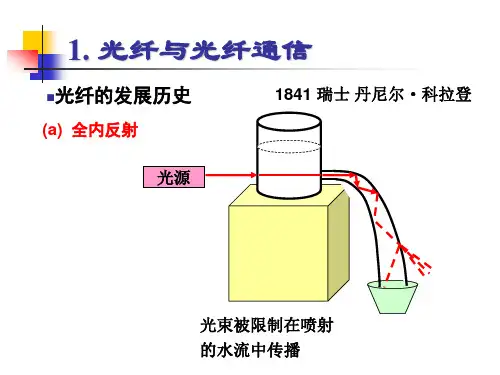
Dispersion Shifted Fibre
• dispersion shifted fibre is designed with a dispersion zero point at around 1550 nm. • However, it is not always possible or indeed desirable: • In many cases we can't have DSF because the fibre we must use is already installed. • four-wave mixing effectively prohibit the use of DSF.
是未来大容量传输,DWDM系统用光纤的理想选择。
三种光纤色散情况比较
普通光纤(SMF) 非色散位移光纤(NDSF,G.652) 已有光纤的>95% 18
正常色散区
DWDM 波长范围
反常色散区
色散 0 ps/nmkm 1310nm 波长 1550nm 色散位移光纤(DSF,G.653) 非零色散位移光纤(NZDSF,G.655)
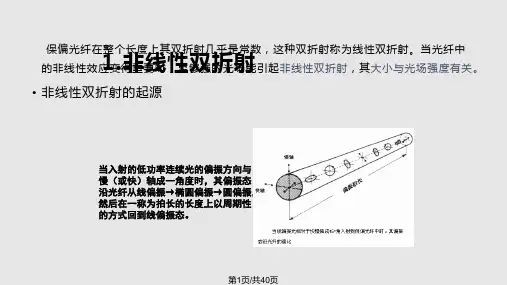
Polarisation Mode Dispersion (PMD)
• There is usually a very slight difference in RI for each polarisation. It can be a source of dispersion, usually less than .5 ps/nm/km. • The effect is to cause a circular or elliptical polarisation to form as the signal travels along the fibre. • Dispersion resulting from the birefringent properties of fibre is called “Polarisation Mode Dispersion” (PMD).