急性左心衰竭个案
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.62 MB
- 文档页数:30

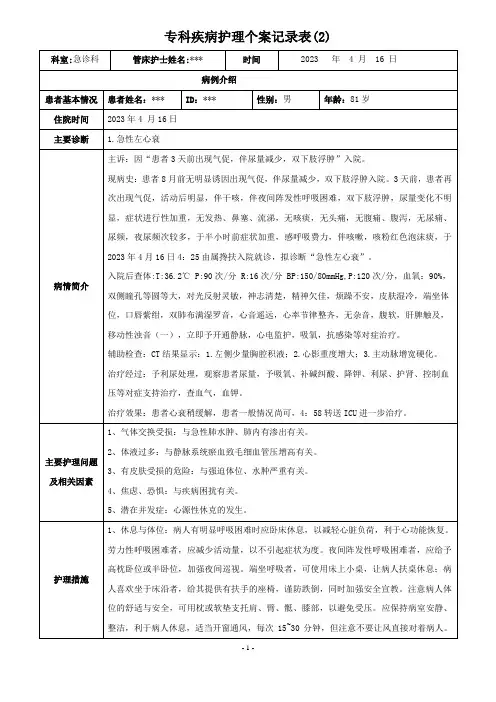
急性左心衰个案护理范文一、患者基本情况。
老张,男,65岁,那可是个“老烟枪”,烟龄都有40多年了。
平时呢,就有点高血压,也没太当回事儿。
结果有一天,突然就喘得不行,脸也憋得紫紫的,被家人紧急送到了我们医院。
一检查,好家伙,急性左心衰。
二、护理评估。
# (一)身体状况。
1. 呼吸困难。
老张刚送来的时候,那喘气就像拉风箱似的,大口大口地喘着粗气。
半卧位都不行,非要坐起来,还把床头摇得高高的,整个人就像刚跑完马拉松似的,累得不行。
2. 面色和皮肤。
脸色紫绀,就像被人掐住了脖子一样。
皮肤呢,又湿又冷,感觉就像刚从水里捞出来的一样,可把我们吓坏了。
3. 生命体征。
血压也不听话了,忽高忽低的。
心率呢,快得像打鼓,都快130次/分了。
呼吸频率更是吓人,达到了30 40次/分,感觉他每呼吸一次都用尽了全身的力气。
# (二)心理状况。
1. 焦虑恐惧。
老张躺在病床上,眼睛里满是恐惧。
他一直拉着我的手说:“护士啊,我是不是快不行了?”看得出来,他特别担心自己的病情,毕竟这种突然的重病,换谁都害怕。
三、护理措施。
# (一)一般护理。
1. 体位安置。
我们赶紧把老张安置在一个舒适的体位,让他坐在床边,双腿下垂。
这就像给心脏减轻了负担一样,让他能稍微舒服点。
老张还开玩笑说:“这个姿势像个大虾米,不过还真感觉喘得没那么厉害了。
”2. 休息与活动。
告诉老张现在得好好休息,啥事儿都别想。
在病情稳定之前,活动范围就只能在床上了。
老张开始还不乐意,说自己闲不住,我们就耐心地给他解释:“张大爷,您现在就像一辆破了胎的汽车,得先把胎补好才能跑啊。
”3. 饮食护理。
饮食上可不能马虎。
给他安排了低盐、低脂、易消化的食物。
老张开始还抱怨说没味道,我们就跟他说:“大爷,您现在身体里的‘小河流’(血液循环)都堵住了,盐吃多了就更堵了,等病好了,您再吃点好的。
”# (二)病情观察。
1. 生命体征监测。
我们就像老张的小跟班一样,密切观察着他的生命体征。


急性左心衰个案护理范文英文回答:Acute left heart failure, also known as acute pulmonary edema, is a medical emergency that requires prompt and effective nursing care. The main goals of nursing care for a patient with acute left heart failure are to improve oxygenation and relieve symptoms, stabilize the patient's condition, and prevent further complications.Firstly, the nurse should closely monitor the patient's vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation. Any changes in these parameters should be promptly reported to the healthcare team. In addition, the nurse should assess the patient's respiratory status, paying attention to the presence of dyspnea, cough, and frothy pink sputum.To improve oxygenation, the nurse should administer supplemental oxygen as prescribed and ensure that thepatient is in an upright position to facilitate lung expansion. The nurse should also encourage deep breathing exercises and provide emotional support to help alleviate anxiety and promote relaxation.To relieve symptoms, the nurse should administer diuretics as prescribed to reduce fluid overload and decrease pulmonary congestion. Close monitoring of urine output is essential to assess the effectiveness of diuretic therapy. In addition, the nurse should administer medications to improve cardiac function, such as vasodilators and inotropic agents, as prescribed by the healthcare team.Stabilizing the patient's condition involves maintaining a stable fluid balance and preventing fluid overload. The nurse should closely monitor the patient's intake and output, as well as daily weights, to assessfluid status. Strict fluid and sodium restrictions may be necessary, and the nurse should educate the patient and family members about the importance of adhering to these restrictions.Preventing further complications is crucial in the management of acute left heart failure. The nurse should closely monitor for signs of worsening heart failure, such as increased dyspnea, orthopnea, or peripheral edema. In addition, the nurse should educate the patient and family members about the importance of medication compliance, regular follow-up appointments, and lifestyle modifications, such as a low-sodium diet and regular exercise.In conclusion, nursing care for a patient with acuteleft heart failure involves closely monitoring vital signs and respiratory status, improving oxygenation, relieving symptoms, stabilizing the patient's condition, and preventing further complications. Prompt and effective nursing interventions are essential in managing thismedical emergency.中文回答:急性左心衰竭,也称为急性肺水肿,是一种需要迅速和有效的护理的医疗急症。

急性左心衰个案护理范文英文回答:Acute left heart failure is a medical emergency that requires prompt and appropriate nursing care. The primary goal of nursing care for a patient with acute left heart failure is to stabilize the patient's condition, relieve symptoms, and prevent complications. Here is a nursing care plan for a patient with acute left heart failure:1. Monitor vital signs: Regularly assess the patient's blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation. Any significant changes should be reported immediately.2. Administer oxygen therapy: Provide supplemental oxygen to maintain adequate oxygenation. Monitor thepatient's oxygen saturation levels and adjust the oxygen flow rate as needed.3. Assess respiratory status: Monitor the patient's respiratory effort, breath sounds, and oxygen saturation. Auscultate lung sounds for crackles or wheezes. Administer prescribed bronchodilators or diuretics to relieve pulmonary congestion.4. Monitor fluid balance: Assess the patient's intake and output, including urine output, to evaluate fluid status. Administer diuretics as prescribed to promote diuresis and reduce fluid overload.5. Elevate the head of the bed: Position the patient ina semi-Fowler's position to promote optimal lung expansion and reduce dyspnea.6. Administer medications as prescribed: Administer medications such as vasodilators (e.g., nitroglycerin) or inotropic agents (e.g., dobutamine) to improve cardiac function and reduce preload and afterload.7. Provide emotional support: Assess the patient's emotional status and provide reassurance and support.Encourage the patient to express feelings and concerns.8. Educate the patient and family: Provide education about the condition, including signs and symptoms of worsening heart failure, medication management, andlifestyle modifications such as a low-sodium diet andregular exercise.中文回答:急性左心衰竭是一种需要迅速和适当护理的医疗急症。

一、预案背景急性左心衰是指心脏的左心室泵血功能突然降低,导致肺循环淤血和心输出量下降的一种危急重症。
患者常表现为呼吸困难、咳嗽、气促、胸痛等症状,如不及时救治,可迅速危及生命。
为提高我院对急性左心衰的救治能力,确保患者生命安全,特制定本预案。
二、预案目标1. 提高医护人员对急性左心衰的认识和应急处置能力。
2. 优化救治流程,缩短救治时间,降低患者死亡率。
3. 加强科室间的协作,提高整体救治水平。
三、预案组织架构1. 成立急性左心衰救治小组,由科主任担任组长,主治医师、护士长、护士等组成。
2. 明确各岗位职责,确保救治工作有序进行。
四、预案内容(一)早期识别1. 医护人员应具备急性左心衰的早期识别能力,对具有心脏病史、高血压、糖尿病等高危人群,应密切观察病情变化。
2. 当患者出现呼吸困难、咳嗽、气促、胸痛等症状时,应立即怀疑急性左心衰,立即启动应急预案。
(二)救治流程1. 立即通知医生,启动应急预案。
2. 保持呼吸道通畅:协助患者取端坐位,两腿下垂,清除呼吸道分泌物,必要时给予吸氧。
3. 立即给予高流量吸氧,流量为6-8L/min,湿化瓶内加入20-30%乙醇溶液,减轻缺氧症状。
4. 遵医嘱给予镇静、平喘、利尿、强心、扩血管等药物。
5. 严密观察病情,监测生命体征,包括心率、血压、呼吸频率、血氧饱和度等。
6. 建立静脉通路,遵医嘱给予药物。
7. 必要时给予止血带轮流结扎四肢阻断静脉回流,以减少回心血量。
8. 及时上报,并填写护理不良事件登记表。
(三)科室协作1. 心内科、呼吸科、重症医学科等科室应加强协作,共同救治急性左心衰患者。
2. 加强与急诊科的沟通,确保患者得到及时救治。
(四)持续改进1. 定期开展急性左心衰救治培训,提高医护人员应急处置能力。
2. 分析急性左心衰救治案例,总结经验教训,持续改进救治流程。
五、预案实施1. 医护人员应熟悉本预案内容,提高对急性左心衰的认识。
2. 定期组织应急演练,提高医护人员应对急性左心衰的能力。




急性左心衰个案护理范文一、患者基本情况。
咱这个患者呀,是个挺和蔼的大叔呢。
大叔今年六十岁啦,有高血压病史好多年了。
那天呀,大叔突然就感觉喘不上气来,可把家里人吓坏了。
被紧急送到咱们医院的时候,大叔的脸都是煞白煞白的,整个人特别难受,就像被什么东西紧紧勒住了一样,大口大口地喘气。
二、病情观察。
1. 呼吸方面。
大叔的呼吸那叫一个急促呀,就像刚刚跑完马拉松似的。
咱得时刻盯着他的呼吸频率,那数字就像调皮的小精灵一样,一会儿快一会儿慢的。
有时候一分钟能达到三十多次呢,可把咱紧张坏了。
而且呼吸还特别浅,感觉就像没吸进去多少空气似的。
2. 血压监测。
大叔本来就有高血压,这时候血压更是像坐过山车一样不稳定。
咱得小心翼翼地给他量血压,一会儿高一会儿低的。
高的时候能达到一百八、一百九呢,低的时候又让人担心得不行。
这血压呀,就像个不听话的小娃娃,得时刻关注着。
3. 心率变化。
大叔的心率也乱了套了。
像小兔子在心里乱蹦跶一样,快得很。
每分钟能有一百多次呢。
每次看到那个心率数字,都感觉大叔的心脏在拼命地工作,可心疼了。
三、护理措施。
1. 体位护理。
咱得赶紧让大叔采取半卧位或者端坐位,就像坐在椅子上那样,但是要更舒服一点。
这样能让大叔呼吸稍微顺畅一点,就像给被堵住的河道开了个小口一样。
大叔一开始还不太习惯这个姿势呢,咱就耐心地给他调整,还跟他开玩笑说,这可是专属的舒服姿势,能让他快快好起来。
2. 吸氧护理。
氧气对于大叔来说就像救命的甘露一样。
咱们给他接上了高流量的氧气面罩,那氧气呼呼地往大叔鼻子里灌。
刚开始大叔还觉得这个面罩有点闷,咱就哄着他说,这可是能让他呼吸顺畅的神奇面罩呢。
而且要时刻注意氧流量,可不能让这宝贵的氧气供应不足呀。
3. 药物护理。
大叔得打好多针,吃好多药呢。
像那些利尿的药,能让大叔身体里多余的水分排出去,就像给身体做个大扫除一样。
但是这些药也有副作用呀,咱就得特别小心地观察大叔的反应。
给他打针的时候,大叔还有点害怕呢,咱就跟他说,这针就像小蚂蚁咬一口,很快就不疼了,打完针就会好很多的。
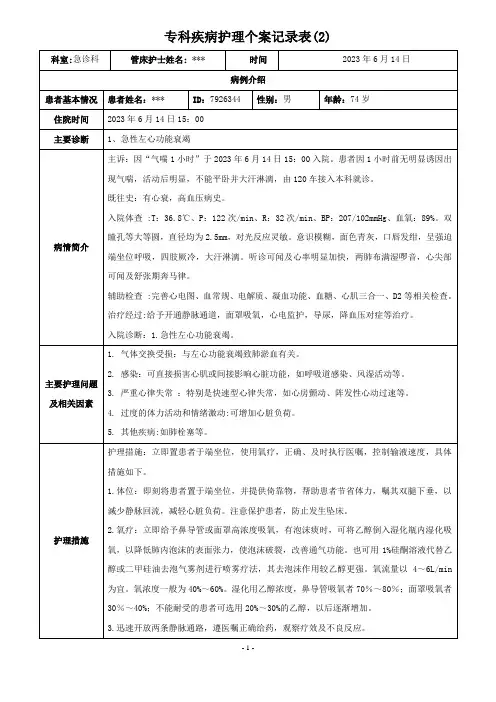
一例左心衰的个案护理一例急性左心衰患者的护理一、病情介绍患者钱某,女,79岁,诊断:急性左心衰。
患者由于“突发心悸、气促1小时。
”自觉症状加重,伴心悸,面色苍白,出大汗,于2015年5月15日16:50由家人呼叫我院120车接回抢救室,体查:患者神志清,面色苍白,烦躁不安,大汗淋漓,皮肤湿冷,鼻翼煽动,口唇发绀,颈软,颈静脉充盈,双肺呼吸音粗,两肺可闻及散在干、湿罗音,心尖听诊呈奔马律,有少许咳嗽,无咳痰,脉搏:122次/分,呼吸:35次/分,血压:178/101mmHg,端坐卧位,SPO2:56%。
既往有高血压,糖尿病病史。
入院后即于端坐卧位,高流量鼻导管吸氧(6L/分),持续心电监护、遵医嘱予单硝酸异山梨酯针10ml+0.9%NS100静脉微量泵入扩张冠状动脉、降压,并抽血常规、电解质、肾功六项、凝血四项等送检,患者气促症状缓解不明显,血压仍高,改予0.9%NS250+硝酸甘油40mg静脉滴注,20ml/h静脉微量泵入,予吗啡10mg+0.9%NS10ml静脉推注,予呋塞米20mg静脉推注,当血压降至140/80mmHg,予西地兰0.2mg+0.9%NS20ml缓慢推注,改予单硝酸异山梨酯针组液静滴扩冠、降压,同时再建立另一条静脉输液输注0.9%NS250+氨茶碱0.25g+地米10mg溶液进行平喘,约18:30症状逐渐缓解,在医护人员陪同下于车床送入ICU进一步治疗。
二、护理过程1.心输出量减少1.1评估患者神志清,面色苍白,烦躁不安,大汗淋漓,皮肤湿冷,口唇发绀,脉搏:122次/分。
1.2目标与计划患者经抢救后唇甲转红,皮肤温度回暖,每小时尿量大于40ml。
1.3措施(1)遵医嘱予单硝酸异山梨酯针10ml+0.9%NS100ml以30ml/h 静脉微量泵入扩张冠状动脉降压,并抽血常规、电解质、肾功六项、凝血四项等送检。
静滴10分钟后,患者气促症状缓解不明显,血压:175/100mmHg,R:34次/分,改予0.9%NS250+硝酸甘油40mg静脉滴注,20ml/h静脉微量泵入扩张小静脉及冠脉血管,降低心脏供氧,首次剂量10mgiv缓推,5分钟后测量一次血压,后渐行原嘱,每15—30分钟复测血压,并予吗啡10mg+10mlNS静脉推注,iv注射10分钟,过程中测心率、呼吸,防止呼吸抑制。
急性左心衰个案护理范文一、病例介绍。
咱们这位患者呀,是个65岁的大爷,平时就有点高血压,也没太当回事儿。
那天呢,正吃着饭,突然就觉得喘不上气来,胸口像压了块大石头似的,脸也憋得通红,可把家里人吓坏了,赶紧就送医院来了。
二、护理评估。
# (一)身体状况。
1. 呼吸系统。
大爷那喘气就跟拉风箱似的,呼哧呼哧的,特别费劲。
口唇都紫绀了,就像涂了一层深紫色的口红,一点都不好看。
双肺满布湿啰音,就像水在肺里咕噜咕噜响呢。
2. 心血管系统。
心率快得像打鼓一样,每分钟都130多次了。
血压也高得吓人,都180/110 mmHg 了。
心脏听诊的时候,能听到奔马律,就像马在胸腔里奔跑一样,这可不是什么好兆头。
3. 其他。
大爷整个人精神状态特别差,烦躁不安的,感觉他特别难受又不知道怎么表达,只能在那哼哼唧唧的。
# (二)心理状况。
大爷心里肯定害怕呀,本来好好的突然这样了。
家里人也着急得不行,围在旁边团团转。
大爷就担心自己是不是得了什么绝症,以后是不是就好不了了。
三、护理诊断。
# (一)气体交换受损。
你想啊,大爷肺里那么多水,喘气都困难,氧气肯定进不去呀,所以这气体交换就受损了。
就像窗户被堵住了,新鲜空气进不来一样。
# (二)体液过多。
这急性左心衰的时候,心脏功能不好,血液就不能好好地循环,都淤积在身体里了,水就跑到组织间隙里了,所以大爷全身都有点肿肿的,这就是体液过多啦。
# (三)焦虑。
前面也说了,突然生病,又难受,不知道啥情况,大爷和家人能不焦虑嘛。
# (四)潜在并发症:心源性休克。
如果心脏功能一直不好,不能把血液泵出去供应全身,那身体各个器官就没血用了,就可能发生休克,这可是很危险的呢。
四、护理目标。
# (一)短期目标。
1. 让大爷呼吸能顺畅点,口唇紫绀减轻,肺里的啰音减少。
2. 减轻大爷的焦虑情绪,让他能安静点,别那么烦躁。
# (二)长期目标。
1. 控制大爷的体液量,让他的水肿慢慢消退。
2. 预防心源性休克等严重并发症的发生,让大爷慢慢好起来。