TGF-β信号传导通路及其生物学功能
- 格式:doc
- 大小:4.18 MB
- 文档页数:18


tgf-β信号传导通路及其生物学功能
TGFB(Transforming growth factor-beta)信号传导通路是一
种调节细胞增殖、分化、凋亡和细胞外基质的生长因子信号传导通路。
TGFB家族包括TGFB1、TGFB2、TGFB3、BMPs(骨形态发生蛋白)等多
种生长因子,它们可用于在发生炎症、受到外部刺激、治疗过程中起
到两种完全相反的作用:促进细胞的增殖和转化,或促进细胞的凋亡。
TGFB信号传导通过将信号从TGFB受体I和受体II上转导至内皮体中的Smad蛋白来实现。
受体I和受体II与TGFB1结合,从而形成
复合物。
复合物使受体II激酶催化受体I激酶的磷酸化,最终激活Smad蛋白。
活化的Smad蛋白进入细胞核并调节基因表达,从而参与细胞增殖、分化、凋亡等过程。
在生物学中,TGFB信号传导通路可参与一系列生物学过程。
例如,在胚胎发育中,它可调控神经元的分化和细胞迁移。
在免疫系统中,
它可调节T细胞的功能和表达、B细胞的分化和细胞因子的产生。
在皮肤组织再生中,它亦可以促进创面愈合。
总之,TGFB信号传导通路在细胞生理中扮演着至关重要的角色,并有望成为治疗和预防各种疾病的重要靶点。

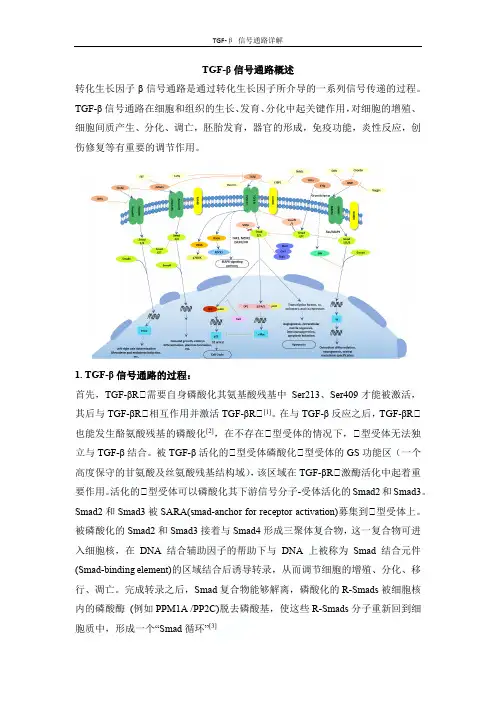
TGF-β信号通路概述转化生长因子β信号通路是通过转化生长因子所介导的一系列信号传递的过程。
TGF-β信号通路在细胞和组织的生长、发育、分化中起关键作用,对细胞的增殖、细胞间质产生、分化、调亡,胚胎发育,器官的形成,免疫功能,炎性反应,创伤修复等有重要的调节作用。
1. TGF-β信号通路的过程:首先,TGF-βRⅡ需要自身磷酸化其氨基酸残基中Ser213、Ser409才能被激活,其后与TGF-βRⅡ相互作用并激活TGF-βRⅡ[1]。
在与TGF-β反应之后,TGF-βRⅡ也能发生酪氨酸残基的磷酸化[2],在不存在Ⅱ型受体的情况下,Ⅱ型受体无法独立与TGF-β结合。
被TGF-β活化的Ⅱ型受体磷酸化Ⅱ型受体的GS功能区(一个高度保守的甘氨酸及丝氨酸残基结构域),该区域在TGF-βRⅡ激酶活化中起着重要作用。
活化的Ⅱ型受体可以磷酸化其下游信号分子-受体活化的Smad2和Smad3。
Smad2和Smad3被SARA(smad-anchor for receptor activation)募集到Ⅱ型受体上。
被磷酸化的Smad2和Smad3接着与Smad4形成三聚体复合物,这一复合物可进入细胞核,在DNA结合辅助因子的帮助下与DNA上被称为Smad结合元件(Smad-binding element)的区域结合后诱导转录,从而调节细胞的增殖、分化、移行、凋亡。
完成转录之后,Smad复合物能够解离,磷酸化的R-Smads被细胞核内的磷酸酶(例如PPM1A /PP2C)脱去磷酸基,使这些R-Smads分子重新回到细胞质中,形成一个“Smad循环”[3]2.TGF-β1/Smads信号通路的影响因子:在生物体中,TGF-β信号通路受多种因素控制,如微环境条件[4] [5]、激素[6]、细胞因子和生长因子[7]、microRNAs(MiRNAs) [8]、长的非编码RNA[9]、磷酸化和去磷酸化激酶[3],泛素连接酶和去泛素酶[10]以及其他因子。

TGF信号传导通路及其生物学功能转化生长因子(Transforming Growth Factor,TGF)是一种重要的细胞因子家族,参与了多种生物学过程,包括细胞增殖、分化、凋亡以及免疫调节等。
TGF信号传导通路是细胞内的重要信号转导途径之一,对于维持机体正常生理功能和病理过程具有重要意义。
TGF信号传导通路主要包括TGF受体、Smad蛋白家族以及下游效应分子等组成部分。
TGF受体是一类具有激酶活性的跨膜蛋白,包括TGF-RTGF-R2等亚型。
当TGF与受体结合后,TGF-R1和TGF-R2发生二聚化,并激活其激酶活性,进而磷酸化Smad蛋白家族中的Smad2和Smad3。
Smad2和Smad3与Smad4形成复合物,进入细胞核内,与下游效应分子相互作用,调节基因表达。
TGF信号传导通路在多种生物学过程中发挥着重要作用。
以下是其主要功能的一些概述:细胞增殖与分化:TGF能够促进某些细胞的增殖和分化,如成骨细胞、软骨细胞等。
TGF信号传导通路通过调节下游基因的表达,促进细胞增殖和分化。
细胞凋亡:TGF也能够诱导某些细胞的凋亡,如黑色素瘤细胞等。
这种凋亡作用是通过激活Smad3和抑制抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2实现的。
免疫调节:TGF能够抑制免疫细胞的活化和增殖,具有免疫抑制作用。
在某些自身免疫性疾病和移植排斥反应中,TGF的表达水平会升高,发挥免疫保护作用。
肿瘤发生:TGF信号传导通路在肿瘤发生过程中也发挥了重要作用。
一些研究表明,TGF信号通路的异常激活与多种肿瘤的发生和发展密切相关,如肺癌、乳腺癌等。
TGF信号通路的异常激活可能导致细胞增殖失控、凋亡受抑制以及血管生成增加等,促进肿瘤的生长和扩散。
TGF信号传导通路在生物学过程中具有多种重要作用,包括调节细胞增殖与分化、细胞凋亡、免疫调节以及肿瘤发生等。
深入了解TGF信号传导通路的作用机制及其在各种生物学过程中的作用,有助于为疾病的治疗提供新的靶点和思路。

TGF-β/Smad 信号通路图TGF-β(转化生长因子-β)信号通路在调控干细胞活性和器官形成中发挥着重要的作用,当TGF-β信号通路各成员活性未激活时,体内会自发性发生多种癌症,这表明TGF-β定向调节干细胞对癌症形成也具有不可或缺的功能。
TGF-β超家族包含接近30个生长和分化因子,其中有TGF-βs,活化素(activin),inhibins和骨形态发生蛋白(BMPs) 。
下游的跨膜TGF-β受体是多个SMAD蛋白,这些蛋白是TGF-β超家族信号传递的重要调控分子,并在不同层面上受多种多样精确的调控。
TGF-β与TGF-βII型受体(TGF-βRII)结合后,再激活募集TGF-β I型受体(TGF-β RI)组合后形成二聚体形式的受体复合物。
TGF-β RII磷酸化TGF-β RI的甘氨酸-丝氨酸富集区域(GS序列)并活化TGF-β RI的丝氨酸/苏氨酸活性。
活化的TGF-β RI反过来又磷酸化受体相关smad蛋白。
脊椎动物中目前发现的smad蛋白至少有9种,分别是:(a)受体调节的Smads (R-Smads):Smad 1, Smad 2, Smad 3, Smad 5, and Smad 8;(b)共调节Smads: Smad 4 and Smad 10;(c)抑制性Smads(I-Smads): Smad 6 and Smad 7。
Smad 2,和Smad 3参与TGF-β和活化素信号通路,而Smad 1、Smad 5和Smad 8调节BMP信号通路。
R-Smads和Smad 4 主要位于细胞质中,它们的活性主要受衔接蛋白调节,如Smad锚定受体激活蛋白(SARA)和ELF。
Smad 2和Smad 3直接被TGF-β RI磷酸化, 使得构象发生改变从而从受体复合物中释放出来。
Smad 4蛋白的MH2结构域识别R-Smads C端的磷酸丝氨酸从而形成异质二聚体复合物(R-Smad/C-Smad)。


TGF-β信号转导通路信号转导通路:在细胞中,各种信号转导分子相互识别、相互作用,将信号进行转换和传递,构成信号转导通路。
当外界环境变化时,单细胞生物可以直接做出反应,多细胞生物则通过复杂的信号传递系统来传递信息,从而调控机体活动。
传导方式包括相邻细胞直接接触、细胞分泌各种化学物质来调节其他细胞代谢和功能。
跨膜信号转导的一般步骤包括:特定的细胞释放信息物质,细胞物质经扩散或血循环到达靶细胞,与靶细胞受体特异性的结合,受体对信号进行转换并启动细胞内信使系统,靶细胞产生生物学效应。
转化生长因子β(TGF-β)是一个庞大的家族。
脊椎动物TGF-β超家族包括TGF-β、激活素、抑制素和骨形态发生蛋白。
哺乳动物TGF-β共有三种:TGF-β1、TGF-β2和TGF-β3。
研究发现,三种亚型由不同的基因编码,虽然具有相似的生物活性但其基因的表达具有明显的组织及发育特异性,其中肝脏含量最高且具有生物活性的TGF-β1。
TGF-β在肿瘤中主要参与刺激细胞生长,诱导细胞凋亡和分化,抑制天然免疫以及基质代谢的精细调节等活动。
TGF-β可以通过Smad依赖通路和非Smad 依赖通路发挥作用。
TGF-β信号通过激活受体TGF-βR1和TGF-βRⅡ丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性,使受体激活Smad(R-Smad)磷酸化,R-Smad与共同型Smad( Co-Smad)形成复合体,信号传递到细胞核内。
细胞核内Smads寡聚体结合DNA 和相关的转录因子调控靶基因的表达。
R-Smad和Co-Smad可以在胞浆和细胞核间穿梭。
抑制型Smad(I-Smad ) 可阻断受体磷酸化R-Smad,启动泛素化作用,受体复合物降解,这样抑制了信号的传导。
STRAP 可以稳定 TGF-βRⅠ、TGF-βRⅡ与 I-Smad 形成的复合体,EGF 受体和其他酪氨酸激酶受体的活化都可以诱导 I-Smad 的表达,抑制 TGF-β信号转导。
普遍认为该通路的激活与TGF-β发挥肿瘤抑制作用有关。

TGF-β信号传导通路及其生物学功能*刘镕,赵琴平,董惠芬,蒋明森**(武汉大学基础医学院医学寄生虫学教研室,湖北武汉430071)【摘要】TGF-β信号传导通路是一个包含众多成员的多功能细胞因子大家族,根据配体分子激活的不同的下游特异性通路可以分为TGF-β/Activin/Nodal和BMP/GDF/MIS两个亚家族通路。
该信号通路的激活首先是TGF-βs配体分子与受体结合,从而使受体TβRs磷酸化,磷酸化的TβR-I直接作用于底物Smads蛋白,活化的Smads就将配体与受体作用的信号从细胞膜、胞浆传递到细胞核内,再与其他核内因子协同激活或者抑制靶基因的转录。
TGF-β信号通路就是通过调节细胞的生长、增殖、分化、迁移和凋亡等过程,在组织与器官的发生和形成(胚胎发育、骨骼等器官形成)、机体的免疫反应等生物过程发挥重要的功能。
【关键词】TGF-β信号传导通路;生物学功能;生殖发育;胚胎发育;免疫应答;综述The TGF-β signaling pathways and their biological functionsLIU Rong, ZHAO Qin-ping, DONG Hui-fen, JAING Ming-sen (Department of Medical Parasitology, School of Basic Medical Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, China)【Abstract】The transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway is a superfamily with a large number of multifunctional cytokines, and it, based on the classification of the ligands, was divided into two subfamilies - TGF-β/Activin/Nodal and BMP/GDF/MIS signaling pathways. The activation of this signaling pathway initiates from the binding of TGF-βs ligand to the ir receptors, and then the phosphorylation of the receptors TβRs happens, in which the phosphorylated TβR-I acts directly on the substrates Smads, and finally the activated Smads together with other nuclear factors play either an activation or a repression effect on the transcription of the target genes, finishing passing the signal from cell membrane to the nucleus. The TGF-β signaling pathway participates in many biological processes like the formation of tissues and organs and immune response in both developing embryos and adult organisms through regulating cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, cellular homeostasis and other cellular functions.【Key words】TGF-β signaling pathways; biological functions; reproductive development; embryonic development; immune response; reviewTGF-β信号通路是一个包含众多成员的多功能细胞因子的大家族,主要通过调节细胞的生长、增殖、分化、迁移和凋亡等过程,参与介导组织与器官的正常生长和发育(胚胎发育、骨骼等器官形成)、机体的免疫反应等生物过程,尤其在胚胎的发育和形成、组织和器官的形成与修复以及免疫应答调节等方面发挥重要的作用(Wikipedia,/wiki/Transforming_growth_factor_beta)。

TGF-β信号通路相关分子在皮肤创伤愈合过程中的作用及机制的开题报告导言皮肤创伤和创伤性疾病是众所周知的全球性公共卫生问题,给个人和社会带来了重大的健康和经济负担。
皮肤创伤愈合是一个复杂的过程,包括敷料形成、炎症反应、再生重建和修复。
近年来,许多研究表明TGF-β信号通路在皮肤创伤愈合中起着重要的作用。
TGF-β信号通路是一条广泛涉及细胞增殖、细胞间相互作用、细胞存活和分化的重要途径。
本文将介绍TGF-β信号通路及其分子在皮肤创伤愈合中的作用和机制。
一、TGF-β信号通路的概述TGF-β是一种多功能生长因子,在胚胎发育和组织修复中扮演重要角色。
它被广泛表达于众多组织和细胞类型中,包括成纤维细胞、肌肉细胞、免疫细胞和皮肤细胞等。
TGF-β发挥作用通过两种主要的信号传导途径:Smad依赖和Smad非依赖途径。
Smad依赖途径在TGF-β信号通路中起着主要作用。
在此途径中,TGF-β与其细胞膜受体结合,导致受体激活并发生丝氨酸/苏氨酸磷酸化。
磷酸化的受体结合Smad2/3形成复合物,然后进入细胞核,在转录因子上响应特定的基因和通路程序。
除了Smad依赖途径,TGF-β还通过Smad非依赖途径来调控其他通路。
这些通路包括小GTP酶、Src/Ras/ERK、JNK和p38等。
二、TGF-β信号通路分子在皮肤创伤愈合中的作用1. TGF-β1TGF-β1是TGF-β家族中最为重要的成员之一,对皮肤创伤愈合具有重要作用。
TGF-β1过表达可以促进上皮细胞增生、胶原合成和细胞外基质沉积,有助于修复皮肤。
另外,TGF-β1还能抑制炎症反应,减少免疫细胞浸润。
但是,如果TGF-β1过度激活,会导致瘢痕组织形成。
2. Smad3Smad3是TGF-β信号通路中的一个重要转录因子,起着广泛的生物学作用。
Smad3表达在皮肤创伤愈合过程中的增加提示其在皮肤创伤愈合中具有关键作用。
Smad3通过调节细胞外基质合成来促进创伤部位的愈合和修复。
tgf-β诱导启动子合成生物学TGF-β(转化生长因子-β)是一个多功能的细胞信号分子,参与许多生物学过程的调控。
它对胚胎发育、组织再生、免疫调节以及肿瘤转移等具有重要作用。
TGF-β的信号传导途径包括通过启动子启动信号转导,使信号被传递到细胞内部。
在过去的几十年中,研究人员已经揭示了TGF-β启动子合成生物学的重要性,并通过这种方法探索了与TGF-β相关的多种疾病的治疗策略。
启动子是基因表达调控的关键元件,它位于基因序列的上游区域,与转录因子相互作用以启动转录。
TGF-β启动子在TGF-β信号通路中发挥着重要的调控作用。
研究表明,TGF-β通路的正常调控取决于启动子的正确功能。
TGF-β启动子的合成生物学研究主要集中在其序列特征、转录因子结合位点以及启动子区域的调控机制上。
TGF-β启动子序列的特征对于该基因的表达和调控至关重要。
许多研究表明,TGF-β启动子序列具有高度保守的区域,这些区域在物种间具有相似性。
这些保守区域通常包含转录因子结合位点,其中一些与TGF-β信号传导的调控有关。
例如,Smad蛋白是TGF-β信号通路中的关键组成部分,可以结合TGF-β启动子序列上的Smad结合位点,从而调控TGF-β基因的转录。
此外,其他转录因子如AP-1、NF-κB和Sp1等也被证明可以通过与TGF-β启动子相互作用来调控其转录活性。
TGF-β启动子区域的调控机制也是TGF-β启动子合成生物学研究的重要内容。
研究发现,DNA甲基化和组蛋白修饰可以影响TGF-β启动子的活性。
DNA甲基化是一种常见的表观遗传标记,可以对基因启动子进行直接调控。
研究表明,TGF-β启动子的高度甲基化与TGF-β信号通路的失调和癌症转化有关。
此外,组蛋白修饰如乙酰化和甲基化等也可以调控TGF-β启动子的活性。
这些发现为TGF-β启动子合成生物学的研究提供了新的方向。
过去几十年来,TGF-β启动子合成生物学的研究促进了与TGF-β相关的多种疾病的治疗策略开发。
细胞控制生长的信号传导通路细胞是构成生命的基本单位,其生长和分裂是生命活动的重要表现。
而细胞的生长控制是通过信号传导通路实现的。
信号传导通路是一种细胞内分子网络,连接了细胞表面的成分和它们在细胞内部的作用机制。
这篇文章将介绍几种常见的细胞控制生长的信号传导通路。
1. Wnt信号通路Wnt信号通路是控制细胞分化和增殖的一种重要通路。
Wnt信号通路通过配体与细胞表面的Frizzled肽类受体结合并激活它们,进而引发一系列链式反应。
Wnt信号通路激活后会导致β-catenin 向细胞核内转移,与TCF/LEF转录因子结合,推动细胞进入增殖周期并诱导细胞分化。
Wnt信号通路在胚胎发育、干细胞分化以及很多肿瘤中都发挥着重要作用。
2. Hedgehog信号通路Hedgehog信号通路是细胞增殖与分化的另一种重要调节方式。
Hedgehog信号通路通过细胞表面蛋白Ptch和HH的配体结合来激活这一通路。
激活后,Downstream-of-Fused(Dofu)磷酸化并激活色素体转录因子Gli族蛋白,在细胞核内与DNA结合,进而影响基因表达、调节细胞增殖和分化。
在发育过程、组织修复以及很多肿瘤中都有Hedgehog信号通路的参与。
3. TGF-β信号通路TGF-β信号通路是细胞增殖和分化的重要调节机制。
TGF-β可以与细胞表面的受体结合来激活这一通路。
激活后,活化的受体会磷酸化Smad蛋白,使其成为HDAC(组蛋白去乙酰化酶)诱导的共转录因子,参与基因转录和细胞增殖调控。
TGF-β信号通路在胚胎发育、器官发育以及很多肿瘤中都扮演着重要角色。
4. MAPK信号通路MAPK信号通路是一种丝裂原激活蛋白激酶(MAPK)介导的细胞增殖和分化调控机制。
这一通路可以通过细胞表面受体、酪氨酸蛋白激酶、MAPK激酶激活继而传导兴奋信号。
活化的MAPK可以进入细胞核内,调节下游基因的转录,促进细胞增殖和分化。
MAPK信号通路在生长、免疫应答以及肿瘤形成中都发挥重要作用。
tgf-β因子-概述说明以及解释1.引言1.1 概述概述TGF-β因子(Transforming Growth Factor-beta)是一类具有重要生物功能的蛋白质因子,它在细胞的生长和发育过程中起着重要的调控作用。
TGF-β因子最早是在20世纪70年代被发现并命名的,它具有广泛的分布和多种生物学功能。
TGF-β因子家族是一个多基因家族,包括TGF-β1、TGF-β2、TGF-β3等几种不同的同源物质。
它们在结构上相似,但在组织分布和功能上有所不同。
TGF-β因子可以通过细胞外基质的合成、细胞增殖和分化的调控、免疫细胞的调节等多种方式影响细胞和组织的功能。
TGF-β因子具有双重生物学功能,既可以促进细胞的生长和增殖,又可以抑制细胞的增殖和诱导细胞凋亡。
这种双重功能使得TGF-β因子在细胞生物学研究和临床医学中引起了广泛的关注。
TGF-β因子通过与细胞表面的特定受体结合,激活复杂的信号传导通路,进而调控细胞内的基因表达和蛋白质合成。
它的信号传导机制涉及多个信号分子、细胞因子和细胞内的信号转导分子,其中包括Smad蛋白家族的激活和转位等关键步骤。
最近的研究表明,TGF-β因子在多种疾病中的异常表达和功能失调与疾病的发生和发展密切相关。
它在肿瘤、炎症、纤维化等疾病的发生中发挥重要作用。
因此,对TGF-β因子的深入研究不仅可以揭示其在细胞生物学中的重要功能,还有助于开发与其相关的疾病的治疗方法。
本文将重点介绍TGF-β因子的定义、作用、生物合成和信号传导机制,并探讨它在疾病中的作用和潜在应用。
此外,我们还将对TGF-β因子的进一步研究和发展方向进行讨论,以期为深入理解TGF-β因子的生物学功能和开发相关疾病的治疗方法提供理论依据。
1.2 文章结构文章结构部分的内容大致如下:文章结构部分旨在介绍本文的组织结构和各个章节的内容安排。
通过清晰地阐明文章的整体组织,读者可以更好地理解本文的逻辑结构和阅读顺序。
tgf-βrii分子式TGF-βRII分子式及其在人类体内的重要作用TGF-βRII,全称为转化生长因子β受体II型,是一种重要的细胞膜受体,在人类体内发挥着关键的生物学功能。
它的分子式为C_180H_263N_47O_52S,由多个氨基酸残基组成,通过细胞信号传导途径参与调节细胞生长、分化和功能。
TGF-βRII的主要功能是传递转化生长因子β(TGF-β)的信号,这是一类重要的细胞因子,能够调控细胞增殖、分化和胚胎发育等生理过程。
TGF-βRII作为TGF-β信号通路中的重要组成部分,能够与TGF-βRI相互作用,形成活性受体复合物,进而激活下游信号分子,参与调控各种细胞功能。
在人类体内,TGF-βRII的表达广泛分布于各种组织和细胞类型中。
它在胚胎发育过程中起着至关重要的作用,参与调控胚胎干细胞的命运决定、器官形成和组织修复等关键过程。
此外,TGF-βRII还能够调控免疫系统的功能,影响免疫细胞的增殖、活化和分化,参与调控免疫应答和炎症反应。
除了在正常生理过程中的重要作用,TGF-βRII在疾病的发生和发展中也扮演着重要角色。
一些研究发现,TGF-βRII的异常表达或功能缺陷与多种疾病的发生相关,如肿瘤、免疫疾病和心血管疾病等。
因此,TGF-βRII成为了一些疾病的潜在治疗靶点,研究人员通过调控TGF-βRII的表达或功能,试图干预相关疾病的发展进程。
TGF-βRII作为转化生长因子β信号通路的重要组成部分,在人类体内发挥着关键的生物学功能。
它参与调控细胞生长、分化和功能,影响胚胎发育、免疫系统的功能以及多种疾病的发展。
进一步的研究将有助于深入理解TGF-βRII的作用机制,并为相关疾病的治疗提供新的思路和策略。
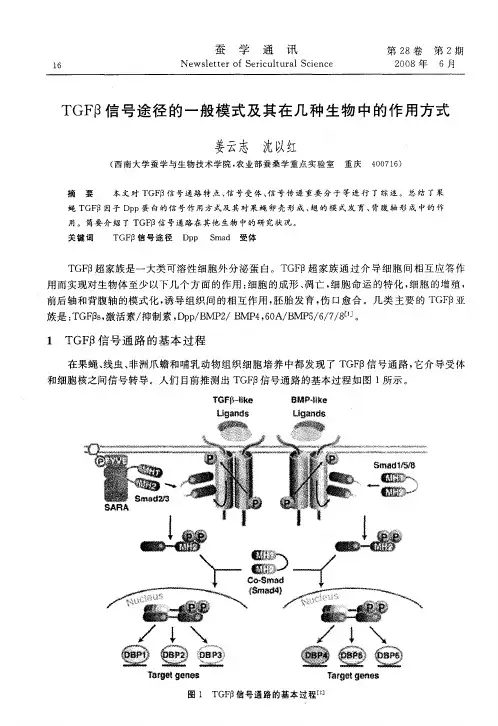
▲TGF-β/ Smad信号通路图一、TGF-β / Smad调节过程转化生长因子β(Transforming growth factor beta,TGF-β)信号通路参与生物体和胚胎发育的多种细胞过程,包括细胞生长、细胞分化、凋亡、细胞稳态等。
尽管TGF-β信号通路调节的细胞过程范围很广,但是该过程相对简单。
TGF-β超家族配体结合一个II型受体,其募集并磷酸化一个I型受体。
该I型受体然后磷酸化受体调节的SMAD(receptor-regulated SMADs ,R-SMADs),其结合coSMAD SMAD4。
R-SMAD / coSMAD复合物积聚在细胞核中,作为转录因子并参与靶基因表达的调控。
TGF-β配体结合受体TGF-β超家族配体包括:骨形态发生蛋白(Bone morphogenetic proteins,BMPs),生长和分化因子(Growth and differentiation factors,GDFs),抗缪勒氏管激素(Anti-müllerian hormone,AMH),激活素(Activin),Nodal和TGF-β。
配体分为两个分支:(1)TGF-β/激活素分支和(2)BMP/ GDF分支。
TGF-β/激活素分支包括TGF-β,激活素,Nodal。
BMP / GDF分支包括BMP,GDF和AMH配体。
信号传导从TGF-β超家族配体与TGF-βII型受体的结合开始。
II型受体是丝氨酸/苏氨酸受体激酶,其催化I型受体的磷酸化。
每种类型的配体结合特异性II 型受体,在哺乳动物中有七种已知的I型受体和五种II型受体。
II型受体募集I型受体和磷酸化TGF-β配体结合II型受体二聚体,其募集I型受体二聚体,与配体形成杂四聚体复合物。
II型受体磷酸化I型受体的丝氨酸残基。
I型受体磷酸化R-SMAD有5个受体调节的SMAD:SMAD1,SMAD2,SMAD3,SMAD5和SMAD9(有时称为SMAD8)。
胚胎发育中TGFβ超家族受体在基因转录和信号途径中的作用TGFβ超家族是一类具有重要生物学功能的跨膜受体,涉及胚胎发育、细胞增殖、分化和修复等多种生理过程。
其在生物体内广泛存在,包括四种TGFβ超家族成员,分别是转化生长因子β(TGFβ)、增强型转化生长因子β(TGFβ)、骨形态发生蛋白(BMP)和睾丸素降调素(AMH),以及其对应的受体。
TGFβ超家族成员参与胚胎发育的调控,细胞的分化、增殖和迁移、免疫反应调控和组织修复。
TGFβ超家族受体包括两类:经典的信号转导途径和非经典的信号转导途径。
其中,经典的信号转导途径是指连接受体和细胞核的分子通路,经过活性酪氨酸激酶的自磷酸化作用,激活特定的细胞核转录因子,从而启动基因表达并控制生物学过程。
而非经典的信号转导途径是通过蛋白质的酶解与其他细胞途径相互作用,例如蛋白酶切割、磷酸酰化和金属离子与蛋白酶的激活。
这种非经典的信号转导途径在TGFβ超家族中有着重要的作用。
在胚胎发育中,TGFβ超家族受体通过多种途径调节基因转录。
例如,在胚胎早期发育中,TGFβ超家族成员可与其受体结合,从而启动特定的细胞核转录因子。
这些细胞核转录因子可以与DNA相互作用,并调控哪些基因可进行转录。
此外,通过对历史修饰酶的调节,TGFβ超家族受体还可以在胚胎发育过程中直接控制某些基因的修饰,从而调整其表达速度和表达量。
TGFβ超家族受体还通过信号通路调节胚胎发育。
这些信号通路涉及许多不同的细胞途径,包括Smad、MAPK/ERK、PI3K-Akt、Wnt和Notch等,并通过多种方式控制组织生长和分化。
举例来说,Smad信号通路是TGFβ超家族的一个重要分支,它在TGFβ受体与Smad核转录因子之间建立了联系。
具体来说,TGFβ超家族的成员可以让其受体自磷酸化,激活特定的Smad蛋白,并将其引导到细胞核中,进而控制某些目标基因的转录和表达。
除了在胚胎发育中扮演重要角色之外,TGFβ超家族还在组织修复、免疫反应和癌症的发生和发展中起着重要的作用。
TGF-β信号传导通路及其生物学功能*刘镕,赵琴平,董惠芬,蒋明森**(武汉大学基础医学院医学寄生虫学教研室,湖北武汉430071)【摘要】TGF-β信号传导通路是一个包含众多成员的多功能细胞因子大家族,根据配体分子激活的不同的下游特异性通路可以分为TGF-β/Activin/Nodal和BMP/GDF/MIS两个亚家族通路。
该信号通路的激活首先是TGF-βs配体分子与受体结合,从而使受体TβRs磷酸化,磷酸化的TβR-I直接作用于底物Smads蛋白,活化的Smads就将配体与受体作用的信号从细胞膜、胞浆传递到细胞核内,再与其他核内因子协同激活或者抑制靶基因的转录。
TGF-β信号通路就是通过调节细胞的生长、增殖、分化、迁移和凋亡等过程,在组织与器官的发生和形成(胚胎发育、骨骼等器官形成)、机体的免疫反应等生物过程发挥重要的功能。
【关键词】TGF-β信号传导通路;生物学功能;生殖发育;胚胎发育;免疫应答;综述The TGF-β signaling pathways and their biological functionsLIU Rong, ZHAO Qin-ping, DONG Hui-fen, JAING Ming-sen (Department of Medical Parasitology, School of Basic Medical Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, China)【Abstract】The transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway is a superfamily with a large number of multifunctional cytokines, and it, based on the classification of the ligands, was divided into two subfamilies - TGF-β/Activin/Nodal and BMP/GDF/MIS signaling pathways. The activation of this signaling pathway initiates from the binding of TGF-βs ligand to the ir receptors, and then the phosphorylation of the receptors TβRs happens, in which the phosphorylated TβR-I acts directly on the substrates Smads, and finally the activated Smads together with other nuclear factors play either an activation or a repression effect on the transcription of the target genes, finishing passing the signal from cell membrane to the nucleus. The TGF-β signaling pathway participates in many biological processes like the formation of tissues and organs and immune response in both developing embryos and adult organisms through regulating cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, cellular homeostasis and other cellular functions.【Key words】TGF-β signaling pathways; biological functions; reproductive development; embryonic development; immune response; reviewTGF-β信号通路是一个包含众多成员的多功能细胞因子的大家族,主要通过调节细胞的生长、增殖、分化、迁移和凋亡等过程,参与介导组织与器官的正常生长和发育(胚胎发育、骨骼等器官形成)、机体的免疫反应等生物过程,尤其在胚胎的发育和形成、组织和器官的形成与修复以及免疫应答调节等方面发挥重要的作用(Wikipedia,/wiki/Transforming_growth_factor_beta)。
本文将对TGF-β信号传导通路中的配体、受体与效应分子的组成(表1)和激活方式,及其参与调节的生物学功能作一综述,以进一步全面而深入地总结和介绍有关TGF-β信号通路的最新研究进展。
表1 TGF-β家族成员及其受体与信号分子Table 1 TGF-β family members and their receptors and effectorsTGFβ亚家族TGF-β/Activin/Nodal BMP/GDF/MIS配体TGF-βs, Activins, Nodal BMPs, GDFs, MISII型受体TβR-II, ActR-II, ActR-IIB BMPR-II, ActR-II, ActR-IIBI型受体TβR-I, ActR-I, ActR-IB BMPR-IA, BMPR-IB, ActR-I通路特异性Smads Smad 2, Smad 3 Smad 1, Smad 5, Smad 8共同Smad Smad 4 Smad 4抑制性Smads Smad 6, Smad 7 Smad 6, Smad 7生物学效应抑制有丝分裂;诱导细胞外基质合成;诱导背部中胚层的形成;诱导网织红细胞的分化;诱导促卵泡激素的释放。
诱导腹侧中胚层的形成;诱导软骨和骨的形成;诱导细胞凋亡。
1 TGF-β配体(TGF-βs ligands)TGF-β超家族成员包括至少30种相关的配体分子,根据分子之间的相似性和它们激活的下游特异性信号通路途径可以分为TGF-β/Activin/Nodal和BMP/GDF/MIS两个亚家族,其中已知TGF-βs包括TGF-β1~5,Activin包括Inhb A、B,BMPs包括BMP2~16(BMP1是一种金属蛋白酶,不属于TGF-β超家族成员),GDFs包括GDF1~15 [1, 2]。
以前文献[1, 3-5]报道,TGF-β超家族分子具有一些共同的结构特征:(1)所有合成的前体分子的相对分子量都比较大,包含N-端信号肽、前体区和成熟区,前体分子在二元位点或者RXXR位点经酶切裂解后释放出一个活性分子;(2)各配体分子都含有高度保守的7个半胱氨酸(Cys)残基,其中6个Cys残基通过链内二硫键连接几个β片层结构而形成一个刚性结构(称为半胱氨酸结),两个单体通过各自的第7个Cys残基以链间二硫键连接形成具有生物活性的二聚体;但是GDF3和GDF9缺失链间二硫键,单体间靠疏水键来维持。
不过,我们借助常用的信号肽预测工具(SignalP 4.0 Server,SIG-Pred: Signal Peptide Prediction和SPdb)分析后发现,日本血吸虫BMP(SjBMP)分子没有信号肽序列[6],这与Freitas等学者[7]报道的曼氏血吸虫BMP(SmBMP)分子也没有信号肽序列的结果是一致的。
为此,我们又进一步分析了一些其它物种的BMP分子,发现其中还有一些BMP分子经预测工具分析也没有信号肽序列,例如大黄蜂Bombus terrestris BMP10,旋毛虫Trichinella spiralis BMP7,真涡虫Schmidtea mediterranea BMP等(图1)。
不过,上述结果仅是根据理论分析推断的,有待于通过实验进一步检测和验证。
图1 不同物种的BMP分子的信号肽预测分析以上列出的氨基酸序列为各物种BMP分子的N-末端序列。
绿色标记的氨基酸表示用SignalP 4.0 Server和SIG-Pred工具预测均得出有信号肽,黄色标记的氨基酸表示用SignalP 4.0 Server或SIG-Pred工具预测得出阳性结果,未标记的表示用SignalP 4.0 Server和SIG-Pred工具预测均得出没有信号肽。
Figure 1 Signal sequences prediction of BMPs from different organisms The listed sequences represent the N-terminal parts of the appropriate protein sequences. The colored (green and yellow) amino acids indicate the SPs, in which the SPs with green were predicted and confirmed by both SignalP 4.0 Server and SIG-Pred. Yellow marks SPs that were recognized by SIG-Pred but not by SignalP 4.0 Server. Black indicates no SP was found according to prediction results of both the two tools.2 TGF-β受体(TβRs)根据分子的结构和功能特征不同来分类,TβRs家族包括I型受体(TβR-I)、II型受体(TβR-II)和III型受体(TβR-III,也称为附属受体Sub-receptor,包括Betaglycan和Endoglin),均属单个跨膜α螺旋受体[1]。
I型受体主要包括ActR-I B、TβR-I、XTr-I、ALR7、ATR-1、BMPR-1A、ACTR-1等,其结构可分为四部分:信号肽、含大量Cys的亲水性胞外区、跨膜区和由GS区与激酶区共同组成的胞内区。
II型受体包括ActR-II、ActR-II B、Punt、TβR-II、BMPR-II等,其也由四部分构成:信号肽、亲水胞外区、跨膜区和由激酶区与富含Ser/Thr的短尾共同构成的胞内区。
TβR-I和TβR-II均属于跨膜型受体丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶(receptor serine/threonine kinases)家族,它们具有以下共同特征:①都是糖蛋白,包含以上四部分结构;②都含有10个或更多Cys残基,它们决定了在胞外区的折叠方式,其中3个Cys在靠近膜的区域形成特征性的簇,其它Cys的位置可变;③胞内区都含有丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶区。