海运提单bill of lading
- 格式:doc
- 大小:66.50 KB
- 文档页数:5


Ocean (Marine) Bills of Lading 海运提单1. 定义:The bill of lading (B/L) , issued by the carrier or his agent to the shipper, serves as a receipt for goods,(货物收据)an evidence of the contract of carriage(运输合同的证明), and a documentNote:关于提单缮制的详细说明如下:No.1.Shipper 托运人:托运人一般是出口商,除非信用证另有规定。
No.2.Consignee 收货人:也叫提单的抬头。
在信用证支付方式下,收货人一般做成指示抬头,凭托运人或开证行指示,要严格按照信用证的要求缮制。
参见“指示提单“。
No.3. Notify Party被通知人:被通知人一般是进口方,有时是货代或者开证行,必须按照信用证的规定填写。
船到港后,船公司会寄Arrival Notice 给被通知人,故地址和公司名称必须正确完整。
如果Consignee 和Notify Party 是同一个公司,可在此栏缮制“SAME”或”CONSIGNEE”的字样。
No.7 and No. 8 Loading Port and Unloading Port:意义不言而喻。
但来证规定:”China Port“ or “ European Main Port”, 应列出具体港口名。
如需要转运到内陆城市,如“Marseilles in transit to Geneva”,到货港填“Marseilles”,在货名或唛头栏内注上:”In transit to Geneva”.又如北美加拿大地区,来证规定:Los Angeles O.C.P. Chicago (Overland Common Points内陆地区),到货港制“Los Angeles O.C.P.” 在货名或唛头栏内注”O.C.P. Chicago”。


SEAWAY BILL 和BILL OF LADING 有什么本质的区别?海运单/提单SEAWAY BILL 跟电放是差不多的,海运单目的港收货人只要凭传真件和有效身份证明即可提货,而提单则是物权证明,无论谁持有都有提货的权利,而海运单则必须是海运单上面的收货人才能够提货,所以类似于电放!海运单有别于提单《中华人民共和国海商法》第80条规定:承运人签发提单以外的单证用以证明收到待运货物的,此项单证即为订立海上货物运输合同和承运人接收该单证中所列货物的初步证据。
承运人签发的此类单证不得转让。
因此,海运单如同提单可作为货物的收据和运输合同的证明,但它不可通过背书转让,因而在交货时无需出具海运单原件给承运人。
此外,海运单并非物权凭证, 也非货物交付的单证, 它只能是记名的, 不可签“TO ORDER”字样。
海运单适用于:中途不被转售的机制成品货物的班轮运输;出售给跨国公司的一家分公司或卖给一家联营公司、相关公司之间的贸易;以记帐贷款为基础的买卖;结算方式为直接汇付、往来帐户、现金的贸易;其他不需要信用证的贸易。
对于那些需转让、流通的货物,虽并不期望转售,但买卖方要求那种只能由物权凭证付款所提供的担保,在对买方的偿付能力或卖方的履行合同能力与意愿有任何怀疑的情况时,或在以银行商业信用证付款的场合,海运单就不能取代传统的提单。
海运单与提单有着一定的差别。
那么,调整提单的国际公约诸如海牙规则等是否也制约于海运单呢?1990年国际海事委员会第34届大会通过的《国际海事委员会海运单统一规则》第四条第一款规定,运输合同应受适用于该合同的、或者当运输合同由提单或类似的物权凭证包含时,强制适用于该合同的国际公约或国内法的制约。
由此可见,上述调整提单的国际公约或国内法制约仍适用于海运单。
操作注意事项在承运人接管货物或将货物装船后,海运单和提单一样应按托运人的要求,由承运人、承运人的代理人或船长签发。
托运人凭海运单和其它单证如商业发票到银行结汇。

提单种类大全范文在商务和贸易领域中,提单(Bill of Lading)是一种重要的贸易文件,用于确认货物的收发和运输情况。
不同的贸易和运输方式通常会有不同类型的提单。
下面是一些常见的提单种类的介绍:1. 海运提单(Ocean Bill of Lading):海运提单是应用最广泛的提单种类之一,用于确认海洋货物的收发和运输情况。
海运提单包括全套提单(Full Set Bill of Lading)和半套提单(Short Form Bill of Lading)两种形式。
2. 空运提单(Air Waybill):空运提单是用于确认航空货物的收发和运输情况的文件。
与海运提单不同,空运提单通常是一份非谈判性的文件,无需被提货人持有以领取货物。
3. 陆运提单(Truck Bill of Lading):陆运提单是用于确认陆地货物的收发和运输情况的文件。
它常用于货物由陆路运输或集装箱从港口运到目的地的过程中。
4. 铁路提单(Railway Bill):铁路提单是用于确认铁路货物的收发和运输情况的文件。
它通常由铁路运输公司或承运人提供给货主或收货人。
5. 内河运输提单(Inland Bill of Lading):内河运输提单是用于确认内河货物的收发和运输情况的文件。
它通常适用于由内河船只或驳船运输的货物。
6. 多式联运提单(Multimodal Bill of Lading):多式联运提单是一种综合性的提单,用于确认多种运输方式组合运输的货物的收发和运输情况。
它能够覆盖货物从起运地到目的地的整个运输过程。
7. 仓库提单(Warehouse Receipt):仓库提单是确认仓库中存储货物的证明文件。
它通常由仓储公司或物流公司提供给货主或收货人。
8. 分单(Split Bill of Lading):分单是指在一份主提单下提取多份分运单的过程。
当一个主提单上载有多个运输目的地的货物时,货主可以请求拆分成多个分提单以便对每个运输目的地的货物进行独立处理。

海运提单的种类(Sorts of Bill of Lading)海运提单的种类(Sorts of Bill of Lading)按不同的分类标准,提单可以划分为许多种类:(一)按提单收货人的抬头划分1.记名提单(Straight B/L)记名提单又称收货人抬头提单,是指提单上的收货人栏中已具体填写收货人名称的提单。
提单所记载的货物只能由提单上特定的收货人提取,或者说承运人在卸货港只能把货物交给提单上所指定的收货人。
如果承运人将货物交给提单指定的以外的人,即使该人占有提单,承运人也应负责。
这种提单失去了代表货物可转让流通的便利,但同时也可以避免在转让过程中可能带来的风险。
使用记名提单,如果货物的交付不涉及贸易合同下的义务,则可不通过银行而由托运人将其邮寄收货人,或由船长随船带交。
这样,提单就可以及时送达收货人,而不致延误。
因此,记名提单一般只适用于运输展览品或贵重物品,特别是短途运输中使用较有优势,而在国际贸易中较少使用。
2.指示提单(Order B/L)在提单正面“收货人”一栏内填上“凭指示”(To order)或“凭某人指示”(Order of……)字样的提单。
这种提单按照表示指示人的方法不同,指示提单又分为托运人指示提单、记名指示人提单和选择指示人提单。
如果在收货人栏内只填记“指示”字样,则称为托运人指示提单。
这种提单在托运人未指定收货人或受让人之前,货物所有权仍属于卖方,在跟单信用证支付方式下,托运人就是以议付银行或收货人为受让人,通过转让提单而取得议付货款的。
如果收货人栏内填记“某某指示”,则称为记名指示提单,如果在收货人栏内填记“某某或指示”,则称为选择指示人提单。
记名指示提单或选择指示人提单中指名的“某某”既可以是银行的名称,也可以是托运人。
指示提单是一种可转让提单。
提单的持有人可以通过背书的方式把它转让给第三者,而不须经过承运人认可,所以这种提单为买方所欢迎。
而不记名指示(托运人指示)提单与记名指示提单不同,它没有经提单指定的人背书才能转让的限制,所以其流通性更大。

海运提单的含义和性质作用海运提单的含义和性质作用海运提单,简称提单(Bill of Lading,简称B/L)是货物的承运人或其代理人收到货物后,签发给托运人的一种证件。
这个证件说明了货物运输有关当事人,如承运人、托运人和收货人之间的权利与义务。
提单的作用主要表现为以下几个方面:(1)提单是承运人或其代理人签发的货物收据(Receipt for the goods),证明已按提单所列内容收到货物。
(2)提单是一种货物所有权的凭证(Documents of title)。
提单的合法持有人凭提单可在目的港向轮船公司提取货物,也可以在载货船舶到达目的港之前,通过转让提单而转移货物所有权,或凭以向银行办理押汇货款。
(3)提单是托运人与承运人之间所订立的运输契约的证明(Evidence of contract of carrier)。
在班轮运输的条件下,它是处理承运人与托运人在运输中产生争议的依据;包租船运输的条件下,承运人或其代理人签发的提单也是运输契约的证明。
这种运输的契约是租船合同(Charter Party),它是处理承运人(船东)与租船人在运输中的权利义务的依据。
2.提单的种类。
提单可以从不同角度加以分类,主要有以下几种:(1)根据货物是否装船可分为已装船提单和备运提单。
已装船提单(On Board B/L or Shipped B/L),是指承运人已将货物装上指定的船只后签发的提单。
这种提单的特点是提单上面有载货船舶名称和装货日期。
备运提单(Received for Shipment B/L),是指承运人收到托运的货物待装船期间,签发给托运人的提单。
这种提单上面没有装船日期,也无载货的具体船名。
在国际贸易中,一般都必须是已装船提单。
《跟单信用证统一惯例》规定,在信用证无特殊规定的情况下,要求卖方必须提供已装船提单。
银行一般不接受备运提单。
(2)根据货物表面状况,有无不良批注分为清洁和不清洁提单。


概念海运提单(Ocean Bill of Lading),是承运人收到货物后出具的货物收据,也是承运人所签署的运输契约的证明,提单还代表所载货物的所有权,是一种具有物权特性的凭证。
种类运输单据的种类很多,包括海运提单(Ocean Bill of Lading)、海运单(Sea Waybill)、航空运单(Air Waybill)、铁路运单(Rail Waybill)、货物承运收据(Cargo Receipt)和多式联运单据(MTD)等。
海运提单可以从不同角度,可以分类:※根据货物是否装船,可分为“已装船提单”(Shipped B/L)和“备运提单”(Received for shipment B/L)。
“备运提单’上加注“已装船注记”后,即成为“已装船提单”。
※根据报单上对货物外表状况有无不良批注,可分为“清洁提单”和“不清洁提单”。
国际贸易结算中,银行只接受“清洁提单”,即承运人未在提单上批注货物外表状况有任何不良情况。
※根据提单“收货人”栏内的书写内容,可分为“记名提单’和“指示提单”。
提单”收货人”栏,又称提单抬头,表明货物所有权的归属。
记名提单,该栏记载特定收货人名称,只能由该收货人提货,不能转让。
指示提单,又分不记名指示和记名指示:不记名指示提单仅填写“To order“(凭指定),必须由托运人背书后才能转让,又称“空白抬头”。
记名指示提单填写“To the order of...”(凭某某指定),该某某即为具体的指示人,提单由其背书后可以转让,通常为受托银行;背书又分两种形式:一种由有权背书人单纯签署,称为空白背书;另一种除背书人签署外,还写明被背书人(受让人)的名称,称为记名背书。
在国际贸易中,通常采用“凭指示空白背书提单”习惯上称“空白抬头、空白背书”。
※船舶运营方式的不同,可分为班轮提单和租船提单。
班轮握本上载明运输合同的条款,船货双方受其约束。
而租船提单则受另行制定的租船合同约束,故在使用该提单时,往往要提供租船合同副本。

1) 提单 BILL OF LADING是指⼀种⽤以证明海上运输合同和货物由承运⼈接管或装船,以及承运⼈据以保证在⽬的港交付的单证。
2) 货运提单 HOUSE B/L是指由货运代理⼈签发的提单。
货运提单往往是货物从内陆运出并运⾄内陆时签发的。
国际货代通常都使⽤此种提单。
⼀般货代为满⾜客户的倒签或其他船东⽆法满⾜的要求时也使⽤这种提单。
3) 船东提单 MASTER B/L是指由船东签发的提单。
4) 已装船提单 SHIPPED OR BOARD B/L指承运⼈向托运⼈签发的货物已经装船的提单。
5) 收货待运提单或待运提单 RECEIVED FOR SHIPPING B/L指承运⼈虽已收到货物但尚未装船时签发的提单。
6) 直达提单 DIRECT B/L指货物⾃装货港装船后,中途不经换船直接驶到卸货港卸货⽽签发的提单。
8) 联运提单或称转船提单 THROUGH B/L指承运⼈在装货港签发的中途得以转船运输⽽⾄⽬的港的提单。
9) 多式联运提单 MT B/L指货物由海上、内河、铁路、公路、航空等两种或多种运输⽅式进⾏联合运输⽽签的适⽤于全程运输的提单。
10) 班轮提单 LINER B/L班轮是在⼀定的航线上按照公布的时间表,在规定的港⼝间连续从事货运的船舶。
班轮可分定线定期和定线不定期两种。
11) 租船合同提单 CHARTER PARTY B/L⼀般指⽤租船承运租船⼈的全部货物,船东签给租船⼈的提单,或者并⾮全部装运租船⼈的货物,⽽由船东或租船⼈所签发的提单。
12) 记名提单 STRAIGHT B/L是指只有提单上指名的收货⼈可以提货的提单,⼀般不具备流通性。
简介提单(Bill of Lading,B/L)是由船长或承运人或承运人的代理人签发,证明收到特定货物,允许将货物运至特定目的地并交付于收货人的凭证。
一、提单的作用1. 提单是运输合同的证明2. 提单是货物收据3.提单是物权凭证分类二、提单的分类1. 按货物是否已装船区分1 已装船提单(Shipped B/L or on Board B/L)。
2 收货待运提单(Received for Shipment B/L)。
2.按提单抬头区分1 记名提单(Straight B/L),又称收货人抬头提单。
2 指示提单(Order B/L)。
3 不记名提单(Blank B/L or Open B/L)。
3.按无影响结汇的批注区分1 清洁提单(Clean B/L)。
2 不清洁提单(Foul B/L)。
4.按收费方式区分1 运费预付提单(Freight Prepaid B/L)。
2 运费到付提单(Freight Collect B/L)。
5.按船舶的经营方式区分1 班轮提单(Liner B/L)。
2 租船提单(Charter Parth B/L)。
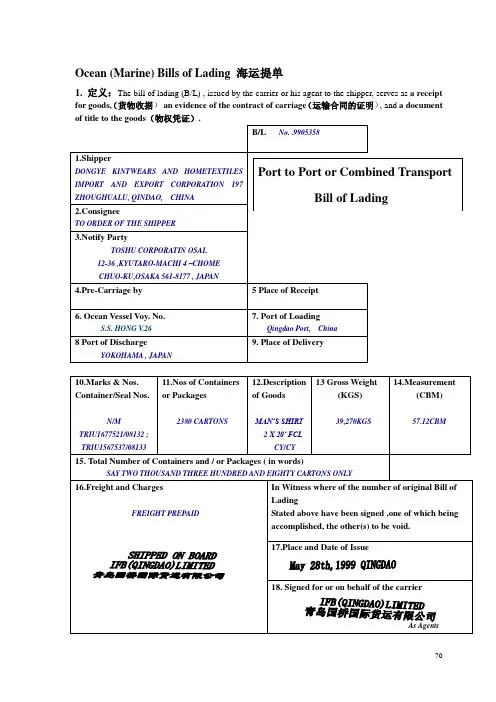
三、提单的缮制与签发1.托运人(Shipper)2.收货人(Consignee)3.通知人(Notify Party)4.前段运输(Pre-Carriage by)5.收货地点(Place of Receipt)6.海运船舶及航次(Ocean Vesse) 7.装货港(Port of Loading)8.卸货港(Port of Discharge) 9.交货地点(Place of Delivery)10. 唛头和号码、集装箱箱号和铅封号(Marks & Nos.、Container.Seal No.)11.集装箱数或件数(No of Container or P kgs)12.包装种类、货物名称(Kind of Packages、Description of Goods)13.毛重(Gross Weight kgs)14.体积(Measurement)15.运费和费用、付款地点及付款方式(Freight & Charges、Prepaid at、Payable at、Pre-paid、Collect)16.提单号和正本提单份数(B/L No.、No.of Original B(s)/L)17.签单地点和日期(Place and Date of Issue)18.代表承运人签字(Signed for the Carrier)区别四、B/L与D/O的区别B/L:BILL OF LADING提单,是货物的物权凭证。
Bill of Lading 海运提单A bill of lading is a receipt for goods shipped on board a vessel, signed by the person (or his agent) who contracts to carry them, and stating the conditions in which the goods were delivered to (and received by) the ship. It is not the actual contract, but forms excellent evidence of the terms of the contract. It is a document of title to the goods, enabling the shipper or owner of the goods to endorse title to other parties, sell goods in transit, and present to banks with other documents in seeking payment under documentary credits. Abbreviated generally as B/L, it is the most important document for sea transport.There are different types of bill of lading:(1)Shipped (On Board) B/L and received for shipment B/L已装船提单和备运提单·Shipped B/L is issued by the shipping company after the goods are actually shipped on board the designatedvessel. Since shipped bill of lading provides better guarantee for the consignee to receive the cargo at the destination, the importer will normally require the exporter to produce shipped B/L and most bill of lading forms are preprinted as “Shipped Bill”.·Received for Shipment B/L arises where the word “shipped” does not appear on the bill of lading. It merely confirms that the goods have been handed over to, and are in the custody of the shipowner. The buyer under a CIF contract will not accept such a B/L because, in the absence of the date of shipment, he is in no position to anticipate the arrival of the consignment.(2)Clean B/L and unclean B/L清洁提单和不清洁提单· A clean bill of lading is the one that states that the goods have been “shipped in apparent good order and condition”. It is issued when the goods do not show any defects on their exteriors at the time of loading at the port of shipment. This type is favored by the buyer and the banks for financial settlement purposes.·If defects are found on the exteriors of the goods, or the shipping company does not agree to any of the statements in the B/L, the bill will be marked as “unclean”, “foul” or “… packages in damaged condition”. Unclean B/L is usually unacceptable to the buyer and banks.(3)Straight, blank and order B/L记名、不记名和指示提单·Straight bill of lading has a designated consignee. Under this bill, only the named consignee at the destination is entitled to take delivery of the cargo. As it is not transferable, it is not commonly used in international trade and normally applies to high-value shipments or goods for special purposes.·Blank B/L also called Open B/L or Bearer B/L, means that there is no definite consignee of the goods. There usually appear in the box of consignee words lik e “To bearer”. Anyone who holds the bill is entitled to the goods the bill represents. No endorsement is needed for the transfer of the blank bill. Due to the exceedingly highrisk involved, this bill is rarely used.·Order B/L is widely used in international trade. It means that the goods are consigned or destined to the order of a named person. In the box of consignee, “To order”, “To order of the shipper”, or “To order of the consignee” is marked. It can be transferred only after endorsement is made. I f the B/L is made out “To order of the shipper”, the shipper will endorse the bill. If it is made out “To order of the consignee”, the consignee will endorse the bill to transfer it. A blank endorsement is usually required for a “To order” bill.(4)Direct, transshipment, through bill of lading 直运、转船和联运提单·Transhipment B/L means that the goods need to be transshipped at an intermediate port as there is no direct service between the shipment port and the destination port.·It is sometimes necessary to employ two or more carriers to get the goods to their final destination. In thiscase, usually the first carrier will sign and issue a through bill of lading. The on-carriage may be either by a second vessel or by a different form of transport.(5)Liner B/L, container B/L and combined transport B/L班轮、集装箱和多式联运提单·Liner bill of lading is issued by a liner company for shipment on scheduled port calls through scheduled routes.·Container B/L is becoming more common in use with the development of containerization. It covers the goods from port to port or from inland point of departure to inland point of destination.·Combined transport B/L is issued by combined transport operator that covers the multi-modal transport on a door-to-door basis in one contract of carriage. It is ideal for container movements. It differs from “through B/L” in that combined transport is operated by only one carrier.(6)Long form B/L and short form B/L全式提单和简式提单·Long form B/L is more detailed with shipping contract clause printed on the back of the page.·Short form B/L, as the name implies, is an abbreviated type of document, smaller and not containing the long list of detailed clauses that generally appear on bills of lading. In certain circumstances it may not, therefore, be considered a suitable form of evidence of contract or affreightment.(7)On Deck B/L, stale B/L, ante-dated B/L and advanced B/L舱面提单、过期提单、倒签提单和预签提单·On Deck B/L is issued when the cargo is loaded on the ship’s deck. It applies to goods like livestock, plants, dangerous cargo, or awkwardly-shaped goods that can not fit into the ship’s holds. In this case, the goods are exposed to greater risks and therefore usually specific insurance must be taken out against additional risks.·It is important that the Bill of Lading is available at the port of destination before the goods arrive or, failing this, at the same time. Bills presented to the consignee or buyer or his bank after the goods are due at the port of destination are described as “Stale Bs/L”. As a cargo cannot be collected by the buyer without the Bill of Lading, the late arrival of this all-important document may have undesirable consequences such as warehouse rent, etc. and therefore should be avoided. Sometimes especially in the case of short sea voyages, it is necessary to add a clause of “Stale B/L is acceptable”.·Ante-dated B/L means when the actual shipment date is later than that stipulated in the L/C, the carrier sometimes, at the shipper’s request, issues a B/L with a date of signature that suits the requirement so as to avoid non-acceptance by the bank. Due to the risk of the goods being rejected by the buyer arising from the issuance of such a bill, it is advisable to avoid this mal practice even when it seems necessary in certain circumstances.·Advanced B/L is issued when the expiry date of the L/C is due but the exporter hasn’t yet got the goods ready for shipment. The purpose of issuing such a bill is to negotiate payment with the bank in time within the validity of the L/C. it is also regarded as unlawful and risky and should be avoided.Still there are some other types of B/L such as Groupage B/L which covers a number of consignments from different shippers, and House B/L issued by a freight forwarder to each individual shipper, and so on. House B/L is issued By the freight forwarder before he gets one groupage B/L from the shipowner.All the above mentioned bills are not independent of each other. Several types may be combined into one like “Clean on board, to order, blank endorsed B/L”. A received for shipment bill may also be a straight and clean bill. Bills of lading are made out in sets, consisting of a number of originals (usually three) and a number of copies and marked” and “copy” respectively. Only the originals signed by the carrier enable the consignee totake delivery of the goods. The copies are just for reference.Types of Risks, Losses and Expenses Covered(1)Two types of risks are covered by ocean marine insurance:One is the perils of the sea, including both natural calamities and unexpected accidents. Natural calamities include heavy weather, lightening, Tsunami, earthquake, volcanic eruption and so on. Accidents refer to fire, explosion, vessel being stranded, grounded, sunk or capsized, collision or contact of vessel with any external object other than water, etc.The other type of risks is external (extraneous) risks including general external risks and special external risks. General external risks include theft and pilferage, contamination, leakage, breakage, sweating and/or heating, taint of odor, rusting, hook damage, fresh and/or rain water damage, short-delivery and non-delivery, shortage in weight, clashing and so on. Special risks include war, strike, failure to deliver due to some special laws or regulations.(2)Two types of losses are covered by marine cargo insurance. One is total loss and the other partial loss.Total loss is divided into actual total loss and constructive total loss. Actual total loss means the complete loss of the insured cargo in value.A constructive total loss occurs when the cost of salvaging the shipment would be more than the salvaged value of the merchandise. The shipment insured is reasonably abandoned as any further efforts at salvage would be fruitless. Most insurance policies provide for the payment of a total loss up to the insured amount.Partial loss means the loss of part of the insured cargo. It can be divided into generalaverage and particular average:General average is based upon a relationship between the shipowner and all the shippers who have cargo aboard the same vessel on a particular voyage. All these parties are bound together in the “adventure”. S ometimes, when the whole ship was threatened by a peril of the sea or some other hazard, in order to save he ship and some of the cargo or vessel have to be sacrificed, then an act of general average would be declared. According to maritime law, those interests whose property was saved must contribute proportionally to cover the losses of the one whose property was voluntarily sacrificed.·Particular average means a partial loss suffered by part of the cargo. It occurs when a storm or fire damages part of the shipper’s cargo and no one else’s cargo has to be sacrificed to save the voyage. The cargo owner whose goods were damaged or lost should refer to his insurance company, provided hispolicy covers the specific type of loss suffered.(3)Ocean cargo insurance also covers the expenses incurred to avoid or reduce the damage to or loss of the subject matter insured. There are mainly two types of expenses. One is sue and labor expenses paid by the assured or his agent. The other is salvage charge paid by the party other than the insurer and /or the insured.Main Types of Insurance 主要的保险种类There are mainly two types of insurance coverage, basic coverage and additional coverage. Basic coverage mainly includes FPA, WPA and All Risks. Additional coverage includes general additional coverage and special additional coverage.(1)FPA (Free from Particular Average) is alimited form of cargo insurance cover under which no partial loss or damage is recoverable. It only provides coverage for total losses and general average emerging from the actual “marine perils” like vessel being stranded, grounded or sunk.(2)WPA (With Particular average) is a wider cover than FPA. It provides extensive cover against all loss or damage due to marine perils throughout the duration of the policy, including partial loss or damage which may be attributed to natural calamities like heavy weather.(3)All Risks is the most comprehensive of the three basic coverages under which the insurer is responsible for all total or partial loss of, or damage to the goods insured either arising from sea perils or general external causes. However, it does not cover loss, damage or expense caused by delay, inherentvice or nature of the goods insured, or special external risks of war, strike, etc.(4)General additional risks include TPND (Theft, Pilferage and Non-delivery), Fresh and/or Rain Water Damage, Risk of Shortage, Risk of Intermixture and Contamination, Risk of Leakage, Risk of Clash and Breakage, Risk of Odor, Damage caused by Heating and/or Sweating, Hook Damage, Risks of Rust, etc. These additional risks can not be covered independently and should go with FPA or WPA and are included in All Risks coverage.(5)Special additional risks include War Risk, Strikes Risk(SRCC, Strikes, Riots & Civil Commotions), Failure to Delivery Risk, Import Duty Risk, On Deck Risk, Rejection Risk, etc., among which war risk and strikes risk are more common. These additional coverages are usually taken out together with FPA, WPA and All risks.To choose an insurance coverage that is both economical and effective, the exporter or the importer should be aware of the possible losses to be expected of a particular consignment. Different items have different natures and may apply to different insurance types. For example, cargo like iron ore faces little risk of partial loss, so FPA will be sufficient. Most manufactured goods are covered against All Risks as they are prone to damage caused by sea perils or external risks. It is important that the Bill of Lading is available at the port of destination before the goods arrive or, failing this, at the same time. Bills presented to the consignee or buyer or his bank after the goods are due at the port of destination are described as “Stale Bs/L”. As a cargo cannot be col lected by the buyer without the Bill of Lading, the late arrival of this all-important document may have undesirable consequences such aswarehouse rent, etc. and therefore should be avoided. Sometimes especially in the case of short sea voyages, it is necessary to add a clause of “Stale B/L is acceptable”.> shipping advice -- to importer ]. It is due.We have informed your agents,name], who will arrange for the consignment to be sent on to you, as you requested. Our bank's, will hand over the following documents once you have accepted our bill:We hope the goods will arrive in perfect condition and find a ready market in your country.Sincerely yours,Letter 11.As the contracted time of delivery is rapidly falling due, it is imperative that you inform us the delivery time without any further delay.Letter 21.Today we’ll ship the above consignment on board S.S“Nellore” which sails for your port tomorrow.2.Fill: fulfill; executeLetter 31.As our client requires us to ship the goods not later than July 15, please quote us for a shipping container from HongKong to the above mentioned port before that deadline2.Take loads: 装载Letter 41.There are about 2 to 3 sailings weekly from Shanghai to Hong Kong.2.Freight : 运费Letter 51. The main reason is that their steamers offer the shortest time for the journey between China and Germany. We shall appreciate it if you will endeavor to ship the consignments as follows.Letter 61. We enclose our invoice and shall present shipping documents and our draft for acceptance through the Royal Bank, Shanghai Office, as agreed. According to the terms of Contract No.318, shipment is to be effected by the 20th Jan., and we must have the B/L by the 31st at the latest. We trust you will ship the order within the stipulated time as any delay would cause us no little inconvenience and financial loss. We regret our inability to comply with your request for shipping the goods in early December, because the direct steamer sailingfor London calls at our Port only around the 20th every month.We are pleased to inform you that the goods under your Order No.1234 were shipped by the direct steamer “Red Star ” on Nov.30, and the relevant shipping samples had been dispatched to you by air before the steamer sailed.With regard to your Order No. 80 for 500 Sewing Machines, we shipped the goods by s.s. “East Wind”on 30th Nov. We trust that this shipment will arrive at your end shortly. Please let us have the comments of your end-users on the quality of our Sewing Machines.Write a letter to your customer to urge shipment of Blue Wollen Serge under Order No.5781. The relevant L/C has been extended to 31st match.Dear sirs,We wish to invite your attention to our Order No.5781 covering 500 pieces Blue Woolen Serge, forwhich we sent to you about 30 days ago an irrevocable L/C expiration date 31st March.As the season is rapidly approaching, our buyers are badly in need of the goods. We shall be very much obliged if you will effect shipment as soon as possible, thus enabling them to catch the brisk demand at the start of the season. We would like to emphasize that any delay in shipping our booked order will undoubtedly involve us in no small difficulty.We thank you in advance for your cooperation.Yours faithfully,。
Ocean (Marine) Bills of Lading 海运提单1. 定义:The bill of lading (B/L) , issued by the carrier or his agent to the shipper, serves as a receipt for goods,(货物收据)an evidence of the contract of carriage(运输合同的证明), and a documentNote:关于提单缮制的详细说明如下:No.1.Shipper 托运人:托运人一般是出口商,除非信用证另有规定。
No.2.Consignee 收货人:也叫提单的抬头。
在信用证支付方式下,收货人一般做成指示抬头,凭托运人或开证行指示,要严格按照信用证的要求缮制。
参见“指示提单“。
No.3. Notify Party被通知人:被通知人一般是进口方,有时是货代或者开证行,必须按照信用证的规定填写。
船到港后,船公司会寄Arrival Notice 给被通知人,故地址和公司名称必须正确完整。
如果Consignee 和Notify Party 是同一个公司,可在此栏缮制“SAME”或”CONSIGNEE”的字样。
No.7 and No. 8 Loading Port and Unloading Port:意义不言而喻。
但来证规定:”China Port“ or “ European Main Port”, 应列出具体港口名。
如需要转运到内陆城市,如“Marseilles in transit to Geneva”,到货港填“Marseilles”,在货名或唛头栏内注上:”In transit to Geneva”.又如北美加拿大地区,来证规定:Los Angeles O.C.P. Chicago (Overland Common Points内陆地区),到货港制“Los Angeles O.C.P.” 在货名或唛头栏内注”O.C.P. Chicago”。
海运业务词汇(常用海运英文)1. 运输术语Bill of Lading (B/L): 提单,是海运货物交接的凭证,证明承运人已收到货物并承诺按照合同条款运输。
Container: 集装箱,用于装载货物的标准尺寸的金属箱。
Freight: 货物,泛指运输的物品。
Charter Party: 租船合同,船东与租船人之间订立的协议,规定船舶的租赁条款。
Cargo Manifest: 货物清单,列明船上所有货物的详细信息。
Customs Clearance: 清关,指货物进出口时,必须经过海关的检查和批准。
2. 船舶术语Vessel: 船舶,泛指各种水上交通工具。
Ship: 船,通常指较大的船舶。
Barge: 驳船,用于运输货物的小型船只。
Hull: 船体,指船舶的主体结构。
Deck: 甲板,船舶的上层结构。
Hold: 货舱,用于装载货物的船舱。
Bridge: 驾驶室,船舶的指挥中心。
3. 货物类型Dry Bulk: 干散货,指非液体、非包装的散装货物,如煤炭、矿石等。
Liquid Bulk: 液体散货,指液体状态的散装货物,如原油、化学品等。
General Cargo: 杂货,指各种类型的货物,通常需要包装。
Reefer Cargo: 冷藏货物,指需要冷藏运输的货物,如冷冻食品、药品等。
Dangerous Goods: 危险品,指具有易燃、易爆、有毒等特性的货物。
4. 其他常用术语ETD (Estimated Time of Departure): 预计离港时间。
ETA (Estimated Time of Arrival): 预计到港时间。
Voyage: 航次,指船舶从一个港口到另一个港口的航行。
Port of Loading: 装货港,指货物装船的港口。
Port of Discharge: 卸货港,指货物卸船的港口。
Shipper: 托运人,指将货物交给承运人运输的人或公司。
Consignee: 收货人,指从承运人处接收货物的人或公司。
海上货物运输法规课程-4:提单1. 提单的定义提单(Bill of Lading,简称B/L)是指在海上货物运输中,由承运人(船东或船运代理人)向货主(托运人)发给的一种书面凭证,用于证明货物的装运和接收。
2. 提单的作用提单在海上货物运输中具有以下几个重要的作用:2.1 货物的证明提单是证明货物已经交由承运人承运的正式文件。
货主可以根据提单上的信息证明自己对该批货物的所有权,并且可以通过提单来要求承运人交付货物。
2.2 货物的装运和交付提单记录了货物的装运日期、装运港口以及目的港口等信息,承运人在接收货物时需要与提单上的信息进行核对。
同时,承运人在目的港口通过提单来确认货物的交付给收货人。
2.3 证明货物状况和数量提单上通常会记录货物的状况、数量以及包装方式等信息,这些信息对于货物的损失、损坏以及索赔等问题都至关重要。
因此,提单可以作为货物状况和数量的证据。
2.4 货物的质押和转让提单上的货物所有权可以通过背书或转让来变更,货主可以将货物的所有权转让给其他人。
此外,提单还可以用作货物质押的凭证,货主可以通过将提单质押给银行来获取融资支持。
根据受益人的不同,提单可以分为以下几种类型:3.1 直达提单直达提单是将货物直接运输到目的港口的提单,承运人会在目的港口将货物交付给收货人。
这种提单通常用于整船运输或长途直达运输。
3.2 转运提单转运提单是指货物需要经过中转港口的提单,承运人会在中转港口将货物交付给中转代理人,中转代理人会负责将货物运输到最终目的地。
这种提单通常用于多式联运或者货物需要经过多个港口的情况。
3.3 分单分单是指将一份提单拆分为多份以便不同的收货人接收货物,每份分单都具有相同的信息,但只能由指定的收货人使用。
这种提单通常用于拆分整船货物或者一个提单有多个收货人的情况。
空白提单是指没有填写具体收货人信息的提单,任何持有空白提单的人都可以成为货物的合法受益人。
空白提单通常由货主签发,并且可以多次转让所有权。
Bill of Lading提单B/L is the short form of Bill of Lading which is one of the most important documents in international business. A Bill of Lading represents both a receipt for goods shipped and a contract for shipment between the shipping company and the shipper. It is also a document of entitlement to the goods, giving the holder or the assignee the right to possess the goods. It is issued and signed by a shipping company or its authorized agent.B/L是Bill of Lading的缩写形式,是在国际贸易中最重要的单据之一。
提单既作为承运货物的收据,又代表承运人和托运人之间的运输合同。
它也是货物所有权的证件,因而给予持有人或受让人提货的权力。
它由承运人或其授权代理签署。
1. The main functions of a B/L 提单的主要作用1. It is a cargo receipt made out by the ship owner; 它是船方填制的货物收据;2. It is the evidence of a contract of carriage between the consignor and the shipping company;是托运人与承运人间的运输合同证明;3.B/L is a document of title to the goods. 是货物所有权证明单据。
2. Types of B/L 提单类型On board B/L已装船提单;Shipped B/L 已装船提单;Direct B/L 直达提单;Received for Shipment B/L 备运提单;Transshipment B/L 转船提单;Through B/L联运提单;Clean B/L 清洁提单;Unclean B/L 或Foul B/L 不清洁提单;Straight B/L记名提单;Open B/L不记名提单;Bearer B/L 不记名提单;Order B/L指示提单;Long Form B/L全式提单;Short Form B/L简式提单;On Deck B/L 舱面提单;Stale B/L过期提单;Ante Dated B/L倒签提单;Freight at Destination B/L 运费到付提单;Advanced B/L预借提单;Freight prepaid B/L运费预付提单;3.Specimen B/L 提单样本ShipperCHINA WEIFANG RC OIL AND FA T CO., LTD.2, BEIHAI, KUIWEN, WEIFANG, SHANDONG, 261041 CHINA B/L NO.: COS271234中国远洋运输总公司CHINA OCEAN SHIPPING CO.DIRECT TRANSPORTBILL OF LADINGORIGINALConsigneeTO OPENING BANK’S ORDERNotify PartyGISBERT BRINKSCHULTEGMBH & CO., KG UNIVERSITAETSALLEE11-13,D-2800BREMEN 33.F.R.GERMANYPre-carriage by Place of ReceiptOcean VesselV oy. No.YUN FENG 9455 Port of Loading QINGDAOPort of Discharge ROTTEDAM Final Destination Freight Payable atQINGDAONumbers of Original B/LTHREE (3)Marks & Nos. Container. No./Seal No. GB BREMENNO.1-UP DIN-NO.Container No./Seal No.1×20’FULLFBZU0032453-0032462 No.of Containers orpackages180 PALLETS 3600BAGSKind of Packages:Destination ofGoodsFIRST GRADE12-HSA IN 50KGBAGGrossWeight180,000KGSMeasurement180CBMTotal Packages (in words): ONE HUNDRED AND EIGHTY PALLETS ONLYFreight & Charges CLEAN ON BOARD FREIGHT PREPAID Place and Date of Issue:QINGDAO OCT 23, 2007Signed for the Carrier:(盖章) FOR THE CARRIER NAMED ABOVE4.The Main Contents and Notes of B/L 提单内容及说明1.Shipper or Consignor 发货人或托运人It is the exporter who is the beneficiary in the L/C.说明:即与承运人签订运输契约,委托运输的货主,即发货人。
在信用证支付方式下,一般以受益人为托运人;托收方式以托收的委托人为托运人。
另外,根据《ucp500》第31条规定:除非信用证另有规定,银行将接受表明以信用证受益人以外的第三者为发货人的运输单据。
2. Consignee 收货人If it is stiputalted in L/C as follows: 如果信用证中这样规定:1) “Full set of B/L consigned to XXX Co”–---托运给XXX公司的全套提单说明:记名收货人,在收货人一栏直接填写上指定的公司或企业名称。
该种提单不能背书转让,必须由收货人栏内指定的人提货或收货人转让。
2) “Full set of B/L made out to order”---- 凭指示填制的全套提单说明:即在收货人栏留空不填,或填“to bearer”(交来人/持票人)。
这种方式承运人交货凭提单的持有人,只要持有提单就能提货。
3) “B/L issued to order of XXX”按XXX指示出的提单You should make out respectively:1) “Consigned to XXX Co”2) “To order”3) “To order of XXX”说明:指示式的收货人又分为不记名指示和记名指示两种。
不记名指示,是在收货人一栏填“to bearer”,又称空白抬头。
该种提单,发货人必须在提单背面背书,才能转让。
背书又分为记名背书和不记名背书(空白背书)两种。
前者是指在提单背面填上“deliver to ×××”,“endorsed to ×××”,然后由发货人签章;后者是发货人在背面不做任何说明只签章即可。
记名背书后,其货权归该记名人所有,而且该记名人不可以再背书转让给另外的人。
不记名背书,货权即归提单的持有人。
记名指示,是在收货人一栏填“to order of shipper”,此时,发货人必须在寄单前在提单后背书;另外还有凭开证申请人指示即L/C中规定“to order of applicant”,在收货人栏就填“to order of ××× Co”;凭开证行指示,即L/C中规定“to order of issuing bank”,则填“to order of ××× bank”。
3. B/L No. 提单号码It is given by shipping company or its agent. 由承运人或其代理人指定。
说明:一般位于提单的右上角,是为便于工作联系和核查,承运人对发货人所发货物承运的编号。
其它单据中,如保险单、装运通知的内容往往也要求注明提单号。
4. Notify Party, addressed to 被通知人和地址If it belongs to straight Bill of Lading, the consignee’s address is written in details; if it states otherwise, fill in the blank as the requirement in the L/C. 若为直达提单,收货人地址应详细填写;若另行规定,按信用证要求填写。
说明:原则上该栏一定要按信用证的规定填写。
被通知人即收货人的代理人或提货人,货到目的港后承运人凭该栏提供的内容通知其办理提货,因此,提单的被通知人一定要有详细的名称和地址,供承运人或目的港及时通知其提货。
若L/C中未规定明确地址,为保持单证一致,可在正本提单中不列明,但要在副本提单上写明被通知人的详细地址。
托收方式下的被通知人一般填托收的付款人。
5. Ocean Vessel and Voyage No. 船和船名If transshipment is allowed, the second ship’s name is filled in here; If transshipment is not allowed, the first ship’s name is filled in. 若允许转船,第二艘船名填在此处;若不许转船,第一艘船名填写在此。
说明:即由承运人配载的装货的船名,班轮运输多加注航次。
6. Port of Loading 装货港Fill in the name of port, e.g. “Tianjin”, “Qingdao”, it can not be written as “Chinese port” on CIF or CFR basis. 填港口名称,如:“天津港”、“青岛港”,在CIF和CFR条件下,不能填“中国港”。
说明:填实际装运货物的港名。