INCA使用说明
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:3.71 MB
- 文档页数:28


INCA使⽤说明INCA6.2 使⽤说明天津同步动⼒有限公司尚震1.介绍本教程适⽤于使⽤INCA 的新⼿,INCA 主要特点:测量和标定。
使⽤此教程需要最基本的WINDOWS 操作能⼒。
1.1准备开始本教程必须保证系统装有INCA 软件。
本教程中的任务可以在演⽰模式下进⾏,这意味着你不需要任何实际硬件。
硬件模拟在ETK 测试设备和V A DI 测试设备。
该装置会随着INCA 软件安装。
确认0400.hex 和0400.a2l 这两个⽂件在\ETA SData\INCA6.2\Data\Demo 中。
最后请确认您使⽤本教程的计算机有⼀个互联⽹浏览器。
1.2建⽴⼀个DA TABA SE点击Database 选择new,然后输⼊⼯程的名字点击OK1.3 创建⼀个顶层⽂件夹点击Edi t->A dd->A dd to fol der输⼊⽂件夹名称并按回车键1.4 创建⼀个⼯作区单击Edi t->A dd->A dd fol der 并把⽂件夹命名为w orkspace选中w orkspac e 的⽂件夹,单击Edi t->A dd->Workspac e 并命名为OneETK1.5 添加⼀个⼯程先新建⼀Fol der 命名为004 并将其选中,单击Edi t->A dd->ECU proj ec t(A2L)然后添加\i nc a6.2\data\04001.6把⼯程添加到w orkspac e 中选中⼯作区OneETK,单击4 proj ec t/devi c e 下⾯打开按钮右边的选中 0400 单击OK单击 4 proj ec t/devi c e会出现许多设备,选中 ETKtestdevi c e 单击 OKINCA 界⾯会变成1.7添加V A DI 硬件组件下⾯的单击5 H ardw are选中ETK test devi c e 单击右键选中Insert选中V A DI test devi c e 单击OK然后会出现下⾯的界⾯关闭上⾯对话框返回硬件连接会显⽰然后 H ardw are->H ardware status会显⽰2.建⽴⼀个实验下⾯将学习如何将变量和窗⼝添加到实验中,并如何配置功能。



INCA使用技巧1.了解INCA的基本概念和功能:在开始使用INCA之前,先了解一些基本的概念和功能是非常重要的。
INCA提供了一些主要的特性,如数据收集和存储、数据可视化、报告和警报等。
了解这些功能将帮助您更好地使用INCA。
2.选择合适的数据源:INCA可以从多个数据源收集和分析数据。
在选择数据源时,确保它们与您所关注的网络和通信行为相关,并且具有高质量的数据。
常见的数据源包括防火墙、路由器、交换机等。
4.进行数据分析:使用INCA的数据分析功能可以帮助您理解网络和通信行为。
您可以根据不同的指标和标准来分析数据,如流量、延迟、丢包等。
通过对数据进行分析,您可以发现网络和通信中的潜在问题,并采取相应的措施来解决它们。
5.可视化数据:INCA提供了强大的数据可视化功能,可以将收集到的数据转化为易于理解和分析的图表和图形。
通过可视化数据,您可以更直观地了解网络和通信行为,并快速识别异常或问题。
使用INCA的数据可视化功能可以轻松地创建自定义报表和仪表板,以满足您的需求。
6.利用警报和报告功能:INCA提供了警报和报告功能,可以根据设定的标准和条件自动发送警报和生成报告。
您可以通过配置警报来监控网络和通信行为,并及时采取措施应对问题。
报告功能可以帮助您总结和分析数据,为管理决策提供支持。
7.持续监控和维护:使用INCA进行网络和通信分析是一个持续的过程,需要定期监控和维护。
确保数据源的正常工作和数据采集的准确性是非常重要的。
您还可以根据需要对INCA进行配置和调整,以满足不同的分析和监控需求。
8.参与培训和社区交流:INCA是一个功能强大且复杂的工具,为了更好地利用它,建议您参加INCA的培训课程或加入相关的社区。
培训课程可以帮助您快速上手和掌握INCA的使用技巧,而社区交流可以与其他INCA用户分享经验和解决问题。
总结起来,使用INCA进行网络和通信分析需要掌握一些基本的使用技巧和方法。
通过了解INCA的基本概念和功能,选择合适的数据源,并配置数据采集,然后进行数据分析和可视化,最后利用警报和报告功能监控和维护系统,您将能够更好地利用INCA来管理和优化网络和通信行为。

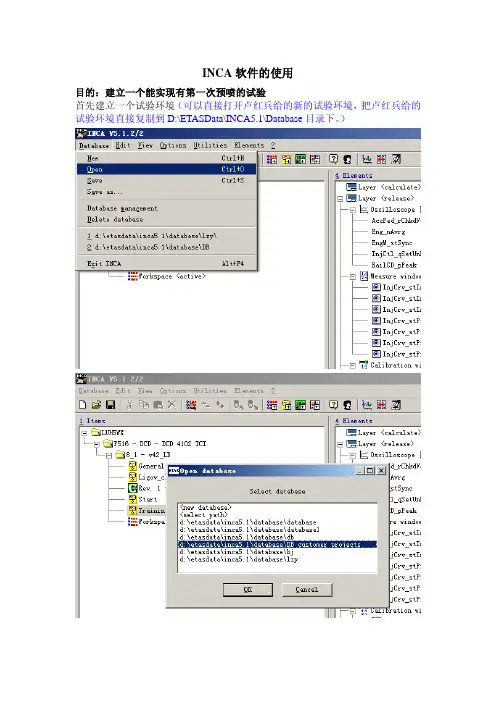
INCA软件的使用目的:建立一个能实现有第一次预喷的试验首先建立一个试验环境(可以直接打开卢红兵给的新的试验环境,把卢红兵给的试验环境直接复制到D:\ETASData\INCA5.1\Database目录下。
)1.先建立一个新的试验,如图所示。
更名为test(随便,可以是任何名字)2.这时选择工作区(workspace),在expreiment窗口更换试验到test试验。
然后双击workspace 进入试验test的工作区。
如下图切换试验到test切换试验到test双击workspace之后出现下面窗口,这就是test试验的工作界面。
3.一般在工作区域下要建立几个层,这样是为了使工作区有条理性,比如说建立一个监测层和一个用于预喷计算的计算层。
(这是针对本次试验而建的)出现下面的界面建立两个层,并重命名这样在图的下方出现了两个层4.现在一个典型的工作区已经建好了,那么下面的工作就是如何实现自己想要的试验。
首先要考虑一般试验要监测的基本参数,比如说发动机的转速(eng_nAvrg)、油门踏板比率和安全检查(AccPed_rChkdVal,其实主要是用来看踩油门踏板的百分比,可在说明文件的80找到)、共轨的压力(Railcd_pPeak,最后10秒轨压的最大值,说明文件的428页)、当前的喷油量(Injctl_qsetUnBal,当前的喷射量,可在说明文件的416页找到)、发动机机械状况(EngM_stSync,可在说明文件650页找到)选择变量点击后出现下面窗口选择变量(可以在变量区直接输入变量的名称进行查找),点击一下即可选择。
选择好后的情况下面对所选的变量进行定义出现下面界面定义参数的类型,以及显示类型为了便于观测,定义为示波器形式。
确定后出现下面的窗口。
另外还有一部分变量是应该监测的。
对于本次试验还要监测InjCrv_stInjCharDes_mp(用户想得到的喷射特性,具体请看说明文件的691页)、InjCrv_stInjCharsetVal(喷射特性设定值,具体请看说明文件的708页)、InjCrv_stInjCharActVal(喷射特性的现行值,具体看说明文件的469页)、InjCrv_stPiIRlsStruct_mp(预喷放行的结构,具体看说明文件的690页),因为喷射特性的实际值和用户想得到的喷射特性不一定一样,这样就出现了问题,这与上面的InjCrv_stPiIRlsStruct_mp有关。


INCA软件的使用与安装1. 简介INCA是一种用于汽车发动机控制系统开发和测试的软件套件。
它提供了一个用户友好的界面,方便用户进行系统参数配置、数据采集和分析等操作。
本文将介绍INCA软件的基本安装步骤和使用方法。
2. 安装步骤以下是安装INCA软件的步骤:1.在官方网站上下载INCA软件安装包。
2.运行安装包,选择合适的安装路径并接受软件许可协议。
3.选择要安装的组件,根据需要进行选择。
4.点击“安装”按钮开始安装过程。
5.等待安装完成后,点击“完成”按钮退出安装程序。
3. 软件界面INCA软件的主界面如下所示:INCA软件界面INCA软件界面界面上有多个功能区,包括菜单栏、工具栏和数据显示区。
用户可以根据需要调整界面布局和显示选项。
4. 软件使用4.1 参数配置在使用INCA软件进行汽车发动机控制系统开发和测试之前,需要先进行参数配置。
可以通过以下步骤进行参数配置:1.点击菜单栏中的“参数配置”选项。
2.在参数配置窗口中,选择要配置的参数,如发动机转速、燃油喷射量等。
3.配置参数值和范围,可以手动输入或导入外部文件。
4.点击“应用”按钮保存配置。
4.2 数据采集INCA软件支持对汽车发动机控制系统进行数据采集。
可以按照以下步骤进行数据采集:1.点击菜单栏中的“数据采集”选项。
2.在数据采集窗口中,选择要采集的数据信号,如发动机转速、燃料压力等。
3.配置采样率和采样时间,并选择保存路径。
4.点击“开始采集”按钮开始数据采集。
4.3 数据分析INCA软件提供了强大的数据分析功能,可以对采集的数据进行处理和分析。
可以按照以下步骤进行数据分析:1.点击菜单栏中的“数据分析”选项。
2.在数据分析窗口中,选择要分析的数据文件。
3.选择分析方法,如曲线拟合、统计分析等。
4.根据需要进行参数设置。
5.点击“开始分析”按钮开始数据分析。
5. 总结本文介绍了INCA软件的基本安装步骤和使用方法,包括参数配置、数据采集和分析等功能。

INCA 5.4 使用手册解释1.1总览和目标1。
1。
1介绍本文档介绍主要围绕测量和标定两个主要任务介绍各个实用的步骤,不要求有INCA的任何知识,但需要有使用windows系统的能力1。
1.2 准备在介绍该指导书之前,你需要准备如下系统(1) 必须要安装INCA系统软件(2)有A2L,HEX文件(3)确保系统有网页浏览器,因为。
HTM的文档需要实用网页浏览器打开1.1.3 INCA连接步骤(1)建立数据库,包括workspace,project,hardware,experiment(最好提前建好)(2)初始化硬件,连接设备,注意链接前要进行网络设置(utilities—〉ETAS networking setting—〉选default IP)(3) download数据到控制器(4)测量与标定1.1。
4 重要概念●测量任务(measuring task):发动机的状态是通过传感器得知的,传感器能够测量发动机参数,传递给控制器得到具体数值。
测量任务包括采集一定时间内所有的传感器数值。
●标定任务(calibration task):标定是用于控制发动机按照预定目标运行的行为.控制器使用一个闭环控制行为去实现:它首先用传感器测量发动机状态,然后用执行器改变发动机状态使之达到目标状态。
新的状态不断地得到调整,直到达到平衡.标定就是这个调整过程,它调整其中的参数,使发动机运行在目标状态。
●INCA: INCA是一种测量和标定工具,它提供给标定工程师图像化的界面和连接控制器硬件的手段。
●存储器仿效(memory emulation):一般控制器包含只读存储器,标定数据放在只读存储器中不能被修改。
我们可以使用一定的硬件和INCA软件去嫁接只读存储器和随机存储器,标定数据同时下载到INCA的随机储存器,这样标定工程师就能在线修改标定数据,而不需要修改实际存储器中的标定数据。
●变量和匹配值(variable and calibration value):变量表征发动机状态,不可修改;匹配值可以由匹配工程师进行修改。
INCA软件的使用目的:建立一个能实现有第一次预喷的试验首先建立一个试验环境(可以直接打开卢红兵给的新的试验环境,把卢红兵给的试验环境直接复制到D:\ETASData\INCA5.1\Database目录下。
)1.先建立一个新的试验,如图所示。
更名为test(随便,可以是任何名字)2.这时选择工作区(workspace),在expreiment窗口更换试验到test试验。
然后双击workspace 进入试验test的工作区。
如下图切换试验到test切换试验到test双击workspace之后出现下面窗口,这就是test试验的工作界面。
3.一般在工作区域下要建立几个层,这样是为了使工作区有条理性,比如说建立一个监测层和一个用于预喷计算的计算层。
(这是针对本次试验而建的)出现下面的界面建立两个层,并重命名这样在图的下方出现了两个层4.现在一个典型的工作区已经建好了,那么下面的工作就是如何实现自己想要的试验。
首先要考虑一般试验要监测的基本参数,比如说发动机的转速(eng_nAvrg)、油门踏板比率和安全检查(AccPed_rChkdVal,其实主要是用来看踩油门踏板的百分比,可在说明文件的80找到)、共轨的压力(Railcd_pPeak,最后10秒轨压的最大值,说明文件的428页)、当前的喷油量(Injctl_qsetUnBal,当前的喷射量,可在说明文件的416页找到)、发动机机械状况(EngM_stSync,可在说明文件650页找到)选择变量点击后出现下面窗口选择变量(可以在变量区直接输入变量的名称进行查找),点击一下即可选择。
选择好后的情况下面对所选的变量进行定义出现下面界面定义参数的类型,以及显示类型为了便于观测,定义为示波器形式。
确定后出现下面的窗口。
另外还有一部分变量是应该监测的。
对于本次试验还要监测InjCrv_stInjCharDes_mp(用户想得到的喷射特性,具体请看说明文件的691页)、InjCrv_stInjCharsetVal(喷射特性设定值,具体请看说明文件的708页)、InjCrv_stInjCharActVal(喷射特性的现行值,具体看说明文件的469页)、InjCrv_stPiIRlsStruct_mp(预喷放行的结构,具体看说明文件的690页),因为喷射特性的实际值和用户想得到的喷射特性不一定一样,这样就出现了问题,这与上面的InjCrv_stPiIRlsStruct_mp有关。
一、发动机台架欧3机连接线束说明:1.ECU上接有三个线束,比较大的一个是整车线束(1),共89个针脚。
两个稍小一点的分别为传感器线束(2)和喷油器线束(3)。
其中传感器线束共36个针脚,喷油器线束共16个针脚。
2.台架试验中整车线束一般接16根线,其中电源线4根正极(2,3,8,9)接24V稳压电源正极,4根负极(5,6,10,11)接24V 稳压电源负极;点火开关(40)接24V稳压电源正极;踏板线束6根(76,77,78,79,80,84);K线(89)与INCA软件通讯用。
3.传感器线束一共包括5个传感器:凸轮轴传感器(9,10)、曲轴转速传感器(19,23);进气压力传感器(25,33,34,36);水温传感器(15,26);轨压传感器(12,13,14);喷油器线束除6个缸以外,还有高压泵的流量计量单元(ZME,9,10)。
4.标定工具ES590或ES690上连接与电脑通讯的网线一根,接24V稳压电源的电源线一根,与带ETK的ECU通讯的ETK线一根,与ECU通讯的K线一根。
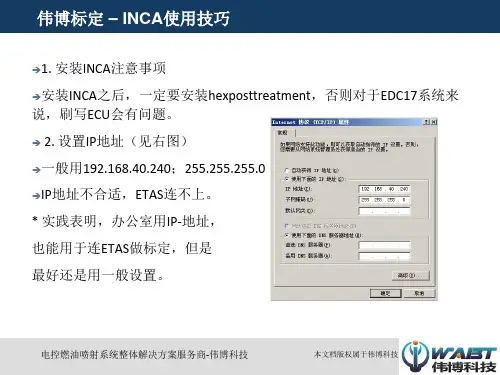
其中K线红(接24V稳压电源正极),黑(接24V稳压电源负极),黄(接信号线1.89)二、INCA(Integrated Calibration and Application)软件基本操作1. 网址设置(Network Setting)要使计算机与ES590正常通讯,必须正确设置网址。
首先将控制面板中所用的网卡IP设置为192.168.40.2(→10)其次在INCA软件菜单中→Utilities→ETAS Network settings →Continue→Default→Continue→Finish2. INCA基本操作①建立数据库(items)、工作区(workspace)、环境文件(Experiments)、选取硬件(Hardware)。
②建立数据库时,在items中右键→Add→Add top folder,items右键→Add→ECU project(A2L),此时出现选择.a2l文件的对话框。
INCA软件最新版操作⼿册INCA EnergyOperator Manualf??ìé=OKN=g~?ì~êó=OMMSOxford Instruments AnalyticalHalifax RoadHigh Wycombe HP12 3SE, UKSection 1 - INCA Energy System Overview1Section 2 - Introduction to INCA Energy Software2 Navigators23 DataManagementHelp 10 Energy Options12Section 3 – Description of Main Steps131.Optimum Microscope Conditions Setup for X-ray Microanalysis142.Quant optimization - Why do we need to do it?173.Selecting Optimum Acquisition Conditions for X-ray Acquisition194.Start/Stop/Resume Spectrum Acquisition215.Automatic Peak Identification (AutoID)216.Manually Identifying Peaks237.Spectrum Display and Manipulation258.Spectrum Export259.Four Modes of Spectra Acquisition2510.Acquiring Spectra from Lines and Grids of Beam Points27 /doc/9e651c43eff9aef8941e069d.html pare2912.Quantitative Analysis3113.SmartMap4514.Element Maps4815.LineScan5016.Cameo+5217.PhaseMap53QuantMap5718.19.AutoMate59Montage 6520.21.Feature6884Report22.Section 1 - INCA Energy System OverviewThe main components that make up an INCA Energy system are:PCx-stream module to control X-ray acquisition and/ or mics module to control imaging EDS detector to detect X-raysThe PC is loaded with the INCA Energy software and an IEEE 1394 card.System Block DiagramFigure 1: INCA Energy SystemPage 1Page 2Section 2 - Introduction to INCA Energy SoftwareThe INCA software platform has four main components:Navigators ?Data Management ?Help ?Energy OptionsNavigatorsThe INCA software platform has unique navigators for guiding the user through the stages of the microanalysis process from starting a new project to producing a hardcopy report.You can easily switch between a Navigator, which directs the work flow, and the data tree which keeps avisual record of work progress.Point & ID Navigator Data treeData ManagementData within INCA Energy and Energy TEM is archived in a logical and easily accessible manner and can be directly viewed in the Data tree. To access the Data tree, press the Data tab to the right of the Navigator tab.ProjectsWithin INCA Energy, data is managed within Projects as illustrated by the Data tree shown above. As you acquire data, you will see your data build up in the Data tree. The entries in theData tree can be renamed within the Data tree view.Within a Project you may examine more than one Sample, and on each Sample, more than one Site of Interest. Data acquired from an individual Site of Interest is stored together for example electron or Cameo+ image, spectra and maps as easily recognizable icons as displayed below:Page 3Page 4SpectrumProjectSmartMapSampleSite of InterestReconstructed spectrumSynthesized spectrumPhaseMapCameo+imageElement MapISIS Imported spectrumElectron imageOther images (e.g. ISIS Importedimage)Combined ED/WD spectrumNote that more than one Project can be viewed at any one time in the Data tree. ?A Project is a single file with the extension .ipj which can be saved in any directory on any drive in the conventional Windows? way. Note that the name of the current Project is displayed as partof the Menu Title.At any time you can save your Project by going to the main menu, under File and selecting 'Save Project as' or using Ctrl and S on the keyboard. Autosaving your ProjectYou can set the Autosave function to save your current Project at regular intervals. This can be set by going to the main menu, under Options, and checking the box in Preferences under'Saving'.If you open a Project and you have the Autosave function on, Autosave will save the Project ontop of the original.If you create a Project and save it and you have the Autosave function on, further autosaves will save the Project to the original saved location.If you create a new Project and you have the Autosave function on, Autosave will save the Project to a recovery file.The recovery file is located under Program files\INCA\Data. If you wish to open this file, make a copy of this file with a different name in a different directory.Note that Autosave does not take effect during data acquisition.Autosave does not function on read-only Projects.If you have multiple Projects open, ensure that you save your Projects.Samples and Site of InterestWithin a Project you may analyze more than one Sample, and on each Sample, more than one Site of Interest.Data acquired from an individual Site of Interest is stored together for example electron or Cameo+ image, spectra and maps as easily recognizable icons. The current analytical conditions such as kV, Mag and Quant optimization data are also stored with the data.Thumbnail images of the individual images and spectra can be easily viewed by hovering over the data labels with the mouse.Page 5Exporting spectra, images, maps, linescans and Cameo+ dataElectron images, maps, linescans, Cameo+ images and spectra can be exported from INCA in a variety of formats thus allowing them to be read by appropriate software packages. You can export either from the data tree or from theimage/spectrum viewer:Data treeTo export from the Data tree click with the right hand mouse button on the data label and select Export. This enables the user to convert and export the data in file formats such as JPG and TIF:Image ViewerWhen you click with the right hand mouse button on an image or map you have two options for exporting:?ExportThis allows the data to be converted as a bitmap (BMP), TIFF (TIF), or JPEG(JPG, with optional high compression) file. You can select the image size fromthe drop-down list. The default size is set to the size of the original image. Enterthe file name and select a folder in which you wish to save the image:Page 6Page 7Export Data OnlyThis allows the raw data to be exported in suitable formats for further processinge.g., 8-bit or 16-bit TIF and TSV (Tab Separated Variable). Only raw data isexported without contrast enhancement or annotation. However, the TIFF Coloroption will save a color image with contrast enhancement. The scalinginformation is also included in the exported data.If you have analySIS ?software (Soft Imaging Systems) installed on your computer you can export the data to the analySIS ?database. There are two options for exporting data to the analySIS ?database:analySIS ?database: Use this option if you wish to export the raw data. analySIS ?database (color): Use this option if you wish to export eithera Cameo+ image or a contrast enhanced image. Spectrum ViewerWhen you click with the right hand mouse button on the spectrum you are allowed to convert and export the spectrum as BMP, TIF, JPG or WMF(Metafile). You can also export the spectrum inEMSA or ISIS format. If you have analySIS software installed on your computer you can exportthe data to the analySIS database.Linescan ViewerYou can export a linescan in a variety of formats. When you click with the right hand mousebutton on the linescan you are allowed to convert and export the linescan as BMP, JPG or TSVetc.Note that it is the data as currently displayed which is exported. Therefore, if the current image has been zoomed, the contrast or brightness, the color or the spectrum scaling has beenchanged, this will be included in the conversion.Note also that images exported to files include the scalemarker.Exporting SmartMap dataYou can export the current SmartMap data by selecting 'Export SmartMap' under File from the main menu.Exporting data in an INCA formatElectron images, maps, Cameo+ images and energy dispersive (ED) spectra can be exported from INCA in an INCA format. These can be displayed within INCA Viewer.Click with the right hand mouse button on the data label, select Export and then, INCA Export Format. This allows the data to be converted and exported in file formats: .iex for spectra and .mcv for images. INCA ViewerINCA Viewer is installed with INCA although INCA Viewer can be installed separately if desiredTo start INCA Viewer either:Double click on the exported file from Windows ExplorerSelect INCA Viewer from Start/Programs/Oxford Instruments menuCopying spectra, images, maps, linescans and Cameo+ dataSpectra, electron images, maps, linescans, Cameo+ images and spectra can be copied to the clipboard from INCA Energy in two ways:1.By clicking with the right hand mouse button on the data label and selecting Copy.2.By clicking with the right hand mouse button on the image, linescan etc and selecting Copy. Hereyou are allowed to choose the size of the image before you copy it to the clipboard:The data will be copied to the Clipboard. You can then use your desired application into which you wish to transfer the image etc from the Clipboard.Note that it is the data as currently displayed which is copied. Therefore, if the current image has been zoomed, the contrast or brightness, the color, or the spectrum scaling has been changed;this will be included in the copying.Note also that images copied to the clipboard include the scalemarker.Page 8Deleting images, spectra, samples and Sites of InterestSpectra, electron images, maps, linescans, Cameo+ images and spectra can be deleted from INCA Energy by clicking with the right hand mouse button on the data label and selecting delete.Projects, Sites of Interest and Samples can also be deleted directly from the Data tree by clicking with the right hand mouse button on the appropriate icon.Note: You can not delete the last Site of Interest in a Sample and last Sample in a Project. Page 9Page 10HelpThere is an expert multimedia user Help system, which is fully integrated with the applications software. The Help has the following features:On-line Bubble help and tool tips for expert advice and guidance through each stage of the microanalysis process.A fully integrated and indexed microanalysis encyclopaedia that provides comprehensive description of key microanalysis terms, background, and theory.Multimedia training and background tutorials with movie based modules.‘Getting Started’ multimedia tutorial for immediate training of new user.Also, advice on using the application to achieve good results.INCA Bubble HelpINCA TutorialsPage 11Energy OptionsThe basic packaged system has two navigators:AnalyzerMappingThe advanced packaged system has three navigators:AnalyzerPoint & IDMappingThere are additional software options such as Cameo+, Spectrum Synthesis, PhaseMap, Matching, AutoMate, GSR, QuantMap and Feature. The basic system can be upgraded in steps by adding new software options easily.Application KeysEach software application is supplied as a key-enabled locked module. You need to have an appropriate key for unlocking each application.Page 12Section 3 – Description of Main StepsThis manual describes the main steps to enable the users to carry out analysis using the INCA Energy system. Comprehensive INCA Energy Help is available within the software that users can easily access for further information. List of topics described in the manual are:1. Optimum Microscope Conditions Setup for X-ray Microanalysis2. Quant Optimization3. Selecting Optimum Conditions for X-ray Acquisition4. Start/Stop/Resume Spectrum Acquisition5. AutoMatic Peak Identification (AutoID)6. Manually Identifying Peaks7. Spectrum Display and Manipulation8. Spectrum Export9. Four Modes of Spectrum Acquisition10. Acquiring Spectra from Lines & Grids of Beam Points11. Compare12. QuantitativeAnalysis13. SmartMapMaps14. Elementscans15. Line16. Cameo+17. PhaseMap18. QuantMap19. AutoMate20. Montage21. Feature22. ReportPage 131. Optimum Microscope Conditions Setup for X-ray MicroanalysisThe main purpose of this step is to enable you to set up an appropriate X-ray count rate from your sample to use for your analysis before you start collecting data into your Project.If you are starting a new session with INCA Energy, there are a few things we recommend you optimize on your microscope, which will ensure that you get the best results for your analysis.The main points to consider are listed below.1.1 Are you working with tilted samples?If you are working with tilted samples and you are going to use the spectrum for quantitative analysis, it is important to enter the correct value of the sample tiltIf you have purchased Microscope Control (the application for controlling and reading the electron beam and column parameters ) and you have a motorized tilt stage, the current tilt angle will be automatically read by the software.More commonly, the stage tilt will not be motorized; in which case you will need to enter the value into Microscope Control.1.2 What value of accelerating voltage should I use?Initially you need to choose a kV to get an image of your sample and then you can adjust the beam current such that you get sufficient X-rays in your spectrum. You may want to refine the kV once you have performed a more detailed analysis on your sample.20kV is a good starting point, particularly if the sample is unknown. This kV will excite most X-ray lines from most elements and these will be automatically identified in the spectrum.Choose a lower kV if you are concerned about:1. Accuracy of quantification of light elements since the lower penetration into the samplewill reduce the absorption correction.2. Analysis of a small particle, inclusion or a film less than 10mm in depth since a smallerexcitation volume will enhance the contribution from these features.If you have purchased Microscope (column) control INCA Energy will automatically read the current microscope accelerating voltage.If you have not purchased Microscope (column) control and you are working in Point & ID, you will need to go to the ‘Site of Interest step’ in the Navigator and manually enter the currentkV on your microscope into the space provided. Alternatively, select Microscope (column)control under Options from the main menu and enter the kV in the space provided.1.3 Setting up the beam currentIt is generally easiest to setup the microscope if you operate in secondary electron imaging mode.The next stage is to produce a stable beam of electrons for X-ray microanalysis. You may have a tungsten,LaB6 emitter or a field emission gun each requiring its own type of setup procedure.The degree of electron emission can be monitored in more than one way, depending on your microscope. If you have a tungsten or LaB6gun, it is good practice to increase the filament current slowly as this will preserve the lifetime of the filament. Initially, as you increase the filament or heating current, the beamPage 14current increases to an initial maximum, before dropping and then rising again to a point above which the beam current no longer increases. This is known as the saturation point, and any further increase in heating current just reduces the lifetime of the filament.With the filament operating at the saturation point, emission is stabilized and this is where you should operate if you wish the beam to be stable.You can observe the saturation point for a filament by viewing the trace variation on the CRT, or waveform monitor, which represents the signal from the sample. Increase the filament current such that you no longer produce an increase in the height of the waveform above the baseline. At this point, you have reached filament saturation.Another common way of monitoring the emission from a gun is by observing the so called ‘emission image’.1.4 Working distanceThe working distance is defined as the distance between the lower pole piece of the objective lens and the plane at which electrons are focused.1.4.1 Which value of working distance should I use for X-ray microanalysis?Ensure that the working distance, as displayed in millimeters on your microscope monitor, is the desired value for performing X-ray microanalysis. This is specific to the geometry of the detector mount on the SEM chamber.The recommended value for your instrument can be viewed by going to Microscope Control from the Options menu on the INCA menu bar.If you have purchased Microscope (column) Control, the value of the working distance displayed on your microscope monitor will be automatically read by INCA Energy. If you do not have Microscope (column) control installed, you should manually enter the working distance by selecting Microscope (column) control under Options from the main menu.1.4.2 How do I adjust the working distance?Adjust the strength of the objective lens by adjusting the ‘focus’ on your microscope until your microscope monitor displays the recommended working distance. Note that your image may now appear out of focus.Carefully adjust the sample height using the Z drive of your stage so that the image comes into focus. Check for excessive lens hysterisis.If you move to another area of the sample or move to another sample completely, don’t adjust the focus, but adjust the Z drive of the stage to bring the image into focus. This means that X-rays are always generated at the same position within the microscope, which gives the correct geometry for the detector. Take care that if you have a large sample, or have many samples of different heights mounted on the stage, that any sample does not collide with any detector mounted directly below the pole piece of the objective lens (e.g. backscattered electron detector).1.4.3 How to improve image qualityBy now you should see a focused image on your microscope monitor.The quality of your image will very much depend on how well your column has been aligned. Your image quality will be optimized if your filament has been exactly centered in the gun area, and the electron beam travels exactly down the optic axis of the column before it strikes the sample. There are a variety of methods provided on microscopes to achieve these optimum conditions.Page 15Some microscopes have a ‘Wobbler’ button to check the alignment of the objective aperture which when activated fluctuates the objective lens current about a fixed value. Alternatively you can manually increase and decrease the focus about a fixed point.If you do this, look at your secondary electron image, it will appear to go through focus but will distort if the objective aperture is not centered. When correctly centered, the image will appear to go in and out of focus, without moving or distorting.You may further improve the quality of the image by adjusting the stigmators on your microscope. Astigmatism manifests itself in images by causing streaking of features as you change the focus about a fixed point. You can reduce any astigmatism by adjusting the stigmators in conjunction with the focus.If you are going to perform any X-ray analysis, make sure that you re-adjust the focus to ensure that you are operating at your recommended working distance and bring your image into focus using the Z drive of the stage.Page 16。
INCA软件教学1.INCA基础在使⽤INCA软件建⽴试验环境时必须⽤到两个⽂件A2L、HEX·A2L描述⽂件(*.a2l)包含数据和控制单元程序的物理描述,它包括— 结构信息— 地址范围— 存储器⼤⼩— 每个参数和测量信号的地址范围— 每个参数和测量信号的名字·HEX⽂件(*.hex、*.s19)包含控制单元程序的代码和数据,这些内容能直接读取到控制单元并且被各⾃的处理器执⾏。
2.建⽴⼀个新的试验环境Inca软件界⾯打开之后下图:这时点开database菜单并指向new标签确定打开⼀个new database 对话框,在框内键⼊dcd(你想⽤的任何名字)确定后如下图:导⼊要⽤的A2L⽂件选择A2L⽂件选择HEX⽂件确定后会发现出现⼀个对话框,正在读取a2l⽂件和hex⽂件读取完成后界⾯如下:在界⾯右侧显⽰的就是刚才读取HEX⽂件,⽽左侧是A2L⽂件。
这时增加⼀个试验同样你也可以对试验进⾏命名,我们姑且把它命名为dcd增加⼀个⼯作区workspace我们也可以对⼯作区进⾏命名因为在⼀个根⽬录下你不能使⽤相同的名字,如果你把试验命名为dcd,同样也把⼯作区命名为dcd的话,它会默认⽣成dcd_1这样的名字,同时我们也可以对根⽬录更改名字。
点击⼯作区dcd_1,在整个窗⼝的右侧出现如下图的界⾯,点击改变试验(红线)这时会出现⼀个选择试验的对话框,将刚才我们建⽴的试验dcd导⼊导⼊硬件配置和数据,点击如下图的打开窗⼝,会出现在⼀个选择的对话框,然后选择硬件配置和数据,点OK确定。
完成后如下图:下⾯配置PC和ETAS690的通讯系统点击如下图菜单及选项会出现⼀个对话框,来进⾏⽹络配置我们可以点击缺省设置(如果PC机上的⽹络已经配置过,这时应注意没有禁⽤相应的⽹络)下⾯我们搜索⼀下可⽤的硬件连接,此时注意⼀下是否所有的硬件已经连接好,包括发动机线束和整车线束与ECU的连接、ETAS⼯具和ECU的连接以及各种供电设备。
INCA基本使用INCA是一种用于汽车和发动机控制系统开发和测试的工具。
INCA (Integrated Calibration and Application Platform)集成了测量、校准、诊断和过程管理等功能,为工程师提供了一种全面而强大的工具来开发和测试机械和电子控制系统。
下面将介绍INCA的基本使用方法。
首先,INCA提供了丰富的测量和数据采集功能。
工程师可以通过选择和配置适当的测量设备来测量和记录各种传感器的信号和控制模块的输出。
INCA支持多种类型的采样率和数据格式,可以根据需要进行设置并保存相应的配置文件。
此外,INCA还提供了一些实时监控功能,可以实时显示和记录采集到的数据。
其次,INCA还提供了校准功能。
校准是指通过调整控制模块中的参数来改变系统的行为。
通过INCA的校准功能,工程师可以获取实时数据、修改参数并重新加载校准数据。
INCA通过与控制模块的通信,实时更新参数,并提供即时的反馈信息。
此外,INCA还提供了一些辅助工具,如曲线拟合和优化算法,以帮助工程师更轻松地进行校准工作。
INCA还提供了强大的诊断功能。
工程师可以通过INCA监测和记录控制模块的故障码和错误状态,快速诊断和解决问题。
INCA还可以与车辆的诊断接口进行通信,读取和清除故障码,并通过INCA的用户界面提供详细的诊断信息。
此外,INCA还提供了过程管理功能。
通过INCA,工程师可以创建和管理整个开发过程中的任务和工作流程。
INCA提供了一个用户友好的界面,可以轻松创建、分配和跟踪任务,并根据需要进行管理和优化。
INCA还提供了一些报表和数据分析工具,可以帮助工程师更好地理解和解释测试和校准结果。
INCA还具有良好的兼容性和扩展性。
INCA可以与各种测量设备、控制模块和诊断接口进行通信,并支持多种数据格式和通信协议。
此外,INCA还提供了一些API接口,可以与其他软件和工具进行集成,以满足特定的需求。
总结来说,INCA是一种功能强大的汽车和发动机控制系统开发和测试工具。