英语语法基础知识——动名词
- 格式:doc
- 大小:71.00 KB
- 文档页数:10
英语语法知识——动名词动名词动名词是非限定动词的一种形式,由动词原形+ing 构成。
它既有动词的特征,又有名词的特征,故称。
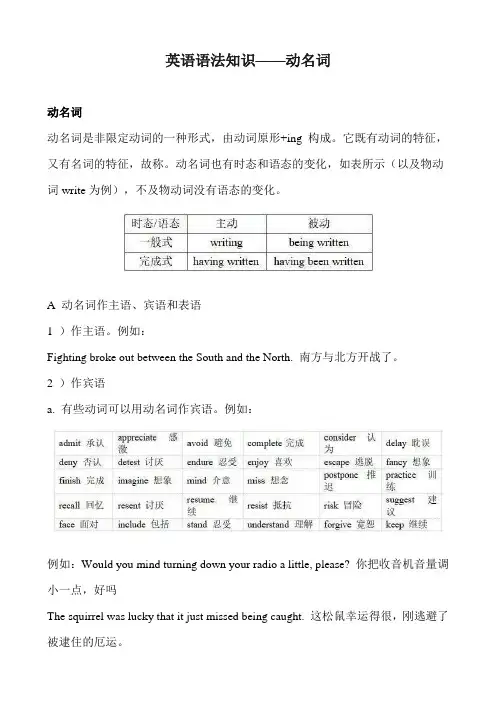
动名词也有时态和语态的变化,如表所示(以及物动词write为例),不及物动词没有语态的变化。
A 动名词作主语、宾语和表语1 )作主语。
例如:Fighting broke out between the South and the North. 南方与北方开战了。
2 )作宾语a. 有些动词可以用动名词作宾语。
例如:例如:Would you mind turning down your radio a little, please? 你把收音机音量调小一点,好吗The squirrel was lucky that it just missed being caught. 这松鼠幸运得很,刚逃避了被逮住的厄运。
b. 有些结构后面可以用动名词作宾语或其他成分。
例如:3 )作表语,对主语说明、解释。
例如:Her job is washing, cleaning and taking care of the children. 她的工作是洗刷、清扫和照顾孩子。
比较:She is washing, cleaning and taking care of the children.4 )作定语,一般表示所修饰名词事物的用途。
例如:a writing desk=a desk for writing 写字台a swimming pool=a pool swimming 游泳池有些动名词作定语,与所修饰的名词关系比较复杂。
例如:boiling point=a temperature point at which something begins to boil 沸点a walking tractor=a tractor which a driver can operate while he or she is walking behind it手扶拖拉机B worth 的用法worth, worthy, worthwhile 都是形容词,意为"值得"。

初中核心语法---动名词用法汇总动名词属于非谓语动词的一种,它的基本结构和用法在初中阶段也是必考点。
1. 动名词概说动名词既具有动词的性质,又具有名词的性质,因此叫动名词。
(归根结底动名词的词性是名词。
)①动名词的动词性质表现在,它可以组成动名词短语,如:My job is arranging the agenda for my boss.我的工作是为老板安排日程。
I finished the project in a month by working overtime.我靠加班在一个月内做完了这个项目。
②动名词的名词性质表现在,它可以在句中用作主语、宾语等,如:Studying abroad can be a good experience.留学是一种很好的经历。
(作主语)I regret telling her the truth.我后悔告诉她事实真相了。
(作宾语)2. 动名词的形式和特征①动名词的主动形式:doing②动名词的被动形式:being done③动名词的复合结构:形容词性物主代词/名词所有格/名词/宾格人称代词+动名词在动名词复合结构中,物主代词或名词所有格是动名词的逻辑主语,这种复合结构多用作主语或宾语,也可用作表语或介词宾语。
当动名词短语作宾语,放在动词或介词后时,名词所有格或物主代词分别可用名词普通格或人称代词宾格代替,如:She suggested us forgiving him.她建议我们原谅他。
(作宾语)His not knowing English brought him a lot of inconvenience.他不懂英语,这给他带来许多麻烦。
(作主语)Our only worry is George’s overestimating himself.我们唯一担心的就是乔治高估了他自己。
(作表语)I strongly object to your delivering the speech.我强烈反对你发表讲话。

初中英语知识点归纳动名词的用法动名词是英语中的一个重要语法形式,它在句子中可以充当名词的作用。
动名词的构成方式是在动词的原形基础上加上-ing。
本文将就初中英语中动名词的用法进行归纳,帮助同学们更好地理解和运用。
一、作主语1. 表示一种普遍的、持久的或重复性的行为或状态。
例句:Swimming is good for health.(游泳对健康有益。
)2. 表示一种爱好、兴趣或需要。
例句:Reading books is my favorite hobby.(读书是我最喜欢的爱好。
)3. 表示一种抽象的行为或观念。
例句:Lying is not acceptable in any situation.(撒谎在任何情况下都是不可接受的。
)二、作宾语1. 某些动词后接动名词作宾语,表示持续的或习惯性的行为。
例句:I enjoy dancing.(我喜欢跳舞。
)2. 某些动词后接动名词作宾语,表示停止或开始行为。
例句:I stopped smoking last year.(我去年戒烟了。
)3. 某些动词后接动名词作宾语,表示喜欢或讨厌的行为。
例句:She hates cooking.(她讨厌做饭。
)三、作表语动名词作表语通常用来表示现在或过去某种特定的行为、活动或状态。
例句:Her favorite activity is swimming.(她最喜欢的活动是游泳。
)四、作宾补某些动词后接动名词作宾补,表示完成或实现动作。
例句:I saw him running in the park.(我看到他在公园里跑步。
)五、作介词宾语动名词可以作为介词的宾语,用来表示目的、原因、方法等。
例句:She always studies English by listening and speaking.(她总是通过听和说来学习英语。
)六、作定语动名词可以作为名词的定语,用来修饰名词。
例句:I bought a running shoes.(我买了一双跑步鞋。

【英语学习方法】高中英语语法――动名词1.动名词的句法功能:动名词由动词加ing构成,与现在分词的形式相同。
动名词主要起名词作用,在句中担任主语、表语、宾语和定语。
①作主语,可以直接放在句首,也可以用先行代词it作为形式主语,而把动名词后置。
eg.seeingisbelieving.(眼见为实)sayingiseasierthandoing.collectingstampsisagoodhobby.(单个动名词短语并作主语时,动词用单数)动名词作主语还有以下两个习惯表答法:itisnouse(good)动名词:搞某事没用eg.it'snousecryingoverspiltmilk.(覆水难收)thereisno动名词(=itisimpossibletodosth.)eg.thereisnoknowingwhatmayhappen.(未来的事无法知道)②并作未来式:通常就是表明主语的内容,特别注意它与谓语动词展开时的区别eg.hishobbyiscollectingstamps.(此句为svc结构)可改为:collectingstampsishishobby.cf.heiscollectingstamps.(iscollecting就是谓语动词展开时,此句为svo结构)不能改为:collectingstampsishe.③并作宾语a.作及物动词的宾语(enjoy,mind,finish,appreciate,avoid,consider,delay,escape,pratise,suggest,keep (on),miss)eg.2021年上海卷no.32hegotwell-preparedforthejobinterview,forhecouldn'trisk_____thegoodopportunity.a.toloseb.losingc.tobelostd.beinglost答案为b有些动词(attempt,begin,continue,hate,like,love)后面既可以直奔不定式并作宾语,也可以直奔动名词并作宾语,意义差别并不大。

初三英语语法基础知识大全【导语】练习是巩固知识的有效途径,可以采取练习的方式,培养紧急感、提高效率。
练习应当放在复习之落后行,做题顺序是先易后难。
每次练习后都要养成仔细检查的习惯,不要一做完就立刻对答案。
下面是作者为您整理的《初三英语语法基础知识大全》,仅供大家参考。
1.初三英语语法基础知识大全篇一动名词(doing)动名词相当于名词,在句子中可以做主语、宾语、表语、定语等。
1. 作主语Fighting broke out between the South and the North.南方与北方开战了。
2. 作宾语Would you mind turning down your radio a little, please?请问你介意调小一点收音机的音量吗?3. 作表语Babysister’s job is washing,cooking and taking care ofthe children.保姆的工作是洗衣服,作饭和照看孩子。
neither与nor的用法1.如前句是否定式从句,则主句用neither,而不用nor.If you don't do it,neither should I.如果你不干,我也不干.2.如后连续有几个否定句式,则用nor,不用neither.He can't sing,nor dance,nor skate.2.初三英语语法基础知识大全篇二连词及其用法1.连词是一种虚词,它不能独立担负句子成分而只起连接词与词,短语与短语以及句与句的作用。
2.常见的连词and(和,与;而且;于是,然后;因此)but(但是;通常用not...but...不是...而是...;可是,然而;表示惊奇,不同意等--喔,哇;用来加强语句重复部分的语气--一定;用来引入新话题--那就;常用于否定句--而不,若不;用于含doubt,question等字的否定句中相当于that--对于)or(或者,还是;用于否定句或问句--也不;否则,要不然;也就是说,换言之)nor(用在neither之后--也不;用在no,not,never之后--也不;用在句首,句子需倒装--也不)so(因此,所以;因此,从而)yet(可是,却,然而)for(由于,由于)both…and(既...又...;不但...而且)not only…but also(不但,而且)either…or(不是...就是;要么...要么)neither…nor(既不...也不...)3.并列连词:①and 与or;②both …and两者都;③not only…but ...as well as=not only...but also不但…而且;④neither…nor意思为"既不……也不……"谓语动词采取就近原则,与nor后的词保持一致。

英语语法,动名词用法图表详解,一目了然,备考收藏
今天全面详细解读动名词的用法,相信对大家的英语语法学习会有所启发。
动名词的用法是中考高考重要考点之一,它是英语语法中很重要的一部分,动名词既具有动词的性质,又具有名词的性质,因此叫动名词。
接下来将从动名词的功能、动名词的复合结构等方面进行详细解读。
相信大家看完后会对动名词的用法掌握的更加透彻。
动名词的句法功能
口诀巧记
动名词的复合结构
动名词复合结构由“物主代词或名词所有格+动名同”构成。
在动名词复合结构中,物主代词或名词所有格是动名词的逻辑主语。
这种复合结构多用作主语或宾语,也可用作表语或介词宾语。
当动名词短语作宾语,放在动词或介词后时,名词所有格或物主代词分别可用名词普通格或人称代词宾格代替。
以上总结详细全面,可以收藏以备用。

专题10 重点语法复习(动名词作主语和宾语)养成良好的答题习惯,是决定高考英语成败的决定性因素之一。
做题前,要认真阅读题目要求、题干和选项,并对答案内容作出合理预测;答题时,切忌跟着感觉走,最好按照题目序号来做,不会的或存在疑问的,要做好标记,要善于发现,找到题目的题眼所在,规范答题,书写工整;答题完毕时,要认真检查,查漏补缺,纠正错误。
总之,在最后的复习阶段,学生们不要加大练习量。
在这个时候,学生要尽快找到适合自己的答题方式,最重要的是以平常心去面对考试。
英语最后的复习要树立信心,考试的时候遇到难题要想“别人也难”,遇到容易的则要想“细心审题”。
越到最后,考生越要回归基础,单词最好再梳理一遍,这样有利于提高阅读理解的效率。
另附高考复习方法和考前30天冲刺复习方法。
动名词1. 基础知识动名词是非谓语动词的一种形式。
它既有动词的特征,又有名词的特征,故称动名词。
动名词也有时态和语态的变化,如表所示(以及物动词write为例),不及物动词没有语态的变化。
动词ing形式作主语通常表示抽象的或习惯性的动作。
也可用t作形式主语,动词-ing形式作真正的主语放在句末。
下列句型中常用动词-ing形式作主语:1. It is/was a waste (of...)/no use/no good doing sth.2. There is/was no sense/no point...(in) doing sth.It is no good coming before that.在那之前来没有用。
There is no sense(in)worrying about it now.现在大可不必为那件事忧虑。
特别注意:名师点津区分动词不定式及动词-ing形式作主语(1)动词-ing形式多表示一般的、抽象的、泛指的概念或一个已经完成了的动作,而不定式则表示具体的某一次行为或将来的动作,不过有时二者之间区别很小。
To look after these naughty boys is really difficult.照看这些淘气的男孩真是难。

小升初英语语法知识要点:动名词分类动名词 1动名词是动词的一种非谓语形式,由动词原形加-ing构成,它在句中起名词的作用,可以在句子中用作主语、表语、宾语、宾语补语、状语和定语。
1、动名词作主语Walking is good exercise. 走路是很好的运动Seeing is believing. 眼见为实。
Smoking may cause cancer. 吸烟可能导致癌症。
Coming to Hangzhou by train takes about 16 hours. 乘火车到杭州要16个小时。
Swimming develops the muscles. 游泳可以发展肌肉。
通常为了避免句子主语过于冗长,用it作形式主语。
如:It's nice talking with you.和你谈话很高兴。
It's no use arguing with him.跟他争论没用。
It is no use sending him over. It’s too late already. 派他去没用,已经太晚了。
It was very difficult getting everything ready in time. 要把一切按时准备好很困难。
“There + be + no + -ing”结构,如:There is no joking about such matters. 这种事开不得玩笑。
There is no harm in doing so. 这样做没有害处。
There is no denying the fact that the new method has greatly raised labour productivity。
不容否认新方法大大提高了劳动生产率。
2、动名词作表语Her job is raising pigs. 她的工作是养猪。
This food smells inviting. 这种食物香味怡人。

中考英语语法专题—动名词在中考英语中,语法是重要的考查内容之一,而动名词则是其中较为复杂但又常考的一个知识点。
为了帮助同学们更好地理解和掌握动名词,咱们一起来深入探讨一下。
首先,咱们得明白啥是动名词。
简单来说,动名词就是动词的一种形式,它兼具动词和名词的特点。
它的形式是动词+ing,比如“swimming”“reading”“writing”等等。
动名词有很多作用。
其一,它可以作主语。
比如说,“Swimming is good for your health”在这个句子里,“swimming”就是主语,表达游泳这个动作对于健康有益。
再比如,“Reading books can broaden our horizons”这里“reading books”就是主语,表示读书这个行为能拓宽我们的视野。
动名词还能作宾语。
常见的动词后面需要接动名词作宾语,比如“enjoy”“finish”“practice”等。
例如,“I enjoy reading novels in my spare time”“He finished doing his homework early”“We should practice speaking English every day”有的短语后面也得接动名词,像“be used to”“look forward to”“pay attention to”等等。
“I am used to getting up early”“We are looking forward to meeting you”“You should pay attention to listening carefully in class”动名词还能作定语。
比如“a swimming pool”“a reading room”,这里的“swimming”和“reading”就是定语,分别修饰“pool”和“room”,表示用途。
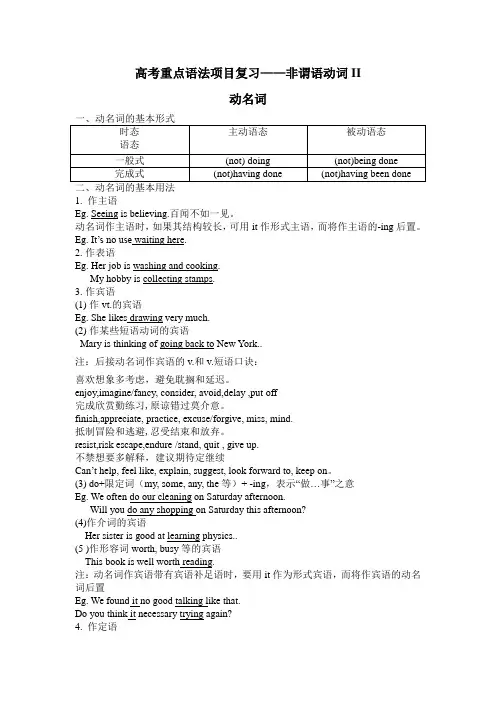
高考重点语法项目复习——非谓语动词II动名词一、动名词的基本形式主动语态被动语态时态语态一般式(not) doing (not)being done完成式(not)having done (not)having been done二、动名词的基本用法1. 作主语Eg. Seeing is believing.百闻不如一见。
动名词作主语时,如果其结构较长,可用it作形式主语,而将作主语的-ing后置。
Eg. It’s no use waiting here.2.作表语Eg. Her job is washing and cooking.My hobby is collecting stamps.3.作宾语(1)作vt.的宾语Eg. She likes drawing very much.(2)作某些短语动词的宾语Mary is thinking of going back to New York..注:后接动名词作宾语的v.和v.短语口诀:喜欢想象多考虑,避免耽搁和延迟。
enjoy,imagine/fancy, consider, avoid,delay ,put off完成欣赏勤练习,原谅错过莫介意。
finish,appreciate, practice, excuse/forgive, miss, mind.抵制冒险和逃避,忍受结束和放弃。
resist,risk escape,endure /stand, quit , give up.不禁想要多解释,建议期待定继续Can’t help, feel like, explain, suggest, look forward to, keep on。
(3) do+限定词(my, some, any, the等)+ -ing,表示“做…事”之意Eg. We often do our cleaning on Saturday afternoon.Will you do any shopping on Saturday this afternoon?(4)作介词的宾语Her sister is good at learning physics..(5 )作形容词worth, busy等的宾语This book is well worth reading.注:动名词作宾语带有宾语补足语时,要用it作为形式宾语,而将作宾语的动名词后置Eg. We found it no good talking like that.Do you think it necessary trying again?4. 作定语There is a swimming pool in our school. (a pool for swimming)三、动名词的复合结构。

中考英语语法专题—动名词在中考英语中,语法是非常重要的一部分,而动名词则是语法中的一个关键知识点。
今天,咱们就来好好聊聊中考英语中的动名词。
首先,咱们得搞清楚啥是动名词。
简单来说,动名词就是动词的ing 形式,它既有动词的特征,又有名词的性质。
比如说,“swimming”(游泳)、“reading”(阅读),这就是动名词。
那动名词都有啥作用呢?它主要有这么几个用途。
其一,动名词可以作主语。
举个例子,“Swimming is my favorite sport”(游泳是我最喜欢的运动。
)在这个句子里,“swimming”就是主语,它表示一种动作或活动。
其二,动名词可以作宾语。
像“ I enjoy reading books ”(我喜欢读书。
)这里的“reading books”就是宾语,表明喜欢的具体内容。
其三,动名词还能作表语。
比如说,“Her job is teaching English”(她的工作是教英语。
)“teaching English”在这儿就是表语,用来说明主语的身份或职业。
接下来,咱们再说说动名词的一些常见搭配和固定用法。
比如“be used to doing sth”(习惯于做某事),“look forward to doing sth”(期待做某事),“prefer doing sth to doing sth”(比起做某事更喜欢做某事)等等。
这些固定搭配在中考中可是经常出现的,大家一定要牢记。
再说说动名词和现在分词的区别。
这也是容易让同学们混淆的地方。
动名词强调的是一种动作的名称或者用途,而现在分词强调的是动作正在进行。
比如说,“The sleeping baby is so cute”(这个正在睡觉的宝宝太可爱了。
)这里的“sleeping”是现在分词,强调“正在睡”这个动作;而“Sleeping is necessary for our health”(睡觉对我们的健康是必要的。
英语语法大全之动名词初中英语语法大全之动名词【—之动名词】如果一个动词加上了ing变成了名词,那么这个词称动名词。
下面就是老师为同学们带来的对动名词的详细讲解,供同学们学习的参考。
总结如果一个动词加上了ing变成了名词,那么这个词称动名词。
由于动名词是由动词变化而来,它仍保留着动词的某些特征,具有动词的某些变化形式,用以表达名词所不能表达的较为复杂的意念。
动名词的名词特征表现在它可在句子中当名词来用,作主语、宾语、表语、定语。
它也可以被副词修饰或者支配宾语。
一、动名词的作用1、作主语1)、直接位于句首做主语。
例如:Swimmingisagoodsportinsummer.2)、用it作形式主语,把动名词(真实主语)置于句尾作后置主语。
动名词做主语时,不太常用it作先行主语,多见于某些形容词及名词之后。
例如:Itisnousetellinghimnottoworry.3)、动名词作主语与动词不定式作主语的比较:动词不定式和动名词都可以用作主语。
在意义上相近。
但动名词多用来表示泛指或抽象动作,不定式多用来表示特指或具体动作。
比较:Smokingisnotgoodforhealth.Itisnotgoodforyoutosmokesomuch.2、作表语动名词作表语时句子主语常是表示无生命的事物的名词或what引导的名词性从句。
表语动名词与主语通常是对等的关系,表示主语的内容,主语、表语可互换位置。
Yourtaskiscleaningthewindows.你的任务就是擦窗户。
(Cleaningthewindowsisyourtask.)WhatIhatemostisbeinglaughedat.我最痛恨的就是被别人嘲笑。
(BeinglaughedatiswhatIhatemost.)3、作定语动名词作定语往往表示被修饰词的某种用途。
如:awashingmachine=amachineforwashing=amachinewhichisusedf orwashing。
★动名词★〈第09卷〉动名词的用法一.动名词的用法◆当主词1.Remembering other people’s names is difficult for me.=It is difficult for me to remember others’ names.◆当补语1.The best exercise in winter is skiing2.One American tradition is eating turkey on Thanksgiving day ▲重点不定词当补语=表:目的,计划,意愿,未完成的事动名词当补语=表:经验,已知的事His hobby is fishing in the lake.√His hobby is to fish in the lake.◆当及物动词的受词1.You have to give up traveling.2.My father enjoys playing golf very much.3.The old man kept standing all the while.◆当介词的受词1.His got scolded for being late for school.2.He left the room without saying a word.▲重点to作介词+Ving1.I like to listen to music.2.I’m looking forward to seeing you again.3.I’m used to getting up early.I used to get up late.4.He devoted his whole life to curing the sick in Africa.5.他爱说谎He is given to lying.6.He prefers skiing to(prep.) skating.He prefers to ski (toV) rather than skate.◆ to+VR/to+Ving1.He is accustomed to live/living alone.2.I came(went) near(差一点) to run/running over a cat.我差一点碾到一只猫3.He took to drink/drinking after the death of his son.〈第10卷〉用不定词/动名词当受词二、用不定词/动名词当受词To+VR/to+Ving区别A)to+VR当受词1.The police consented to detect the crime without delay.警察同意立刻调查该项罪行.2.He professed to know a lot about China.B)Ving1.Have you finished writing an answer to his letter?你写好了给他的回信了吗?I will answer the door. 我去开门.2.Fortunately, he escaped getting hurt. 免于受伤.A)toVR=toVing 意思一样1.They ceased singing/to sing.Stop toVR和toVing不同2.I intend majoring/to major in economics in college. mayor ['mεə]n. 市长B)toVR不同于toVing1.The boy tired to movie the heavy sofa. >try toVR 设法去做(不定做没做)The boy tried moving the heavy sofa. >try Ving 尝试(已经在做了)2.Remember to lock the door. >祈使句一般都是要去做的I remember locking the door last night3.I’ll never forget hearing her song.I forget to hear her song.4.He stopped having breakfast. > break打破 fast斋戒>前一天晚上斋戒未吃,今天第一餐He stopped to have a cup of coffee.5.I regret not taking care of myself. >regret Ving 后悔(做了某事)I regret to say that I can’t help you. >regret toVR 抱歉遗憾(没有做某事)take good care of〈第11卷〉动词意义上的主词三、动词意义上的主词1.Philip dislikes Amy's/Amy wearing mini-skirts.like v.喜欢,dislike prep.像look like, unlikeAmy wear miniskirts> Philip dislikes Amy wearing mini-skirts.Wearing miniskirts> Philip dislikes Amy's wearing mini-skirts.2.I can’t bear/stand him/his shouting when he is angry.3.I am confident of our team’s /our team winning the tournament.4.She is proud of her son/her son’s being clever.pride是名词和动词:n. 自豪常用的结构:take pride in sth. 为某事骄傲例句:They take great pride in her daughter who is now a famous scientist.他们为他那科学家的女儿而感到自豪v.使自夸常用结构:pride oneself on例句: We prided ourselves on our good work. 我们为自己工作的表现而自豪。
高三英语语法讲解及练习动名词第一部分知识透析第一节动名词的基本形式主动被动1. 一般式(not) doing(not) being done(常用来泛指一个动作,没有特别的时间意义,有时也可以表示在谓语动词之前或之后发生的动作)Swimming is her favorite sport.Learning to use electronic products is necessary in modern society.I remembered sending him an e-mail last week.He suggested taking my daughter to the zoo the next Sunday.I can’t stand being kept waiting.His not coming made everyone very disappointed.2. 完成式(not) having done(not) having been done(动名词的动作在谓语动词的动作之前发生)1 really regretted having missed such a wonderful musical.He denied having cheated in the exam.I heard of his having been chosen to be the coach of the team.I remember not having returned the book to the library.第二节动名词的用法1. 动名词作主语/表语动名词作主语/表语表示泛指的经常性的事情Collecting information is very important to businessmen.My hobby is collecting stamps.One of my bad habits is biting nails.2. 动名词作宾语1)一些动词后面只能跟动名词作宾语,如:ban consider delay deny escapefeel like finish forbid involve appreciatekeep practise recommend quit suggestadmit permit avoid enjoy mentionimagine include mind miss resistRisk prohibit allow advise encouragedislike forgive advocate postpone fancyHe denied having been there.We enjoy walking along the Bund.Don’t risk going to the forest alone.The old should avoid eating oily food.注意:allow, advise,encourage,forbid, permit,recommend 后接动名词作宾语,接不定式作补语。
动名词动名词是动词的另外一种非限定形式,通常由动词+-ing形式构成。
它具备动词的某些特点,有时态和语态上的变化,可以有自己的宾语或状语;也具备名词的特点,可以带冠词,被形容词、代词及名词所有格所修饰,在句中起名词的作用,单独或引起短语作主语,表语,宾语,或介词的宾语等。
一、动名词的形式和意义1. 动名词的一般式通常表示一般性动作(即不是明确地在过去、现在或将来发生的动作),或是表示与谓语所表示的动作同时发生的动作。
e.g. I) They are interested in climbing mountains.II) He took a great delight in helping others.2. 如果动名词所代表的动作在谓语所表示的动作之前发生,则通常用动名词的完成形式。
e.g. I) He denied having peeked at his neighbor’s t est paper. 他否认偷看了他同桌的考卷。
II) He was praised for having made such a contribution to the country.【注】在某些动词后或成语中,也常用动名词的一般形式表示在谓语动词所表示的动作之前所发生的动作。
e.g. I) I don’t remember ever seeing him anywhere.II) Thank you for giving us so much help.3. 当一个动名词逻辑上的主语所表示的是这动作的对象时,这动名词一般要用被动形式。
如果动名词所表示的动作在谓语表示的动作之前发生,有时还需用动名词的完成被动式。
e.g. I) He could not bear being made fun of like that. 人家这样开他的玩笑他受不了。
II) You can’t eat anything before being operated on.III) I don’t remember having ever been given a chance to try this metho d. 我不记得谁给我试验这方法的机会。
【注】在want, need, deserve, require等动词后,尽管表示的是被动的意思,却要用动名词的主动形式。
在worth这个形容词后也是如此。
在这类结构中,动名词和句子的主语有着动宾关系,因此如果这个动名词是个不及物动词,后面还应当用一个适当的介词。
e.g. I) This problem requires studying (to be studied) with great care.II) Who needs looking after (= to be looked after)?III) The picture is not worth looking at.4. 由于动名词同时具备名词的特征,所以可以在前面加一个物主代词来表示这个名词短语逻辑上的主语,或者用一个名词所有格来完成这种结构。
e.g. I) Do you think my going there will be of any help?II) What we felt uneasy about was Mary’s having too much confidence i n herself.我们感到不安的是小林过于自信。
二、动名词的句法功能1. 作主语e.g. I) Swimming develops the muscles.II) Tony’s being always late for class affected his final grades.2. 作表语e.g. I) The real problem is getting to know the needs of the people.II) Her job is raising pigs.3. 作宾语a) 在下面这些动词后面,通常用动名词作宾语,而不能用动词不定式:suggest, finish, avoid (避免), stop, cant’ help (禁不住), mind (在乎), admit (承认), enjoy, leave off (停止), require, postpone (推迟), put off, delay, practice, fancy (喜欢), excuse, pardon, advise, consider, deny (否认), endure (忍耐), escape (逃避), miss等。
e.g. I) He avoided giving us a definite answer. 他避免给我们作肯定回答。
II) We’d better put off discussing it till next week.b) 在love, like, hate, prefer, dislike, begin, start, continue, intend (打算), attempt (尝试), can’t bear, propose, want, ne ed, remember, forget, regret, neglect, try, deserve, can’t afford等动词后,可以用动名词作宾语,也可以用动词不定式作宾语。
有时两种结构之间意义差别不是很大,如在like, hate, prefer等词后,如果表示一般倾向,多用动名词作宾语;如果表示特定的或具体的某次行动,用动词不定式时则更多一些。
e.g. I) I like reading books of this kind. 我喜欢看这类书。
I’d like to read that book. 我想看那一本书。
II) They prefer walking to cycling. 他们情愿走路,不愿骑车。
I prefer to stay at home today. 今天我情愿呆在家里。
【注】在remember, forget, regret, try, mean, go on, quit, stop等词后面跟动名词和跟动词不定式作宾语时意思则有明显的差别。
在remember, forget, regret等词后面接的动名词往往表示动作已经发生过了,而动词不定式则表示动词的尚未发生或将要发生。
try后面接的动名词表示试着做某事,而动词不定式则表示设法做某事。
mean后面接的动名词表示意味着,而动词不定式则表示企图、打算。
在quit (停止), stop后面接动名词表示“停止做某事”,而动词不定式则表示“停下来去做某事”。
同样,go on后面接的动名词和动词不定式意义也不同,接动名词时表示“继续做同一件事情”,而接动词不定式则表示“继续做不同的事情”。
e.g. I) I remember seeing her once somewhere. 我记得在哪里见过她。
I must remember to take my notebooks with me. 我必须记住把笔记本带着。
II) I regret not having accepted your advice. 我后悔没有听你的劝告。
I regret to tell you the bad news. 我很遗憾要告诉你这个不幸的消息。
III) We must try to get everything done in time. 我们必须设法及时把一切做好。
Let’s try doing the job some oth er way. 我们用另一种方法试试看。
IV) Success means working very hard.John meant to drive there, but his car broke down.V) He went on working in spite of (尽管) the noise around him.He gave us a brief (简短的) introduction and went on to show us around the campus (校园).V I) We’ll start as soon as it quits snowing.At noon, all the worker quit to take a nap (打盹,小睡).c) 动名词常可用在某些成语后面充当作介词宾语,常见的有:insist on, persist in, think of, dream of, object to (反对), hear of, approve of (赞成), prevent … from, keep … from, stop … from, be e ngaged in (忙于), when it comes to … (当谈到……的时候), look forward to, oppose to (反对), depend on, thank … for, feel like, excuse … for, aim at, devote … to (投身于), set about (开始,着手), spend … in, get used to, be fond of, be capable of (能够), be afraid of, be tired of, be sick of, succeed in, be interested in, feel ashamed of, be proud of, be keen on (热衷于), be responsible for (对……负责) 等。
e.g. I) I’ve been looking forward to coming to Beijing for a long time.II) Have you got used to working on the night shift? 你习惯了上夜班了没有?4. 动名词也可以和about, against, at, before, after, by, besides, for, from, in, on, upon, without等介词构成短语作状语用。
也可以和with a view to (以……为目的), for the purpose of (为了), in case of (万一), in the event of (如果……发生), instead of, apart from, for fear of (为了避免)等成语构成短语,作状语等用。