四种时态的特殊用法
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:136.50 KB
- 文档页数:14

英语动词时态总结一、一般现在时(Simple Present Tense)表示经常性动作、惯性动作、普遍真理等。
1. 动词原形:- I, you, we, they + 动词原形- He, she, it + 动词原形 + -s/-es2. 特殊用法:- 表示客观事实或普遍真理:The sun rises in the east.- 表示经常性或惯性动作:I often go for a run in the morning.二、一般过去时(Simple Past Tense)表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。
1. 动词过去式:- 一般情况下,动词过去式在词尾加-ed。
- 不规则动词过去式需单独记忆。
2. 特殊用法:- 表示过去的经历或事件:We traveled to France last summer.三、一般将来时(Simple Future Tense)表示将来发生的动作或存在的状态。
1. will/shall + 动词原形:- I, you, he, she, it, we, they + will + 动词原形- I, we + shall + 动词原形2. 特殊用法:- 表示决定、承诺、意愿等:I will help you with your homework.四、现在进行时(Present Continuous Tense)表示现在正在进行的动作。
1. be(am/is/are) + 动词-ing:- I + am + 动词-ing- He, she, it + is + 动词-ing- You, we, they + are + 动词-ing2. 特殊用法:- 表示现在进行的动作:I am studying for the exam.五、过去进行时(Past Continuous Tense)表示过去某个时间正在进行的动作。
1. was/were + 动词-ing:- I, he, she, it + was + 动词-ing- You, we, they + were + 动词-ing2. 特殊用法:- 表示过去正在进行的动作:She was watching TV when I arrived.六、将来进行时(Future Continuous Tense)表示将来某个时间正在进行的动作。


动词时态与语态在时间状语从句中的特殊用法和语气表达方式及其使用技巧动词时态和语态在语言表达中起着至关重要的作用。
在时间状语从句中,时态和语态的使用不仅影响到语句的意思和语气,还可以表达出不同的情感和态度。
本文将介绍动词时态和语态在时间状语从句中的特殊用法和语气表达方式,以及一些使用技巧。
一、动词时态在时间状语从句中的特殊用法和语气表达方式1. 一般现在时一般现在时常用于表示客观事实或普遍真理。
在时间状语从句中,一般现在时可以用来表示将来的时间点或某个事件的发生时间。
例如:- When he comes back, we will have a party.- I will visit my grandparents when I finish my homework.2. 一般过去时一般过去时常用于表示过去发生的事情。
在时间状语从句中,一般过去时可以用来表示过去某个时间点发生的事件或者已经完成的动作。
例如:- She told me that she had already seen the movie.- I felt tired after I finished the race.3. 一般将来时一般将来时常用于表示将来发生的动作或者存在的状态。
在时间状语从句中,一般将来时可以用来表示主句之后发生的动作。
例如:- I will call you when I arrive at the airport.- Don't forget to bring an umbrella if it rains tomorrow.4. 现在进行时现在进行时常用于表示现阶段正在进行的动作。
在时间状语从句中,现在进行时可以用来表示将来某个时间点正在进行的动作。
例如:- He will be sleeping when you get home.- They will be waiting for the bus when it arrives.5. 过去进行时过去进行时常用于表示过去某个时间点正在进行的动作。

pep小学英语时态总结一.一般现在时表示一般情况下按照某种频度发生的事,或者存在的某种状态。
特征:句子中一般有usually often 等表示频度的词。
1.陈述句句子结构。
a、主语(非第三人称单数)+动词原形+ 时间、地点等例: Usually I play football on the weekend.b、主语(第三人称单数)+动词(单三形式)+时间、地点例:Usually he plays football on the weekend.2.特殊疑问句结构。
疑问代词(what等)+do/does+ 主语+时间等其他?例:What do you do on the weekend?3.一般疑问句机构。
Do/Does +陈述句+?回答: Yes, 主语+do/does. No, 主语+don't/doesn't.例:Do you play football on the weekend?Yes, I do.No, I don't.二.现在进行时。
表示现在正在进行的动作。
1.陈述句。
主语+be(is,am,are)+动词ing形式+ 地点。
例:I am playing football on the playground.2.特殊疑问句。
疑问代词(what等)+be+主语+doing+?例:What are you doing?3.一般疑问句。
Be+主语+动词ing形式+?Yes,主语+be。
No,主语+be的否定形式例:Are you playing football?Yes,I am. No,I am not.三、一般将来时。
表示将要或者准备发生的事,句子中一般有表示将来的时间词(如:next weekend等)1.陈述句。
主语+be(is,am,are) going to +动词原形+ 时间、地点等例:I am going to play football next weekend.2.特殊疑问句。

动词时态在时间状语从句中的特殊用法时间状语从句用来表示一个动作或状态发生的时间,其中动词时态的选择非常重要。
在时间状语从句中,动词的时态可以有一些特殊的用法和规则。
本文将就动词时态在时间状语从句中的特殊用法进行详细探讨。
一、一般现在时态1. 当主句是一般现在时,表示经常性的、习惯性的动作或状态时,时间状语从句使用一般现在时态。
例如:“He always goes to the gym when he has free time.”(当他有空时,他总是去健身房。
)2. 当主句是将来时,表示按计划或安排要发生的动作时,时间状语从句使用一般现在时态。
例如:“She will visit her parents when she arrives in the city tomorrow.”(她明天到达这个城市时会去看望她的父母。
)二、一般过去时态当主句是一般过去时,表示过去某一时间发生的动作或状态,时间状语从句的动词时态使用一般过去时态。
例如:“He called me when he arrived home last night.”(他昨晚回家时给我打电话了。
)三、过去进行时态当主句是过去进行时,表示过去某一时间正在进行的动作,时间状语从句的动词时态使用过去进行时态。
例如:“I was studying when she called me yesterday.”(昨天她给我打电话时,我正在学习。
)四、现在完成时态当主句是现在完成时,表示过去某一时间发生并与现在有关的动作或状态,时间状语从句的动词时态使用现在完成时态。
例如:“She has already left when I arrived home.”(我回到家时,她已经离开了。
)五、将来完成时态当主句是将来完成时,表示将来某一时间之前已经完成的动作或状态,时间状语从句的动词时态使用将来完成时态。
例如:“I will have graduated when you come back next year.”(明年你回来时,我已经毕业了。

英语四个时态的结构英语中有四个基本时态:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和现在进行时。
它们有不同的结构和用法,下面将详细介绍每个时态的结构。
一、一般现在时:1.肯定句结构:主语+动词原形/第三人称单数形式+其他例如:I play football every weekend.2. 否定句结构:主语 + do/does + not + 动词原形 + 其他例如:They do not like tomatoes.3. 疑问句结构:Do/Does + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:Do you like ice cream?4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词 + do/does + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?二、一般过去时:1.肯定句结构:主语+动词过去式+其他例如:She watched a movie last night.2. 否定句结构:主语 + did not + 动词原形 + 其他例如:He did not eat dinner yesterday.3. 疑问句结构:Did + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:Did you go to the party?4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词 + did + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:When did you arrive?三、一般将来时:1. 肯定句结构:主语 + will + 动词原形 + 其他例如:I will visit my grandma next week.2. 否定句结构:主语 + will not + 动词原形 + 其他3. 疑问句结构:Will + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:Will you go to the concert?4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词 + will + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?例如:Where will you travel next summer?四、现在进行时:1. 肯定句结构:主语 + am/is/are + 动词-ing + 其他例如:She is watching TV now.2. 否定句结构:主语 + am/is/are + not + 动词-ing + 其他例如:They are not studying for the exam.3. 疑问句结构:Am/Is/Are + 主语 + 动词-ing + 其他?例如:Are you playing basketball?4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词 + am/is/are + 主语 + 动词-ing + 其他?例如:What are you doing tonight?以上就是英语四个基本时态的结构和用法。

千里之行,始于足下。
小学四种英语时态的归纳总结小学英语时态的归纳总结在小学阶段学习英语,掌握四种基本的时态是非常重要的。
这四种时态分别是一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和现在进行时。
以下是对这四种时态的归纳总结。
一、一般现在时(Simple Present Tense)1. 表示经常性的动作或状态。
例如:I play basketball every Saturday.2. 在陈述句中,主语和动词要一致。
例如:He likes to watch movies.3. 在否定句中,用do / does + not + 动词原形。
例如:She does not like vegetables.4. 在疑问句中,用do / does + 主语 + 动词原形?例如:Do you have any pets?5. 用于表示客观事实、经验等。
二、一般过去时(Simple Past Tense)1. 表示过去发生的动作或状态。
例如:I watched a movie yesterday.2. 在陈述句中,动词过去式的变化规则是直接加-ed。
例如:We played soccer last week.3. 在否定句中,用did + not + 动词原形。
例如:She did not go to school yesterday.4. 在疑问句中,用did + 主语 + 动词原形?例如:Did you finishyour homework?第1页/共3页锲而不舍,金石可镂。
三、一般将来时(Simple Future Tense)1. 表示将来发生的动作或状态。
例如:I will go to the park tomorrow.2. 在陈述句中,用will / shall + 动词原形。
例如:She will visither grandparents next week.3. 在否定句中,用will not / won't + 动词原形。

时态的转换及用法归纳时态是语法中的一个重要概念,能够准确地表达动作或状态发生的时间。
在英语中,时态的转换及使用是学习者必须掌握的技能之一。
本文将对时态的转换和用法进行归纳总结,帮助读者更好地理解和运用不同时态。
一、一般现在时一般现在时表示目前的事实、常规或经常发生的动作。
主要的动词形式是原形动词,第三人称单数要在动词后加“s”。
一般现在时的肯定、否定和疑问句的构成如下:- 肯定句:主语 + 动词原形 + 其他- 否定句:主语 + do/does + not + 动词原形 + 其他- 疑问句:(特殊疑问词) + do/does + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他例如:- I eat breakfast every morning.(我每天早上吃早餐。
)- He doesn't like coffee.(他不喜欢咖啡。
)- Do you play basketball?(你打篮球吗?)二、一般过去时一般过去时表示过去某个时间或时期发生的动作或状态。
最常用的动词形式是动词的过去式,疑问句和否定句使用助动词did。
一般过去时的肯定、否定和疑问句的构成如下:- 肯定句:主语 + 动词过去式 + 其他- 否定句:主语 + did not + 动词原形 + 其他- 疑问句:(特殊疑问词) + did + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他例如:- She studied English last night.(昨晚她学习了英语。
)- We didn't go to the park.(我们没有去公园。
)- Did you eat lunch?(你吃午饭了吗?)三、一般将来时一般将来时表示将要发生的动作或状态,常用的句型是"will + 动词原形"。
一般将来时的构成如下:- 肯定句:主语 + will + 动词原形 + 其他- 否定句:主语 + will not + 动词原形 + 其他- 疑问句:(特殊疑问词) + will + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他例如:- I will visit my grandmother tomorrow.(我明天会去看望我的奶奶。
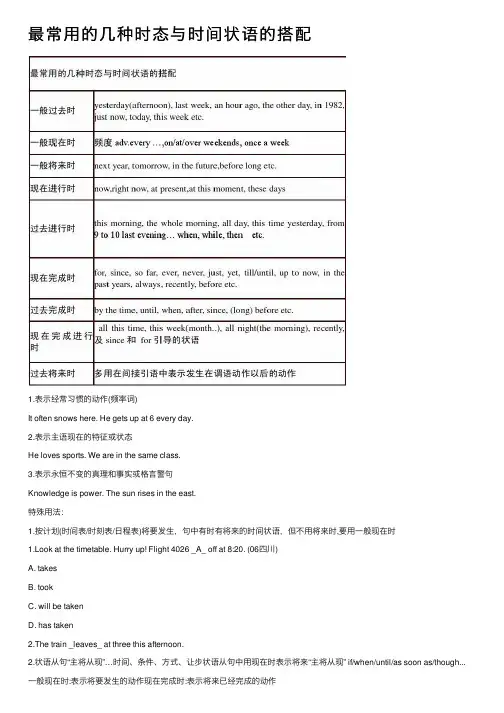
最常⽤的⼏种时态与时间状语的搭配1.表⽰经常习惯的动作(频率词)It often snows here. He gets up at 6 every day.2.表⽰主语现在的特征或状态He loves sports. We are in the same class.3.表⽰永恒不变的真理和事实或格⾔警句Knowledge is power. The sun rises in the east.特殊⽤法:1.按计划(时间表/时刻表/⽇程表)将要发⽣,句中有时有将来的时间状语,但不⽤将来时,要⽤⼀般现在时1.Look at the timetable. Hurry up! Flight 4026 _A_ off at 8:20. (06四川)A. takesB. tookC. will be takenD. has taken2.The train _leaves_ at three this afternoon.2.状语从句“主将从现”…时间、条件、⽅式、让步状语从句中⽤现在时表⽰将来“主将从现” if/when/until/as soon as/though...⼀般现在时:表⽰将要发⽣的动作现在完成时:表⽰将来已经完成的动作1.If their marketing plans succeed, they _A_ their sales by 20 percent. (2008全国2)A. will increaseB. have been increasingC. have increasedD. would be increasing2.I _C_ leave at the end of this month.Really? I don’t think you should leave until you __ another job.A. am going to, findB. will, will foundC. am going to, have foundD. will, had found⼆、⼀般过去时1.表在过去发⽣的和现在没有联系的动作或状态明⽰:yesterday, ago, last …, just now, in 1990暗⽰:when I was a little girl, when he put on his coat2.描述过去的情况⾔外之意:只有过去如此现在并⾮如此Edward, you play so well. But I __ you played the piano. (2009全国I)A. didn't knowB. hadn't known (A)C. don't knowD. haven't known三、⼀般将来时1.表⽰将要发⽣的动作或存在的状态I’ll return you the book next week. She’ll be twenty years old next year.2.表⽰⼀种倾向或习惯动作We’ll die without air or water. Whenever I’m in trouble, he’ll come to help me.表⽰将来时的六种形式①will /shall +动词原形(单纯的将来/说话时的临时决定)②be going to do(客观计划)③be about to do(即将/马上要做某事)④be to do(表⽰职责命令,相当于should/must;或表⽰“注定”)(可⽤于条件句中)⑤be doing(瞬间动词⽤表将来)⑥⼀般现在时(强调动作“列⼊⽇程”)1) be going to 表⽰即将发⽣的或最近打算进⾏的事情,⽽will表⽰谈话时临时决定的意图,具有临时性和偶然性。


小学英语四大时态语法知识点小学英语主要是如下的四大时态:一般现在时、现在进行时、一般过去时、一般将来时。
01一般现在时一、标志词always(总是)usually(通常)often(经常)sometimes(有时)never(从不)every(每一)二、基本用法1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。
2.表示经常性、习惯性的动作。
3.表示客观现实。
三、构成1.be动词:主语+be动词(am isare)+其它.2.行为动词:主语+行为动词+其它。
四、句型肯定句:A. be 动词:be+主语+其它。
B. 行为动词:主语+动词(注意人称变化)+其它。
否定句:A.be动词:主语+be+not+其它。
B.行为动词:主语+助动词(do/does)+not+d动词原形+其它一般疑问句:A.be动词:be+主语+其它。
B.行为动词:助动词(Do/Does)+主语+动词原形+其他.特殊疑问词:疑问词+一般疑问句02现在进行时一、标志词now(现在), look(看),listen(听)二、基本用法表示现阶段正在进行的动作三、基本结构1.肯定句:主语+be动词+动词现在分词(ing)+其它。
2.否定句:主语+be动词+not+动词现在分词(ing)+其它。
3.一般疑问句:be动词+主语+现在分词(ing)+其它。
4.特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句。
03一般将来时一、标志词tomorrow(明天),soon(不久),will(将要=be going to)二、基本用法表示在在将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态。
三、基本结构1.肯定句:主语+ be going to + 动词原形。
主语+will+动词原形。
2.否定句:主语+ be going to +动词原形。
主语+won’t + 动词原形3.一般疑问句:Be + 主语+ going to+动词原形Will + 主语+ 动词原形4.特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句04一般过去时一、标志词yesterday(昨天),ago(以前),before(在...之前)二、用法1.表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常和表示过去的时间状语连用。
小学英语时态和语法总结一、现在时态(Present Simple)1. 用法:表示经常性的动作、习惯、常态、真理等。
2. 构成:主语 + 动词原形(第三人称单数要加-s)3. 特殊用法:a) 认真、真诚的祈使句:Be satisfied with your life.b) 当现在是将来动作或安排:My plane leaves in one hour.c) 描述本能或内在特征:The earth moves around the sun.d) 当主语是it,后面是名词从句时:It seems that she knows the answer.e) 表示世界真理或普遍真理:The sun rises in the east.4. 注意事项:a) 第三人称单数动词要加-s。
b) 当主语是第一或第二人称,或者是复数,动词不变。
二、现在进行时态(Present Continuous)1. 用法:表示现在正在进行的动作。
2. 构成:主语 + am / is / are + 动词的现在分词(-ing形式)3. 特殊用法:a) 表示近期打算:I am going to the cinema tonight.b) 表示变化发展的情况:The weather is getting worse.c) 表示接下来安排好的未来动作:I am seeing a movie tomorrow.d) 表示抱怨或责备:You are always misbehaving!4. 注意事项:动词的现在分词的构成规则需要注意。
如:study - studying, play - playing, run - running。
第1页/共5页三、过去时态(Past Simple)1. 用法:表示过去发生的动作或状态。
2. 构成:主语 + 动词过去式3. 特殊用法:a) 表示“过去经常性的动作”:I often walked to school when I was young.b) 表示“在过去的某个时间发生的动作”:I visited my grandparents last weekend.c) 用于条件句中,表示假设:If I had enough money, I would buya car.4. 注意事项:动词的过去式需要根据规则进行变化,如:study - studied, play - played, run - ran。
英语时态总结及用法英语时态总结及用法英语时态是指用来表示动作发生的时间的一种语法现象。
根据时间的不同,英语时态可以分为一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、将来进行时、过去完成时、将来完成时等多种时态。
下面将对这些时态的用法进行详细阐述。
一、一般现在时表示经常性、习惯性、普遍性和客观真理的动作或状态。
一般现在时的谓语动词通常是动词原形。
例如:I go to school every day.(我每天去学校。
)The sun rises in the east.(太阳从东方升起。
)二、一般过去时表示过去某个时间内所发生的动作或存在的状态。
一般过去时的谓语动词通常是动词的过去式。
例如:She lived in New York for three years.(她在纽约住了三年。
)They went to the park yesterday.(他们昨天去了公园。
)三、一般将来时表示将来某时将要发生的动作或存在的状态。
一般将来时的谓语动词通常是动词原形前面加上助动词will或shall。
例如:I will visit my grandparents next week.(下周我将去看望我的祖父母。
)They shall arrive at the airport tomorrow.(他们明天将到达机场。
)四、现在进行时表示现在正在进行的动作或存在的状态。
现在进行时的谓语动词由be动词的相应形式(am/is/are)加上动词的现在分词来构成。
例如:He is watching TV now.(他正在看电视。
)We are studying English at the moment.(我们此刻正在学习英语。
)五、过去进行时表示过去某时正在进行的动作或存在的状态。
过去进行时的谓语动词由过去式的be动词(was/were)加上动词的现在分词来构成。
例如:She was reading a book when I saw her.(当我看见她时,她正在读书。
⼩学六年级英语四种时态总结⼩学六年级英语四种时态总结⼀、⼀般现在时标志词:always(总是) usually(通常) often(经常) sometimes(有时) never(从不) every(每⼀)⾏为动词词型变化形式⼀般现在时动词只有第三⼈称有词形变化,其他⼈称(第⼀⼈称:I, we;第⼆⼈称:you;第三⼈称复数:they、my friends)动词均⽤原形当主语是第三⼈称单数时,⼀般动词在⼀般现在时句⼦中的变化规律:1、多数在动词后加s play—plays like—likes ,2、以s,x,sh,ch,o结尾的动词加es wash–washes catch–catches do–does3、以辅⾳字母加y结尾,把y改i再加es fly—flies study—studies4、以元⾳字母加y结尾,直接加s buy –buys5、不规则变化have—has⼀般现在时基本⽤法功能1.表⽰事物或⼈物的特征、状态。
如:The sky is blue.天空是蓝⾊的。
2.表⽰经常性或习惯性的动作。
如:I get up at six every day.我每天六点起床。
3.表⽰客观现实。
如:The earth goes around the sun.地球绕着太阳转。
The earth is round.构成1. be动词:主语+be(am,is,are)+其它。
如:I am a boy.我是⼀个男孩。
2.⾏为动词:主语+⾏为动词(+其它)。
如:We study English.我们学习英语。
句型肯定句:A.be动词:主语+ be + 其它成分He is a worker.B.⾏为动词:主语+动词(注意⼈称变化) +其它成分We like the little cat.否定句:A.be动词:主语+ be + not +其它成分They are not students.B.⾏为动词:主语+助动词(do/does) + not +动词原形+其它成分We don't like the little cat.⼀般疑问句:A.be动词:Am / Is /Are +主语+ 其它成分Are you a teacher? Yes, I am. / No, I am not.Are they students of your school.Yes they are / No they aren,t.B.⾏为动词:助动词(Do/Does)+主语+动词原形+ 其它成分Do you like it? Yes, I do. / No. I don't .Does he(she) like it? Yes, he( she )does. / No, he ( she )doesn't.特殊疑问句:疑问词+ ⼀般疑问句A.be动词:How many students are there in your school?B.⾏为动词:What do you usually do on Sunday?⼀般现在时动词be和have的变化形式。
一. 现在进行时1. 表此时此刻正在进行的动作。
now / at the ( this ) moment / at this time /right now / at presentNow she is planning our schedule for the trip.2. 表示现阶段正在进行的动作 (说话时不一定正在进行) 。
These days / this month (term, semester)e.g. Wushu, a Chinese martial art, is still trying to get into the Olympics.Teenagers are damaging their health because they play computer games too much.I’m not doing anything at present / these days.I have to go to work by taxi because my car is being repaired at the garage.I’m taking up four courses this term.3. 用always / continually / constantly / frequently / forever 表感情色彩。
e.g. Why are you always coming late for class?He’s constantly changing her mind.That son of yours is always making trouble.4. 进行表将来:go / leave / come / start / arrive / return / stay / take / do / have / wear / work/ sleep / play / stop /bee.g. --- Are you still busy? --- Yes, I am just finishing my work, and it won’t take long.Are you doing anything tomorrow afternoon?We’re getting married on April 10 this year.We’re having a few guests tonight.The prices for vegetables are going up towards the end of the year.Because the shop is closing down, all the T-shirts are sold at half price.What are you doing after class?5. look / listen 开头的句子。
初中英语时态的归类区别和特殊⽤法初中英语时态的归类区别和特殊⽤法动词的过去、现在和未来动词时态⼀览表下⾯,我们来看看各个时态的⽤法:⼀般过去时⽤法索引在确定的过去时间⾥所发⽣的动作或存在的状态。
时间状语有:yesterday, last week, an hour ago, the other day, in 1982等。
Where did you go just now?表⽰在过去⼀段时间内,经常性或习惯性的动作。
When I was a child, I often played football in the street.特殊句型(需重点掌握)It is time for sb. to do sth. “到……时间了”、“该……了”It is time sb. did sth. “时间已迟了”、“早该……了”It is time for you to go to bed. 你该睡觉了。
It is time you went to bed. 早该睡觉了。
would (had) rather sb. did sth. 表⽰“宁愿某⼈做某事”I'd rather you came tomorrow.请你注意:⼀般过去时的时间状语应该是表⽰过去某个时间的词或词组,如:yesterday, last month, in 1999, two days ago 等,绝对不可与recently, in the past 10 years, this month等连⽤,因为这样的时间状语都与现在有关系,应该⽤现在完成时或⼀般现在时。
过去进⾏时⽤法索引表⽰过去某个时刻或某⼀阶段正在进⾏的动作. 构成:be(was,were)+现在分词,常⽤的时间状语:at 10:30 last night , this time yesterday eveningEg1.What were you doing at three o’clock yesterday afternoon?⽤于when, while 引导的时间状语从句中。