金融学导论成人教育考试作业二
- 格式:docx
- 大小:212.64 KB
- 文档页数:10

一、单选题(客观)参考答案:每题只有一个正确的选项1(5.0分)消除了种种风险溢价后补偿机会成本的利率是指()。
A)基准利率B)实际利率C)无风险利率D)名义利率参考答案: C2(5.0分)投资人可以随时根据需要向基金购买股票以实现投资,也可以回售股票以撤出投资的投资基金是()。
A)私募基金B)封闭式基金C)开放式基金D)公募基金参考答案: C3(5.0分)商业银行的()是最主要的负债业务。
A)自有资本B)吸收存款C)向中央银行借款D)同业拆借参考答案: B4(5.0分)货币的产生是()。
A)由金银的天然属性决定的B)国家的发明创造C)商品交换过程中商品内在矛盾发展的产物D)人们相互协商的结果参考答案: C5(5.0分)()是商业银行的资金运用业务。
A)负债业务B)中间业务C)其他业务D)资产业务参考答案: D6(5.0分)关于汇率对物价的影响,本币对外贬值时()。
A)进口商品的国内价格上涨B)进口商品的国内价格降低C)有可能获得较廉价的进口品D)出口品有可能降价参考答案: A7(5.0分)利息率的变动范围是()。
A)小于零B)大于零C)高于平均利润率D)大于零低于平均利润率参考答案: D8(5.0分)中央银行提高法定存款准备率,则商业银行交存的存款准备金增加,超额准备减少或准备金不足,贷款减少,使信贷量和货币量()。
A)扩大B)缩小C)不变D)不确定变化参考答案: B9(5.0分)在货币政策中介指标的选择上,凯恩斯主义主张以()为宜。
A)货币供应量B)基础货币C)利率D)超额准备参考答案: C10(5.0分) 以下哪一项不是我国政策性银行资金来源的主要渠道?A)财政拨付B)由原来的各专业银行划出的资本金C)发行票据D)发行金融债券参考答案: C二、判断题(客观)参考答案:判断下列说法是否正确11(5.0分)金融市场是指货币资金融通和金融工具交易的场所和行为的总和。
A) 正确参考答案:正确12(5.0分)交易性货币需求是指个人或企业为了应付日常交易需要而产生的持有货币需要。

《金融学》教案大纲及习题解答第一章:金融学导论1.1 金融学的定义与意义金融学的概念金融学的研究对象与内容金融学的重要性1.2 金融市场与金融体系金融市场的概念与类型金融体系的组织结构金融市场与金融体系的关系1.3 金融学的应用领域企业金融个人金融宏观金融第二章:金融市场与金融工具2.1 金融市场的概念与类型金融市场的定义金融市场的类型与特点金融市场的作用与功能2.2 金融工具与金融产品金融工具的定义与分类金融产品的特点与功能金融工具与金融产品的选择与运用2.3 金融市场的参与者金融市场的主体与客体金融市场的投资者与融资者金融市场的服务机构第三章:金融市场的基本原理3.1 供求关系与价格机制金融市场的供求关系价格机制的作用与影响市场均衡与市场失灵3.2 金融市场的基本原理与应用金融市场的效率与有效性金融市场的风险与收益金融市场的信息与信号传递3.3 金融市场的微观结构金融市场的交易机制金融市场的信息不对称问题金融市场的交易成本与效率第四章:金融机构与金融体系4.1 金融机构的概念与类型金融机构的定义与特点商业银行与其他金融机构的比较金融机构的职能与作用4.2 金融体系的组织结构金融体系的构成要素金融体系的层次结构金融体系的监管与调控机制4.3 金融体系的功能与目标金融体系的基本功能金融体系的宏观调控目标金融体系的微观审慎监管目标第五章:金融市场与宏观经济5.1 金融市场与经济增长金融市场对经济增长的影响金融市场的规模与经济增长的关系金融市场的结构与经济增长的关系5.2 金融市场与货币政策货币政策的概念与目标金融市场在货币政策传导中的作用货币政策对金融市场的影响5.3 金融市场与金融稳定性金融稳定性的概念与意义金融市场在金融稳定性维护中的作用金融市场风险管理与监管的策略与措施《金融学》教案大纲及习题解答第六章:商业银行与存款货币银行6.1 商业银行的组织结构与运营模式商业银行的定义与特点商业银行的组织结构与管理体系商业银行的运营模式与业务流程6.2 存款货币银行的存款创造与信贷扩张存款创造的概念与机制信贷扩张的过程与影响存款货币银行的风险管理与信贷政策6.3 商业银行的金融服务与产品商业银行的存款与贷款产品商业银行的支付结算服务商业银行的金融服务创新第七章:资本市场与证券交易7.1 资本市场的概念与类型资本市场的定义与特点股票市场与债券市场的比较资本市场的功能与作用7.2 证券交易与投资分析证券交易的基本流程投资分析的方法与工具投资者偏好与投资组合的选择7.3 资本市场的效率与有效性资本市场效率的定义与衡量资本市场的有效性假说资本市场效率与有效性的实证研究第八章:金融衍生品市场8.1 金融衍生品的概念与类型金融衍生品的定义与特点期货、期权和掉期的比较金融衍生品市场的功能与作用8.2 金融衍生品的定价与风险管理金融衍生品的定价原理金融衍生品的风险类型与风险管理策略金融衍生品市场的风险监管与调控8.3 金融衍生品市场的应用与影响金融衍生品在企业金融中的应用金融衍生品在个人理财中的应用金融衍生品市场对金融体系的影响第九章:国际金融与外汇市场9.1 国际金融市场的概念与类型国际金融市场的定义与特点国际资本市场与国际外汇市场的比较国际金融市场的作用与影响9.2 外汇市场的运行机制与交易策略外汇市场的组织结构与交易机制外汇市场的汇率决定与变动外汇市场的交易策略与风险管理9.3 国际金融市场的关系与影响国际金融市场之间的联系与互动国际金融市场对国内经济的影响国际金融市场风险的识别与应对第十章:金融监管与金融政策10.1 金融监管的概念与目标金融监管的定义与意义金融监管的目标与原则金融监管的机构与体系10.2 金融政策的概念与工具金融政策的定义与类型货币政策与财政政策的比较金融政策的工具与传导机制10.3 金融政策的效应与评估金融政策的宏观经济效应金融政策的微观经济效应金融政策的评估方法与指标《金融学》教案大纲及习题解答第十一章:金融创新与金融科技11.1 金融创新的定义与类型金融创新的含义与动力金融创新的产品与服务金融创新的风险与监管11.2 金融科技的发展与应用金融科技的概念与特点数字货币与区块链技术金融科技在金融服务中的应用11.3 金融创新与金融监管的关系金融监管对金融创新的影响金融创新对金融监管的挑战金融监管与金融创新的平衡策略第十二章:金融风险与管理12.1 金融风险的定义与类型金融风险的概念与特征市场风险、信用风险和流动性风险的比较金融风险的管理与控制12.2 金融风险评估与度量金融风险评估的方法与模型金融风险度量的指标与工具金融风险评估的实践应用12.3 金融风险管理的策略与工具金融风险管理的框架与程序金融风险规避、分散与转移金融风险管理的创新与挑战第十三章:企业金融与公司财务13.1 企业金融的概念与功能企业金融的定义与目标企业金融的资本结构与投资决策企业金融的融资与理财策略13.2 公司财务的理论与实践公司财务的基本原则与目标公司财务的财务报表分析与估值公司财务的资本预算与资本结构13.3 企业金融与公司财务的挑战与趋势企业金融与公司财务的国际化企业金融与公司财务的可持续发展企业金融与公司财务的创新与发展第十四章:个人金融与理财规划14.1 个人金融的概念与内容个人金融的定义与意义个人资产与个人负债的管理个人金融产品的选择与运用14.2 理财规划的理论与方法理财规划的基本原则与步骤理财规划的工具与技术理财规划的实际操作与案例分析14.3 个人金融与理财规划的挑战与趋势个人金融市场的变化与趋势理财规划在个人金融中的应用个人金融与理财规划的创新与发展第十五章:金融伦理与职业道德15.1 金融伦理的概念与重要性金融伦理的定义与特点金融伦理在金融行业中的重要性金融伦理的挑战与问题15.2 职业道德的标准与原则职业道德的内涵与要求职业道德的实践与遵守职业道德的监督与教育15.3 金融伦理与职业道德的发展趋势金融伦理与职业道德的改进与完善金融行业职业道德建设的措施与方法金融伦理与职业道德的未来发展重点和难点解析本文档详细地编写了《金融学》教案大纲及习题解答,涵盖了金融学的基本概念、原理和应用。
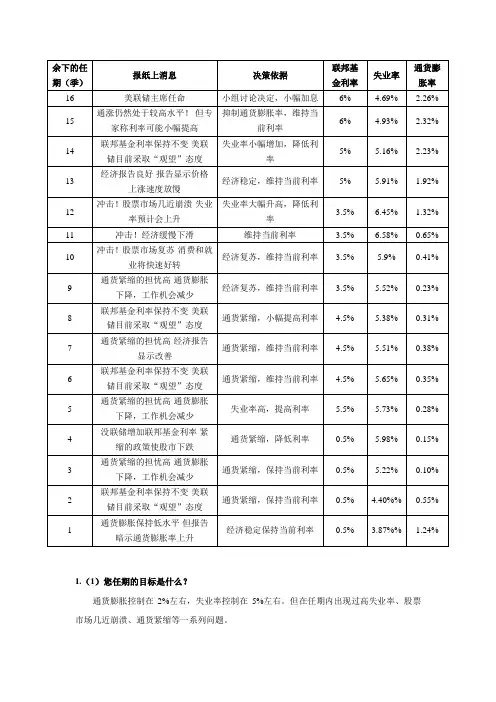
1.(1)您任期的目标是什么?通货膨胀控制在2%左右,失业率控制在5%左右。
但在任期内出现过高失业率、股票市场几近崩溃、通货紧缩等一系列问题。
(2)在您的任期中,经济状况有什么变化,发生了什么样的冲击?股票市场动荡,通货膨胀率持续下行,存在通货紧缩压力,同时也存在高失业率阶段。
(3)您是如何进行应对的,应对的效果如何?您认为央行行长的目标是否容易达到?不断调整联邦基金利率,降低失业率和通货膨胀率。
在任期后期持续降低联邦基金利率,逐渐稳定通货膨胀率下行,并提高通货膨胀率;目标通过关注市场反应及时调整利率,可以修正并逐渐向正常值靠拢。
(4)并说明您这样认为的理由是什么?利率与通货膨胀率和失业率相关联。
(5)请登陆“扩展资源”板块,观看“前沿讲座”,并查阅推荐的“相关网站”,如“财经门户”,“经济信息”等,获取世界经济状况信息,比较与游戏场景有什么相同和不同点?相同点:世界经济复苏基础仍不稳固,金融市场缺乏实体经济的有力支撑。
不同点:游戏只是模拟世界经济的一个形式,在游戏中我们可以依据金融规律,通胀压力时采用稳健的财政政策,通缩时采用积极的财政政策,通过及时采取调整利率的办法来实现目标值。
而在现实生活中的金融界复杂的经济因素都会影响投资者信心和金融市场稳定,各种冲击都会存在,全球金融市场动荡的可能性仍然较大,比游戏场景复杂得多。
2.游戏体会:经过对游戏的操作和课外资料的查询发现实际的金融世界有复杂的经济原因,影响金融变动的原因非常多,而且各种原因会同时出现,作为决策保持经济稳定非常不易。
美联储通过控制通货与信贷,运用公开市场业务、银行借款贴现率和金融机构法定准备金比率三大杠杆来调节美国经济。
调整利率是美联储宏观调控美国经济的主要手段。
如果经济过热,它就提高利率,收缩银根,使经济速度放慢,减少通货膨胀压力。
如果经济不景气,它就降低利率,促使经济增长。
其关键是根据经济形势对利率提高和降低进行调控,并要恰到好处。

重庆开放大学2024年秋金融基础形考任务二试卷总分:100 得分:1001.()是货币时间价值的具体体现。
A.汇率B.利息C.股息D.收益率2.在多种利率并存的条件下起决定作用的利率是( )A.实际利率B.名义利率C.基准利率D.市场利率3.某投资者进行股票投资的时候,买了不同行业的好几支股票进行多元化投资,请问,多元化投资分散了()。
A.利率风险B.信用风险C.非系统风险D.系统风险4.一般来说,收益(C)是本金(P)与()的乘积。
A.时间(t)B.利率(r)C.储蓄率(s)D.投资率(i)5.在借贷期内根据市场上货币资金供求状况的变化情况而定期进行调整的利率称为()。
A.固定利率B.浮动利率C.官定利率D.行业利率6.利用利率调节信贷资金结构,一般的做法是,对有发展前景的新兴产业、国民经济发展中的短线行业、经济发展重点部门实行()。
A.名义利率B.较高的存款利率C.较低的贷款优惠利率D.浮动利率7.当名义利率低于通货膨胀率时,实际利率为()A.正利率B.负利率C.零D.无穷大8.传统利率决定理论也被称为()A.实际利率理论B.名义利率理论C.凯恩斯的利率决定理论D.马克思的利率决定理论9.利率是()的简称。
A.利息额B.所贷资金额的C.利息率D.回报率10.由于市场利率变动而对证券资产的价值带来的风险是()。
A.货币风险B.利率风险C.流动性风险D.信用风险11.市场汇率是指在外汇市场上由()决定的汇率。
A.国家货币管理当局B.外汇供求C.国际货币基金组织D.世界银行12.一国出现持续性的国际收支顺差,则可能会导致或加剧()。
A.通货膨胀B.失业C.经济危机D.货币贬值13.自由浮动制是指一国汇率水平基本上由市场决定,偶尔的外汇干预旨在缓和汇率变动,防止汇率过度波动,政府对汇率的干预次数为(),且每次不超过3个工作日A.6个月内2次以上B.6个月内3次以上C.6个月内控制在2次以内D.6个月内控制在3次以内14.将两国货币兑换比率表示出来的方法叫做()A.汇率标价法B.直接标价法C.间接标价法D.利率平价理论15.自由浮动又称为(),指货币当局不对外汇市场进行任何干预,完全由外汇市场供求决定汇率的涨落。


东北财经大学年秋季金融学在线作业二答案东北财经大学年秋季金融学在线作业二答案1某2年期债券的年收益率为8%,期间通货膨胀率为每年2.5%,那么该债券的实际年收益率为(a )。
A. 5.37%B. 5.5%C. 5%D. 3%满分:4 分2. 对同一发行主体的债券而言,债券的到期日越长,债券的价值(b)。
A. 越大B. 越小C. 与之无关D. 不确定满分:4 分3. 可转换债券是指债券的持有人在一定条件下可按事先确定的转换比率将所持有的债券转换成公司的(a )。
A. 普通股股票B. 优先股股票C. 可赎回债券D. 附息债券满分:4 分4. 一般而言,风险与收益会呈现(a)的关系。
A. 正比率B. 反比率C. 不确定D. 以上都有可能满分:4 分5. 2年期、面值为100元的纯贴现债券的到期收益率为6.5%,该债券当前的合理售价为(c )。
A. 881.66元B. 100元C. 88.17元D. 923.66元满分:4 分6. 债券期限越长,其利率风险(b )。
A. 越小B. 越大C. 为零D. 越无法确定满分:4 分7. 随着年龄的增长,一个人的人力资本(d)。
A. 必然会增加B. 必然会降低C. 保持不变D. 不确定满分:4 分8. 新学期开学需要教材,李同学发现购买新教材需要50元,如果和其他同学合买一本教材一起用,则只需要15元。
李同学在决定独自购买还是合买的决策属于(b)。
A. 投资决策B. 消费决策C. 融资决策D. 风险管理决策满分:4 分9. 某风险资产组合的预期收益率为18%,无风利率为5%。
如果想用该风险资产组合和无风险资产构造一个预期收益率为12%的投资组合,那么投资于无风险资产的比率应为(c)。
A. 53.85%B. 63.85%C. 46.15D. -46.15%满分:4 分10. 本年年末存入100元,求第十年末的款项,应用(a)。
A. 复利终值系数B. 复利现值系数C. 年金终值系数D. 年金现值系数满分:4 分11. 当前面值为100元的1年期零息国债价格为90元,面值为1000元的2年期零息国债的价格为880元,2年期付息债券的到期收益率为(a )。
![金融学导论作业二2024年[1]](https://uimg.taocdn.com/4ba00d8f9fc3d5bbfd0a79563c1ec5da50e2d6be.webp)
金融学导论作业二引言概述:金融学导论作业二
正文:
A. 金融市场
1. 金融市场的定义
2. 金融市场的分类
3. 金融市场的参与者
4. 金融市场的功能
5. 金融市场的发展趋势
B. 金融工具
1. 金融工具的定义
2. 金融工具的种类
3. 金融工具的特点
4. 金融工具的风险与回报
5. 金融工具的选择和交易
C. 金融管理
1. 金融管理的定义
2. 金融管理的目标
3. 金融管理的安排与实施
4. 金融管理的风险控制
5. 金融管理的评估与监控
D. 金融风险管理
1. 金融风险的概念和分类
2. 金融风险管理的目标
3. 金融风险管理的方法
4. 金融风险管理的工具
5. 金融风险管理的实施与应用
E. 金融市场监管
1. 金融市场监管的定义和目的
2. 金融市场监管的法律法规
3. 金融市场监管的机构和职责
4. 金融市场监管的执行和处罚
5. 金融市场监管的挑战和前景
总结:
通过对金融学导论作业二的五个大点进行阐述,我们了解了金融市场的定义、分类和功能;金融工具的类型和选择;金融管理的目标和方法;金融风险管理的策略和工具;以及金融市场监管的目
的、机构和挑战。
本文旨在帮助读者深入了解和应用金融学的相关知识,并为未来的学习和研究提供理论基础。

解答:一、信用与利率的关系信用与货币是两个不同的经济范畴。
信用是一种借贷行为,是不同所有者之间调剂财富余缺的一种形式。
货币是一般等价物,作为价值尺度,媒介商品所有者之间的商品交换。
二者之间的关系必须用历史的眼光来考察。
二、利率发挥作用的世界性趋势利率不但能够反映货币与信用的供给状态,而且能够表现供给与需求的相对变化。
利率水平趋高被认为是银根紧缩,利率水平趋低则被认为是银根松弛。
因此,西方传统的货币政策均以利率为中介目标。
为了控制投资的高速增长,在央行采取的诸多货币政策操作中,被西方金融界称为货币政策“猛药”的存款准备金率一调再调,而调整法定存贷款利率这一传统的政策工具,却一直没有使用。
这让市场感到很意外。
我们认为,央行之所以迟迟没有提高法定存贷款利率,除了考虑CPI、经济增长速度等正常的经济指标外,还受到一些特殊的外部因素的约束。
在我国利率发挥作用还不具备条件。
在发达市场经济国家,利率政策非常有效,因而成为主要的货币政策工具。
中国的情况十分复杂。
统计分析显示,在中国,货币供应量的变动同利率变动的关系不大。
并且,利率水平的降低对存款总量的增长以及增长的速度都没有产生明显的影响。
之所以出现上述情况,其主要原因是:地方政府、国有企业是主要的贷款需求者,贷款需求的利率弹性必然较低;作为贷款的主要供给方,银行、特别是国有银行的利率敏感性一直较低。
另外,人民币汇率升值的压力,将导致大量短期资本涌入到国内,从而达不到提高利率紧缩信用的目的。
因此,有研究人员认为升息不能解决经济过热问题。
三、我国利率改革的方向及其在宏观和微观经济中的重要作用利率市场化是指所有利率均由市场决定,即由资金供求关系确定。
利率市场化是我国利率管理体制改革的方向。
在利率制度方面,国家应尽早建立并完善利率决定机制以及利率风险管理制度,保证利率决定机制在最大程度的灵活性和自主性的基础上实现利率风险水平的最小化;在规范微观主体行为方面,应首先解决长期以来困扰我国经济发展的国有企业问题,加速国有企业改革,逐步建立和完善现代企业管理制度,同时进一步推进国有商业银行的改革进程,在产权制度和银行治理结构等方面加大改革力度;在金融市场方面,国家应努力朝着建立统一,开放,竞争,有序的金融体系的目标迈进,为市场上的各类竞争主体提供一个尽可能公平,公正的投融资环境,从而为利率市场化改革的最终实现创造条件。

《金融学》作业说明:1、根据《金融学》课程的学科特点,未设置客观题。
由于金融学与实践联系较为紧密,因此在部分章节后设置了开放式学习题,要求学生在课外通过查阅相关资料,对金融的热点问题进行分析和思考,开放式学习题将作为考核中论述题的主要来源,且随着金融热点的变化而不断更新,可能会超出习题集的范围。
2、所有开放式学习题属于选做作业,其他题目属于必做作业。
3、作业集的参考答案中部分题目以提供要点为限。
部分习题的详细答案请参见课件。
第一章:金融学导论1、为什么说金融与我们的生活息息相关,试举几个生活中与金融相关的例子。
答:金融不仅是宏观的金融系统的概念,同时也是与我们微观的经济主体紧密联系着的。
我们如果有资产需要投资,或者是需要借钱,这两种基本的行为都与金融有关。
举例如下:旅游与信用卡、电子商务与e 支付(淘宝网);投资渠道的多样性:股票基金国债;住房买车与按揭;2、金融学在国外被称为货币、银行与金融市场,那么为什么要研究货币?为什么要研究银行?为什么要研究金融市场?答:货币与商业周期、物价水平、通货膨胀、利率、货币政策都有紧密的关系。
银行作为金融体系的核心组成部分,为投资部门和储蓄部门的资金融通提供了中介桥梁,同时银行也是金融创新的源泉。
金融市场在金融系统中的比重越来越大,是直接融资的主要场所。
金融市场改变着个人的财富分配,影响着企业的行为,是资源配置的有效场所。
3、开放式学习题:我国近几年的宏观经济情况如何?近几年的金融总体运行情况如何?衡量宏观经济和金融运行情况一般采用哪些指标?答:我国近几年宏观经济的总体评价是:经济运行平稳,经济高速增长总量迅速增长,但通货膨胀有所抬头。
金融领域中以M1、M2 衡量的货币流动性较大,实际利率有时为负,同时外汇储备成为世界第一。
衡量宏观经济的指标一般有:GDP、GDP 增长率、城镇登记失业率、外商直接投资额、CPI 等。
衡量金融运行的主要指标:流动性(M1、M2)以及增长率、城镇居民储蓄余额、金融机构存贷款总额、人民币汇率、外汇储备总额、股市市值等。

第一题:Functions of the Bank of Finance England1)Bank to the government●The Bank of England maintains accounts on behalf of the government.●The main account is the Exchequer Account. Government receipts from taxation, borrowing.●The accounts of government departments are also held at the Bank of England.2)Banker to the banksHigh street banks keep hold of their cash reserves at the bank of England.The bank of England maintains a current account for banks for:●Operational balances for cleaning●Non-operational balances for cash deposit ratios●Special deposits from time to time3)Note issueNote issue in the UK is fiduciary. The Bank of England is the sole bank for note issue.4)Management of the national debt●The Bank of England's registrar's department continues to maintain a register of holders ofgilts.●The Bank of England is responsible for management the national debt since 1751 to 1998.●This responsibility has been passed to the DMO.5)Monetary policy implementationIt is responsible for the control of interest rates and money supply growth in the economy.6)Lender of Last ResortThis involves providing liquidity. This helps to stabilize the banking system. The bank of England must legally provide liquidity at all times.7)International relations●The Bank of England works closely with other central banks and provides services for them.●It is a member of various international financial institutions such as the InternationalMonetary Fund and has representation on committees of central banks.8)Managing the exchange equalization accountThe EEA was set up in 1932 to stabilize the value of sterling in relation to other currencies and consists of the country's gold and foreign currency.9)Private bankingThe Bank of England has limited number of old established private banking customers whose accounts were opened prior to nationalization in 1946,plus staff members' accounts.10)Open market operations●The main aim of the Bank of England's operations in sterling money markets is to meet theMPC'S interest rate decisions.●The buying and selling of government bonds on the open market by all bank of England.11)payment and settlement systems●The bank of England monitors trading, clearing and settlement systems relating to, e.g.:equities, bonds and exchange-traded derivatives.●The bank of England plays a critical role in payment and settlement systems by ensuringstability in the UK's clearing and settlement procedures.第二题:Credit cardsAll high street banks offer credit card facilities through either the VISA or MasterCard systems. The bank offer cardholders the opportunity to obtain goods and services on credit with the option of repaying the balance of the account in full without interest penalty or paying the balance in installments’, subject to payment of interest.(is sued for people transfer of funds between accounts. The banker automated Clearing System the computerized version of APACS allows automated transfer of wages and salaries, standing orders and direct debits, etc. for full details of the types of transactions that are effected an APACS and for details of its membership,第三题:How to raise money?●Companies raise fresh capital through the stock exchange, which brings lenders andborrowers together and encourages of those with funds to invest.●It satisfies the requirements of those in need of funds, whether government.Why issue the shares in the primary market?● A government or company wishing to raise money sells securities and receives money.●Companies issue stocks and shares. A stock refers to fixed interest securities that pay aguaranteed interest rate.● A listing will be sought on the listed market or the smaller, less regulated market known asthe alternative investment market.●Reasons for such issues vary but the main reason is to cover any anticipated budget deficitwhere government spending is expected to exceed income from taxes.第四题:Advantages and disadvantages of quotation/listingAdvantages:1.Personal guarantees of directors are not usually required for borrowing.2.Offering employees extra incentive by granting shares IPO option.3.It being a public company can provide customers and suppliers with added reassurance.4.The company may gain a higher public profile which can be good for business.5. A float makes it easier for company and other investors to realize your investment.Disadvantages:1.The cost of quotation can be substantial and there are also ongoing costs such as higherprofession fees.2.The company may have to give up some management control of the business and ultimatelythere is a risk that the company could be taken over.3.Managers could be distracted from running the business by the demands of the floatationprocess, and by dealing with investors.4.If the market conditions change during the quotation process you may have to abandon thequotation.5.The business may become vulnerable to market fluctuations which are outside your control.第五题:Negotiable CDs1.Negotiable CDs are certificates acknowledging deposit of funds, the ownership of which canbe transferred to third parties.2.These are guaranteed by the bank and can usually be sold in a highly liquid secondary market,but they cannot be cashed-in before maturity.3.They are issued at par and carry a rate of interest that is usually fixed for the life of thecertificate, although occasionally floating rate CDs are issued.4. A certificate of deposit with a minimum face value of $100,000.5.Payable to the bearer, which means that the owner’s name does not appear anywhere on thecertificate.6.Technically, a certificate can be transferred to a third party by simply delivering it by hand.7.Issued on terms of 3 months to 5 years8.For amounts usually ranging from 50,000 to 500,000 pounds.9.Dollar is the main non-sterling currency of denomination but other currencies are used aswell.10.Institutions often use these as a way to invest in a low-risk, low-interest security.11.Due to their large denominations, NCDs are bought most often by large institutionalinvestors.第六题:Options1)Call optionsA call option gives the buyer the right, in return for paying a premium, to buy a share at a predetermined price up to a specified date.An investor would buy a call option if he/she expected the market price of the share to rise.2)Put optionsA put option gives the buyer the right, in return for paying a premium, to sell a share at a predetermined price up to a specified date.An investor would buy a put option if he/she expected the market price of the share to fall. Futures:●If the investor buys the contract, he/she must take delivery.●If the investor sells the contract, he/she must make delivery.●If the investor wishes to avoid having to take or make delivery investor must close outinvestor position.●The primary difference between options and futures is that options give the holder the right tobuy or sell the underlying asset at expiration, while the holder of a futures contract is obligated to fulfill the terms of his/her contract.。

金融业导论期末1 other function of Bank of England(选择)[Note issue]Bank of England should ensure that there are sufficient banknotes circulating in the financial market, and whether the issued note could be accepted by public relies on people’s trust rather than backed by gold. And issue banknotes also be permitted in other seven banks in the UK expect Bank of England. Three of them are in Scotland, and the rest four are in Northern Ireland.[International Relations] It means Bank of England should work with other Central Banks in the world and services are provided for them. Except that, Bank of England also is a member of many international financial institutions such as the International Monetary Fund. [Private banking] Bank of England provide this service only limited to the accounts were opened before nati onalisation in 1946 and the staff members’ accountsMonetary stabilityMonetary stability means stable prices and confidence in the currency. To achieve these, Bank of England should support the government economic objectives which focussed on economic growth and employment.Price stability is an aspect of monetary stability, which means Bank should take actions to ensure stable price and confidence in sterling. The stable prices are defined by the government’s inflation target, which the Bank seeks to mee t through the decisions taken by the Monetary Policy Committee.Market division is a responsibility of Bank to implement the monetary policy decisions which taken by Monetary Policy Committee through take actions in the sterling and foreign exchange marketQuantitative easing is an unconventional form of monetary policy, it means effectively creates new money into the economy through buying financial assets, rather than printing new notes directly. Aim of this process is to increase private sector spending in the economy Financial stabilityThere are five main activities to achieve financial stability.[First is through the work of Financial Policy Committee]. There are two types of policy could be used to support its work, directions and recommendations. Directions means there are valid instructions to the Prudential Regulation Authority and Financial Conduct Authority as example to make financial institutions raise or lower the capitalization in their balance sheet. Recommendations means the requests that can be made to anybody requesting a change in legislation to support their activities. The institutions that are required have the right to opt not to do so, but they should explain the reasons for that.[Second is the Bank’s financial operation], acting as lender of last resort are included. But today the phrase of ‘lender of last resort’ is replace by word ’liquidity insurance’. That is the Bank of England Cash Ratio Deposit requirement, which means all organisations operate as a bank in the UK are required an account in the Bank of England.[Third is the regulation of the financial institutions by the Prudential Regulatory Authority.] The PRA is a part of England and it has responsibility to supervise banks, to build societies and credit unions, insurers and major investment firms.[Fourth is oversight of the payment, clearing and settlement processes in the UK.] The two main interbank systems are CHAPS and CERST, respectively. CHAPS is the same day electronic funds transfer system for high value or wholesale market payments in the UK. CREST is an all-encompassing communications system for UK securities transactions, and it also includes a settlement function.[Fifth is managing resolutions.] That means in terms of the failing institution, Bank will apply the published framework to manage the document of the problem.The role of the Merchant (investment) bank.There are four main roles of a merchant bank, including [new issues, setting up mezzanine finance arrangements, providing capitals through acceptance credit facilities and the treasury services].Merchant take actions as a bridge that links companies that wish to raise capitals through issuing shares to the public with those clients who want to make a large investment. As well as underwriting the issue, merchant bank will help with inscribing of the companies. Based on their understanding of the current situation of market and companies, Bank also will give suggestions to the company as to the timing for new issue.Mezzanine finance is a hybrid of debt and equity financing that is often used to finance the expansion of existing companies. Merchant bank will focus on the arrangement about the issue of the debt capital, and sometimes it might also provide the mezzanine finance.An acceptance credit is a type of letter of credit, which is a facility that allows a client of the merchant bank to issue a bill of exchange, drawn on the merchant bank to achieve the bill’s value as its pre-arranged one. The merchant bank accepts the bill and then the drawer can arrange to discount the bill either at the merchant bank or another bank so that they could receive the funds right now.In term of multinational companies, the Treasury services have become important. This service is provided to companies whose future cash management strategy has been agreed with the merchant bank. Bank will monitor all the real time information about the receipts and payments on company accounts as well as the global exchange rates and interest rates, and then take actions immediately based on the agreed strategy to maximise the benefits for the multinational company.2 The stock ExchangeThe stock exchange is a financial intermediary who provides a means to government, industry and investors so that the saving of personal and institutional investors can meet those who need capitals.It has four main functions: 1. It provides a market where ensures investors could buy or sell securities easily and quickly. 2. The UK stock systems help with the fairness of price at which a deal is done. 3. The ready secondary market makes it easier for bodies who want to raise capital to buy or sell stock quickly. 4. It allows the short-terms saving from pooling of investors to reach the companies who have long-term requirements. (The companies can raise capital at once on the first market, if there is no chance to do so, the investment can be happened on the secondary market.)The existence of regulation in the market is considered to be strength and a significant feature of the stock exchange. In this connection, the Financial Conduct Authority who applies strict conduct on business rules for all engaged in activities relating to dealing with securities supports The Stock Exchange a lot. And it is the regulation is carried out by the market that appealing more overseas investors invest in British.3.The ways company can enter the marketIntroduction: this method is suitable for companies whose aim is not to raise capital in the market. To do this the 25% of the company shares should in the public hands and the company’s aims is to help with the future marketability of their shares and increasing the visibility of the company to potential investors.Placing: this method is suitable the company who target particular institutional investors and is a most common method of listing at present. The merchant bank will advise the company arrange for the shares which have been transferred to public ownership to be placed with other institutions. The institutions will usually pay a discounted price than the shares would have been achieved on the market. Especially the small companies are advised to use this method to enter the market, because of the less cost and the higher control rights.Initial public offering: this method involves a wider offering to public and private investors, which is advised in the financial press and set up a closing date. Though offerings can be made by tender auctions, typically now the price is fixed before adverting. The bank leading as advisor will have underwritten the sale, guaranteeing that all the shares will be sled as they will take up any shares not sold.4.LIBOR ( London interbank offered rate)It is a benchmark rate that some of the world’s leading banks charge each other for short-term loans. LIBOR is administered by the ICE Benchmark Administration.1. LIBOE is an indication of the average daily rate at which contributor banks were able to borrow loans on an unsecured basis from other banks in the London interbank market. The data received from between 11 and18 contributor banks is the basis for calculation of the rate.2. Before 11.am London time contributor banks will be asked question as follow:‘At what rate could you borrow funds, were you to do so, by asking for and then accepting interbank offers in a reasonable market size?’3. LIBOR is based on the lowest rate the banks perceive they would be able to do trades at.4. LIBOR is based on major five currencies: Sterling, the US Dollar, the Euro, the Swiss Franc and the Japanese Yen.5. The LIBOR serves seven time periods which range from overnight to one year. Therefore there are 35 LIBOR rates in fact, rather than stands for a single rate.Derivatives markets5.FutureIt is a legally binding obligation to buy or sell a given quantity of a specified asset at a fixed price on a fixed future date. The assets can be financial or a range of products. Financial one including Foreign Exchange Future and the products can be cotton, copper, crude oil, etc. For example selling 1500 shares in Royal Bank of Scotland on 23 June 2018 at 82p each, it could be a future, i.e. whether the price of the shares over or below 82p on 23 June 2018, the future should be exercised at 82p each. That means if at that day the price has risen to 85p, the investor who hold the future will have lost out, vice versa. To reduce this risk, before the agreed date investor could sell the future to those who believe the share’s price will fall.Option It is a right to buy or sell a given quantity of an individual security at a fixed price and this option can be exercised at any time.A call option means the right for buyer to buy a share at a predetermined price up to a specified date, in return for paying a premium. And investor will buy the call option if he expected the market price of the share to riseA put option means the right to sell a share at a predetermined price up to a specified date, in return for paying a premium. Investors will buy this if he expected the share market price to fall.The seller of the option has to honour the commitment they wrote when the holder of the option exercises it, though the price is not advantageous for themThe buyer of the option will exercised the option when it is to their advantage, if not they will let it expire.。
引言概述:金融学作为一门重要的学科,探索了与货币、资本、投资和风险管理等相关的经济活动。
本文是对金融学导论作业的第二部分,将从五个大点阐述金融学的相关内容。
正文将探讨金融市场与金融机构、金融工具与金融交易、金融市场的效率、货币与利率以及金融风险管理。
正文内容:点一:金融市场与金融机构1.1.金融市场的定义与功能:介绍金融市场的概念及其重要性,包括资源配置、风险管理等功能。
1.2.主要的金融市场:介绍股票市场、债券市场、外汇市场等主要的金融市场的特点和运作方式。
1.3.金融机构的角色和职能:介绍商业银行、证券公司、保险公司等金融机构的角色和职能。
点二:金融工具与金融交易2.1.金融工具的分类:介绍金融工具的分类,包括股票、债券、期货、期权等不同类型的金融工具。
2.2.金融交易的概念与方式:介绍金融交易的概念,包括场内交易和场外交易等不同的交易方式。
点三:金融市场的效率3.1.弱式市场效率:介绍弱式市场效率的概念和假设,以及市场中信息的作用。
3.2.半强式市场效率:介绍半强式市场效率的概念和假设,以及投资者的行为与市场反应的关系。
3.3.强式市场效率:介绍强式市场效率的概念和假设,以及股票市场的例子。
点四:货币与利率4.1.货币的定义与特性:介绍货币的功能和特点,包括价值尺度、储藏手段、交换媒介等。
4.2.利率的概念与影响因素:介绍利率的概念,以及货币供给与需求、通货膨胀等因素对利率的影响。
点五:金融风险管理5.1.金融风险的种类与特点:介绍金融风险的种类,包括市场风险、信用风险、操作风险等,并分析其特点。
5.2.金融风险管理的方法:介绍风险管理的基本原则和方法,包括多元化投资、衍生品市场等。
总结:金融学导论作业的第二部分主要介绍了金融市场与金融机构、金融工具与金融交易、金融市场的效率、货币与利率以及金融风险管理等内容。
通过对这些内容的学习,我们可以更好地理解金融学作为一门学科的重要性和其在现代社会中的作用。
浙江大学远程教育学院《金融学》课程作业参考答案说明:1、作业的参考答案中部分题目以提供要点为限。
部分习题的详细答案请参见课件。
2、部分章节设置的【思考题】,不要求上交,也不提供标准答案,仅供学有余力的同学进一步思考并进行探索性学习。
第一章:金融学导论1、金融对于一个社会而言,其主要功能有哪些?答:金融的主要功能有:资金融通、转移风险。
此外还有切割股份、提供激励、价格发现等重要功能。
2、金融业的主要范畴包括哪些具体的业态?答:包括银行、证券(期货)、保险,还有一些新兴业态,比如互联网金融(金融科技)、融资租赁、股权投资等。
3、【思考题】:现有比例大约是直接融资20%,间接融资80%。
发展多层次资本市场,提高直接融资比重,有助于降低企业债务比率,并通过资本市场壮大自身实力,提升品牌。
第二章:货币、货币制度与信用1、名词解释:M0:流通中现金。
M1:流通在外的现金和活期存款M2:广义货币,大致包括现金+活期存款+定期存款。
CDs:可转让大额定期存单,是由美国花期银行 1961 年创造的一项金融工具。
CD 是在银行定期存款的凭据上注明存款金额、期限、利率,到期持有人提取本金和利息的一种债务凭证。
本票:是一个人向另一个人签发的,保证即期或定期或在可以确定的将来的时间,对某人或其指定人或持票人支付一定金额的无条件书面承诺。
汇票:是由出票人签发的,要求付款人在见票时或在一定期限内,向收款人或持票人无条件支付一定款项的票据。
消费信用:是由企业、银行或其他消费信用机构向消费者个人提供的信用。
消费信用根据提供商的不同可以分为企业提供的消费信用和银行提供的消费信用等种类。
其中由企业提供的消费信用主要有赊销和分期付款两种形式。
赊销主要是对那些没有现款或现款不足的消费者采取的一种信用出售的方式;而分期付款则更多地是运用于某些价值较高的耐用消费品的购买行为中。
2、简述货币的职能。
答:货币的职能:价值尺度、流通手段、贮藏手段、支付手段、世界货币。
金融学导论作业二 Document number:BGCG-0857-BTDO-0089-2022作业二:模拟联邦公开市场操作委员会运作姓名:梁变变学号:7任务内的目标:通货膨胀控制在2%左右,失业率控制在5%左右。
但在任调整利率是美联储宏期内出现过通胀压力,美元升值,通货紧缩等一系列问题。
游戏体会:经过与组内成员商讨,依据金融法律,通胀压力时我采用稳健的财政政策,通缩时采用积极的财政政策。
通过课程外的了解,发现实际的金融世界有复杂的经济原因,影响金融变动的原因非常多,而且各种原因会同时出现,作为决策保持经济稳定非常不易。
控制通货与信贷,运用公开市场业务,银行贷款贴现率和金融机构法定准备金率三大杠杆来调节美国经济。
调整利率是美联储宏观调控美国经济的主要手段。
如果经济过热,它就提高利率,收缩银根,使经济速度放慢,减少通货膨胀压力。
如果经济不景气,它就降低利率,放松银根,促使经济增长。
其关键是根据经济形势对利率提高和降低进行调控,并要恰到好处。
货币杠杆是美联储多年来对经济实施调控的最有效武器。
美联储调整利率不仅对美国经济举足轻重,对世界经济也有重要影响。
作为美国的中央银行,美联储从美国国会获得权利。
它被看作是独立的中央银行,因其决议无需获得美国总统或者立法机关的任何高层的批准。
它不接受美国国会的拨款,其成员任期也跨域多届总统及国会任期。
其财政独立是由其巨大的盈利保证的,主要归于其对政府公债的所有权。
它每年向政府返还几十亿。
当然美联储服从于美国国会的监督,后者定期观察其职务并通过法令来改变其职能。
同时,美联储必须在政府建立的经济和金融政策的总体框架下工作。
根据银行的性质不同,美国的金融监管实行的是联邦和州两级管理体制。
目前,美国共有8500多家银行,其中的2300多家事依美国联邦法注册成立的银行,其余的都是依据各州法律成立的银行。
依联邦法成立的银行都归美联储管理,而依据法律成立的银行中有1000多家申请成了联储成员,也归美联储监管,其余的归各州金融监管部门管理。
浙江大学远程教育学院《金融学》课程作业参考答案说明:1、作业的参考答案中部分题目以提供要点为限。
部分习题的详细答案请参见课件。
2、部分章节设置的【思考题】,不要求上交,也不提供标准答案,仅供学有余力的同学进一步思考并进行探索性学习。
第一章:金融学导论1、金融对于一个社会而言,其主要功能有哪些?答:金融的主要功能有:资金融通、转移风险。
此外还有切割股份、提供激励、价格发现等重要功能。
2、金融业的主要范畴包括哪些具体的业态?答:包括银行、证券(期货)、保险,还有一些新兴业态,比如互联网金融(金融科技)、融资租赁、股权投资等。
3、【思考题】:现有比例大约是直接融资20%,间接融资80%。
发展多层次资本市场,提高直接融资比重,有助于降低企业债务比率,并通过资本市场壮大自身实力,提升品牌。
第二章:货币、货币制度与信用1、名词解释:M0:流通中现金。
M1:流通在外的现金和活期存款M2:广义货币,大致包括现金+活期存款+定期存款。
CDs:可转让大额定期存单,是由美国花期银行 1961 年创造的一项金融工具。
CD 是在银行定期存款的凭据上注明存款金额、期限、利率,到期持有人提取本金和利息的一种债务凭证。
本票:是一个人向另一个人签发的,保证即期或定期或在可以确定的将来的时间,对某人或其指定人或持票人支付一定金额的无条件书面承诺。
汇票:是由出票人签发的,要求付款人在见票时或在一定期限内,向收款人或持票人无条件支付一定款项的票据。
消费信用:是由企业、银行或其他消费信用机构向消费者个人提供的信用。
消费信用根据提供商的不同可以分为企业提供的消费信用和银行提供的消费信用等种类。
其中由企业提供的消费信用主要有赊销和分期付款两种形式。
赊销主要是对那些没有现款或现款不足的消费者采取的一种信用出售的方式;而分期付款则更多地是运用于某些价值较高的耐用消费品的购买行为中。
2、简述货币的职能。
答:货币的职能:价值尺度、流通手段、贮藏手段、支付手段、世界货币。
作业二:模拟联邦公开市场操作委员会运作姓名:梁变变学号:7任务内的目标:通货膨胀控制在2%左右,失业率控制在5%左右。
但在任调整利率是美联储宏期内出现过通胀压力,美元升值,通货紧缩等一系列问题。
游戏体会:经过与组内成员商讨,依据金融法律,通胀压力时我采用稳健的财政政策,通缩时采用积极的财政政策。
通过课程外的了解,发现实际的金融世界有复杂的经济原因,影响金融变动的原因非常多,而且各种原因会同时出现,作为决策保持经济稳定非常不易。
控制通货与信贷,运用公开市场业务,银行贷款贴现率和金融机构法定准备金率三大杠杆来调节美国经济。
调整利率是美联储宏观调控美国经济的主要手段。
如果经济过热,它就提高利率,收缩银根,使经济速度放慢,减少通货膨胀压力。
如果经济不景气,它就降低利率,放松银根,促使经济增长。
其关键是根据经济形势对利率提高和降低进行调控,并要恰到好处。
货币杠杆是美联储多年来对经济实施调控的最有效武器。
美联储调整利率不仅对美国经济举足轻重,对世界经济也有重要影响。
作为美国的中央银行,美联储从美国国会获得权利。
它被看作是独立的中央银行,因其决议无需获得美国总统或者立法机关的任何高层的批准。
它不接受美国国会的拨款,其成员任期也跨域多届总统及国会任期。
其财政独立是由其巨大的盈利保证的,主要归于其对政府公债的所有权。
它每年向政府返还几十亿。
当然美联储服从于美国国会的监督,后者定期观察其职务并通过法令来改变其职能。
同时,美联储必须在政府建立的经济和金融政策的总体框架下工作。
根据银行的性质不同,美国的金融监管实行的是联邦和州两级管理体制。
目前,美国共有8500多家银行,其中的2300多家事依美国联邦法注册成立的银行,其余的都是依据各州法律成立的银行。
依联邦法成立的银行都归美联储管理,而依据法律成立的银行中有1000多家申请成了联储成员,也归美联储监管,其余的归各州金融监管部门管理。
和其他国家的中央银行一样,美联储的监管内容主要也是执照的核发,资本金的按比例存储,提交结算报告等。
成人高等教育金融学期末考试复习题及参考答案成人高等教育金融学期末考试复习题及参考答案课程名称:金融学年级:2019级(答案见卷后)一、单项选择题(本大题共 10 小题,每小题 3 分,共 30 分。
在每小题列出的备选项中只有一项是最符合题目要求的,请将其选出。
)1、有价证券的二级市场是指()。
A、货币市场B、证券发行市场C、资本市场D、证券转让市场2、科学的货币本质观是()。
A、货币金属说B、货币名目说C、马克思的劳动价值说D、国家发明创造说3、信用是()。
A、买卖关系B、赠予行为C、救济行为D、各种借贷关系的总和4、商业信用是企业之间由于()而相互提供的信用。
A、生产联系B、产品调剂C、物质交换D、商品交易5、()膨胀是引起财政赤字和银行信用膨胀的主要原因A、消费需求B、投资需求C、社会总储蓄D、社会总需求6、银行持有的流动性很强的短期有价证券是商业银行经营中的()A、第一道防线B、第二道防线C、第三道防线D、第四道防线7、银行在大城市设立总行,在本市及国内外各地普遍设立分支行的制度是()A、单一银行制B、总分行制C、持股公司制D、连锁银行制8、信用的基本特征()A、无条件价值单方面让渡B、以偿还为条件的价值单方面转移C、无偿的赠与或援助D、平等的价值交换9、金本位制下,()是决定两国货币汇率的基础A、货币含金量B、铸币平价C、中心汇率D、货币实际购买力10、专门向经济不发达会员国的私营企业提供贷款和投资的国际金融组织是()A、国际开发协会B、国际金融公司C、国际货币基金组织D、国际清算银行二、判断题(本大题共10小题,每小题2分,共20分)1、现金漏损与贷款余额之比称为现金漏损率,也称提现率。
()2、经济发展的商品化是货币化的前提与基础,但商品化不一定等于货币化。
()3、基准利率一般属于长期利率。
()4、暂时退出流通处于静止状态的货币,执行贮藏手段职能。
()5、按照管理方式不同,利率分为单利和复利两种。