VB中利用FSO对象对文件夹操作
- 格式:docx
- 大小:37.29 KB
- 文档页数:5

四、VBA获取目录、文件路径简明代码(VB语句、FSO两种方式)(一)VB语句方式''''程序入口↓''''获取所有文件路径Sub GetFileList()Call GetFolderList ''''调用GetFolderList()过程获取所有文件夹路径Columns(2).ClearDim fileName, folderPath As StringDim rowIndexA, rowIndexB, maxRow, lastRowA As Integer maxRow = Rows.CountlastRowA = Cells(maxRow,1).End(xlUp).RowFor rowIndexA =1To lastRowAfolderPath = Cells(rowIndexA,1).ValuefileName = Dir(folderPath)rowIndexB = Cells(maxRow,2).End(xlUp).Row +1Do While fileName <>""Cells(rowIndexB,2).Value = folderPath & fileNamerowIndexB = rowIndexB +1fileName = DirLoopNext rowIndexAEnd Sub''''获取GetMainDirectory拾取文件夹路径下的所有文件夹,放到A列Sub GetFolderList()Dim folderName As StringDim i, k As IntegerColumns(1).ClearCells(1,1).Value = GetMainDirectory(msoFileDialogFolderPicker)&"\"i =1k =1Do While i <= kfolderName = Dir(Cells(i,1).Value, vbDirectory)DoIf InStr(folderName,".")=0And _(GetAttr(Cells(i,1).Value & folderName)And vbDirectory)= vbDirectory Thenk = k +1Cells(k,1).Value = Cells(i,1).Value & folderName &"\"End IffolderName = DirLoop Until folderName =""i = i +1LoopEnd Sub''''函数,拾取一个文件夹路径,返回路径字符串Function GetMainDirectory(ByVal DialogType As MsoFileDialogType)As StringWith Application.FileDialog(DialogType)If.Show =True ThenGetMainDirectory =.SelectedItems(1)End IfEnd WithEnd Function(二)FSO方式''''##############################''''工具——引用类库文件"Microsoft Scripting Runtime"''''##############################''''程序入口↓''''获取文件列表Sub FsoGetFileList()Dim folderPath As StringDim maxRow, lastRow, maxRowB, LastRowB As IntegerDim i As IntegerDim folder, allFiles As ObjectDim fso As New FileSystemObjectCall FsoGetFolderList ''''调用FsoGetFolderList方法获取目录列表Columns(2).ClearmaxRow = Rows.CountlastRow = Cells(maxRow,1).End(xlUp).RowFor i =1To lastRowfolderPath = Cells(i,1).ValueSet folder = fso.GetFolder(folderPath)Set allFiles = folder.FilesmaxRowB = Rows.CountLastRowB = Cells(maxRowB,2).End(xlUp).Row +1For Each File In allFilesCells(LastRowB,2).Value = File.PathLastRowB = LastRowB +1NextNext iEnd Sub''''获取文件夹列表Sub FsoGetFolderList()Dim rowIndex As IntegerDim folderPath As String''''调用函数获取主文件夹目录folderPath = GetMainDirectory(msoFileDialogFolderPicker) rowIndex =1Columns(1).ClearDoIf rowIndex =1ThenGetFolderPath (folderPath)Cells(rowIndex,1).Value = folderPathElseGetFolderPath (Cells(rowIndex,1).Value)End IfrowIndex = rowIndex +1Loop Until Cells(rowIndex,1).Value =""End Sub''''定义函数,作用是获取给定文件夹路径(mainFolderPath)的子文件夹Function GetFolderPath(mainFolderPath)Dim mainFolder, childFolders As ObjectDim index As Integer''''创建FileSystemObject对象fsoDim fso As New FileSystemObject''''从路径获得folder对象mainFolderSet mainFolder = fso.GetFolder(mainFolderPath)''''获得mainFolder的子目录集合childFoldersSet childFolders = mainFolder.SubFolders''''行号初始值设定为A列最后一个非空行的+1行,第一次执行的时候index=2index = Cells(Rows.Count,1).End(xlUp).Row +1''''for each ……in 遍历集合取每一个子目录childFolder的路径pathFor Each childfolder In childFoldersCells(index,1).Value = childfolder.Path ''''路径index = index +1NextEnd Function''''函数,拾取一个文件夹路径,返回路径字符串Function GetMainDirectory(ByVal DialogType As MsoFileDialogType)As StringWith Application.FileDialog(DialogType)If.Show =True ThenGetMainDirectory =.SelectedItems(1)End IfEnd WithEnd Function。

利用FSO的创建文件夹,文件,删除文件重命名等等fso的创建文件夹,文件,删除文件,重命名等等千万要支持下哦!不明白的可电话联系我134********<%'/doc/3312896609.html,Function AutoCreateFolder(strPath) ' As BooleanOn Error Resume NextDim astrPath, ulngPath, i, strTmpPathDim objFSOIf InStr(strPath, "\") <=0 Or InStr(strPath, ":") <= 0 ThenAutoCreateFolder = FalseExit FunctionEnd IfSet objFSO = Server.CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")If objFSO.FolderExists(strPath) ThenAutoCreateFolder = TrueExit FunctionEnd IfastrPath = Split(strPath, "\")ulngPath = UBound(astrPath)strTmpPath = ""For i = 0 To ulngPathstrTmpPath = strTmpPath & astrPath(i) & "\"If Not objFSO.FolderExists(strTmpPath) Then' 创建objFSO.CreateFolder(strTmpPath)End IfNextSet objFSO = NothingIf Err = 0 ThenAutoCreateFolder = TrueElseAutoCreateFolder = FalseEnd IfEnd Function%>papername=session("paperName")username=session("user_name")'自动创建文件夹pathsub1=papernameMyPath = server.mappath(pathsub1)AutoCreateFolder(MyPath)====================================== ============================='建立文件filename = year(date()) & month(date()) & day(date()) & hour(time()) & minute(time()) &second(time()) & ".txt"Set fso = Server.createobject("scripting.filesystemobject")thepath = Server.mappath(filename)Set thefile = fso.createTextfile(thepath)thefile.writeline "新建立文件"thefile.closeSet fso = Nothing'删除文件Sub DelFile(filename)Dim fo,filenamestrSet fo = Server.Createobject("Scripting.FileSystemObject") filenamestr = Server.MapPath(filename)If fo.FileExists(filenamestr) Then fo.DeleteFile filenamestrSet fo = NothingEnd Sub重命名<%Dim fsoSet fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")fso.MoveFile server.mappath("tupian.jpg"),server.mappath("图片.jpg")Set fso=Nothing%>方法二:<%Dim fso,fSet fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")Set f = fso.GetFile(server.mappath("tupian.jpg"))/doc/3312896609.html,="图片.jpg"Set f=NothingSet fso=Nothing%>fso中判断文件夹是否存在set fso = server.createobject("ing.filesystemobject")if fso.FolderExists(server.mappath("../folderName"))=false thenREsponse.write("此文件夹不存在")end iffso中判断文件是否存在set fso = server.createobject("ing.filesystemobject")iffso.fileexists(server.mappath("../folderName/fileName.htm")) = true thenResponse.write("文件存在")end if一,fso.GetFile提取文件相应的 File 对象1,getfile.asp<%whichfile=Server.MapPath("cnbruce.txt")Set fso = CreateObject("s cripting.FileSystemObject")Set f1 = fso.CreateTextFile(whichfile,true)f1.Write ("This is a test.My Name is cnbruce.")f1.CloseSet f2 = fso.GetFile(whichfile)s = "文件名称:" & /doc/3312896609.html, & ""s = s & "文件短路径名:" & f2.shortPath & ""s = s & "文件物理地址:" & f2.Path & ""s = s & "文件属性:" & f2.Attributes & ""s = s & "文件大小: " & f2.size & ""s = s & "文件类型: " & f2.type & ""s = s & "文件创建时间: " & f2.DateCreated & ""s = s & "最近访问时间: " & f2.DateLastAccessed & ""s = s & "最近修改时间: " & f2.DateLastModifiedresponse.write(s)%>其效果正如右键某文件,看到的具体属性信息。

VBA中的文件夹批量操作技巧与示例在进行VBA编程时,经常需要对文件夹进行批量操作,例如批量创建文件夹、批量复制或移动文件夹、批量删除文件夹等。
本文将介绍如何使用VBA实现这些文件夹的批量操作,并给出相应的示例代码。
1. 批量创建文件夹在VBA中,可以使用FileSystemObject对象的CreateFolder方法来创建文件夹。
首先,需要引用Microsoft Scripting Runtime库,然后使用下面的代码示例来批量创建文件夹:```vbaSub CreateFolders()Dim fso As ObjectDim folderPath As StringDim i As IntegerSet fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")folderPath = "C:\Folder\" '指定要创建的文件夹路径For i = 1 To 10 '指定要创建的文件夹数量fso.CreateFolder folderPath & "Folder" & iNext iSet fso = NothingEnd Sub上述代码使用了循环结构和字符串拼接来批量创建指定数量的文件夹。
你只需修改folderPath变量的值为你想要创建文件夹的路径,并修改循环的起始值和终止值即可。
2. 批量复制或移动文件夹在VBA中,可以使用FileSystemObject对象的CopyFolder和MoveFolder方法来实现文件夹的复制和移动操作。
下面是示例代码:```vbaSub CopyOrMoveFolders()Dim fso As ObjectDim sourceFolderPath As StringDim destinationFolderPath As StringSet fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")sourceFolderPath = "C:\Folder1\" '指定要复制或移动的文件夹路径destinationFolderPath = "C:\Folder2\" '指定目标文件夹路径'复制文件夹fso.CopyFolder sourceFolderPath, destinationFolderPath'或者移动文件夹'fso.MoveFolder sourceFolderPath, destinationFolderPathSet fso = NothingEnd Sub在上述示例代码中,你需要将sourceFolderPath和destinationFolderPath变量的值修改为你要复制或移动的文件夹路径和目标文件夹路径。

VBS中FSO文件与文件夹的基本操作VBS中FSO文件的基本操作一、文件属性:在windows中,文件的属性一般用数字来表示:0 代表normal,即普通文件未设置任何属性。
1 代表只读文件。
2 代表隐藏文件。
4 代表系统文件。
16 代表文件夹或目录。
32代表存档文件。
1024代表链接或快捷方式。
例如:set fs=wscript.createobject(“scripting.filesystemobject”)set f=fs.getfile(“d:\index.txt”)msgbox f.Attributes ‘attributes函数的作用是显示文件属性需要说明的是:msgbox显示的结果往往不是上面说明的数字,而是有关属性代表数字的和二、创建文件:object.createtextfile方法,注意创建前一般需要检查文件是否存在。
例如:set fso=wscript.createobject(“scripting.filesystemobject”)if fso.fileexists(“c:\kk.txt”) thenmsgbox “文件已存在”else set f=fso.createtextfile(“c:\kk.txt”)end if如需要强制覆盖已存在的文件,则在文件名后加true参数。
三、复制、移动、删除文件:使用copyfile方法、movefile方法、deletefile方法。
例如:set fso=wscript.createobject(“scripting.filesystemobject”)fso.copyfile “c:\kk.txt”,”d:\1\kk.txt”,true //如上文说述,true代表强制覆盖fso.movefile “c:\kk.txt”, “d:\”//移动文件fso.deletefile “c:\kk.txt”//删除文件四、文件的读写:1、打开文件:使用opentextfile方法如:set ts=fso.opentextfile(“c:\kk.txt”,1,true)说明:第二个参数为访问模式1为只读、2写入、8为追加第三个参数指定如文件不存在则创建。

VB遍历文件目录的实现方法总结2009-04-25 20:44VB遍历文件夹的实现方法总结一共三种,如下:1 使用FSO对象模型'===================================================================== ========'描述:需要Scripting类型库(Scrrun.dll)支持。
实际使用时需要引用Microsoft Scripting Runtime'优点:测试当中没有错误。
可以检测隐藏文件。
'示例:一个文本标签、一个ListBox、一个命令按钮。
都取默认名称即可'===================================================================== ========Dim fso As New FileSystemObjectDim fld As FolderPrivate Sub Command1_Click()Dim nDirs As Long, nFiles As Long, lSize As CurrencyDim sDir As String, sSrchString As StringsDir = InputBox("Type the directory that you want to search for", _"FileSystemObjects example", "C:\")sSrchString = InputBox("Type the file name that you want to search for", _"FileSystemObjects example", "vb.ini")MousePointer = vbHourglassLabel1.Caption = "Searching " & vbCrLf & UCase(sDir) & "..."lSize = FindFile(sDir, sSrchString, nDirs, nFiles)MousePointer = vbDefaultMsgBox Str(nFiles) & " files found in" & Str(nDirs) & _" directories", vbInformationMsgBox "Total Size = " & lSize & " bytes"End SubPrivate Function FindFile(ByVal sFol As String, sFile As String, _nDirs As Long, nFiles As Long) As CurrencyDim tFld As Folder, tFil As File, FileName As StringOn Error GoTo CatchSet fld = fso.GetFolder(sFol)FileName = Dir(fso.BuildPath(fld.Path, sFile), vbNormal Or _vbHidden Or vbSystem Or vbReadOnly)While Len(FileName) <> 0FindFile = FindFile + FileLen(fso.BuildPath(fld.Path, _FileName))nFiles = nFiles + 1List1.AddItem fso.BuildPath(fld.Path, FileName) ' Load ListBoxFileName = Dir() ' Get next fileDoEventsWendLabel1 = "Searching " & vbCrLf & fld.Path & "..."nDirs = nDirs + 1If fld.SubFolders.Count > 0 ThenFor Each tFld In fld.SubFoldersDoEventsFindFile = FindFile + FindFile(tFld.Path, sFile, nDirs, nFiles)NextEnd IfExit FunctionCatch: FileName = ""Resume NextEnd Function2 Api方法'===================================================================== ==========='描述:使用Api。

Excel-VBA操作文件四大方法之三三、利用FileSystemObject对象来处理文件FileSystemObject对象模型,是微软提供的专门用来访问计算机文件系统的,具有大量的属性、方法和事件。
其使用面向对象的“object.method”语法来处理文件夹和文件,使用起来十分方便(需Office 2000以后版本)。
FileSystemObject并不是VBA的一部分,它是以一个COM 组件的形式提供的。
因此,要使用先要创建FileSystemObject对象。
FileSystemObject对象模型包含了下面的对象和集合:·FileSystemObject 主对象,包含用来创建、删除和获得有关信息,以及用来操作驱动器、文件夹和文件的方法和属性。
·Drive 对象,包含用来获得信息的方法和属性,这些信息是关于连接在系统上的驱动器的,如有多少可用空间等。
驱动器不一定是硬盘,也可以是CD-ROM、U盘甚至是通过网络在逻辑上连接的硬盘(如公司里部门共享的服务器网络硬盘)。
·Drives 集合,提供驱动器的列表,这些驱动器以实物或在逻辑上与系统相连接。
Drives集合包括所有驱动器,与类型无关。
·File 对象,包含用来创建、删除或移动文件的方法和属性。
·Files 集合,提供包含在文件夹内的所有文件的列表。
·Folder 对象,包含用来创建、删除或移动文件夹的方法和属性。
·Folders 集合,提供包含在文件夹内的所有文件夹的列表。
·TextStream 对象,用来读写文本文件。
(一)准备工作要使用FileSystemObject对象,先要创建它。
创建FileSystemObject对象要使用CreatObject 函数。
CreateObject 函数用来创建并返回一个对ActiveX 对象的引用。
语法:CreateObject(class,[servername])class 是要创建的应用程序名称和类。

VBA中的文件和文件夹管理指南在VBA中,文件和文件夹的管理是一个重要的任务。
无论是创建、复制、移动还是删除文件和文件夹,都需要使用VBA中的特定函数和方法。
本文将带领大家了解VBA中文件和文件夹的管理指南,并提供一些实用的代码示例。
1. 创建文件夹在VBA中,我们可以使用FileSystemObject对象的CreateFolder方法来创建一个新的文件夹。
下面是一个简单的代码示例,演示了如何创建一个名为"NewFolder"的文件夹:```Sub CreateFolderExample()Dim fso As ObjectDim folderPath As StringfolderPath = "C:\NewFolder"Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")fso.CreateFolder folderPathEnd Sub```以上代码中,首先我们声明了一个FileSystemObject对象,并将其赋值给变量fso。
然后,我们定义了一个名为folderPath的字符串变量,用于指定新文件夹的路径。
接下来,我们使用fso.CreateFolder方法创建新文件夹。
2. 复制文件在VBA中,可以使用FileSystemObject对象的CopyFile方法来复制文件。
下面是一个示例代码,演示了如何将名为"SourceFile.txt"的文件复制到"DestinationFolder"文件夹中:```Sub CopyFileExample()Dim fso As ObjectDim sourcePath As StringDim destinationPath As StringsourcePath = "C:\SourceFile.txt"destinationPath = "C:\DestinationFolder\SourceFile.txt"Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")fso.CopyFile sourcePath, destinationPathEnd Sub```在上述代码中,我们指定了两个路径。

fso.getfolder方法是在VBScript中常用的方法之一,用于获取指定文件夹的对象。
通过该方法,我们可以轻松地遍历文件夹中的所有文件,对文件进行排序、筛选、复制等操作。
在本文中,我们将详细介绍fso.getfolder方法的使用,以及如何对获取的文件夹对象进行排序。
一、fso.getfolder方法的基本语法在VBScript中,我们可以通过以下语法来使用fso.getfolder方法:Set objFolder = fso.GetFolder(folderPath)其中,objFolder表示获取到的文件夹对象,fso表示文件系统对象,folderPath表示要获取的文件夹路径。
二、fso.getfolder方法的常见用法1. 获取文件夹对象我们可以使用fso.getfolder方法来获取指定文件夹的对象,从而对文件夹中的文件进行操作。
我们可以使用以下代码获取名为“test”的文件夹对象:Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")Set objFolder = fso.GetFolder("C:\test")2. 遍历文件夹中的文件通过获取文件夹对象后,我们可以使用递归的方法来遍历文件夹中的所有文件。
下面是一个简单的示例代码:Sub ListFiles(objFolder)For Each objFile in objFolder.Files' 对文件进行操作NextFor Each objSubFolder in objFolder.SubFoldersListFiles objSubFolderNextEnd Sub3. 对文件夹中的文件进行排序在实际的开发过程中,我们经常需要对文件夹中的文件进行排序,以便按照特定的顺序进行处理。
通过fso.getfolder方法获取到文件夹对象后,我们可以使用各种排序算法对文件进行排序,例如按照文件名、文件大小、文件类型等进行排序。
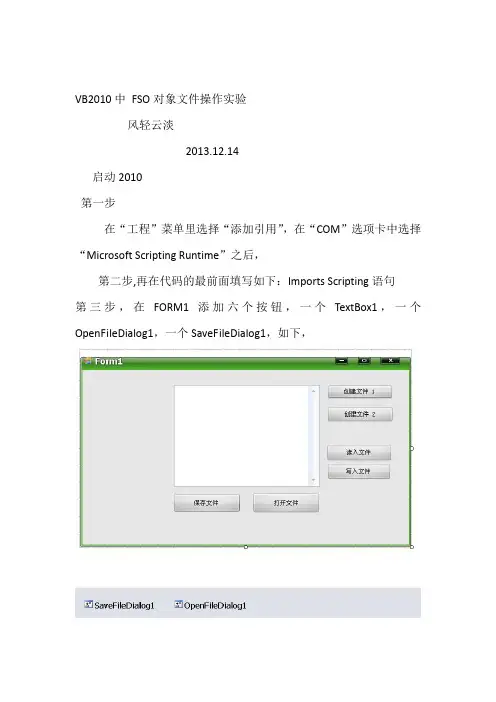
VB2010中FSO对象文件操作实验风轻云淡2013.12.14启动2010第一步在“工程”菜单里选择“添加引用”,在“COM”选项卡中选择“Microsoft Scripting Runtime”之后,第二步,再在代码的最前面填写如下:Imports Scripting语句第三步,在FORM1添加六个按钮,一个TextBox1,一个OpenFileDialog1,一个SaveFileDialog1,如下,下面分别是各个对象的代码:【在输入代码的时候,都有提示供选择,特别要注意有多个参数可以选择时,自己可以分别试试,】Public Class Form1Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.ClickDim fso As New FileSystemObjectDim Fil1 As File'创建文件-1If (fso.FileExists("d:\120.txt")) = False Thenfso.CreateTextFile("d:\120.txt")MsgBox("120.txt:创建成功")ElseMsgBox("120.txt:已经存在")End IfEnd SubPrivate Sub Form1_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.LoadEnd SubPrivate Sub Button2_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button2.Click'创建文件-2Dim fso As New FileSystemObjectDim Fil1 As FileDim duxie As TextStream'带OpenTextFile创建文件duxie = fso.OpenTextFile("d:\321.txt", IOMode.ForReading, True, Tristate.TristateUseDefault)'有四个参数[1文件名和路径,2访问方式,布尔值,读或写的格式]'参数说明:访问方式有:ForAppending,ForWriting,ForReading'布尔值:true和false'读写格式,在输入代码的时候,都有提示供选择End SubPrivate Sub Button3_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button3.Click'读入文件,文件存在,才可以读,没有的话,也就谈不上读了,Dim fso As New FileSystemObjectDim Fil1 As FileDim duxie As TextStreamDim zfc As Stringduxie = fso.OpenTextFile("d:\321.txt", IOMode.ForReading, True, Tristate.TristateUseDefault)zfc = duxie.ReadAll '有duxie.Read,duxie.Readline,duxie.ReadAll,TextBox1.Text = zfcduxie.Close() '关闭打开的对象End SubPrivate Sub Button4_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button4.Click'保存文件Dim fso As New FileSystemObjectDim Fil1 As FileDim duxie As TextStreamDim zfc As Stringzfc = TextBox1.Textduxie = fso.OpenTextFile("d:\321.txt", IOMode.ForAppending, True, Tristate.TristateUseDefault)duxie.WriteLine(zfc)duxie.Close()End SubPrivate Sub Button5_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button5.Click'打开文件Dim fso As New FileSystemObjectDim Fil1 As FileDim duxie As TextStreamDim zfc As StringDim dlg As OpenFileDialog = New OpenFileDialog()dlg.Title = "打开文件" '设置打开对话框的标题dlg.InitialDirectory = ("d:\") '设置默认路径为:d:\dlg.Filter = "文本文件|*.txt|所有文件|*.*" '设置文件过滤器dlg.FileName = OpenFileDialog1.FileName '文件名dlg.ShowDialog() '显示对话框'下面是打开文件进行操作duxie = fso.OpenTextFile(dlg.FileName, IOMode.ForReading, True, Tristate.TristateUseDefault)zfc = duxie.ReadAll '有duxie.Read,duxie.Readline,duxie.ReadAll,TextBox1.Text = zfc '读出的内容送到TextBox1,观察duxie.Close() '关闭打开的对象End SubPrivate Sub Button6_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button6.ClickDim dlg As SaveFileDialog = New SaveFileDialog()Dim fso As New FileSystemObjectDim Fil1 As FileDim duxie As TextStreamDim zfc As Stringdlg.Title = "保存文件"dlg.InitialDirectory = ("d:\") '设置默认路径为:d:\dlg.Filter = "文本文件|*.txt|所有文件|*.*"dlg.FileName = SaveFileDialog1.FileNamedlg.ShowDialog()zfc = TextBox1.Textduxie = fso.OpenTextFile(dlg.FileName, IOMode.ForAppending, True, Tristate.TristateUseDefault) duxie.WriteLine(zfc)duxie.Close()End SubEnd Class到这里,代码工作已经完成,但要注意的是:1:限于文本文件【笔者目的也暂时只是针对文本文件】2:请参考FSO对象的属性和方法3:没有写错误处理代码。

VBA FSO对象模型详解一、简介文件系统对象FSO的英文全称是File System Object ,这种对象模型提出了有别于传统的文件操作语句处理文件和文件夹的方法。
通过采用object.method这种在面向对象编程中广泛使用的语法,将一系列操作文件和文件夹的动作通过调用对象本身的属性直接实现。
FSO 对象模型不仅可以象使用传统文件操作语句那样实现文件的创建、改变、移动和删除,而且可以检测是否存在指定的文件夹,如果存在,那么,这个文件夹又位于磁盘上的什么位置。
更令人高兴的是FSO 对象模型还可以获取关于文件和文件夹的信息,如名称、创建日期或最近修改日期等以及当前系统中使用的驱动器的信息,如驱动器的种类是CD-ROM还是可移动磁盘,当前磁盘的剩余空间还有多少。
而以前要获取这些信息必须通过调用Windows API函数集中的相应函数才能实现。
FSO对象模型包含在Scripting 类型库(Scrrun.Dll)中,它同时包含了Drive、Folder、File、FileSystemObject 和TextStream五个对象。
其中Drive用来收集驱动器的信息,如可用磁盘空间或驱动器的类型;Folder用于创建、删除或移动文件夹,同时可以进行向系统查询文件夹的路径等操作;File的基本操作和Folder基本相同,所不同的是Files的操作主要是针对磁盘上的文件进行的;FileSystemObject是FSO对象模型中最主要对象,它提供了一套完整的可用于创建、删除文件和文件夹,收集驱动器、文件夹、文件相关信息的方法。
需要注意的是,FSO对象模型提供的方法是冗余的,也就是说在实际使用中,FSO对象模型中包含的不同对象的不同方法进行的却是同样的操作,而且FileSystemObject对象的方法直接作用于其余对象,所以在后面的文章中并没有单独提到FileSystemObject对象,千万不要以为没有提到就不重要,事实上FileSystemObject对象在整个FSO 对象模型中无处不在;最后的TextStream对象则是用来完成对文件的读写操作的。

VBA中的文件夹操作方法与实例在VBA编程中,文件夹操作是一个常见的需求。
它可以帮助我们管理文件夹的创建、重命名、删除等操作,从而实现更高效、自动化的数据处理和文件管理。
本文将介绍VBA中常用的文件夹操作方法,并提供一些实际应用实例。
一、创建文件夹如果我们需要在VBA中创建一个新的文件夹,可以使用FileSystemObject对象的CreateFolder方法。
下面是一个创建文件夹的示例代码:```vbaSub CreateFolderExample()Dim fso As ObjectSet fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")Dim folderPath As StringfolderPath = "C:\NewFolder"If Not fso.FolderExists(folderPath) Thenfso.CreateFolder folderPathMsgBox "文件夹创建成功!"ElseMsgBox "文件夹已存在!"End IfSet fso = NothingEnd Sub```在上述示例代码中,首先我们创建了一个FileSystemObject对象,并将其分配给变量fso。
然后定义了一个文件夹路径,这里我们创建了一个名为"NewFolder"的文件夹。
接下来,使用FolderExists方法判断文件夹是否已经存在,如果不存在,则使用CreateFolder方法创建文件夹,并通过消息框提示创建成功。
如果文件夹已经存在,则通过消息框提示文件夹已存在。
二、重命名文件夹在VBA中重命名文件夹同样使用FileSystemObject对象的MoveFolder方法。
下面是一个重命名文件夹的示例代码:```vbaSub RenameFolderExample()Dim fso As ObjectSet fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")Dim oldFolderPath As StringDim newFolderPath As StringoldFolderPath = "C:\OldFolder"newFolderPath = "C:\NewFolder"If fso.FolderExists(oldFolderPath) Thenfso.MoveFolder oldFolderPath, newFolderPathMsgBox "文件夹重命名成功!"ElseMsgBox "文件夹不存在!"End IfSet fso = NothingEnd Sub```在上述示例代码中,我们首先创建了一个FileSystemObject对象,并将其分配给变量fso。
VBA中的文件操作技巧分享VBA(Visual Basic for Applications)是一种用于自动化任务的编程语言,特别适用于在Microsoft Office套件中实现自定义功能。
在VBA中,文件操作是一项常见的任务,包括文件的创建、复制、重命名、删除以及打开等。
本文将分享一些在VBA中进行文件操作的技巧和方法,帮助您更高效地处理文件。
一、创建新文件在VBA中,使用File System Object(FSO)可以轻松地创建新文件。
FSO提供了一组用于操作文件和文件夹的方法和属性。
下面是一个创建新文件的示例:```VBASub CreateNewFile()Dim FSO As ObjectDim MyFile As ObjectSet FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")Set MyFile = FSO.CreateTextFile("C:\path\to\file.txt")MyFile.CloseSet FSO = NothingSet MyFile = NothingEnd Sub```上述代码中,首先创建了一个FSO对象,然后使用`CreateTextFile`方法创建了一个名为"file.txt"的新文件。
最后,通过调用`Close`方法关闭文件。
最后,记得释放相关的对象的引用。
二、复制文件在VBA中,复制文件可以使用FSO的`CopyFile`方法。
下面是一个复制文件的示例:```VBASub CopyFile()Dim FSO As ObjectSet FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject") FSO.CopyFile "C:\path\to\file.txt","C:\path\to\newfile.txt"Set FSO = NothingEnd Sub```上述代码中,通过调用`CopyFile`方法将"file.txt"文件复制到"newfile.txt"。
VBA中的文件操作技巧VBA(Visual Basic for Applications)是一种在Microsoft Office应用程序中编写宏的编程语言。
通过使用VBA,用户可以自动化执行各种任务,例如对文件进行操作。
本文将介绍VBA中的一些文件操作技巧,帮助读者更好地利用VBA来处理文件。
1. 文件路径和名称操作在VBA中,我们可以使用File System Object(FSO)对象来操作文件。
首先,我们需要声明一个FSO对象,并使用其CreateObject方法来创建该对象。
```vbaDim fso As ObjectSet fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")```接下来,我们可以使用FSO对象的方法来处理文件路径和名称。
例如,要获取文件的完整路径,可以使用GetAbsolutePathName方法。
```vbaDim fullPath As StringfullPath = fso.GetAbsolutePathName("文件名")```同样地,我们可以使用GetBaseName方法来获取文件的基本名称(即不包括扩展名的部分)。
```vbaDim baseName As StringbaseName = fso.GetBaseName("文件名")```另外,如果我们想要获取文件的文件夹路径,可以使用GetParentFolderName方法。
```vbaDim folderPath As StringfolderPath = fso.GetParentFolderName("文件名")```使用这些方法,我们可以方便地处理文件的路径和名称。
2. 文件的复制和移动在VBA中,我们可以使用FSO对象的CopyFile方法来复制文件。
该方法需要提供源文件路径和目标文件路径作为参数。
VBA中的文件夹遍历技巧VBA是一种广泛使用的编程语言,用于在Microsoft Office套件中自动化任务。
其中一个常见的任务是在文件夹中查找特定类型的文件或处理文件夹中的所有文件。
为了实现这些功能,您需要了解VBA中的文件夹遍历技巧。
文件夹遍历是指迭代一个文件夹中的所有文件或子文件夹。
通过使用递归或循环结构,您可以遍历整个文件夹结构,并对其中的每个文件或文件夹执行所需的操作。
在VBA中,您可以使用File System Object(FSO)来遍历文件夹。
FSO提供了许多有用的方法和属性,可以帮助您处理文件夹和文件。
要使用FSO,请先添加对Microsoft Scripting Runtime库的引用,并在代码中声明一个FileSystemObject对象。
以下是一些常用的文件夹遍历技巧:1. 遍历文件夹中的所有文件:对于需要处理文件夹中的所有文件的任务,您可以使用File对象和Files集合来实现。
通过使用FSO的GetFolder方法,您可以获取指定路径下的文件夹对象。
然后,使用Files属性遍历该文件夹中的所有文件。
```vbaSub TraverseFiles()Dim FSO As ObjectDim Folder As ObjectDim File As ObjectSet FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject") Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:\Path\To\Folder\")For Each File In Folder.Files' 处理文件的操作Next FileSet FSO = NothingSet Folder = NothingSet File = NothingEnd Sub```2. 遍历文件夹中的所有子文件夹:如果您需要遍历文件夹及其所有子文件夹中的文件,可以使用Folders集合和File对象的递归方法。
VB中利用FSO对象对文件夹操作windows还给我们提供了一个叫做FileSystemObject(简称FSO)对象。
FSO对象模型中包括了计算机文件系统所有的对象。
见下。
利用这些对象可以更方便的操作文件系统。
对象功能Drive允许收集系统的驱动器信息,诸如驱动器的可用空间Folder允许创建、删除或移动文件夹,并向系统查询文件夹的名称、路径等等Files允许创建、删除或移动文件,并向系统查询文件的名称、路径等等FileSysterObject此为主要对象,提供一整套用于创建、删除、搜集相关信息,以及通常的操作驱动器,文件夹,和文件的方法。
TextStream允许读写文本文件下面我们一起来看看怎样用FSO对象来显示、新建、修改以及删除目录。
FSO对象模型包含在Scripting的类型库中,此类型库存在于Scrrun.dll文件中.使用FSO 对象模型,首先要建立一个FileSystemObject对象。
有两种方法可以实现。
一种是从”工程”菜单中的”引用”对话框选择”Microsoft Scripting Runtime”项,然后在代码窗口中声明一个FileSystemObject类型的变量.语句如下:Dim fso As New FileSystemObject另一种方法是在代码中使用CreatObject方法动态的创建一个FileSystemObject对象.语句如下:Dim fso As Object … 声明对象变量Set fso = CreatObject(“Scripting. FileSystemObject”) …创建FSO对象我们具体看看FileSystemObject的主要属性.1、驱动器(1) Drives属性是FileSystemObject对象的唯一属性,它返回Drives集合中所有可用驱动器的只读集合。
对于可删除的驱动器,不需要将媒体插入其中,就可以在Drives集合中显示出来。
VBAFSO文件操作系统VBA文件操作系统Setfso=CreateObject(“Sripting.FileSystemObject”)Fso.CreateTe xtFileFileName,Owerite创建一个文件Fso.CreateFolder(FolderName)创建文件夹Fso.OpenTextFile(FileName,IOMode,Create)打开一个文件,IOMode:ForReading,ForWriting,ForAppending(奇怪:如何关闭一个文件呢?)Fso.CopyFileSource,Destination,OverWrite拷贝文件Fso.CopyFolderSource,Destination,OverWrite拷贝文件夹Fso.MoveFileSource,Destination移动文件,Destination要指定新的FullnameFso.Mo veFolderSource,Destination移动文件夹,Destination要指定新的FullnameFso.Del eteFileFileName,Force删除文件Fso.DeleteFolderFoldername,Force删除文件夹Fso.FolderExists(FolderName)判断文件夹是否存在,返回逻辑值Fso.FileExists(FileName)判断文件是否存在,返回逻辑值Fso.GetFile(FileName)获取文件对象,然后可以进一步用属性、方法。
方法没有FSO强,只使用与Copy,move,delete。
故建议方法还是用fso好。
Fso.GetFolder(FolderName)获取文件夹对象Fso.GetDrive(DriveName)获取驱动器对象属性描述TotalSize总空间Freesize空闲空间Dri veLetter盘符FileSystemNTFS,FAT32IsReady就绪否?DreveType驱动器类型驱动器属性属性描述属性描述Name名称DateCreated文件创建日期path完整路径DateLastModified文件最后修改日期Size以字节表示的文件夹大小,e.g.fso.getfolder(“D:\test”).size/1024/1024DateLastAccessed文件最后访问日期Drive获取所在的盘符Attributes获取或设置文件夹的属性信息,e.g,vbNomal,vbReadOnly,vbHidden,vbSystem,vbDirectory等ParentFolder文件夹的父文件夹SubFolders文件夹的子文件夹eg.CountFiles获取当前文件夹中的文件,是文件集合。
VB6中的FSO对象模型--------------------------------------------------------------------------------在编程中,我们经常需要对文件系统中的驱动器、文件夹和文件进行处理,比如收集驱动器的相关信息;创建、添加、移动或删除文件夹和文件等。
在VB6中新提供了一套称为FSO (File System Object)对象模型来对文件系统进行访问处理。
该模型提供了一个基于对象的工具,通过它所提供的一系列属性和方法,我们可以在应用程序中更简单、灵活地对文件系统进行各种操作。
一、FSO简介FSO对象模型包含以下几种对象:Drive对象:允许收集系统物理或通过LAN与系统逻辑连接的硬盘、CD-ROM等驱动器的可用空间、共享名等信息。
Folder对象:允许创建、删除或移动文件夹,并向系统查询文件夹的名称、路径等。
Files对象:允许创建、删除或移动文件,并向系统查询文件的名称、路径等。
TextStream对象:允许创建和读写文本文件。
FileSystemObject对象:提供一整套用于驱动器、文件夹和文件操作的方法,在功能上可以把它看作是上面几个对象的集合并且经常与它们配合使用。
与该对象相关联的很多方法重复了前面四个对象中的方法,因此我们既可以通过FileSystemObject对象来对驱动器、文件夹和文件进行大多数操作,也可以通过对应的驱动器、文件夹或文件对象对这些组件进行操作。
FSO模型通过两种方法实现对同一对象的操作,其操作效果是相同的,提供这种冗余功能的目的是为了实现最大的编程灵活性。
FSO对象模型包含在一个称为Scripting的类型库中,此类型库位于Scrrun.dll文件中,可从“工程”选单的“引用”对话框中选择“Microsoft Scripting Runtime”项来引用此文件。
创建一个FileSystemObject对象,可以通过如下两种方法来完成:1 将一个变量声明为FileSystemObject对象类型:Dim fso As New FileSystemObject;2 使用CreateObject方法来创建:Set fso=CreateObject(″Scripting.FileSystemObject″)。
VB中利用FSO对象对文件夹操作
在VB中,可以使用FileSystemObject (FSO) 对象进行文件夹的操作。
FSO对象是VB的内置对象,可用于访问文件系统。
下面将详细介绍在VB中如何使用FSO对象对文件夹进行一些常见的操作。
一、创建文件夹
要在VB中创建文件夹,可以使用FSO对象的CreateFolder方法。
下面是一个创建文件夹的例子:
```vb
Dim fso As New FileSystemObject
Dim folderPath As String
folderPath = "C:\Test"
fso.CreateFolder folderPath
```
在这个例子中,首先创建了一个FSO对象,然后指定了要创建的文件夹的路径,最后调用CreateFolder方法创建文件夹。
二、删除文件夹
要删除文件夹,可以使用FSO对象的DeleteFolder方法。
下面是一个删除文件夹的例子:
```vb
Dim fso As New FileSystemObject
Dim folderPath As String
folderPath = "C:\Test"
fso.DeleteFolder folderPath, True
```
在这个例子中,首先创建了一个FSO对象,然后指定了要删除的文件夹的路径,最后调用DeleteFolder方法删除文件夹。
需要注意的是,DeleteFolder方法的第二个参数可选,默认为False,表示删除非空文件夹时会产生错误,如果希望删除非空文件夹,则需要将第二个参数设置为True。
三、判断文件夹是否存在
要判断文件夹是否存在,可以使用FSO对象的FolderExists方法。
下面是一个判断文件夹是否存在的例子:
```vb
Dim fso As New FileSystemObject
Dim folderPath As String
folderPath = "C:\Test"
If fso.FolderExists(folderPath) Then
MsgBox "文件夹存在"
Else
MsgBox "文件夹不存在"
End If
```
在这个例子中,首先创建了一个FSO对象,然后指定了要判断的文件夹的路径,最后调用FolderExists方法进行判断。
如果文件夹存在,将弹出一个消息框显示“文件夹存在”,否则显示“文件夹不存在”。
四、遍历文件夹
要遍历文件夹中的文件和子文件夹,可以使用FSO对象的GetFolder 方法获取文件夹对象,然后使用Files和SubFolders属性遍历。
下面是一个遍历文件夹的例子:
```vb
Dim fso As New FileSystemObject
Dim folderPath As String
folderPath = "C:\Test"
Dim folder As Folder
Set folder = fso.GetFolder(folderPath)
Dim file As File
For Each file In folder.Files
MsgBox
Next
Dim subFolder As Folder
For Each subFolder In folder.SubFolders
MsgBox
Next
```
在这个例子中,首先创建了一个FSO对象,然后使用GetFolder方法获取文件夹对象,再通过Files属性遍历文件,通过SubFolders属性遍历子文件夹。
在遍历文件夹的过程中,可以对文件和子文件夹进行一些操作,例如显示文件和子文件夹的名称。
五、复制和移动文件夹
要复制和移动文件夹,可以使用FSO对象的CopyFolder和MoveFolder方法。
下面是一个复制和移动文件夹的例子:
```vb
Dim fso As New FileSystemObject
Dim sourceFolderPath As String
sourceFolderPath = "C:\SourceFolder"
Dim destinationFolderPath As String
destinationFolderPath = "C:\DestinationFolder"
fso.CopyFolder sourceFolderPath, destinationFolderPath
fso.MoveFolder sourceFolderPath, destinationFolderPath
```
在这个例子中,首先创建了一个FSO对象,然后指定要复制和移动的源文件夹路径和目标文件夹路径,最后分别调用CopyFolder和MoveFolder方法进行复制和移动操作。
综上所述,通过FSO对象可以方便地进行文件夹的创建、删除、判断存在与否、遍历以及复制和移动等操作。
在实际应用中,可以根据具体需求使用FSO对象对文件夹进行灵活的操作。