java实验报告实验六Java图形用户界面
- 格式:doc
- 大小:560.50 KB
- 文档页数:28

图形界面(GUI)程序设计一、课题内容和要求内容:设计和编写一个用于将人民币转换为等值的美元的程序,界面要求可以输入人民币的金额并可以得到转换后的结果。
要求:学习和理解JAVA SWING中的容器,部件,布局管理器和部件事件处理方法。
通过编写和调试程序,掌握JAVA图形界面程序设计的基本方法。
二、设计思路分析class RMBtoDollar:主类,调用主函数。
class change:设置界面,并通过界面上的事件触发实现汇率转换。
三、概要设计public class RMBtoDollar{public static void main(String[] args);}class change extends JFrame implements MouseListener { JLabel l1, l2,l3;JTextField tf1, tf2;JButton b;double RMB, Dollar;public change();public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e);public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e);public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e);public void mouseExited(MouseEvent e);public void mouseReleaseed(MouseEvent e);//鼠标释放时进行转换}四、详细设计import java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.*;import javax.swing.*;public class RMBtoDollar {public static void main(String[] args) {new change();}}class change extends JFrame implements MouseListener { JLabel l1, l2,l3;JTextField tf1, tf2;JButton b;double RMB, Dollar;public change() {//添加组件和设置布局l1 = new JLabel("人民币/元:");l2 = new JLabel("美元/dollar:");l3=new JLabel("(汇率:6.17)");tf1 = new JTextField(12);tf2 = new JTextField(12);b = new JButton("转换");add(l1);add(tf1);add(l2);add(tf2);add(l3);add(b);setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER));setTitle("人民币转换为美元");setBounds(300, 300, 300, 150);setVisible(true);setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);b.addMouseListener(this);//鼠标事件监视器}public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {if (tf2.getText() != null) {// tf2 test 默认初始设为空tf2.setText("");}}public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) {}public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e) {}public void mouseExited(MouseEvent e) {}public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e) {if (tf1.getText() != null) {// 检查tf1 test 是否为空try {// 取异常RMB = Double.parseDouble(tf1.getText());// 字符转为double型Dollar = RMB / 6.17;//转换tf2.setText("" + Dollar);// 显示} catch (Exception ex) {tf1.setText("");// 如果输入不是数字,设为空}}}}五、测试数据及其结果分析1正常输入:2输入字符串不能转为double型时清空输入框:3结果:输出正常。

西安邮电大学(计算机学院)课内实验报告实验名称:图形用户界面专业名称:计算机科学与技术班级:计科1405班学生姓名:高宏伟学号:04141152指导教师:刘霞林实验日期:2016.11.24一、实验目的了解图形用户界面基本组件窗口、按钮、文本框、选择框、滚动条等的使用方法,了解如何使用布局管理器对组件进行管理,以及如何使用Java 的事件处理机制。
二、实验要求1. 掌握使用布局管理器对组件进行管理的方法。
2. 理解Java 的事件处理机制,掌握为不同组件编写事件处理程序的方法。
3. 掌握编写独立运行的窗口界面的方法。
4. 掌握组件的使用方法。
5. 了解对话框的使用方法。
三、实验内容(一)算术测试。
✧实验要求:编写一个算术测试小软件,用来训练小学生的算术能力。
程序由3个类组成,其中Teacher类对象负责给出算术题目,并判断回答者的答案是否正确;ComputerFrame类对象负责为算术题目提供视图,比如用户可以通过ComputerFrame类对象提供的GUI界面看到题目,并通过该GUI界面给出题目的答案;MainClass是软件的主类。
✧程序模板:Teacher.javapublic class Teacher{ int numberOne,numberTwo;String operator="";boolean right;public int giveNumberOne(int n){ numberOne=(int)(Math.random()*n)+1;return numberOne;}public int giveNumberT wo(int n){ numberTwo=(int)(Math.random()*n)+1;return numberTwo;}public String giveOperator(){ double d=Math.random();if(d>=0.5)operator="+";elseoperator="-";return operator;}public boolean getRight(int answer){ if(operator.equals("+")){ if(answer==numberOne+numberTwo)right=true;elseright=false;}else if(operator.equals("-")){ if(answer==numberOne-numberTwo)right=true;elseright=false;}return right;}}ComputerFrame.javaimport java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.*;public class ComputerFrame extends Frame implements ActionListener { TextField textOne,textTwo,textResult;Button getProblem,giveAnwser;Label operatorLabel,message;Teacher teacher;ComputerFrame(String s){ super(s);teacher=new Teacher();setLayout(new FlowLayout());textOne=【代码1】 //创建textOne,其可见字符长是10textTwo=【代码2】 //创建textTwo,其可见字符长是10textResult=【代码3】 //创建textResult,其可见字符长是10operatorLabel=new Label("+");message=new Label("你还没有回答呢");getProblem=new Button("获取题目");giveAnwser=new Button("确认答案");add(getProblem);add(textOne);add(operatorLabel);add(textTwo);add(new Label("="));add(textResult);add(giveAnwser);add(message);textResult.requestFocus();textOne.setEditable(false);textTwo.setEditable(false);【代码4】//将当前窗口注册为getProblem的ActionEvent事件监视器【代码5】//将当前窗口注册为giveAnwser的ActionEvent事件监视器【代码6】//将当前窗口注册为textResult的ActionEvent事件监视器 setBounds(100,100,450,100);setVisible(true);validate();addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){ public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) { System.exit(0);}});}public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){ if(【代码7】) //判断事件源是否是getProblem{ int number1=teacher.giveNumberOne(100);int number2=teacher.giveNumberTwo(100);String operator=teacher.givetOperator();textOne.setText(""+number1);textTwo.setText(""+number2);operatorLabel.setText(operator);message.setText("请回答");textResult.setText(null);}if(【代码8】) //判断事件源是否是giveAnwser{ String answer=textResult.getText();try{int result=Integer.parseInt(answer);if(teacher.getRight(result)==true){ message.setText("你回答正确");}else{ message.setText("你回答错误");}}catch(NumberFormatException ex){ message.setText("请输入数字字符");}}textResult.requestFocus();validate();}}MainClass.javapublic class MainClass{ public static void main(String args[]){ ComputerFrame frame;frame=【代码9】//创建窗口,其标题为:算术测试}}✧实验后的练习:1. 给上述程序增加测试乘、除的功能。
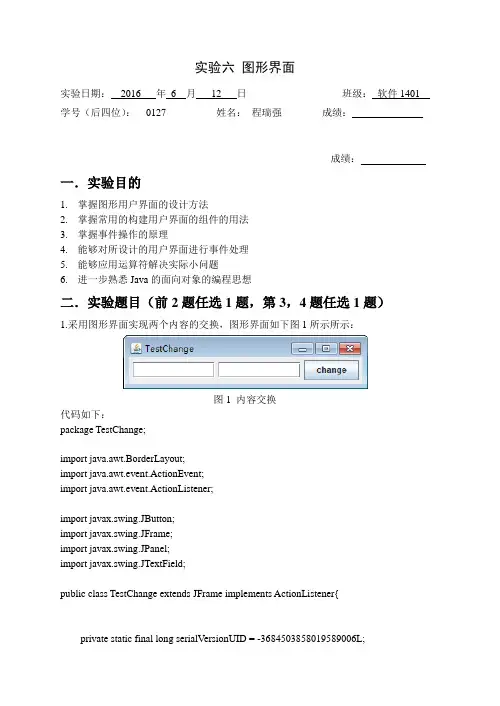
实验六图形界面实验日期:2016 年6 月12 日班级:软件1401 学号(后四位):__0127_______ 姓名:_程瑞强_______ 成绩:成绩:一.实验目的1.掌握图形用户界面的设计方法2.掌握常用的构建用户界面的组件的用法3.掌握事件操作的原理4.能够对所设计的用户界面进行事件处理5.能够应用运算符解决实际小问题6.进一步熟悉Java的面向对象的编程思想二.实验题目(前2题任选1题,第3,4题任选1题)1.采用图形界面实现两个内容的交换,图形界面如下图1所示所示:图1 内容交换代码如下:package TestChange;import java.awt.BorderLayout;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;import javax.swing.JButton;import javax.swing.JFrame;import javax.swing.JPanel;import javax.swing.JTextField;public class TestChange extends JFrame implements ActionListener{private static final long serialVersionUID = -3684503858019589006L;JPanel panel;JTextField tt1;JTextField tt2;JButton button;public TestChange(){this.setTitle("TestChange");this.setSize(355, 85);this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);panel = new JPanel();tt1 = new JTextField(10);tt2 = new JTextField(10);button = new JButton("Change");button.addActionListener(this);panel.add(tt1);panel.add(tt2);panel.add(button);this.add(panel, BorderLayout.NORTH);this.setResizable(false);this.setVisible(true);}public static void main(String[] str){new TestChange();}@Overridepublic void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {if(e.getSource() == button){String temp = tt1.getText();tt1.setText(tt2.getText());tt2.setText(temp);}}}2. 采用图形界面设计如下图2所示的界面。


java图形用户界面实验报告Java图形用户界面实验报告一、引言图形用户界面(Graphical User Interface,简称GUI)是现代软件开发中不可或缺的一部分。
通过GUI,用户能够直观地与程序进行交互,提高了软件的易用性和用户体验。
本实验旨在通过使用Java编程语言,实现一个简单的GUI应用程序,并介绍相关的技术和方法。
二、实验目标本实验的目标是设计并实现一个简单的GUI应用程序,要求具备以下功能:1. 显示一个窗口,并在窗口中心显示一个标签;2. 在窗口中添加一个按钮,并实现按钮的点击事件;3. 当按钮被点击时,标签的文本发生变化。
三、实验过程1. 环境准备在开始实验之前,需要确保已经安装了Java开发环境(JDK)和集成开发环境(IDE),例如Eclipse或IntelliJ IDEA。
2. 创建GUI应用程序首先,创建一个Java项目,并创建一个名为"GUIApplication"的类。
在该类中,引入Java的GUI库,并继承JFrame类,实现一个窗口。
3. 设计窗口布局在窗口的构造方法中,设置窗口的标题、大小和关闭方式。
然后,创建一个JPanel对象,并将其添加到窗口中。
在JPanel中,使用布局管理器(例如FlowLayout或GridBagLayout)来安排组件的位置和大小。
4. 添加标签和按钮在JPanel中,创建一个JLabel对象,并设置其文本和位置。
然后,创建一个JButton对象,并设置其文本和点击事件。
在点击事件中,通过修改JLabel的文本来实现标签内容的变化。
5. 运行程序完成以上步骤后,编译并运行程序。
将会显示一个窗口,其中包含一个标签和一个按钮。
当按钮被点击时,标签的文本会发生变化。
四、实验结果经过以上步骤,成功实现了一个简单的GUI应用程序。
运行程序后,窗口显示如下图所示:(插入程序运行截图)在窗口中心显示了一个标签,标签的文本为"Hello, GUI!"。


信息工程学院1Java 程序设计实习报告JAVA 图形用户界面实验六Java 图形用户界面1. 实验目的(1) 掌握图形用户界面基本组件。
(2) 了解如何使用布局管理器对组件进行管理。
(3) 掌握Java 事件处理机制。
2. 实验内容实验题1编写一个模拟计算器的程序,使用面板和网格布局,添加一个文本框,10个数字按钮(0-9) , 4个加减乘除按钮,一个等号按钮,一个清除按钮,要求将计算 公式和结果显示在文本框中。
运行结果:实验报告的内容与格式按任课教师的要求书写。
,小程序亘看器:paclcagel.Calculator.dass口 I 回加法:主要代码:private void in itComp onen ts() {jButt on1 = :new javax.swing.JButton();jButt on2 = :new javax.swing.JButton();jButt on3 = :new javax.swing.JButton();jButt on4 = :new javax.swing.JButton();jButt on5 = :new javax.swing.JButton();jButt on6 = :new javax.swing.JButton();jButt on7 = :new javax.swing.JButton();jButt on8 = :new javax.swing.JButton();jButt on9 = :new javax.swing.JButton();jButto n10 =new javax.swing.JButton();jButto n11 =new javax.swing.JButton();jButto n12 =new javax.swing.JButton();jButto n13 =new javax.swing.JButton();jButto n14 =new javax.swing.JButton();jButto n15 =new javax.swing.JButton();jTextField1 =new javax.swing.JTextField();setStub( null ); jButton1 .setText( "3" );jButton1 .addActionListener( new java.awt.event.ActionListener() {public void actionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton1ActionPerformed(evt); }});jButton2 .setText( "1" );jButton2 .addActionListener( new java.awt.event.ActionListener() {public void actionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton2ActionPerformed(evt); }});jButton3 .setText( "5" );jButton3 .addActionListener( new java.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) { jButton3ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton4 .setText( "2" );jButton4 .addActionListener( new java.awt.event.ActionListener() {public void actionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton4ActionPerformed(evt); }});jButton5 .setText( "6" );jButton5 .addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public void actionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton5ActionPerformed(evt); }});jButton6 .setText( "8" );jButton6 .addActionListener( newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton6ActionPerformed(evt); }});jButton7 .setText( "4" );jButton7 .addActionListener( newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public void actionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton7ActionPerformed(evt); }});jButton8 .setText( "7" );jButton8 .addActionListener( newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public void actionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton8ActionPerformed(evt); }});jButton9 .setText( "0" );jButton9 .addActionListener( newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton9ActionPerformed(evt); }});jButton10 .setText( "9" );jButton10 .addActionListener( new java.awt.event.ActionListener() {public void actionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) { jButton10ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton11 .setText( "\u00f7" );jButton11 .addActionListener( new java.awt.event.ActionListener() {public void actionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton11ActionPerformed(evt); }});jButton12 .setText( "\u00d7" );jButton12 .addActionListener( new java.awt.event.ActionListener() {public void actionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton12ActionPerformed(evt); }});jButton13 .setText( "-" );jButton13 .addActionListener( new java.awt.event.ActionListener() {public void actionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton13ActionPerformed(evt);});jButton14 .setText( "+" );jButton14 .addActionListener( newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton14ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton15 .setText( "=" );jButton15 .addActionListener( newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton15ActionPerformed(evt);}});实验题2 编写一个程序,有一个窗口,该窗口为BorderLayout 布局。

java图形实验报告篇一:java实验报告实验六Java图形用户界面信息工程学院Java程序设计实习报告JAVA图形用户界面实验六Java图形用户界面1.实验目的(1)掌握图形用户界面基本组件。
(2)了解如何使用布局管理器对组件进行管理。
(3)掌握Java事件处理机制。
2.实验内容实验题1 编写一个模拟计算器的程序,使用面板和网格布局,添加一个文本框,10个数字按钮(0-9),4个加减乘除按钮,一个等号按钮,一个清除按钮,要求将计算公式和结果显示在文本框中。
运行结果:实验报告的内容与格式按任课教师的要求书写。
加法:主要代码:private void initComponents() {setStub(null); jButton1 = new ; jButton2 = new ; jButton3 = new ; jButton4 = new ; jButton5 = new ;jButton6 = new ; jButton7 = new ; jButton8 = new ; jButton9 = new ; jButton10 = new ; jButton11 = new ; jButton12 = new ; jButton13 = new ; jButton14 = new ; jButton15 = new ; jTextField1 = new ;jButton1.setText("3"); jButton1.addActionListener(new {public voidactionPerformed( evt) {jButton2.setText("1"); jButton2.addActionListener(new}); } jButton1ActionPerformed(evt); {public voidactionPerformed( evt) {jButton3.setText("5"); jButton3.addActionListener(new}); } jButton2ActionPerformed(evt); {public voidactionPerformed( evt) {jButton4.setText("2"); jButton4.addActionListener(new}); } jButton3ActionPerformed(evt); {public voidactionPerformed( evt) {jButton5.setText("6");}); } jButton4ActionPerformed(evt);jButton5.addActionListener(new {public voidactionPerformed( evt) {jButton6.setText("8"); jButton6.addActionListener(new}); } jButton5ActionPerformed(evt); {public voidactionPerformed( evt) {jButton7.setText("4"); jButton7.addActionListener(new}); } jButton6ActionPerformed(evt); {public voidactionPerformed( evt) {jButton8.setText("7"); jButton8.addActionListener(new}); } jButton7ActionPerformed(evt); {public voidactionPerformed( evt) {jButton9.setText("0");jButton9.addActionListener(new}); } jButton8ActionPerformed(evt); {public voidactionPerformed( evt) {jButton10.setText("9"); jButton10.addActionListener(new}); } jButton9ActionPerformed(evt); {public voidactionPerformed( evt) {jButton11.setText("\u00f7"); jButton11.addActionListener(new}); } jButton10ActionPerformed(evt); {public voidactionPerformed( evt) {jButton12.setText("\u00d7"); jButton12.addActionListener(new}); } jButton11ActionPerformed(evt); {public voidactionPerformed( evt) {jButton13.setText("-"); jButton13.addActionListener(new}); } jButton12ActionPerformed(evt); {public voidactionPerformed( evt) {篇二:JAVA实验报告附件2:实验报告封皮20 —学年第学期课程实验报告学院:计算机科学技术专业:软件工程班级:姓名:学号:任课教师:王薇实验日期:XX年 11 月 02 日-1--2-实验日期:XX年 11 月 06 日-3--4-篇三:java图形用户界面实验报告南京工程学院实验报告课程名称 JAVA基础实验项目名称图形用户界面设计实验学生班级实验学生姓名学号同组学生姓名无实验时间 XX年11月实验地点实验成绩评定指导教师签字年月日一、实验目的和要求1.目的:掌握java AWT及Swing组件的使用方法,包括窗口、框架、对话框、布局方式、面板、文本编辑器、按钮、组合框等,合理利用委托事件处理模型,掌握不同组件,不同事件的事件处理方法,设计出能够响应事件的java图形用户界面。

JA V A实验报告实验目的:学习组件布局和组件事件的处理。
实验要求:编写程序,实现成绩的查询和排序。
具体要求为:①选择合适的布局管理设计美观的界面,包含成绩输入、成绩查询、成绩排序功能。
②成绩输入:从界面上输入学生的学号和成绩,点击“确认”按钮进行保存。
③成绩查询:输入学生的学号,点击“查询”按钮,显示该学生成绩。
④成绩排序:点击“排序”按钮,将按成绩从高到低显示学生的学号和成绩。
实验步骤:①定义一个类表示学生,包含学号和成绩两个域;②用java提供的V ector或Arrays类(也可使用自定义类)存储输入的学生信息,使用java 提供的方法或使用自定义方法实现学生信息的查询和排序;③界面设计,可考虑以下的界面设计策略:ⅰ在界面上放置成绩查询、成绩输入、成绩排序三个按钮和一个文本区:按下成绩输入按钮则弹出一个窗口,该窗口上有学号输入和成绩输入文本框,输入完毕关闭窗口后输入的学生信息出现在文本区中;按下成绩查询按钮弹出一个与成绩输入类似的窗口,在学号文本框中输入学号后,在成绩文本框中立即显示成绩;按下排序按钮,在文本区中显示排序后的结果。
ii 可在界面上用三个Panel分别实现查询、输入、排序功能,分别在各Panel上放置按钮、文本框、文本区等控件。
此步中,要求学生会使用各种布局管理器设计美观的界面。
④为程序添加事件处理机制。
ⅰ为查询、输入、排序按钮添加事件处理;ⅱ为学号、成绩输入文本框添加事件处理;ⅲ为窗口的关闭添加事件处理。
import java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.*;public class jj extends Frame implements ActionListener {private Button add=new Button("添加");private Button search=new Button("查询");private Button up=new Button("排序");private Label snLabel=new Label("学号");private Label gLabel=new Label("成绩");private List list=new List();private TextField taskInput =new TextField();public class WindowsCloser extends WindowAdapter{public void WindowClosing (WindowEvent we){System.exit(0);}}private viod setup(){Panel buttons=new Panel();buttons.setLayout(new FlowLayout());buttons.add(add);buttons.add(search);buttons.add(up);Panel input =new Panel();input.setLayout(new BorderLayout());input.add("West",snLabel);input.add("Center",taskInput);input.add("west",snLabel);input.add("Center",taskInput);Panel top=new Panel();top.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1));}public TaskList(){}public void actionperformed(ActionEvent ae) {}public static void main (String args[]){List t1 =new List();}}。

河南工业大学实验报告专业班级:计科F1401 学号:姓名:实验单元八【实验目的】1、掌握???????程序设计方法2、掌握???????程序设计方法3、掌握???????程序设计方法4、掌握???????程序设计方法5、掌握使用????程序设计方法。
【实验环境】安装了jdk软件的PC机。
【实验内容】第18章、图形界面。
【程序功能内容说明】设置标签的显示字体、大小背景及颜色。
【实验程序原码】import java.awt.Dimension ;import java.awt.Color ;import java.awt.Font ;import java.awt.Point ;import javax.swing.JLabel ;import javax.swing.JFrame ;public class JLabelDemo02{public static void main(String args[]){JFrame frame = new JFrame("Welcome To MLDN") ;JLabel lab = new JLabel("MLDN",JLabel.CENTER) ; // 实例化标签对象Font fnt = new Font("Serief",Font.ITALIC + Font.BOLD,28) ;lab.setFont(fnt) ;frame.add(lab) ; // 将组件件入到面板之中Dimension dim = new Dimension() ;frame.setBackground(Color.WHITE) ;//设置窗体的背景颜色dim.setSize(200,70) ;frame.setSize(dim) ;Point point = new Point(300,200) ; // 设置坐标frame.setLocation(point) ;frame.setVisible(true) ;}};【实验结果】【该程序关键技术说明】JFrame作为基本容器用于创建窗口。
北京建筑大学理学院信息与计算科学专业实验报告课程名称java语言程序设计实验名称java图形界面实验地点大兴专业机房姓名班级信141 学号201407010 指导教师靳旭玲成绩日期2016.11.9(1)了解Java系统图形用户界面的工作原理和界面设计步骤。
(2)掌握图形用户界面的各种常用组件的使用方法。
(3)掌握图形用户界面各种布局策略的设计与使用。
(4)掌握鼠标事件编程方法。
(5)掌握AWT中Color和Font类的使用方法。
【实验任务】(1)阅读给定的Java Application程序,按要求回答问题并写出运行结果。
(2)按要求编写一个Java Application程序,并编译、运行这个程序。
【实验内容】1.输入下面的Java Application程序,运行该程序,说明程序的功能。
import java.awt.*;public class TestFlowLayout {public static void main(String args[]) {Frame f = new Frame("Flow Layout");Button button1 = new Button("确定");Button button2 = new Button("打开");Button button3 = new Button("关闭");Button button4 = new Button("取消");f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());f.add(button1);f.add(button2);f.add(button3);f.add(button4);f.setSize(100,100);f.setVisible(true);}}2.编写一个Java Application程序,该程序运行的运行结果如下所示。
Java图形用户界面设计实验总结1. 简介本文档是关于Java图形用户界面(GUI)设计实验的总结。
我们将对Java GUI 的基本概念和原理进行介绍,并提供一些实验总结和经验分享。
Java GUI是一种用于创建用户友好界面的技术,在开发各种应用程序时非常重要。
2. Java GUI的基本概念和原理2.1 Java GUI库Java提供了一些库来帮助开发人员创建GUI应用程序。
其中最常用的库是Java Swing和JavaFX。
Swing提供了一组类和方法,用于创建和管理各种GUI组件,例如按钮、文本框、标签等。
JavaFX是一个更现代化的GUI库,提供了更好的图形渲染和动画效果。
2.2 GUI组件Java GUI应用程序通常由一系列GUI组件组成。
最常见的GUI组件包括:•按钮(Button):用于触发各种操作;•标签(Label):用于展示文本信息;•文本框(TextField):用于输入文本;•列表框(ListBox):用于显示一个选项列表;•组合框(ComboBox):同时兼具列表框和文本框的功能;•复选框(CheckBox):用于选择一个或多个选项;•单选按钮(RadioButton):用于从一组选项中选择一个。
2.3 事件处理Java GUI应用程序通常需要对用户的操作做出响应。
为此,需要使用事件处理机制。
事件处理机制通常由两个主要部分组成:事件源和事件监听器。
事件源可以是任何GUI组件,例如按钮、文本框等。
事件监听器是一个类,用于响应和处理特定事件。
3. 实验总结和经验分享在完成Java GUI设计实验时,我得出了以下总结和经验分享:•熟悉GUI组件的使用:在开始实验之前,我花了一些时间学习和理解不同GUI组件的使用方法。
这让我能够更好地选择和使用适当的组件来实现我的GUI应用程序。
•构建用户友好的界面:一个好的GUI应用程序应该是用户友好的。
在实验中,我学会了如何通过合理的布局、适当的颜色和字体选择来创建一个用户友好的界面。
2012—2013学年第 1 学期合肥学院数理系实验报告课程名称:《面向对象程序设计》实验项目:图形用户界面实验类别:综合性□设计性√验证性□专业班级:10信息与计算科学班姓名:学号:实验地点:校内机房实验时间:2012.11.19 —2012.11.25指导教师:钱泽强成绩:一、实验目的掌握Java中图形界面设计的基本元素和方法,熟练使用常用组件设计图形界面,掌握布局管理器的使用,掌握事件的处理方法。
二、实验内容1、设计图形界面,掌握FlowLayout、BorderLayout、CardLayout、GridLayout布局管理器的使用,并掌握组件的精确定位方式;2、掌握事件处理的三种常见的实现方式:·通过主类创建监听器对象的实现方式;·通过自定义内部类创建监听器对象的实现方式;·在注册时通过匿名类直接创建监听器对象的实现方式。
3、设计图形用户界面的应用程序。
三、实验方案(程序设计说明)[题目1] 编写图形界面用户程序,采用事件处理的三种实现方法求一个数的平方。
1、在图形界面中提供“文本框、标签、按钮”,文本框用于输入数据,标签显示数据的平方,单击按钮可以实现求数据的平方;2、分别采用事件处理的三种方法实现。
[题目2] 编写图形界面用户程序,实现“幸运数”游戏。
要求如下:1、在图形界面用户程序中提供“按钮、标签”等组件;2、标签用于显示随机数,单击按钮可以改变随机数并实现对随机数的判断:若两数相等,则出现相等提示,否则出现不等提示。
四、实验程序和运行结果请附页记录正确的源程序五、实验总结六、教师评语及成绩1、求平方import javax.swing.*;import java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.*;//通过主类创建监听器对象class myFrame extends JFrame implements ActionListener{ JLabel l; JButton b; JTextField t;myFrame(JFrame f){ l=new JLabel("0"); b=new JButton("求平方"); t=new JTextField("0");f.setLayout(null);f.add(l); f.add(b); f.add(t);t.setBounds(1,1,60,20); b.setBounds(71,1,60,20); l.setBounds(141,1,60,20);b.addActionListener(this); }public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){ int x=Integer.parseInt(t.getText());int y=x*x; l.setText(Integer.toString(y)); }}//通过自定义内部类创建监听器对象class myFrame extends JFrame{ JLabel l; JButton b; JTextField t;myFrame(JFrame f){ l=new JLabel("0"); b=new JButton("求平方"); t=new JTextField("0");f.setLayout(null);f.add(l); f.add(b); f.add(t);t.setBounds(1,1,60,20); b.setBounds(71,1,60,20); l.setBounds(141,1,60,20); BHandler h=new BHandler();b.addActionListener(h); }private class BHandler implements ActionListener {public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){ int x=Integer.parseInt(t.getText());int y=x*x; l.setText(Integer.toString(y)); }}}//在注册时通过匿名类直接创建临听器对象class myFrame extends JFrame{ JLabel l; JButton b; JTextField t;myFrame(JFrame f){ l=new JLabel("0"); b=new JButton("求平方"); t=new JTextField("0");f.setLayout(null);f.add(l); f.add(b); f.add(t);t.setBounds(1,1,60,20); b.setBounds(71,1,60,20); l.setBounds(141,1,60,20);b.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){ int x=Integer.parseInt(t.getText());int y=x*x; l.setText(Integer.toString(y)); }});}}public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {JFrame jf=new JFrame("平方数"); jf.setBounds(100,100,400,300); jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);jf.setVisible(true);myFrame myf=new myFrame(jf); }}2、幸运数import javax.swing.*;import java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.*;import java.util.Random;class myJFrame extends JFrame implements ActionListener{ private JButton jb;private JLabel [] jl;public myJFrame(JFrame f){ f.setSize(300,300);f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());jl=new JLabel[3];for(int i=0; i<3; i++){ jl[i]=new JLabel("*");f.add(jl[i]); }jl[2].setText("试一试");jb=new JButton("开始");jb.addActionListener(this);f.add(jb);}public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){ Random x=new Random();Random y=new Random();jl[0].setText(Integer.toString(x.nextInt(10)));jl[1].setText(Integer.toString(x.nextInt(10)));if (jl[0].getText().equals(jl[1].getText()))jl[2].setText("恭喜您");elsejl[2].setText("再试试");}}public class test{public static void main(String[] args) {JFrame f=new JFrame("我的窗口");f.setBounds(100,100,400,300);f.setVisible(true);f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); myJFrame m=new myJFrame(f); }}。
java实验报告GUI与JDBCJava 实验报告:GUI 与 JDBC一、实验目的1、深入理解和掌握Java 图形用户界面(GUI)的设计和实现方法,能够使用常用的 GUI 组件创建具有交互功能的界面。
2、熟悉和掌握 Java 数据库连接(JDBC)技术,能够实现与数据库的连接、数据查询、插入、更新和删除等操作。
3、通过将 GUI 与 JDBC 结合,开发具有实际应用价值的数据库管理系统,提高综合运用 Java 知识解决实际问题的能力。
二、实验环境1、操作系统:Windows 102、开发工具:Eclipse IDE3、数据库:MySQL 80三、实验内容(一)GUI 设计1、创建一个简单的登录界面,包括用户名和密码输入框以及登录和取消按钮。
使用布局管理器对界面组件进行合理布局,使其美观、易用。
2、设计一个主界面,包含菜单、工具栏、列表框、文本框等组件。
实现菜单和工具栏的功能响应,如文件的打开、保存,数据的查询、添加、修改和删除等。
(二)JDBC 操作1、建立与 MySQL 数据库的连接,配置数据库驱动程序和连接参数。
2、实现对数据库中用户表的查询操作,将查询结果显示在列表框中。
3、完成用户信息的添加、修改和删除功能,并及时更新界面显示。
(三)GUI 与 JDBC 整合1、在登录界面中,验证用户输入的用户名和密码是否与数据库中的用户信息匹配。
若匹配成功,进入主界面;否则,提示登录失败。
2、在主界面中,通过菜单或工具栏触发相应的 JDBC 操作,实现对数据库的管理,并将操作结果实时反馈到界面上。
四、实验步骤(一)GUI 设计步骤1、创建一个新的 Java 项目,并在项目中创建一个新的 Java 类作为登录界面。
2、导入所需的 GUI 组件库,如`javaawt`和`javaxswing`。
3、使用`JFrame`类创建登录窗口,并设置窗口的标题、大小和位置等属性。
4、在窗口中添加用户名和密码输入框,使用`JTextField`类创建。
南京工程学院实验报告课程名称 JAVA基础实验项目名称图形用户界面设计实验学生班级实验学生姓名学号同组学生姓名实验时间实验地点实验成绩评定指导教师签字年月日一、实验目的和要求1.掌握Java Swing组建的使用方法,包括窗口、框架、对话框、面板、文本编辑框、按钮、组合框等多种布局方式,掌握窗口菜单和快捷菜单设计方式。
2.理解委托时间处理模型,掌握不同组件、不同事件的事件处理方法,设计出能够响应事件的Java图形用户界面。
3.熟悉在组件上绘图的方法。
二、实验题目用表格存储并显示个人所得税税率表,给定一个月收入值,计算应缴的个人所得税。
三、实验方法与步骤(需求分析、算法设计思路、流程图等)算法设计思路:本次实验题目为计算个人所得税,所以本人从网上找到了国家最新的税收政策,以下为截图:因此,我设计了以下核心算法public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){if(e.getSource()==button_b){doublewage=Double.parseDouble((String)text_wage.getText());double tax = 0;if(wage<=3500)tax=0;if(wage>3500&&wage<=5000)tax=(wage-3500)*0.03;if(wage>5000&&wage<=8000)tax=(wage-3500)*0.1-105;if(wage>8000&&wage<=12500)tax=(wage-3500)*0.2-555;if(wage>12500&&wage<=38500)tax=(wage-3500)*0.25-1005;if(wage>38500&&wage<=58500)tax=(wage-3500)*0.3-2755;if(wage>58500&&wage<=83500)tax=(wage-3500)*0.35-5505;if(wage>83500)tax=(wage-3500)*0.45-13505;text.setText(""+tax);}}以上算法是根据税率表设计的,具体为:我国规定个人收入在3500元起征个人所得税,分了多个阶段:3500以下:不收税3500以上到5000以下部分:3%5000以上到8000以下部分:10%8000以上到以下部分:20%125000以上到385000以下部分:25%385000以上到585000以下部分:30%585000以上到835000以下部分:35%83500以上:45%首先算出每个阶段的速扣数,然后用此公式:应纳个人所得税税额=(应纳税所得-扣除标准)*适用税率-速算扣除数。
图形用户界面设计实验1Nested PanelsThe program Nested Panels.java is from Listing 3.8 of the text. Save the program to your directory and do the following:pile and run the program. Experiment with resizing the frame and observe the effect on the components.运行程序后出现如下界面:改变窗口的大小,观察到:〔见下列图〕〔1〕两个子面板one和two的尺寸都保持不变。
〔2〕蓝色的主面板随着窗口的变大而扩展。
〔3〕蓝色面板变长,one和two子面板都不变,当蓝色面板变宽时,两个子面板随着它移动,并保持居中状态。
〔4〕缩小窗口,根据流式布局的形式,two子面板因为位置容不下,自动被放在下一行的位置。
2. Modify the program by adding a third subpanel that is twice as wide, butthe same height, as the other two subpanels. Choose your own label and color for the subpanel (the color should not be red, green, or blue). Add the panel to the primary panel after the other two panels.修改的代码如下:JPanel subPanel3 = new JPanel() ;subPanel3.setPreferredSize (new Dimension(300, 100)); ubPanel3.setBackground (Color.red);JLabel label3 = new JLabel ("Three");subPanel3.add (label3);primary.add (subPanel3);3. Compile and run the modified program. Again, experiment with resizing the frame and observe the effect on the components.改变窗口的大小,3个子面板变化情况跟第一步实验的类似。
信息工程学院Java程序设计实习报告JAVA图形用户界面实验六Java图形用户界面1.实验目的(1)掌握图形用户界面基本组件。
(2)了解如何使用布局管理器对组件进行管理。
(3)掌握Java事件处理机制。
2.实验内容实验题1 编写一个模拟计算器的程序,使用面板和网格布局,添加一个文本框,10个数字按钮(0-9),4个加减乘除按钮,一个等号按钮,一个清除按钮,要求将计算公式和结果显示在文本框中。
运行结果:实验报告的内容与格式按任课教师的要求书写。
加法:主要代码:private void initComponents() {jButton1 = new javax.swing.JButton();jButton2 = new javax.swing.JButton();jButton3 = new javax.swing.JButton();jButton4 = new javax.swing.JButton();jButton5 = new javax.swing.JButton();jButton6 = new javax.swing.JButton();jButton7 = new javax.swing.JButton();jButton8 = new javax.swing.JButton();jButton9 = new javax.swing.JButton();jButton10 = new javax.swing.JButton();jButton11 = new javax.swing.JButton();jButton12 = new javax.swing.JButton();jButton13 = new javax.swing.JButton();jButton14 = new javax.swing.JButton();jButton15 = new javax.swing.JButton();jTextField1 = new javax.swing.JTextField();setStub(null);jButton1.setText("3");jButton1.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton1ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton2.setText("1");jButton2.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton2ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton3.setText("5");jButton3.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton3ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton4.setText("2");jButton4.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton4ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton5.setText("6");jButton5.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton5ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton6.setText("8");jButton6.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton6ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton7.setText("4");jButton7.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton7ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton8.setText("7");jButton8.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton8ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton9.setText("0");jButton9.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton9ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton10.setText("9");jButton10.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton10ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton11.setText("\u00f7");jButton11.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton11ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton12.setText("\u00d7");jButton12.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton12ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton13.setText("-");jButton13.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton13ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton14.setText("+");jButton14.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton14ActionPerformed(evt);}});jButton15.setText("=");jButton15.addActionListener(newjava.awt.event.ActionListener() {public voidactionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {jButton15ActionPerformed(evt);}});实验题2 编写一个程序,有一个窗口,该窗口为BorderLayout布局。
窗口的中心添加一个Panel容器:pCenter,pCenter的布局是7行7列的GridLayout布局,pCenter 的中放置49个标签,用来显示日历。
窗口北面添加一个Panel容器pNorth,其布局是FlowLayout布局,pNorth放置两个按钮:nextMonth和previousMonth按钮,单击nextMonth,可以显示当前月的下一个月的日历;单击previousMonth按钮,可以显示当前月的上一个月的日历。
窗口的南面添加一个Panel容器pSouth,其布局是FlowLayout 布局,pSouth中放置一个标签用来显示一些信息。
运行结果如图所示。
图3.8 运行结果图[基本要求] 编写完整程序。
运行结果:主要代码:private JLabel[] buttonDay = new JLabel[42]; private JButton[] buttonWeek = new JButton[7]; private JLabel labelMonth = new JLabel();private JButton buttonLastMonth = new JButton(); private JButton buttonNextMonth = new JButton(); private JPanel pCenter=new JPanel();private JPanel pNorth=new JPanel();private JPanel pSouth=new JPanel();private JLabel time=new JLabel();public Calender() {super("Calender");setBounds(250, 200, 600, 500);setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);buttonLastMonth.setText("上月");buttonLastMonth.addActionListener(this);pNorth.add(buttonLastMonth);buttonNextMonth.setText("下月");buttonNextMonth.addActionListener(this);pNorth.add(buttonNextMonth);getContentPane().add(pNorth,BorderLayout.NORTH);getContentPane().add(pCenter,BorderLayout.CENTER);pCenter.setLayout(new GridLayout(7,7));for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {buttonWeek[i] = new JButton();buttonWeek[i].setText(stringWeekCn[i]);pCenter.add(buttonWeek[i]);}for (int i = 0; i < 42; i++) {buttonDay[i] = new JLabel();buttonDay[i].setText(" ");pCenter.add(buttonDay[i]);}实验题3 实现如图3.9所示的布局方式功能:前两个文本框输入整型数据。