宏观经济学 曼昆 习题答案 章节9
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:864.26 KB
- 文档页数:9

第9章经济增长Ⅱ:技术、经验和政策一、概念题1.劳动效率(efficiency of labor)答:劳动效率是指单位劳动时间的产出水平,反映了社会对生产方法的掌握和熟练程度。
当可获得的技术改进时,劳动效率会提高。
当劳动力的健康、教育或技能得到改善时,劳动效率也会提高。
在索洛模型中,劳动效率(E)是表示技术进步的变量,反映了索洛模型劳动扩张型技术进步的思想:技术进步提高了劳动效率,就像增加了参与生产的劳动力数量一样,所以在生产函数中的劳动力数量上乘以一个劳动效率变量,形成了有效工人概念,这使得索洛模型在稳态分析中纳入了外生的技术进步。
2.劳动改善型技术进步(labor-augmenting technological progress)答:劳动改善型技术进步是指技术进步提高了劳动效率,就像增加了参与生产的劳动力数量一样,所以在生产函数中的劳动力数量上乘以一个劳动效率变量,以反映外生技术进步对经济增长的影响。
劳动改善型技术进步实际上认为技术进步是通过提高劳动效率而影响经济增长的。
它的引入形成了有效工人的概念,从而使得索洛模型能够以单位有效工人的资本和产量来进行稳定状态研究。
3.内生增长理论(endogenous growth theory)答:内生增长理论是用规模收益递增和内生技术进步来说明一个国家长期经济增长和各国增长率差异的一种经济理论,其重要特征就是试图使增长率内生化。
根据其依赖的基本假定条件的差异,可以将内生增长理论分为完全竞争条件下的内生增长模型和垄断竞争条件下的内生增长模型。
按照完全竞争条件下的内生增长模型,使稳定增长率内生化的两条基本途径就是:①将技术进步率内生化;②如果可以被积累的生产要素有固定报酬,那么可以通过某种方式使稳态增长率受要素的积累影响。
内生增长理论是抛弃了索洛模型外生技术进步的假设,以更好地研究技术进步与经济增长之间的关系的理论。
它认为经济增长是可以内生持续的,不会达到索洛模型的稳定状态。

曼昆《宏观经济学》(第9版)章节习题精编详解第2篇古典理论:长期中的经济第7章失业一、概念题1.自然失业率(natural rate of unemployment)答:自然失业率又称“有保证的失业率”、“正常失业率”、“充分就业失业率”等,它是经济围绕其波动的平均失业率,是经济在长期中趋近的失业率,是充分就业时仍然保持的失业水平。
自然失业率是在没有货币因素干扰的情况下,让劳动市场和商品市场自发供求力量起作用时,总供给和总需求处于均衡状态时的失业率。
“没有货币因素干扰”是指失业率的高低与通货膨胀率的高低之间不存在替代关系。
自然失业率决定于经济中的结构性和摩擦性的因素,取决于劳动市场的组织状况、人口组成、失业者寻找工作的能力愿望、现有工作的类型、经济结构的变动、新加入劳动者队伍的人数等众多因素。
任何把失业降低到自然失业率以下的企图都将造成加速的通货膨胀。
任何时候都存在着与实际工资率结构相适应的自然失业率。
自然失业率是弗里德曼对菲利普斯曲线发展的一种观点,他将长期的均衡失业率称为“自然失业率”,它可以和任何通货膨胀水平相对应,且不受其影响。
2.摩擦性失业(frictional unemployment)答:摩擦性失业指劳动力市场运行机制不完善或者因为经济变动过程中的工作转换而产生的失业。
摩擦性失业是劳动力在正常流动过程中所产生的失业。
在一个动态经济中,各行业、各部门和各地区之间劳动需求的变动是经常发生的。
即使在充分就业状态下,由于人们从学校毕业或搬到新城市而要寻找工作,总是会有一些人的周转。
摩擦性失业量的大小取决于劳动力流动性的大小和寻找工作所需要的时间。
由于在动态经济中,劳动力的流动是正常的,所以摩擦性失业的存在也是正常的。
3.部门转移(sectoral shift)答:部门转移是指劳动力在不同部门和行业的重新配置。
由于许多原因,企业和家庭需要的产品类型一直在变动。
随着产品需求的变动,对生产这些产品的劳动力的需求也在改变,因此就出现劳动力在部门之间的转移。

第4篇 经济周期理论:短期中的经济第9章 经济波动导论课后习题详解跨考网独家整理最全经济学考研真题,经济学考研课后习题解析资料库,您可以在这里查阅历年经济学考研真题,经济学考研课后习题,经济学考研参考书等内容,更有跨考考研历年辅导的经济学学哥学姐的经济学考研经验,从前辈中获得的经验对初学者来说是宝贵的财富,这或许能帮你少走弯路,躲开一些陷阱。
以下内容为跨考网独家整理,如您还需更多考研资料,可选择经济学一对一在线咨询进行咨询。
一、概念题1.奥肯定律(Okun ’s law )答:奥肯定律是表示失业率与实际国民收入增长率之间关系的经验统计规律,由美国经济学家奥肯在20世纪60年代初提出。
其主要内容是:失业率每高于自然失业率1个百分点,实际GDP 将低于潜在GDP 2个百分点。
奥肯定律的一个重要结论是:实际GDP 必须保持与潜在GDP 同样快的增长,以防止失业率的上升。
如果政府想让失业率下降,那么,该经济社会的实际GDP 的增长必须快于潜在GDP 的增长。
根据奥肯的研究,在美国,失业率每下降1%,实际国民收入增长2%。
但应该指出的是:①奥肯定律表明了失业率与实际国民收入增长率之间是反方向变动的关系;②两者的数量关系1∶2是一个平均数,在不同的时期,这一比率并不完全相同;③这一规律适用于经济没有实现充分就业时的情况。
在经济实现了充分就业时,这一规律所表示的自然失业率与实际国民收入增长率之间的关系要弱得多,一般估算是1∶0.76。
2.领先指标(leading indicators )答:领先指标是指一般先于整体经济变动的变量,可以帮助经济学家预测短期经济波动。
由于经济学家对前导指标可靠意见看法的不一致,导致经济学家给出不同的预测,其中就包括短期经济波动情况的预测。
领先指标的大幅度下降预示经济很可能会衰退,大幅度上升预示经济很可能会繁荣。
3.总需求(aggregate demand )答:总需求是指整个经济社会在任何一个给定的价格水平下对产品和劳务的需求总量。

第1章宏观经济学科学一、概念题1.宏观经济学(macroeconomics)答:宏观经济学与微观经济学相对,是一种现代的经济分析方法。
它以国民经济总体作为考察对象,研究经济生活中有关总量的决定与变动,解释失业、通货膨胀、经济增长与波动、国际收支及汇率的决定与变动等经济中的宏观整体问题,所以又称之为总量经济学。
宏观经济学的中心和基础是总需求—总供给模型。
具体来说,宏观经济学主要包括总需求理论、总供给理论、失业与通货膨胀理论、经济增长与经济周期理论、开放经济理论、宏观经济政策等内容。
对宏观经济问题进行分析与研究的历史十分悠久,但现代意义上的宏观经济学直到20世纪30年代才得以形成和发展起来。
现代宏观经济学诞生的标志是凯恩斯于1936年出版的《就业、利息和货币通论》。
宏观经济学在20世纪30年代奠定基础,二战后逐步走向成熟并得到广泛应用,20世纪60年代后的“滞胀”问题使凯恩斯主义的统治地位受到严重挑战并形成了货币主义、供给学派、理性预期等学派对立争论的局面,20世纪90年代新凯恩斯主义的形成又使国家干预思想占据主流。
宏观经济学是当代发展最为迅猛,应用最为广泛,因而也是最为重要的经济学学科。
2.实际GDP(real GDP)答:实际GDP指用以前某一年的价格作为基期的价格计算出来的当年全部最终产品的市场价值。
它衡量在两个不同时期经济中的产品产量变化,以相同的价格或不变金额来计算两个时期所生产的所有产品的价值。
在国民收入账户中,以2010年的价格作为基期来计算实际GDP,意味着在计算实际GDP时,用现期的产品产量乘以2010年的价格,便可得到以2010年价格出售的现期产出的价值。
3.通货膨胀与通货紧缩(inflation and deflation)答:(1)通货膨胀是指在一段时期内,一个经济中大多数商品和劳务的价格水平持续显著地上涨。
它包含三层含义:①通货膨胀是经济中一般价格水平的上涨,而不是个别商品或劳务的价格上涨;②通货膨胀是价格的持续上涨,而非一次性上涨;③通货膨胀是价格的显著上涨,而非某些微小的上升,例如每年上升0.5%,不能视为通货膨胀。


思考与练习1.名词解释需求管理政策供给管理政策财政预算财政政策货币政策自动稳定器法定准备金率货币乘数基础货币再贴现公开市场业务政策效应财政财政效应货币政策效应挤出效应双松政策双紧政策2.试述宏观经济政策的目标及其相互关系。
3.功能财政思想与平衡预算的财政思想有何区别?4.试述财政政策的自动稳定器功能?是否税率越高,税收作为自动稳定器的作用越大? 5.什么是权衡性的财政政策?如何操作?6.什么是货币乘数,它是如何起作用的?7.说明货币政策的传导机制与内容。
8.中央银行的货币政策工具主要有哪些?9.试述货币创造乘数及影响因素.10.试述财政政策效果及影响因素。
11.试述货币政策效果及影响因素。
12.试述货币财政政策挤出效应的制约因素.13.什么是挤出效应?挤出效应的制约因素有哪些?14.试述货币政策的局限性。
15.画图说明IS曲线斜率对财政政策效果的影响。
16.画图说明LM曲线斜率对财政政策效果的影响.17.画图说明IS曲线斜率对货币政策效果的影响。
18.画图说明LM曲线斜率对货币政策效果的影响。
19.试述财政政策和货币政策配合使用具体有哪几种方式?20.货币是否存在挤出效应?为什么?21.画图说明双松的政策效应。
22.画图说明双紧的政策效应。
23.画图说明财政松货币紧的政策效应。
24.画图说明财政紧货币松的政策效应。
25.假定经济起初处于充分就业状态,现在政府要改变总需求构成,增加私人投入而减少消费支出,但不改变总需求水平,试问应当实行一种什么样的混合政策?并用IS-LM图形表示这一政策建议。
25.假定政府要削减税收,试用IS-LM模型表示以下两种情况下减税的影响:(1)用适应性货币政策保持利率不变。
(2)货币存量不变.1.名词解释(1)需求管理政策:指通过调节总需求来达到一定宏观经济目标的政策措施。
(2)供给管理政策:通过调节总供给来达到一定的宏观经济目标的政策措施。
(3)财政预算:指政府逐年估算未来财政年度的收入与支出,以促进宏观经济目标的实现。

宏观经济学课后习题答案(共9篇)宏观经济学课后习题答案(一): 这是曼昆的宏观经济学的24章的课后习题,求高手解答,我要详细的计算过程!答案我已经知道,是变动0.4美元在长期中,糖果的价格从0.10美元上升到0.60美元。
在同一时期中,消费物价指数从150上升到300。
根据整体通货膨胀进行调整后,糖果的价格变动了多少我要详细的解答过程,怎么算的就行了!由CPI可知,通货膨胀率=(300-150)/150*100%=100%糖果的原始价格P=0.1在这段时间通过通货膨胀变为0.1*(1+通货膨胀率)=0.2实际上糖果在后来卖到了0.6,所以糖果实际价格变动了0.6-0.2=0.4美元宏观经济学课后习题答案(二): 曼昆宏观经济学26章课后题答案是不是错了假设政府明年借债比今年多了200亿美元,对于可贷资金市场的利率和投资,供给和需求曲线的变动,答案是不是有错答案说是供给曲线不变,需求曲线右移,我认为是需求曲线不动,供给曲线左移……财政政策当然变动的是需求,供给怎么可能变动,你可能是总供给和总需求有些混淆,我开始的时候也不是很清楚,多看几遍就明白了,供给曲线可能因为劳动力变动,而合财政货币政策无关.这些政策变动的都是需求.另外右移就是借钱多了,就是投资需求多了,就是G多了,那就是需求曲线右移了宏观经济学课后习题答案(三): 谁有高鸿业版《西方经济学》宏观部分——第十七章课后题答案第十七章总需求——总供给模型1、(1)总需求是经济社会对产品和劳务的需求总量,这一需求总量通常以产出水平来表示.一个经济社会的总需求包括消费需求、投资需求、.政府购买和国外需求.总需求量受多种因素的影响,其中价格水平是一个重要的因素.在宏观经济学中,为了说明价格对总需求量的影响,引入了总需求曲线的概念,即总需求量与价格水平之间关系的几何表示.在凯恩斯主义的总需求理论中,总需求曲线的理论来源主要由产品市场均衡理论和货币市场均衡理论来反映.(2)在IS—LM模型中,一般价格水平被假定为一个常数(参数).在价格水平固定不变且货币供给为已知的情况下,IS曲线和LM曲线的交点决定均衡的收入水平.现用图1—62来说明怎样根据IS—LM图形推导总需求曲线.图1—62分上下两部.上图为IS—LM图.下图表示价格水平和需求总量之间的关系,即总需求曲线.当价格P的数值为时,此时的LM曲线与IS曲线相交于点 , 点所表示的国民收入和利率顺次为和 .将和标在下图中便得到总需求曲线上的一点 .现在假设P由下降到 .由于P的下降,LM曲线移动到的位置,它与IS曲线的交点为点. 点所表示的国民收入和利率顺次为和 .对应于上图的点 ,又可在下图中找到 .按照同样的程序,随着P的变化,LM曲线和IS曲线可以有许多交点,每一个交点都代表着一个特定的y和p.于是有许多P与的组合,从而构成了下图中一系列的点.把这些点连在一起所得到的曲线AD便是总需求曲线.从以上关于总需求曲线的推导中看到,总需求曲线表示社会中的需求总量和价格水平之间的相反方向的关系.即总需求曲线是向下方倾斜的.向右下方倾斜的总需求曲线表示,价格水平越高,需求总量越小;价格水平越低,需求总量越大.2、财政政策是政府变动税收和支出,以便影响总需求,进而影响就业和国民收入的政策.货币政策是指货币当局即中央银行通过银行体系变动货币供应量来调节总需求的政策.无论财政政策还是货币政策,都是通过影响利率、消费和投资进而影响总需求,使就业和国民收入得到调节的,通过对总需求的调节来调控宏观经济,所以称为需求管理政策.3、总供给曲线描述国民收入与一般价格水平之间的依存关系.根据生产函数和劳动力市场的均衡推导而得到.资本存量一定时,国民收入水平碎就业量的增加而增加,就业量取决于劳动力市场的均衡.所以总供给曲线的理论来源于生产函数和劳动力市场均衡的理论.4、总供给曲线的理论主要由总量生产函数和劳动力市场理论来反映的.在劳动力市场理论中,经济学家对工资和价格的变化和调整速度的看法是分歧的.古典总供给理论认为,劳动力市场运行没有阻力,在工资和价格可以灵活变动的情况下,劳动力市场得以出清,使经济的就业总能维持充分就业状态,从而在其他因素不变的情况下,经济的产量总能保持在充分就业的产量或潜在产量水平上.因此,在以价格为纵坐标,总产量为横坐标的坐标系中,古典供给曲线是一条位于充分就业产量水平的垂直线.凯恩斯的总供给理论认为,在短期,一些价格是粘性的,从而不能根据需求的变动而调整.由于工资和价格粘性,短期总供给曲线不是垂直的,凯恩斯总供给曲线在以价格为纵坐标,收入为横坐标的坐标系中是一条水平线,表明经济中的厂商在现有价格水平上,愿意供给所需的任何数量的商品.作为凯恩斯总供给曲线基础的思想是,作为工资和价格粘性的结果,劳动力市场不能总维持在充分就业状态,由于存在失业,厂商可以在现行工资下获得所需劳动.因而他们的平均生产成本被认为是不随产出水平变化而变化.一些经济学家认为,古典的和凯恩斯的总供给曲线分别代表着劳动力市场的两种极端的说法.在现实中工资和价格的调整经常介于两者之间.在这种情况下以价格为纵坐标,产量为横坐标的坐标系中,总供给曲线是向右上方延伸的,这即为常规的总需求曲线.总之,针对总量劳动市场关于工资和价格的不同假设,宏观经济学中存在着三种类型的总供给曲线.5、解答:宏观经济学在用总需求—总供给说明经济中的萧条,高涨和滞涨时,主要是通过说明短期的收入和价格水平的决定来完成的.如图1—63所示. 从图1—63可以看到,短期的收入和价格水平的决定有两种情况.第一种情况是,AD是总需求曲线, 使短期供给曲线,总需求曲线和短期供给曲线的交点E决定的产量或收入为y,价格水平为P,二者都处于很低的水平,第一种情况表示经济处于萧条状态.第二种情况是,当总需求增加,总需求曲线从AD向右移动到时,短期总供给曲线和新的总需求曲线的交点决定的产量或收入为 ,价格水平为 ,二者都处于很高的水平,第二种情况表示经济处于高涨状态.现在假定短期供给曲线由于供给冲击(如石油价格和工资等提高)而向左移动,但总需求曲线不发生变化.在这种情况下,短期收入和价格水平的决定可以用图1—64表示.在图1—64中,AD是总需求曲线,是短期总供给曲线,两者的交点E决定的产量或收入为,价格水平为P.现在由于出现供给冲击,短期总供给曲线向左移动到,总需求曲线和新的短期总供给曲线的交点决定的产量或收入为,价格水平为,这个产量低于原来的产量,而价格水平却高于原来的价格水平,这种情况表示经济处于滞涨状态,即经济停滞和通货膨胀结合在一起的状态.6、二者在“形式”上有一定的相似之处.微观经济学的供求模型主要说明单个商品的价格和数量的决定.宏观经济中的AD—AS模型主要说明总体经济的价格水平和国民收入的决定.二者在图形上都用两条曲线来表示,在价格为纵坐标,数量为横坐标的坐标系中,向右下方倾斜的为需求曲线,向右上方延伸的为供给曲线.但二者在内容上有很大的不同:其一,两模型涉及的对象不同.微观经济学的供求模型是微观领域的事物,而宏观经济中的AD—AS模型是宏观领域的事物.其二,各自的理论基础不同.微观经济学中的供求模型中的需求曲线的理论基础是消费者行为理论,而供给曲线的理论基础主要是成本理论和市场理论,它们均属于微观经济学的内容.宏观经济学中的总需求曲线的理论基础主要是产品市场均衡和货币市场均衡理论,而供给曲线的理论基础主要是劳动市场理论和总量生产函数,它们均属于宏观经济学的内容.其三,各自的功能不同.微观经济学中的供求模型在说明商品的价格和数量的决定的同时,还可以来说明需求曲线和供给曲线移动对价格和商品数量的影响,充其量这一模型只解释微观市场的一些现象和结果.宏观经济中的AD—AS模型在说明价格和产出决定的同时,可以用来解释宏观经济的波动现象,还可以用来说明政府运用宏观经济政策干预经济的结果.7、(1)由得;2023 + P = 2400 - P于是 P=200, =2200即得供求均衡点.(2)向左平移10%后的总需求方程为:于是,由有:2023 + P = 2160 – PP=80 , =2080与(1)相比,新的均衡表现出经济处于萧条状态.(3)向右平移10%后的总需求方程为:于是,由有:2023 + P = 2640 – PP=320 , =2320与(1)相比,新的均衡表现出经济处于高涨状态.(4)向左平移10%后的总供给方程为:于是,由有:1800 + P = 2400 – PP=300 , =2100与(1)相比,新的均衡表现出经济处于滞涨状态.(5)总供给曲线向右上方倾斜的直线,属于常规型.宏观经济学课后习题答案(四): 宏观经济学问题题号:11 题型:单选题(请在以下几个选项中选择唯一正确答案)本题分数:5内容:一般把经济周期分为四个阶段,这四个阶段为().选项:a、兴旺,停滞,萧条和复苏b、繁荣,停滞,萧条和恢复c、繁荣,衰退,萧条和复苏d、兴旺,衰退,萧条和恢复题号:12 题型:单选题(请在以下几个选项中选择唯一正确答案)本题分数:5内容:“面粉是中间产品”这一命题()选项:a、一定是对的b、一定是不对的c、可能是对的也可能是不对的d、以上三种说法全对.题号:13 题型:单选题(请在以下几个选项中选择唯一正确答案)本题分数:5内容:下列哪种情况下执行财政政策的效果较好(选项:a、LM陡峭而IS平缓b、LM平缓而IS陡峭c、LM和IS一样平缓d、LM和IS一样陡峭题号:14 题型:单选题(请在以下几个选项中选择唯一正确答案)本题分数:5内容:政府财政政策通过哪一个变量对国民收入产生影响().选项:a、进口b、消费支出c、出口d、政府购买.题号:15 题型:单选题(请在以下几个选项中选择唯一正确答案)本题分数:5内容:在国民收入核算体系中,计入GDP的政府支出是指().选项:a、政府购买物品的支出b、政府购买物品和劳务的支出c、政府购买物品和劳务的支出加上政府的转移支出之和d、政府工作人员的薪金和政府转移支出题号:16 题型:是非题本题分数:5内容:长期总供给曲线所表示的总产出是经济中的潜在产出水平选项:1、错2、对题号:17 题型:是非题本题分数:5内容:GDP中扣除资本折旧,就可以得到NNP选项:1、错2、对题号:18 题型:是非题本题分数:5内容:在长期总供给水平,由于生产要素等得到了充分利用,因此经济中不存在失业选项:1、错2、对题号:19 题型:是非题本题分数:5内容:个人收入即为个人可支配收入,是人们可随意用来消费或储蓄的收入选项:1、错2、对题号:20 题型:是非题本题分数:5内容:GNP折算指数是实际GDP与名义GDP的比率选项:1、错2、对C,C,A,D,B对,对(NNP国民生产净值),错(可能还有摩擦失业),错,错宏观经济学课后习题答案(五): 一道宏观经济学的习题,求答案及解析7、将一国经济中所有市场交易的货币价值进行加总a、会得到生产过程中所使用的全部资源的市场价值b、所获得的数值可能大于、小于或等于GDP的值c、会得到经济中的新增价值总和d、会得到国内生产总值`b 正确市场交易的可能有中间产品,如此中间产品加上最终产品,则重复计算的结果大于GDP;不在国内市场交易,出口销往国外的漏算,则计算结果会小于gdp;如果重复的和漏算的正好相等,则结果可能等于gdp。

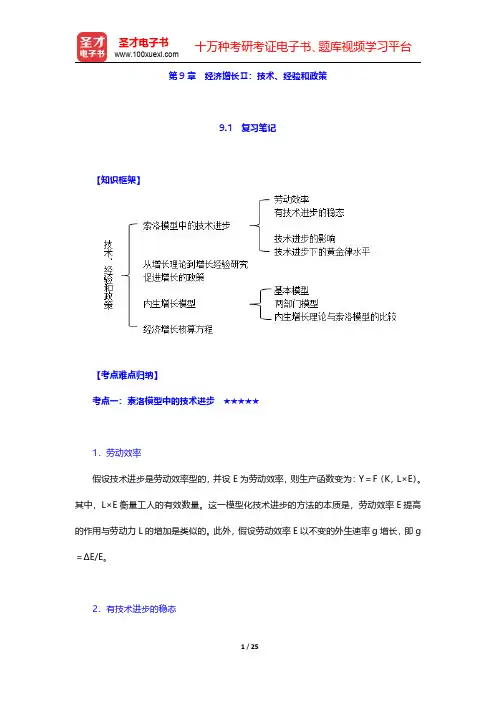
第9章经济增长Ⅱ:技术、经验和政策9.1复习笔记【知识框架】【考点难点归纳】考点一:索洛模型中的技术进步★★★★★1.劳动效率假设技术进步是劳动效率型的,并设E为劳动效率,则生产函数变为:Y=F(K,L×E)。
其中,L×E衡量工人的有效数量。
这一模型化技术进步的方法的本质是,劳动效率E提高的作用与劳动力L的增加是类似的。
此外,假设劳动效率E以不变的外生速率g增长,即g =ΔE/E。
2.有技术进步的稳态设y=Y/(L×E),k=K/(L×E),对生产函数两边同除以L×E,可得单位效率工人产出函数,即y=f(k)。
该函数形式虽然与上一章完全相同,但是意义已经发生了改变。
因为单位效率工人的储蓄(投资)为:sy=sf(k),而单位效率工人的补偿投资(资本扩展化)为:(δ+n+g)k。
因此,当单位效率工人的储蓄和补偿投资相等时,即Δk=sf (k)-(δ+n+g)k=0,经济达到稳定状态。
如图9-1所示,k*表示稳态的资本存量,在这一水平,有效工人的人均资本和有效工人的人均产出保持不变。
图9-1技术进步和索洛模型3.技术进步的影响(见表9-1)表9-1技术进步的影响4.技术进步下的黄金律水平因为c*=y*-i*=f(k*)-(δ+n+g)k*,当c*达到最大化时,有:MPK=δ+n+g 或MPK-δ=n+g。
这说明,在黄金律资本水平,资本的边际产出减去折旧率等于人口增长率与技术进步的和。
由于现实经济既有人口增长,又有技术进步,所以,必须用这个标准来评价经济的资本存量与黄金律稳态水平的关系。
考点二:从增长理论到增长经验研究★1.平衡的增长平衡的增长是指技术进步引起许多变量在稳态的数值一起上升。
根据索洛模型,在稳态,人均产出Y/L和人均资本存量K/L以技术进步的速率g增长。
技术进步也影响要素价格。
在稳态,实际工资以技术进步的速率增长。
而资本的实际租赁价格随着时间的推移是不变的。

曼昆宏观经济经济学第九版英文原版答案完整版曼昆宏观经济经济学第九版英文原版答案集团标准化办公室:[VV986T-J682P28-JP266L8-68PNN]A n s w e r s t o T e x t b o o k Q u e s t i o n s a n d P r o b l e m sCHAPTER 7Unemployment and the Labor MarketQuestions for Review1. The rates of job separation and job finding determine the naturalrate of unemployment. The rate of job separation is the fraction of people who lose their job each month. The higher the rate of jobseparation, the higher the natural rate of unemployment. The rate of job finding is the fraction of unemployed people who find a job each month. The higher the rate of job finding, the lower the natural rate of unemployment.2. Frictional unemployment is the unemployment caused by the time ittakes to match workers and jobs. Finding an appropriate job takes time because the flow of information about job candidates and job vacancies is not instantaneous. Because different jobs requiredifferent skills and pay different wages, unemployed workers may not accept the first job offer they receive.In contrast, structural unemployment is the unemployment resulting from wage rigidity and job rationing. These workers are unemployed not because they are actively searching for a job that best suits their skills (as in the case of frictional unemployment), but because at the prevailing real wage thequantity of labor supplied exceeds the quantity of labor demanded. If the wage does not adjust to clear the labor market, then these workers must wait for jobs to become available. Structural unemployment thus arises because firms fail to reduce wages despite an excess supply of labor.3. The real wage may remain above the level that equilibrates laborsupply and labor demand because of minimum wage laws, the monopoly power of unions, and efficiency wages.Minimum-wage laws cause wage rigidity when they prevent wages from falling to equilibrium levels. Although most workers are paid a wage above the minimum level, for some workers, especially the unskilled and inexperienced, the minimum wage raises their wage above theequilibrium level. It therefore reduces the quantity of their labor that firms demand, and creates an excess supply of workers, which increases unemployment.The monopoly power of unions causes wage rigidity because the wages of unionized workers are determined not by the equilibrium of supply and demand but by collective bargaining between union leaders and firm management. The wage agreement often raises the wage abovethe equilibrium level and allows the firm to decide how many workers to employ. These high wages cause firms to hire fewer workers than at the market-clearing wage, so structural unemployment increases.Efficiency-wage theories suggest that high wages make workers more productive. The influence of wages on worker efficiency may explain why firms do not cut wages despite an excess supply of labor. Even though a wage reduction decreasesthe firm’s wage bill, it may also lower worker productivity and therefore the firm’s profits.4. Depending on how one looks at the data, most unemployment can appearto be either short term or long term. Most spells of unemployment are short; that is, most of those who became unemployed find jobs quickly.On the other hand, most weeks of unemployment are attributable to the small number of long-term unemployed. By definition, the long-term unemployed do not find jobs quickly, so they appear on unemployment rolls for many weeks or months.5. Europeans work fewer hours than Americans. One explanation is thatthe higher income tax rates in Europe reduce the incentive to work. A second explanation is a larger underground economy in Europe as aresult of more people attempting to evade the high tax rates.A third explanation is the greater importance of unions in Europe and their ability to bargain for reduced work hours. A final explanation isbased on preferences, whereby Europeans value leisure more thanAmericans do, and therefore elect to work fewer hours.Problems and Applications1. a. In the example that follows, we assume that during the school yearyou look for a part-time job, and that, on average, it takes 2 weeks to find one. We also assume that the typical job lasts 1semester, or 12 weeks.b. If it takes 2 weeks to find a job, then the rate of job finding in weeks isf = (1 job/2 weeks) = 0.5 jobs/week.If the job lasts for 12 weeks, then the rate of job separation in weeks iss = (1 job/12 weeks) = 0.083 jobs/week.c. From the text, we know that the formula for the natural rate of unemployment is(U/L) = [s/(s + f )],where U is the number of people unemployed, and L is the number of people in the labor force.Plugging in the values for f and s that were calculated in part (b), we find(U/L) = [0.083/(0.083 + 0.5)] = 0.14.Thus, if on average it takes 2 weeks to find a job that lasts 12 weeks, the natural rate of unemployment for this population ofcollege students seeking part-time employment is 14 percent.2. Call the number of residents of the dorm who are involved I, thenumber who are uninvolved U, and the total number of students T = I + U. In steady state the total number of involved students is constant.For this to happen we need the number of newly uninvolved students,(0.10)I, to be equal to the number of students who just becameinvolved, (0.05)U. Following a few substitutions:(0.05)U = (0.10)I= (0.10)(T – U),soWe find that two-thirds of the students are uninvolved.3. To show that the unemployment rate evolves over time to thesteady-state rate, let’s begin by defining how the number of people unemployed changes over time. The change in the number of unemployed equals the number of people losing jobs (sE) minus the number finding jobs (fU). In equation form, we can express this as:U–U t= ΔU t + 1 = sE t–fU t.t + 1Recall from the text that L = E t + U t, or E t = L –U t, where L is the total labor force (we will assume that L is constant). Substituting for E t in the above equation, we findΔU t + 1 = s(L –U t) –fU t.Dividing by L, we get an expression for the change in the unemployment rate from t to t + 1:ΔU t + 1/L = (U t + 1/L) –(U t/L) = Δ[U/L]t + 1 = s(1 –U t/L) –fU t/L.Rearranging terms on the right side of the equation above, we end up with line 1 below. Now take line 1 below, multiply the right side by (s + f)/(s + f) and rearrange terms to end up with line 2 below:Δ[U/L]t + 1= s – (s + f)U t/L= (s + f)[s/(s + f) – U/L].tThe first point to note about this equation is that in steady state, when the unemployment rate equals its natural rate, the left-handside of this expression equals zero. This tells us that, as we found in the text, the natural rate of unemployment (U/L)n equals s/(s + f).We can now rewrite the above expression, substituting (U/L)n for s/(s + f), to get an equation that is easier to interpret: Δ[U/L]t + 1 = (s + f)[(U/L)n–U t/L].This expression shows the following:If U t/L > (U/L)n (that is, the unemployment rate is above its natural rate), then Δ[U/L]t + 1 is negative: the unemployment rate falls.If U t/L < (U/L)n (that is, the unemployment rate is below its natural rate), then Δ[U/L]t + 1 is positive: the unemployment raterises.This process continues until the unemployment rate U/L reaches the steady-state rate (U/L)n.4. Consider the formula for the natural rate of unemployment,If the new law lowers the chance of separation s, but has no effect on the rate of job finding f, then the natural rate of unemployment falls.For several reasons, however, the new law might tend to reduce f.First, raising the cost of firing might make firms more careful about hiring workers, since firms have a harder time firing workers who turn out to be a poor match. Second, if job searchers think that the new legislation will lead them to spend a longer period of time on a particular job, then they might weigh morecarefully whether or not to take that job. If the reduction in f is large enough, then the new policy may even increase the natural rate of unemployment.5. a. The demand for labor is determined by the amount of labor that aprofit-maximizing firm wants to hire at a given real wage. The profit-maximizing condition is that the firm hire labor until the marginal product of labor equals the real wage,The marginal product of labor is found by differentiating the production function with respect to labor (see Chapter 3 for more discussion),In order to solve for labor demand, we set the MPL equal to the real wage and solve for L:Notice that this expression has the intuitively desirable feature that increases in the real wage reduce the demand for labor.b. We assume that the 27,000 units of capital and the 1,000 units oflabor are supplied inelastically (i.e., they will work at anyprice). In this case we know that all 1,000 units of labor and 27,000 units of capital will be used in equilibrium, so we can substitute these values into the above labor demand function and.solve for WPIn equilibrium, employment will be 1,000, and multiplying this by10 we find that the workers earn 10,000 units of output. The totaloutput is given by the production function:Y=5Y13Y23Y=5(27,00013)(1,00023)Y=15,000.Notice that workers get two-thirds of output, which is consistent with what we know about the Cobb–Douglas production function from Chapter 3.c. The real wage is now equal to 11 (10% above the equilibrium levelof 10).Firms will use their labor demand function to decide how manyworkers to hire at the given real wage of 11 and capital stock of 27,000:So 751 workers will be hired for a total compensation of 8,261units of output. To find the new level of output, plug the new value for labor and the value for capital into the production function and you will find Y = 12,393.d. The policy redistributes output from the 249 workers who becomeinvoluntarily unemployed to the 751 workers who get paid more than before. The lucky workers benefit less than the losers lose as the total compensation to the working class falls from 10,000 to 8,261 units of output.e. This problem does focus on the analysis of two effects of theminimum-wage laws: they raise the wage for some workers whiledownward-sloping labor demand reduces the total numberof jobs.Note, however, that if labor demand is less elastic than in this example, then the loss of employment may be smaller, and thechange in worker income might be positive.6. a. The labor demand curve is given by the marginal product of laborschedule faced by firms. If a country experiences a reduction inproductivity, then the labor demand curve shifts to the left as in Figure 7-1. If labor becomes less productive, then at any givenreal wage, firms demand less labor.b. If the labor market is always in equilibrium, then, assuming afixed labor supply, an adverse productivity shock causes adecrease in the real wage but has no effect on employment orunemployment, as in Figure 7-2.c. If unions constrain real wages to remain unaltered, then asillustrated in Figure 7-3, employmentfalls to L1 and unemployment equals L –L1.This example shows that the effect of a productivity shock on aneconomy depends on the role of unions and the response of collective bargaining to such a change.7. a. If workers are free to move between sectors, then the wage in each sector will be equal. If thewages were not equal then workers would have an incentive to move to the sector with the higherwage and this would cause the higher wage to fall, and the lower wage to rise until they wereequal.b. Since there are 100 workers in total, L S = 100 – L M. We cansubstitute this expression into the labor demand for services equation, and call the wage w since it is the same in bothsectors:L S = 100 – LM= 100 – 4wLM= 4w.Now set this equal to the labor demand for manufacturing equation and solve for w:4w = 200 – 6ww = $20.Substitute the wage into the two labor demand equations to find L M is 80 and L S is 20.c. If the wage in manufacturing is equal to $25 then L M is equal to 50.d. There are now 50 workers employed in the service sector and the wage w S is equal to $12.50.e. The wage in manufacturing will remain at $25 and employment will remain at 50. If thereservation wage for the service sector is $15 then employment in the service sector will be 40. Therefore, 10 people are unemployed and the unemployment rate is 10 percent.8. Real wages have risen over time in both the United Statesand Europe,increasing the reward for working (the substitution effect) but also making people richer, so they want to “buy” more leisure (theincome effect). If the income effect dominates, then people want to work less as real wages go up. This could explain the Europeanexperience, in which hours worked per employed person have fallen over time. If the income and substitution effects approximatelycancel, then this could explain the U.S. experience, in which hours worked per person have stayed about constant. Economists do not have good theories for why tastes might differ, so they disagree onwhether it is reasonable to think that Europeans have a larger income effect than do Americans.9. The vacant office space problem is similar to the unemploymentproblem; we can apply the same concepts we used in analyzingunemployed labor to analyze why vacant office space exists. There isa rate of office separation: firms that occupy offices leave, eitherto move to different offices or because they go out of business.There is a rate of office finding: firms that need office space (either to start up or expand) find empty offices. It takes time to match firms with available space. Different types of firms require spaces with different attributes depending on what theirspecific needs are. Also, because demand for different goods fluctuates, there are “sectoral shifts”—changes in the composition of demand among industries and regions that affect the profitability and office needs of different firms.。

第4篇经济周期理论:短期中的经济第9章经济波动导论跨考网独家整理最全经济学考研真题,经济学考研课后习题解析资料库,您可以在这里查阅历年经济学考研真题,经济学考研课后习题,经济学考研参考书等内容,更有跨考考研历年辅导的经济学学哥学姐的经济学考研经验,从前辈中获得的经验对初学者来说是宝贵的财富,这或许能帮你少走弯路,躲开一些陷阱。
以下内容为跨考网独家整理,如您还需更多考研资料,可选择经济学一对一在线咨询进行咨询。
一、判断题1.由于股票市场价格上升而导致财富的增加会引起经济沿着现存的总需求曲线移动。
()【答案】F【解析】物价水平的变动才能使得经济沿着总需求曲线移动。
股票市场价格,并不等同于实体经济中的价格,股票价格上升导致的财富的增加可能会增加消费和投资,从而使得总需求曲线向外移动。
2.实际GDP的波动只由总需求变动引起,不为总供给变动所影响。
()【答案】F【解析】长期而言,实际GDP是由总供给决定的,随着影响总供给曲线的劳动、资本以及技术的变动而变动。
3.如果作为总供给减少的反应,政府增加货币供应,失业率将回到自然失业率水平,但是价格甚至还要上涨。
()【答案】T【解析】当经济面临不利的总供给冲击时,总供给曲线向左上方移动,而中央银行可以通过增加货币供应以增加总需求,阻止产出的下降,但这种政策的代价是更高的价格水平。
4.无论产量减少是由总需求减少还是总供给减少引起,作为产出减少的反应,经济都会回到其初始价格水平和初始产量水平。
()【答案】F【解析】当经济面临不利的总供给冲击时,中央银行可以增加总需求来防止产出的下降,使产出回到初始产量水平,但中央银行这种反应的代价是更高的价格水平。
5.如果在总供给曲线的水平阶段上总需求增加,一部分扩张性财政政策的效果将转化为通货膨胀。
()【答案】F【解析】在总供给曲线水平的阶段上,总需求增加,使得扩张性财政政策的效果全部转化为产出。
6.单位生产成本下降会使总供给曲线向左移动。
曼昆宏观经济学第9版章节习题详解本书是曼昆《宏观经济学》(第9版)教材的学习辅导书,严格按照曼昆《宏观经济学》(第9版)教材内容进⾏编写,共分20章。
每⼀章(除了第15章,因为各⾼校考试很少涉及到这章内容)都精⼼挑选经典常见考题,并予以详细解答。
熟练掌握本书考题的解答,有助于学员理解和掌握有关概念、原理,并提⾼解题能⼒。
编者温馨提⽰:考虑到本书部分考题有⼀定的难度,建议学员在考研考博复习过程中强化阶段使⽤,效果最佳。
另外,学员千万不要觉得⾃⼰所报院校不考判断题和单项选择题,⽽忽视这两种题型的练习。
事实上,很多⾼校研究⽣⼊学考试主观考题就是本书判断题和单项选择题适当修改⽽成。
本书提供电⼦书及打印版,⽅便对照复习。
第1篇 导 ⾔第1章 宏观经济学科学⼀、判断题1.作为基本分析⼯具的供给和需求分析正如在微观经济学中⼀样,在宏观经济学中也处于核⼼地位。
( )【答案】T查看答案【解析】宏观经济学和微观经济学都是研究市场经济中经济活动参与者的⾏为及其后果的,⽽市场经济中所有经济活动参与者的⾏为都是⼀定意义上的供给和需求⾏为,宏观经济学与微观经济学的主要相同之处就在于都是通过需求曲线和供给曲线决定价格和产量。
2.宏观经济模型中的“外⽣”变量包含政策变量,如政府防务采购。
( )【答案】T查看答案【解析】政策性变量,如军事⽀出,是已知变量,因此根据定义,它在模型中没有⾏为⽅程。
同样地,考虑经济条件对军事经济的影响,这个考虑要求将军事⽀出的⾏为“模型化”,以使这个变量由外⽣变为内⽣。
⼆、单项选择题1.⼤多数经济学家相信,价格( )。
A.在长短期中都是黏性的B.在短期中是灵活的,长期中⼤部分是黏性的C.在长短期中都是灵活的D.在长期中是灵活的,短期中⼤部分是黏性的【答案】D查看答案【解析】弹性价格是指可以对供求变动作出即时调整的价格,反之,调整⽐较缓慢的价格被称为黏性价格。
古典经济学派认为商品或劳务的价格是有弹性的,但凯恩斯学派则认为短期内价格是黏性的,长期内才是完全伸缩的。
曼昆《宏观经济学》(第9版)章节习题精编详解第6篇宏观经济政策专题第20章金融系统:机会与危险一、关键概念1.金融系统(financial system)答:金融系统是指代经济中促进储蓄者和投资者之间资金流动的机构的概括性术语,其主要职能是将来自储蓄者的资源引导到各种形式的投资中去。
金融系统的一个部分是金融市场的集合,另一个部分是金融中介的集合。
2.金融市场(financial markets)答:金融市场是指资金融通市场,资金供给者和资金需求者双方通过信用工具进行交易而融通资金的市场。
广义的金融市场是指实现货币借贷、资金融通、办理各种票据和有价证券交易活动的场所。
通过金融市场,家庭能够直接为投资提供资源。
两个重要的金融市场是债券市场和股票市场。
3.债券(bonds)答:债券代表债券持有人给企业的贷款。
通过发行债券来筹集投资资金称为债券融资。
债券是直接融资形式之一,发行者通常是公司或政府。
4.股票(stocks)答:股票代表企业股东的所有权要求。
通过发行股票来筹集资金称为股权融资。
股票是直接融资形式之一。
5.债务融资(debt finance)答:债务融资是指企业通过发行债券来筹集投资资金,资金供给者作为债权人享有到期收回本息的一种融资方式。
债务融资属于直接融资,其经营风险较小,预期收益也相对较小。
6.股权融资(equity finance)答:股权融资是指通过发行股票,引进新股东来筹集资金,企业无须还本付息,但是新老股东共享企业的收益。
股权融资属于直接融资,主要用于解决企业运营资金短缺的问题。
7.金融中介(financial intermediaries)答:金融系统是金融中介的集合,通过金融中介,家庭能够间接地为投资提供资源。
金融中介连接市场的两端,帮助金融资源流向它们的最佳用途。
商业银行是最广为人知的金融中介类型。
它们从储蓄者那里吸收存款,用这些存款给那些需要为投资项目融资的人放贷。
8.厌恶风险(risk averse)答:投资天生是有风险的。
Answers to Textbook Questions and ProblemsCHAPTER 9 Economic Growth II: Technology, Empirics, and PolicyQuestions for Review1. In the Solow model, we find that only technological progress can affect the steady-state rate of growthin income per worker. Growth in the capital stock (through high saving) has no effect on the steady-state growth rate of income per worker; neither does population growth. But technological progress can lead to sustained growth.2. In the steady state, output per person in the Solow model grows at the rate of technological progress g.Capital per person also grows at rate g. Note that this implies that output and capital per effectiveworker are constant in steady state. In the U.S. data, output and capital per worker have both grown at about 2 percent per year for the past half-century.3. To decide whether an economy has more or less capital than the Golden Rule, we need to compare themarginal product of capital net of depreciation (MPK –δ) with the growth rate of total output (n + g).The growth rate of GDP is readily available. Estimating the net marginal product of capital requires a little more work but, as shown in the text, can be backed out of available data on the capital stock relative to GDP, the total amount o f depreciation relative to GDP, and capital’s share in GDP.4. Economic policy can influence the saving rate by either increasing public saving or providingincentives to stimulate private saving. Public saving is the difference between government revenue and government spending. If spending exceeds revenue, the government runs a budget deficit, which is negative saving. Policies that decrease the deficit (such as reductions in government purchases or increases in taxes) increase public saving, whereas policies that increase the deficit decrease saving. A variety of government policies affect private saving. The decision by a household to save may depend on the rate of return; the greater the return to saving, the more attractive saving becomes. Taxincentives such as tax-exempt retirement accounts for individuals and investment tax credits forcorporations increase the rate of return and encourage private saving.5. The legal system is an example of an institutional difference between countries that might explaindifferences in income per person. Countries that have adopted the English style common law system tend to have better developed capital markets, and this leads to more rapid growth because it is easier for businesses to obtain financing. The quality of government is also important. Countries with more government corruption tend to have lower levels of income per person.6. Endogenous growth theories attempt to explain the rate of technological progress by explaining thedecisions that determine the creation of knowledge through research and development. By contrast, the Solow model simply took this rate as exogenous. In the Solow model, the saving rate affects growth temporarily, but diminishing returns to capital eventually force the economy to approach a steady state in which growth depends only on exogenous technological progress. By contrast, many endogenous growth models in essence assume that there are constant (rather than diminishing) returns to capital, interpreted to include knowledge. Hence, changes in the saving rate can lead to persistent growth. Problems and Applications1. a. In the Solow model with technological progress, y is defined as output per effective worker, and kis defined as capital per effective worker. The number of effective workers is defined as L E (or LE), where L is the number of workers, and E measures the efficiency of each worker. To findoutput per effective worker y, divide total output by the number of effective workers:Y LE =K12(LE)12LEY LE =K12L12E12LEY LE =K12 L1E1Y LE =KLE æèççöø÷÷12y=k12b. To solve for the steady-state value of y as a function of s, n, g, and δ, we begin with the equationfor the change in the capital stock in the steady state:Δk = sf(k) –(δ + n + g)k = 0.The production function ycan also be rewritten as y2 = k. Plugging this production functioninto the equation for the change in the capital stock, we find that in the steady state:sy –(δ + n + g)y2 = 0.Solving this, we find the steady-state value of y:y* = s/(δ + n + g).c. The question provides us with the following information about each country:Atlantis: s = 0.28 Xanadu: s = 0.10n = 0.01 n = 0.04g = 0.02 g = 0.02δ = 0.04δ = 0.04Using the equation for y* that we derived in part (a), we can calculate the steady-state values of yfor each country.Developed country: y* = 0.28/(0.04 + 0.01 + 0.02) = 4Less-developed country: y* = 0.10/(0.04 + 0.04 + 0.02) = 12. a. In the steady state, capital per effective worker is constant, and this leads to a constant level ofoutput per effective worker. Given that the growth rate of output per effective worker is zero, this means the growth rate of output is equal to the growth rate of effective workers (LE). We know labor grows at the rate of population growth n and the efficiency of labor (E) grows at rate g. Therefore, output grows at rate n+g. Given output grows at rate n+g and labor grows at rate n, output perworker must grow at rate g. This follows from the rule that the growth rate of Y/L is equal to thegrowth rate of Y minus the growth rate of L.b. First find the output per effective worker production function by dividing both sides of theproduction function by the number of effective workers LE:Y LE =K 13(LE )23LE YLE =K 13L 23E 23LEY LE =K 13L 13E 13Y LE =K LE æèçöø÷13y =k 13To solve for capital per effective worker, we start with the steady state condition:Δk = sf (k ) – (δ + n + g )k = 0.Now substitute in the given parameter values and solve for capital per effective worker (k ):Substitute the value for k back into the per effective worker production function to find output per effective worker is equal to 2. The marginal product of capital is given bySubstitute the value for capital per effective worker to find the marginal product of capital is equal to 1/12.c. According to the Golden Rule, the marginal product of capital is equal to (δ + n + g) or 0.06. In the current steady state, the marginal product of capital is equal to 1/12 or 0.083. Therefore, we have less capital per effective worker in comparison to the Golden Rule. As the level of capital per effective worker rises, the marginal product of capital will fall until it is equal to 0.06. To increase capital per effective worker, there must be an increase in the saving rate.d. During the transition to the Golden Rule steady state, the growth rate of output per worker will increase. In the steady state, output per worker grows at rate g . The increase in the saving rate will increase output per effective worker, and this will increase output per effective worker. In the new steady state, output per effective worker is constant at a new higher level, and output per worker is growing at rate g . During the transition, the growth rate of output per worker jumps up, and then transitions back down to rate g .3. To solve this problem, it is useful to establish what we know about the U.S. economy: • A Cobb –Douglas production function has the form y = k α, where α is capital’s share of income.The question tells us that α = 0.3, so we know that the production function is y = k 0.3.• In the steady state, we know that the growth rate of output equals 3 percent, so we know that (n +g ) = 0.03.• The deprec iation rate δ = 0.04. • The capital –output ratio K/Y = 2.5. Because k/y = [K /(LE )]/[Y /(LE )] = K/Y , we also know that k/y =2.5. (That is, the capital –output ratio is the same in terms of effective workers as it is in levels.)a. Begin with the steady-state condition, sy = (δ + n + g)k. Rewriting this equation leads to a formulafor saving in the steady state:s = (δ + n + g)(k/y).Plugging in the values established above:s = (0.04 + 0.03)(2.5) = 0.175.The initial saving rate is 17.5 percent.b. We know from Chapter 3 that with a Cobb–Douglas production function, capital’s share ofincome α = MPK(K/Y). Rewriting, we haveMPK = α/(K/Y).Plugging in the values established above, we findMPK = 0.3/2.5 = 0.12.c. We know that at the Golden Rule steady state:MPK = (n + g + δ).Plugging in the values established above:MPK = (0.03 + 0.04) = 0.07.At the Golden Rule steady state, the marginal product of capital is 7 percent, whereas it is 12 percent in the initial steady state. Hence, from the initial steady state we need to increase k to achieve the Golden Rule steady state.d. We know from Chapter 3 that for a Cobb–Douglas production function, MPK = α (Y/K). Solvingthis for the capital–output ratio, we findK/Y = α/MPK.We can solve for the Golden Rule capital–output ratio using this equation. If we plug in the value0.07 for the Golden Rule steady-state marginal product of capital, and the value 0.3 for α, we findK/Y = 0.3/0.07 = 4.29.In the Golden Rule steady state, the capital–output ratio equals 4.29, compared to the current capital–output ratio of 2.5.e. We know from part (a) that in the steady states = (δ + n + g)(k/y),where k/y is the steady-state capital–output ratio. In the introduction to this answer, we showed that k/y = K/Y, and in part (d) we found that the Golden Rule K/Y = 4.29. Plugging in this value and those established above:s = (0.04 + 0.03)(4.29) = 0.30.To reach the Golden Rule steady state, the saving rate must rise from 17.5 to 30 percent. Thisresult implies that if we set the saving rate equal to the share going to capital (30 percent), we will achieve the Golden Rule steady state.4. a. In the steady state, we know that sy = (δ + n + g)k. This implies thatk/y = s/(δ + n + g).Since s, δ, n, and g are constant, this means that the ratio k/y is also constant. Since k/y =[K/(LE)]/[Y/(LE)] = K/Y, we can conclude that in the steady state, the capital–output ratio isconstant.b. We know that capital’s share of income = MPK ⨯ (K/Y). In the steady state, we know from part (a)that the capital–output ratio K/Y is constant. We also know from the hint that the MPK is afunction of k, which is constant in the steady state; therefore the MPK itself must be constant.Thus, capital’s share of income is constant. Labor’s share of income is 1 – [C apital’s Share].Hence, if capital’s share is constant, we see that labor’s share of income is also constant.c. We know that in the steady state, total income grows at n + g, defined as the rate of populationgrowth plus the rate of technological change. In part (b) we showed that labor’s and capital’s share of income is constant. If the shares are constant, and total income grows at the rate n + g, thenlabor income and capital income must also grow at the rate n + g.d. Define the real rental price of capital R asR = Total Capital Income/Capital Stock= (MPK ⨯K)/K= MPK.We know that in the steady state, the MPK is constant because capital per effective worker k isconstant. Therefore, we can conclude that the real rental price of capital is constant in the steadystate.To show that the real wage w grows at the rate of technological progress g, defineTLI = Total Labor IncomeL = Labor ForceUsing the hint that the real wage equals total labor income divided by the labor force:w = TLI/L.Equivalently,wL = TLI.In terms of percentage changes, we can write this asΔw/w + ΔL/L = ΔTLI/TLI.This equation says that the growth rate of the real wage plus the growth rate of the labor forceequals the growth rate of total labor income. We know that the labor force grows at rate n, and,from part (c), we know that total labor income grows at rate n + g. We, therefore, conclude that the real wage grows at rate g.5. a. The per worker production function is F (K, L )/L = AK α L 1–α/L = A (K/L )α = Ak α b. In the steady state, Δk = sf (k ) – (δ + n + g )k = 0. Hence, sAk α = (δ + n + g )k , or, after rearranging:k *=sA d +n +g éëêêùûúúa 1-a æèççöø÷÷.Plugging into the per-worker production function from part (a) givesy *=A a 1-a æèççöø÷÷s d +n +g éëêêùûúúa 1-a æèççöø÷÷.Thus, the ratio of steady-state income per worker in Richland to Poorland isy *Richland/y *Poorland ()=s Richland d +n Richland +g /s Poorlandd +n Poorland +g éëêêùûúúa1-a =0.320.05+0.01+0.02/0.100.05+0.03+0.02éëêêùûúúa1-c. If α equals 1/3, then Richland should be 41/2, or two times, richer than Poorland.d. If 4a 1-a æèççöø÷÷= 16, then it must be the case that a 1-a æèççöø÷÷, which in turn requires that α equals 2/3.Hence, if the Cobb –Douglas production function puts 2/3 of the weight on capital and only 1/3 on labor, then we can explain a 16-fold difference in levels of income per worker. One way to justify this might be to think about capital more broadly to include human capital —which must also be accumulated through investment, much in the way one accumulates physical capital.6. How do differences in education across countries affect the Solow model? Education is one factoraffecting the efficiency of labor , which we denoted by E . (Other factors affecting the efficiency of labor include levels of health, skill, and knowledge.) Since country 1 has a more highly educated labor force than country 2, each worker in country 1 is more efficient. That is, E 1 > E 2. We will assume that both countries are in steady state. a. In the Solow growth model, the rate of growth of total income is equal to n + g , which isindependent of the work force’s level of education. The two countries will, thus, have the same rate of growth of total income because they have the same rate of population growth and the same rate of technological progress.b. Because both countries have the same saving rate, the same population growth rate, and the samerate of technological progress, we know that the two countries will converge to the same steady-state level of capital per effective worker k *. This is shown in Figure 9-1.Hence, output per effective worker in the steady state, which is y* = f(k*), is the same in bothcountries. But y* = Y/(L E) or Y/L = y*E. We know that y* will be the same in both countries, but that E1 > E2. Therefore, y*E1 > y*E2. This implies that (Y/L)1 > (Y/L)2. Thus, the level of incomeper worker will be higher in the country with the more educated labor force.c. We know that the real rental price of capital R equals the marginal product of capital (MPK). Butthe MPK depends on the capital stock per efficiency unit of labor. In the steady state, bothcountries have k*1= k*2= k* because both countries have the same saving rate, the same population growth rate, and the same rate of technological progress. Therefore, it must be true that R1 = R2 = MPK. Thus, the real rental price of capital is identical in both countries.d. Output is divided between capital income and labor income. Therefore, the wage per effectiveworker can be expressed asw = f(k) –MPK • k.As discussed in parts (b) and (c), both countries have the same steady-state capital stock k and the same MPK. Therefore, the wage per effective worker in the two countries is equal.Workers, however, care about the wage per unit of labor, not the wage per effective worker.Also, we can observe the wage per unit of labor but not the wage per effective worker. The wageper unit of labor is related to the wage per effective worker by the equationWage per Unit of L = wE.Thus, the wage per unit of labor is higher in the country with the more educated labor force.7. a. In the two-sector endogenous growth model in the text, the production function for manufacturedgoods isY = F [K,(1 –u) EL].We assumed in this model that this function has constant returns to scale. As in Section 3-1,constant returns means that for any positive number z, zY = F(zK, z(1 –u) EL). Setting z = 1/EL,we obtainY EL =FKEL,(1-u)æèççöø÷÷.Using our standard definitions of y as output per effective worker and k as capital per effective worker, we can write this asy = F[k,(1 –u)]b. To begin, note that from the production function in research universities, the growth rate of laborefficiency, ΔE/E, equals g(u). We can now follow the logic of Section 9-1, substituting thefunction g(u) for the constant growth rate g. In order to keep capital per effective worker (K/EL) constant, break-even investment includes three terms: δk is needed to replace depreciating capital, nk is needed to provide capital for new workers, and g(u) is needed to provide capital for thegreater stock of knowledge E created by research universities. That is, break-even investment is [δ + n + g(u)]k.c. Again following the logic of Section 9-1, the growth of capital per effective worker is thedifference between saving per effective worker and break-even investment per effective worker.We now substitute the per-effective-worker production function from part (a) and the function g(u) for the constant growth rate g, to obtainΔk = sF [k,(1 –u)] – [δ + n + g(u)]kIn the steady state, Δk = 0, so we can rewrite the equation above assF [k,(1 –u)] = [δ + n + g(u)]k.As in our analysis of the Solow model, for a given value of u, we can plot the left and right sides of this equationThe steady state is given by the intersection of the two curves.d. The steady state has constant capital per effective worker k as given by Figure 9-2 above. We alsoassume that in the steady state, there is a constant share of time spent in research universities, so u is constant. (After all, if u were not constant, it wouldn’t be a ―steady‖ state!). Hence, output per effective worker y is also constant. Output per worker equals yE, and E grows at rate g(u).Therefore, output per worker grows at rate g(u). The saving rate does not affect this growth rate.However, the amount of time spent in research universities does affect this rate: as more time is spent in research universities, the steady-state growth rate rises.e. An increase in u shifts both lines in our figure. Output per effective worker falls for any givenlevel of capital per effective worker, since less of each worker’s time is spent producingmanufactured goods. This is the immediate effect of the change, since at the time u rises, thecapital stock K and the efficiency of each worker E are constant. Since output per effective worker falls, the curve showing saving per effective worker shifts down.At the same time, the increase in time spent in research universities increases the growth rate of labor efficiency g(u). Hence, break-even investment [which we found above in part (b)] rises at any given level of k, so the line showing breakeven investment also shifts up.Figure 9-3 shows these shifts.In the new steady state, capital per effective worker falls from k1 to k2. Output per effective worker also falls.f. In the short run, the increase in u unambiguously decreases consumption. After all, we argued inpart (e) that the immediate effect is to decrease output, since workers spend less time producingmanufacturing goods and more time in research universities expanding the stock of knowledge.For a given saving rate, the decrease in output implies a decrease in consumption.The long-run steady-state effect is more subtle. We found in part (e) that output per effective worker falls in the steady state. But welfare depends on output (and consumption) per worker, not per effective worker. The increase in time spent in research universities implies that E grows faster.That is, output per worker equals yE. Although steady-state y falls, in the long run the fastergrowth rate of E necessarily dominates. That is, in the long run, consumption unambiguously rises.Nevertheless, because of the initial decline in consumption, the increase in u is not unambiguously a good thing. That is, a policymaker who cares more about current generationsthan about future generations may decide not to pursue a policy of increasing u. (This is analogous to the question considered in Chapter 8 of whether a policymaker should try to reach the GoldenRule level of capital per effective worker if k is currently below the Golden Rule level.)8. On the World Bank Web site (), click on the data tab and then the indicators tab.This brings up a large list of data indicators that allows you to compare the level of growth anddevelopment across countries. To explain differences in income per person across countries, you might look at gross saving as a percentage of GDP, gross capital formation as a percentage of GDP, literacy rate, life expectancy, and population growth rate. From the Solow model, we learned that (all else the same) a higher rate of saving will lead to higher income per person, a lower population growth rate will lead to higher income per person, a higher level of capital per worker will lead to a higher level of income per person, and more efficient or productive labor will lead to higher income per person. The selected data indicators offer explanations as to why one country might have a higher level of income per person. However, although we might speculate about which factor is most responsible for thedifference in income per person across countries, it is not possible to say for certain given the largenumber of other variables that also affect income per person. For example, some countries may have more developed capital markets, less government corruption, and better access to foreign directinvestment. The Solow model allows us to understand some of the reasons why income per person differs across countries, but given it is a simplified model, it cannot explain all of the reasons why income per person may differ.More Problems and Applications to Chapter 91. a. The growth in total output (Y) depends on the growth rates of labor (L), capital (K), and totalfactor productivity (A), as summarized by the equationΔY/Y = αΔK/K + (1 –α)ΔL/L + ΔA/A,where α is capital’s share of output. We can look at the effect on output of a 5-percent increase in labor by setting ΔK/K = ΔA/A = 0. Since α = 2/3, this gives usΔY/Y = (1/3)(5%)= 1.67%.A 5-percent increase in labor input increases output by 1.67 percent.Labor productivity is Y/L. We can write the growth rate in labor productivity asD Y Y =D(Y/L)Y/L-D LL.Substituting for the growth in output and the growth in labor, we findΔ(Y/L)/(Y/L) = 1.67% – 5.0%= –3.34%.Labor productivity falls by 3.34 percent.To find the change in total factor productivity, we use the equationΔA/A = ΔY/Y –αΔK/K – (1 –α)ΔL/L.For this problem, we findΔA/A = 1.67% – 0 – (1/3)(5%)= 0.Total factor productivity is the amount of output growth that remains after we have accounted for the determinants of growth that we can measure. In this case, there is no change in technology, so all of the output growth is attributable to measured input growth. That is, total factorproductivity growth is zero, as expected.b. Between years 1 and 2, the capital stock grows by 1/6, labor input grows by 1/3, and output growsby 1/6. We know that the growth in total factor productivity is given byΔA/A = ΔY/Y –αΔK/K – (1 –α)ΔL/L.Substituting the numbers above, and setting α = 2/3, we findΔA/A = (1/6) – (2/3)(1/6) – (1/3)(1/3)= 3/18 – 2/18 – 2/18= – 1/18= –0.056.Total factor productivity falls by 1/18, or approximately 5.6 percent.2. By definition, output Y equals labor productivity Y/L multiplied by the labor force L:Y = (Y/L)L.Using the mathematical trick in the hint, we can rewrite this asD Y Y =D(Y/L)Y/L+D LL.We can rearrange this asD Y Y =D YY-D LL.Substituting for ΔY/Y from the text, we findD(Y/L) Y/L =D AA+aD KK+(1-a)D LL-D LL =D AA+aD KK-aD LL=D AA+aD KK-D LLéëêêùûúúUsing the same trick we used above, we can express the term in brackets asΔK/K –ΔL/L = Δ(K/L)/(K/L)Making this substitution in the equation for labor productivity growth, we conclude thatD(Y/L) Y/L =D AA+aD(K/L)K/L.3. We know the following:ΔY/Y = n + g = 3.6%ΔK/K = n + g = 3.6%ΔL/L = n = 1.8%Capital’s Share = α = 1/3Labor’s Share = 1 –α = 2/3Using these facts, we can easily find the contributions of each of the factors, and then find the contribution of total factor productivity growth, using the following equations:Output = Capital’s+ Labor’s+ Total FactorGrowth Contribution Contribution ProductivityD Y Y =aD KK+(1-a)D LL+D AA3.6% = (1/3)(3.6%) + (2/3)(1.8%) + ΔA/A.We can easily solve this for ΔA/A, to find that3.6% = 1.2% + 1.2% + 1.2%Chapter 9—Economic Growth II: Technology, Empirics, and Policy 81We conclude that the contribution of capital is 1.2 percent per year, the contribution of labor is 1.2 percent per year, and the contribution of total factor productivity growth is 1.2 percent per year. These numbers match the ones in Table 9-3 in the text for the United States from 1948–2002.Chapter 9—Economic Growth II: Technology, Empirics, and Policy 82。
曼昆《宏观经济学》第9版章节习题精编详解(政府债务和预算⾚字)【圣才出品】曼昆《宏观经济学》(第9版)章节习题精编详解第6篇宏观经济政策专题第19章政府债务和预算⾚字⼀、概念题1.资本预算(capital budgeting)答:资本预算是⼀种既衡量负债⼜衡量资产的预算程序,它考虑到了资本的变动。
采⽤资本预算,净国债等于政府资产减去政府负债。
按现⾏的预算程序,当政府出售其资产时,预算⾚字会减少。
但在资本预算中,从出售中得到的收⼊并没有减少⾚字,因为债务的减少被资产的减少所抵消了。
同样,在资本预算中,政府借贷为购买资本品筹资并不会增加⾚字。
经济学家对资本预算的看法不⼀。
资本预算的反对者认为,虽然这个体系在原则上优于现⾏体系,但它在实践中难以实施。
资本预算的⽀持者认为,即使对资本资产的不完善处理也⽐完全忽略资本资产好。
2.周期调整性预算⾚字(cyclically adjusted budget deficit)答:周期调整性预算⾚字有时称为充分就业预算⾚字,它的计算是根据对经济在其产出和就业⾃然率运⾏时政府⽀出与税收收⼊的估算⽽作出的。
周期调整性预算⾚字是⼀个有⽤的衡量指标,因为它反映了政策的变动⽽不是经济周期的当前阶段。
3.李嘉图等价(Ricardian equivalence)答:李嘉图等价定理是英国经济学家李嘉图提出,并由新古典主义学者巴罗根据理性预期重新进⾏论述的⼀种理论。
该理论认为,在政府⽀出⼀定的情况下,政府采取征税或发⾏公债来为政府筹措资⾦,其效应是相同的。
李嘉图等价理论的思路是:假设政府预算在初始时是平衡的。
政府实⾏减税以图增加私⼈部门和公众的⽀出,扩⼤总需求,但减税导致财政⾚字。
如果政府发⾏债券来弥补财政⾚字,由于在未来某个时点,政府将不得不增加税收,以便⽀付债务和积累的利息。
具有前瞻性的消费者知道,政府今天借债意味着未来更⾼的税收。
⽤政府债务融资的减税并没有减少税收负担,它仅仅是重新安排税收的时间。
【最新整理,下载后即可编辑】Answers to Textbook Questions and ProblemsCHAPTER 9 Economic Growth II: Technology, Empirics, and Policy Questions for Review1. In the Solow model, we find that only technological progress canaffect the steady-state rate of growth in income per worker. Growth in the capital stock (through high saving) has no effect on the steady-state growth rate of income per worker; neither does population growth.But technological progress can lead to sustained growth.2. In the steady state, output per person in the Solow model grows at the rate of technological progress g. Capital per person also grows at rate g. Note that this implies that output and capital per effective worker are constant in steady state. In the U.S. data, output and capital per worker have both grown at about 2 percent per year for the past half-century.3. To decide whether an economy has more or less capital than theGolden Rule, we need to compare the marginal product of capital net of depreciation (MPK –δ) with the growt h rate of total output (n + g). The growth rate of GDP is readily available. Estimating the netmarginal product of capital requires a little more work but, as shown in the text, can be backed out of available data on the capital stockrelative to GDP, the total amount of depreciation relative to GDP, and capital’s share in GDP.4. Economic policy can influence the saving rate by either increasingpublic saving or providing incentives to stimulate private saving. Public saving is the difference between government revenue and government spending. If spending exceeds revenue, the government runs a budget deficit, which is negative saving. Policies that decrease the deficit (such as reductions in government purchases or increases in taxes) increase public saving, whereas policies that increase the deficit decrease saving.A variety of government policies affect private saving. The decision bya household to save may depend on the rate of return; the greater thereturn to saving, the more attractive saving becomes. Tax incentives such as tax-exempt retirement accounts for individuals and investment tax credits for corporations increase the rate of return and encourage private saving.5. The legal system is an example of an institutional difference betweencountries that might explain differences in income per person.Countries that have adopted the English style common law systemtend to have better developed capital markets, and this leads to more rapid growth because it is easier for businesses to obtain financing. The quality of government is also important. Countries with moregovernment corruption tend to have lower levels of income per person.6. Endogenous growth theories attempt to explain the rate oftechnological progress by explaining the decisions that determine the creation of knowledge through research and development. By contrast, the Solow model simply took this rate as exogenous. In the Solowmodel, the saving rate affects growth temporarily, but diminishingreturns to capital eventually force the economy to approach a steady state in which growth depends only on exogenous technologicalprogress. By contrast, many endogenous growth models in essenceassume that there are constant (rather than diminishing) returns tocapital, interpreted to include knowledge. Hence, changes in the saving rate can lead to persistent growth.Problems and Applications1. a. In the Solow model with technological progress, y is defined asoutput per effective worker, and k is defined as capital per effective worker. The number of effective workers is defined as L E (orLE), where L is the number of workers, and E measures theefficiency of each worker. To find output per effective worker y,divide total output by the number of effective workers:Y LE =K12(LE)12LEY LE =K12L12E12LEY LE =K12 L12E12Y LE =KLE æèççöø÷÷12y=k1b. To solve for the steady-state value of y as a function of s, n, g, andδ, we begin with the equation for the change in the capital stock in the steady state:Δk = sf(k) –(δ + n + g)k = 0.The production function ycan also be rewritten as y2 = k.Plugging this production function into the equation for the changein the capital stock, we find that in the steady state:sy –(δ + n + g)y2 = 0.Solving this, we find the steady-state value of y:y* = s/(δ + n + g).c. The question provides us with the following information about each country:Atlantis: s = 0.28 Xanadu: s = 0.10n = 0.01 n = 0.04g = 0.02 g = 0.02δ = 0.04δ = 0.04Using the equation for y* that we derived in part (a), we cancalculate the steady-state values of y for each country.Developed country: y* = 0.28/(0.04 + 0.01 + 0.02) = 4Less-developed country: y* = 0.10/(0.04 + 0.04 + 0.02) = 1 2. a. In the steady state, capital per effective worker is constant, and thisleads to a constant level of output per effective worker. Given that the growth rate of output per effective worker is zero, this means the growth rate of output is equal to the growth rate of effective workers (LE). We know labor grows at the rate of population growth n and the efficiency of labor (E) grows at rate g. Therefore, output grows at rate n+g. Given output grows at rate n+g and labor grows at rate n,output per worker must grow at rate g. This follows from the rule that the growth rate of Y/L is equal to the growth rate of Y minus the growth rate of L.b. First find the output per effective worker production function by dividing both sides of the production function by the number of effective workers LE:Y LE =K13(LE)23LEYLE=K13L23E23LEYLE=K13L13E13YLE=KLEæèçöø÷13y=k13To solve for capital per effective worker, we start with the steady state condition:Δk = sf(k) –(δ + n + g)k = 0.Now substitute in the given parameter values and solve for capital per effective worker (k):Substitute the value for k back into the per effective workerproduction function to find output per effective worker is equal to2. The marginal product of capital is given bySubstitute the value for capital per effective worker to find themarginal product of capital is equal to 1/12.c. According to the Golden Rule, the marginal product of capital isequal to (δ + n + g) or 0.06. In the current steady state, the marginal product of capital is equal to 1/12 or 0.083. Therefore, we have less capital per effective worker in comparison to the Golden Rule. Asthe level of capital per effective worker rises, the marginal product of capital will fall until it is equal to 0.06. To increase capital pereffective worker, there must be an increase in the saving rate.d. During the transition to the Golden Rule steady state, the growth rateof output per worker will increase. In the steady state, output perworker grows at rate g. The increase in the saving rate will increaseoutput per effective worker, and this will increase output pereffective worker. In the new steady state, output per effective worker is constant at a new higher level, and output per worker is growing at rate g. During the transition, the growth rate of output per workerjumps up, and then transitions back down to rate g.3. To solve this problem, it is useful to establish what we know about the U.S. economy:• A Cobb–Douglas production function has the form y = kα, where α is capital’s share of income. The question tells us that α = 0.3,so we know that the production function is y = k0.3.•In the steady state, we know that the growth rate of output equals 3 percent, so we know that (n + g) = 0.03.•The deprec iation rate δ = 0.04.•The capital–output ratio K/Y = 2.5. Because k/y =[K/(LE)]/[Y/(LE)] = K/Y, we also know that k/y = 2.5. (That is, the capital–output ratio is the same in terms of effective workers as it is in levels.)a. Begin with the steady-state condition, sy = (δ + n + g)k. Rewritingthis equation leads to a formula for saving in the steady state:s = (δ + n + g)(k/y).Plugging in the values established above:s = (0.04 + 0.03)(2.5) = 0.175.The initial saving rate is 17.5 percent.b. We know from Chapter 3 that with a Cobb–Douglas production function, capital’s share of income α = MPK(K/Y). Rewriting, we haveMPK = α/(K/Y).Plugging in the values established above, we findMPK = 0.3/2.5 = 0.12.c. We know that at the Golden Rule steady state:MPK = (n + g + δ).Plugging in the values established above:MPK = (0.03 + 0.04) = 0.07.At the Golden Rule steady state, the marginal product of capital is 7 percent, whereas it is 12 percent in the initial steady state. Hence, from the initial steady state we need to increase k to achieve theGolden Rule steady state.d. We know from Chapter 3 that for a Cobb–Douglas production function, MPK = α (Y/K). Solving this for the capital–outputratio, we findK/Y = α/MPK.We can solve for the Golden Rule capital–output ratio using this equation. If we plug in the value 0.07 for the Golden Rule steady-state marginal product of capital, and the value 0.3 for α, we findK/Y = 0.3/0.07 = 4.29.In the Golden Rule steady state, the capital–output ratio equals4.29, compared to the current capital–output ratio of 2.5.e. We know from part (a) that in the steady states = (δ + n + g)(k/y),where k/y is the steady-state capital–output ratio. In theintroduction to this answer, we showed that k/y = K/Y, and in part(d) we found that the Golden Rule K/Y = 4.29. Plugging in thisvalue and those established above:s = (0.04 + 0.03)(4.29) = 0.30.To reach the Golden Rule steady state, the saving rate must risefrom 17.5 to 30 percent. This result implies that if we set the saving rate equal to the share going to capital (30 percent), we will achieve the Golden Rule steady state.4. a. In the steady state, we know that sy = (δ + n + g)k. This implies thatk/y = s/(δ + n + g).Since s, δ, n, and g are constant, this means that the ratio k/y is also constant. Since k/y = [K/(LE)]/[Y/(LE)] = K/Y, we can conclude that in the steady state, the capital–output ratio is constant.b. We know that capital’s share of income = MPK (K/Y). In thesteady state, we know from part (a) that the capital–output ratioK/Y is constant. We also know from the hint that the MPK is afunction of k, which is constant in the steady state; therefore theMPK itself must be constant. Thus, capital’s share of income isconstant. Labor’s share of income is 1 – [C apital’s Share].Hence, if capital’s share is constant, we see that labor’s share of income is also constant.c. We know that in the steady state, total income grows at n + g,defined as the rate of population growth plus the rate oftechnological change. In part (b) we showed that labor’s andcapital’s share of income is constant. If the shares are constant,and total income grows at the rate n + g, then labor income andcapital income must also grow at the rate n + g.d. Define the real rental price of capital R asR = Total Capital Income/Capital Stock= (MPK K)/K= MPK.We know that in the steady state, the MPK is constant becausecapital per effective worker k is constant. Therefore, we canconclude that the real rental price of capital is constant in the steady state.To show that the real wage w grows at the rate of technological progress g, defineTLI = Total Labor IncomeL = Labor ForceUsing the hint that the real wage equals total labor income divided by the labor force:w = TLI/L.Equivalently,wL = TLI.In terms of percentage changes, we can write this asΔw/w + ΔL/L = ΔTLI/TLI.This equation says that the growth rate of the real wage plus thegrowth rate of the labor force equals the growth rate of total labor income. We know that the labor force grows at rate n, and, frompart (c), we know that total labor income grows at rate n + g. We, therefore, conclude that the real wage grows at rate g.5. a. The per worker production function isF(K, L)/L = AKαL1–α/L = A(K/L)α = Akαb. In the steady state, Δk = sf(k) –(δ + n + g)k = 0. Hence, sAkα = (δ + n + g)k, or, after rearranging:k*=sAd+n+géëêêùûúúa1-aæèççöø÷÷.Plugging into the per-worker production function from part (a) givesy *=A a 1-a æèççöø÷÷s d +n +g éëêêùûúúa 1-a æèççöø÷÷.Thus, the ratio of steady-state income per worker in Richland to Poorland isy *Richland /y *Poorland ()=s Richland d +n Richland +g /s Poorland d +n Poorland +g éëêêùûúúa 1-a=0.320.05+0.01+0.02/0.100.05+0.03+0.02éëêêùûúúa 1-ac. If α equals 1/3, then Richland should be 41/2, or two times, richer than Poorland.d. If 4a 1-æèççöø÷÷= 16, then it must be the case that a 1-a æèççöø÷÷, which in turnrequires that α equals 2/3. Hence, if the Cobb –Douglasproduction function puts 2/3 of the weight on capital and only 1/3 on labor, then we can explain a 16-fold difference in levels ofincome per worker. One way to justify this might be to think about capital more broadly to include human capital —which must also be accumulated through investment, much in the way one accumulates physical capital.6. How do differences in education across countries affect the Solowmodel? Education is one factor affecting the efficiency of labor , which we denoted by E . (Other factors affecting the efficiency of laborinclude levels of health, skill, and knowledge.) Since country 1 has amore highly educated labor force than country 2, each worker in country 1 is more efficient. That is, E1 > E2. We will assume that both countries are in steady state.a. In the Solow growth model, the rate of growth of total income is equal to n + g, which is independent of the work force’s level of education. The two countries will, thus, have the same rate ofgrowth of total income because they have the same rate ofpopulation growth and the same rate of technological progress. b. Because both countries have the same saving rate, the samepopulation growth rate, and the same rate of technological progress, we know that the two countries will converge to the same steady-state level of capital per effective worker k*. This is shown in Figure 9-1.Hence, output per effective worker in the steady state, which is y* = f(k*), is the same in both countries. But y* = Y/(L E) or Y/L = y* E. We know that y* will be the same in both countries, but that E1> E2. Therefore, y*E1 > y*E2. This implies that (Y/L)1 > (Y/L)2.Thus, the level of income per worker will be higher in the countrywith the more educated labor force.c. We know that the real rental price of capital R equals the marginalproduct of capital (MPK). But the MPK depends on the capitalstock per efficiency unit of labor. In the steady state, both countries have k*1= k*2= k* because both countries have the same saving rate, the same population growth rate, and the same rate of technological progress. Therefore, it must be true that R1 = R2 = MPK. Thus, the real rental price of capital is identical in both countries.d. Output is divided between capital income and labor income.Therefore, the wage per effective worker can be expressed asw = f(k) –MPK • k.As discussed in parts (b) and (c), both countries have the samesteady-state capital stock k and the same MPK. Therefore, the wage per effective worker in the two countries is equal.Workers, however, care about the wage per unit of labor, not the wage per effective worker. Also, we can observe the wage per unitof labor but not the wage per effective worker. The wage per unitof labor is related to the wage per effective worker by the equationWage per Unit of L = wE.Thus, the wage per unit of labor is higher in the country with the more educated labor force.7. a. In the two-sector endogenous growth model in the text, theproduction function for manufactured goods isY = F [K,(1 –u) EL].We assumed in this model that this function has constant returns to scale. As in Section 3-1, constant returns means that for anypositive number z, zY = F(zK, z(1 –u) EL). Setting z = 1/EL, we obtainY EL =FKEL,(1-u)æèççöø÷÷.Using our standard definitions of y as output per effective worker and k as capital per effective worker, we can write this asy = F[k,(1 –u)]b. To begin, note that from the production function in research universities, the growth rate of labor efficiency, ΔE/E, equals g(u).We can now follow the logic of Section 9-1, substituting the function g(u) for the constant growth rate g. In order to keep capital per effective worker (K/EL) constant, break-even investment includes three terms: δk is needed to replace depreciating capital, nk is needed to provide capital for new workers, and g(u) is needed to provide capital for the greater stock of knowledge E created by research universities. That is, break-even investment is [δ +n + g(u)]k.c. Again following the logic of Section 9-1, the growth of capital pereffective worker is the difference between saving per effectiveworker and break-even investment per effective worker. We now substitute the per-effective-worker production function from part (a) and the function g(u) for the constant growth rate g, to obtainΔk = sF [k,(1 –u)] – [δ + n + g(u)]kIn the steady state, Δk = 0, so we can rewrite the equation above assF [k,(1 –u)] = [δ + n + g(u)]k.As in our analysis of the Solow model, for a given value of u, we can plot the left and right sides of this equationThe steady state is given by the intersection of the two curves. d. The steady state has constant capital per effective worker k as givenby Figure 9-2 above. We also assume that in the steady state, there is a constant share of time spent in research universities, so u is constant. (After all, if u were not constant, it wouldn’t be a“steady” state!). Hence, output per effective worker y is also constant. Output per worker equals yE, and E grows at rate g(u). Therefore, output per worker grows at rate g(u). The saving ratedoes not affect this growth rate. However, the amount of timespent in research universities does affect this rate: as more time is spent in research universities, the steady-state growth rate rises.e. An increase in u shifts both lines in our figure. Output per effectiveworker falls for any given level of capital per effective worker, since less of each worker’s time is spent producing manufactured goods. This is the immediate effect of the change, since at the time u rises, the capital stock K and the efficiency of each worker E are constant.Since output per effective worker falls, the curve showing savingper effective worker shifts down.At the same time, the increase in time spent in research universities increases the growth rate of labor efficiency g(u). Hence, break-even investment [which we found above in part (b)] rises at any given level of k, so the line showing breakeven investment also shifts up.Figure 9-3 shows these shifts.In the new steady state, capital per effective worker falls from k1 to k2. Output per effective worker also falls.f. In the short run, the increase in u unambiguously decreasesconsumption. After all, we argued in part (e) that the immediateeffect is to decrease output, since workers spend less timeproducing manufacturing goods and more time in researchuniversities expanding the stock of knowledge. For a given saving rate, the decrease in output implies a decrease in consumption.The long-run steady-state effect is more subtle. We found in part(e) that output per effective worker falls in the steady state. But welfare depends on output (and consumption) per worker, not per effective worker. The increase in time spent in research universities implies that E grows faster. That is, output per worker equals yE. Although steady-state y falls, in the long run the faster growth rate of E necessarily dominates. That is, in the long run, consumption unambiguously rises.Nevertheless, because of the initial decline in consumption, theincrease in u is not unambiguously a good thing. That is, apolicymaker who cares more about current generations than aboutfuture generations may decide not to pursue a policy of increasing u.(This is analogous to the question considered in Chapter 8 ofwhether a policymaker should try to reach the Golden Rule level ofcapital per effective worker if k is currently below the Golden Rulelevel.)8. On the World Bank Web site (), click on the datatab and then the indicators tab. This brings up a large list of dataindicators that allows you to compare the level of growth anddevelopment across countries. To explain differences in income per person across countries, you might look at gross saving as a percentage of GDP, gross capital formation as a percentage of GDP, literacy rate, life expectancy, and population growth rate. From the Solow model, we learned that (all else the same) a higher rate of saving will lead to higher income per person, a lower population growth rate will lead to higher income per person, a higher level of capital per worker will lead to a higher level of income per person, and more efficient orproductive labor will lead to higher income per person. The selected data indicators offer explanations as to why one country might have a higher level of income per person. However, although we mightspeculate about which factor is most responsible for the difference in income per person across countries, it is not possible to say for certain given the large number of other variables that also affect income per person. For example, some countries may have more developed capital markets, less government corruption, and better access to foreigndirect investment. The Solow model allows us to understand some of the reasons why income per person differs across countries, but givenit is a simplified model, it cannot explain all of the reasons why income per person may differ.More Problems and Applications to Chapter 91. a. The growth in total output (Y) depends on the growth rates oflabor (L), capital (K), and total factor productivity (A), assummarized by the equationΔY/Y = αΔK/K + (1 –α)ΔL/L + ΔA/A, where α is capital’s share of output. We can look at the effect onoutput of a 5-percent increase in labor by setting ΔK/K = ΔA/A =0. Since α = 2/3, this gives usΔY/Y = (1/3)(5%)= 1.67%.A 5-percent increase in labor input increases output by 1.67 percent.Labor productivity is Y/L. We can write the growth rate in labor productivity asD Y Y =D(Y/L)Y/L-D LL.Substituting for the growth in output and the growth in labor, we findΔ(Y/L)/(Y/L) = 1.67% – 5.0%= –3.34%.Labor productivity falls by 3.34 percent.To find the change in total factor productivity, we use the equationΔA/A = ΔY/Y –αΔK/K – (1 –α)ΔL/L.For this problem, we findΔA/A = 1.67% – 0 – (1/3)(5%)= 0.Total factor productivity is the amount of output growth that remains after we have accounted for the determinants of growththat we can measure. In this case, there is no change in technology, so all of the output growth is attributable to measured input growth.That is, total factor productivity growth is zero, as expected.b. Between years 1 and 2, the capital stock grows by 1/6, labor inputgrows by 1/3, and output grows by 1/6. We know that the growthin total factor productivity is given byΔA/A = ΔY/Y –αΔK/K – (1 –α)ΔL/L.Substituting the numbers above, and setting α = 2/3, we findΔA/A = (1/6) – (2/3)(1/6) – (1/3)(1/3)= 3/18 – 2/18 – 2/18= – 1/18= –0.056.Total factor productivity falls by 1/18, or approximately 5.6 percent.2. By definition, output Y equals labor productivity Y/L multiplied by the labor force L:Y = (Y/L)L.Using the mathematical trick in the hint, we can rewrite this asD Y Y =D(Y/L)Y/L+D LL.We can rearrange this asD Y Y =D YY-D LL.Substituting for ΔY/Y from the text, we findD(Y/L) Y/L =D AA+aD KK+(1-a)D LL-D LL =D AA+aD KK-aD LL=D AA+aD KK-D LLéëêêùûúúUsing the same trick we used above, we can express the term in brackets asΔK/K –ΔL/L = Δ(K/L)/(K/L) Making this substitution in the equation for labor productivity growth, we conclude thatD(Y/L) Y/L =D AA+aD(K/L)K/L.3. We know the following:ΔY/Y = n + g = 3.6%ΔK/K = n + g = 3.6%ΔL/L = n = 1.8%Capital’s Share = α = 1/3Labor’s Share = 1 –α = 2/3Using these facts, we can easily find the contributions of each of the factors, and then find the contribution of total factor productivitygrowth, using the following equations:Output = Capital’s+ Labor’s+ Total FactorGrowth Contribution ContributionProductivityD Y Y = aD KK+ (1-a)D LL+ D AA3.6% = (1/3)(3.6%) + (2/3)(1.8%) +ΔA/A.We can easily solve this for ΔA/A, to find that3.6% = 1.2% + 1.2% + 1.2%We conclude that the contribution of capital is 1.2 percent per year, the contribution of labor is 1.2 percent per year, and the contribution of total factor productivity growth is 1.2 percent per year. These numbers match the ones in Table 9-3 in the text for the United States from 1948–2002.。
第4篇经济周期理论:短期中的经济第9章经济波动导论跨考网独家整理最全经济学考研真题,经济学考研课后习题解析资料库,您可以在这里查阅历年经济学考研真题,经济学考研课后习题,经济学考研参考书等内容,更有跨考考研历年辅导的经济学学哥学姐的经济学考研经验,从前辈中获得的经验对初学者来说是宝贵的财富,这或许能帮你少走弯路,躲开一些陷阱。
以下内容为跨考网独家整理,如您还需更多考研资料,可选择经济学一对一在线咨询进行咨询。
一、判断题1.由于股票市场价格上升而导致财富的增加会引起经济沿着现存的总需求曲线移动。
()【答案】F【解析】物价水平的变动才能使得经济沿着总需求曲线移动。
股票市场价格,并不等同于实体经济中的价格,股票价格上升导致的财富的增加可能会增加消费和投资,从而使得总需求曲线向外移动。
2.实际GDP的波动只由总需求变动引起,不为总供给变动所影响。
()【答案】F【解析】长期而言,实际GDP是由总供给决定的,随着影响总供给曲线的劳动、资本以及技术的变动而变动。
3.如果作为总供给减少的反应,政府增加货币供应,失业率将回到自然失业率水平,但是价格甚至还要上涨。
()【答案】T【解析】当经济面临不利的总供给冲击时,总供给曲线向左上方移动,而中央银行可以通过增加货币供应以增加总需求,阻止产出的下降,但这种政策的代价是更高的价格水平。
4.无论产量减少是由总需求减少还是总供给减少引起,作为产出减少的反应,经济都会回到其初始价格水平和初始产量水平。
()【答案】F【解析】当经济面临不利的总供给冲击时,中央银行可以增加总需求来防止产出的下降,使产出回到初始产量水平,但中央银行这种反应的代价是更高的价格水平。
5.如果在总供给曲线的水平阶段上总需求增加,一部分扩张性财政政策的效果将转化为通货膨胀。
()【答案】F【解析】在总供给曲线水平的阶段上,总需求增加,使得扩张性财政政策的效果全部转化为产出。
6.单位生产成本下降会使总供给曲线向左移动。
77
If the Fed cares about keeping output and employment at their natural-rate levels, then it should increase aggregate demand by increasing the money supply. This policy response shifts the aggregate demand curve upwards, as shown in the
shift from AD
1to AD
2
in Figure 9–12. I n this case, the economy immediately
reaches a new equilibrium at point C. The price level at point C is permanently
higher, but there is no loss in output associated with the adverse supply shock.
If the Fed cares about keeping prices stable, then there is no policy response it can implement. In the short run, the price level stays at the higher level P
2
. If the Fed increases aggregate demand, then the economy ends up with a permanently higher price level. Hence, the Fed must simply wait, holding aggregate demand constant. Eventually, prices fall to restore full employment at the old price level
P
1
. But the cost of this process is a prolonged recession.
Thus, the two Feds make a different policy choice in response to a supply shock.
4.From the main NBER web page (), I followed the link to Business
Cycle Dates (downloaded February 19, 2009). As of this writing, the latest turning point was in December 2007, when the economy switched from expansion to con-traction. As of this writing, the recession is still ongoing.
Previous recessions (contractions) over the past three decades were March 2001 to November 2001; July 1990 to March 1991; July 1981 to November 1982;
January 1980 to July 1980; and November 1973 to March 1975.。