java第三章上机练习题
- 格式:doc
- 大小:39.00 KB
- 文档页数:5

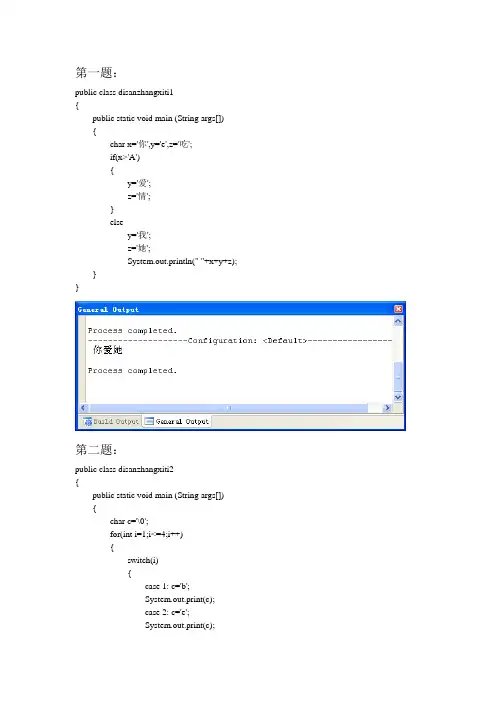
第一题:public class disanzhangxiti1{public static void main (String args[]){char x='你',y='e',z='吃';if(x>'A'){y='爱';z='情';}elsey='我';z='她';System.out.println(" "+x+y+z);}}第二题:public class disanzhangxiti2{public static void main (String args[]){char c='\0';for(int i=1;i<=4;i++){switch(i){case 1: c='b';System.out.print(c);case 2: c='e';System.out.print(c);break;case 3: c='p';System.out.print(c);default: System.out.print("!");}}}}第三题:public class disanzhangxiti3{public static void main (String args[]){int sum=0,a=1;int i=1;while(i<=10){sum=sum+a;i=i+1;a=a*i;}System.out.println("sum="+sum);}}第四题:public class disanzhangxiti4{public static void main(String agrs[]){int i,j,count=0;for(j=2;j<=100;j++){for(i=2;i<=j/2;i++){if(j%i==0)break;}if(i>j/2){count++;System.out.println(""+j+"");}}System.out.println("count="+count);}}第五题:public class disanzhangxiti5{public static void main(String agrs[]){double sum=0,a=1,i=1;do{i++;sum=sum+a;a=a*(1.0/i);}while(i<=3);System.out.println("sum="+sum);}}public class disanzhangxiti5_for{public static void main(String agrs[]){double sum=0,a=1,i=1;for(i=1;i<=2;i++){sum=sum+a;a=a*(1.0/i);}System.out.println("sum="+sum);}}第六题:public class disanzhangxiti6{public static void main(String agrs[]){int a,i,sum;for(a=2;a<=1000;a++){for(sum=0,i=1;i<=a/2;i++)if(a%i==0)sum+=i;if(sum==a)System.out.println(a);}}}第七题:public class disanzhangxiti7{public static void main(String args[]){long sum=0,a=8,item=a,n=10,i=1;for(i=1;i<=n;i++){sum=sum+item;item=item*10+a;}System.out.println(sum);}}public class disanzhangxiti7_while{public static void main(String args[]){long sum=0,a=8,item=a,n=10,i=1;while(i<=10){i++;sum=sum+item;item=item*10+a;}System.out.println(sum);}}第八题:public class disanzhangxiti8{public static void main(String agrs[]){int sum=0,i,n=1;for(i=1;i<=n;i++){sum=sum+i;if(sum<8888)n++;if(sum>=8888)break;}System.out.println("sum="+sum);System.out.println("i="+i);}}。

java⾯向对象第三章课后习题 1、输⼊⼀批整数,输出其中的最⼤值与最⼩值,输⼊为0时结束循环。
代码如下:package com.bd22;import java.util.Scanner;public class Integer {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);int min =0;int max =0;do {System.out.println("");System.out.println("请输⼊⼀个整数(输⼊0结束):");int a = sc.nextInt();if(a==0) {break;}min=min<a?min:a;max=max>a?max:a;}while(true);System.out.println("最⼩值为:"+min);System.out.println("最⼤值为:"+max);}}运⾏结果: 2、⽤键盘输⼊⼀位整数,当输⼊1~7时,显⽰对应的英⽂星期名称的缩写,输⼊其他数字时提⽰⽤户重新输⼊,输⼊0时结束程序。
程序代码:package com.bd22;import java.util.Scanner;public class Week {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);while(true){System.out.print("请输⼊数字1-7(输⼊0时结束):");int num = input.nextInt();//如果输⼊0则程序结束退出if(num==0) {System.out.println("程序结束!");break;}//按照输⼊的数不同选择输出的星期switch(num) {case 1:System.out.println("今天是 MON");break;case 2:System.out.println("今天是 TUE");break;case 3:System.out.println("今天是 WED");break;case 4:System.out.println("今天是 THU");break;case 5:System.out.println("今天是 FRI");break;case 6:System.out.println("今天是 SAT");break;case 7:System.out.println("今天是 SUN");break;default:System.out.println("请重新输⼊");break;}}}}运⾏结果: 3、假如机票原价为5000元,4-10⽉份为旺季,旺季头等舱打9折,经济舱打6折,其他⽉份为淡季,淡季头等舱打5折,经济舱打4折。


1.用穷举法求出3位数中百、十、个位数的立方和就是该数的数。
public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){int a,b,c,x=100;while(x<1000){a=x%10;b=(x%100-a)/10;c=(x-x%100)/100;if(a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c==x)System.out.println(x);x+=1;}}}2.编程实现打印以下图案:************************************public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){int i,j,k; // i控制行数, k控制*的个数,j控制空格数for(i=1;i<=6;i++){for(j=1;j<=i-1;j++)System.out.print(" "); //打印空格for(k=1;k<=13-i*2;k++)System.out.print("*"); //打印*号System.out.println(); //换行}}}3. 统计1至1万共有多少个数是素数。
public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ int i,j,count=0;label:for(i=1;i<=10000;i++) //查找1到10000以内的素数{ for(j=2;j<i;j++) //检验是否不满足素数条件if (i%j==0) //不满足continue label; //跳过后面不必要的检验count++; //计数}System.out.println("个数:"+count);}}4.读程序,写结果。

1. 一个类可以生成多个对象,并且这些对象都具有相同的属性。
A. 错误B. 正确2. 对于构造函数,下列叙述正确的是()。
A. 构造函数是类的一种特殊函数,它的方法名必须与类名相同。
B. 构造函数的返回类型只能是void型。
C. 构造函数的主要作用是完成对类的对象的初始化工作。
D. 一般在创建新对象时,系统会自动调用构造函数3. 有的类定义时可以不定义构造函数,所以构造函数不是必需的。
A. 错误B. 正确4. 即使一个类中未显式定义构造函数,也会有一个缺省的构造函数,缺省的构造函数是无参的,函数体为空。
A. 错误B. 正确5. 同一个类中定义多个参数列表不同的同名方法,叫做方法的重载。
A. 错误B. 正确6. 为了区分重载多态中同名的不同方法,要求( )。
A. 形式参数个数或者类型不同B. 返回值类型不同C. 调用时用类名或对象名做前缀D. 形式参数名称不同7.Which two overload the ConstOver constructor? (Choose Two)A.ConstOver ( ) { }B.protected int ConstOver ( ) { }C.private ConstOver (int z, int y, byte x) { }D.public Object ConstOver (int x, int y, int z) { }E.public void ConstOver (byte x, byte y, byte z) { }8.Given:1.public class MethodOver {2. public void setVar (int a, int b, float c) {3. }4.}Which two overload the setVar method? (Choose Two)A.private void setVar (int a, float c, int b) { }B.protected void setVar (int a, int b, float c) { }C.public int setVar (int a, float c, int b) {return a;}D.public int setVar (int a, int b, float c) {return a;}E.protected float setVar (int a, int b, float c) {return c;}9. 编译并运行下面的程序,运行结果为( ). public class T1 {public static void main (String[] args){T1 a=new T1();a.method(8);a.method(1.2f);}void method(float i) {System.out.println("float: "+i);}void method(long i) {System.out.println("long: "+i);}}A. 程序有编译错误,因为两个method()方法必须定义为静态(static)的。


3-16public interface back{public void append(Object obj) throws Exception;public Object delete() throw Exception;public Object getFront() throw Exception;public boolean notEmpty();}public class Forback implements back {static final int defauleSize = 10;int front;int rear;int count;int maxSize;Object[] data;int tag=0;public Forback() {initiate(defauleSize);}public Forback(int sz) {initiate(sz);}private void initiate(int sz) {maxSize = sz;front = rear = 0;count = 0;data = new Object[sz];}public void append(Object obj) throws Exception { if (count > 0 && front == rear) {throw new Exception("出错了");}data[rear]=obj;rear=(rear+1)%maxSize;count++;tag=1;}public Object delete() throws Exception {if(count==0){throw new Exception("队列已空");}Object temp=data[front];front=(front+1)%maxSize;count--;tag=0;return temp;}public Object getFront() throws Exception {if(count==0){throw new UnsupportedOperationException("队列已空");}return data[front];}public boolean notEmpty() {return count!=0;}}public class Text_for_16 {public static void main(String[]args){int n=10;SeQueue m=new SeQueue(n);int temp=11;try{for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){m.append(i);}System.out.println();System.out.println( "取值: "+m.getFront());System.out.println("删除: "+m.delete());System.out.println("所得结果为"+temp);m.append(temp);System.out.print(m.getFront()+" ");if(m.rear==m.front&&m.tag==0){System.out.println("");}else{System.out.println("所得结果为");}m.delete();System.out.println("所得的结果为:");for(int i=0;i<n;i++){System.out.print(m.delete()+" ");}}catch(Exception e){System.out.print(e.getMessage());}}}3-17public interface back {public void append(Object obj)throws Exception;public Object delete()throws Exception;public Object getFront()throws Exception;public boolean notEmpty();}public class tpback implements back{static final int defauleSize = 10;int front;int rear;int count;int maxSize;Object[] data;int tag=0;public tpbak() {initiate(defauleSize);}public tpback(int sz) {initiate(sz);}private void initiate(int sz) {front = rear = 0;count = 0;data = new Object[sz];}public void append(Object obj) throws Exception {if (count > 0 && front == (rear+1)%maxSize) {throw new Exception("队列已空");}data[rear]=obj;front=(rear+1)%maxSize;count++;}public Object delete() throws Exception {if(count==0){throw new Exception("队列空");}Object temp=data[front];front=(front+1)%maxSize;count--;return temp;}public Object getFront() throws Exception {if(count==0){throw new UnsupportedOperationException("已满");}return data[front];}public boolean notEmpty() {return count!=0;}}public class Test_for_17 {public static void main(String[]args){int n=10;SeQueue m=new SeQueue(n);try{for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){m.append(i);}System.out.println();System.out.println("删除: "+m.delete());System.out.println( "取值: "+m.getFront());System.out.println("结果为"+temp);m.append(temp);System.out.print(m.getFront()+" ");if(m.rear==m.front&&m.tag==0){System.out.println("结果为");}else{System.out.println("结果为);}m.delete();System.out.println("结果为:");for(int i=0;i<n;i++){System.out.print(m.delete()+" ");}}catch(Exception e){System.out.print(e.getMessage());}}}3-18public interface dps {public void push(Object obj)throws Exception;public Object pop()throws Exception;public Object getTop()throws Exception;public boolean notEmpty();}public class Lindps implements dps{Node head;int size;public void Lindps(){head=null;size=0;}public void push(Object obj) throws Exception { head=new Node(obj,head);size++;}public Object pop() throws Exception {if(size==0){throw new Exception("鍫嗘爤宸茬┖");}Object obj=head.element;head=head.next;size--;return obj;}public Object getTop() throws Exception {return head.element;}public boolean notEmpty() {return head!=null;}}public class Dot {Object element;Dot next;Dot(Node nexttval){next=nexttval;}Dot(Object obj,Node nexttval){element=obj;next=nexttval;}public Dot getNext(){return next;}public void setNext(Dot nexttval){next=nexttval;}public Object getElement(){return element;}public void setElement(Object obj){element=obj;}public String toString(){return element.toString();}}public class postback {public static void postExp(String ch) throws Exception {tpback s = new tpback();Object x1, x2;s.push('#');for (int i = 0; i <ch.length(); i++) {x2 = ch.charAt(i);x1 = s.getTop();if (x2.equals('+') || x2.equals('-') || x2.equals('*') || x2.equals('/')||x2.equals('#')) {if (x1.equals('#')) {s.push(x2);} else if ((x2.equals('*') || x2.equals('/')) && (x1.equals('+') || x1.equals('-'))) {s.push(x2);} else if ((x2.equals('*') || x2.equals('/')) && (x1.equals('*') || x1.equals('/'))) {System.out.print(s.pop());s.push(x2);} else if (x2.equals('+') || x2.equals('-')) {System.out.print(s.pop());if(s.getTop().equals('+')||s.getTop().equals('-')){System.out.print(s.pop());}s.push(x2);}if(x2.equals('#')){System.out.print(s.pop());if(s.getTop().equals('+')||s.getTop().equals('-')){System.out.print(s.pop());}}}else {System.out.print(x2);}}}}public class Test_for_18 {public static void main(String[] args) {postback PE = new postback();System.out.println("值为");Scanner sca = new Scanner(System.in);String s;s = sca.next();System.out.println("所得结果为");try {PE.postback(s);} catch (Exception e) {System.out.print(e.getMessage());}}}。

第3章习题解答1. Java语言的注释有哪几种?分别给出一个例子。
答:Java语言的注释有3种,分别是单行注释、多行注释和文档注释。
单行注释的例子如下:public static Point origin = new Point(0, 0); //类初始化时,创建一个原点实例多行注释的例子如下:/* 类初始化时,创建一个原点实例 */public static Point origin = new Point(0, 0);文档注释的例子如下:/**** @类名:Point* @类简介:坐标点类,可以初始化其坐标x和y。
* @编程人:林福平* @编程日期:2012-8-9* @修改日期:2012-8-10**/2. Java语言中分隔符有哪几种?空白符有哪些?答:Java语言中的分隔符有空白符、注释和普通分隔符三种。
Java语言中的空白符(White Space)包括空格(SP,space)、制表符(‘\t’,Tab键)、走纸换页(‘\f’)、回车(‘\r’)和换行(‘\n’)。
3. 简述标识符的用途。
下列字符串中,哪些是标识符?PIx2 -length a+b _bytes $long MIN_VALUE答:Java语言中的标识符用于对类、方法、变量、类型、数组和文件等进行命名。
上述字符串中,以下这些是Java语言的标识符:PIx2 _bytes $long MIN_VALUE4. 下列字符串中,哪些是关键字?true for int null $float _double答:上述字符串中,以下这些是Java语言的关键字:true for int null5. Java语言的基本数据类型分为那几大类?答:Java语言的基本数据类型分为数值类型(包括整数类型和浮点类型)、字符类型(char)和布尔类型(Boolean)。
整数类型有byte、 short、 int和long。
浮点类型有float和double。

Java语言程序设计(郑莉)第三章课后习题答案1.设N为自然数:n!=1*2*3*….*n称为n的阶乘,并且规定0!=1.试编程计算2!,4!,6!he 10!.并将结果输出到屏幕上。
答:public class Mul{public static void main(String args[]){int i,n;float s;for(n=0;n<=10;n=n+2){if(n==0)System.out.println("0!=1\n");else{s=1;for(i=1;i<=n;i++)s=s*i;System.out.println(n+"!="+s+"\n");}}}}2.编写程序,接收用户从键键盘上输入的三个整数x,y,z..从中选出最大和最小者,并编程实现。
答:public class Math{public static void main(String args[]){int[] IntArg = new int[args.length];for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++){IntArg[i] = Integer.parseInt(args[i]);}int max,min;max=IntArg[0]>IntArg[1]?IntArg[0]:IntArg[1];max=max>IntArg[2]?max:IntArg[2];min=IntArg[0]<IntArg[1]?IntArg[0]:IntArg[1];min=min<IntArg[2]?min:IntArg[2];System.out.println("max="+max);System.out.println("min="+min);}}3.求出100一枚的宿舍,并将这些数在屏幕上5个乙杭地显示出来。

一、判断题1、一个Java源程序可有多个类,但只仅有一个public类,而且程序名与public类名相同。
对2、如果类A和类B在同一个包中,则除了私有成员外,类A可以访问类B中所有的成员。
对3、接口中的成员变量全部为常量,方法为抽象方法。
对4、抽象类可以有构造方法,可以直接实例化。
错5、对static方法的调用可以不需要类实例。
对6、包含抽象方法的类一定是抽象类。
对7、方法中的形参可以和方法所属类的属性同名。
对8、接口无构造器,不能有实例,也不能定义常量。
错9、类的实例对象的生命周括实例对象的创建、使用、废弃、垃圾的回收。
对10、Java应用程序的入口main方法只有一种定义法。
对二、选择题1、下列答案正确的是(A)A) 在同一个Java源文件中可以包含多个类,只能有一个被声明为publicB) 在同一个Java源文件中只能包含一个类,并被声明为publicC) 在同一个Java源文件中可以包含多个类,都可以被声明为publicD) 在同一个Java源文件中可以包含多个类,只能有一个被声明为default2、Java实现动态多态性是通过( B )实现的。
A) 重载B) 覆盖C) 接口D) 抽象类3、下列哪一个是正确的方法重载描述(A)A) 重载方法的参数类型必须不同B) 重载方法的参数名称必须不同C) 返回值类型必须不同D) 修饰词必须不同4、final关键字不可以用来修饰( D )A) 类B) 成员方法C) 域D) 接口5、接口的所有成员方法都具有( B )属性A) private, final B) public, abstractC) static, protected D) static6、Java的封装性是通过(A)实现的A) 访问控制B) 设计内部类C) 静态域和静态方法D) 包7、下列接口或类不属于java.util.*包的是( D )A) Collection B) V ector C) Map D) Integer8、下述哪一组方法,是一个类中方法重载的正确写法?(A)A) int addV alue( int a, int b ){return a+b;}float addV alue ( float a, float b) {return a+b;}B) int addV alue (int a, int b ){value=a+b; }float addV alue ( int a, int b) {return (float)(a+b);}C) int addV alue( int a, int b ){return a+1;}int addV alue ( int a, int b) {return a+b;}D) int addV alue( int a, int b ) {return a+b;}int addV alue ( int x, int y ) {return x+y;}9、下列说法哪个是正确的?( C )A) 子类不能定义和父类同名同参数的方法B) 子类只能继承父类的方法,而不能重载C) 重载就是一个类中有多个同名但有不同形参和方法体的方法D) 子类只能覆盖父类的方法,而不能重载10、对于下列代码:public class Parent {public int addV alue( int a, int b) {int s;s = a+b;return s;}}class Child extends Parent {}下述哪个方法不可以加入类Child? ( B )A) public int addV alue( int a, int b,int c ){// do something...}B) public void addV alue (int a, int b ){// do something...}C) public int addV alue( int a ){// do something...}D) public int addV alue( int a, int b ) {//do something...}11、以下程序段输出结果的是( B )public class A implements B {public static void main(String args[]) {int i;A c1 = new A();i= c1.k;System.out.println("i="+i);}}interface B {int k = 10;}A) i=0 B) i=10 C) 程序有编译错误D) i=true12、阅读下面的程序,输出结果是( B )public class TestDemo {int m=5;public void some(int x) {m=x;}public static void main(String args []) {new Demo().some(7);}}class Demo extends TestDemo {int m=8;public void some(int x) {super.some(x);System.out.println(m);}}A) 5 B) 8 C) 7 D) 编译错误13、下述哪个说法是不正确的?(A)A) 局部变量在使用之前无需初始化,因为有该变量类型的默认值B) 类成员变量由系统自动进行初始化,也无需初始化C) 参数的作用域就是所在的方法D) for语句中定义的变量,当for语句执行完时,该变量就消亡了14、下述那一个保留字不是类及类成员的访问控制符。
1、class Scoop{static int thrower() throws Exception { return 42; }public static void main(String[] args) {try{int x = thrower();}catch(Exception e) {x++;}finally {System.out.println(“x = ” + ++x);}What is the result?A. x = 42B. x = 43C. x = 44D. Compilation failsE. The code runs with no output答案:D变量x的作用域只在try块内,而不在catch和finally里2、what is the result when you compil and run the following code? D class Example{static int myArg=1;public static void main(String [] args){Int myArg;System.out.println(myArg);}}Select all right answer:A、this code compiles and displays 0 in the statndard output when runB、t his code compiles and displays 1 in the statndard output when runC、t his code does not compile because you can‟t define a local variable names the same as staticvariableD、this code doesn‟t compile because the local vriable is used before it is initialized局部变量myArg;在使用前必须被初始化3、what is the result when you compile and run the following code? D class Example{static int i;public static void main(String [] args){System.out.println(i);}}Select all right answer:A、Error variable I may not have been initializedB、N ullC、1D、0属性有默认值4、what is the result when you compile and run the following code? B class Example{static boolean Paddy;public static void main(String [] args){System.out.println(Paddy);}}Select all right answer:A、compile time error;B、c ompilation and output of false;C、c ompilation and output of trueD、compilation and output of null属性有默认值5、what is the result when you compile and run the following code? D class Example{public static void main(String [] args){ int i=012;int j=034;int k=056;int l=078;System.out.println(i);System.out.println(j);System.out.println(k);}}Select all right answer:A、p rints 12,34 and 56B、prints 24,68and 112C、prints 10,28and 46D、c ompilation error八进制数前加0,但l表示的数超过八进制数的范围了6、what is the result when you compile and run the following code? Aclass Example{ void fun(){static int i=0;}public static void main(String [] args){ Example obj=new Example();obj.fun();obj.fun();}}Select all right answer:A、compilation errorB.run time errorC、1D、2Static不能修饰局部变量7、what is the result when you compile and run the following code? D class Example{public static void main(String [] args){ String elements[ ]={“for”,”tea”,”too”};String first=(elements.length>0)?elements[0]:null;System.out.println(first);}}Select all right answer:pilation fails;B.an exception thrown at runtimeC.prints:nullD.prints:for考察数组的length属性和条件运算符8、what is the result when you compile and run the following code? A,C,D String s=“hello”;String t=”hello”;char c[]={…h‟,‟e‟,‟l‟,‟l‟,‟o‟};Select all right answer:A s.equals(t);B t.equals(c)C s==tD t.equals(new String (“hello”))E t==c==比较的是两端操作数是否是同一个对象,由于s和t并非用new创建,因此指向内存池中同一字符串常量,故C对,equals比较两个String内容是否相等9、Given the following code: E class Example{public static void main(String [] args){If(args.length==1 | args[1].equals(“test”))System.out.println(“test case”);ElseSystem.out.println(“production ”+arg[0]);}}And the command-line invocation: java Example live2What is the result?select all right answer?A、test caseB、productionC、test case live2D、complilation failsE、An xception is throw at runtime考察逻辑短路运算,但|不属于逻辑短路,尽管args.length==1的结果为true,但后边的仍需计算,但因为数组只接受了一个参数,故arg[1]导致异常10、what is the result when you compile and run the following code? Cclass Example{public static void main(String [] args){ byte B=10;byte D=12;byte I=B*D;}}Select all right answer:A、the code will compile and runB、c ompile time error while declaring variableC、c ompile time error while multiplicationD、none of the above说明:二元运算,若一个为float double 或long,则另一个也转换成对应的,否则都转换成int11、what is the result when you compile and run the following code? Dclass Example{void test(int i){ System.out.println(“I am a Int”);}void test(String s){ System.out.println(“I am a String”);}public static void main(String [] args){ Example t=new Example();char ch=‟y‟;t.test(ch);}}Select all right answer:A not compile,because void methods can‟t be overriddenB not compile,because there is no version of test() that rakes a char argumentC the code will complile but will throw an exceptionD the code will compile and produce the following output: I am an int因为char的表示范围小于int,所以和test(int i)匹配上12、what is the result when you compile and run the following code? Dclass Example{static final long tooth=343L;static long doIt(long tooth){System.out.println(++tooth+””);return ++tooth;}public static void main(String [] args){ System.out.println(tooth+”“);final long tooth=340L;new Example().doIt(tooth);System.out.println(tooth);}}Select all right answer:A 343 340 340B 343 340 342C 343 341 342D 343 341 340E 343 341 343F compilation failsG An exception in thrown at runtime本题考察变量的使用范围:三个tooth同名变量,第一个是类成员,第二个是形参在方法内doIt().第三个是main的局部变量,范围在main内。
第三章Java语言面向对象的特征一、选择题1、下列对封装性的描述中,错误的是 B 。
A.封装体包含了属性和行为B.封装体中的属性和行为的访问权限是相同的C.被封装的某些信息在封装体外是不可见的D.封装使得抽象的数据类型提高了可重用性2、在类的修饰符中,规定只能被同一包类所使用的修饰符是 B 。
A.public B.默认C.final D.abstract3、在成员变量的修饰符中,规定只允许该类自身访问的修饰符是 A 。
A.private B.public C.默认D.protected4、下列关于构造方法的特点的描述中,错误的是 A 。
A.不可重载B.方法名同类名C.无返回类型D.系统自动调用5、下列关于关于静态方法的描述中,错误的是 D 。
A.在类体内说明静态方法使用关键字B.静态方法只能处理静态变量或调用静态方法C.静态方法不占用对象的内存空间,非静态方法占用对象的内存空间D.静态方法只能用类名调用6、下列关于抽象类的描述中,错误的是 C 。
A.抽象类是用修饰符abstract说明的B.抽象类是不可以定义对象的C.抽象类是不可以有构造方法的D.抽象类通常要有它的子类7、下列关于接口的描述中,错误的是 B 。
A.接口实际上是由常量和抽象方法构成的特殊类B.一个类只允许继承一个接口C.定义接口使用的关键字是interfaceD.在继承接口的类中通常要给出接口中定义的抽象方法的具体实现8、下列关于包的描述中,错误的是 A 。
A.包是一种特殊的类B.包是若干个类的集合C.包是使用package语句创建的D.包有有名包和无名包两种9、下列常用包中,存放用户图形界面类库的包是 A 。
A.java.awtB.ngC.java.utilD.java.io10、下列是系统提供的常用的类,所有类的父类的类是 B 。
A.MathB.ObjectC.SystemD.String二、判断题1、类是一种类型,也是对象的模板。
java每章经典练习题Java是一种面向对象的编程语言,具有良好的可移植性和跨平台性,被广泛应用于软件开发和网络编程。
对于学习Java的人来说,经典的练习题可以帮助他们巩固所学的知识并提升编程能力。
本文将为大家介绍一些Java每章经典练习题,以供学习者参考。
1. 第一章练习题1.1 编写一个程序,输出"Hello, World!"。
1.2 编写一个程序,计算1到100之间所有偶数的和。
1.3 编写一个程序,将一个字符串反转。
2. 第二章练习题2.1 编写一个程序,输入两个整数,输出它们的和。
2.2 编写一个程序,输入一个字符串,统计其中的字母个数。
2.3 编写一个程序,实现两个字符串的比较。
3. 第三章练习题3.1 编写一个程序,输入一个数字n,输出n的阶乘。
3.2 编写一个程序,输入一个数字n,输出n以内的所有质数。
3.3 编写一个程序,实现两个整数数组的合并。
4. 第四章练习题4.1 编写一个程序,输入一个字符串,判断其是否为回文字符串。
4.2 编写一个程序,输入一个字符串,统计其中的单词个数。
4.3 编写一个程序,实现二维数组的转置。
5. 第五章练习题5.1 编写一个程序,输入一个正整数,输出其二进制表示。
5.2 编写一个程序,输入一个字符串,将其中的每个单词首字母大写。
5.3 编写一个程序,实现矩阵的乘法。
通过完成以上练习题,学习者可以逐渐掌握Java编程的基本知识和技巧。
同时,在实践中解决问题,培养了解决实际编程难题的思维能力。
在编写程序时,学习者需要注意代码的简洁性和可读性,合理利用面向对象的思想,提高代码的重用性和可维护性。
总结:本文介绍了一些Java每章经典练习题,涵盖了从基本的输出到复杂的矩阵运算等多个知识点。
通过完成这些练习题,学习者可以巩固所学的知识,提高编程能力,为日后的Java开发和应用奠定基础。
希望本文能够对Java学习者有所帮助。
习题1. 数据类型转换应用【案例简介】下例说明了整型、浮点型、字符串型之间的相互转换。
【案例目的】掌握Java中两个不兼容类型能够的数据格式之间的转换。
【技术要点】高精度到低精度的数据转换时候需要进行强制转换,低精度向高精度进行转换的时候的会自动进行,字符串到其他类型的转换需要用到特定的方法。
【代码分析】public class Conversation{public static void main(String [] args){String str = "123";int j;byte b;int i=257;double d = 323.142;System.out.println("\nConversion of int to byte.");//i强制转换成byte型System.out.println("i and b "+ i + " "+b);System.out.println("\nConversion of double to int.");//d强制转换成int型System.out.println("d and i "+ d + " "+i);//d强制转换成byte型System.out.println("d and b "+ d + " "+b);j=Integer.parseInt(str); //str转换成int型System.out.println("j="+j);}}【相关知识】数据类型转换(1)简单数据类型中各类型数据间的优先关系和相互转换不同类型数据间的优先关系如下低----------------------------------------------->高byte->short->char-> int -> long -> float -> double自动类型转换规则整型,实型,字符型数据可以混合运算。
《Java语言程序设计(基础篇)》(第10版梁勇著)第三章练习题答案《Java语言程序设计(基础篇)》(第10版梁勇著)第三章练习题答案3.1public class Exercise03_01 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("Enter a, b, c: ");double a = input.nextDouble();double b = input.nextDouble();double c = input.nextDouble();double discriminant = b * b - 4 * a * c;if (discriminant < 0) {System.out.println("The equation has no real roots");}else if (discriminant == 0) {double r1 = -b / (2 * a);System.out.println("The equation has one root " + r1);}else { // (discriminant > 0)double r1 = (-b + Math.pow(discriminant, 0.5)) / (2 * a);double r2 = (-b - Math.pow(discriminant, 0.5)) / (2 * a);System.out.println("The equation has two roots " + r1 + " and " + r2);}}}3.1附加public class Exercise03_01Extra {public static void main(String args[]) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("Enter a numerator: ");int numerator = input.nextInt();System.out.print("Enter a denominator: ");int denominator = input.nextInt();if (numerator < denominator) {System.out.println(numerator + " / " + denominator + " is a proper fraction");}else if (numerator % denominator == 0) {System.out.print(numerator + " / " + denominator + " is an improper fraction ");System.out.println("and it can be reduced to " + numerator / denominator);}else {System.out.print(numerator + " / " + denominator + " is an improper fraction ");System.out.println("and its mixed fraction is " + numerator / denominator + " + " +numerator % denominator + " / " + denominator);}}}3.2public class Exercise03_02 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);int number1 = (int)(System.currentTimeMillis() % 10);int number2 = (int)(System.currentTimeMillis() * 7 % 10);int number3 = (int)(System.currentTimeMillis() * 3 % 10);System.out.print("What is " + number1 + " + " + number2 + " + " +number3 + "? ");int answer = input.nextInt();System.out.println(number1 + " + " + number2 + " + " + number3 +" = " + answer + " is " +(number1 + number2 + number3 == answer));}}3.2附加public class Exercise03_02Extra {public static void main(String args[]) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("Enter the coordinates for two points: ");double x1 = input.nextDouble();double y1 = input.nextDouble();double x2 = input.nextDouble();double y2 = input.nextDouble();double m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1);double b = y1 - m * x1;System.out.print("The line equation for two points (" + x1 + ", " + y1 + ") and (" + x2 + ", " + y2 + ") is " + "y = ");if (m == -1)System.out.print("-x");else if (m == 1)System.out.print("x");elseSystem.out.print(m + "x");if (b > 0)System.out.println(" + " + b);else if (b < 0)System.out.println(" - " + (-1 * b));else// b is 0System.out.println();}}3.3public class Exercise03_03 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter a, b, c, d, e, f: ");double a = input.nextDouble();double b = input.nextDouble();double c = input.nextDouble();double d = input.nextDouble();double e = input.nextDouble();double f = input.nextDouble();double detA = a * d - b * c;if (detA == 0) {System.out.println("The equation has no solution"); }else {double x = (e * d - b * f) / detA;double y = (a * f- e * c) / detA;System.out.println("x is " + x + " and y is " + y);}}}3.3附加public class Exercise03_03Extra {public static void main(String[] args) {final double RADIUS = 5;double angle = Math.random() * 2 * Math.PI;double x = RADIUS * Math.random() * Math.cos(angle);double y = RADIUS * Math.sin(angle);double distance = Math.pow(x * x + y * y, 0.5);System.out.println("The point is (" + x + ", " + y + ") and its distance to the center is " + distance);}}3.4public class Exercise03_04 {public static void main(String[] args) {int number = (int)(Math.random() * 12) + 1;// or int number = (int)(System.currentTimeMillis() % 12 + 1);// or int number = (int)(Math.random() * 12) + 1;if (number == 1)System.out.println("Month is Januaray");else if (number == 2)System.out.println("Month is Feburary");else if (number == 3)System.out.println("Month is March");else if (number == 4)System.out.println("Month is April");else if (number == 5)System.out.println("Month is May");else if (number == 6)System.out.println("Month is June");else if (number == 7)System.out.println("Month is July");else if (number == 8)System.out.println("Month is August");else if (number == 9)System.out.println("Month is September");else if (number == 10)System.out.println("Month is October");else if (number == 11)System.out.println("Month is November");else// if (number == 12)System.out.println("Month is December");}}3.5public class Exercise03_05 {public static void main(String[] args) {java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);// Prompt the user to enter an integer for todaySystem.out.print("Enter today抯 day: ");int today = input.nextInt();System.out.print("Enter the number of days elapsed since today: ");int elapsedDays = input.nextInt();String nameForToday;if (today == 0)nameForToday = "Sunday";else if (today == 1)nameForToday = "Monday";else if (today == 2)nameForToday = "Tuesday";else if (today == 3)nameForToday = "Wednesday";else if (today == 4)nameForToday = "Thursday";else if (today == 5)nameForToday = "Friday";else// if (today == 6)nameForToday = "Saturday";int futureDay = (today + elapsedDays) % 7; String nameForFutureDay;if (futureDay == 0)nameForFutureDay = "Sunday";else if (futureDay == 1) nameForFutureDay = "Monday";else if (futureDay == 2) nameForFutureDay = "Tuesday";else if (futureDay == 3) nameForFutureDay = "Wednesday";else if (futureDay == 4) nameForFutureDay = "Thursday";else if (futureDay == 5) nameForFutureDay = "Friday";else// if (futureDay == 6) nameForFutureDay = "Saturday";System.out.println("Today is " + nameForToday+ " and the future day is " + nameForFutureDay); } }3.6public class Exercise03_06 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);// Prompt the user to enter weight in pounds System.out.print("Enter weight in pounds: "); double weight = input.nextDouble();// Prompt the user to enter heightSystem.out.print("Enter feet: ");double feet = input.nextDouble();System.out.print("Enter inches: ");double inches = input.nextDouble();double height = feet * 12 + inches;// Compute BMIdouble bmi = weight * 0.45359237 / ((height * 0.0254) * (height * 0.0254));// Display resultSystem.out.println("BMI is " + bmi);if (bmi < 18.5)System.out.println("Underweight");else if (bmi < 25)System.out.println("Normal");else if (bmi < 30)System.out.println("Overweight");elseSystem.out.println("Obese");}}3.7/** Break down an amount into smaller units* Display the non-zero denominations only, and display singular* words for single units like 1 dollars, 1 penny, and display plural * words for more than one unit like 2 dollars, 3 pennies.*/public class Exercise03_07 {// Main methodpublic static void main(String[] args) {java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);// Receive the amount entered from the keyboardSystem.out.print("Enter an amount in double, for example 11.56: ");double amount = input.nextDouble();int remainingAmount = (int)(amount * 100);// Find the number of one dollarsint numberOfOneDollars = remainingAmount / 100;remainingAmount = remainingAmount % 100;// Find the number of quarters in the remaining amountint numberOfQuarters = remainingAmount / 25;remainingAmount = remainingAmount % 25;// Find the number of dimes in the remaining amountint numberOfDimes = remainingAmount / 10;remainingAmount = remainingAmount % 10;// Find the number of nickels in the remaining amountint numberOfNickels = remainingAmount / 5;remainingAmount = remainingAmount % 5;// Find the number of pennies in the remaining amountint numberOfPennies = remainingAmount;// Display resultsif (amount < 0) {System.out.println("Your amount is negative");System.exit(1);}else if (amount < 0) {System.out.println("Your amount is zero");System.exit(2);}System.out.println("Your amount " + amount + " consists of ");if (numberOfOneDollars > 1)System.out.println(numberOfOneDollars + "\ dollars");else if (numberOfOneDollars == 1)System.out.println(numberOfOneDollars + "\ dollar");if (numberOfQuarters > 1)System.out.println(numberOfQuarters + "\ quarters");else if (numberOfQuarters == 1)System.out.println(numberOfQuarters + "\ quarter");if (numberOfDimes > 1)System.out.println(numberOfDimes + "\ dimes");else if (numberOfDimes == 1)System.out.println(numberOfDimes + "\ dime");if (numberOfNickels > 1)System.out.println(numberOfNickels + "\ nickels");else if (numberOfNickels == 1)System.out.println(numberOfNickels + "\ nickel");if (numberOfPennies > 1)System.out.println(numberOfPennies + "\ pennies");else if (numberOfPennies == 1)System.out.println(numberOfPennies + "\ penny");}}3.8public class Exercise03_08 {public static void main(String[] args) {java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in); // Enter three numbersSystem.out.print("Enter three integers: ");int number1 = input.nextInt();int number2 = input.nextInt();int number3 = input.nextInt();if (number1 > number2) {int temp = number1;number1 = number2;number2 = temp;}if (number2 > number3) {int temp = number2;number2 = number3;number3 = temp;}if (number1 > number2) {int temp = number1;number1 = number2;number2 = temp;}System.out.println("The sorted numbers are "+ number1 + " " + number2 + " " + number3);}}public class Exercise03_09 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);// Prompt the user to enter an integerSystem.out.print("Enter the first 9 digits of an ISBN as integer: ");int number = input.nextInt();// Calculate checksum (You may write a loop to simplify it in Ch4int checksum =((number / 100000000 % 10) * 1 +(number / 10000000 % 10) * 2 +(number / 1000000 % 10) * 3 +(number / 100000 % 10) * 4 +(number / 10000 % 10) * 5 +(number / 1000 % 10) * 6 +(number / 100 % 10) * 7 +(number / 10 % 10) * 8 +(number % 10) * 9) % 11;System.out.print("The ISBN-10 number is ");// Display leading zeros, improve the solution using loops in the next chapterif (number / 100000000 == 0) {System.out.print("0");if (number / 10000000 == 0) {System.out.print("0");if (number / 1000000 == 0) {System.out.print("0");if (number / 100000 == 0) {System.out.print("0");if (number / 10000 == 0) { System.out.print("0");if (number / 1000 == 0) { System.out.print("0");if (number / 100 == 0) {System.out.print("0");if (number / 10 == 0) {System.out.print("0");if (number == 0) {System.out.print("0");}}}}}}}}}System.out.print(number);if (checksum == 10)System.out.print("X");elseSystem.out.print(checksum);}}3.10public class Exercise03_10 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. Generate two random single-digit integersint number1 = (int)(Math.random() * 10);int number2 = (int)(Math.random() * 10);// 2. Prompt the student to answer 搘hat is number1 + number2?? System.out.print("What is " + number1 + " + " + number2 + "? "); Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);int answer = input.nextInt();// 4. Grade the answer and display the resultString replyString;if (number1 + number2 == answer)replyString = "You are correct!";elsereplyString = "Your answer is wrong.\" + number1 + " + "+ number2 + " should be " + (number1 + number2);System.out.println(replyString);}}3.11public class Exercise03_11 {public static void main(String[] args) {java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);// Prompt the user to enter inputSystem.out.print("Enter a month in the year (e.g., 1 for Jan): ");int month = input.nextInt();System.out.print("Enter a year: ");int year = input.nextInt();int numberOfDaysInMonth = 0;switch (month) {case 1:System.out.print("January " + year);numberOfDaysInMonth = 31;break;case 2:System.out.print("February " + year);if (year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)) { numberOfDaysInMonth = 29;}else {numberOfDaysInMonth = 28;}break;case 3:System.out.print("March " + year);numberOfDaysInMonth = 31;break;case 4:System.out.print("April " + year);numberOfDaysInMonth = 30;break;case 5:System.out.print("May " + year);numberOfDaysInMonth = 31;break;case 6:System.out.print("June " + year);numberOfDaysInMonth = 30;break;case 7:System.out.print("July " + year);numberOfDaysInMonth = 31;break;case 8:System.out.print("August " + year);numberOfDaysInMonth = 31;break;case 9:System.out.print("September " + year);numberOfDaysInMonth = 30;break;case 10:System.out.print("October " + year);numberOfDaysInMonth = 31;break;case 11:System.out.print("November " + year);numberOfDaysInMonth = 30;break;case 12:System.out.print("December " + year);numberOfDaysInMonth = 31;break;}System.out.print(" has " + numberOfDaysInMonth + " days"); }}3.12public class Exercise03_12 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("Enter a three-digit integer: ");int number = input.nextInt();if (number / 100 == number % 10)System.out.println(number + " is a palindrome");elseSystem.out.println(number + " is not a palindrome");}}3.13public class Exercise03_13 {public static void main(String[] args) {java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);// Prompt the user to enter filing statusSystem.out.print("(0-single filer, 1-married jointly or qualifying widow(er),"+ "\2-married separately, 3-head of household)\" + "Enter the filing status: ");int status = input.nextInt();// Prompt the user to enter taxable incomeSystem.out.print("Enter the taxable income: ");double income = input.nextDouble();// Compute taxdouble tax = 0;if (status == 0) { // Compute tax for single filersif (income <= 8350) {tax = income * 0.10;} else if (income <= 33950) {tax = 8350 * 0.10 + (income - 8350) * 0.15;} else if (income <= 82250) {tax = 8350 * 0.10 + (33950 - 8350) * 0.15 + (income - 33950)* 0.25; } else if (income <= 171550) {tax = 8350 * 0.10 + (33950 - 8350) * 0.15 + (82250 - 33950) * 0.25 + (income - 82250) * 0.28;} else if (income <= 372950) {tax = 8350 * 0.10 + (33950 - 8350) * 0.15 + (82250 - 33950) * 0.25 + (171550 - 82250) * 0.28 + (income - 171550) * 0.33;} else {tax = 8350 * 0.10 + (33950 - 8350) * 0.15 + (82250 - 33950) * 0.25 + (171550 - 82250) * 0.28 + (372950 - 171550) * 0.33 + (income - 372950) * 0.35;}} else if (status == 1) { // Compute tax for married file jointly if (income <= 16700) {tax = income * 0.10;} else if (income <= 67900) {tax = 16700 * 0.10 + (income - 16700) * 0.15;} else if (income <= 137050) {tax = 16700 * 0.10 + (67900 - 16700) * 0.15 + (income - 67900) * 0.25; } else if (income <= 208850) {tax = 16700 * 0.10 + (67900 - 16700) * 0.15 + (137050 - 67900) * 0.25 + (income - 137050) * 0.28;} else if (income <= 372950) {tax = 16700 * 0.10 + (67900 - 16700) * 0.15 + (137050 - 67900) * 0.25 + (208850 - 137050) * 0.28 + (income - 208850) * 0.33;} else {tax = 16700 * 0.10 + (67900 - 16700) * 0.15 + (137050 - 67900) * 0.25 + (171950 - 137050) * 0.28 + (372950 - 208850) * 0.33+ (income - 372950) * 0.35;}} else if (status == 2) { // Compute tax for married separately if (income <= 8350) {tax = income * 0.10;} else if (income <= 33950) {tax = 8350 * 0.10 + (income - 8350) * 0.15;} else if (income <= 68525) {tax = 8350 * 0.10 + (33950 - 8350) * 0.15 + (income - 33950) * 0.25; } else if (income <= 104425) {tax = 8350 * 0.10 + (33950 - 8350) * 0.15 + (68525 - 33950) * 0.25 + (income - 68525) * 0.28;} else if (income <= 186475) {tax = 8350 * 0.10 + (33950 - 8350) * 0.15 + (68525 - 33950) * 0.25 + (104425 - 68525) * 0.28 + (income - 104425) * 0.33;} else {tax = 8350 * 0.10 + (33950 - 8350) * 0.15 + (68525 - 33950) * 0.25 + (104425 - 68525) * 0.28 + (186475 - 104425) * 0.33 + (income - 186475) * 0.35;}} else if (status == 3) { // Compute tax for head of household if (income <= 11950) {tax = income * 0.10;} else if (income <= 45500) {tax = 11950 * 0.10 + (income - 11950) * 0.15;} else if (income <= 117450) {tax = 11950 * 0.10 + (45500 - 11950) * 0.15 + (income - 45500) * 0.25; } else if (income <= 190200) {tax = 11950 * 0.10 + (45500 - 11950) * 0.15 + (117450 - 45500) * 0.25 + (income - 117450) * 0.28;} else if (income <= 372950) {tax = 11950 * 0.10 + (45500 - 11950) * 0.15 + (117450 - 45500) * 0.25 + (190200 - 117450) * 0.28 + (income - 190200) * 0.33;} else {tax = 11950 * 0.10 + (45500 - 11950) * 0.15 + (117450 - 45500) * 0.25 + (190200 - 117450) * 0.28 + (372950 - 190200) * 0.33+ (income - 372950) * 0.35;}} else {System.out.println("Error: Wrong filing status");System.exit(1);}// Display the resultSystem.out.println("Tax is " + (int) (tax * 100) / 100.0);}}3.14public class Exercise03_14 {public static void main(String[] args) {// Obtain the random number 0 or 1int number = (int)(Math.random() * 2);// Prompt the user to enter a guessjava.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("Guess head or tail? " +"Enter 0 for head and 1 for tail: ");int guess = input.nextInt();// Check the guessif (guess == number)System.out.println("Correct guess");else if (number == 0)System.out.println("Sorry, it is a head");elseSystem.out.println("Sorry, it is a tail");}}3.15public class Exercise03_15 {public static void main(String[] args) {// Generate a lotteryint lottery = (int)(Math.random() * 1000);// Prompt the user to enter a guessjava.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter your lottery pick (three digits): ");int guess = input.nextInt();// Get digitsint l1 = lottery / 100;int l2 = (lottery % 100) / 10; // l2 = (lottery / 10) % 10int l3 = lottery % 10;int g1 = guess / 100;int g2 = (guess % 100) / 10;int g3 = guess % 10;System.out.println("Lottery is " + lottery);// Check the guessif (guess == lottery)System.out.println("Exact match: you win $10,000");else if (g1 == l1 && g3 == l2 && g2 == l3 ||g2 == l1 && g1 == l2 && g3 == l3 ||g2 == l1 && g3 == l2 && g1 == l3 ||g3 == l1 && g1 == l2 && g2 == l3 ||g3 == l1 && g2 == l2 && g1 == l3)System.out.println("Match all digits: you win $3,000"); else if (g1 == l1 || g1 == l2 || g1 == l3 ||g2 == l1 || g2 == l2 || g2 == l3 ||g3 == l1 || g3 == l2 || g3 == l3)System.out.println("Match one digit: you win $1,000"); elseSystem.out.println("Sorry, no match");}}3.16public class Exercise03_16 {public static void main(String[] args) {double x = Math.random() * 100 - 50;double y = Math.random() * 200 - 100;System.out.println(x + ", " + y);}}3.17public class Exercise03_17 {public static void main(String[] args) {// Generate scissor, rock, paperint computerNumber = (int)(Math.random() * 3);// Prompt the user to enter scissor, rock, or paper java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("scissor (0), rock (1), paper (2): ");int userNumber = input.nextInt();// Check the guessswitch (computerNumber) {case 0:if (userNumber == 0)System.out.print("The computer is scissor. You are scissor too. It is a draw");else if (userNumber == 1)System.out.print("The computer is scissor. You are rock. You won");else if (userNumber == 2)System.out.print("The computer is scissor. You are paper. You lost");break;case 1:if (userNumber == 0)System.out.print("The computer is rock. You are scissor. You lost");else if (userNumber == 1)System.out.print("The computer is rock. You are rock too. It is a draw");else if (userNumber == 2)System.out.print("The computer is rock. You are paper. You won");break;case 2:if (userNumber == 0)System.out.print("The computer is paper. You are scissor. You won");else if (userNumber == 1)System.out.print("The computer is paper. You are rock. You lost");else if (userNumber == 2)System.out.print("The computer is paper. You are paper too.It is a draw");break;}}}3.18public class Exercise03_18 {public static void main(String args[]) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("Enter package weight: ");double w = input.nextDouble();if (w <= 1) {System.out.println("The shipping cost is $3.5");}else if (w <= 3) {System.out.println("The shipping cost is $5.5");}else if (w <= 10) {System.out.println("The shipping cost is $8.5");}else if (w <= 20) {System.out.println("The shipping cost is $10.5");}else {System.out.println("The package cannot be shipped");}}}3.19public class Exercise03_19 {public static void main(String[] args) {java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in); // Enter three edgesSystem.out.print("Enter three edges (length in double): ");double edge1 = input.nextDouble();double edge2 = input.nextDouble();double edge3 = input.nextDouble();。
习题1. 数据类型转换应用【案例简介】下例说明了整型、浮点型、字符串型之间的相互转换。
【案例目的】掌握Java中两个不兼容类型能够的数据格式之间的转换。
【技术要点】高精度到低精度的数据转换时候需要进行强制转换,低精度向高精度进行转换的时候的会自动进行,字符串到其他类型的转换需要用到特定的方法。
【代码分析】public class Conversation{public static void main(String [] args){String str = "123";int j;byte b;int i=257;double d = 323.142;System.out.println("\nConversion of int to byte.");//i强制转换成byte型System.out.println("i and b "+ i + " "+b);System.out.println("\nConversion of double to int.");//d强制转换成int型System.out.println("d and i "+ d + " "+i);//d强制转换成byte型System.out.println("d and b "+ d + " "+b);j=Integer.parseInt(str); //str转换成int型System.out.println("j="+j);}}【相关知识】数据类型转换(1)简单数据类型中各类型数据间的优先关系和相互转换不同类型数据间的优先关系如下低----------------------------------------------->高byte->short->char-> int -> long -> float -> double自动类型转换规则整型,实型,字符型数据可以混合运算。
运算中,不同类型的数据先转化为同一类型,然后进行运算,转换从低级到高级。
(2)强制类型转换高级数据要转换成低级数据,需用到强制类型转换,如:int i;byte b=(byte)i; //把int型变量i强制转换为byte型(3)其他转换数字变为字符串用如下方法转换相应类型的数字:Double.toString(double);Float.toString(float);Long.toString(float);Integer.toString(float);Short.toString(float);Byte.toString(Byte);也可以使用字符串类的valueOf方法:String.valueOf(各种类型的数值变量);还可以用空字符串连接数字,将数字转换为字符串。
如:""+25。
数字类型转换为各种常用进制的字符串类toBinaryString(long or int):转换为二进制形式的字符串类。
toOctalString(long or int):转换为八进制形式的字符串类。
toSexString(long or int):转换为十六进制形式的字符串类。
字符串转换为数字Byte.parseByte(string):转换为字节型的数值。
Short.parseShort(string):转换为短整型的数值。
Integer.parseInt(string):转换为整型的数值。
Long.parseLong(string):转换为长整型的数值。
Float.parseFloat(string):转换为单精度型的数值。
Double.parseDouble(string):转换为双精度型的数值。
2.4 数组和字符串习题2. 求平均成绩【案例简介】数组A中存放有10个学生某门课程的成绩、输出这10个学生的平均成绩。
【案例目的】掌握Java一维数组的使用方法,包括数组的动态初始化、静态初始化等。
【技术要点】数组的静态初始化方法及访问方法。
【代码分析】public class Score{public static void main(String[] args){int a[] ={ 90,87,67,81,89,96,76,71,91,57},i,sum=0;double ave;//求平均成绩aveSystem.out.println("Average="+ave);}}【相关知识】1.数组的概念数组是Java语言中的一种复合数据类型,它是由类型相同的元素组成的有顺序的数据集合。
在一个数组中每个元素的数据类型都是相同的,数组元素可以是基本类型、对象类型,也可以是数组类型。
数组要经过定义、分配内存及赋值后才能使用。
2.数组的定义type arrayName[ ];type [ ]arrayName;type arrayName[ ][ ];type [ ][ ]arrayName;类型(type)可以为Java中任意的数据类型,包括简单类型和复合类型。
例如:int intArray[ ];Date dateArray[];int b[][];3.数组的初始化(1)静态初始化例如:int intArray[]={1,2,3,4};String stringArray[]={"abc", "How", "you"};int intArray[ ][ ]={{1,2},{2,3},{3,4,5}};注意:Java语言中,由于把二维数组看作是数组的数组,数组空间不是连续分配的,所以不要求二维数组每一维的大小相同。
(2)动态初始化简单类型的数组例如:int intArray[];intArray = new int[5];int a[][] = new int[2][3];int b[][] = new int[2][ ];b[0] = new int[3];b[1] = new int[5];4.数组元素的引用一维数组元素的引用方式为:arrayName[index]index为数组下标,它可以为整型常数或表达式,下标从0开始。
每个数组都有一个属性length指明它的长度,例如:intArray.length指明数组intArray的长度。
二维数组中元素的引用方式为:arrayName[index1][index2]例如:num[1][0];的一个。
习题3. 多维数组矩阵转置【案例简介】将3*4的多维数组转置为4*3的多维数组。
【案例目的】掌握多维数组以及交错数组的使用方法。
【技术要点】数组的静态初始化方法及访问方法。
【代码分析】public class Matrix{public static void main(String[] args){int a[][]={{1,2,3,4},{2,3,4,5},{3,4,5,6}};int b[][]= new int[4][3];int i,j;System.out.println("转换前");//利用两重循环进行显示数组//利用两重循环进行转置System.out.println("转换后");//利用两重循环进行显示数组}}2.5流程控制习题4. 打印出九九乘法表【案例目的】掌握Java循环流程的控制。
习题5. 求一元二次方程的根。
【案例目的】掌握Java分支流程的控制。
【技术要点】根据参数的不同,分别进行有根、无根、重根的判别。
方程求根提示:Math.sqrt(a) 求a的平方根【代码分析】public class roots{public static void main(String [] args){int a,b,c;float x1,x2;int check;a=1;b=2;c=1;System.out.println("方程式为:"+a+"x^2+"+b+"x+"+c+"=0");System.out.println("方程解为:");//如果有重根//如果有不同两个根//否则无根}}【相关知识】1. 控制语句Java程序通过控制语句来执行程序流,完成一定的任务。
程序流是由若干个语句组成的,语句可以是单一的一条语句,如c=a+b,也可以是用大括号{}括起来的一个复合语句。
Java中的控制语句有以下几类:◇分支语句:if-else,switch◇循环语句:while,do-while,for◇与程序转移有关的跳转语句:break,continue,return2. 分支语句分支语句提供了一种控制机制,使得程序的执行可以跳过某些语句不执行,而转去执行特定的语句。
(1)条件语句if-elseif(boolean-expression)statement1;[else statement2;](2)多分支语句switchswitch (expression){case value1 : statement1;break;case value2 : statement2;break;…………case valueN : statemendN;break;[default : defaultStatement; ]}◇expression的返回值类型必须是这几种类型之一:int,byte,char,short。
◇case子句中的值valueN必须是常量,各case子句中的值应是不同的。
◇default子句是可选的。
◇break语句用来在执行完一个case分支后,使程序跳出switch语句,即终止switch语句的执行(在一些特殊情况下,多个不同的case值要执行一组相同的操作,这时可以不用break)。
2-6 习题习题6:猜数字游戏编写一个Java应用程序,实现以下功能:程序随机分配一个1~100之间的整数,用户在输入自己的猜测,程序返回提示信息,分别是“猜大了”、“猜小了”、“猜对了”。
用户可以根据提示信息再次输入猜测,直到提示信息是“猜对了”提示:// 新建一个随机数产生器,然后生成一个0到10之间的整数,代码如下:import java.util.Random;Random random = new Random();int number = random.nextInt(10);//获取控制台整数输入,代码如下:import java.util.Scanner;Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);int guess_number=sc.nextInt();完整代码:。