中药鉴定学英语课件-1
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:3.63 MB
- 文档页数:39

中药鉴定学英文**英文部分:**In the global context of traditional medicine, the art of identifying Chinese herbal medicines stands as a unique and rich legacy. The identification of herbal medicines, known as "Zhongyao Jianding Xue" in Chinese, is a crucial discipline that ensures the authenticity, quality, and safety of herbal preparations. As the world increasingly turns to alternative therapies, the demand for accurate and reliable information on Chinese herbal medicines has grown exponentially.The foundation of Zhongyao Jianding Xue lies in the intricate knowledge of botanical taxonomy, pharmacology, and traditional Chinese medicine theory. This discipline demands a profound understanding of the morphological, anatomical, and phytochemical characteristics of various herbal species. It also involves the identification ofherbal preparations, including their processing methods, storage conditions, and compatibility with other herbs.The challenges in the identification of Chinese herbal medicines are numerous. The vast diversity of herbal species, their often subtle morphological differences, and the presence of numerous adulterants and substitutes in the marketpose significant hurdles. Therefore, the role of modern analytical techniques, such as chromatography, spectroscopy, and molecular biology methods, has become increasingly important.The integration of traditional knowledge with modern analytical techniques is crucial for the advancement of Zhongyao Jianding Xue. This approach not only enhances the accuracy and reliability of herbal identification but also provides a platform for international collaboration and standardization. By standardizing identification methods and promoting the use of scientific nomenclature, the international recognition and acceptance of Chinese herbal medicines can be significantly enhanced.The teaching and dissemination of Zhongyao Jianding Xue in English is also vital for its globalization. By makingthis knowledge accessible to a wider international audience, it can foster greater understanding and appreciation of Chinese herbal medicines. This, in turn, can lead to increased research and development in this field,potentially leading to the discovery of new therapeutic agents and the improvement of existing ones.In conclusion, the exploration and practice of Zhongyao Jianding Xue in English is not just about the translationof knowledge but also about the bridging of culturaldivides and the promotion of global health. It is a journey that requires dedication, collaboration, and innovation,but the rewards it offers in terms of enhanced healthcare and cultural understanding are immense.**中文部分:****中药鉴定学的英文探索与实践**在全球传统医学的舞台上,中药鉴定学作为一门独特且丰富的遗产,占据了举足轻重的地位。
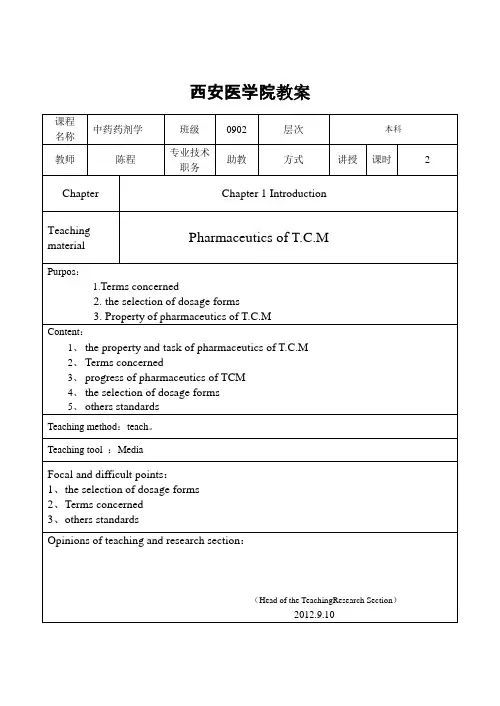



中药部分内源性的:end ogenous外源性的:ex ogenous激动剂:agonists部分激动:redesigned or modified agonists 拮抗剂:antagonists or blockers 药典:Pharmacopoeia各论、专论:monographs中药:Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCM) 中药材:Chinese materia Medica (CMM)饮片:decoction pieces1、来源:Origin药材英文名称is the 药用部位(名词单数) of 植(动)物拉丁学名[属名和种(变种)加词为斜体字](科名).药用部位:根:root根茎:rhizome 皮:bark木:wood 叶:leaf 花:flower 果实:fruit 种子:seed 全草:herb2. 采收与加工采收:The drug is collected in 季节洗净泥土:wash clean除去杂质:removed from foreign matter 晾干:dried in the air阴干:dried in the shade 晒干:dried in the sun3.性状:description外表:external(ly + adj.)主根:main root(principal root )根茎:rhizome须根:rootlets支根:branch root不定根:adventitious root痕:scars皱纹:wrinkles环纹:annulations皮孔:lenticels突起:protrusions稀疏的:sparse密集的:dense明显的:distinct不明显的:inconspicuous间断的:interrupted不平坦的:uneven粗糙的:coarse 散在的:scattered质地:texture较:relatively + adj.坚硬的:hard坚实的:compact松脆的:lax and fragile 易折断的:easily broken 易弯曲的:flexible折断面:fracture纹理:striations,星点:star spots角质样的:horny粉性的:starchy粘性的:viscous味:taste微:slightly + adj.淡:weak甜的:sweet辛辣的:pungent气:odour特异:characteristic 芳香的:aromatic 形状:圆锥形:conical圆柱形:cylindrical 纺锤形:fusiform 近、类:sub-近三角形:subtriangular 类圆形:subrounded类多角形:subpolygonal 近方形:subsquare菱形:rhombic不规则的:irregular人参性状:Main roots fusiform(纺锤形)or cylindrical(圆柱形), 3-15 cm long, 1-2 cm in diameter; externally grayish-yellow, the upper part or entire root exhibiting sparse(稀疏的), shallow (浅的), interrupted(间断的)and coarse(粗糙的)transverse-striations(横纹)and distinct longitudinal wrinkles(纵皱纹); the lower part bearing 2-3 branch roots(支根)and numerous slender(细长的)rootlets(须根)with inconspicuous(不明显的)minute(微小的)rubercles(疣状粒).3.鉴别显微特征:microscopical characters横切面:transverse section纵切面:longitudinal section木栓层:cork栓内层:phelloderm韧皮部:phloem裂缝、裂隙:cracks(clefts)薄壁细胞:parenchymatous cells 形成层:cambium木质部:xylem射线:ray导管:vessels网纹的:reticulated梯纹的:scalariform螺纹的:spiral环纹的:annular纤维:fibres木化的:lignified 树脂道:resin canal草酸钙簇晶:clusters of calcium oxalate 具缘纹孔:bordered-pitted淀粉粒:starch granules脐点:hilum髓:pith中空的:hollow丰富的:abundant宽的:broad窄的:narrow间断的:interrupted散在的:scattered聚集的:grouped理化鉴别:physical and chemical identification超声处理:ultra sonicate加热回流:heat under reflux on a water bath 提取:extract残渣:residue浸泡:macerate润湿:moisten 稀释:dilute过滤:fliter溶解:disslove逐滴的:dropwise点样于:apply separately to 展开剂:mobile phase荧光的:fluorescentTo上述操作…… as the test solution.取本品粉末……(经上述操作)……作为供试品溶液。



中药鉴定学课件(一)中药鉴定学课件教学内容1.介绍中药鉴定学的定义和意义2.中药鉴定的基本原理和方法3.常用的中药鉴定技术和设备4.中药鉴定的实践操作和案例分析教学准备1.讲台和投影仪2.中药鉴定学的教材和参考书目3.实验室用具和中药样本4.示范实验操作和案例分析的准备材料教学目标1.理解中药鉴定学在中医药学中的重要性和应用价值2.掌握中药鉴定的基本原理和常用方法3.熟悉中药鉴定的实践操作和案例分析4.提高学生的中药鉴定能力和综合实验水平设计说明1.以理论与实践相结合的方式教学,注重学生的参与和操作2.通过案例分析,引导学生进行中药鉴定的实际操作和判断3.结合中药学和中药鉴定学的知识点,深化学生对中药学科的理解和应用4.通过课程设计,提高学生的自主学习和解决问题的能力教学过程1.导入部分–介绍中药鉴定学的定义和意义2.中药鉴定的基本原理和方法–分析中药的特征和成分–讲解中药鉴定的基本原理和步骤–介绍常用的鉴定方法,如显微镜鉴定、色谱法、光谱法等3.常用的中药鉴定技术和设备–讲解常用的鉴定技术和设备,如高效液相色谱法、红外光谱仪等–演示使用常用设备进行中药鉴定的操作4.中药鉴定的实践操作和案例分析–分配学生进行中药鉴定实验操作–提供中药样本和实验指导–案例分析,引导学生进行判断和鉴定5.总结和评价–学生回答问题,并进行讨论和总结–评价学生的实验操作和鉴定能力–引导学生思考中药鉴定学在中医药学中的应用前景和发展课后反思•教学过程中,学生参与度和操作的效果如何?•是否激发了学生对中药鉴定学的兴趣和学习动力?•是否达到了培养学生实验和分析能力的目标?•对于课程设计和教学方式有什么改进的地方?以上为中药鉴定学课件的框架,通过明确教学内容、教学准备、教学目标等方面的要求,能够更好地指导教师对该课程进行教学设计和实施。
教师可以根据具体情况进行内容的扩充和设计的调整,以提高教学效果。
中药鉴定学课件教学内容1.介绍中药鉴定学的定义和意义–中药鉴定学的定义–中药鉴定学在中医药学中的重要性和应用价值2.中药鉴定的基本原理和方法–中药的特征和成分分析–中药鉴定的基本原理和步骤3.常用的中药鉴定技术和设备–高效液相色谱法(HPLC)–红外光谱仪(FTIR)–质谱仪(MS)等4.中药鉴定的实践操作和案例分析–示范实验操作流程–案例分析和讨论教学准备1.讲台和投影仪–用于展示教学内容和示范操作2.中药鉴定学的教材和参考书目–供学生复习和进一步学习3.实验室用具和中药样本–高效液相色谱仪等鉴定设备–各种中药样本4.示范实验操作和案例分析的准备材料–示范实验操作步骤和结果–中药鉴定案例和相应的数据教学目标1.理解中药鉴定学在中医药学中的重要性和应用价值2.掌握中药鉴定的基本原理和常用方法3.熟悉常用的中药鉴定技术和设备4.提高学生的实验操作和鉴定能力设计说明1.通过理论和实践相结合,提高学生的学习积极性和参与度2.引导学生分析和讨论案例,培养分析和判断能力3.示范实验操作,使学生熟悉中药鉴定的实际操作流程4.结合中药学和中药鉴定学的知识,加深学生对中药学科的理解和应用教学过程1.导入部分–介绍中药鉴定学的定义和意义–提出中药鉴定的基本问题,引发学生思考和讨论2.中药鉴定的基本原理和方法–通过讲解中药的特征和成分分析,引导学生了解中药鉴定的重要性–介绍中药鉴定的基本原理和步骤,强调对中药的综合分析3.常用的中药鉴定技术和设备–讲解常用的鉴定技术和设备,如高效液相色谱法、红外光谱仪和质谱仪等,以及它们的原理和应用领域–示范使用鉴定设备进行中药鉴定的操作,让学生熟悉实际操作流程4.中药鉴定的实践操作和案例分析–分配学生进行中药鉴定的实验操作–提供中药样本和实验指导,以便学生独立完成实验–分析和讨论案例,加深学生对中药鉴定的理解和判断能力5.总结和评价–学生回答问题,并进行讨论和总结–老师评价学生的实验操作和鉴定能力,提供建议和指导–引导学生思考中药鉴定学在中医药学中的应用前景和发展课后反思•学生积极参与了实验操作和鉴定案例的分析和讨论吗?他们是否充分理解了中药鉴定学的重要性和应用价值?•学生掌握了中药鉴定的基本原理和常用方法吗?他们的实验操作和鉴定能力有何提高?•教学过程中是否存在不足之处?有哪些方面需要改进?以上是中药鉴定学课件的具体内容和教学过程设计,通过明确的教学目标和合理的教学准备,能够有效地引导学生学习并提高他们的实验操作和判断能力。


