝汽器凝→给水泵→蒸汽发生器安全设计:严格遵守核电站安全三要素:反应性控制、堆芯冷却和放射性产物的包容。
采用了多道安全屏障和纵深防御的原则环境保护:对核电厂的放射性进行热屏蔽、生物屏蔽;设臵放射性废物处理系统;严格遵守核废物处理的原则:分类处理,尽量回收,把排放量和放射性水平减至最小。
核电发展战略:坚持发展百万千瓦级先进压水堆核电技术路线,目前按照热中子反应堆—快中子反应堆—受控核聚变堆“三步走”的步骤开展工作。
2、掌握反应堆的基本结构、组成,各功能组件的组成、原理等;压力容器内冷却剂的流动方向等。
基本结构:1、反应堆压力容器2、反应堆堆内构件3、堆芯4、驱动机构组成:堆芯、压力容器、堆内构件和控制棒驱动机构3、掌握RCP系统、各设备的主要功能、主要组成、重要特征参数、运行参数等,自然循环的原理。
系统主要功能:1、热量传输2、中子慢化3、反应性控制4、压力控制5、阻止放射性物质扩散6、稳压器的安全阀起超压安全保护作用系统组成:由反应堆和与其相连的三个环路组成,每条环路包含一台蒸汽发生器、一台主泵及相应的管道。
一台稳压器是三个环路公用,经波动管连接在一环路的热管段上。
运行参数:系统运行压力14.7~15.7MPa(常用15.5MPa)——指什么地方压力?(稳压器汽腔压力)(1)反应堆进口冷却剂温度280~300℃(2)反应堆出口冷却剂温度310~330℃(3)反应堆进出口冷却剂温升30~40℃自然循环的原理:蒸汽发生器位置高于反应堆的位置,在蒸汽发生器中,冷(水)柱和热(水)柱之间的密度差为工质的循环提供驱动压头。
-1-1•通常将一回路及核岛辅助系统、专设安全设施和厂房称为核岛。
2. 反应堆冷却剂系统可分为冷却系统、压力调节系统和超压保护系统。
3. 压水堆本体由堆芯、堆芯支撑结构、反应堆压力容器及控制棒传动机构组成。
4•燃料组件骨架由24根控制棒导向管、1根中子注量率测量管与上下管座焊接而成。
5•蒸汽发生器是分隔一、二回路工质的屏障,它对于核电厂的安全运行十分重要。
6. 稳压器的基本功能是建立并维持一回路系统的压力,避免冷却剂在反应堆内发生容积沸腾。
7. 放射性废水有可复用废水和不可复用废水,可复用废水经过处理分离成水和硼酸再利用,这是硼回收系统的任务。
8. 专设安全设施包括:安全注射系统、安全壳、安全壳喷淋系统、安全壳隔离系统、安全壳消氢系统、辅助给水系统和应急电源。
9. 安全注入系统通常分为高压安全注入系统、蓄压箱注入系统、低压安全注入系统。
10•反应堆硼和水补给系统是一个两台机组共用的系统。
11. 核电站运行中产生的放射性废气分为含氢废气和含氧废气。
12. 核电厂主要厂房包括:反应堆厂房(安全壳)、燃料厂房、核辅助厂房、汽轮机发电厂房、控制厂房。
13. 核电厂设计一般遵循的安全设计原则有:多道屏障、纵深防御、单一故障原则、抗自然灾害、辐照剂量标准。
14•燃料组件由燃料元件、定位架格和组件骨架组成。
15•堆芯支撑结构包括下部支撑结构、上部支撑结构和堆芯仪表支撑结构16. 阻力塞棒是封闭的不锈钢管,其长度较短,约20cm17. 大亚湾压水堆核电厂的控制棒组件中黑棒采用的中子吸收剂材料为―Ag-In-Gr 银-铟-镉)灰棒材料为不锈钢—,控制棒驱动采用电磁步进式方式;18. 大亚湾核电厂的蒸汽发生器采用的是在压水堆核电站最为常见的立式自 然循环U 型管蒸汽发生器;19. 天然铀所含有的三种同位素中,属于易裂变核素的是铀-235;20•反应堆冷却剂泵主要分为两大类型分别是屏蔽电机泵和轴封泵;21. 蒸汽发生器传热管面积占一回路承压边界面积的80%左右;22. 压水堆核电厂使用较广泛的有三种:立式U 型管自然循环蒸汽发生器、卧式自然循环蒸汽发生器、立式直流蒸汽发生器一、填空题(共20分,每题2分)二、名词解释(共25分,每题5分)23.现代压水堆采用硼酸控制反应性。
一、词汇简写与翻译1、聚变fusion 裂变fission2、安全壳Containment Structure3、包壳Cladding4、控制棒Control Rods5、压力容器Reactor Vessel6、汽轮机Turbine7、冷凝器Condenser8、RCP反应堆冷却剂泵Reactor Coolant Pumps9、SG 蒸汽发生器Steam Generator10、SFR 钠冷快堆系统Sodium Cooled Fast Reactor System11、LFR铅冷快堆系统Lead Alloy Cooled Fast Reactor System12、GFR气冷快堆系统Gas Cooled Fast Reactor System13、VHTR超高温堆系统Supercritical Water Cooled Reactor System14、MSR熔盐堆系统Molten Salt Reactor System15、RPV 反应堆压力容器Reactor Pressure Vessel16、IAEA 国际原子能组织International Atomic Energy Agency17、EPR 欧洲压水堆European Pressurized Reactor18、ABWR先进的沸水反应堆Advanced Boiling Water Reactor19、PWR 压水堆Pressure Water Reactor20、BWR沸水堆Boiling Water Reactor21、CEFR 中国实验快堆China Experiment Fast Reactor22、DOE 美国能源部Department of Energy23、NRC 美国核管理委员会Nuclear Regulatory Commission24、CNNC 中国核工业集团总公司The China National Nuclear Corporation25、CGN26、CSS安全壳喷淋系统Containment Spray System27、RCS 反应堆冷却剂系统Reactor Coolant System28、OBE 运行基准地震Operating Basis Earthquake29、DBA 设计基准事故Design Basic Accident30、QA质量保证Quality Assurance31、ASME美国机械工程师协会American Society of Mechanical Engineers32、CVCS化学和容积控制系统Chemical and Volume Control System33、RBWM/REA 反应堆硼和水的补给系统Reactor Boron and Water Make up34、RHR 余热排出系统Residual Heat Removal35、CCWS/RRI 设备冷却系统Component Cooling Water System36、ESWS/SEC 重要厂用水系统Essential Service Water System37、PTR 反应堆换料水池和乏燃料池冷却和处理系统Reactor Cavity and Spent Fuel Pool Cooling and Treatment38、WTS 废物处理系统Waste Treatment System39、热管段:hot leg 冷管段:cool leg40、PPM 百万分之一Parts Per Million41、RX:安全壳厂房KX:燃料厂房及换料水池1.核能在人类生产和生活中的应用的主要形式是核电。
《核电厂系统与设备复习资料》第一章:绪论1、从能源的供应结构来看, 目前世界上消耗的能源主要来自煤、石油、天然气三大资源,不仅利用率低, 而且对生态环境造成严重的污染。
2、为了缓解能源矛盾, 除了应积极开发太阳能、风能、潮汐能以及生物质能等再生能源外, 核能是被公认的唯一现实的可大规模替代常规能源的既清洁又经济的现代能源。
3、按慢化剂分类:轻水堆(压水堆和沸水堆);重水堆;石墨堆。
沸水堆:效率高。
缺点:水有放射性压水堆:汽水分离再热器。
再热:提高干度。
回热:提高效率第二章:压水堆核电厂2 .1 概述1、从生产的角度讲, 核岛利用核能生产蒸汽, 常规岛用蒸汽生产电能。
核岛:反应堆冷却剂系统;专设安全系统;核辅助系统;三废处理系统。
常规岛:汽轮机回路;循环冷却水系统;电气系统。
2、反应堆冷却剂系统将堆芯核裂变放出的热能带出反应堆并传递给二回路工质以产生蒸汽。
通常把反应堆、反应堆冷却剂系统及其辅助系统合称为核供汽系统。
每一条环路由一台蒸汽发生器、一台或两台反应堆冷却剂泵及相应的管道组成, 在其中一个环路的热管段上, 通过波动管与一台稳压器相连。
一回路内的高温高压含硼水,由反应堆冷却剂泵输送, 流经反应堆堆芯, 吸收了堆芯核裂变放出的热能, 再进入蒸汽发生器, 通过蒸汽发生器传热管壁, 将热量传给蒸汽发生器二次侧给水, 然后再由反应堆冷却剂泵唧送回反应堆。
如此循环往复, 构成封闭回路。
整个一回路系统设有一台稳压器。
一回路系统的压力靠稳压器调节, 且保持稳定。
3、为了保证反应堆和反应堆冷却剂系统的安全运行, 核电厂还设置了一系列核辅助系统和专设安全设施系统。
4、核辅助系统主要用来保证反应堆和一回路系统的正常运行。
专设安全设施系统为核电厂重大的事故提供必要的应急冷却措施, 并防止放射性物质的扩散。
5、二回路系统由汽轮机、发电机、凝汽器、凝结水泵、给水加热器、除氧器、给水泵、蒸汽发生器、汽水分离再热器等设备组成。
核电厂系统及设备讲义1. 引言核电厂是一种利用核能产生电能的设施,其系统和设备具有重要的作用。
本讲义将重点介绍核电厂系统及设备的基本概念、组成和工作原理。
2. 核电厂的系统核电厂系统是由多个相互关联的子系统组成的。
下面介绍核电厂常见的主要系统。
2.1 堆芯系统堆芯是核电厂的核心部分,主要包括燃料组件、控制棒和冷却剂。
堆芯系统实现核裂变反应,产生大量的热能。
2.2 主冷却系统主冷却系统是用于吸收核反应堆中生成的热能,并将其转化为电能的核心系统。
该系统包括主循环泵、蒸汽发生器和蒸汽涡轮机等设备。
2.3 辅助冷却系统辅助冷却系统用于处理主循环泵和蒸汽发生器之外的热量。
常见的辅助冷却系统包括冷却塔和冷却水循环设备。
2.4 电力系统核电厂的电力系统用于将机械能转化为电能,并向外部供电。
该系统包括发电机、变压器和配电系统等设备。
2.5 安全系统安全系统是核电厂的重要组成部分,用于保障核电厂的运行安全。
包括放射性防护、事故保护和事故处理等系统。
3. 核电厂的设备核电厂的设备多种多样,而核心设备主要包括以下几类。
3.1 压水堆压水堆是一种常见的核反应堆类型,其中的冷却剂以高压状态循环,将热能带离核反应堆。
3.2 汽轮机汽轮机是核电厂的关键设备之一,它通过蒸汽的压力驱动转子,从而产生机械能,进而转化为电能。
3.3 电动机电动机是核电厂中的核心动力设备,用于驱动各种机械设备的转动,如泵和风扇等。
3.4 发电机发电机是核电厂将机械能转化为电能的关键设备,通过旋转磁场产生感应电动势。
3.5 控制系统控制系统用于监测和控制核电厂的运行状态,保证其正常运行。
3.6 安全设备安全设备包括防护罩、安全阀和紧急停机系统等,用于保障核电厂的运行安全。
4. 核电厂的工作原理核电厂的工作原理主要分为以下几个步骤:1.核反应堆中的燃料组件发生核裂变反应,产生大量热能。
2.主冷却系统中的冷却剂吸收核反应堆中的热能,并在主循环泵的推动下循环流动。
核电厂系统与设备知识点2020年前要新建核电站31座,今后每年平均需要建设两个百万千瓦级核电机组我国发展核电的基本政策是:坚持集中领导,统一规划,并与全国能源和电力发展相衔接;核电政策:自主,国产化,与压水堆配套;引进的基础上,消化,改进,国产化。
在核电布局上优先考虑一次能源缺乏、经济实力较强的东南沿海地区。
坚持“质量第一,安全第一”,坚持“以我为主,中外合作”我国确定发展压水堆核岛:一回路系统及其辅助系统、安全设施及厂房。
常规岛:汽轮发电机组为核心的二回路及其辅助系统和厂房。
配套设施:除核岛、常规岛的其余部分。
压水堆核电厂将核能转变为电能是分四个环节,在四个主要设备中实现的:1)核反应堆:将核能经转变为热能,并将热能传给反应堆冷却剂,是一回路压力边界的重要部件。
2)蒸汽发生器:将反应堆冷却剂的热量传递给二回路的水,使其变为蒸汽。
在此只进行热量交换,不进行能量形态的转变;3)汽轮机:将蒸汽的热能转变为高速旋转的机械能;4)发电机:将汽轮机传来的机械能转变为电能。
大亚湾核电厂共有348个系统核电厂平面布置原则:a.区分脏净,脏区尽可能在下风口;b.满足工艺要求,便于设备运输,减少管线迂回纵横交叉;c.反应堆厂房为中心,辅助厂房,燃料厂房设在同一基岩的基垫层上,防止因厂房承载或地震所产生的沉降差导致管线断裂.d.以反应堆厂房为中心,辅助厂房,燃料厂房,主控制室应急柴油发电机厂房四周.双机组厂可采用对称布置,公用部分辅助厂房.布置分区:核心区、三废区、供排水区、动力供应区、检修及仓库区、厂前区核心区布置按反应堆厂房与汽轮机厂房的相对位置,有T型与L型布置:T型:汽轮机叶片旋转平面与安全壳不相交.占地大,单独汽机厂房。
L型:汽轮机叶片旋转平面与安全壳相交,须设置防止汽轮机飞车时汽轮机叶片对安全壳和冲击的屏障.占地少,两台以上机组可公用汽轮机厂房,仅用一台吊车。
我国采用T型布置。
安全分级的目的是正确选择用于设备设计、制造、检验的规范标准安全功能:1 安全停堆和维持安全停堆状态;2 停堆后余热导出;3 事故后防止放射性物质释放,以保证放射性物质释放不超过容许值。