Oracle biee12c新功能介绍
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.88 MB
- 文档页数:21

Oracle 12C引入了CDB与PDB的新特性,在ORACLE 12C数据库引入的多租用户环境(Multitenant Environment)中,允许一个数据库容器(CDB)承载多个可插拔数据库(PDB)。
CDB全称为Container Database,中文翻译为数据库容器,PDB全称为Pluggable Database,即可插拔数据库。
在ORACLE 12C之前,实例与数据库是一对一或多对一关系(RAC):即一个实例只能与一个数据库相关联,数据库可以被多个实例所加载。
而实例与数据库不可能是一对多的关系。
当进入ORACLE 12C后,实例与数据库可以是一对多的关系。
下面是官方文档关于CDB与PDB的关系图。
其实大家如果对SQL SERVER比较熟悉的话,这种CDB与PDB是不是感觉和SQL SERVER的单实例多数据库架构是一回事呢。
像PDB$SEED可以看成是master、msdb等系统数据库,PDBS可以看成用户创建的数据库。
而可插拔的概念与SQL SERVER中的用户数据库的分离、附加其实就是那么一回事。
看来ORACLE也“抄袭”了一把SQL SERVER 的概念,只是改头换面的包装了一番。
CDB组件(Components of a CDB)一个CDB数据库容器包含了下面一些组件:ROOT组件ROOT又叫CDB$ROOT, 存储着ORACLE提供的元数据和Common User,元数据的一个例子是ORACLE提供的PL/SQL包的源代码,Common User 是指在每个容器中都存在的用户。
SEED组件Seed又叫PDB$SEED,这个是你创建PDBS数据库的模板,你不能在Seed中添加或修改一个对象。
一个CDB中有且只能有一个Seed. 这个感念,个人感觉非常类似SQL SERVER中的model数据库。
PDBSCDB中可以有一个或多个PDBS,PDBS向后兼容,可以像以前在数据库中那样操作PDBS,这里指大多数常规操作。
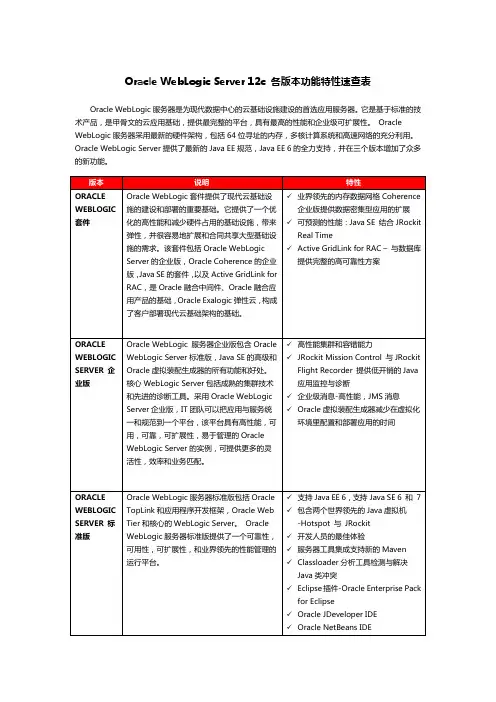
Oracle WebLogic Server 12c 各版本功能特性速查表
Oracle WebLogic服务器是为现代数据中心的云基础设施建设的首选应用服务器。
它是基于标准的技术产品,是甲骨文的云应用基础,提供最完整的平台,具有最高的性能和企业级可扩展性。
Oracle WebLogic服务器采用最新的硬件架构,包括64位寻址的内存,多核计算系统和高速网络的充分利用。
Oracle WebLogic Server提供了最新的Java EE规范,Java EE 6的全力支持,并在三个版本增加了众多的新功能。
注:以上版本的说明和特性按版本高低自动包含。
既企业版包含标准版所有功能特性,套件版包含企业版所有功能特性。

作为甲骨文全球大会OpenWorld 2012中的重要产品发布,新版Oracle Database 12c汇集了参会者最多的目光,Larry Ellison也在开幕演讲中重点介绍了12c 的一些新特性。
对于Oracle DBA来说,虽然数据库12c正式发布的日期还要等到明年年初,但依旧希望能够提前了解它的一些新功能、新特性。
在OpenWorld 2012的技术讲座环节,Oracle技术大师Tom Kyte集中介绍了Oracle Database 12c的十二大新特性,而Oracle ACE总监杨廷琨也对此进行了总结,希望让国内DBA一睹为快。
1.PL/SQL性能增强:类似在匿名块中定义过程,现在可以通过WITH语句在SQL中定义一个函数,采用这种方式可以提高SQL调用的性能。
2.改善Defaults:包括序列作为默认值;自增列;当明确插入NULL时指定默认值;METADATA-ONLY default值指的是增加一个新列时指定的默认值,和11g 中的区别在于,11g的default值要求NOT NULL列。
3.放宽多种数据类型长度限制:增加了VARCHAR2、NVARCHAR2和RAW类型的长度到32K,要求兼容性设置为12.0.0.0以上,且设置了初始化参数MAX_SQL_STRING_SIZE为EXTENDED,这个功能不支持CLUSTER表和索引组织表;最后这个功能并不是真正改变了VARCHAR2的限制,而是通过OUT OF LINE的CLOB 实现。
4.TOP N的语句实现:在SELECT语句中使用“FETCH next N rows”或者“OFFSET”,可以指定前N条或前百分之多少的记录。
5.行模式匹配:类似分析函数的功能,可以在行间进行匹配判断并进行计算。
在SQL中新的模式匹配语句是“match_recognize”。
6.分区改进:Oracle Database 12c中对分区功能做了较多的调整,Oracle ACE总监杨廷琨花了较大的篇幅对分区提升进行了解读,其中共分成6个部分:INTERVAL-REFERENCE分区:把11g的interval分区和reference分区结合,这样主表自动增加一个分区后,所有的子表、孙子表、重孙子表、重重重...孙子表都可以自动随着外接列新数据增加,自动创建新的分区。

Oracle白皮书2013 年 7 月Oracle WebLogic Server 12c 简介第 12.1.2 版跨传统环境与云环境的头号应用服务器执行概要 (4)云部署的灵活性 (6)为下一代应用程序提供任务关键的云平台 (7)使用优化的 Oracle WebLogic Server 和 Oracle 数据库集成实现高 RASP、多租户 .. 8使用动态集群实现云的灵活性 (12)使用 Oracle Exalogic 中间件云服务器优化实现高达 3 倍的性能提升 (13)使用自有云管理简化运营 (14)使用统一安装和修补框架提高效率 (14)一致的 Oracle Coherence 管理 (14)Java 消息服务 (JMS) 的灵活伸缩 (15)Oracle Enterprise Manager 12c 提供的额外的云管理功能 (16)使用现代开发平台缩短上市时间 (18)使用简化的 Maven 集成实现快速开发 (18)使用移动开发框架支持智能电话和平板电脑 (19)使用 WebSocket 和 Toplink 数据服务开发创新型移动应用程序 (19)使用适用于 HTML5 的 JSON-REST 服务释放数据 (20)Oracle WebLogic Server:市场领先的应用服务器 (21)结论 (23)免责声明以下内容旨在概述产品的总体发展方向。
该内容仅供参考,不可纳入任何合同。
其内容不构成提供任何材料、代码或功能的承诺,并且不应该作为制定购买决策的依据。
所描述的有关 Oracle 产品的任何特性或功能的开发、发布和时间安排均由 Oracle 自行决定。
执行概要如今的企业领导对IT 提出了挑战性的需求。
根据最近的一项IDC 调查,CIO 们将降低成本、快速推出新的和改进的产品以及提高生产效率列为首要任务。
1 许多组织都在努力满足这些迫切需要。
原因何在?竞争激烈的市场、业务模式、消费者喜好都在快速变化,要跟上变化的步伐,必须更改现有软件或编写全新的应用程序。


Top Oracle Database 12cHigh Availability Innovations A Technical DrilldownWei Hu, Vice President of Development, High Availability Technologies, OracleBest Innovations Make Things Easy▪Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic - Arthur C. Clarke▪Any technology that is distinguishable from magic is not sufficiently advanced - Gregory Benford▪This talk will give an overview of the new high availability features introduced in Oracle Database 12c▪Then describes some of the internal innovations that make these features powerful and easy to useOracle Database 12c▪Oracle Database 12c introduces significant new HA capabilities that–Drastically cut down planned and unplanned downtime –Eliminate compromises between HA and Performance –Tremendously boost operational productivity▪These take Availability to unprecedented new levels–Next-generation Maximum Availability Architecture (MAA) –Optimized for OracleExtreme AvailabilityOracle Maximum Availability ArchitectureActive Data Guard–Data Protection, DR–Query OffloadGoldenGate–Active-active –HeterogeneousRMAN, Oracle Secure Backup–Backup to tape / cloudActive ReplicaEdition-based Redefinition,Online Redefinition, Data Guard, GoldenGate– Minimal downtime maintenance, upgrades, migrationsRAC–Scalability –Server HAFlashback–Human error correctionProduction SiteApplication Continuity–Application HAGlobal Data Services–Service Failover / Load BalancingOracle Database 12cHigh Availability Key* New Features ▪Application Continuity▪Global Data Services▪Data Guard Enhancements▪RMAN Enhancements▪Flex ASM▪Other HA Enhancements▪GoldenGate Update▪MAA at PayPal▪ *Nearly a hundred new HA features in 12cDatabase outages can cause in-flightwork to be lost, leaving users and applications in-doubt -–User frustration –Cancelled work –Duplicate submissions –Rebooting mid-tiers –Developer painsPre-12c SituationIn-Flight Work: Dealing with OutagesApplication ServersDatabase ServersEnd User▪Replays in-flight work on recoverable errors▪Masks many hardware, software, network, storage errors and outages ▪Supports JDBC-Thin, Universal Connection Pool (UCP), WebLogic Server, 3rd Party Java apps/mid-tiers ▪RAC, RAC One, & Active Data Guard ▪Better end user experienceApplication ContinuityMasks unplanned/planned outages when successfulApplication ServersDatabase ServersEnd UserDatabase RequestReplayedApplication Continuity SubtletiesThe hardest part of replay is deciding when NOT to replay▪Application Continuity minimizes divergence by re-executing SQL at original SCN (when possible) and rebuilding original environment–Stops replay (and returns error) if replayed request returns different result than original (e.g., two users concurrently updating same row)▪Application Continuity does not attempt replay (and returns error) if –Error is not recoverable – e.g., constraint violation–DDLs such as SHUTDOWN ABORT, DROP TABLESPACE are executed–Request has been explicitly disabled for replay – e.g., disbursing money–Failure occurred too long ago – don’t automatically replay a request from yesterday ▪Application Continuity is safe; only replays incomplete requests – Will not pay for the same item twiceafter outagesTransaction GuardPreserve & Retrieve COMMIT Outcome▪Tracks outcome of the last transaction ▪Without Transaction Guard, retry can cause logical corruption▪Transaction Guard allows applications to deal correctly with failures▪Application Continuity uses Transaction Guard▪Transaction Guard also available for applications that do not use Application ContinuityApplication Continuity I nternalsOracle Database 12cHigh Availability Key New Features▪Application Continuity▪Global Data Services▪Data Guard Enhancements▪RMAN Enhancements▪Flex ASM▪Other HA Enhancements▪GoldenGate UpdateDatabases in Replicated EnvironmentsChallenges▪Maximum Availability ArchitectureActive Data Guard and GoldenGate with RAC▪Want to optimize utilization ofActive Data Guard and GoldenGate databases–Efficiently use all availabledatabases–Automated load balancing and faulttolerancePrimary Active Standby Active StandbyGlobal Data Services•Extends RAC-style service failover, loadbalancing (within and across datacenters), and management capabilities to a set of replicated databases•Takes into account network latency,replication lag, and service placement policies•Achieve higher availability, improvedmanageability and maximize performanceLoad Balancing and Service Failover for Replicated Databases▪Reporting client routed to ‘best’ database–Based on location, response time, data, acceptabledata lag–Reports will automatically run on least loaded server▪Reporting client failover–If preferred database not available, will route toanother database in same region or a remote database▪Global service migration–Automatically migrates services based onfailover/switchover - if primary database is down, start Call Center service on the new primaryActive Data Guard ExampleActive Data GuardReporting ServiceCall Center Service▪Call Center Client connections andrequests transparently routed to the closest / best database–Runtime load balancing metrics give client real-timeinformation on which database to issue next request▪If a database fails, its global services arerestarted on another replicaGoldenGate ExampleGoldenGateCall Center ServiceLoad Balancing is Very ComplicatedGlobal Data Service (GDS) Load Balancing▪Supports connect-time and run-time (per-request) load balancing▪Load balancing is easy if all your machines and workload are uniform–GDS supports heterogeneous environment – RAC + non-RAC, powerful and less powerful machines (important since some customers have less powerful machines for DR)▪Load balancing is NOT equal load on all machines–Instead, GDS minimizes average response time across all requests–If database 1 much faster than database 2, then 100% of requests might go to machine database 1–Sometimes, request to lightly-loaded database in remote region might complete faster than request to heavily loaded database in local region–Equalization of average response time done for all clients in each region (remote requests expected to be longer) ▪Load balancing must balance responding rapidly to changing workloads and avoiding oscillations▪Uses internal database metrics, does not blindly rely on external metrics–More accurate (factors out network variability), handles workload generated external to global services, & handles planned shutdown caseGlobal Data Services: SummaryGlobally Replicated, High Availability Architecture••• GSM - Global Service ManagerLocal StandbyLocal StandbyData Center #2 EMEAAPACGuardData GuardPrimaryLocal StandbyActiveData GuardGDSCTLGDS Catalog PrimaryGDS Catalog StandbyMasterOracleGoldenGate Active GuardSALES POOL (sales_reporting_srvc, sales_entry_srvc)HR POOL(hr_apac_srvc, hr_emea_srvc)All GDS client databases connected to all GSMsMasterRemote StandbyReader FarmActive Data GuardGlobal Service ManagersGlobal Service ManagersOracle Database 12cHigh Availability Key New Features▪Application Continuity▪Global Data Services▪Data Guard Enhancements▪RMAN Enhancements▪Flex ASM▪Other HA Enhancements▪GoldenGate UpdateZero Data Loss ChallengeThe longer the distance, the larger the performance impactSynchronous Communication Leads To Performance Trade-OffsPrimaryStandbyCommitCommit AckNetwork SendNetwork AckStandbyData Guard Async – TodaySome Data Loss Exposure Upon DisasterZero Data Loss For Async Deployments▪Far Sync: light-weight Oracle instance: standby control file, standby redo logs, archived redo logs, no data files▪Receives redo synchronously from primary, forwards redo asynchronously in real-time to standby▪Upon Failover: Async standby transparently obtains last committed redo from Far Sync and applies: zero data loss failover▪Second Far Sync Instance can be pre-configured to transmit in reverse direction after failover/switchover▪Terminal standbys required to be Active Data Guard StandbysPrimaryStandbyFar SyncInstanceStandbyFar SyncInstanceActive Data Guard Far SyncMuch work done to make things work ‘like magic’▪Looks just like SYNC. So Fast Start Failover (FSFO) works – automatic, zero data loss failover to far destination▪If Far Sync instance fails, can failover to another Far Sync (recommended), or go into async mode directly to standby (using remote alternate log_archive_dest_x)▪Sophisticated logic to make failovers seamless–When primary dies, Far Sync keeps track of state of async connections to terminal standby to ship the exact redo needed for zero data loss–Works with RAC (multiple threads of redo)▪Smart gap resolution – if the primary is missing redo, it can fetch from Far Sync instance. Far Sync instance will transparently fetch from primary & forward to standbyActive Data Guard Far SyncSummary of Benefits▪Best data protection, least performance impact▪Low cost and complexity▪Best way to implement a near DR + Far DR model▪Relevant to existing Data Guard ASYNC configurations▪Data Guard Failover? No Problem! Just do it – No Data Loss!Active Data Guard Real-Time CascadingEliminates Propagation DelayPrimary▪In 12.1, Standby 1 forwards redo to Standby 2 in real-time, as it isreceived: no propagation delay for a log switch▪Standby 2 (Active Data Guard Standby) is up-to-date for offloadingread-only queries and reports▪In 11.2, Standby 1 waits till log switch before forwarding redo fromarchived logs to Standby 2Data Guard Fast SyncReduced Primary Database Impact for Maximum AvailabilityLogsStandbyRedoLogsCommitCommitAcknowledge▪For SYNC transport: remote siteacknowledges received redo beforewriting it to standby redo logs▪Reduces latency of commit on primary▪Better DR – increased SYNC distance▪If network round-trip latency less thantime for local online redo log write,synchronous transport will not impactprimary database performance▪Can use Fast Sync from Primary to FarSync , and Fast Sync works with FSFO CommitCommitAcknowledgeAcknowledgereturned on receiptLogsStandbyRedoLogsData GuardOther New Features in Oracle Database 12cOracle Database 12cHigh Availability Key New Features▪Application Continuity▪Global Data Services▪Data Guard Enhancements▪RMAN Enhancements▪Flex ASM▪Other HA Enhancements▪GoldenGate UpdateFine-grained Table Recovery From Backup▪Simple RECOVER TABLE command torecover one or more tables (mostrecent or older version) from an RMANbackup▪Eliminates time and complexityassociated with manual restore, recover& export–Enables fine-grained point-in-timerecovery of individual tables instead ofthe contents of the entire tablespaceRMANBackupsCross-Platform Backup & Restore▪Simplifies procedure for platform migration▪Minimize read-only impact with multiple incremental backupsSimplified Platform MigrationSource Database (AIX)Backup to Disk/Tape (data files, optional endian conversion,metadata export)Restore Backup (optional endian conversion, metadata import)Destination Database (Solaris)▪Backup and recover specific pluggable databases with new PLUGGABLE DATABASE keywords:RMAN> BACKUP PLUGGABLE DATABASE <PDB1>, <PDB2>;▪Familiar BACKUP DATABASE command backs up CDB, including all PDBs ▪PDB Complete Recovery–RESTORE PLUGGABLE DATABASE <PDB>; –RECOVER PLUGGABLE DATABASE <PDB>;▪PDB Point-in-Time Recovery–RMAN> RUN {–SET UNTIL TIME 'SYSDATE-3'; –RESTORE PLUGGABLE DATABASE <PDB>; –RECOVER PLUGGABLE DATABASE <PDB>;–ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE <PDB> OPEN RESETLOGS; }▪Familiar RECOVER DATABASE command recovers CDB, including all PDBsPluggable Database Backup & RestoreFine-Grained Backup & Recovery to Support ConsolidationOracle Database 12cHigh Availability Key New Features▪Application Continuity▪Global Data Services▪Data Guard Enhancements▪RMAN Enhancements▪Flex ASM▪Other HA Enhancements▪GoldenGate UpdateAutomatic Storage Management (ASM) OverviewASM Cluster Pool of StorageDisk Group BDisk Group A Shared Disk GroupsWide File StripingOne to OneMapping of ASM Instances to ServersASM InstanceASM DiskRAC ClusterNode4Node3Node2Node1Node5ASMASM ASM ASMASMASM InstanceDatabase InstanceDB ADB A DB BDB BDB CDB BCurrent StateFlex ASM: Eliminate 1:1 Server MappingNew: ASM Storage Consolidation in Oracle Database 12cASM Cluster Pool of StorageDisk Group BDisk Group A Shared Disk GroupsWide File StripingDatabases share ASM instancesASM InstanceDatabase InstanceASM DiskRAC ClusterNode5Node4Node3Node2Node1Node5 runs as ASM Client to Node4Node1Node2 Node4Node2 runs as ASM Client to Node3 ASM ASM ASMASM InstanceDB ADB A DB BDB BDB CDB BFlex ASM: Supporting Oracle Database 11gPrevious Database Versions Will Host Local ASM InstanceASM Cluster Pool of StorageDisk Group BDisk Group A Shared Disk GroupsWide File StripingDatabases share ASM instancesASM InstanceDatabase InstanceASM DiskRAC ClusterNode5Node4Node3Node2Node1ASM ASM ASMDB ADB A DB BDB BDB C DB BASMASM11.2DB11.2DBOracle Database 12cHigh Availability Key New Features▪Application Continuity▪Global Data Services▪Data Guard Enhancements▪RMAN Enhancements▪Flex ASM▪Other HA Enhancements▪GoldenGate UpdateOther HA EnhancementsOracle Database 12cHigh Availability Key New Features▪Application Continuity▪Global Data Services▪Data Guard Enhancements▪RMAN Enhancements▪Flex ASM▪Other HA Enhancements▪GoldenGate UpdateNote: A single DR copy may be multi-purposed for any combination of the use cases describedData Guard Redo TransportSYNC or ASYNCOracle DatabaseOracle Active Data GuardReal-Time Data Protection and AvailabilityStandby First Patching, Exact copy of primary Query & Report OffloadOpen Read-Only Snapshot StandbyConvert to Test Database(open read-write)Single Command Refresh of primary Offload RMAN Backups of primary Far Sync, Database Backup Appliance, GoldenGateExact copy of primarySource for thin snaps/clones Exact copy of primary Extract offload, source for GoldenGate ALO modeOracle & Non-OracleMessage BusOracle Database12c *Oracle GoldenGate 12c*Low-Impact, Real-Time Data Integration & Transactional ReplicationData IntegratorNew DB/ HW/OS/APP Fully Active Distributed DBReporting Database DataWarehouse ODSZero Downtime Upgrade& Migration Query & Report Offloading Data Synchronization within theEnterprise Real-time BI, OperationalReporting, MDMEvent Driven Architecture, SOAActive-Active High AvailabilityMessage BusGlobal Data Centers Logical Copy of Primary Disaster Recovery for Non-Oracle Databases *: GoldenGate 12c for Oracle Database 12c will be available in CY2013GoldenGate Zero Downtime Migration/Upgrade Seamless Migration and Upgrades to Oracle Database 12c* •Consolidate/migrate/maintain systems withoutdowntime•Minimize risk withfailback option•Validate data beforeswitchover•Use Active-Active replication for phased user migrationERP Oracle ERP*: GoldenGate 12c for Oracle Database 12c will be available in CY2013 Oracle10.2CRM11.2DWOracle GoldenGate for Active-Active DatabasesIncrease ROI on Existing Servers & Synchronize Data•Utilize secondarysystems for transactions •Enable continuousavailability during unplanned & planned outages•Synchronize data acrossglobal data centers •Use intelligent conflictdetection & resolution*: GoldenGate 12c for Oracle Database 12c will be available in CY2013Oracle 10.2 App2Oracle 11.2 App3Non-Oracle AppHeterogeneous Bi-DirectionalOracle Database 12c▪Oracle Database 12c offers a tremendously sophisticatedset of high availability (HA) capabilities▪These capabilities–Further reduce downtime–Significantly improve productivity–Eliminate traditional compromisesExtreme Availability: SummaryResources▪OTN HA Portal:/goto/availability▪Maximum Availability Architecture (MAA):/goto/maa▪MAA Blogs:/maa▪Exadata on OTN:/technetwork/database/exadata/index.html▪Oracle HA Customer Success Stories on OTN:/technetwork/database/features/ha-casestudies-098033.htmlKey HA Sessions and Demos by Oracle DevelopmentMonday, 23 September Moscone South10:45a Oracle DB 12c—Eng’d for Clouds and Big Data, North D1:45p Oracle Exadata—What’s New and What’s Coming, 1033:15p Top Oracle DB 12c HA Innovations - A Technical Drill-down, 103 4:45p RMAN in Oracle DB 12c: New Features and Best Practices, 102 4:45p Compression and Performance in Oracle Database 12c, 104Tuesday, 24 September Moscone South10:30a Always Available: Oracle Exadata and Oracle MAA, 10210:30a Oracle RAC 12c Best Practices, 10412:00p A Revolutionary New Way to Do DB Backup and Recovery, 102 12:00p Oracle Flex Cluster: Optimized Resource Mgmt. for Cloud, 104 12:00p Storage Optimization with Oracle Database 12c, 3013:45p Oracle DB 12c Best Practices for Data Availability andDisaster Protection, 1025:15p Optimize Oracle Active Data Guard and Oracle GoldenGate:Wednesday, 25 September Moscone South10:15a Best Practices for Integrating GoldenGate w/ Act. Data Guard, 104 11:45a The Next Big Thing!, 10311:45a Best Practices for Oracle Exadata Backup and Recovery, 20011:45a Cloning and Snapshots with Oracle Database 12c, 1021:15p Redefining Backup and Recovery with Oracle Eng’d Systems, 200 3:30p Oracle Active Data Guard: Next-Generation Data Protection, 103 5:00p Oracle Exadata Storage Availability Best Practices, 2005:00p Integrated Apply: Scalable Replication with GoldenGate, North 131 5:00p Exadata Planned Maintenance for Zero Downtime, Westin Metro. IThursday, 26 September Moscone South11:00a Oracle Database-Aware Flash: Maximizing Performance andAvailability for Your Database, 2362:00p Oracle MAA Best Practices for the Oracle Multitenant Option, 102 2:00p Maximize Availability by Using DB Services with Oracle RAC, 103。

oracle database 12c 介绍和概要Oracle Database 12c 是一款由 Oracle 公司开发的数据库管理系统,它是目前最流行的关系型数据库之一。
在 Oracle Database 12c 中,引入了许多新特性和改进,使得数据库的可用性、可扩展性和性能得到了进一步提升。
Oracle Database 12c 引入了多租户架构,允许多个数据库实例共享同一套 Oracle 数据库软件,从而降低了成本和资源消耗。
同时,它还支持各种不同的计算环境,包括 x86、x64 和 zSeries 等。
Oracle Database 12c 提供了丰富的功能和工具来支持数据管理、事务处理和数据分析等任务。
其中,最受欢迎的功能之一是闪回(Flashback),它允许管理员在误操作或数据损坏后快速恢复到以前的数据库状态。
此外,Oracle Database 12c 还提供了许多其他的内置工具,例如自动存储管理(ASM)、自动数据优化(AOP)和数据安全等。
Oracle Database 12c 的主要组件包括数据库实例、数据文件、控制文件、日志文件和表空间等。
数据库实例是由多个进程和内存结构组成的,它负责访问和控制数据库。
数据文件用于存储数据库的数据,控制文件包含了数据库元数据和磁盘文件的信息,日志文件记录了对数据的所有更改信息。
表空间则是由一个或多个数据文件组成的逻辑容器,用于存储用户的数据。
总之,Oracle Database 12c 是一款功能强大、易于使用和管理的关系型数据库,适用于各种不同的应用场景。
它提供了许多先进的功能和工具,可以帮助企业降低成本、提高性能和可靠性,是数据库管理员的理想选择。

Oracle BIEE 12c SampleApp v511 Virtual Appliance Quick Deployment Guide-root/Admin123-oracle/Admin123-12c db. system/Admin123-virtual machine auto logon as user oracle-by default image is set with NAT networkingo change to bridge networking if your VM isusing DHCP-1st Startup time for BI services is between 7-10minutes-All 12c BI related product logons are prodney/Ad-min123-All WLS related logons are weblogic/Admin123-Users that obtained the image from OTN please seethe disclaimer below regarding necessary R packagesSTART HERE:-See desktop icon ‘v511 image details’ for full detailson this releaseAbout 12c SampleAppv511This virtual machine is intended to showcase the functionality and capabilities of Oracle BI 12c. All standard OOB Sam-pleApp content from v506 has been updated and enhanced for this releaseNOTE: Users who download V511 from OTN. Many examples in this release use external R packages in order to getR/ORE and BI-AA examples to work. To install these packages and enable the OOB examples follow the directionsin the FIRST_README.txt from /home/oracle/scripts/RSampleApp Deployment Guide IndexVirtual machine download &deployment (2)Extraction and Import (3)Virtual Machine Settings (3)Starting Services overview (4)Start Here: Getting to Know SampleAppv511 and BI 12c (5)Virtual machine download &deployment1.Prepare your host system.Minimum 8GB, 16 GB ram and SSD are recommended.Turn on Virtual Assist features in the BIOS (usually done by default). Refer to Troubleshooting tips in Step 12 for more details.~ 100 GB of temp disk space needed to download and install. (Includes zips files that total 18 GB, and an 18 GB .ova, 55 GB deployed image) note: ova and zip files can be deleted once the import is completed-Download and install Free Download Manager or an ftp client of your choice.-Download and install md5sum (optional)2.Download and install Oracle Virtual Box (4.3.x and above is supported, 5.10 is the current version)3.Click Here to open the SampleApp OTN Pagea.Sign into OTN prior to starting your download4.Navigate to the SampleAppv511 Sectiona.You must accept the licensing terms prior to proceedingDownload files SampleAppv511p-appliance.zip .001 through .004Extraction and Import4a. When all zip files are downloaded into a single directory, unpack them with 7zip or zip utility of your choice.Extract your zip files (note: you only need to select zip file .001 when extracting, the rest will automatically unpack)Linux users can run the following command as shown below. Users with a graphical zip utility can right click on .zip.001 and choose extract-7za x SampleAppv511p-appliance.zip.001-(Typical extraction time will take between 5 and 10 minutes depending on your host machine) when completed a folder called SampleAppv511p-appliance will be created containing a SampleAppv511p-appliance.ova file5. Start Oracle Virtual Box Manager Click File / Import Appliance /Open appliance (you can also double click your.ova file to open virtual box manager-Navigate to the location you downloaded the SampleAppv511rc3-10-15.ova file-Click import (typical import time is between 10 to 20 minutes)Check [x] Reinitialize the MACaddress of all network cardsO NCE YOUR VM IMPORT IS COMPLETED PROCEED TO STEP 6Virtual Machine Settings6. Virtual Machine Settings(Review this section fully before powering on)By default your vm is configured with the following parameters which is ideal for an 8GB host system - 6.2 GB ram- 2 processors-NAT Network adaptero By default your VM once powered on will have a IP address 10.0.2.15o See how to setup port forwarding on YouTube. Port forwarding allows you to access your VM from a local web browser directly on your host machine-Users with more physical host memory can allocate more memory to the virtual machineo You can edit any of the VM configurations by clicking on edit/settings-If your VM can obtain a DHCP address change your networking to bridged7.Start your VM Your VM will auto logon as oracle/Admin123. Upon logon your IP address will be displayed with further instructions on configuring your vm. Note: If your VM does not have an active network connection no IPaddress will be displayed.NOTE: if your VM is having issues obtaining a IP address power down the VM and refresh the MAC addressif you are using bridge networking and your VM does not have a IP address at boot up you must either assign it one manually or power off and switch to NAT networking in order for services to start properly8.Adjust your screen resolution to fit your host machine-From your toolbar menu click on system/preferences/display and select a screen resolution as needed-Your screen should auto adjust automaticallyVBox Tools /shared folders/guest extensions: ensure your virtual box tools are up to date and your Vbox guest exten-sion pack is installed to ensure maximum performance and stability. For recordings on these topics as well as creating shared folders click hereP ROCEED TO STEP 9 TO REVIEW THE SERVICE STARTUP PROCESSStarting Services overview9. Starting ServicesClick on the desktop icon “v511 image details”> starting services tab for instructions on starting services -Typical 1st start time is between 7 to 10 minutes (subsequent service starts are substantially faster)-Follow the ‘recommended startup’ processo Note: start/stop all scripts are available-Subsequent services startup will be faster-Download the bi thin client here click hereSampleApp v511 DesktopStart Here: Getting to Know SampleAppv511 and BI 12cAll Users should start with the v511 image details launch Pad for details, tips and deployment options, service control and users and URLs for this release.NOTE: service control tab contains all port numbers used in 12c。



串串⾏行行到并⾏行行解读Oracle 12.2的核⼼心新特性孙雪云和恩墨墨•Agility – 敏捷–Rapid provisioning, cloning, movement•Elasticity – 弹性–Scale-out CPU cores, storage, memory•Cloud-scale Operations–Manage many databases as-one •Transforming Data Management–From Disk-based to In-Memory Databases –From Data Warehouse to Big Data–From On-Prem to Database Optimized CloudOracle 12c 的设计理理念转型深度转型速度适应性⾏行行业 重塑型⾏行行业迟钝型⾏行行业互补性⾏行行业Oracle 在12c中做了了什什么⾼高可⽤用⽤用于数据仓库的Data Guard;表的在线迁移和分区DBCA创建standbyIn-Memory IM expressions; Virtual Column;Fast Start;Join groupCore Improvement 实时索引配置情绪分析和搭配提取⽂文档单词的同义词创建只读分区Sharding分⽚片⾃自动部署;⽣生命周期管理理⾃自动管理理智能路路由RAC and GridActiveData GuardBig andData WarehouseMultitenantFlex ASM;Flex ClusterExtended RAC的配置⽀支持远程AWR;ADG⽀支持 SQL tuning advisor基于快照的standby只读实例例,local temp tablespace;并⾏行行递归with的增强SQL执⾏行行计划的增强管理理Application container;Domain based on PDBProxy PDB串串⾏行行的世界说多了了都是泪串串⾏行行到并⾏行行为什什么如此重要企业应⽤用的变化:业务系统增多业务数据量量变⼤大并发访问严重⽽而系统⾯面临的问题:通过CPU主频提升,软件能够⾃自动提升性能的时代已经⼀一去不不复返;⽽而⽤用户对于性能,响应速度要求更更⾼高在⾼高并发系统中,串串⾏行行就是等待⾼高配置⾼高并发⾼高等待阿姆达尔定律律串串⾏行行到并⾏行行,Slave 进程的引⼊入RAC 并⾏行行优化:LMs ! RMVn,CRn 单库并⾏行行优化:LGWR !LGnn 132Dg 并⾏行行优化:Multi MRP单实例例并⾏行行:LGWR! LGnn1、LGWR的作⽤用:2、LGWR相关的等待: Foreground:Log file Sync Background:Log file parallel write3、 Log file Sync产⽣生的原因:commit 过于频繁? Log buffer 过⼤大?CPU负载⾼高?4、什什么时候会产⽣生log file sync等待1)commit操作2)rollback操作3)DDL操作(DDL操作实施前都会⾸首先进⾏行行⼀一次commit)4)DDL操作导致的数据字典修改所产⽣生的commit5)某些能递归修改数据字典的操作:⽐比如查询SEQ的next值,可能会导致修改数据字典。
Oracle Database 12c 版本介绍Oracle Database 12 c有三种版本,提供多种企业版选件来满足客户对各种领域(性能和可用性、安全性和合规性、数据仓储和分析、非结构化数据和可管理性)的特定需求。
Oracle Database 12 c 标准版1企业级的性能和安全性Oracle Database 12 c 标准版1经过了优化,适用于部署在小型企业、各类业务部门和分散的分支机构环境中。
该版本可在单个服务器上运行,最多支持两个插槽。
Oracle Database 12c 标准版1可以在包括Windows Linux和Unix在内的所有Oracle支持的操作系统上使用。
概述快速安装和配置,具有内置的自动化管理适用于所有类型的数据和所有应用公认的性能、可靠性、安全性和可扩展性使用通用代码库,可无缝升级到Oracle Database12c 标准版或OracleDatabase 12 c 企业版优势以极低的每用户180美元起步(最少5个用户)以企业级性能、安全性、可用性和可扩展性支持所有业务应用可运行于Windows Linux和Unix操作系统通过自动化的自我管理功能轻松管理借助Oracle Application Express 、Oracle SQL Developer 和Oracle面向Windows的数据访问组件简化应用开发Oracle Database 12 c 标准版经济实惠、功能全面的数据库Oracle Database 12 c 标准版是面向中型企业的一个经济实惠、功能全面的数据管理解决方案。
该版本中包含一个可插拔数据库用于插入云端,还包含Oracle真正应用集群用于实现企业级可用性,并且可随您的业务增长而轻松扩展。
支持使用一个可插拔数据库实现入门级云计算和整合跨平台恢复内置的Oracle真正应用集群支持更高水平的系统正常运行时间简化的安装和配置适用于所有类型的数据和所有应用向上兼容Oracle Database 12 c 企业版,从而保护您的初期投资优势每用户350美元(最少5个用户),您可以只购买目前需要的许可,然后使用Oracle真正应用集成随需扩展,从而节省成本提高服务质量,实现企业级性能、安全性和可用性可运行于Windows Linux和Unix操作系统通过自动化的自我管理功能轻松管理借助Oracle Application Express 、Oracle SQL Developer 和Oracle面向Windows的数据访问组件简化应用开发Oracle Database 12 c 企业版插入云端全球首屈一指的数据库推出最新版本Oracle Database 12 c 现已推出,可在各种平台上使用。
Program AgendaWindows Platform Support Oracle Database 12c Release 2Cloud123Windows Platform SupportWindows Server 2016 and Windows 10 Supported Editions•Windows Server 2016 editions–Datacenter, Essentials, and Standard Edition •Windows 10 editions–Education, Enterprise, and ProDatabase Certification on 32-bit WindowsOS11.2 DB and client112.1 client2 Windows 7Yes Yes Windows Server 2008Yes Yes Windows Server 2008 R2Yes Yes Windows 811.2.0.4Yes Windows 8.111.2.0.412.1.0.2 Windows Server 201211.2.0.4 Yes Windows 10No12.1.0.2#1RAC 11.2 and higher does not support for 32-bit Windows#2For 12.1 and higher, only DB Client supports 32-bit WindowsNote: Oracle Database Client 12.2 and higher will only support Windows x64.Database Certification on 64-bit WindowsOS11.212.1 12.2 Windows 71Yes Yes Yes Windows Server 2008Yes Yes No Windows Server 2008 R2 Yes Yes No Windows 8111.2.0.4Yes Yes Windows 8.1111.2.0.4 12.1.0.2 Yes Windows Server 201211.2.0.412.1.0.2Yes Windows Server 2012 R211.2.0.412.1.0.2Yes Windows 101No12.1.0.2Yes Windows Server 2016No No Yes2 Note: 32-bit Oracle Client is supported on Windows x64#1RAC and some server features not supported on Windows clients#2To be certified shortly post-releaseDatabase Certification on Windows Hyper-VGuest OS11.212.112.2 Windows Server 2008 R211.2.0.4 (SI only)12.1.0.2 (SI only) No Windows Server 201211.2.0.4 (SI and RAC)12.1.0.x (SI only) 12.2 (SI and RAC) Windows Server 2012 R211.2.0.4 (SI and RAC)12.1.0.2 (SI and RAC)12.2 (SI and RAC) (Generation 1)Windows Server 2012 R2No12.1.0.2 (SI and RAC)12.2 (SI and RAC) (Generation 2)•Host OS: Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2012 and 2012 R2 are certified •Host OS: Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016 will be certifiedOracle Database 12c Release 2 SecuritySecurity•Oracle Home User•Windows Native Authentication •Kerberos and ASM enhancementsOracle Home User Support•Run Windows Services for Oracle using a standard Windows account •Specify a standard (not an administrator) Windows User Account as Oracle Home User during install and upgradeMicrosoft Windows User Types Overview Built-inAccountLocalSystem (Full Administrator Privileges)LocalService(Minimumprivileges)User AccountAdministrator(Local orDomain user)Standard User(Local orDomain User)ManagedService Acct(Domain User)•Account needs to be associated withspecific computer system (s)•No password management needed onlocal hosts•No need to provide passwords duringWindows service configurationVirtual Account(for WindowsService)New Windows User Account Types Supported•Virtual Account–Introduced by Microsoft in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2–Each Windows Service has it’s own virtual account name–No password management–Can work in a workgroup or domain–Ability to access the network with a computer identity in a domain environment •Group Managed Service Account (gMSA)–Introduced by Microsoft in Windows Server 2012–Single Group Managed Service Account (gMSA) can be used on multiple hosts –No password management needed on local hosts–No need to provide passwords during Windows service configurationOracle Database Server InstallOracle Home User•Different from Oracle Installation User who must have OS administration privileges•Services for the Oracle Home run with this user name•Can be Windows Built-in Account or Virtual Account or a standard Windows User Account•Can not be changed post install•Have similarities with ‘oracle’ user on Linux, though you can not log in as the Oracle Home User on Windows and perform administration tasks (e.g. Create DB, Install, Upgrade)Virtual Account Support•New default for Single Instance Oracle Database Server install•Only supported for Single Instance Oracle Database Server install •No need to manage user name or password for Oracle Home User •Database files are owned by the virtual account for the Oracle Database Windows Service (e.g. NT Service\OracleServiceORCL) •Note: DB Client, built-in account option, uses LocalService and Service SIDs for client side Windows services, and is very similar to how Virtual Account worksGroup Managed Service Account support•Supported for all Oracle Database installs (DB Client, Single Instance Oracle Database, RAC and Grid Infrastructure)•Works like any other domain user but no need to create Oracle wallet and/or provide password for any database operationOracle RAC Database InstallOracle Grid Infrastructure InstallDatabase Client Install•For Built-in Accountoption, WindowsServices run underLocalService (notLocalSystem) forDatabase ClientInstallWindows Account option for Oracle Home User Needs to bepre-created?Password neededduring DBoperations?DBServer(SI)DBClientDBServer(RAC)GridInfra-structureVirtual Account N N Y N N N Built-in Account (internally, useLocalSystem)N N Y N Y YBuilt-in Account (internally, useLocalService)#2N N N Y N N Local User Account#2N Y Y#1Y N N Managed Services Account Y N Y Y N N Group Managed Services Account Y N Y Y Y Y Domain Account Y Y Y Y Y Y#1 –Windows OS authentication can not be used across systems#2 –Windows Services can not access any secure shared network resource using its own Windows identity`Oracle Database Services on WindowsOracle ListenerServiceDatabasesOracle DatabaseServiceORACLE BASEORACLE HOMEOther FilesWindows ServicesFile System ACLs•Services run as a Windows User (e.g. domain1\frank)•Each service also has a unique Service SID (e.g. Database sid orcl has service SID: NTAUTHORITY\OracleServiceORCL)•Either user name or Service SID can be used to grant privileges or set ACLs for file system access•Oracle sets appropriate ACLs for Oracle Home and Oracle Base•For customer specific files/directories in non-standard locations, ACLs may need to be changed to make them accessible to Oracle ServicesPlease check Oracle Database Platform Guide for Microsoft Windows for more information.Database Creation•Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA) is used to create or modify Oracle Database as a part of install or as post install action •Administrator, invoking the tools, needs to be an OS Administrator and should have appropriate database privileges•Use the icon Database Configuration Assistant(the icon is set up to “run as administrator”) to invoke DBCA•As Windows Service creation requires both user id and password, DBCA will ask for the password of Oracle Home User (if needed) in order to create the Windows Service•For Single Instance DB, password is needed for Windows Local User and Domain User•For RAC, the customer has the option to store password in wallet; if not stored, the password needs to be input for Windows Domain UserDatabase 1 (12c)Database 1 (11.2)Oracle Database UpgradeORACLE_BASEORADATAORACLE_HOME (11.2)Database 2 (11.2)ORACLE_BASEORADATAORACLE_HOME (11.2)Database 2 (11.2)ORACLE_HOME (12c)Oracle Home and Database Upgrade•Database Upgrade Assistant (DBUA) is used for database upgrade across Oracle Homes as a part of install or as post install action •Administrator, invoking the tools, needs to be an OS Administrator and should have appropriate database privileges•Use the icon Database Upgrade Assistant (the icon is set up to “run as administrator”)•Requirement to enter Oracle Home User and Password is similar to Database creation•When a database is upgraded, it will ask for password of Oracle HomeUser (if needed)Administration Tools•All GUI tools (e.g. DBCA, NETCA) enhanced to support Oracle Home User and ask for password if needed•All command line tools (e.g. ORADIM, LSNRCTL, CMCTL) enhanced to accept Oracle Home User name and password through stdin for service creation•Silent Install and Cloning enhanced to support Oracle Home User •CRSCTL can be used to create wallet for storing password of Oracle Home User (RAC environment)•Enterprise Manager support of Oracle Home User for provisioning, patching, and service creationManagement of Oracle Home User•As it is a standard Windows user, Windows tools can be used to manage the Windows account (e.g. add privileges, change password)•For changing password of the Oracle Home User account–Use Windows tools to change the password–Windows also requires all Windows Services to be updated to use the new password –For all Windows Services used by Oracle, you can use the icon Update Password for Oracle Home User to:•update password for all Windows services used by Oracle on a computer (Single Instance Database or Client)•change password in Oracle wallet and update password for all Windows services used by Oracle ina cluster (for RAC)You can also use the tool Oracle Home User Control (orahomeuserctl) in command line (run as administrator)Recommendations for Oracle Home User•For DB server (SI)–Use Virtual Account to avoid password management (12.2)–For 12.1, specify a Windows user account during install•For RAC DB and Grid Infrastructure install–Use a domain user or group managed service account–For a group managed service account (12.2), you do not need to provide the password for any database operation•If you want to separate out administration domains (e.g. Production and Test databases) of different Oracle Homes for security reasons:–Use Virtual Account and specify distinct Oracle Base directory for each administration domain –Use distinct Oracle Home User account (and Oracle Base directory) for each administration domain •For DB client install, use Built-in Account optionSecurity•Oracle Home User•Windows Native Authentication •Kerberos and ASM enhancementsWindows Native Authentication (NTS)•Enabled by default and can work across Windows systems•Windows user logon credentials used for database authentication •Windows Explorer or Oracle Administration Assistant can be used to manage user authentication and role authorization•Works for Pluggable Databases•New client-side parameter in sqlnet.ora:–"no_ntlm“, which may be set to true for security reasons. (Only works for domain users) –Examples: CONNECT / AS SYSDBA or CONNECT /Windows Native AuthenticationSYSDBA and SYSOPER Privileges•ORA_DBA–SYSDBA privileges for all Oracle Databases on the system •ORA_OPER–SYSOPER privileges for all Oracle Databases on the system •ORA_<HomeName>_DBA (12cR1)–SYSDBA privileges for Oracle Databases on a specific Oracle Home •ORA_<HomeName>_OPER (12cR1)–SYSOPER privileges for Oracle Databases on a specific Oracle HomeAll the groups are on the server systemWindows Native AuthenticationSeparation of Privileges•ORA_<HomeName>_ SYSBACKUP (12cR1)–Backup privileges (SYSBACKUP) for databases of a specific Oracle Home •ORA_<HomeName>_SYSDG (12cR1)–Data Guard Privileges (SYSDG) for databases of a specific Oracle Home•ORA_<HomeName>_ SYSKM (12cR1)–Encryption Key Management privileges (SYSKM) for databases of a specific Oracle HomeAll the groups are on the server systemWindows Native Authentication•ORA_ASMADMIN (12cR1)–SYSASM administration privileges on the computer•ORA_ASMDBA (12cR1)–SYSDBA privileges for ASM Instance on the computer•ORA_ASMOPER (12cR1)–SYSOPER privileges for ASM Instance on the computer•ORA_DBA and ORA_OPER group members no longer get privileges for ASM instance Administrative Privileges for ASM InstanceAll the groups are on the server systemSecurity•Oracle Home User•Windows Native Authentication •Kerberos and ASM enhancementsKerberos and ASM Enhancements•Kerberos–Security enhancements that were introduced in the MIT Kerberos Release 1.8 distribution–In sqlnet.ora, setSQLNET.KERBEROS5_CC_NAME = MSLSA: (instead of OSMSFT:)•ASM file access control–Restrict access of database files to the owner of the database homeOracle Database 12c Release 2 Scalability and PerformanceLarge Pages•Improve performance with large pages support–2 MB Page size (instead of 4 KB)•If Oracle Home User is a standard Windows account, administrator must grant the "Lock pages in memory" privilege to Oracle Home User or Service SID of Oracle Database Service (NTAUTHORITY\OracleService<sid>)Large Pages•Under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLE\KEY_HOMENAME–Create ORA_LPENABLE or ORA_SID_LPENABLE–Set the value to 1 for regular mode and 2 for mixed mode–Mixed mode is the new option to allow use of large pages but fall back to small pages if OS is not able to allocate large pages–ORA_SID_LPMAXTIME is the optional time parameter for mixed mode•If a server has been running for some time and memory is fragmented, OS may fail to allocate large pages–Mixed mode can be used to ensure that DB comes up in such casesMultiple Processor Groups•Support max of 10 processor groups with up to 64 CPUs in each group in 12.1.0.2 (12.1.0.1 supports 4 processor groups)•ORACLE_AFFINITY enhanced to enable affinity of Oracle threads to CPUs in multiple processor groups–processorgroup is an optional parameter designating Windows CPU group •On systems with 64+ logical CPUs, Windows divides all available CPUs into 4 groups (0,1,2,3) with each group containing no more than 64 logical CPUs•Details in Oracle Database Platform Guide for Microsoft WindowsDNFS Client and Resilient File System•Database 12c DNFS client–Standard NFS path formats allow user to utilize standard URN notation for NFS in oranfstab config file and while working with oradnfs utility•e.g.“nfs://server/share/file”•Windows Resilient File System supportOracle Database 12c Release 2 Ease of Management and DevelopmentOracle Database Instance Manager Available as Microsoft Management Console Snap-InORADIM as an MMC Snap-In•ORADIM performs DB create, edit, delete, start, and shutdown operations •All ORADIM operations available in snap-in•Benefits–Centralized instance management for all Oracle Database Homes–Familiar Windows GUI management tool•Found in path ORACLE_HOME\MMC Snap-Ins\oradim or click on ORADIM shortcut in Oracle Home.NET DevelopmentODAC•DB Client 12.2–Application Continuity–Sharding•ODAC 12.2–Connection pool tagging– Database Resident Connection Pooling (DRCP)–Oracle Multitenant improvements–Oracle Edition-Based Redefinition improvements–Offline Schema Compare in Visual StudioCloud Windows and .NETOracle Compute Cloud ServiceDeploy .NET applications to Oracle IaaS on Windows •Windows 2012 R2and Windows 2008 R2VMs available from Oracle Cloud Marketplace to–Free during promotional period–Deploy to Oracle Compute•Deploy and configure IIS, .NET, and apps to Oracle Compute–How To White Paper: Deploying Microsoft Web ApplicationServer on Oracle Compute Cloud ServiceDevelopment & Test Easy On-Ramp to Oracle Database Cloud Services Dedicated Exadata Full-Instance Enterprise ExadataExpressHighest Availability, Scalability, Performance SMB, Departmental ApplicationsEnterprise ApplicationsThe Best Cloud Database for Windows Developers •Popular language drivers–•Multiple interfaces–Full Oracle Net (SQL*Net)–REST API, JSON storage •Updated tools–Oracle Developer Tools for VS –SQL Developer, Data Modeler –Powerful new command-lineDATABASE12cR2Oracle APEXOracle SQLDeveloperOracle Database Exadata Express Cloud Service Connect from On-premises•Use and ODT 12.1 for Oracle Public Cloud or higher –ODT for VS 2015 and VS 2013–Managed and unmanaged •How to connect:–Developing .NET Applications for Oracle Database Exadata Express Cloud Service–Uses Oracle Net Services with Oracle Wallet to secure connectionOracle Database Cloud Service (non-Exadata Express) Connect from On-premises•Use and ODT 12.1 for Oracle Public Cloud or higher–ODT for VS 2015 and VS 2013–Managed and unmanaged •How to connect:–Developing .NET Applications for Oracle Database as a Service–Secure Shell (SSH) required to secure connection•Use SSH client to create tunnel, such as PuTTY•PuTTY can also generate private and public SSH key pairQ&A。
Oracle 数据库12c新特性总结导读:本系列文章是Oracle ACE总监Syed Jaffer Hussain对Oracle数据库12c的一些新特性总结,包括数据库管理、RMAN、高可用性以及性能调优等内容。
关键词:Oracle数据库12c RMAN PGA限制不可见字段【TechTarget中国原创】编者按:甲骨文公司近日正式发布了新版旗舰级数据库Oracle Database 12c,在TechTarget数据库网站之前的一些报道中,我们曾对12c的一些新特性进行了介绍(参考:尝鲜Oracle Database 12c的十二大新特性)而随着产品正式GA,相关技术文档也披露了更多关于12c数据库的细节。
本系列文章是Oracle ACE总监Syed Jaffer Hussain对Oracle 数据库12c的一些新特性总结,包括数据库管理、RMAN、高可用性以及性能调优等内容。
Oracle 数据库12c新特性总结(一)在第一部分中,我们将介绍:1. 在线迁移活跃的数据文件2. 表分区或子分区的在线迁移3. 不可见字段4. 相同字段上的多重索引5. DDL日志6. 临时undo7. 新的备份用户特权8. 如何在RMAN中执行SQL语句9. RMAN中的表级别恢复10. PGA的大小限制问题1. 在线重命名和重新定位活跃数据文件不同于以往的版本,在Oracle数据库12c R1版本中对数据文件的迁移或重命名不再需要太多繁琐的步骤,即把表空间置为只读模式,接下来是对数据文件进行离线操作。
在12c R1中,可以使用ALTER DATABASE MOVE DATAFILE这样的SQL语句对数据文件进行在线重命名和移动。
而当此数据文件正在传输时,终端用户可以执行查询,DML以及DDL方面的任务。
另外,数据文件可以在存储设备间迁移,如从非ASM迁移至ASM,反之亦然。
重命名数据文件:SQL> ALTER DATABASE MOVE DATAFILE '/u00/data/users01.dbf' TO '/u00/data/u sers_01.dbf';从非ASM迁移数据文件至ASM:SQL> ALTER DATABASE MOVE DATAFILE '/u00/data/users_01.dbf' TO '+DG_DATA ';将数据文件从一个ASM磁盘群组迁移至另一个ASM磁盘群组:SQL> ALTER DATABASE MOVE DATAFILE '+DG_DATA/DBNAME/DATAFILE/users_0 1.dbf ' TO '+DG_DATA_02';在数据文件已存在于新路径的情况下,以相同的命名将其覆盖:SQL> ALTER DATABASE MOVE DATAFILE '/u00/data/users_01.dbf' TO '/u00/data_ new/users_01.dbf' REUSE;复制文件到一个新路径,同时在原路径下保留其拷贝:SQL> ALTER DATABASE MOVE DATAFILE '/u00/data/users_01.dbf' TO '/u00/data_ new/users_01.dbf' KEEP;当通过查询v$session_longops动态视图来移动文件时,你可以监控这一过程。
Introduction CHA Architecture and Operation Details Using CHA from the Command Line Using CHA from EMCC for Alerts and Corrective Actions Using the CHA GUI to Perform Root-Cause Analysis Calibrating CHA to your RAC deployment Q & A – Further Information1234567Introduction CHA Architecture and Operation Details Using CHA from the Command Line Using CHA from EMCC for Alerts and Corrective Actions Using the CHA GUI to Perform Root-Cause Analysis Calibrating CHA to your RAC deployment Q & A – Further Information1234567Introducing…Oracle 12c AutonomousHealthFrameworkPowered By Machine LearningCluster Verification Utility ORAchk Cluster Health Monitor Cluster Health AdvisorTrace File AnalyzerHang Manager Memory Guard Quality of Service Management Introducing… Oracle 12c Autonomous Health Framework Working For You ContinuouslyDiscovers Potential Cluster & DB Problems - Notifies with Corrective ActionsOracle 12c Cluster Health AdvisorIntroducing Oracle 12c Cluster Health AdvisorProactive Health Prognostics System•Real time monitoring of Oracle RAC database systems and their hosts •Early detection of impending as well as ongoing system faults •Diagnoses and identifies the most likely root causes•Provides corrective actions for targeted triage.•Generates alerts and notifications for rapid recoveryAgendaIntroduction CHA Architecture and Operation Details Using CHA from the Command Line Using CHA from EMCC for Alerts and Corrective Actions Using the CHA GUI to Perform Root-Cause Analysis Calibrating CHA to your RAC deployment Q & A – Further Information1234567Cluster Health Advisor (CHA) Architecture Overview OS Data GIMRCHADDriver DB Data CHMNode Health Prognostics Engine Database Health Prognostics Engine OS Model DB Model•cha – Cluster node resource•Single Java oracle.cha.server.CHADDriver daemonper node•Reads Cluster Health Monitor data directly frommemory •Reads DB ASH data from SMR w/o DB connection•Uses OS and DB models and data to performprognostics •Stores analysis and evidence in the GIManagement Repository•Sends alerts to EMCC Incident Manager per target EMCC AlertCluster Health Advisor - Scope of Problem Detection Best Effort Immediate Guided Diagnosis•Over 30 node and database problems have been modeled •Over 150 OS and DB metric predictors identified•Problem network model created based upon its signature •Problem Detection in 12.2.0.1 includes–Interconnect , Global Cache and Cluster Problems–Host CPU and Memory , PGA Memory stress–IO and Storage Performance issues–Reconfiguration and Recovery issues–Workload and Session abnormal variationsData Sources and Data PointsCluster Health AdvisorTimeCPUASM IOPSNetwork % util Network_Packets Dropped Log filesyncLog file parallel writeGC CR requestGC current request GC current block 2-wayGC current block busy Enq: CF -conten tion…15:16:00 0.90 4100 13% 0 2 ms 600 us 0 0 300 us 1.5 ms 0A CHA Data Point contains > 150 signals (statistics and events) from multiple sourcesOS, ASM , NetworkDB ( ASH, AWR session, system and PDB statistics )Statistics are collected at a 1 second internal sampling rate , synchronized, smoothed and aggregated to a Data Point every 5 secondsModels Capture the Dynamic Behavior of all Normal OperationModels Capture all Normal Operating Modes50001000015000200002500030000350004000010:002:006:0051009025402423504100 220501000021000440025004900800 IOPSuser commits (/sec)log file parallel write (usec)log file sync (usec)A model captures the normal load phases and their statistics over time , and thus thecharacteristics for all load intensities and profiles . During monitoring , any data point similar to one of the vectors is NORMAL. One could say that the model REMEMBERS the normal operational dynamics over timeIn-Memory Reference Matrix (Part of “Normality” Model )IOPS#### 2500 4900 800 ####User Commits #### 10000 21000 4400 #### Log File Parallel Write #### 2350 4100 22050 #### Log File Sync#### 5100 9025 4024 #### ………………CHA Model: Find Similarity with Normal ValuesObserved values (Part of a Data Point )CHA estimator /predictor (ESEE): “based on my normality model, the value of IOPS should be in the vicinity of ~ 4900, but it is reported as 10500, this is causing a residual of ~ 5600 in magnitude ”, CHA fault detector: “such high magnitude of residuals should be tracked carefully! I’ll keep an eye on the incoming sequence of this signal IOPS and if it remains deviant I’ll generate a fault on it ”.In-Memory Reference Matrix (Part of “Normality” Model )IOPS #### 2500 4900 800####User Commits #### 10000 21000 4400 #### Log File Parallel Write #### 2350 4100 22050 #### Log File Sync#### 5100 9025 4024 #### ………………10500 20000 4050 10250 …Residual Values (Part of a Data Point )5600 -1000-50 325…Observed - Predicted =Inline and Immediate Fault Detection and Diagnostic InferenceMachine Learning, Pattern Recognition, & BN EnginesTimeCPUASM IOPS Network % util Network_Packets DroppedLogfile syncLog file parallel writeGC CR requestGC current request GC current block 2-way GC current block busyEnq: CF -conten tion… 15:16:00 0.90 4100 88% 105 2 ms 600 us 504 ms 513 ms 2 ms 5.9 ms 015:16:00OK OK HIGH1 HIGH 2OK OKHIGH 3 HIGH 3 HIGH 4 HIGH 4OKInput : Data Point at Time tFault Detection and ClassificationDiagnostic Inference15:16:00Symptomswork Bandwidth Utilizationwork Packet Loss3.Global Cache Requests Incomplete4.Global Cache Message LatencyRoot Cause(Target of Corrective Action)Network Bandwidth UtilizationDiagnosticInferenceEngineCluster Health Advisor (CHA) Operation Overview •SRVCTL lifecycle daemon management•Enabled by default - Activates when 1stRAC instance starts•New CHACTL command line tool for alllocal operations•Java Interactive GUI Tool available on OTN •Integrated into EMCC Incident Manager and notifications•Monitoring has no impact onDB performance or availabilityCHACTL ClientCHA Java GUI ClientSRVCTL OS DataGIMRDB DataCHMNodeHealthPrognosticsEngineDatabaseHealthPrognosticsEngineOSModelDBModelLocal to ClusterEMCloudControlCHADDriverAgendaIntroductionCHA Architecture and Operation Details Using CHA from the Command LineUsing CHA from EMCC for Alerts and Corrective Actions Using the CHA GUI to Perform Root-Cause Analysis Calibrating CHA to your RAC deployment Q & A – Further Information1 2 3 4 5 6 7Using CHA From the Command LineOverview•CHA is enabled by default•Autonomously monitors nodes once a RAC DB starts in the cluster •RAC or RAC One Node Database must be explicitly monitored – opt in •CHACTL Command Line supports–Start/Stop Monitoring–Diagnosing Health Issues and Corrective Actions–Model Calibration, Activation and Lifecycle Management–CHA Repository Data Lifecycle ManagementCluster Health Advisor – Command Line Operations Monitoring Your Databases and Nodes with CHACTLEnable CHA monitoring on RAC database with optional model$ chactl monitor database –db oltpacdb [-model model_name]Enable CHA monitoring on RAC database with optional verbose$ chactl status –verbosemonitoring nodes svr01, svr02 using model DEFAULT_CLUSTERmonitoring database oltpacdb, instances oltpacdb_1, oltpacdb_2 using model DEFAULT_DBCHA Command Line OperationsChecking for Health Issues and Corrective Actions with CHACTL QUERY DIAGNOSIS$ chactl query diagnosis -db oltpacdb -start "2016-10-28 01:52:50" -end "2016-10-28 03:19:15"2016-10-28 01:47:10.0 Database oltpacdb DB Control File IO Performance (oltpacdb_1) [detected]2016-10-28 01:47:10.0 Database oltpacdb DB Control File IO Performance (oltpacdb_2) [detected]2016-10-28 02:59:35.0 Database oltpacdb DB Log File Switch (oltpacdb_1) [detected]2016-10-28 02:59:45.0 Database oltpacdb DB Log File Switch (oltpacdb_2) [detected]Problem: DB Control File IO PerformanceDescription: CHA has detected that reads or writes to the control files are slower than expected.Cause: The Cluster Health Advisor (CHA) detected that reads or writes to the control files wereslow because of an increase in disk IO.The slow control file reads and writes may have an impact on checkpoint and Log Writer (LGWR) performance. Action: Separate the control files from other database files and move them to faster disks or SolidState Devices.Problem: DB Log File SwitchDescription: CHA detected that database sessions are waiting longer than expectedfor log switch completions.Cause: The Cluster Health Advisor (CHA) detected high contention during log switchesbecause the redo log files were small and the redo logs switched frequently.Action: Increase the size of the redo logs.Cluster Health Advisor – Command Line Operations HTML Diagnostic Health Output Available (-html <file_name>)AgendaIntroduction CHA Architecture and Operation Details Using CHA from the Command Line Using CHA from EMCC for Alerts and Corrective Actions Using the CHA GUI to Perform Root-Cause Analysis Calibrating CHA to your RAC deployment Q & A – Further Information1234567CHA has detected a service degradation due to higher than expected I/O latencies.CHA has detected a service degradation due to higher than expected I/O latencies.Cluster Health AdvisorCHA/DB HealthCHA detected a for service degradation due to higher than expected I/O latencies.CHA/DB Health: I/O problemCHA has detected a service degradation due to higher than expected I/O latencies.Cluster Health AdvisorCHA/DB Health: I/O problemCHA detected a for service degradation due to higher than expected I/O latencies.CHA/DB HealthCluster Health AdvisorThe degradation is caused by a higher than expected utilization of shared storage devices for thisdatabase. No evidence of significant increase in I/O demand on the local node.Problem Confidence Action 95.17%Validate whether there is increase in I/O demand on other nodes than the local and find I/O intensive SQL . Addmore disks to disk group or move database to faster disks.proddb_1proddb_2Using EMCC for Alerts and Corrective ActionsAgendaIntroduction CHA Architecture and Operation Details Using CHA from the Command Line Using CHA from EMCC for Alerts and Corrective Actions Using the CHA GUI to Perform Root-Cause Analysis Calibrating CHA to your RAC deployment Q & A – Further Information1234567Using the CHA GUI to Perform Root-Cause Analysis Overview•Standalone Java GUI Client•Must be run on local cluster node•Can be run against live GIMR or MDB(dump) filechactl export repository -formatmdb -start '2017-05-01 00:00:00'-end '2017-05-10 00:00:00'•Used internally for development•Will be available and maintained onOracle Technology Networksvr01svr02svr03myclusterCHA (on SVR01) V0.57.6, Data V0.17 – OTN Version (on SVR01)Cluster ‘mycluster ’ Sep -16 21:20:25 Cluster ‘mycluster ’devdbprodtestdbwebdb Cluster mycluster , Hosts:3, DB’s:4svr01svr02svr03myclusterCHA (on SVR01) V0.57.6, Data V0.17 – OTN Version (on SVR01)devdbprodtestdbwebdb Cluster mycluster , Hosts:3, DB’s:4Host ‘svr01’Host ‘svr02’Host ‘svr03’CHA (on SVR01) V0.57.6, Data V0.17 – OTN Version (on SVR01)svr01svr02svr03 svr02 Host svr02myclustersvr01svr02svr03DB prod in mycluster Sep-16 22:16:35 DB prod in myclustersvr01 svr02 svr03svr01 svr02 svr03svr01 svr02 svr03svr01 svr02 svr03svr01 svr02 svr03svr01 svr02 svr03svr01svr02svr03DB prod in mycluster Sep-16 22:16:35 DB prod in myclustersvr01 svr02 svr03svr01 svr02 svr03svr01 svr02 svr03svr01 svr02 svr03“We also deployed the CHA GUI which has been designed specifically to visualize abnormalities in OS and RDBMS statistics data streams which are detected and diagnosed by CHA in real time. It stands out as a successful visualization of the real time and historical monitoring data and diagnostics in our Oracle RAC database environment.”–Jens-Christian Pokolm, Head of DatabasesPostbank Systems AGAgendaIntroduction CHA Architecture and Operation Details Using CHA from the Command Line Using CHA from EMCC for Alerts and Corrective Actions Using the CHA GUI to Perform Root-Cause Analysis Calibrating CHA to your RAC Deployment Q & A – Further Information1234567Overview•Calibration Goal: Increase sensitivity and accuracy with sufficient warning •Release ships with conservative models to minimize false warnings–DEFAULT_CLUSTER for each cluster node–DEFAULT_DB for each database instance•Use your own data for periods of “normal operations” to increase sensitivity–Recommended minimum 6 hour period–Should include all normal workload phases for that model•Models may be changed dynamically online using CHACTLChoosing a Data Set for Calibration –Defining “normal”$ chactl query calibration –cluster –timeranges ‘start=2016-10-28 07:00:00,end=2016-10-28 13:00:00’ Cluster name : myclusterStart time : 2016-10-28 07:00:00End time : 2016-10-28 13:00:00Total Samples : 11524Percentage of filtered data : 100%1) Disk read (ASM) (Mbyte/sec)MEAN MEDIAN STDDEV MIN MAX 0.11 0.00 2.62 0.00 114.66<25 <50 <75 <100 >=100 99.87% 0.08% 0.00% 0.02% 0.03%2) Disk write (ASM) (Mbyte/sec)MEAN MEDIAN STDDEV MIN MAX 0.01 0.00 0.15 0.00 6.77 <50 <100 <150 <200 >=200 100.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 3) Disk throughput (ASM) (IO/sec)MEAN MEDIAN STDDEV MIN MAX 2.20 0.00 31.17 0.00 1100.00<5000 <10000 <15000 <20000 >=20000 100.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00%4) CPU utilization (total) (%)MEAN MEDIAN STDDEV MIN MAX 9.62 9.30 7.95 1.80 77.90 <20 <40 <60 <80 >=80 92.67% 6.17% 1.11% 0.05% 0.00%Creating a new CHA Model with CHACTL•Create and store the new model$ chactl query calibrate cluster –model daytime –timeranges ‘start=2016-10-28 07:00:00, end=2016-10-28 13:00:00’•Begin using the new model$ chactl monitor cluster –model daytime•Confirm the new model is being used$ chactl status –verbosemonitoring nodes svr01, svr02 using model daytimemonitoring database qoltpacdb, instances oltpacdb_1, oltpacdb_2 using model DEFAULT_DBAgendaIntroduction CHA Architecture and Operation Details Using CHA from the Command Line Using CHA from EMCC for Alerts and Corrective Actions Using the CHA GUI to Perform Root-Cause Analysis Calibrating CHA to your RAC deployment Q & A – Further Information1234567For Further Information•Oracle 12c Autonomous Health Framework User’s Guide•Oracle 12c Clusterware Administration and Deployment Guide •Oracle Autonomous Health Framework on OTN。