ISO9001-2015不合格品处理程序(中英文)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:171.00 KB
- 文档页数:20

ISO/DIS 9001:2015质量管理体系—要求 Quality management system—Requirements目录 0 引言 (04)0.1 总则 (04)0.2 ISO标准的质量管理 (04)0.3 过程方法 (05)0.4 PDCA 循环 (06)0.5 基于风险的思维 (06)0.6 与其他管理体系标准的相容性 (06)1 范围 (08)2 规范性引用文件 (08)3 术语和定义 (08)4 组织的背景 (20)4.1 理解组织及其背景 (20)4.2 理解利益相关方的需求和期望 (20)4.3 确定质量管理体系的范围 (20)4.4 质量管理体系及其过程 (21)5 领导 (21)5.1 领导和承诺 (21)5.1.1 领导和质量管理体系承诺 (21)5.1.2 以顾客为关注焦点 (21)5.2 质量方针 (22)5.3 组织角色、职责和权限 (22)6 质量管理体系策划 (22)6.1 应对风险和机遇的措施 (22)6.2 质量目标及其实现策划 (23)6.3 变更策划 (23)7 支持 (23)7.1 资源 (23)7.1.1 总则 (23)7.1.2 人 (24)7.1.3 基础设施 (24)7.1.4 过程作业环境 (24)7.1.5 监视和测量资源 (24)7.1.6 组织的知识 (25)7.3 意识 (25)7.4 沟通..................................................... .................. .. (25)7.5 文件信息................................................... .................. (25)7.5.1 总则 (25)7.5.2 创建和更新............................................................... (26)7.5.3 文件信息控制....................................................... (26)8 运作........................................................................ . (26)8.1 运作策划和控制......................... .................. .. (26)8.2 产品和服务要求的确定 (27)8.2.1 顾客沟通............................................................... .. (27)8.2.2 与产品和服务有关的要求的确定................................... (27)8.2.3 与产品和服务有关的要求的评审 (27)8.3 产品和服务的设计与开发............................. .................. .. (27)8.3.1 总则 (27)8.3.2 设计和开发策划....................................... .. (28)8.3.3 设计和开发输入 (28)8.3.4 设计和开发控制 (28)8.3.5 设计和开发输出 (28)8.3.6 设计和开发变更 (29)8.4 外部供应产品和服务的控制 (29)8.4.1 总则 (29)8.4.2 外部供应的控制类型和程度 (29)8.4.3 外部供应商的信息 (29)8.5 产品和服务提供 (30)8.5.1 产品和服务提供的控制 (30)8.5.2 标识和可追溯性 (30)8.5.3 属于顾客或外部供应商的财产 (30)8.5.4 防护 (30)8.5.5 交付后活动 (30)8.5.6 变更控制 (31)8.6 产品和服务的放行 (31)8.7 不合格过程输出、产品和服务的控制 (31)9 绩效评价 (31)9.1 监视、测量、分析和评价 (31)9.1.2 顾客满意 (32)9.1.3 分析和评价 (32)9.2 内部审核 (32)9.3 管理评审 (33)10 改进 (33)10.1 总则 (33)10.2 不合格和纠正措施 (34)10.3 持续改进 (34)附录A(规范性附录)新结构、术语和概念的说明(省略) (35)附录B(规范性附录)质量管理原则(省略) (35)附录C(规范性附录)ISO10000 质量管理标准组合(略) (35)参考文献(省略) (35)0 引言 0.1 总则采用质量管理体系应该是组织的一项战略性决策。


ISO9001:2015质量管理体系要求原文翻译完全版1 范围本标准为有下列需求的组织规定了质量管理体系要求:a)需要证实其具有稳定地提供满足顾客要求和适用法律法规要求的产品和服务的能力;b)通过体系的的有效应用,包括体系持续改进的过程,以及保证符合顾客和适用的法律法规要求,旨在增强顾客满意。
注 1:在本标准一中,术语“产品”仅适用于:预期提供给顾客或顾客所要求的商品和服务;注 2:法律法规要求可称作为法定要求。
2 规范性引用文件下列文件中的条款通过本标准的引用而构成本标准的条款。
凡是注日期的引用文件,只有引用的版本适用。
凡是不注日期的引用文件,其最新版本(包括任何修订)适用于本标准。
ISO9000:2015 质量管理体系-基础和术语3 术语和定义本标准采用ISO9000:2015 中所确立的术语和定义。
4 组织的背景环境4.1 理解组织及其背景环境组织应确定哪些与其宗旨和战略方向有关且影响质量管理体系实现其预期结果的能力的外部和内部情况。
组织应监视和评审这外部和内部情况的信息。
注 1:事宜可能是正面和负面的因素或要考虑的情况注 2:理解外部的环境,可以通过考虑源于国际、国家、地区的或本地的法律法规、技术、竞争、市场、文化、社会和经济环境的情况,促进对外部情境的了解。
注3:理解组织内部环境,可以通过考虑与价值、文化、知识和组织绩效有关的情况,促进对内部情境的了解。
4.2 理解相关方的需求和期望:出于对组织持续地提供满足顾客和适用法律法规要求的产品和服务的能力的影响或潜在影响,组织应确定:a)与质量管理体系有关的相关方;b)与质量管理体系有关的相关方的要求。
组织应监视和评审有关相关方及其有关要求的信息。
4.3 确定质量管理体系的范围组织应界定质量管理体系的边界和应用,以确定其范围。
在确定此范围时,组织应考虑:a)标准 4.1 条款中提到的内部和外部情况;b)标准 4.2 条款中涉及的有关相关方的要求;c)组织的产品和服务。

ISO9001程序文件-中英文1.0目的:为确保质量管理体系持续有效运行,使其充分符合ISO9001:2000标准的要求,特制定本程序,以规定开展相应的审核活动,来评价本厂质量管理体系是否有效,是否需要采取纠正及预防措施。
Purpose: In order to ensure the effective and continuous implementation of the quality management, fully meet the requirements of ISO9001:2000 standard, specially make the procedure so as to implement audit action and verify the effectiveness of the quality management system and to take corrective or preventive action if needed.2.0 范围:本厂所开展的内部质量审核的全部活动均适用本程序。
Scope: applies to all the actions relating to internal quality audit.3.0 职责 Responsibility3.1 管理者代表:负责年度内审计划的拟定并计划组织实施。
Management Representative: responsible for the annual internal audit plan and its implementation.3.2 内审组长:负责制定审核日程并具体组织、指导内审作业。
Internal audit leader: responsible for making audi agenda and instructing audit.3.3 内审员:负责按审核计划要求对相关单位实施审核。

进料检验不合格品处理程序(ISO9001:2015)1目的制定组件进料检验发现的不合格品的处理办法,确保材料出现不合格时能有效及时的处理。
2范围本办法适用于公司IQC检验范围内所有不合格物料的处理。
3相关文件3.1不合格品控制程序4定义4.1不合格品:所有来料检验发现的不符合质量标准的原物料。
4.2退/换货:将不合格物料全部退回供应商或部分与供应商更换。
4.3特采:不合格物料因客户、生产需求急迫,客户或销售部代表客户同意授权,或投入后不影响产品功能、构造机能、特殊外观要求及应用功能性,不造成人身安全,可满足最终客户使用品质的不合格品做特殊接收的状态,等同让步接收。
4.4厂内挑选:经过协商,由公司相关部门代为厂商全检不合格品,挑选合格品投入生产,不合格品由采购部负责办理退/换货,并由厂商赔偿工时损失。
4.5供应商挑选:由供应商负责按照我司要求对不合格品进行全检(可派人员来我司进行挑选等)。
5职责5.1质量部(IQC):物料的检验及物料不合格的及时反馈。
5.2质量部(PQC):针对特采物料上线使用情况进行跟踪及数据统计。
5.3SQE:不合格物料的评审,联系供应商对已发现的不合格物料进行确认及推动改善。
5.4采购部:不合格物料的评审,联系供应商对不合格物料进行处理。
5.5PMC:物料安全库存的确认;及特采物料上线使用前的信息发布。
5.6工程部:负责对材料的安全性、功能性使用的影响进行评审判定,必要时实施相关实验。
5.7生产部:不合格物料的评审,在线不合格物料的及时提报,配合做好厂内挑选工作,确保合格品投入生产。
5.8仓库:不合格物料的分类存放。
5.9质量部:负责对不合格材料作出最终判定;6环境满足客户要求,符合行业标准7职业健康安全满足客户要求,符合行业标准8管理内容8.1特采原则8.1.1对产品的使用,确定安全性、公害性及功能性的顾虑原则,不致产生客户抱怨事件发生时。
8.1.2对产品功能及产品价值的影响很微小时。

ISO9001-2015客户退货处理程序(中英⽂)客户退货处理程序Customer Returned Product Handling(ISO9001:2015)1.0⽬的Purpose:对客户退货有效控制,并正确处理,为改善措施提供分析资源,⽤以指导⽣产。
To provide a system, handle customer returned products including the authorization, transfer and replacement, and find the root cause, to support thorough improvement action then get smooth process.2.0范围Scope:客户退货Customer returned goods3.0定义Definition3.1RMA: RMA is short for Return Material Authorization. 客户退货批准书3.2批退:指客户IQC检验不合格后,需整批⼀次退货量。
Returned batchsize: Means the quantity of once returned products from a customer IQC inspection non-conformity.3.3PM:Program Manager 项⽬经理3.4PA:Program Assistant 项⽬助理3.5QE:Quality Engineer 品质⼯程师3.6FQC: Final Quality Control终检3.7QD:Quality Department品管部3.8ME:Manufacturing Engineer制程⼯程师3.9ISF: Inventory Scrap Form. The form no is QF-PM-016. 报废单,表格编号为:QF-PM-0163.10RMA Area:Customer Return Area which is designated to place allcustomer returned products.客户退货区,专门⽤于存放客户退货。

ISO9001:2015一整套程序文件-英文版Procedure: [Change Mgmt Doc Title]1.0SUMMARY1.1.The purpose of this procedure is to define the methods for managing changes to processes andother aspects of the management system in a controlled manner.1.2.Where this document discusses changes to processes, this shall be understood to mean the top-level processes identified in the [Quality Manual Doc Title].1.3.The [who?] is responsible for implementation and management of this procedure.2.0REVISION AND APPROVAL3.0CHANGES TO PROCESSES3.1.Management system processes will undergo changes, typically when:3.1.1.Improvement opportunities have been identified, typically to improve processeffectiveness3.1.2.Nonconformities within a process are identified and require corrective action3.1.3.Conditions in the industry or company change, requiring a process to be updated3.1.4.New processes are added which impact on existing processes, requiring changes3.1.5.Customer requirements result in a need to change processes3.1.6.Any other reason determined by management3.2.In such cases, the process must be changed in a controlled manner to ensure properauthorization and implementation of the changes.3.3.At a minimum, process changes shall include the steps herein:3.3.1.The request for a process change shall be documented, typically in a [CAR Form Name]per the procedure [Corrective Preventive Action Proc. Title]. The justification for thechange shall be recorded.3.3.2.The change shall be reviewed by appropriate management, including the senior mostmanager responsible for the process. Changes must be approved prior toimplementation.3.3.3.The appropriate [Process Definition Doc Title] will be updated to reflect the change.This document will undergo review and approval per the procedure [Control ofDocuments Proc. Title]. The revision indicator of the [Process Definition Doc Title]will be incremented, and the nature of the change recorded. [ Delete last sentenceif you are not using Process Definition documents.]3.3.4.The follow-up verification step of the [CAR Form Name] process shall seek to ensurethe change has had the intended effect, and/or has improved the process. If not, thechange may be rolled back or a new change made to correct any new issues that ariseas a result of the change.4.0CHANGES TO DOCUMENTATION4.1.Management system documents undergo changes when there is a need to revise them.4.2.Changes to documentation are done in accordance with the procedure [Control of DocumentsProc. Title].5.0CHANGES TO ORDERS OR CONTRACTS5.1.Changes to active orders or contracts may occur when the customer changes the requirementsafter the work has begun, or may be initiated by [Short Client Name] when unforeseencircumstances are encountered.5.2.Changes to orders or contracts are done in accordance with the procedure [Quoting and OrdersDoc Title].Procedure: [Identification & Traceability Proc. Title]1. SUMMARY1.1. This procedure defines the methods used to identify and (where applicable) provide uniquetraceability for [Short Client Name] products. This procedure includes methods:1.1.1. To define the methods for identifying products (what they are)1.1.2. To define the methods for identifying products as to their current inspection or teststatus1.1.3. To define the methods for segregating and discriminating between product andtooling when their appearance is similar1.1.4. To define the methods for providing traceability, including unique serialization, orproduct as applicable1.2. The [who?] is responsible for implementation and management of this procedure.2. REVISION AND APPROVAL3. APPLICATION3.1. This procedure applies to all departments which use, handle, transport, store, inspect ormanufacture product, raw materials and tooling, at all [Short Client Name] facilities.3.2. This procedure not only applies to typical product, but also deliverables from services, such asreports, schedules, etc.3.3. Non-critical materials or supplies, which are not incorporated into final product or which serveonly to support facilities or operations, are not subject to this procedure.4. DEFINITIONS4.1. Product4.1.1. “Product” includes any of the following:∙Any part, assembly or item ordered by the customer∙Deliverable reports or documents∙Product may refer to finished product, or work in process (WIP)4.2. Raw Materials4.2.1. “Raw materials” include any of the following:∙Any materials or items (metals, plastics, components, pre-built assemblies, small parts) which become part of the finished product’s physical construction; some ofthese items may sometimes be referred to as “consumables”.∙Coatings, paint, plating, adhesives, chemicals or materials which will be incorporated into (or onto) the final product.4.3. Tooling4.3.1. “Tooling” can include any of the following:∙Devices used by manufacturing for setup or production, including fixtures and jigs.∙Devices used by inspection for determining acceptance of product, including test fixtures.∙Shop aids, which are simple devices (blocks, spacers, shapes) used to assist in production or development, but which are not precision tools and which can be usedfor a variety of applications.4.3.2. Tooling does not include:∙Cutting tools, drill bits, etc.∙Hand tools∙Machining equipment5. PRODUCT5.1. There are many ways to identify product; this procedure presents the most typical, acceptablemethods. Additional product identification methods may be called out in the design orproduction documentation.5.2. Identification typically includes the part number, revision, Work Order # and unique serialnumber (if applicable).5.3. Identification is done through any of the following methods:5.3.1. Part marking, by way of ink marking, etching or some other method.5.3.2. Bag-and-tag methods, especially for small parts.5.3.3. Placement of parts on shelves or in containers that are properly marked, withsignage or other methods.5.3.4. Placement of parts near associated paperwork, for the purpose of identification andtraceability, may be used if the paperwork can clearly be identified as relating to theparts in question, typically by way of the inclusion of a drawing which can becompared to the product.5.3.5. Segregating entire areas of the production floor with belt stanchions and attachedsignage, indicating what type of items are allowed, or disallowed, within theenclosed area.5.4. Where unique serialization is required for traceability, the parts shall be identified with a serialnumber in accordance with customer requirements, or in a manner developed to ensure that no two parts are given the same number. Serial number logs may be used to control this; workorders shall reference the serial numbers under which the unique parts were built.5.5. All product may be assumed to be inspected and/or tested and found to be acceptable for useif identified in accordance with the rules above, unless it is marked as nonconforming product.For the methods of identifying nonconforming product, see procedure [Control of NCP Proc.Title].6. RAW MATERIALS6.1. Raw materials requiring traceability back to heat lot numbers, manufacturer lot or batchnumbers, certificates of conformity or analysis, etc., must be marked in a way that provides this traceability. This is typically done by marking the raw materials with the [Short Client Name]purchase order number under which the items were purchased, and the supplier’s lot number.6.2. When raw materials are used, any remaining material that will be returned to stock and used inthe future must be re-identified before re-entry into inventory.6.3. Raw materials which are determined to require identification and traceability, but which lacksuch identification, may not be used for flight hardware. These may be used for tooling stock or other non-product purposes.6.4. All raw materials may be assumed to be inspected and/or tested and found to be acceptable foruse if identified in accordance with the rules above, unless it is marked as nonconforming. For the methods of identifying nonconforming raw materials, see procedure [Control of NCP Proc.Title].7. PRODUCTION TOOLING7.1. Tooling used for production (fixtures, molds, jigs, setup devices, product supports or stands,etc.) shall be designed and built according to engineering data, and then validated to ensurethe tool performs the intended function without risk or harm to product. Validation of tooling istypically done by using the tooling and inspecting the resulting parts to ensure the toolingresults in parts that meet dimensional or other requirements.7.2. Once validated and approved for use, the tool will be marked with a tooling ID number, which istypically the part number for which the tool is to be used.7.3. Tools that produce production hardware or are used to accept hardware must undergoinspection before release. [QC or QA Preferred Term] must stamp or mark the tool as accepted before it can be used.7.4. Shop aids for setup of production operations, supporting a part temporarily, or other simple ortemporary use, may not require identification with a unique identifier. Instead, these must beidentified as tooling by either marking the item itself as “TOOLING” (or similar language) orplacement in an area, shelf, cabinet or other container that is properly marked as “TOOLING”or “SHOP AIDS”(or similar language). T he marking must allow tooling to clearly bedistinguished from raw material or product (whether flight or development).7.5. Tooling used for lifting shall be proof load tested and include an upper load lift limit, as requiredby regulations.7.6. Tooling found to be nonconforming shall be tagged to prevent use until fixed, repaired ordeemed acceptable. Segregation of nonfonconforming tooling from the production area shouldbe performed when possible.7.7. When approved tooling undergoes modification, the identification must be updated to reflect thechange; this is typically done by editing or re-marking the item with the latest revision of theengineering part number.8. SERVICE DELIVERABLES (← delete if not applicable)8.1. Service deliverables, such as reports and schedules, shall be identified with a title and, ifapplicable, reference to the project or contract under which they are developed.8.2. Customer contracts may indicate additional methods for identification of service deliverables.8.3. In all cases, the deliverable will be identified in a way that makes it clearly understood forwhich contract or project the deliverable is subject to.8.4. As required, service deliverables may be subject to date and revision control, to distinguishearlier versions or submittals.9. STAMP CONTROL (← delete this section if QC stamps are not used)9.1. Quality stamps or employee initials are used to indicate product acceptance or for other quality-related notations. Individual authorities for signing off for inspection, testing and operations aredefined on the Stamp & Signature Control Log; this log is maintained to identify the owner of each stamp.9.2. The [who?] shall maintain the Stamp and Signature Control Log.9.3. Stamps are numbered, and taken out of service for six months after an employee leaves thecompany; after the six-month period, the stamp may be reissued to a different employee.9.4. No employee may use any stamp except that which was issued to them.。
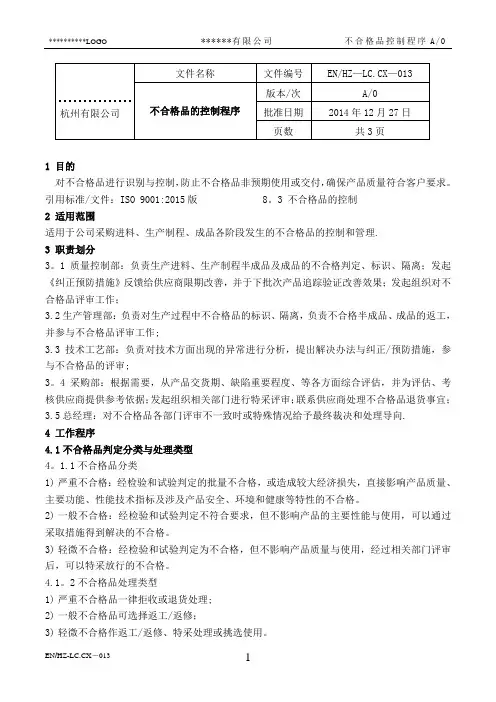
1 目的对不合格品进行识别与控制,防止不合格品非预期使用或交付,确保产品质量符合客户要求。
引用标准/文件:ISO 9001:2015版 8。
3 不合格品的控制2 适用范围适用于公司采购进料、生产制程、成品各阶段发生的不合格品的控制和管理.3 职责划分3。
1质量控制部:负责生产进料、生产制程半成品及成品的不合格判定、标识、隔离;发起《纠正预防措施》反馈给供应商限期改善,并于下批次产品追踪验证改善效果;发起组织对不合格品评审工作;3.2生产管理部:负责对生产过程中不合格品的标识、隔离,负责不合格半成品、成品的返工,并参与不合格品评审工作;3.3技术工艺部:负责对技术方面出现的异常进行分析,提出解决办法与纠正/预防措施,参与不合格品的评审;3。
4采购部:根据需要,从产品交货期、缺陷重要程度、等各方面综合评估,并为评估、考核供应商提供参考依据;发起组织相关部门进行特采评审;联系供应商处理不合格品退货事宜;3.5总经理:对不合格品各部门评审不一致时或特殊情况给予最终裁决和处理导向.4 工作程序4.1不合格品判定分类与处理类型4。
1.1不合格品分类1)严重不合格:经检验和试验判定的批量不合格,或造成较大经济损失,直接影响产品质量、主要功能、性能技术指标及涉及产品安全、环境和健康等特性的不合格。
2)一般不合格:经检验和试验判定不符合要求,但不影响产品的主要性能与使用,可以通过采取措施得到解决的不合格。
3)轻微不合格:经检验和试验判定为不合格,但不影响产品质量与使用,经过相关部门评审后,可以特采放行的不合格。
4.1。
2不合格品处理类型1)严重不合格品一律拒收或退货处理;2)一般不合格品可选择返工/返修;3)轻微不合格作返工/返修、特采处理或挑选使用。
4。
2 进料不合格品的管理4.2.1进料检验不合格品的标识、隔离、记录进料报检后,质控部IQC检验员根据对应来料检验标准(规范)、包装文件及图纸等文件进行抽检(样)/检验,对出现的不合格品用红色不良标签进行标识并隔离,并在检验报告注明:异常现象、抽检比例、不良数、检验人员名称及检验日期等要点;标识完成后,及时将不合格品隔离,(或通知相关部门/人员搬运到不合格品放置区域);做好不合格品记录备注,出具IQC检验报告交由部门负责人审核确认,在检验报告中需要体现:不良现象描述(简洁明了,必要时可以照片记录)、抽检比例等关键要素。

不合格品处理流程英文Nonconforming Product Handling Procedure.Purpose.The purpose of this procedure is to establish a consistent and effective process for handling nonconforming products to prevent their unintentional use or release.Scope.This procedure applies to all nonconforming products, including raw materials, components, subassemblies,finished goods, and services.Definitions.Nonconforming product: A product that does not meet specified requirements.Hold: To prevent the use or release of a product until its disposition is determined.Disposition: The final determination of what to do with a nonconforming product.Procedure.1. Identification and Hold.Nonconforming products shall be identified and immediately placed on hold to prevent their unintentional use or release.The hold shall be clearly marked and labeled with the reason for the nonconformance.2. Investigation.An investigation shall be conducted to determine the cause of the nonconformance.The investigation shall be documented, including the date, time, product description, nonconformance details, and corrective actions taken.3. Disposition.The disposition of the nonconforming product shall be determined based on the severity of the nonconformance and the potential risk to the end user.Possible dispositions include:Rework: The product can be repaired or reworked to meet specifications.Scrap: The product cannot be repaired or reworked and must be discarded.Return to supplier: The product is returned to the supplier for credit or replacement.Use-as-is: The product can be used as-is, with thecustomer's knowledge and approval, if the nonconformance does not affect the intended use of the product.4. Documentation.All actions taken regarding the nonconforming product shall be documented, including:Identification of the product.Date and time of hold.Investigation findings.Disposition of the product.Corrective actions taken.5. Corrective Action.Corrective actions shall be taken to address the root cause of the nonconformance and prevent its recurrence.Corrective actions may include:Revising specifications or design.Improving manufacturing processes.Training employees.Implementing new inspection or testing methods.6. Release.Nonconforming products that have been repaired or reworked and meet specifications shall be released for use.The release shall be documented and approved by authorized personnel.Responsibilities.Production staff: Identify and hold nonconformingproducts.Quality control staff: Investigate nonconformances and determine dispositions.Management: Ensure the implementation and effectiveness of the procedure.All employees: Comply with the procedure and report any nonconformances.Forms and Records.Nonconformance Report.Investigation Report.Disposition Report.Revision History.Version 1.0: Initial release.Version 1.1: Updated to include use-as-is disposition.Version 1.2: Added requirement for management approval of release.。

strategicdirection of the organization. Management of theprocesses and the system as a whole can be achieved using thePDCA cycle (see 0.3.2) with an overall focus on risk-basedthinking (see 0.3.3) aimed at taking advantage of opportunitiesand preventing undesirable results.The application of the process approach in a quality managementsystem enables:a) understanding and consistency in meeting requirements;b) the consideration of processes in terms of added value;c) the achievement of effective process performance;d) improvement of processes based on evaluation of data andinformation.Figure 1 gives a schematic representation of any process andshows the interaction of its elements. The monitoring andmeasuring check points, which are necessary for control, arespecific to each process and will vary depending on the relatedrisks.Figure 1 — Schematic representation of the elements of asingle process0.3.2 Plan-Do-Check-Act cycleThe PDCA cycle can be applied to all processes and to the qualitymanagement system as a whole. Figure 2 illustrates how Clauses4 to 10 can be grouped in relation to the PDCA cycle.NOTE Numbers in brackets refer to the clauses in this International维(见0.3.3)对过程和整个体系进行管理,旨在有效利用机遇并防止发生不良结果。

FINAL DRAFTISO/TC 176/SC 2 Secretariat: BSI Voting begins on:20150709 Voting terminates on:20150909RECIPIENTS OF THIS DRAFT ARE INVITED TOSUBMIT, WITH THEIR COMMENTS, NOTIFICATION OF ANY RELEVANT PATENT RIGHTS OF WHICH THEY ARE AWARE AND TO PROVIDE SUPPOR TING DOCUMENTATION.IN ADDITION TO THEIR EVALUATION AS BEING ACCEPTABLE FOR INDUSTRIAL, TECHNOLOGICAL, COMMERCIAL AND USER PURPOSES, DRAFTINTERNATIONAL STANDARDS MAY ON OCCASION HAVE TO BE CONSIDERED IN THELIGHT OF THEIR POTENTIAL TO BECOMESTANDARDS TO WHICH REFERENCE MAY BE MADE IN NATIONAL REGULATIONS.INTERNATIONAL ISO/FDISSTANDARD 9001Quality management systems — RequirementsSystèmes de management de la qualité — ExigencesPlease see the administrative notes on page iii质量管理体系 要求ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)ii© ISO 2015 – All rights reservedISO/CEN PARALLEL PROCESSINGThis final draft has been developed within the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and processed under the ISO-lead mode of collaboration as defined in the Vienna Agreement. The final draft was established on the basis of comments received during a parallel enquiry on the draft. This final draft is hereby submitted to the ISO member bodies and to the CEN member bodies for a parallel two-month approval vote in ISO and formal vote in CEN. Positive votes shall not be accompanied by comments.Negative votes shall be accompanied by the relevant technical reasons.COPYRIGHT PROTECTED DOCUMENT© ISO 2015, Published in SwitzerlandAll rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, no part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized otherwise in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, or posting on the internet or an intranet, without prior written permission. Permission can be requested from either ISO at the address below or ISO’s member body in the country of the requester.ISO copyright officeCh. de Blandonnet 8 • CP 401CH-1214 Vernier, Geneva, Switzerland Tel. +41 22 749 01 11 Fax +41 22 749 09 47copyright@ ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)© ISO 2015 – All rights reservediiiContents 目录Foreword 前言0 Introduction 引言0.1 General 总则0.2 Quality management principles 质量管理原则0.3 Process approach 过程方法0.4 Relationship with other management system standards 与其他管理体系标准的关系1 Scope 范围2 Normative references 规范性引用文件3 Terms and definitions 术语和定义4 Context of the organization 组织环境4.1 Understanding the organization and its context 理解组织及其环境4.2 Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties 理解相关方的需求和期望4.3 Determining the scope of the quality management system 确定质量管理体系的范围4.4 Quality management system and its processes 质量管理体系及其过程5 Leadership5.1 Leadership and commitment 领导作用和承诺5.1.1 General 总则5.1.2 Customer focus 以顾客为关注焦点5.2 Policy 方针5.2.1 Developing the quality policy 制定质量方针5.2.2 Communicating the quality policy 沟通质量方针5.3 Organizational roles, responsibilities and authorities 、职责和权限组织的岗位领导作用ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)6 Planning for the quality management system 质量管理体系策划6.1 Actions to address risks and opportunities 应对风险和机遇的措施6.2 Quality objectives and planning to achieve them 质量目标及其实现的策划6.3 Planning of changes 变更的策划7 Support 支持7.1 Resources 资源7.1.1 General 总则7.1.2 People 人员7.1.3 Infrastructure 基础设施7.1.4 Environment for the operation of processes 过程运行环境7.1.5 Monitoring and measuring resources 监视和测量资源7.1.6 Organizational knowledge 组织的知识7.2 Competence 能力7.3 Awareness 意识7.4 Communication 沟通7.5 Documented information 形成文件的信息7.5.1 General 总则7.5.2 Creating and updating 创建和更新7.5.3 Control of documented information 形成文件的信息的控制8 Operation 运行8.1 Operational planning and control 运行的策划和控制8.2 Determination of requirements for products and services 产品和服务要求的确定8.2.1 Customer communication 顾客沟通8.2.2 Determination of requirements related to products and services与产品和服务有关的要求的确定8.2.3 Review of requirements related to products and services与产品和服务有关的要求的评审8.2.4 Change to requirements for products and services 产品和服务要求的更改iv© ISO 2015 – All rights reservedISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)8.3 Design and development of products and services 产品和服务的设计和开发8.3.1 General 总则8.3.2 Design and development planning 设计和开发策划8.3.3 Design and development Inputs 设计和开发输入8.3.4 Design and development controls 设计和开发控制8.3.5 Design and development outputs 设计和开发输出8.3.6 Design and development changes 设计和开发更改8.4 Control of externally provided processes, products and services外部提供过程、产品和服务的控制8.4.1 General 总则8.4.2 Type and extent of control 控制类型和程度8.4.3 Information for external providers 外部供方的信息8.5 Production and service provision 生产和服务提供8.5.1 Control of production and service provision 生产和服务提供的控制8.5.2 Identification and traceability 标识和可追溯性8.5.3 Property belonging to customers or external providers 顾客或外部供方的财产8.5.4 Preservation 防护8.5.5 Post-delivery activities 交付后的活动8.5.6 Control of changes 更改控制8.6 Release of products and services 产品和服务的放行8.7 Control of nonconforming process outputs 不合格输出的控制9 Performance evaluation 绩效评价9.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation 监视、测量、分析和评价9.1.1 General 总则9.1.2 Customer satisfaction 顾客满意9.1.3 Analysis and evaluation 分析与评价9.2 Internal audit 内部审核© ISO 2015 – All rights reserved vISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)9.3 Management review 管理评审9.3.1 General 总则9.3.2 Management review input 管理评审输入9.3.3 Management review output 管理评审输出10 Improvement 改进10.1 General 总则10.2 Nonconformity and corrective action 不合格和纠正措施10.3 Continual improvement 持续改进Annex A (informative) Clarification of new structure, terminology and concepts附录A(资料性附录)新结构、术语和概念说明Annex B (informative) Other International Standards on quality management and qualitymanagement systems developed by ISO/TC176附录B(资料性附录)ISO/TC176 开发的其他有关质量管理和质量管理体系的国际标准Bibliography 参考文献vi© ISO 2015 – All rights reservedISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E) Foreword 前言ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of national standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work of preparing International Standards is normally carried out through ISO technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject for whicha technical committee has been established has the right to be represented on that committee.International organizations, governmental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.The procedures used to develop this document and those intended for its further maintenance are described in the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 1. In particular the different approval criteria needed for the different types of ISO documents should be noted. This document was drafted in accordance with the editorial rules of the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 2 (see /directives).Attention is drawn to the possibility that some of the elements of this document may be the subject of patent rights. ISO shall not be held responsible for identifying any or all such patentrights. Details of any patent rights identified during the development of the document will be in the Introduction and/or on the ISO list of patent declarations received (see /patents).Any trade name used in this document is information given for the convenience of users and does not constitute an endorsement.For an explanation on the meaning of ISO specific terms and expressions related to conformity assessment, as well as information about ISO’s adherence to the World Trade Organization (WTO) principles in the Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) see the following URL:/iso/foreword.html.The committee responsible for this document is Technical Committee ISO/TC 176, Quality management and quality assurance, Subcommittee SC 2, Quality systems.This fifth edition cancels and replaces the fourth edition (ISO 9001:2008), which has been technically revised, through the adoption of a revised clause sequence and the adaptation of the revised quality management principles and of new concepts.© ISO 2015 – All rights reserved viiISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)viii© ISO 2015 – All rights reservedIntroduction 引言0.1 General 总则The adoption of a quality management system is a strategic decision for an organization that can help to improve its overall performance and provide a sound basis for sustainable development initiatives.采用质量管理体系是组织的一项战略决策,能够帮助其提高整体绩效,基础。
Procedure: [Control of Nonconforming Service Proc Title]1.0SUMMARY1.1.This procedure defines the requirements for identifying, processing and dispositioningnonconforming service.1.2. Nonconforming service can be discovered at any time, by any person or organization, includingemployees, the customer, regulatory authorities, etc.1.3.The [who?] is responsible for implementation and management of this procedure.2.0REVISION AND APPROVAL3.0DEFINITION3.1.“Nonconforming service” is any service provided to customers which is found to not conform torequirements. These requirements may be customer requirements, statutory/regulatoryrequirements, or any other requirement deemed by [Short Client Name].4.0CONTROLLING NONCONFORMING SERVICES4.1.When nonconforming services are discovered by employees, this shall be documented on theNonconforming Service Report (NSR). If the nonconforming service is reported by a third party,including a customer, the appropriate employee shall capture the information provided by thethird party on the Nonconforming Service Report, including referencing any applicable notes,emails, or other documentation.4.2.The Nonconforming Service Report is sent to the [who?] for review and initial confirmation of thenonconformance. If it is determined the nonconformance did not occur, this can be noted andthe NSR closed without further action. If the issue is confirmed, the procedure shall continue.4.3.The [who?] shall then document details of the NSR and conduct a root cause analysis, utilizingother personnel and resources as necessary. The [who?] may delegate this responsibility, ifneeded.4.4.The [who?] will then oversee a disposition of the nonconforming service. This may include arefund, providing new services, providing corrected services, or other actions. All such actionsshall be documented on the NSR form.4.5.If customer approval is sought for the disposition, this shall be recorded on the NSR; if thecustomer approval is provided in another document or email, this shall be reference on the NSRinstead.5.0NONCONFORMANCE DATA ANALYSIS & TRENDING5.1.The [who?] will present service quality trend data to top management as part of periodicManagement Review Meetings.。
成品出货检验及不合格品控制程序(ISO9001:2015)1 目的规范对最终产品的检验及不合格品的控制,确保出货产品品质,满足客户要求.2 适用范围适应于公司所有的成品出货检验及不合格品控制.3 定义无4 职责4.1 生产部拉长: 提交产品供QA检验,安排产品入库;对QA检验不合格批进行返工;对库存产品超过一个月的成品安排全检。
4.2 品质部QA: 对生产出来的成品进行检查,对库存超过有效储存期的产品进行出货前复检,对改善批抽验结果跟踪,监督检验合格产品的入库。
4.3 仓库:对合格产品按照要求进行入库储存;出货前对超过有效储存期的产品进行提出复检.4.4 工程部PE:对QA检查出的不良品进行分析,提供返工方案和改善预防措施.5 作业内容见第3页到第6页页流程图及作业内容6 相关文件《QA作业指导书》7 记录表单《送检单》《出货检验报告》《成品复检通知单》《成品不合格批处理单》流程图及说明作业流程作业内容职能部门 相关表单1.报检生产部将生产好的产品以适当批量,开出《送检单》,交给QA 检验.生产需在送检单上注明产品出货的紧急状态,如未注明则不属于紧急。
生产部《送检单》2.检查QA 根据送检的产品找出对应的资料(如合同评审单\规格书等),依据《QA 作业指导书》对产品进行检验,将检查结果记录在《出货检验报告》中。
检验判定结果分为合格于不合格,具体内容见第3,6点内容品质部《出货检验报告》3.判定合格QA 判定为合格的批次,对箱中的数量进行清点,并通知拉长进行封箱称重,QA 在外箱贴上合格标签。
品质部\4.入库拉长清点数量后将产品入库。
生产部\5.合格产品出货5.1仓管员按照出货计划进行出货,出货前检查产品是否超出储存期,如没有超出储存期则可进行出货. 5.1.1数码电池\笔记本电池\移动电源储存期限:1个月抽样复检,2个月全检性能\外观,容量抽检;5.1.2充电器\相机手柄储存期限:3个月复检,6个月全检性能5.2超期时申请复检如成品超出储存期限,仓管员需开出《成品复检通知单》通知生产\PMC\品质安排复检,复检后送QA 进行抽样检查仓库仓库、生产、PMC 、品质部《成品复检通知单》报检OK贴合格标签入库 出货是否超出存储期限N申请复检Y检查NG。
最终检验及不合格品控制程序(ISO9001:2015)1目的规范对最终产品的检验及不合格品的控制,确保出货产品品质,满足客户要求。
2适用范围适用于公司所有成品出货的检验、不合格品的控制及特采。
3定义评审部门:由品质部/QE、销售部/跟单、工程部/PIE、工程部/工程师、PMC及生产共同组成。
特采:通过书面申请,经过相关评审部门严格评审,批准使用或放行不符合规定要求的产品,是处理不合格品方法之一,该方法不能作为以后类似产品让步接收的先例。
4职责4.1品质部:QA检验员:对生产出来的成品进行检查,对库存超过有效储存期的产品进行出货前复检,对改善批抽验结果跟踪,监督检验合格产品的入库。
QE:对特采产品进行判定评估确认是否需要客户确认,与客户沟通并提供评审意见,对评审的最终结果进行判定。
4.2PIE部:PE:负责对QA检验出的不良品进行分析,提供该批返工方案及预防改善措施.4.3仓库仓管员:对合格产品入库并按要求储存;在出货前对超过有效储存期的产品提出复检。
4.4生产部:组长:提交产品供QA检验,安排合格产品入库;对同意特采的产品安排入库,对QA检验不合格批进行返工.4.5营销中心:营业员:同客户沟通确认,填写评审意见。
4.6工程部:产品在试产阶段特采,同客户沟通确认,填写评审意见。
如有需要,须参加量产阶段特采评审。
4.7副总经理:对特采产品最终结果进行批准。
5工作流程图及流程说明5.1工作流程图见第3页《最终检验及不合格品控制流程图》。
5.2流程说明见第4-6页。
6支持及引用文件6.1《产品交付管理规定》6.2《仓库管理规定》6.3《QA岗位作业流程》7记录表单不合格批处理单。
不合格品管理程序(中英文)不合格品管理程序NONCONFORMING PRODUCT MANAGEMENT PROCEDURE (ISO9001:2015)1. purpose目的为有效地杜绝不合格的物料、半成品及成品的误用、流出; 并对其予以恰当处理.To avoid nonconforming materials, semi-finished products and finished products from misuse andOutflow, and dispose them properly.2. scope范围适用于不同阶段的产品及物料:如进料、制程、成品、库存及客户退货. Applicable for material and products in different level: Incoming, process, finished goods, stock and customer returns.3. Reference Document参考文件3.1《MRB运作程序》MRB operation procedure3.2《记录管理程序》Record control procedure3.3《进料品质控制程序》Incoming quality control procedure3.4《过程质量控制程序》Process quality control procedure3.5《出货质量控制程序》Outgoing quality control procedure3.6《纠正与预防措施管理程序》Corrective and preventive action management procedure3.7《产品标识及追溯性管理程序》Product identification and traceability managementprocedure4. Definition定义4.1 合格:满足要求.Conforming: Satisfy the requirement4.2 不合格:未满足要求.Nonconforming: Disatisfy the rewuirement.5. Responsibility职责5.1 品质部:负责对不合格原料及成品的检验判定及标识。
物料评审程序Material Review Board (MRB)(ISO9001:2015)1.PURPOSE 目的:To establish a procedure for reviewing and disposingnon-conforming materials, semi-product, finished products and RMA control in DXC.本程序规定对来料检验及生产过程中发现的不合格物料,半成品,成品及客户退回品的评审及处置方法.2.SCOPE 范围:This procedure is only applicable to DXC.本程序适用于DXC公司.3.DEFINITIONS 定义:3.1 PRD: Product Department 生產部3.2 ME: Manufacture Engineering 制造工程3.3 RTV: Return To Vendor/Supplier 退回供應商3.4 UAI: Use As It Is 讓步接受3.5 SORT: Segregation Of Bad And Good Unit 選用3.6 SCAR Supplier/Sub-contractor Corrective Action Request (8D) 供應商改進行動要求 (8D)3.7 GRN: Goods Receipt Note 收货单3.8 MRR: Material Review Record 物料评审记录4.REFERENCE DOCUMENT 参考文件:4.1 DXC-7-05 Raw Material Quality Control Procedure原材料质量控制程序4.2 DXC-8-05 Nonconforming Control Procedure 不合格品控制程序4.3 DXC-8-06 Stop Shipment and Purge Order Procedure 停止出貨和清除指令程序.4.4 DXC-8-07 Corrective and Preventive Actions Procedure 纠正及预防措施程序.5.RESPONSIBILITY 职责:5.1 QA is responsible to chair MRB meeting when defective materialare defected in line, QA review the non-conforming productsand issue SCAR (8D) if necessary.当不合格物料在产线发现时,QA负责主持MRB会议, 确认不合格产品, 并在必要的情况下发出SCAR(8D).5.2 PRD is responsible to fill MRB label and inform QA membersto review the non-conforming products, and return them to warehouse.生产部负责填写MRB标签并通知品质部成员评审不合格品, 并将不合格品退回货仓.5.3 PUR/ IQC are responsible to inform supplier of thenon-conforming data, PUR responsible to arrange thenon-conforming materials RTV.采购/IQC负责将不合格批物料状况通告客户或供货商, 采购还负责安排将不合格品退回供货商.5.4 PUR is responsible to charge the supplier ofsorting/reworking cost and other loss due to materialquality issue, and call MRB meeting to review the reject lots of IQC raised.采购负责向供货商索取选用或重工费用及由于物料问题而导致的损失, 并召集MRB会议处理IQC拒收的紧急物料.5.5 ME is responsible to analyze non-conforming products.ME负责分析不合格品.5.6 All MRB members are to propose and decide on defective。
不合格品处理程序
Management of Nonconforming Product
(ISO9001:2015)
1.0目的Purpose:
本程序对不合格品的标识、隔离、评估、处置、记录提供指引。
This procedure provides the instructions for the identification, quarantine, evaluation, disposition,
documentation of non-conformance associated with incoming materials, in-process incoming materials, semi-product, finished product. .
2.0范围Scope:
适用于本厂所有不合格来料,半成品及成品。
Apply to all non-conforming incoming materials, semi-products and finished products.
3.0定义Definition:
3.1DXC: DXC的简称:DXC is short for DXC.
3.2UAI:特采,也称让步接受。
UAI is short for use as it is, also calling concession.
3.3PM/PA: 项目经理/项目助理 Program manager / Program Assistant.
3.4QE: 品质工程师 Quality Engineer
3.5ME: 制程工程师 Manufacturing Engineer
3.6不合格品:不符合既定的品质标准/要求或客户要求的所有来料、半成品、成品。
Nonconforming Product: All incoming materials, WIP, finished products are
non-compliant with established quality standard/requirements or customers’.
3.7可疑物品/物料:检验或试验状态标识不明确或没有标识,或储存超过保存期限或由于包
装受损等原因可能引起品质变异或降低的物料/半成品/成品。
Suspicious products/materials:The status of inspection or testing isn’t
indicated/marked or the quality of materials/semi-products/finished products may
have deteriorated because of package damaged or over shelf life.
3.8WIP:半成品Work In-Process.
3.9PFMEA:过程失效模式及影响分析Process Failure Modes and Effect Analysis
3.10IQC II: 来料检验作业指导书 Incoming Quality Control Inspection Instruction. 3.11QC II: 品质检验作业指导书 Quality Control Inspection Instruction
3.12MRB:物料评审委员会,也称不合格品评审委员会,职责是:定期或紧急状态下,评审及
处理不合格来料及生产线发现的不良半成品及成品。
Material Review Board,also
calling non-conforming product review board, is responsible for reviewing and disposing non-conforming incoming material / WIP / finished products on a regular or urgent basis..
3.13MRB成员如下MRB member for incoming material as below:
LEVEL I:
IQC (仅适用于不良来料处置Only for nonconforming incoming material)
Planner (PPC)
Buyer (Purchasing) (仅适用于不良来料处置Only for nonconforming incoming material) QE (as necessary)
ME (as necessary)
QC Supervisor (仅适用于不良半成品/成品的处置only for nonconforming WIP/Finished Product)
Production Supervisor(仅适用于不良半成品/成品的处置only for nonconforming
WIP/Finished Product)
LEVEL II:
QA Manager
ME Manager
Purchasing Manager (仅适用于不良来料处置Only for nonconforming incoming material)
PPC Manager
Production Manager (as required)
Program Manager (as required)
Plant Manager (as required)
4.0职责Responsibility:
4.1IQC/IPQC/FQC
4.1.1 按规定的检验标准检验来料/生产的半成品及产品,正确地判定来料/生产的产品是
否合格,并对不合格品进行标识。
Inspecting/measuring/testing incoming
materials or WIP/Finished products produced as per the approved quality
control inspection instruction (QC II), and judge whether the incoming
material / WIP/Finished products is pass or fail, and marking the
non-conforming incoming material lot or WIP or finished products with the
established label.
4.1.2 对不合格来料/半成品/成品的处理结果进行跟踪和记录。
Following up and
recording the disposition of nonconforming incoming materials/WIP/finished
products.
4.2IQC主管/工程师负责将发现的来料不良问题及时通告相关的MRB成员,若有必要时安排
并主持MRB会议。
IQC Supervisor/Engineer is responsible for handling nonconforming
incoming materials and informs the related MRB member of the nonconformance. If
necessary, IQC should arrange the MRB meeting.
4.3QC主管/QE负责对制程、终检、出货检查中的不合格品提出处理意见。
当出现的不合格半
成品/成品严重影响到生产进度或交货时,须及时将生产过程中产生的不合格半成品/成品
信息通告给生产部或PPC,或ME,或项目经理和品质部经理,并紧急召集生产部,PPC或
ME或项目经理共同讨论对不合格半成品/成品的处置办法。
QC Supervisor / QE are
responsible for determining the disposition method for nonconforming products
which found by in-process & final inspection & out-going inspection. When。