天然气综合换算表
- 格式:docx
- 大小:23.90 KB
- 文档页数:12

液化天然气各类数值换算结果密度0.46gcm3 (420 ----460kg/m3)1公斤(kg)==2.4 L == m3标方的气体1升(L)==0.42 kg ==0.001m³== N m3标方1m³=600 N m3标方=420千克1吨=2.2 m3=1350 N m3标方1 N m3标方的天然气发热值为9300大卡左右热量单位换算结果卡、千卡、大卡、卡路里、千焦都是热量单位,它们之间的换算是:1卡=1卡路里=焦耳;1千卡=1大卡=1000卡=1000卡路里=4186焦耳=千焦。
卡路里(简称“卡”,缩写为"calorie")的定义为将1克水在1大气压下提升1摄氏度所需要的热量。
1千卡等于1000卡路里,约4186焦耳;脂肪的热量约900大卡每百克;糖类和蛋白质的热量都只有400大卡每百1吨的6000kcal煤折合天然气9000kcal多少立方米是否需要考虑燃烧利用率1000kg×6000÷9000=666.67m³,如果考虑热效率,天然气热效率约92%。
煤在锅炉中,综合热效率约65%,煤燃烧的惯性造成的损失(压货损失)10%;煤在煤气发生炉中的转化率约72%,煤气燃烧热效率与天然气一样;例如:若是以锅炉换算,则(1000××)×6000÷9000÷=424m ³汉刚集团有一个年产石灰12万吨的白灰烧制厂,主要用于炼钢是做为还原剂使用,每烧制1千克的石灰需要热值120大卡,年需要用无烟煤16000吨,无烟煤炭的价格为1600元/吨(含运费);LNG(液化天然气)发热值为每标方9300大卡,价格为6元/千克。
问:如果用LNG代替无烟煤,需要多少吨是否省钱如果省钱,省多少钱解:(1)12万吨白灰等于120000000千克,共需要的热值为:0×120=大卡(2)LNG每标方的发热值为9300大卡,1千克的LNG等于标方的天然气,1千克的LNG的热值为9300×=12090大卡,考虑热效率,天然气热效率约92%。

天然气热值换算表格中的当量换算基本上基于如下标准:1.天然气:1000英热单位/立方英尺=9500大卡/立方米。
(Groningen气为8400大卡/立方米)2.液化石油气:假定其按50/50的丙烷与丁烷的混合比例。
其中r与p分别代表冷冻与压缩状态下的液化石油气。
3.热值,百万英热单位(总量)每吨—液化天然气51.8;液化石油气47.3;油42.3;煤27.3每桶—液化天然气3.8;液化石油气(冷冻)4.45;液化石油气(压缩)4.1;油5.8 每立方米—液化天然气23.8;液化石油气(冷冻)28;液化石油气(压缩)25.8符号和缩写以下的符号和单位不一定与国际气联推荐使的国际计量系统一致,然而,因为使用方便,它们仍被天然气工业系统所广泛采用。
BTU - 英制热量单位MMBTU - 百万英制热量单位ft3 –立方英尺scf –标准立方英尺Mcf –千立方英尺MMcf –百万立方英尺Tcf –万亿立方英尺Nm3 –常态立方米mrd m3 – 109立方米天然气的术语和成分注:本表采用的天然气为: 1000 英热单位/ 立方英尺 = 9500大卡/立方米Groningen 天然气的热值为: 8400大卡/立方米LPG:指 50/50 的丙烷/丁烷含量LNG 液化天然气LPG 液化石油气NGL 天然气凝析液SNG 合成(代替品)天然气表1:天然气:国际燃料价格当量(美元)表2: 天然气:立方米估算当量1 m3 Groningen 天然气=0.88 m3 (9500 千卡)1 m3 (9500 千卡)=1.13 Groningen 天然气表3 天然气:立方英尺估算当量表4 天然气:体积估算当量(干气)等量天然气在条件A下的体积乘以适当的参数得到B条件下的体积表5 天然气:热值估算当量(干气)A栏单位乘以适当参数可以得到B栏单位的相应值表6:液化天然气:体积估算当量表7:液化天然气LNG液态与气态的甲烷估算当量表注:由于液化天然气并非完全由甲烷组成,按不同成分因素,实际估算当量结果会有所不同。
-----------------------------------------------------------------To Convert From To Multiply ByMCF Cubic meters ("m³") 28.174Cubic meters Cubic feet 35.494BBLS (U.S. 42 gallons) Cubic meters ("m³") 0.159Cubic meters ("m³") BBLS 6.290Feet Meters 0.305Meters Feet 3.281Miles Kilometers 1.609Kilometers Miles 0.621Acres Hectares 0.405Hectares Acres 2.471Price Conversions for Natural Gas"US$ 1.00/MMBTU" is equal to:for other fuels expressed in R$multiply by to obtain multiply by to obtain5.46 US$/ barrel of oil Exchange rate x 37.30 US$/ mil m³ natural gas40.22 US$/ ton. fuel oil Exchange Rate x 1.06 US$/ mil ft³ natural gas51.32 US$/ ton. LNG Exchange Rate x 0.10 US$/ therm46.63 US$/ ton. PLG Exchange Rate x 3.97 US$/ cal42.66 US$/ ton. diesel Exchange Rate x 3.42 US$/ mwh13.10 US$/ ton. firewood Exchange Rate x 0.95 US$/ Gjoule26.98 US$/ ton. charcoal Exchange Rate in R$million BTU '000 cubic metersnatural gasTonLNGTonPLGTonfuel oil'000 cubic meters natural gas 37.30 1.00 0.73 0.80 0.93 ton LNG 51.32 1.38 1.00 1.10 1.28ton PLG 46.63 1.25 0.91 1.00 1.16ton diesel 42.66 1.14 0.83 0.91 1.06ton fuel oil 40.22 1.08 0.78 0.86 1.00ton charcoal 26.98 0.72 0.53 0.58 0.67 national coal (4,500 kcal/Kg) 17.86 0.48 0.35 0.38 0.44 ton firewood 13.10 0.35 0.26 0.28 0.33barrel petroleum 5.46 0.15 0.11 0.12 0.14 natural gas: 1 cubic meter = 9,400 Kcal (20º and 1 atm)1 million BTU ( 1 MMBTU) = 26.8 cubic meters ( m³) natural gas.”Engineered Solutions For Combusting Waste Gas"UNIT CONVERSION FACTORSTo convert from units in the left-hand column (A) to units in the right-hand column (B) multiply by the number in the middle column. To convert from units in the right-hand column (B) to units in the left-hand column (A) divide by the number in the middle column. For example:Foot ×304.80= MillimeterMillimeter ÷ 304.80 = FootThe conversion factors are approximate and for reference use only. Conversion factors have been rounded to five significant digits.REV 1 2006/04/19Page 4 of 10REV 1 2006/04/19Page 5 of 10Note:Pressure is usually indicated as gauge pressure, which is the pressure recorded by a pressure gauge and does notinclude the atmospheric pressure. However, most gas property tables use units of absolute pressure; to convert a gauge pressure to absolute pressure the prevailing atmospheric pressure must be added to the gauge pressure.REV 1 2006/04/19Page 6 of 10Notes:1. The standard gas reference temperature and pressure used for US customary units and SI units are not exactly thesame. Therefore, conversion factors for gas volumes used above do not corresponded to those used for ordinaryvolumes.2. A decatherm (also spelled dekatherm) is technically a unit of energy, not volume. One decatherm is approximately1000000 BTU. However the decatherm is sometimes used to express natural gas volumes based on its heating value, for this table a heating value of 1000 BTU/scf was used.Note:The standard gas reference temperature and pressure used for US customary units and SI units are not exactly the same. Therefore, the conversion factors for gas volumes incorporated in the factors above do not corresponded to thoseused for ordinary volumes.REV 1 2006/04/19Page 7 of 10Energy in a Cubic Meter of Natural GasThe Physics Factbook™Edited by Glenn Elert -- Written by his studentsAn educational, Fair Use websitetopic index | author index | special indexREV 1 2006/04/19Page 8 of 10Fuel gases have become prominent since 1900 because of the industrial period. Most fuel gases are made up of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, methane, ethane or other combustibles. One type of fuel gas is natural gas. The term "natural gas" applies to gases with geological components. Natural gas is used for heating because it is very clean, has high heat content, and high flame temperature.Natural gas is sold in volume units. The amount heat that is provided when a unit volume of natural gas is burned is often measured in British thermal units (Btu) per cubic feet. A British thermal unit is a common energy measurement and is defined as the amount of energy required to raise one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.A cubic foot of natural gas accumulations vary in amount and types of gases in it. If more carbon atoms are in the hydrogen gas, the value of Btu is higher.The amount of energy of natural gas can be converted from Btu per cubic feet to Joules per cubic meter. If 1 Btu equals 1055.1 J and 1 ft3 equals 0.028316 m3, thenREV 1 2006/04/19Page 9 of 101000 Btu/ft3 multiplied by 1055.1 J and divided by 0.028316 m3 equals 37 MJ/m3, which is the average energy content of natural gas.Jany Tran -- 2002REV 1 2006/04/19Page 10 of 10。

天然气换算表1千克液化天然气=1.4-1.5立方米天然气(标况气态)1立方米天然气(标况气态)=0.7256千克液化天然气1立方米液化天然气(LNG)可气化600-625立方米天然气(标况气态)1立方米液化天然气的质量约为430-470 千克1升液化天然气=0.001立方米液化天然气=0.6-0.625立方米天然气(标况气态)1升液化天然气=0.001立方米液化天然气其质量为0.43-0.47千克1升天然气(压力为20MPa)=0.001立方米天然气(压力为20MPa)=0.208立方米天然气(标况气态)LNG与柴油比较1.单位体积热值的比较用LNG取代柴油,1 标准立方米天然气相当于1.017升柴油,柴油车百公里消耗燃油27.5升,LNG燃料汽车百公里消耗天然气30标准立方米天然气。
2.续驶里程比较LNG燃料汽车采用低温液态储存方式,能源密度较高,其液化比为1:625,其配置375L车用LNG储气罐,储存量大约234标准立方米天然气,扣除LNG的蒸发量,在满载的情况下可以行驶700公里。
柴油车配置280升油箱,在满载的情况下可以行驶600公里,因此在续驶里程上LNG燃料汽车比柴油车要长些。
3.车辆尾气污染物排放汽车尾气排放是造成空气污染的主要原因之一,据统计汽车尾气排放占了空气污染源总量的40%以上,将汽车燃料由燃油改为天然气后,尾气污染将会明显减少。
LNG燃料汽车尾气中相对于柴油其尾气CO2排放减少24%,CO排放减少31%、NMHE 减少49%,颗粒物和SO2减少100%、烟度为0,不生产苯、铅等致癌物质,因此LNG是汽车最佳的清洁燃料之一。
能够促进污染物排放的减少。
4.车辆的安全性能比较LNG采用密闭真空储存设备储存,不与空气接触,而燃油储油箱内有部分空气,所有从储存方式上来说LNG比燃油更加的安全。
在大气条件下,LNG一旦在系统中发生较小的泄漏,便能很快完全蒸发,不会发生泄漏的LNG聚集的现象,从而杜绝了燃烧及爆炸的可能,保证了乘客及车辆的安全。

石油天然气常用单位换算储量 2010-07-14 09:35:11 阅读260 评论0 字号:大中小订阅体积1立方米(m3)=35.315立方英尺(ft3)=6.29桶(bbl)1立方英尺(ft3)=0.0283立方米(m3)=28.317升(liter)1千立方英尺(mcf)=28.317立方米(m3)1百万立方英尺(MMcf)=2.8317万立方米(m3)10亿立方英尺(bcf)=2831.7万立方米(m3)1万亿立方英尺(tcf)=283.17亿立方米(m3)1桶(bbl)=0.159立方米(m3)热功1焦耳=0.10204千克·米=2.778×10-7千瓦·小时=3.777×10-7公制马力小时=3.723×10-7英制马力小时=2.389×10-4千卡=9.48×10-4英热单位1卡(cal)=4.1868焦耳(J)1英热单位(Btu)=1055.06焦耳(J)1千克力米(kgf·m)=9.80665焦耳(J)1英尺磅力(ft·lbf)=1.35582焦耳(J)1米制马力小时(hp·h)=2.64779×106焦耳(J) 1英马力小时(UKHp·h)=2.68452×106焦耳 1千瓦小时(kW·h)=3.6×106焦耳(J)1大卡=4186.75焦耳(J)油气产量1桶(bbl)=0.14吨(t)(原油,全球平均)1吨(t)=7.3桶(bbl)(原油,全球平均)1桶/日(bpd)=50吨/年(t/a)(原油,全球平均)1千立方英尺/日(Mcfd)=28.32立方米/日(m3/d)=1.0336万立米/年(m3/a)1百万立方英尺/日(MMcfd)=2.832万立方米/日(m3/d)=1033.55万立方米/年(m3/a) 10亿立方英尺/日(bcfd)=0.2832亿立方米/日(m3/d)=103.36亿立方米/年(m3/a)1万亿立方英尺/日(tcfd)=283.2亿立方米/日(m3/d)=10.336万亿立方米/年(m3/a)1桶原油=5.8×106英热单位(Btu)1立方米湿气=3.909×104英热单位(Btu)1立方米干气=3.577×104英热单位(Btu)1吨煤=2.406×107英热单位(Btu)1千瓦小时水电=1.0235×104英热(Btu)热当量1桶原油=5800立方英尺天然气(按平均热值计算)=164立方米1千克原油=1.4286千克标准煤1立方米天然气=1.3300千克标准煤1桶(bbl)=0.14吨(t)(原油,全球平均)1吨(t)=7.3桶(bbl)(原油,全球平均)1桶(bbl)=0.159立方米(m3)=42美加仑(gal)1吨原油=42340立方英尺天然气(按平均热值计算)=1199立方米天然气(按平均热值计算)1000立方米天然气=1.3300吨标准煤1吨原油=1.4286吨标准煤备注:以上为1990年美国平均热值资料来源:美国国家标准局按热量换算,1桶石油≈6百万英热单位≈150立方米天然气。
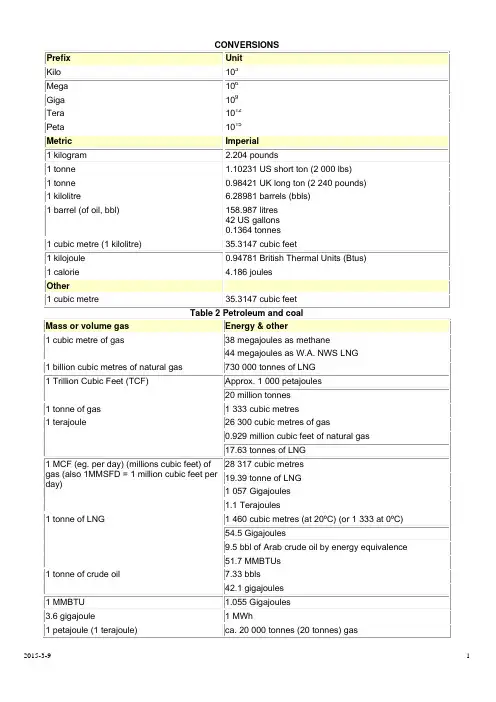
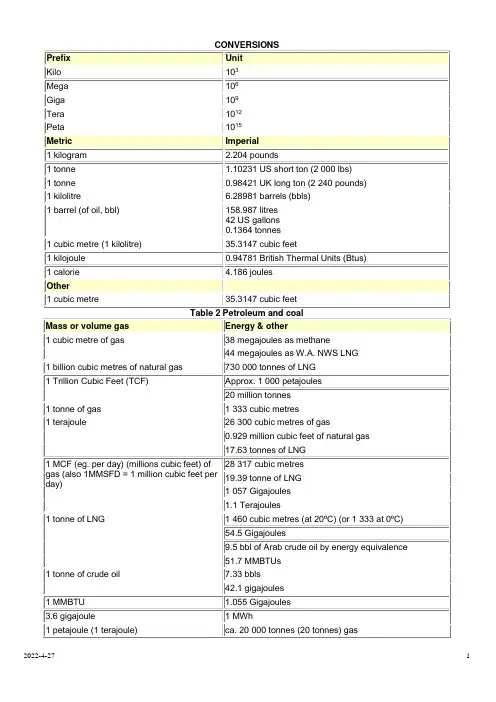
CONVERSIONSPrefix UnitKilo 103Mega 106Giga 109Tera 1012Peta 1015Metric Imperial1 kilogram 2.204 pounds1 tonne 1.10231 US short ton (2 000 lbs)1 tonne 0.98421 UK long ton (2 240 pounds) 1 kilolitre 6.28981 barrels (bbls)1 barrel (of oil, bbl) 158.987 litres42 US gallons0.1364 tonnes1 cubic metre (1 kilolitre) 35.3147 cubic feet1 kilojoule 0.94781 British Thermal Units (Btus) 1 calorie 4.186 joulesOther1 cubic metre 35.3147 cubic feetTable 2 Petroleum and coalMass or volume gas Energy & other1 cubic metre of gas 38 megajoules as methane44 megajoules as W.A. NWS LNG1 billion cubic metres of natural gas 730 000 tonnes of LNG1 Trillion Cubic Feet (TCF) Approx. 1 000 petajoules20 million tonnes1 tonne of gas 1 333 cubic metres1 terajoule 26 300 cubic metres of gas0.929 million cubic feet of natural gas17.63 tonnes of LNG1 MCF (eg. per day) (millions cubic feet) of gas (also 1MMSFD = 1 million cubic feet per day) 28 317 cubic metres 19.39 tonne of LNG 1 057 Gigajoules 1.1 Terajoules1 tonne of LNG 1 460 cubic metres (at 20ºC) (or 1 333 at 0ºC)54.5 Gigajoules9.5 bbl of Arab crude oil by energy equivalence51.7 MMBTUs1 tonne of crude oil 7.33 bbls42.1 gigajoules1 MMBTU 1.055 Gigajoules3.6 gigajoule 1 MWh1 petajoule (1 terajoule) ca. 20 000 tonnes (20 tonnes) gas1 terajoule of gas per day ca. 7 200 tonnes per year.1 million tonnes of LNG per year 1.333 billion cubic metres per year3.65 million cubic metres of natural gas per day 100 MW power station (33% efficiency) ca. 25 terajoules per day (10 Gigajoules/1MWh) Coal ca. 20 Gigajoules per tonneCondensate ca. 32 Megajoules per LitreCrude oil ca. 37 Megajoules per LitreLNG ca 25 Megajoules per LitreNatural gas ca. 38 Megajoules per Cubic MetreAverage Energy Conversion FactorsU.S. Customary Unit Metric EquivalentCrude oil 1 barrel 0.1364 metric tons 5.75 gigajoulesCoal 1 short ton 0.9072 metric tons Natural gas 1 cubic foot 0.0283 cubic meters Natural gas plant liquids 1 barrel 0.0862 metric tons Btu/joule 1 Btu 1 055.1 joulesPetroleum productsMotor gasoline 1 barrel 0.1172 metric tons Distillate fuel oil 1 barrel 0.1340 metric tons Residual fuel oil 1 barrel 0.1502 metric tonscubic metre cubic footgasmillionBtutherm gigajoule kilowatthourcubic metre ofLNGton ofLNG1 cubic meter gas 1 35.3 0.0360.36 0.038 10.54 0.00171 0.0007251 cubicfoot gas0.0283 1 0.00102 0.0102 0.00108 0.299 0.00005 0.000021-millionBtu27.8 981 1 10 1.054 292.7 0.048 0.0192 1 therm 2.78 98.1 0.1 1 0.105448 29.27 0.0048 0.001921gigajoule26.3 930 0.95 9.5 1 277.5 0.045 0.0181 kilowatthour0.0949 3.3 0.0034150.034180.0036 1 0.000162 0.0000651 cubic meter LNG 584 20631 21.04 210.4 22.19 6,173 1 0.4051 tonLNG1,379 48 690 52 520 54.8 15 222 2.47 11 barrel Arabian Lt. 0.152 5350 5.46 54.6 5.75 1597 0.259 0.1051 tonArabianLt.1.111 39 218 40 400 42.2 11 708 1.9 0.769 -----------------------------------------------------------------To Convert From To Multiply ByMCF Cubic meters ("m³") 28.174Cubic meters Cubic feet 35.494BBLS (U.S. 42 gallons) Cubic meters ("m³") 0.159Cubic meters ("m³") BBLS 6.290Feet Meters0.305Meters Feet3.281Miles Kilometers1.609Kilometers Miles0.621Acres Hectares0.405Hectares Acres2.4711 million tones LNG =~ 2.2 million cubic meter LNG1 million tones per year (tpy) LNG =~ 140 million standard cubic per day (MMscfd) gas100 MMscfd gas ~ 730,000 tpy LNG~ 2,100 tpd LNG1 million cubic meter LNG = 6.29 million bbl LNG=~ 460,000 tonnes LNG1 cubic meter LNG ~ 600 cubic meter gas~ 21200 cubic foot gas=~1 standard cubic foot (scf) = 0.0268 normal cubic meter (Nm 3)1 standard cubic meter (scm) = 1.057 normal cubic metter (Nm 3)1 kmole gas = 22.41 Nm 3 @ 101.325kPa(A) and 0 oC1 lb-mole gas = 379.49 scf @ 14.696psia and 60 oFPrice Conversions for Natural Gas"US$ 1.00/MMBTU" is equal to:for other fuels expressed in R$multiply by to obtain multiply by to obtain5.46 US$/ barrel of oil Exchange rate x 37.30 US$/ mil m³ natural gas40.22 US$/ ton. fuel oil Exchange Rate x 1.06 US$/ mil ft³ natural gas51.32 US$/ ton. LNG Exchange Rate x 0.10 US$/ therm46.63 US$/ ton. PLG Exchange Rate x 3.97 US$/ cal42.66 US$/ ton. diesel Exchange Rate x 3.42 US$/ mwh13.10 US$/ ton. firewood Exchange Rate x 0.95 US$/ Gjoule26.98 US$/ ton. charcoal Exchange Rate in R$million BTU '000 cubic metersnatural gasTonLNGTonPLGTonfuel oil'000 cubic meters natural gas 37.30 1.00 0.73 0.80 0.93 ton LNG 51.32 1.38 1.00 1.10 1.28ton PLG 46.63 1.25 0.91 1.00 1.16ton diesel 42.66 1.14 0.83 0.91 1.06ton fuel oil 40.22 1.08 0.78 0.86 1.00ton charcoal 26.98 0.72 0.53 0.58 0.67 national coal (4,500 kcal/Kg) 17.86 0.48 0.35 0.38 0.44 ton firewood 13.10 0.35 0.26 0.28 0.33barrel petroleum 5.46 0.15 0.11 0.12 0.14 natural gas: 1 cubic meter = 9,400 Kcal (20º and 1 atm)1 million BTU ( 1 MMBTU) = 26.8 cubic meters ( m³) natural gas.。

-----------------------------------------------------------------To Convert From To Multiply ByMCF Cubic meters ("m³") 28.174Cubic meters Cubic feet 35.494BBLS (U.S. 42 gallons) Cubic meters ("m³") 0.159Cubic meters ("m³") BBLS 6.290Feet Meters 0.305Meters Feet 3.281Miles Kilometers 1.609Kilometers Miles 0.621Acres Hectares 0.405Hectares Acres 2.471Price Conversions for Natural Gas"US$ 1.00/MMBTU" is equal to:for other fuels expressed in R$multiply by to obtain multiply by to obtain5.46 US$/ barrel of oil Exchange rate x 37.30 US$/ mil m³ natural gas40.22 US$/ ton. fuel oil Exchange Rate x 1.06 US$/ mil ft³ natural gas51.32 US$/ ton. LNG Exchange Rate x 0.10 US$/ therm46.63 US$/ ton. PLG Exchange Rate x 3.97 US$/ cal42.66 US$/ ton. diesel Exchange Rate x 3.42 US$/ mwh13.10 US$/ ton. firewood Exchange Rate x 0.95 US$/ Gjoule26.98 US$/ ton. charcoal Exchange Rate in R$million BTU '000 cubic metersnatural gasTonLNGTonPLGTonfuel oil'000 cubic meters natural gas 37.30 1.00 0.73 0.80 0.93 ton LNG 51.32 1.38 1.00 1.10 1.28ton PLG 46.63 1.25 0.91 1.00 1.16ton diesel 42.66 1.14 0.83 0.91 1.06ton fuel oil 40.22 1.08 0.78 0.86 1.00ton charcoal 26.98 0.72 0.53 0.58 0.67 national coal (4,500 kcal/Kg) 17.86 0.48 0.35 0.38 0.44 ton firewood 13.10 0.35 0.26 0.28 0.33barrel petroleum 5.46 0.15 0.11 0.12 0.14 natural gas: 1 cubic meter = 9,400 Kcal (20º and 1 atm)1 million BTU ( 1 MMBTU) = 26.8 cubic meters ( m³) natural gas.”Engineered Solutions For Combusting Waste Gas"UNIT CONVERSION FACTORSTo convert from units in the left-hand column (A) to units in the right-hand column (B) multiply by the number in the middle column. To convert from units in the right-hand column (B) to units in the left-hand column (A) divide by the number in the middle column. For example:Foot ×304.80= MillimeterMillimeter ÷ 304.80 = FootThe conversion factors are approximate and for reference use only. Conversion factors have been rounded to five significant digits.REV 1 2006/04/19Page 4 of 10REV 1 2006/04/19Page 5 of 10Note:Pressure is usually indicated as gauge pressure, which is the pressure recorded by a pressure gauge and does notinclude the atmospheric pressure. However, most gas property tables use units of absolute pressure; to convert a gauge pressure to absolute pressure the prevailing atmospheric pressure must be added to the gauge pressure.REV 1 2006/04/19Page 6 of 10Notes:1. The standard gas reference temperature and pressure used for US customary units and SI units are not exactly thesame. Therefore, conversion factors for gas volumes used above do not corresponded to those used for ordinaryvolumes.2. A decatherm (also spelled dekatherm) is technically a unit of energy, not volume. One decatherm is approximately1000000 BTU. However the decatherm is sometimes used to express natural gas volumes based on its heating value, for this table a heating value of 1000 BTU/scf was used.Note:The standard gas reference temperature and pressure used for US customary units and SI units are not exactly the same. Therefore, the conversion factors for gas volumes incorporated in the factors above do not corresponded to thoseused for ordinary volumes.REV 1 2006/04/19Page 7 of 10Energy in a Cubic Meter of Natural GasThe Physics Factbook™Edited by Glenn Elert -- Written by his studentsAn educational, Fair Use websitetopic index | author index | special indexREV 1 2006/04/19Page 8 of 10Fuel gases have become prominent since 1900 because of the industrial period. Most fuel gases are made up of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, methane, ethane or other combustibles. One type of fuel gas is natural gas. The term "natural gas" applies to gases with geological components. Natural gas is used for heating because it is very clean, has high heat content, and high flame temperature.Natural gas is sold in volume units. The amount heat that is provided when a unit volume of natural gas is burned is often measured in British thermal units (Btu) per cubic feet. A British thermal unit is a common energy measurement and is defined as the amount of energy required to raise one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.A cubic foot of natural gas accumulations vary in amount and types of gases in it. If more carbon atoms are in the hydrogen gas, the value of Btu is higher.The amount of energy of natural gas can be converted from Btu per cubic feet to Joules per cubic meter. If 1 Btu equals 1055.1 J and 1 ft3 equals 0.028316 m3, thenREV 1 2006/04/19Page 9 of 101000 Btu/ft3 multiplied by 1055.1 J and divided by 0.028316 m3 equals 37 MJ/m3, which is the average energy content of natural gas.Jany Tran -- 2002REV 1 2006/04/19Page 10 of 10。
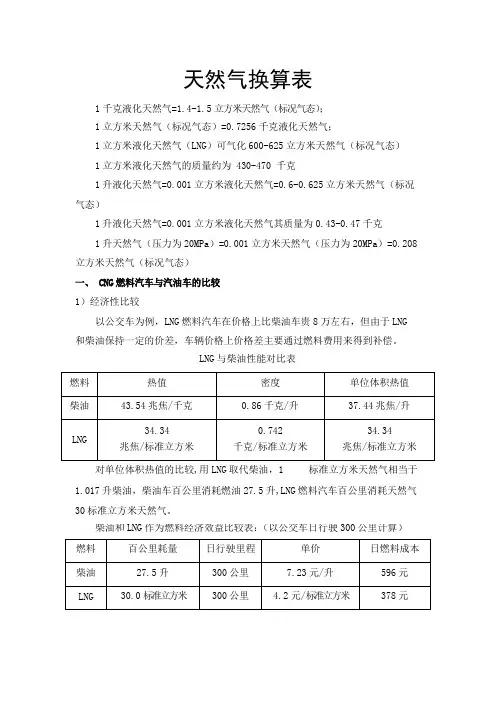
天然气换算表1千克液化天然气=1.4-1.5立方米天然气(标况气态);1立方米天然气(标况气态)=0.7256千克液化天然气;1立方米液化天然气(LNG)可气化600-625立方米天然气(标况气态)1立方米液化天然气的质量约为430-470千克1升液化天然气=0.001立方米液化天然气=0.6-0.625立方米天然气(标况气态)1升液化天然气=0.001立方米液化天然气其质量为0.43-0.47千克1升天然气(压力为20MPa)=0.001立方米天然气(压力为20MPa)=0.208立方米天然气(标况气态)一、CNG燃料汽车与汽油车的比较1)经济性比较以公交车为例,LNG燃料汽车在价格上比柴油车贵8万左右,但由于LNG 和柴油保持一定的价差,车辆价格上价格差主要通过燃料费用来得到补偿。
LNG与柴油性能对比表对单位体积热值的比较,用LNG取代柴油,1标准立方米天然气相当于1.017升柴油,柴油车百公里消耗燃油27.5升,LNG燃料汽车百公里消耗天然气30标准立方米天然气。
柴油和LNG作为燃料经济效益比较表:(以公交车日行驶300公里计算)LNG燃料汽车与柴油车相比较每天燃料成本减少218元,按年运营时间350天计算,年可以节省燃料成本7.6万,购车增加的8.0万元成本可以在运营1年半后收回,按公交车运营寿命为8年,8年内由燃料费用上得到的经济效益为61万元,因此采用LNG燃料汽车相对于柴油车大幅度的降低了车辆的运营成本,为公交公司创造较大的经济利益。
2)续驶里程比较LNG燃料汽车采用低温液态储存方式,能源密度较高,其液化比为1:625,其配置375L车用LNG储气罐,储存量大约234标准立方米天然气,扣除LNG的蒸发量,在满载的情况下可以行驶700公里。
柴油车配置280升油箱,在满载的情况下可以行驶600公里,因此在续驶里程上LNG燃料汽车比柴油车要长些。
3)车辆尾气污染物排放汽车尾气排放是造成空气污染的主要原因之一,据统计汽车尾气排放占了空气污染源总量的40%以上,将汽车燃料由燃油改为天然气后,尾气污染将会明显减少。

常用热力单位换算表一、热量单位换算1、常用热量单位介绍A、焦耳(J)、千焦(KJ)、吉焦(GJ),工程计算广为采用,国际单位制。
热力计算、热计量、热量化验等实际操作中常见,国家标准及图表、线图查询等规范性技术文件中主要表达的单位。
但是,其他导出单位及工程习惯相互交织,使得这种单位在今天热力计算中不是很方便。
B、瓦特(W)、千瓦(KW)、兆瓦(MW),工程导出单位,是供热工程常用单位,如热水锅炉热容量:7MW、14MW、29MW、56MW...等,习惯上常说到的10t、20t、40t、80t...等锅炉,相当于同类容量蒸汽锅炉的设计出力.工程上热水锅炉和换热站热计量仪表、暖通供热设计计算、估算、供热指标等,广泛采用。
C、卡(car)、千卡(Kcal)...,已经淘汰的热量单位,但是工程中还在使用,特别是大量的技术书籍,例如煤的标准发热量7000Kcal。
2、基本计算公式1W=0.86Kcal,1KW=860Kcal,1Kcal=1.163W; 估算:1 KW=0.1m3/h1t饱和蒸汽=0.7MW=700KW=2.5GJ=60万Kcal;1kg标煤=7000Kcal=29300KJ=29.3MJ=0.0293GJ=8141W=8.141KW;1GJ=1000MJ;1MJ=1000KJ;1KJ=1000J1Kcal=4.1868KJ=0.0041868MJ、1MJ=238.846Kcal 、1W=3.6J(热工当量,不是物理关系,但热力计算常用)天然气标况与工况流量换算:工作状态下的流量:Qf=QN×[0.10132×(273.15+T)]÷[(P+0.10132)×273.15] m3/h标准状态下的流量(0℃、latm):QN=Qf×[(P+0.10132)×273.15]÷[0.10132×(273.15+T) ]Nm3/h汽油、柴油、水的升与吨的换算关系1、1升水=0.001吨水1升=1公斤2、1升柴油约合0.00084吨(1吨柴油大约折合1190升)1升=0.8403公斤3、汽油的密度为0.70kg/l-0.73kg/l,即0.0007吨/升—0.00073吨/升。

一、天然气介绍天然气是指埋藏在地下的可燃气体,主要成分为甲烷(CH4)。
天然气形式主要有四种:气田气由气井采出的可燃气体称为纯天然气或气田气。
它的主要成分是甲烷(CH4),约占90%以上,此外还含有少量的乙烷(C2H6),丙烷(C3H8),硫化氢(H2S),一氧化碳(CO),二氧化碳(CO2)等,热值约为38MJ/Nm³。
凝析气田气凝析气田气是指在开采过程中有较多C5及C5以上的石油轻烃馏分可凝析出来,但是没有较重的原油同时采出的天然气。
其主要成分除含有大量的甲烷(CH4)外,还含有2%-5%的C5及C5以上碳氢化合物,热值约46MJ/Nm³。
石油伴生气石油伴生气是指在开采过程中与液体石油一起开采出来的天然气,是采油时的副产品。
它的主要成分也是甲烷,约占70%-80%左右,还含有一些其它烷烃类,以及CO2,H2,N2等。
热值约为42MJ/Nm³。
煤矿矿井气煤矿矿井气是指从井下煤层中抽出的煤矿矿井气,是采煤的副产品。
实际上它是煤层气与空气的混合气。
其主要成分是甲烷(CH4)和氮气(N2),此外还含有O2和CO等。
值得注意的是,矿井气只有当CH4含量在40%以上才能作为燃气供应,CH4体积组分在40%—50%时,矿井气热值约为17MJ/Nm³。
另外,天然气除了常规的气态形式存在于管道当中外,还可以经过加工,变成LNG和CNG。
LNG当天然气在大气压下,冷却至约-162℃时,天然气由气态转变成液态,称为液化天然气(Liquefied Natural Gas,缩写为LNG)。
LNG 无色.无味.无毒且无腐蚀性,天然气液化是一个低温过程,在温度不超过临界温度(-82摄氏度),对气体进行加压0.1MPa以上,液化后其体积约为同量气态天然气体积的1/600,LNG的重量仅为同体积水的45%左右,热值为52MMBtu/t,(百万英热单位/吨)(.52×108cal)。

常用热力单位换算表一、热量单位换算1、常用热量单位介绍A、焦耳(J)、千焦(KJ)、吉焦(GJ),工程计算广为采用,国际单位制。
热力计算、热计量、热量化验等实际操作中常见,国家标准及图表、线图查询等规范性技术文件中主要表达的单位。
但是,其他导出单位及工程习惯相互交织,使得这种单位在今天热力计算中不是很方便。
B、瓦特(W)、千瓦(KW)、兆瓦(MW),工程导出单位,是供热工程常用单位,如热水锅炉热容量:7MW、14MW、29MW、56MW...等,习惯上常说到的10t、20t、40t、80t...等锅炉,相当于同类容量蒸汽锅炉的设计出力.工程上热水锅炉和换热站热计量仪表、暖通供热设计计算、估算、供热指标等,广泛采用。
C、卡(car)、千卡(Kcal)...,已经淘汰的热量单位,但是工程中还在使用,特别是大量的技术书籍,例如煤的标准发热量7000Kcal。
2、基本计算公式1W=0.86Kcal,1KW=860Kcal,1Kcal=1.163W; 估算:1 KW=0.1m3/h1t饱和蒸汽=0.7MW=700KW=2.5GJ=60万Kcal;1kg标煤=7000Kcal=29300KJ=29.3MJ=0.0293GJ=8141W=8.141KW;1GJ=1000MJ;1MJ=1000KJ;1KJ=1000J1Kcal=4.1868KJ=0.0041868MJ、1MJ=238.846Kcal 、1W=3.6J(热工当量,不是物理关系,但热力计算常用)天然气标况与工况流量换算:工作状态下的流量:Qf=QN×[0.10132×(273.15+T)]÷[(P+0.10132)×273.15] m3/h标准状态下的流量(0℃、latm):QN=Qf×[(P+0.10132)×273.15]÷[0.10132×(273.15+T) ]Nm3/h汽油、柴油、水的升与吨的换算关系1、1升水=0.001吨水1升=1公斤2、1升柴油约合0.00084吨(1吨柴油大约折合1190升)1升=0.8403公斤3、汽油的密度为0.70kg/l-0.73kg/l,即0.0007吨/升—0.00073吨/升。