事实行为与法律行为
- 格式:doc
- 大小:24.00 KB
- 文档页数:2

什么是事实行为事实行为的定义导读:我根据大家的需要整理了一份关于《什么是事实行为事实行为的定义》的内容,具体内容:事实行为是指行为人不具有设立、变更或消灭民事法律关系的意图,但依照法律的规定能引起民事法律后果的行为。
那么你对事实行为了解多少呢?以下是由我整理关于什么是事实行为的内容,希望大家喜欢!...事实行为是指行为人不具有设立、变更或消灭民事法律关系的意图,但依照法律的规定能引起民事法律后果的行为。
那么你对事实行为了解多少呢?以下是由我整理关于什么是事实行为的内容,希望大家喜欢!事实行为的定义分类就民法而言,行为区分为民事行为和事实行为两大类。
民事行为民事行为是民事法律行为的上位概念,包括民事法律行为、无效民事行为、可变更或可撤销的民事行为、效力未定的民事行为,不包括侵权行为、违约行为、无因管理行为等事实行为。
区别1、事实行为完全不以意思表示为其必备要素,而民事行为以意思表示为必备要素;2、事实行为依法律规定直接产生法律后果,民事行为依据行为人的意思表示的内容而发生效力;3、事实行为只有在行为人的客观行为符合法定构成要件时才发生法律规定的效果,民事行为的本质在于意思表示,而不在于事实构成;4、事实行为的构成不要求行为人具有相应的民事行为能力,而民事行为以行为人具有民事行为能力为生效条件。
如:先占、加工、无因管理行为、遗失物的拾得行为、埋藏物的发现行为以及债权标的物的给付行为等均属于事实行为。
事实行为的相关内容1、事件和事实行为和法律行为:民事法律事实的发生是否具有直接的人的意志性而将民事法律事实分为事件与行为。
事件,是指其本身不直接包含人的意志性的民事法律事实。
行为,是受人的意志支配的活动。
是否和人的意志有关,是事件区别于行为的关键。
注意:事件与人的意志无关,是指事件本身并不直接含有人的意志性,强调把事件本身与引发事件的原因区别开来,如果事件是由人为原因引起的,人的意志性就与事件发生有间接的联系,但事件本身并不直接含有人的意志性,因而它仍然与行为相区分。


法律行为与事实行为法律行为与事实行为是法律领域的两个重要概念。
法律行为是指具有法律效力的行为,是基于合法权益和法律规定而进行的一种行为,可以产生法律后果。
事实行为则是指人们在社会生活中产生的各种行为,不一定具有法律效果。
首先,法律行为是指人们在法定条件下,根据法律规定,有意识地表达出自己的意愿,产生法律后果的行为。
法律行为可以是单方面行为,如遗嘱、声明等;也可以是多方面的行为,如买卖合同、婚姻等。
法律行为的要素包括主体、客体、形式、内容等。
主体是指能够行使权利和义务的人,主体包括自然人和法人,必须具备完全民事行为能力;客体是指法律上具备交易价值或者具有法律效果的物、权利和利益;形式是指法律行为应当符合的形式要求,例如书面形式、公证等;内容是指法律行为要产生的效果。
事实行为与法律行为相对应,是指人们在日常生活中所表现的行为,但不一定具有法律效果。
例如,举手、行走等动作都是事实行为,但并不具备法律效力。
事实行为可以是人们的自然行为,也可以是人们有目的地为了实现某种目标而进行的行为。
与法律行为相比,事实行为可以在不明确法律规定的情况下进行,不需要符合法律规定的要素,也不具备法律后果。
在实践中,法律行为和事实行为之间存在着一定的联系和辩证关系。
首先,事实行为可以是法律行为的组成部分。
例如,在签订买卖合同过程中,买卖双方的协商、讨价还价等行为属于事实行为,但是这些行为是完成买卖合同的先决条件。
其次,事实行为可以为法律行为提供证据。
例如,当事人在签订合同时,如果有目击证人或者其他证据可以证明签订合同的真实性,这些事实行为可以成为法律行为的证据。
再次,事实行为可以为法律行为的履行提供基础。
例如,若买方未按时支付货款,则卖方可以要求解除合同,这是因为买方的违约行为构成了法律上的事实。
总之,法律行为与事实行为是法律领域中的两个重要概念。
法律行为是指具有法律效力的行为,需要符合一定的法律要素;事实行为是指人们在生活中表现出的行为,不一定具备法律效果。


第1篇一、引言法律作为一种社会规范,旨在维护社会秩序,保障公民权益。
在法律实践中,除了法律行为之外,事实行为也常常产生法律后果。
事实行为是指不以当事人的意志为转移,而是由客观事实所引起的行为。
本文将从事实行为的定义、类型、法律后果等方面进行探讨,以期为法律实践提供有益参考。
二、事实行为的定义事实行为是指不以当事人的意志为转移,而是由客观事实所引起的行为。
它与法律行为相比,具有以下特点:1. 无需当事人意志:事实行为的发生不受当事人意志的制约,而是由客观事实所决定。
2. 法律后果客观:事实行为产生法律后果是客观存在的,不以当事人的主观意愿为转移。
3. 法律适用广泛:事实行为涉及的法律关系广泛,包括合同、侵权、物权、知识产权等领域。
三、事实行为的类型1. 合同事实行为:如交付货物、支付货款等,这些行为虽非合同条款,但与合同关系密切相关。
2. 侵权事实行为:如非法侵入他人住宅、故意毁坏他人财物等,这些行为侵犯了他人的合法权益。
3. 物权事实行为:如抵押、质押、继承等,这些行为涉及物权的设立、变更、消灭。
4. 知识产权事实行为:如创作、发表、实施专利等,这些行为涉及知识产权的取得、保护。
5. 其他事实行为:如失踪、死亡、失踪人财产代管等,这些行为涉及法律关系的变化。
四、事实行为的法律后果1. 合同事实行为的法律后果:在合同关系中,事实行为可能引起合同成立、生效、变更、解除等法律后果。
如交付货物的事实行为可能导致合同成立,支付货款的事实行为可能导致合同生效。
2. 侵权事实行为的法律后果:侵权事实行为可能引起侵权责任,侵权人需承担相应的法律责任,如赔偿损失、恢复原状等。
3. 物权事实行为的法律后果:物权事实行为可能导致物权的设立、变更、消灭。
如抵押、质押行为可能导致物权的设立,继承行为可能导致物权的消灭。
4. 知识产权事实行为的法律后果:知识产权事实行为可能导致知识产权的取得、保护。
如创作行为可能导致著作权的取得,实施专利行为可能导致专利权的保护。
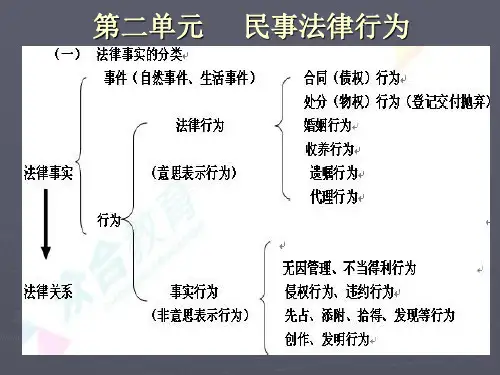

民事法律行为法律关系分为主体(当事人)、客体(权利义务的指向对象)、内容(权利义务关系);法律关系发生的要件:①有主体、②有法律规范、③有法律事实一、民事法律事实的分类:以事实行为与法律行为的区别为中心以法律事实的发生是否与当事人的意志有关,将法律事实分为行为与事件根据事件的发生是否与人的意志有关,能够分成自然事件(海啸)与社会事件(罢工)根据行为的法律后果是否是当事人意欲追求的,行为分为事实行为与民事行为(法律行为)事实行为包含:侵权行为、无因管理行为、部分的不当得利行为(由于有的不当得利是基于事件)、创作行为、发明行为、添附行为、先占行为、拾得遗失物、发现隐(埋)藏物等民事行为的概念引进于德国,我国进行了改造,目前民事行为分为:民事法律行为(civil legal act,合法有效);效力待定的民事行为(当事人能力有瑕疵);可变更、可撤消的民事行为(意思表示有瑕疵);无效的民事行为(内容违法);----但理论结构本身就会产生混乱,如民事法律行为包含合同行为,而合同行为又分为有效、效力待定、可变更可撤消、无效按李建伟说:以后会把民事行为的概念取消,直接让法律行为与事实行为相对应,再把法律行为按种类分为合同行为、婚姻行为、遗嘱行为、收养行为、代理行为等,还能够按法律行为的效力状况分为有效行为、无效行为、效力待定行为、可变更可撤消行为。
法律行为的内容与后果都由当事人自由决定(私法自治),法律只起补充作用法律行为要求当事人具有行为能力事实行为的内容与后果都由法律事先规定,法律表现为强行性规范事实行为不要求当事人具有行为能力从不一致的角度看,一个行为可能同时是事实行为或者法律行为或者纯属事件,比如:甲杀死乙,乙的儿女继承了乙的财产,关于发生的继承法律关系,甲杀死乙属于事件甲杀死乙,甲要承担侵权责任,关于发生的侵权责任,甲杀死乙属于事实行为甲将汽车托乙保管,乙擅自将汽车出租给丙,关于乙丙之间的租赁,乙的行为是法律行为而由于乙擅自出租甲的汽车,因此所获取的租金属于不当得利,出租汽车的行为关于甲乙之间产生的不当得利之债来说属于事实行为二、民事法律行为的分类:1、按主体与意思表示方向的不一致能够分为:单方行为:无须他人意思表示就可成立生效单方行为又分为:有相对人的单方行为:如授权、解除、免除、撤销无相对人的单方行为:如抛弃行为、遗嘱行为双方行为:内容相同方向相反,如合同,需要双方意思表示一致共同行为:意思表示方向相同,如订立合伙协议、公司章程,使用多数决定原则2、按是否需要支付对价能够分为有偿行为与无偿行为(赠与、保证、借用、没有约定利息的民间借贷、没有约定保管费用的保管合同、没有约定报酬的委托合同)区分的意义:关涉行为定性、当事人承担的责任程度不一致、对当事人的行为能力要求不一致3、按是否需要标的物的交付为行为的成立或者者生效的要件能够分为要物行为(实践行为)与不要物行为(诺成行为)要紧的要物合同:动产质押、定金合同、保管合同、借用合同区分意义:当事人承担的法律责任不一致4、按是否需要特定形式还能够分为:要式行为与不要式行为要式行为又分为通常要式(书面形式)与特殊要式(书面+登记或者批准)没有采取通常要式的,合同不成立;没有采取特殊要式的,合同不生效特殊要式合同:中外合资合同、中外合作合同、向外国人转让中国专利5、按行为与原因的关系还能够分为:有因行为(要因行为)、无因行为(不要因行为)分类意义:“原因”的效力对行为效力的影响不一致目前我国现行法上的无因行为包含:债权移转、免责的债务承担、债务免除、票据行为、授权行为6、按行为的效果还能够分为:处分行为(物权性――发生、变更、消灭物权);―――物权行为负担行为(债权性――发生债权债务);―――债权行为二者的要紧区别在于:(1).法律效力不一致。

法律行为事实行为法律行为与事实行为是法律领域中常用的两个术语,二者之间有着明显的区别和联系。
本文将就法律行为与事实行为进行阐述,分别从定义、特征、区别等方面进行探讨。
首先,法律行为可以理解为人们基于自愿意识和法律要求,通过自己的意志对外产生的具有法律效力的行为。
它是指明确的法律主体意愿行为,在法律范围内发生的客观外部表现。
相对而言,事实行为是指人们在无意识或无意愿的情况下,由于自然因素或其他客观因素的影响,而对外展现出来的行为。
事实行为可以包括一系列无意识或无意愿的行为,如呼吸、心跳等。
它是指与主体的意愿无关的客观现象。
其次,法律行为具有一些特征。
首先,法律行为是人们基于自愿进行的行为,是主体的真实意愿表达。
其次,法律行为具有法律效力,即依据法律规定,能够产生相应的法律效果。
再次,法律行为需要符合法律规定,不能违反法律的强制性规定。
最后,法律行为产生的后果是可以预见和计算的,一旦产生后果,法律将会对其进行相应的承担和责任。
而事实行为也具有其特征。
首先,事实行为与主体的意愿无关,不受主体的操控和控制。
其次,事实行为通常是由客观因素引发的,而非主体的意愿引起的。
再次,事实行为的结果往往是难以预见和计算的,主体往往无法对其进行控制和预知。
此外,法律行为与事实行为在实践中也有一些明显的区别。
法律行为需要主体的真实意愿和自愿,而事实行为则无需主体的意愿和自愿。
法律行为往往是出于主体对某种利益的追求,而事实行为则是出于客观因素的作用。
法律行为具有法律效力,而事实行为则通常不具备法律效力。
法律行为需要符合法律规定,而事实行为则无需遵守法律的强制性规定。
综上所述,法律行为和事实行为在定义、特征和实践中都具有明显的差异和联系。
法律行为是主体真实意愿的自愿行为,具有法律效力和法律约束力;而事实行为则是与主体意愿无关的客观现象,通常无法预见和计算其后果。
对于法律领域的实践和理论研究,准确理解和区分法律行为和事实行为的概念将有助于更好地处理相关事务,确保法律的公正和权威性。

行政事实行为通俗易懂
行政事实行为通俗易懂的说法就是行政机关做了但又不产生法律效力的事实行为。
这种行为不以产生一定的法律效果为目的,只是出于行政机关的管理职责和某种社会公益目的而实施的行为。
行政事实行为具有以下特点:
1. 行政性:行政事实行为是行政主体实施的,与行使行政职权有直接联系的事实行为。
2. 行政职责性:行政事实行为是行政机关基于法定职责实施的行为,虽然不具有法定的强制力,但一旦出现意外,行政机关要对其负责。
3. 非法定性:行政事实行为与行政法律行为不同,它不是按照严格的法律规定实施的。
4. 不确定性:行政事实行为所产生的法律效果,往往是不确定的,具有临时性和个别性。
总的来说,行政事实行为是行政机关在行使职权过程中所实施的一系列行为,这些行为可能出于管理职责或公益目的,也可能没有严格的法律规定。
尽管其产生的法律效果不确定,但一旦出现意外,行政机关需要对其负责。

事实行为与法律行为(Factual behavior and juristic act)The fact act and legal act.Txt27 the power of faith is that even in adversity, also can help you sail with the wind; the charm of belief that if meet the risks, you can also call up the courage of life; belief is that even the great misfortune, also can make you keep a noble soul. The main difference is that 1, not in fact behavior means that as its essential elements, and the legal act declaration of essential elements; 2, act in accordance with the law and legal consequences, legal acts according to the behavior of the people that mean the content and effect; 3, the fact that behavior does not require people with the corresponding civil behavior capacity, and the legal behavior of the actor has corresponding capacity.Civil juristic act is the lawful act of citizen or legal person to establish, change and terminate civil rights and civil obligations.Civil juristic acts should meet the following conditions: (1) the actor has the corresponding capacity for civil conduct; (two) meaning is true;(three) do not violate the law or the public interest.As a kind of behavior in civil legal fact, civil juristic act has the following three characteristics, which is different from other civil legal facts.(1) civil juristic act is a legal actCivil juristic act must be legal, because it must be legal act. In order to confirm and protect the state law, it can produce the civil legal consequence of the actor's expectation. Here, the legitimacy of the understanding of the civil legal act should focus on the content and form of which shall be in conformity with the law, and the range of validity is generalized, which should accord with the regulations, but also accord with the public interests and social morality requirements. This is the purpose of civil law to adjust the social and economic life, and also the essential attribute of civil juristic act.(two) civil juristic act is expressed by the intention of the actor1. meaning expression. Declaration of intention refers to the internal meaning of the actor's pursuit of the civil legal consequences (the establishment, alteration or elimination of the civil legal relationship) in a certain way.2. declaration of intention and civil juristic act. Civil juristic act is people's purposeful and conscious behavior. Therefore, declaration of intention is a necessary part of civil juristic act. Every civil juristic act must have the meaning expression. The act of declaration of intention that is confirmed by civil law is not a civil juristic act.It is said the elements of civil legal acts, but not equal to the civil legal act, because civil legal behavior is different, its meaning is not the same form, can be a meaning which is alsocontains two or more meaning.(three) civil juristic act can realize the civil legal consequence that the actor expects: establishment, alteration or elimination of civil legal relationThe civil legal act is a purposeful action, namely to establish, change or terminate civil legal relationship for the purpose, then, the legitimacy of the civil legal act is based on the legal recognition and protection effect of the civil legal act, the expected consequences of perpetrators must be to achieve. It can be seen that the purpose of civil juristic act and the actual consequences are consistent. This characteristic makes the civil juristic act different from the civil illegal act. Because the civil illegal act (such as tort) also contains legal consequences (such as tort liability for damages). However, this kind of legal consequence is not the consequence that the perpetrator pursues when he implements the civil illegal act, but is directly produced according to the legal provisions, and is not based on the party's intention.The difference between factual action and legal actAfter reading Dong Ansheng's book "civil juristic act", he summed up the difference between the two as three points, which is worth learning:1, legal act is expressed by intention as its essential element, and factual act is not necessarily;2. Legal act takes effect on the content of the meaning of theactor,The factual act only has legal consequences directly according to the law;3, the factual act must be constituted by some fact, and it must be involved in the constitutive requirements in law. The adjustment of the law to the juristic act is carried out by the actor's intention.Look, is the answer satisfactory?Legal act can produce legal effect of certain legal effect, behavior is subjective fact, such as contract, administrative punishment and so onLegal fact refers to facts that can cause certain legal effects, including legal facts and legal and juristic actsLegal events refer to the objective facts that can cause certain legal effects, and are not subjective facts, such as the birth of human beingsFactual act refers to the act that the actor has the intention to produce a certain legal effect, but can cause legal consequences according to the provisions of the law, such as tortTypes of legal facts. There are two main types: legal events and legal actions(1) the legal event is the objective fact that the legal relation is not formed by the legal norm, and the legal relation is formed, changed or eliminated. Legal events can be divided into two types: social events and natural events.(2) legal acts can exist as legal facts, which can cause the formation, alteration and elimination of legal relations. Acts can be classified into bona fide act, lawful act and malicious act, and illegal act.In the study of legal facts, we should also see complex phenomena:The same legal fact can lead to the generation, alteration and elimination of various legal relations.The creation, alteration or elimination of the same legal relationship caused by two or more than two legal facts.In jurisprudence, people often refer to the whole of two or more than two legal facts, which is called "fact constitution"".Whether civil law legal fact has direct human will, divides civil legal fact into incident and behavior.Event: refers to its own civil legal fact that does not directly contain human will.Behavior: the activity controlled by the will of man.Whether it is related to man's will is the key to the differencebetween events and actions.Note: the events and people will not refer to the events of the law, will itself does not directly contain people, stressed that the reason of the event itself and trigger events of the distinction, if the event is caused by human reason, will people and events have indirect contact, but the event itself will it does not contain people, so it still distinguish and behavior. For example, a person killed B, and the murder of a person was distinguishable from the death of b..Events include: natural events and human events.Natural events refer to events that are completely unrelated to the will of man and are purely natural. As a man's birth and death, natural disasters, for a period of time after, the natural fruits produced.Human events refer to events triggered by human actions. Such as wars, strikes, riots, man-made accidents, human deaths, and human disappearances.It can be seen that the unity of event and action belongs to civil legal facts.The most fundamental difference between events and behavior is whether the occurrence of legal facts is directly related to the will of human beings, and what is directly related to is behavior, otherwise it is the event.According to whether or not the actor expresses the meaning,the behavior in civil law can be divided into ideographic behavior and non expressive act.Ideographic act refers to the behavior of the actor through the declaration of intention. Ideographic acts include civil juristic acts, changeable and revocable civil acts, pending civil acts and invalid civil acts.Non ideographic behavior refers to the behavior of the party without intention to express it.Mainly includes: factual behavior, illegal behavior.Factual act refers to the fact that the actor does not have the meaning of civil legal relationship subjectively, but acts in accordance with the provisions of the law to result in the consequences of the civil legal relationship. For example,Lost and found objects, found buried, occupation, processing, work, non management, unjust enrichment.In a word, the juristic act and the factual act belong to the category of behavior. The most fundamental difference is whether the behavior contains the meaning of the expression, behavior as the elements of the meaning, is a civil act, otherwise, is the factual behavior.。

第1篇在民事法律关系中,行为是构成法律关系的基本要素。
民事法律后果是指因民事法律关系主体实施某种行为而产生的权利义务关系。
本文将从以下几个方面对引起民事法律后果的行为进行解析。
一、民事法律行为民事法律行为是指民事主体基于意思表示,设立、变更、终止民事法律关系的行为。
根据民事法律行为的效力,可以分为以下几种:1. 有效民事法律行为有效民事法律行为是指符合法律规定的民事法律行为。
有效民事法律行为能够产生预期的法律后果,包括:(1)设立民事法律关系:如签订合同、结婚、设立合伙等。
(2)变更民事法律关系:如转让债权、债务转移、抵押权设定等。
(3)终止民事法律关系:如合同解除、离婚、企业破产等。
2. 无效民事法律行为无效民事法律行为是指不符合法律规定的民事法律行为。
无效民事法律行为不产生法律后果,包括:(1)违反法律、行政法规的强制性规定。
(2)违反公序良俗。
(3)损害国家利益、社会公共利益。
3. 可撤销民事法律行为可撤销民事法律行为是指民事主体在意思表示不真实的情况下,可以请求撤销的民事法律行为。
可撤销民事法律行为在撤销前产生的法律后果仍然有效,但撤销后,民事法律关系自始无效。
4. 可变更民事法律行为可变更民事法律行为是指民事主体在意思表示不真实的情况下,可以请求变更的民事法律行为。
可变更民事法律行为在变更前产生的法律后果仍然有效,但变更后,民事法律关系内容发生变化。
二、事实行为事实行为是指民事主体不通过意思表示,仅基于客观事实而产生民事法律后果的行为。
事实行为可以分为以下几种:1. 无因管理无因管理是指民事主体为他人利益,管理他人事务的行为。
无因管理产生的法律后果是:管理人有权请求被管理人支付必要费用。
2. 侵权行为侵权行为是指民事主体侵害他人合法权益的行为。
侵权行为产生的法律后果是:侵权人应当承担侵权责任,赔偿被侵权人的损失。
3. 无权代理无权代理是指民事主体在未获得授权的情况下,以被代理人的名义实施民事法律行为的行为。
一、名词解释1、意思自治原则:也称私法自治,是指民事主体依法享有在法定范围内广泛的行为自由,并可以根据自己的意志产生、变更、消灭民事法律关系。
2、诚实信用原则:指的是民事主体在从事民事活动时,应本着诚实、善意的态度,讲究信用,恪守诺言,诚实不欺,不仅使当事人之间的利益得到平衡,而且也使当事人与社会之间的利益得到平衡的基本原则。
3、民事权利:是民事主体依法享有的并受法律保护的利益范围或者实施某一行为(作为不作为)以实现某种利益的可能性。
4、民事法律事实:符合民法规范,能够引起民事法律关系发生、变更和消灭的客观现象。
5、法律行为:民事主体旨在设立、变更、终止民事权利义务关系,以意思表示为要素的行为。
6、事实行为:是指行为人不具有设立、变更或者消灭民事法律关系的意图,但依照法律的规定能引起民事法律后果的行为。
7、绝对权:义务人不确定,权利人无须通过其实施积极协助行为即可实现的权利。
8、相对权:义务人为特定人,权利人必须通过其积极行为才能实现的权利。
9、支配权:可以对标的物直接支配并排斥他人干涉的权利。
10、请求权:得请求他人为一定行为或不为一定行为的权利。
11、抗辩权:对抗请求权的权利。
12、形成权:当事人一方可以以自己的意思表示使法律关系发生变动的权利。
13、期待权:成立要件尚未全部实现,将来有可能实现的权利。
14、紧急避险:是指为了使公共利益、本人或他人的合法权益免收现实和紧急的损害危险,不得已而采取的致他人和本人损害的行为。
15、孳息:由原物所产生的额外的收益。
16、民事权利能力:指法律赋予民事主体享有民事权利和承担民事义务的能力。
17、民事行为能力:能够以自己的行为依法行使权利和承担义务,从而使法律关系发生、变更或消灭的资格。
18、合伙:指两个以上的民事主体为实现共同目的,按照协议共同出资、共同经营,依照合同约定或者法律规定承担责任的组织。
19、特殊普通合伙:指以利用专业知识和专门技能为客户提供有偿服务为目的,合伙人依法承担有限责任或无限责任的企业。
2021年9月第23卷第5期㊀东南大学学报(哲学社会科学版)JournalofSoutheastUniversity(PhilosophyandSocialScience)㊀Sep.2021Vol 23No 5论法律行为在法律事实中的归类崔拴林(南京师范大学法学院,江苏南京210046)㊀㊀[摘㊀要]在我国民法理论中,对法律行为归入法律事实中的合法行为存在着争议㊂依据法律规范的构成理论,将法律事实中的行为区分为合法行为与违法行为,并将法律行为归入前者,具有一定的合理性㊂但是,将法律行为归入合法行为,也存在若干不足㊂如果从 民法对相关行为的态度 等角度出发,把 合法/被许可行为 违法/不被许可行为的二分法改造为 民法许可/倡导的行为 民法既不倡导㊁也不禁止的行为 民法完全禁止的行为 等类型系列,则可克服前述二分法以及 表示行为 非表示行为 之二分法的弊端,能够合理解决法律行为在法律事实中的归类问题㊂[关键词]法律行为㊀法律事实㊀合法行为㊀违法行为㊀类型化[基金项目]2019年度国家社会科学基金后期资助项目 论法律行为的本质属性 (19FFXB067)阶段性成果㊂[作者简介]崔拴林(1977 ),山西兴县人,南京师范大学法学院教授,研究方向:民商法㊂①㊀薛军:‘法律行为合法性 迷局之破解“,‘法商研究“2008年第2期㊂②㊀参见王轶‘论民事法律事实的类型区分“,‘中国法学“2013年第1期㊂③㊀参见朱庆育‘民法总论(第二版)“,北京:北京大学出版社,2016年,第80㊁95-97页;王泽鉴‘民法总则“,北京大学出版社,2009年版,第192-193页㊂④㊀参见梁慧星‘民法总论(第五版)“,北京:法律出版社,2017年,第64页;崔建远等著‘民法总论(第三版)“,清华大学出版社,2019年,第152页;魏振瀛主编‘民法(第七版)“,北京:北京大学出版社,2017年,第34页;朱庆育‘民法总论(第二版)“,北京大学出版社,2016年,第80页㊂⑤㊀参见薛军‘法律行为 合法性 迷局之破解“,‘法商研究“2008年第2期㊂⑥㊀参见董安生‘民事法律行为“,北京:中国人民大学出版社,2002年,第80,90页㊂一㊁引言在我国民法学界,法律行为的合法性问题聚讼纷纭,甚至被认为是 我国民法中最大的谜团之一 ①㊂这一争议实际上形成了 问题束 ,涉及三个方面的子问题:第一,有效法律行为是否具备合法性本质?这涉及法律行为的效力来源问题㊂第二,法律行为作为法律事实中的 合法行为 是否妥当?这涉及法律行为在法律事实中的归类问题㊂第三, 法律行为 概念的内涵之中是否应含有 合法 这一本质要素?这涉及 法律行为 概念的界定问题㊂笔者已经撰文分析过第一个子问题,本文拟探讨第二个子问题㊂故此,分析法律行为是否应该归入法律事实中的 合法行为 ,有助于全面解决围绕法律行为的合法性产生的理论争议㊂另外,由于我国民法学理上对于法律事实(特别是其中的行为)的类型区分也存在不同观点②,因此探讨法律行为在法律事实中的归类问题,也有助于在学理上合理地界定法律事实中之行为的类型㊂在德国和我国台湾地区的 民法 理论中,一般认为法律行为属于法律事实中之 行为 里的 合法行为 ,③在我国大陆地区,也有不少学者赞成此说④㊂不过,也不乏反对的观点㊂比如,有学者在主张法律行为具有 规范性本质 的同时,认为法律行为不应该属于法律事实,也不能通过 合法性 标准来评价⑤;据此,法律行为当然不属于法律事实中的 合法行为 ㊂另有学者认为法律行为应该属于法律事实中的 表示行为 而非合法行为⑥㊂由此可见,法律行为作为法律事实中之 合法行为是否妥当,在我国民法理论上仍然存在争议,值得进一步辨析㊂笔者认为,将法律事实中的行为分为 合法行为-违法行为 ,并不能全面反映法律事实中之行为的多种样态,将法律行为归类为合法行为也会造成若干逻辑困境,但反对这种分类的代表性学说(即 表示行为-非表示行为 的二分法)也存在明显的不足㊂故此,理论上应该对法律事实中之行为. All Rights Reserved.的分类㊁法律行为的归类提出新的范式,以解决现有的争议㊂本文拟通过以下四个部分展开论述:首先,主要依据法律规范的构成理论来说明法律事实概念的内涵以及法律事实中的行为分为 合法行为 违法行为 的理由;其次,分析 合法行为 违法行为 之二分法以及法律行为被归入 合法行为 的逻辑缺陷;再次,运用 类型 式思维方式,对法律行为在法律事实中的归类问题提出本文的解决思路;最后,分析法律事实中 表示行为 非表示行为 之二分法的不足㊂二、法律事实中之行为的分类依据与法律行为的传统归类(一) 法律事实 概念的界定法律事实 一词译自德文词juristischeThatsache/Tatsache,根据萨维尼的界定,它指向产生或终止某项法律关系的所有事情,这为后世对法律事实的界定提供了认知基础㊂①不过,学理上应该依据什么样的理论范式来分析法律事实,却存在 规范说 与 事实说 的分歧㊂这种分歧对如何理解法律事实中的 合法行为 ㊁法律行为是否应该归入此等 合法行为 等问题的分析产生了影响㊂在我国民法学界,对法律事实的界定有两种理路㊂一种是偏重于从具体事实的方面出发,将法律事实界定为社会生活中为法律所调整的客观现象,这些现象依法能够引起法律关系的变动㊂这种观点可以称之为 事实说 ②㊂一种是侧重从法律规范构成的角度出发,将法律事实理解为法律规范之构成要件(Tatbestand)的同义词,据之,法律事实就是能作为此等构成要件并引起法律效果的事实㊂这种观点可以称之为 规范说 ③㊂从学理上讲, 事实说 有如下缺陷:①法律事实应该是超越具体事实的抽象事实,但该说却认为,实存的具体事实只要受法律调整,就是法律事实㊂②该说认为,法律事实是因法律的适用,足以发生法律关系变动效果的事实㊂这一认识不够全面,因为与法律事实密切相关的除了法律适用,还有立法环节㊂比如,立法会设计出尚未出现的事实样态,‘民法典“第1077条第1款规定的协议离婚冷静期中的 撤回离婚登记申请 即为适例,若法律中不规定该事实样态,则现实中都不会出现撤回离婚登记申请的具体事实㊂可见,立法中法律规范的构成要件绝对不是具体事实,而是立法者为了调整既存现实或引导社会发展而提炼出来的抽象事实㊂③若将法律事实定位为具体事实,则相关法律概念的内涵与意义会受制于生活经验所形成的常识㊂然而,尽管相关法律概念会与日常用语在表述上有重叠,但二者的意义却绝非必然相同④,而民法学的研究对象只能是前者㊂据此,界定法律事实,应该以法律规范为基础,从规范的逻辑构造㊁价值取向等方面展开,而不能从生活常识上展开㊂⑤相较于 事实说 , 规范说 更有道理,后者的观点主要是:①法律规范最常见的逻辑构造是构成要件及法律效果,从构成要件产生法律效果的角度看,构成要件与法律事实的功能是一致的,所以法律事实就相当于法律规范层面上的构成要件⑥㊂②不同法律规范的构成要件不同,在划分构成要件时,最根本的分类标准也就是不同的法律事实㊂通过划分法律事实/构成要件的类别,相应的具体事实应该归属于哪种法律事实㊁应该由哪种法律规范调整,才有了明确的依据㊂③在接受法律调整之前,具体事实的法律意义无法从其日常意义中得到说明,所以只有当具体事实被它纳入相应的构成要件时,其法律意义才得以确定㊂故此,构成要件乃是涵摄具体事实的标准工具,相应地,具体事05东南大学学报(哲学社会科学版)第23卷①②③④⑤⑥Vgl Schmöckel/Rückert/Zimmermann(Hrsg ),Historisch-kritischerKommentarzunBGB,Bd I,Tübingen2003,s 357ff 转引自常鹏翱:‘事实行为的基础理论研究“,北京大学出版社,2016年,第13页,注②㊂参见王伯琦‘民法总则“,1963年,第119页;黄右昌:‘民法总则诠解“,1960年,第214页;转引自黄茂荣:‘法学方法与现代民法(第五版)“,北京:法律出版社,2007年,第238-239页㊂另见魏振瀛主编:‘民法(第五版)“,北京:北京大学出版社,2013年,第33页;王利明主编‘民法(第六版)“,北京:中国人民大学出版社,2015年,第40页㊂参见洪逊欣‘中国民法总则“,1958年,第231-232页,转引自黄茂荣:‘法学方法与现代民法(第五版)“,北京:法律出版社,2007年,第240页㊂另见梅仲协‘民法要义“,北京:中国政法大学出版社1998年,第4页;史尚宽‘民法总论“,北京:中国政法大学出版社,2000年,第297-298页;常鹏翱‘事实行为的基础理论研究“,北京:北京大学出版社,2016年,第14页㊂比如,法律事实中的 (人的)行为 仅指相关法律事实所产生㊁变更或消灭的法律关系之当事人的行为,并不是指日常用语中的 由人(而非其他生物)实施的行为 ㊂故此,罢工㊁战争虽然属于日常用语中的 人的行为 ,但并不属于法律事实中的 (人的)行为 ㊂参见常鹏翱‘事实行为的基础理论研究“,北京:北京大学出版社,2016年,第13-20㊁54页㊂参见田士永‘物权行为理论研究“,北京:中国政法大学出版社,2002年,第115页㊂. All Rights Reserved.实只有通过涵摄而联结于法律规范,才能具有法律意义①㊂综上,只有基于法律规范的构成理论,才能准确把握法律事实的内涵,也才能了解法律事实中的行为分为 合法行为 和 违法行为 的原因㊂(二)法律规范构成理论是 合法行为 违法行为 之二分法的一个依据基于 规范说 ,法律事实中的 (人的)行为 是以行为为要素的法律要件,如 因故意或过失,不法侵害他人权利 ,而非甲砍伤乙这样的具体行为,这意味着,行为的分类实际是对包含不同构成要件的法律规范的归类,民法学由此不再直面具体行为,而是直指抽象规范㊂故此,具体的行为并无不言自明的法律定性,这种定性是相关法律规范基于特定考量赋予具体行为的㊂比如,就无权处分而言,在我国台湾地区 民法 第118条语境下构成法律行为,在该法第184条第1款语境下则构成侵权行为㊂可见,法律规范的构成要件决定了具体行为的定性,后者要受到前者的塑造㊂根据常鹏翱教授的观点, 合法行为 与 违法行为 二者的分类与名称也是根据两类不同法律规范的构成要件来确定的,理由主要是:从逻辑层面上讲,在法律事实应基于法律规范来理解的前提下,合法行为和违法行为在其对应的法律规范的构成要件和法律效果上都有质的不同㊂这又包含两方面的内容:①从构成要件上看,法律事实中的合法行为㊁违法行为对应着两类不同法律规范的构成要件㊂A 违法行为对应着法律责任规范中的构成要件,符合此等要件的(亦即具备违法性要素的)具体行为,如甲偷窃了乙的财产,就构成违法行为;B 合法行为对应着无制裁导向的法律规范中的构成要件,符合此等要件的(亦即不具备违法性要素的)具体行为,就属于合法行为㊂②从法律效果上看,A 民事责任是违法行为的法律效果形态,这是法律施加的制裁㊂B 合法行为的法律效果不含民事责任,而有多样化的内容㊂亦即,在确定上述两类不同法律规范中的构成要件是合法行为或违法行为时,法律效果起到了决定作用:若某类规范使行为人承担制裁性结果,对应的构成要件就是违法行为,迎合该要件的具体行为就是侵权行为㊁违约行为等;反之,若某类规范并不导向责任承担的效果,对应的构成要件就是合法行为,迎合该要件的具体行为就是法律行为㊁准法律行为㊁事实行为②㊂可见,基于 规范说 的理路,法律事实是产生法律效果的抽象规范要件,合法行为和违法行为由此分别指向构造不同的法律规范,它们在规范形式和实质内容上都无法混同㊂故此,法律规范理论是法律事实中的行为分为 合法行为 违法行为 的一个基本依据㊂(三)法律行为归入 合法行为/被许可行为 的其他理论依据首先需要注意,在德国民法理论中,法律行为所隶属的法律事实中的 合法行为 一词有不同表述,其中较为常见的表述是erlaubteHandlungen㊁rechtmäßigeHandlungen㊁erlaubtesVerhalten㊁rechtmäßigesVerhalten③㊂其中的rechtmäßig只有 根据法律的㊁合法的 之义项,erlaubt一词本意则是 被许可的㊁被允许的 ④㊂Handlungen与Verhalten在这里则都指人的举止或行为⑤㊂故此,erlaubteHandlungen和erlaubtesVerhalten本身也含有 被允许㊁被许可的行为 之义㊂结合法律行为制度的通例,特别是关于法律行为的成立和效力规则来看,法律行为之所以归入法律事实中的 合法行为/被许可行为 ,除了法律规范构成理论之外,还有其他理论依据㊂首先,从法律行为的成立来看,意思表示乃法律行为的核心要素,单个表意人的意思表示是单方法律行为的唯一要素,双方或多方主体的意思表示一致是双方或多方法律行为的核心要素,故此,只要存在相应的意思表示,法律行为即已成型,此时无须考察是否存在违法性因素㊂既然法律行为的成立不要求行为具有违法性要素,则法律行为属于法律事实中的合法行为而非违法行为㊂15第5期崔拴林㊀论法律行为在法律事实中的归类①②③④⑤参见常鹏翱‘事实行为的基础理论研究“,北京:北京大学出版社,2016年,第22-27页㊂参见常鹏翱‘事实行为的基础理论研究“,北京:北京大学出版社,2016年,第67-73页㊂相应地,unerlaubteHandlungen㊁unrechtmäßigeHandlungen㊁RechtswidrigesVerhalten等是 违法行为 的常见表述㊂参见朱庆育‘民法总论(第二版)“,北京:北京大学出版社,2016年,第95-97页㊂潘再平主编:‘新德汉词典“,上海:上海译文出版社,2000年,第933㊁350页㊂在法律事实理论上,Handlungen和Verhalten都指涉人的思想和身体上的有无举止或有无活动等状态㊂参见台湾大学法律学院㊁台大法学基金会编译‘德国民法典“,北京:北京大学出版社,2017年,第79-80页;[日]古田裕清‘日本的法律用语与德语 关于 行为 “,崔延花译,‘比较法研究“2004年第1期,第157页㊂. All Rights Reserved.其次,上面提到,erlaubteHandlungen和erlaubtesVerhalten也含有 被允许㊁被许可的行为 的意涵㊂那么,如何理解这一意涵呢?笔者认为,从价值层面上讲,法律行为的制度设计在初衷上是为了给私人提供私法自治的主要手段,所以,法律行为作为私人旨在实现私法自治的工具,当然是法律上被许可㊁被允许 的行为㊂类似地,尽管准法律行为的效果是法定的,但多数情况下,行为人都是为了引起相应的法律效果而有意识地或者故意做出这种行为,同时,准法律行为的本质或者利益格局决定了这种行为也会类推适用意思表示的规定,如行为能力㊁意思瑕疵㊁代理等规定①㊂故此,准法律行为可以作为实现私法自治的辅助工具㊂另外,事实行为在常态下是行为人不违反法律㊁依据自主意识而引起某种事实后果的行为,有目的意思的事实行为也可以为行为人提供自治的契机㊂比如,虽然先占属于事实行为,但其构成要件之一是 先占人须以所有的意思占有无主物 ②,满足法定构成要件的先占人能够获得物的所有权,这完全符合先占人的主观意愿㊂故此,这种规则设计在一定程度上能为行为人创造自治的空间㊂由此可见,准法律行为和事实行为当然也是法律所许可的㊂反之,行为人违反法定义务或约定义务的侵权行为或违约行为必然是法律所不许可的㊂此外,值得注意的是,即使法律行为因当事人不适格(不具备相应行为能力或没有代理权)㊁有意思瑕疵㊁缺乏处分权而导致无效㊁被撤销或效力待定的,换言之,法律行为并非出于违反禁止规范(特别是合法上的)或违背公序良俗的原因,而是由于违反 限制法律行为形成可能性的规范 ③而存在效力瑕疵的,法秩序对此类行为的态度是既非 许可 也非 不许可 ,这也是在私法自治的理念之下,公权力并不会过度干预私人生活的体现(详见下文的分析)㊂如果理论上把法秩序对于不同行为所持的态度仅仅归结为非此即彼的 许可 和 不许可 ,那么,这类法律行为也只能归入 被允许㊁被许可的行为 之列㊂综上,法律行为的成立并不涉及违法性因素的考察,法律行为制度的立法本旨是为了给私人提供私法自治的主要工具,这两个方面也能作为法律行为被归入 合法行为/被许可的行为 的依据㊂三㊁ 合法行为 违法行为 之二分法以及法律行为之传统归类的不足将法律事实中的行为分为 合法行为 与 违法行为 ,进而将法律行为归入 合法行为 ,并不能合理地描述民法上具有不同特质㊁过渡状态或混合形式的诸多行为,因而存在若干缺陷,兹分述之㊂第一, 合法行为 违法行为 之二分法的最大不足是,在 合法行为 所包含的法律行为之中,存在着 因不合法而有效力瑕疵的法律行为 ,故此:该二分法面临一个基本的逻辑困境:为何存在 不合法 因素的几类法律行为却属于 合法行为 ?申言之,由于私法自治秩序的建立亦须遵循相应的强制规范,故此,①从正面来说,法律行为须 合法(遵循相应的强制规范) 才能有效,这是私法自治的题中应有之义,并不意味着公权力对私人自治的不当管制④㊂所以,法律行为效力规则中的 合法行为 即指 因合法而有效的法律行为 ㊂②从反面来说,法律行为因这些原因 行为人欠缺行为能力㊁意思表示瑕疵㊁行为违反私法上的相关强制规范以及违背善良风俗 而存在效力瑕疵时,这种 不合法 也只是从反面阐述了私法自治的理念 不符合私法自治秩序所内含的强制要求,就不能产生意思自治的效果㊂此外,法律行为因违反公法上的强制规范或违背公共秩序而无效的,则不是私法自治的内部逻辑使然,而是缘于国家认定法律行为具备反社会性,故而从外部强行干预法律行为的效力,使法律行为归于无效,这是一种法律上的制裁⑤㊂据此,法律行为效力规则中的 不合法行为 则有两种内涵:一是 因不符合私法自治秩序所需的强制规范而存在效力瑕疵的法律25东南大学学报(哲学社会科学版)第23卷①②③④⑤LudwigEnneccerus/HansCarlNipperdey,AllgemeinerTeildesBürgerlichenRechts;EinLehrbuch,zweiterhalbband.15.Aufl ,J.C.B Mohr(PaulSiebeck)Tiibingen,1960,S.866参见王泽鉴‘民法物权“(第二版),北京:北京大学出版社,2010年,第189页;梁慧星㊁陈华彬‘物权法“(第六版),北京:法律出版社,2016年,第202页㊂德国学说针对强制规范区分 禁止性规定 与 限制法律行为形成可能性的规范 ㊂作为法律行为生效要件的有关法律行为能力㊁意思表示瑕疵及法律行为之法定要式性的规定都属于后一种规范㊂这种规范旨在限定私法主体自治的范围,并调和不同私法主体之间彼此自由的互相冲突㊂参见胡坚明:‘德国法上违反禁止性规定之法律行为的效力“,‘华东政法大学学报“2018年第2期㊂参见崔拴林‘法律行为的合法性问题再探讨 以法律行为之效力来源为问题导向的分析“,‘江海学刊“2020年第5期,第166-170页㊂参见李宇‘民法总则要义:规范释论与判解集注“,北京:法律出版社,2017年,第631页㊂. All Rights Reserved.行为 ,一是 因反公法上的强制规范或违背公共秩序而无效的法律行为 ㊂由此可见, 合法行为 违法行为 之二分法的首要缺陷就是: 合法行为 这个上位概念难以涵盖法律行为制度中的 合法行为 不合法行为 ,也难以体现 不合法的法律行为 所具有的两种内涵㊂相应地,前述 规范说 在论证法律事实中之行为划分为 合法行为 违法行为 的合理性时,认为 合法行为 (包括法律行为)概念所指涉的具体行为不具备违法性要素,就是有失偏颇的㊂实际上,该观点本身也承认法律行为效力规则中必然涉及行为的 违法性 问题,其具体论述是:法律行为如果违背了法定生效要件,就可以说法律行为 有了违法性 ,就会导致其效力瑕疵㊂ 换言之,在有效要件的角度区分法律行为合法或违法,结果指向有效和效力瑕疵之分,这与作为法律事实的合法行为与违法行为的意义大不相同㊂ ①据此,该观点既然认为法律行为效力规则中也存在 合法(行为) 违法(行为) 的两分法,而且这种两分法与法律事实层面上 合法行为 违法行为 的两分法大相径庭,这就相当于为本文的上述观点提供了佐证㊂第二, 合法行为 包括法律行为㊁准法律行为和事实行为,这三类行为都归入 合法行为 ,在逻辑上也存在缺陷㊂法律行为是行为人旨在创立自治规则的行为,准法律行为㊁事实行为(乃至违法行为)都不是这种行为㊂维尔纳㊃弗卢梅就此指出: 所有可以在抽象 法律行为 概念之下予以理解的行为类型的共同之处在于,它们皆旨在通过制定规则来达到形成㊁变更或者消灭法律关系的目的 , 以此为目的制定的规则正是法律行为与那些法律效果基于法律秩序而产生的法定构成要件之间的区别所在㊂ 此谓 法定构成要件 即指其法律效果完全法定而无意定成分的法律事实,如侵权行为,它不属于行为人旨在制定某种规则的行为,所以它不构成 法律行为 ②㊂据此,只有法律行为才涉及 行为作出的规则是否生效 的问题,而其他几类行为都不涉及 是否生效 ,只涉及 是否成立 的问题㊂由此,一方面,法律行为与准法律行为㊁事实行为的共性在学理上用 合法行为 一词表达,另一方面, 法律行为生效的前提条件 也只能使用 合法 一词来表述,这就造成两个不同语境下的 合法 表述雷同但意义脉络不同的结果㊂可见, 合法行为 这个上位概念只能描述法律行为的成立,而不能描述法律行为的 效力状态 这个迥异于其他行为的独特内容,所以,将法律行为㊁准法律行为和事实行为都归入 合法行为 ,并不能凸显法律行为与后二者之间的重要差异㊂第三,在 合法行为 违法行为 的二分法中,有些兼具法律行为和违法行为特质的㊁具有混合形式的行为难以得到合理的界定㊂从实证法上看,法律事实中存在着 包含意思表示的违法行为 ,特别是违反(公法上的)禁止规范或公序良俗的法律行为,主要包括违反民法中之禁止规范(如‘民法典“第1048条禁止直系血亲结婚的规定)㊁违反刑法中针对某些物的禁止规范(如‘刑法“第347条禁止走私㊁贩卖㊁运输毒品的规定)㊁违反公共秩序(如竞争秩序)㊁违反善良风俗(如性道德)的法律行为,比如,直系血亲之间的婚约㊁买卖毒品的协议㊁串通投标的协议③㊁包养协议等㊂这类行为就是法律绝对不许可或者意在禁止当事人实施的行为㊂但在 合法行为/被许可行为-违法行为/不被许可行为 的二分法中, 包含意思表示的违法行为 一方面包含法律许可其行为模式(即意思表示)㊁其成立时无须作违法性判断的 合法行为 ,一方面又属于违反禁止规范的 违法行为 ,这种兼具两种行为之属性㊁属于两种行为之混合形式的法律事实显然难以为该二分法所容纳㊂第四,并非所有不合法的法律行为都是法律必定 不许可/禁止 的行为㊂比如,对于一些因违反私法上的强行规范而存在效力瑕疵的法律行为,法律实际上并无 不许可(要禁止) 相关行为的意图㊂苏永钦教授即指出,我国台湾地区 民法 第709条之2第3项规定, 无行为能力人及限制行为能力人不得为会首,亦不得参加其法定代理人为会首之合会 ,但若有无行为能力人担任会首,只会发生契约是否生效的问题;正如我国台湾地区 民法 第853条规定, 地役权不得由需役地分离而为35第5期崔拴林㊀论法律行为在法律事实中的归类①②③参见常鹏翱‘事实行为的基础理论研究“,北京:北京大学出版社,2016年,第76页㊂参见[德]维尔纳㊃弗卢梅‘法律行为论“,迟颖译,北京:法律出版社,2013年,第28-29页㊂串通投标是危害市场经济中的竞争秩序的行为㊂参见李宇‘民法总则要义:规范释论与判解集注“,北京:法律出版社,2017年,第681页㊂. All Rights Reserved.。
专题三民事法律行为序言:民事法律事实行为框架图序言:民事法律事实行为1. 行为(1)民事法律行为:有、无、效、撤(2)事实行为:违侵无不发、创先添拾现2. 事件(1)自然事件:生死、灾害、时间(2)社会事件:战罢乱一、民事法律行为的基本原理1. 民事法律行为和事实行为的区别(含义、表意、意定/法定、民事行为能力、效力问题)(1)民事法律行为:如合同(2)事实行为:如侵权行为2. 民事法律行为的分类(1)成立所需意思表示数量与合意形成的方式:单(抛遗)、多(双共)、多数决(股董)(2)效果意思:财产(遗)、身份(婚养)(3)行为与原因的关系:有(物)、无(代票)(4)效力:负(债租)、处(物)(5)成立标志:诺(赠与)、实(定贷保借)二、民事法律行为的效力★★ ★1. 有效的民事法律行为:强公主(行为人)意2. 无效的民事法律行为(1)五种情形:强公主意恶(2)法律效果:①自始、当然、确定、永远、绝对无效,任何人任何时候均可主张;②法院或仲裁机构可主动审查,不受时效限制;③财产应返,不能返则补;有错须赔偿,都错各担责。
(3)注意:①部分有效部分无效以及内外有别的情况;②流质条款、无效的格免、>20%的定金合同、>20 年的租赁合同3. 效力待定的民事法律行为(限民、无权)(1)限民所施与其意不相适应的双方民事法律行为(2)无权代理4. 可撤销的民事法律行为:欺、胁、误、公4.1 四种情形(1)欺诈:无中生有(告知虚假)、指鹿为马(隐瞒真实、知假卖假)(2)胁迫:类比刑法中“敲诈”(3)重大误解:对行为的主要内容认识错误,如性质(把有偿当无偿)、对方当事人、标的物(不知假卖假),与“非意思表示”进行辨析,典型案例教授讲座卖书(4)显失公平:一方利用另一方处于困境、缺乏判断4.2 可撤销的民事法律行为的效力(撤销权)(1)主体:欺诈(受欺诈方)、胁迫(受胁迫方)、显失公平(受损害方)、重大误解(双方)(2)性质:形成权(3)方式:或诉或裁(属于形成诉权)(4)限制:①受欺诈——知应知1 年内;②受胁迫——胁迫中止1 年内;③重大误解知应知3 个月;④显失公平受害方知应知1 年内;⑤以上自行为发生之日起5 年内行驶。
经法纵览法律行为与事实行为的异同———从委托合同与无因管理来比较熊杰摘要: 委托合同与无因管理行分作典型的法律行与事行,二者有明的不同。
但是仔探究会,两者都是了私人利益,只是方式路径有所不同。
本文从委托合同与无因管理角度比分析法律行与事行的异同,来分析两种不同的行制度是如何民法的基本原。
关键词:法律行;委托合同;无因管理一、委托合同与无因管理的概念与特征委托合同是当事人商定,由受托一方处理为了委托一方的利益而处理事务的合同。
委托合同作为一种双方法律行为,其成立标准同法律行为的一般成立要件,即包括当事人、标的、意思表示一致三项内容。
而委托合同具有以下特征: 首先,委托事务不但包括法律行为,还包括事实行为; 其次,委托合同的基础是合同双方当事人之间的信赖关系,没有相互信任和了解,委托合同关系难以成立; 第三,委托合同可以是有偿的,也可以是无偿的; 第四,委托合同是诺成及不要式合同; 最后,是委托合同是双务合同。
无因管理,在我国大陆地区,一般认为: “无因管理,是指没有法定的或约定的义务,为避免他人利益受损失,自愿管理他人事务或为他人提供服务的行为。
①目前的通说认为,无因管理是一种事实行为,而非法律行为。
无因管理的成立要件有: 一、无因管理中的事务必须是他人事务。
二、须有为避免他人利益受到损失而管理的意思。
三、须物法律或合同上的义务。
二、委托合同与无因管理的区别( 一) 二者的法律效果不同。
委托合同成立后并不必然有效。
而无因管理行为本身就是一种适法行为,具有阻却违法性。
其一经成立,便在管理人与本人之间发生债权债务关系,属于一种法定之债。
( 二) 二者的构成要件不同。
委托合同最核心的要素是双方当事人一致的意思表示。
而无因管理不需要管理人和本人具有行为能力为必要。
( 三) 委托合同可以有偿也可以无偿,但无因管理一定是无偿的,无因管理人不得请求报酬。
( 四) 二者的价值取向不同。
委托合同直接体现了民法的平等原则和意思自治原则。
上网找律师就到中顾法律网快速专业解决您的法律问题关于法律行为效力的若干问题(1)——关于法律行为的效力李锡鹤华东政法大学教授关键词: 意思表示/法律行为/效力问题/效力内容提要: 1、民法学提出行为效力问题,是为了评价行为人追求与行为后果之间的关系。
民法学需要法律行为概念,是为了界定系争行为是否存在效力问题。
行为的效力问题只存在于可明确判断行为人追求内容的行为。
2、所谓双方行为,应为须特定人以特定行为配合方可实现效果意思之法律行为。
双方行为是单个行为,配合其完成之特定行为是双方行为的条件,不是双方行为的组成部分。
3、法律行为的积极效力包括许可追求实现效果意思和实现效果意思。
前者为许可效力,后者为实现效力。
4、法律行为效力有统一的法理根据:公权利禁止侵害,私权利意思自治。
一法律行为概念(一)行为效力和行为效力问题上网找律师就到中顾法律网快速专业解决您的法律问题法律规定了可支配稀缺资源的归属。
行为是主观见诸客观的过程,是可以实际损害归属于他人的稀缺资源的手段。
任何社会都必须维持一种社会赖以存在的秩序,都必须对行为作出评价。
法律是有强制力的行为规范,是社会对行为的评价标准。
在存在法律的社会,任何行为完成后,都会发生两种意义上的后果:一种是行为完成后的事实状态,即事实后果;一种是法律对该行为——其实就是对该行为的事实后果——的评价,即法律后果。
如:某人去商店购物——事实后果是某人到了商店;法律后果是该行为属某人正当行使人身自由权,受法律保护。
法律对该行为的评价是肯定的。
又如:某人骑车不慎撞伤他人——事实后果是他人被某人撞伤;法律后果是某人与伤者发生了侵权之债。
法律对该行为的评价是否定的。
行为的事实后果可以理解为行为的事实效力。
行为的法律后果可以理解为行为的法律效力。
法律社会中的任何行为均有此类事实效力和法律效力。
在这一意义上,行为是否存在效力不成为问题,法学无须讨论行为有无效力,是否生效。
法学中的所谓行为效力问题,实际上不是对行为后果的评价问题,而是对行为人追求与行为后果之间关系的评价问题。
1.法律行为以意思表示为其必备要素;事实行为完全不以意思表示
为要素,当事人实施行为的目的并不在于追求民事法律后果。
2.法律行为依行为人意思表示的内容而发生效力;事实行为依法律
的规定直接产生法律后果。
3.法律行为的本质在于意思表示,而不在于事实构成;事实行为只
有在行为人的客观行为符合法定构成要件时,才发生法律规定的后果。
4.法律行为以行为人具有民事行为能力为生效要件;而事实行为不
要求行为人具有相应的民事行为能力。
5.法律行为包括民事法律行为、可变更或可撤销的民事行为、无效
民事行为;事实行为包括无因管理行为、正当防卫行为、紧急避险行为和侵权行为等。
事件、事实行为、法律行为区别:
民法法律事实的发生是否具有直接的人的意志性而将民事法律事实分为事件与行为。
事件,是指其本身不直接包含人的意志性的民事法律事实。
行为,是受人的意志支配的活动。
是否和人的意志有关,是事件区别于行为的关键。
注意:事件与人的意志无关,是指事件本身并不直接含有人的意志性,强调把事件本身与引发事件的原因区别开来,如果事件是由人为原因引起的,人的意志性就与事件发生有间接的联系,但事件本身并不直接含有人的意志性,因而它仍然与行为相区分。
例如,甲将乙杀了,甲的杀人行为与乙的死亡事件是可以区分的。
事件包括:自然事件与人为事件。
自然事件,是指与人的意志完全无关,由自然原因发生的事件。
如人的出生和死亡、自然灾害、一定期间的经过、天然孳息的产生。
人为事件是指由人的行为引发的事件。
如战争、罢工、动乱、人为事故、人为原因引起的死亡、人的失踪。
可以看出,事件与行为一对范畴,统一属于民事法律事实。
事件与行为的最根本的区别是法律事实的发生是否直接与人的意志性有关,有直接关系的就是行为,否则就事件。
根据行为人是否进行意思表示,可以将民法上的行为分为表意行为和非表意行为。
表意行为,是指行为人通过意思表示进行的行为。
表意行为包括民事法律行为、可变更可撤销的民事行为、效力待定民事行为、无效民事行为。
非表意行为是指当事人无须意思表示而实施的行为。
主要包括事实行为、违法行为。
事实行为是指行为人主观上并没有产生民事法律关系的意思,而是依照法律的规定引起民事法律关系后果的行为。
例如,拾得遗失物、发现埋藏物、先
占、加工、著作、无因管理、不当得利等。
总之,法律行为与事实行为统属于行为范畴。
最根本的区别在于行为是否包含意思表示,行为以意思表示为要素的,是民事行为,否则,就是事实行为。
(1)法律行为是立法者精心设计的结果,是法技术的创造物,在本质上仍然属于事实行为,只不过是经过了法律的特别包装;事实行为是未经立法者的刻意塑造而直接赋予其法律效果的人的行为,它直接地体现了人的行为的本质
(2)法律行为是以意思表示为核心要素的,即法律行为的成立必须由行为人将自己的主观心理状态表示出来,所以它又被称之为表示行为;事实行为不以意思表示为要素,即无关乎人的主观心理状态,只要在客观上实施了该行为即可,所以又被称之为非表示行为。
(3)由于法律行为是一种表示行为,所以民法专门为其设置了意思表示和行为能力的规定;事实行为是一种非表示行为,因而民法关于意思表示和行为能力的规定不能适用。
(4)法律行为所产生的法律效果是按照行为人意思表示的内容赋予的,也是行为人所预期的;事实行为所产生的法律效果是由民法直接规定的,行为人有无意思表示一律不予考虑,事实行为的效果是立法者预先通过利益衡量的方法直接进行干预的结果,有时可能与当事人的预期正好相反。
换言之,民法对于法律行为的法律效果只能给予抽象的效力评价,至于其具体效果只能依赖于意思表示加以明确;而对于事实行为的法律后果,民法可直接做出明确而具体的规定,使得当事人的权利义务具有先定力和公示力。
(5)法律行为的抽象性与一般性,导致了民法上的法律行为制度的形成,并且具有普遍适用性。
事实行为的具体性与个别性,决定了它不能成为一般制度,只能分散存在民法中的相关部分。