通信与信息工程专业英语教程参考答案(Communication English)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:141.50 KB
- 文档页数:18

Unit1Exercises(1)Translate the following sentences into Chinese.1.As with series resonance, the greater the resistance in the circuit the lower the Q and,accordingly, the flatter and broader the resonance curve of either line current or circuit impedance.对于串联谐振,电路中的电阻愈大Q值就愈低,相应地线路电流或电路阻抗的谐振曲线也就愈平、愈宽。
2. A wire carrying a current looks exactly the same and weighs exactly the same as it does when itis not carrying a current.一根带电的导线其外表与重量都与不带电导线完全一样。
3.Click mouse on the waveform and drag it to change the pulse repetition rate, or directly enter anew value of the period in the provided dialogue box, while keeping the pulse width unchanged.在波形上点击鼠标并拖动来改变脉冲重复频率,或者在提供的对话框中直接输入新的周期值,而保持脉冲宽度不变。
4.Electronics is the science and the technology of the passage of charged particles in a gas, in avacuum, or in a semiconductor. Please note that particle motion confined within a metal only is not considered electronics.电子学是一门有关带电粒子在气体、真空或半导体中运动的科学技术。

第一课1.将下述句子译成英文。
(1) An analog information source produces messages that are defined on a continuum, whilea digital information source produces a finite set of possible messages.(2) The beacon-fire tower in ancient China was a communications system.(3) Show that the entropy is a maximum when the probability of sending a binary 1 is equalto the probability of sending a binary 0 .(4) Information capacity is a measure of how much information can be transferred through acommunications system in a given period of time .(5) The wider the bandwidth and the longer the time of transmission, the more informationcan be conveyed through the system .2.Answer the following questions :(1) Samuel Morse developed the first electronic communications system in 1837 .(2) Y es.(3) The vacuum-tube triode .(4) Hartley’s law simply states that the wider the bandwidth and the longer the transmissiontime, the more information that can be conveyed through the system . The Shannon’s formula is I=B log2(1+S/N) , where I=information capacity(bps), B=bandwidth(Hz), S/N=signal-to-noise power ratio(unitless) .(5) (a) VLF, (b) MF, (c) SHF第二章信息源1.根据课文回答下列问题。



1."In most cases, these signals originate as sensory data from the real world: seismic vibrations visual images, sound waves, etc. DSP isthe mathematics, the algorithms, and the techniques used to manipulate these signals after they have been converted into a digital form." 在大多数情况下,这些信号来源于人对真实世界的感觉,比如地震的震动,视觉图像,声音波形等。
数字信号处理是一种数学工具,是一种用来处理那些将上述信号转换成数字形式后的信号的算法和技术。
2.Fourier’s representation of functionsas a superposition of sines and cosines has become Ubiquitous for both the analytic and numerical solution of differential equations and for the analysis and treatment of communication signals 函数的傅里叶表示,即将函数表示成正弦和余弦信号的叠加,这种方法已经广泛用于微分方程的解析法和数值法求解过程以及通信信号的分析和处理。
3.If f (t ) is a nonperiodic signal, the summation of the periodic functions ,such as sine and cosine, does not accurately represent the signal. You could artificially extend the signal to make it periodic but it would require additional continuity at the end points . 如果f(t)是非周期信号,那么用周期函数例如正弦和余弦的和,并不能精确的表示该信号f(t)。

通信工程专业英语习题答案练习参考答案第1单元信号与系统1. 完形填空(1) band-limited, cutoff frequencies, to, between, the information rate is proportional to the bandwidth of the channel, on, to, by, by simply increasing the number of levels, noise will cause the receiver to mistake one level for another, no matter how elaborately the data is coded, between, theoretical maxima.(2) from, a loss of information , the twisted pair, addition of noise to the signal, depends on the signal frequency, the high-frequency components of the signal, over, between, through, of, with, including.(3) for, to, In some cases, over, (microwave relay, coaxial cable, or fiber), ADC, to, thereby achieving a reduction in required channel bandwidth, of, signal recovery, (Techniques such as filtering, auto-correlation and convolution).2. 英汉互译(1) “电信”(telecommunication)一词来源于希腊语tele(含义为“遥远的”)和拉丁语communicatio(涵义为“连接”)。



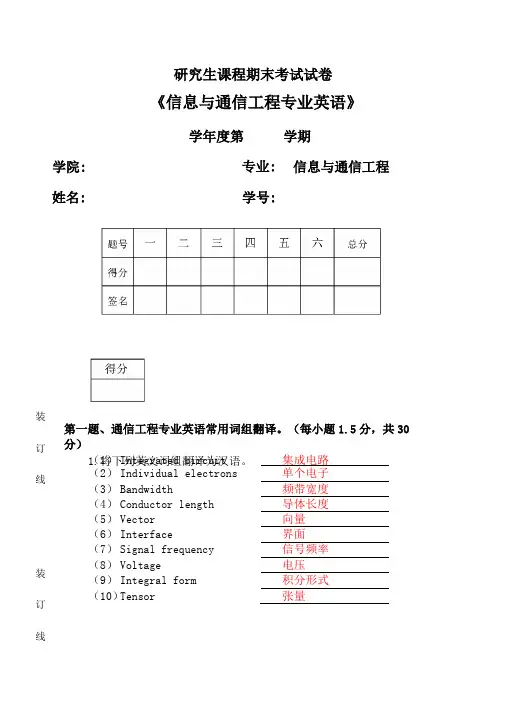
装订线装订线学院:姓名:研究生课程期末考试试卷《信息与通信工程专业英语》学年度第专业:学号:学期信息与通信工程(1)Integrated circuit集成电路(2)Individual electrons单个电子(3)Bandwidth频带宽度(4)Conductor length导体长度(5)Vector向量(6)Interface界面(7)Signal frequency信号频率(8)Voltage电压(9)Integral form积分形式(10)T ensor张量第一题、通信工程专业英语常用词组翻译。
(每小题1.5分,共30分)1.将下列英文词组翻译为汉语。
2.将下列汉语词组翻译为英语。
(1)模拟器simulator(2)传导率conductivity(3)模式识别pattern recognition(4)种类category(5)数字技术digital techniques(6)语音识别speech recognition(7)磁共振magnetic resonance(8)虚拟现实virtual reality(9)放大器amplifier(10)信息技术information technology第二题、英文和汉语词组正确搭(每小组1分,共10分)(a)Modulation sidebands数据信道—f(b)I ntermediate frequency中频—b(c)Analog system有监督学习—e(d)F eedback network载波信道.j(e)Supervised learning模拟系统—c(f)Data channel反馈网络—d(g)Adaptive learning数字信号处理_h(h)D igital signal processing调制边带—a⑴Negative feedback自适应学习—g⑴Bearer channel负反馈_i得分第三题、将下面几段文字翻译为汉语。
U n i t1E x e r c i s e s(1)T r a n s l a t e t h e f o l l o w i n g s e n t e n c e s i n t o C h i n e s e.1.As with series resonance, the greater the resistance in the circuitthe lower the Q and, accordingly, the flatter and broader theresonance curve of either line current or circuit impedance.对于串联谐振,电路中的电阻愈大Q值就愈低,相应地线路电流或电路阻抗的谐振曲线也就愈平、愈宽。
2.A wire carrying a current looks exactly the same and weighsexactly the same as it does when it is not carrying a current.一根带电的导线其外表与重量都与不带电导线完全一样。
3.Click mouse on the waveform and drag it to change the pulserepetition rate, or directly enter a new value of the period in theprovided dialogue box, while keeping the pulse width unchanged.在波形上点击鼠标并拖动来改变脉冲重复频率,或者在提供的对话框中直接输入新的周期值,而保持脉冲宽度不变。
4.Electronics is the science and the technology of the passage ofcharged particles in a gas, in a vacuum, or in a semiconductor.Please note that particle motion confined within a metal only is not considered electronics.电子学是一门有关带电粒子在气体、真空或半导体中运动的科学技术。
参考答案( Communication English )第一章电子通信导论1.将表1-1译成中文。
表1-1 通信大事纪年代事件公元前3000年埃及人发明象形文字公元800年借鉴印度, 阿拉伯人使用我们的现行数制1440年约翰.戈登贝尔发明可移动的金属记录带1752年贝莱明.富兰克林的风筝证明了雷闪是电1827年欧姆发表欧姆定律( I = E / R)1834年 C.F.高斯和E.H.韦伯发明电磁电报1838年W.F.库克和C.维特斯通发明电报1844年S.F.B.莫尔斯演示巴尔的摩和华盛顿的电报线路1850年G.R.基尔赫夫发表基尔赫夫电路定律1858年铺设第一条越洋电缆, 并于26天后举办博览会1864年J.C.麦克斯威尔预言电磁辐射1871年电报工程师协会在伦敦成立1876年 A.G.贝尔发明电话并获专利1883年 A.爱迪生发现真空管中的电子流1884年美国电气工程师协会(AIEE)成立1887年H.赫兹证明麦克斯威的理论1900年G.马可尼传送第一个越洋无线电信号1905年R.芬森登利用无线电传送语音和音乐1906年L.弗雷斯特真空三极管放大器1915年贝尔系统完成美国大陆电话线路1918年 E.H.阿尔莫斯通发明超外差接收机电路1920年第一个定时无线广播J.R.卡尔松将取样用于广播1926年美国演示电视1927年H.布兰克在贝尔实验室发明负反馈放大器1931年电传打字机投入运营1933年 E.H.阿尔莫斯通发明调频1935年R.A.沃特森-瓦特发明第一个实用雷达1936年英国广播公司(BBC)开办第一个电视广播1937年 A.雷弗斯提出脉冲编码调制(PCM)1941年J.V.阿当拉索夫在依俄华州立大学发明计算机1945年ENIAC电子数字计算机研发于宾夕伐尼亚大学1947年布雷登、巴登和肖克利在贝尔实验室研制晶体管S.O.莱斯在贝尔实验室研究噪声的统计表征1948年 C.E.香农发表他的信息理论1950年时分多路用于电话1953年美国提出NTSC彩色电视1957年苏联发射第一个地球卫星Sputnik I1958年 A.L.肖洛和C.H.托莱斯发表激光原理仙童公司的R.诺依斯生第一硅集成电路1961年美国开始立体声调频广播1962年第一个有源卫星, Telstar I , 实现美国与欧洲的电视中继1963年贝尔系统推出按键式电话电气与电子工程师协会(IEEE)成立1963~66年研究纠错码和自适应均衡1964年电子电话交换系统(No.1ESS)投入运营1965年笫一个商用通信卫星,Early Bird,发射1968年开发电缆电视系统1971年Intel公司研制第一个单片微处理器—40041972年摩托罗拉向美国联邦通信委员会(FCC)演示蜂窝式电话1976年推出个人计算机1979年64-kb随机存取存储器标志着进入VLSI时代1980年贝尔系统研发FT3光纤通信, Philips和Sony研发光碟(CD) 1984年苹果公司研发Macintosh计算机1985年传真机普及1989年摩托罗拉推出袖珍移动电话1990~现在用微处理器进行数字信号处理的时代, 数字示波器, 数字调谐接收机, 扩频系统, ISDN, HDTV, 数字卫星系统2.将表1-2译成中文。
•乌养案(< ommunicatioii English ) I «« l.l ifKtt・2 <144 1.2 if tA I X.J MH sin ■文•亢・I."■QC*纸件阳芦个・・■的冈眞*:•仏g 中赳a的・asa低■的■ j纽依电的倦•斂也«iittrj4<t>-f ! rfA I «««««・侧・.U »!••(!* X4U •IMXWHzmi号・:7此话白It■的Lliflb滋口布舟于*/U 2MHr仙讳運眾・t«»:用P橫积欣4何从知5«皿血的出活JUH詈建为454MfcH/ 口说蠶・2進不栓(址含« ftOM*人f K'^的殆号・MAiftt ^/xmMMR.Uft4id电血■酸*运他0时・能"乂处«用11 t叫用倩n论配■宜・n■峻旳仿・WE・ oftweuA^%时ixr^fl的■«・怜进的I9X»<F.W;J:电也丈9$的mo律明Hintey)m出了制宣.忡於时仙QU思幕EZ叙的关条.心^乂疋冷MLmWM 刚151M W41 真・rti*/.ciawt>*etew<M/>^■"負xm・ati:x;A«j.ciAw«tir比,桑檢帯■:和伶・H 曲的tlftiAfck.綁・侑・毎$用0—4礼》<件遇的信—侑■ 巣怜絵时刚tMMnuc久逮过•址伶堪鸽佶・■住現比初受化.• g说心Hgg弓•■余•住怡论时刖片伶送它诙蘿■的讯■人•伶逵诂金斥■nt -1 MH/ n««.・tz 用・・«19需配・2omu枷■而(Mt广・m«UB.Rl*■鳖平$钿&的•■・IW 俅JC.E4HU也■貝尔电话实的W的於贝尔*“荻术•玄t逐灰伦文.屹14 了u・・隹做•上为/ T2M・AWCMM机期S*歎H/L'MUXC■比Mlt 粉.林“血旳U i»tti®ii(;*f;.Wlt^ toiKkMMBt.il I 2AH/.HP;的W 眾比兔G 息專E为f・X9U和.・上暹列阿加鍛尺处上过251H/ 26 Wp» ff9fi 於也見町Ifc的.ftM、Jt用』制■绘.r Md 2 26<^i?nar>M J个itwmua.HI & r«wwwm^n号加“芋件s ■娥・4.将卜址匀f—a©攵・(l> A B ml«f infomtuon towct ptvitvn RBCMMO知*c<M>n»4 ca 4 c^minncn. wbika 气MfiiMnobcM twvr praiam a wi of ^OAibk WM^r*(2> Tic bcaco<i"fn< 9wcr m incunl China ww a cvmrwucwiom 巧wa(3> Sho* tha tkc entropy B < nunnam *he« b probebilrty of Mndit^ 9 brnary 丨B equal10 the prvb<Mx> •( gdin. a b«ur)•・H> lnfor*AiK« it a of hou id inbimauM an be uvi^cnd .g^h a ixmniirMcwiacm In 4gi»c»i pen ml uf iimf(5> The ・Wrr Ik tandu tAf) and l>c tonga the tnx M w»$mi$«on. the wwc infimraaoc*cin be cemed the gem5 A M*<V I W fftUoumti(l>Sowwcl XCorac deveioped iW (irudcctroa* ccmmunKMiom vywlom in 1M3*⑵(3> He mod<(4> Hanky't ・•tmet 4MI■ .Wcr •© bandwidth aad Uc ioaser ik vmsmiMKMuse. the ncrc mbofnuuon tui coa becce>c>cd duoufh Ac tyign The Shttaaoa't icmula «> / utecre /^S MMUXJMI2T tunhukMHy' .V .V-vgMM^om pwo ougfiig(5>la)VtF. (MMF. (clSHFe-«I WWittHSbMHa ・\(l> rWw ant Co. wnpertMH tnl^rrMiMin wn:<«: —d.m«MK. ,(tue«仇andgnfwief ■tUi ⑵TWw weoewv* M<c« frodictaen. «n4 pmermi(3>Tkh>»d»»d*o040«>3l(K41/(4) A SUIM I ddlcn fhMB a s^ec^ ■ tfut ns speanim occupies J much * 3ba»4 of frcq^cacc* ihM nuy cuaid ¥ 3 tbovi I SMb(5) Ibf iynMMiv . ■ edrviMon, m ■ «<Ma>n wMr the «unc 柯*Q. M ■(inmlf. «w tlill(6> I B bbci<*iutw TV. on' a Ivminvicc vjpui 15 needed. Houewr. in cokr TV Acre arc <hctca lamanoBcc M^aoi and a p« of chroairuncc Mgnils.(?>¥«•(N) Nepto* »*€ 4itt hu arc OIIOIOI Foe the oM |MM>. «I cwt ^r1i> bii ef I tkovld be cnM. to lh» lhe lott) numto »T I»11 5. whch nodd(9) LotaAat oompresssoa ope ram b? the redundsnt ■fcmalicci coaumed n thedon M attM Le«iy comtmtnoa mvKn the bti W mtormnon ■ a cMtrolled mamer L OM> I;M|WCWIMI m«> ftfieaw t (AIM■OB ikM AUMM I I I C with lotUcu anohMh(IO! There arc gr <*<ma opcriiiovn roi©-frup<»cy mapping p9><chct»romt»c modchng qum/abon «nd codiot. jnd frane^ed啊2. WU ・U itlTRBM个人itwiupaea为鼻们口维〜矯车诃i姒的滤*.僅们用计口机血发电/ ■rr鱼鼻贞•奧* •'心是的斗utn用人;“,*心4交議城ASCHM行•吗.A$CHI£HS片发的XJJNWIOII伯的■钱亡的第-介了斤弘康/力7o ・ i 的诚创$式・uv*ar^p<tt*Vb<i»«:ia)m (b~y iMW';J. 2 -l»个的m・ Xi八了符壑"斡协好•人斯丫・■礼■報左捕呂.勿如宣・$. %•・«&♦umm ・w i.m「.n. HUfcAOrtfmWTBif^MflfAi Wl»l t ・ jy /f<1. 皿g 妣■弟"氏円总稍这厂松0位啄为也監位.■沖的* C比©"为一金“澈59如Ci)・咼図枝验・ f XIM啲I的■【山佬■: ffMMtt. ■为Att.Mtt. Mtilfl*用Hits. I Af »MI*W・审代・位拓*** .・情为1•刚匕oi«^iftw)tfnv^mr个比歸初啓么.也・个人w 当ASCH*败实乂上肋frr袖E・・w. MS・•卡■♦■am位*个■■个・i W«?ihttUAIUa7HM・ MIM2・2所稹・・ NIVft K»m I. UR»V电1•的a<>・ AW 2-2 'K n': 0 ««I IjtTEtn也分別林矿中号丘电權.h*>好約文4dl饗先仔* RH次tyMftiid4nf,:«>!Cii.-M4aiii^Ai. UHM.血比皿“利MUH・卩何*"Num次KWV■"休1I1R1I・IHF矫和卅步的從介终斜辑产住的倍幼合.秋盘nfIHMH调Rzfcm)以空沿仁追FT■占匕计im卢纶的ewn咤科6臥4宅钓的4乍占* 宜斜•♦他W・个Mi-ffll2WmU0ttRri£flH** ««*«发竹.u<t>i从节“斥・m夬itZEfrihk別•的・・妙从计«r氛的々握忘揍仇弃厦的的克爼e我定发MMJ・怖比Z F.»ttifi Q?fewM?a«i>rxa(;:.賞珂u住说&的・H外.我"«忖射«1从耳地加■診恨恢鼻•卜UlMfW・・ MiKMmf转实用的方状.1人他%«1处”皆•伦・D“・《K・ AiR^«a actw的分別IK行區细w乐・■*!:・<r曲片渺式的・再1从*:① JUBUZf•它玄n右冃則K中的疋兪口U."以。
通信专业英语部分答案(华中科技大学出版社)通信专业英语部分答案(LB整理)私人整理难免会有个别错误请见谅Part1Text 1 Fundament to commu1、信号signal 波特baud 单工simplex同步synchronous 信道channels 模拟analog数字digital 电磁的electromagnetic 串行口serial带宽bandwidth3、baud 波特率asynchronous 异步的full duplex 全双工Parallel 并行electromagnetic 电磁的discrete 离散的Simultaneously 同时的parity平等的4、第三个信道特征是传输模式,包括异步通信模式和同步通信模式。
在异步通信模式中,字符(由几个比特组成)是以不规则的间隔进行传送,用户输入数据时就是这种模式。
为了识别字符的起始时刻,异步通信模式使用了起始位和停止位,有时在字符的结束也使用一个额外的校验位。
校验位用于检错。
异步通信模式常用于低数据率传输应用,也在与PC机相连的大部分通信设备中使用。
Text 2 switching technology1、交换技术switching technique存储转发传输技术the store-and-forward transmission technique 数据块block of data 电路交换circuit switching 分组交换packet switching 带宽bandwidth多路通信Multiplexed communications面向连接Connection-oriented3、分组交换网络是连接计算机常用的方式,它采用(与电路交换方式)完全不同的交换方法。
在分组交换网络中,待传的数据可分为若干个数据包,然后将它们复接到高速线路上传送。
一个数据包通常含有数百个字节,它带有数据标识,使网络硬件可以识别并将它传送到指定的目的地。
参考答案( Communication English )第一章电子通信导论1.将表1-1译成中文。
表1-1 通信大事纪年代事件公元前3000年埃及人发明象形文字公元800年借鉴印度, 阿拉伯人使用我们的现行数制1440年约翰.戈登贝尔发明可移动的金属记录带1752年贝莱明.富兰克林的风筝证明了雷闪是电1827年欧姆发表欧姆定律( I = E / R)1834年 C.F.高斯和E.H.韦伯发明电磁电报1838年W.F.库克和C.维特斯通发明电报1844年S.F.B.莫尔斯演示巴尔的摩和华盛顿的电报线路1850年G.R.基尔赫夫发表基尔赫夫电路定律1858年铺设第一条越洋电缆, 并于26天后举办博览会1864年J.C.麦克斯威尔预言电磁辐射1871年电报工程师协会在伦敦成立1876年 A.G.贝尔发明电话并获专利1883年 A.爱迪生发现真空管中的电子流1884年美国电气工程师协会(AIEE)成立1887年H.赫兹证明麦克斯威的理论1900年G.马可尼传送第一个越洋无线电信号1905年R.芬森登利用无线电传送语音和音乐1906年L.弗雷斯特真空三极管放大器1915年贝尔系统完成美国大陆电话线路1918年 E.H.阿尔莫斯通发明超外差接收机电路1920年第一个定时无线广播J.R.卡尔松将取样用于广播1926年美国演示电视1927年H.布兰克在贝尔实验室发明负反馈放大器1931年电传打字机投入运营1933年 E.H.阿尔莫斯通发明调频1935年R.A.沃特森-瓦特发明第一个实用雷达1936年英国广播公司(BBC)开办第一个电视广播1937年 A.雷弗斯提出脉冲编码调制(PCM)1941年J.V.阿当拉索夫在依俄华州立大学发明计算机1945年ENIAC电子数字计算机研发于宾夕伐尼亚大学1947年布雷登、巴登和肖克利在贝尔实验室研制晶体管S.O.莱斯在贝尔实验室研究噪声的统计表征1948年 C.E.香农发表他的信息理论1950年时分多路用于电话1953年美国提出NTSC彩色电视1957年苏联发射第一个地球卫星Sputnik I1958年 A.L.肖洛和C.H.托莱斯发表激光原理仙童公司的R.诺依斯生第一硅集成电路1961年美国开始立体声调频广播1962年第一个有源卫星, Telstar I , 实现美国与欧洲的电视中继1963年贝尔系统推出按键式电话电气与电子工程师协会(IEEE)成立1963~66年研究纠错码和自适应均衡1964年电子电话交换系统(No.1ESS)投入运营1965年笫一个商用通信卫星,Early Bird,发射1968年开发电缆电视系统1971年Intel公司研制第一个单片微处理器—40041972年摩托罗拉向美国联邦通信委员会(FCC)演示蜂窝式电话1976年推出个人计算机1979年64-kb随机存取存储器标志着进入VLSI时代1980年贝尔系统研发FT3光纤通信, Philips和Sony研发光碟(CD) 1984年苹果公司研发Macintosh计算机1985年传真机普及1989年摩托罗拉推出袖珍移动电话1990~现在用微处理器进行数字信号处理的时代, 数字示波器, 数字调谐接收机, 扩频系统, ISDN, HDTV, 数字卫星系统2.将表1-2译成中文。
表1-2 无线电频段频段名称传播特性典型应用3—30kHz 甚低频(VLF) 地波,昼夜衰减小,大气噪远距导航,海下通信声严重30—300kHz 低频(LF) 类似于VLF,可靠性稍差远距导航,海上通信,白日有吸收无线电航标300—3000 中频(MF) 地波,夜间天波,夜晚衰减小, 海上无线电,定向, kHz 白日衰减大,大气噪声调幅广播3—30MHz 高频(HF) 电离层的反射随昼夜、季业余无线电,国际广节、频率而变播,军用通信,电话,电报,传真30—300MHz甚高频(VHF) 近于视线(LOS)传播,散射电视,调频广播,航空宇宙噪声调幅通信,航空导航0.3—3GHz 超高频(UHF) 视线传播,宇宙噪声电视,移动电动,导航雷达,微波链路,个人通信系统3—30GHz 特高频(SHF) 视线传播,降雨衰减,大气衰卫星通信,减,大的水汽衰减雷达微波链30—300GHz 极高频(EHF) 视线传播,大的水汽衰减, 雷达,卫星,科学实验氧吸收>1000GHz 红外线,可见光视线传播光通信紫外线3.将1.4节的课文译成中文。
1.4带宽和信息容量限制通信系统性能的两个最重要的因素是噪声和带宽。
噪声将在以后讨论。
信息信号的带宽就是信息中包含的最高与最低频率之间的频差;通信信道的带宽(也就是它的通带)是可通过该信道的最高与最低频率之差。
信道的带宽必须足够大(宽),以便所有重要的信息频率都能通过。
换句话说,信道的带宽必须等于或大于信息的带宽。
例如,话音频率包含300Hz 到3000Hz的信号。
因此,话音频率的信道必须具有等于或大于2700Hz的带宽。
假如一个电缆电视传输系统具有从500kHz到5000kHz的通带,则其带宽为4500kHz。
一般说来,信道不能通过含有变化速率大于其通带的信号。
信息论是一种深邃的理论研究,以便通过电子通信系统传送信息时,能有效地利用带宽。
可用信息论来确定通信系统的信息容量。
信息容量是在给定时间内,能通过通信系统传送多少信息的量度。
通信系统能传送的信息量是系统带宽和传输时间的函数。
1920年,贝尔电话实验室的R.哈特莱(Hartley)提出了带宽、传输时间和信息容量之间的关系。
哈特莱定律表明,带宽越宽,传输时间越长,通过系统传送的信息就越多。
在数学上,哈特莱定律表示为I∝B×t。
式中,I=信息容量,B=系统带宽(Hz),t=传输时间(秒)。
这个公式表明,信息容量是正比于系统带宽和传输时间的线性函数。
如果信道带宽增加一倍,可传送的信息量也增加一倍。
如果传输时间增长或缩短,那么通过系统传送的信息量也成比例的变化。
一般说来,信息信号越复杂,在给定时间内传送它所需要的带宽也越大。
传送话音质量的电话信号大约需要3kHz的带宽。
相比之下,传送高保真音乐的商用调频信号需配置200kHz的带宽;而传送广播级的电视信号则需要差不多6MHz的带宽。
1948年,C.E.香农(也是贝尔电话实验室的)在贝尔系统技术杂志上发表论文,论述了以每秒比特数(bps)表示的通信信道的信息容量与带宽及信噪比的关系。
在数学上,香农极限信息容量表示为I=Blog2(1+S/N)。
式中,I=信息容量(bps),B=带宽(Hz),S/N=功率信噪比(无量纲)。
对标准的话音级通信信道,功率信噪比为1000(30dB),带宽为2.7kHz,相应的香农极限信息容量为I=26.9kbps。
香农公式常被误解。
上述例子的结果表示,通过2.7kHz的信道可传送26.9kbps的信息。
这是可能的,但不是用二进制系统。
为了通过2.7kHz的信道,达到26.9kpbs的传输速率,所传送的每一个符号必须包含多于一个比特的信息。
因此,为了达到香农极限信息容量,须采用多于两种输出状态(符号)的数字传输系统。
4.将下述句子译成英文。
(1) An analog information source produces messages that are defined on a continuum, whilea digital information source produces a finite set of possible messages.(2) The beacon-fire tower in ancient China was a communications system.(3) Show that the entropy is a maximum when the probability of sending a binary 1 is equalto the probability of sending a binary 0 .(4) Information capacity is a measure of how much information can be transferred through acommunications system in a given period of time .(5) The wider the bandwidth and the longer the time of transmission, the more informationcan be conveyed through the system .5.Answer the following questions :(1) Samuel Morse developed the first electronic communications system in 1837 .(2) Yes.(3) The vacuum-tube triode .(4) Hartley’s law simply states that the wider the bandwidth and the longer the transmissiontime, the more information that can be conveyed through the system . The Shannon’s formula is I=B log2(1+S/N) , where I=information capacity(bps), B=bandwidth(Hz), S/N=signal-to-noise power ratio(unitless) .(5) (a) VLF, (b) MF, (c) SHF第二章信息源1.根据课文回答下列问题。
(1) There are four important information sources: speech, music, pictures, and computer data.(2) Three successive stages: production, propagation, and perception.(3) The bandwidth of 300 to 3100Hz.(4) A musical signal differs from a speech signal in that its spectrum occupies a much widerband of frequencies that may extend up to about 15kHz.(5) The dynamic pictures, as in television, are in motion; while the static pictures, as infacsimile, are still.(6) In black-white TV, only a luminance signal is needed. However, in color TV, there arethree signals: a luminance signal and a pair of chrominance signals.(7) Yes.(8) Suppose the seven data bits are 0110101. For the odd parity, an extra parity bit of 1should be ended, so that the total number of 1s is 5, which is odd.(9) Lossless compression operates by removing the redundant information contained in thedata of interest. Lossy compression involves the loss of information in a controlled manner.Lossy compression may achieve a compression ratio higher than that attainable with lossless methods.(10) There are four distinct operations: time-frequency mapping, psychoacoustic modeling,quantization and coding, and frame-packing.2.将2.3节译成中文。