HD44780(KS0066)中文数据手册
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:1.41 MB
- 文档页数:16


(001)基于HD44780液晶芯片的16×2字符型液晶(1602)简介声明:本文内容选自《AVR单片机与CPLD/FPGA综合应用入门》及《smc 1 602A LCM 使用说明书》,自用资料存档,请勿转载!否则因此引起的版权问题本人概不负责!液晶显示器以其微功耗、小体积、使用灵活等诸多优点在袖珍式仪表和低功耗应用系统中得到越来越广泛的应用。
液晶显示器通常可分为两大类,一类是点阵型,另一类是字符型。
点阵型液晶通常面积较大,可以显示图形;而一般的字符型液晶只有两行,面积小,只能显示字符和一些很简单的图形,简单易控制且成本低。
目前市面上的字符型液晶绝大多数是基于HD44780液晶芯片的,所以控制原理是完全相同的,为HD44780写的控制程序可以很方便地应用于市面上大部分的字符型液晶。
字符型LCD通常有14条引脚线(市面上也有很多16条引脚线的LCD,多出来的2条线是电源线VCC(15脚)和地线GND(16脚),其控制原理与14脚的LCD 完全一样),定义如下表所示:字符型LCD的引脚定义┌────┬────┬────┬──────┬────────────┐ㄧ引脚号ㄧ引脚名ㄧ电平ㄧ输入/输出ㄧ作用ㄧ├────┼────┼────┼──────┼────────────┤ㄧ 1 ㄧ Vss ㄧㄧㄧ电源地ㄧ├────┼────┼────┼──────┼────────────┤ㄧ 2 ㄧ Vcc ㄧㄧㄧ电源(+5V)ㄧ├────┼────┼────┼──────┼────────────┤ㄧ 3 ㄧ Vee ㄧㄧㄧ对比调整电压ㄧ├────┼────┼────┼──────┼───────────ㄧ 4 ㄧ RS ㄧ 0/1 ㄧ输入ㄧ 0=输入指令ㄧㄧㄧㄧㄧㄧ 1=输入数据ㄧ├────┼────┼────┼──────┼────────────┤ㄧ 5 ㄧ R/W ㄧ 0/1 ㄧ输入ㄧ 0=向LCD写入指令或数据ㄧㄧㄧㄧㄧㄧ 1=从LCD读取信息ㄧ├────┼────┼────┼──────┼────────────┤ㄧ 6 ㄧ E ㄧ 1,1→0 ㄧ输入ㄧ使能信号,1时读取信息,ㄧㄧㄧㄧㄧㄧ 1→0(下降沿)执行指令ㄧ├────┼────┼────┼──────┼────────────┤ㄧ 7 ㄧ DB0 ㄧ 0/1 ㄧ输入/输出ㄧ数据总线line0(最低位)ㄧ├────┼────┼────┼──────┼────────────┤ㄧ 8 ㄧ DB1 ㄧ 0/1 ㄧ输入/输出ㄧ数据总线line1ㄧ├────┼────┼────┼──────┼────────────┤ㄧ 9 ㄧ DB2 ㄧ 0/1 ㄧ输入/输出ㄧ数据总线line2ㄧ├────┼────┼────┼──────┼────────────┤ㄧ 10 ㄧ DB3 ㄧ 0/1 ㄧ输入/输出ㄧ数据总线line3ㄧ├────┼────┼────┼──────┼────────────┤ㄧ 11 ㄧ DB4 ㄧ 0/1 ㄧ输入/输出ㄧ数据总线line4ㄧ├────┼────┼────┼──────┼───────────ㄧ 12 ㄧ DB5 ㄧ 0/1 ㄧ输入/输出ㄧ数据总线line5ㄧ├────┼────┼────┼──────┼────────────┤ㄧ 13 ㄧ DB6 ㄧ 0/1 ㄧ输入/输出ㄧ数据总线line6ㄧ├────┼────┼────┼──────┼────────────┤ㄧ 14 ㄧ DB7 ㄧ 0/1 ㄧ输入/输出ㄧ数据总线line7(最高位)ㄧ└────┴────┴────┴──────┴────────────┘HD44780内置了192个常用字符,存于字符产生器CGROM(Character Gener ator ROM)中,另外还有几个允许用户自定义的字符产生RAM,称为CGRAM(C haracter Generator RAM)。


PIC单片机与基于HD44780液晶显示模块接口的设计作者:林曙光黄超昔武凌摘要:介绍了基于HD44780液晶显示模块的基本特性及其与PIC单片机的接口,并给出了常用的显示子程序。
关键词:单片机;液晶显示;接口;子程序基于HD44780的字符型液晶显示模块是一种常用的液晶显示器件,主控制驱动电路为HD44780(HITACHI),其他一些公司的电路与之全兼容,如NOVATEK 的NT3881,SAMSUNG公司的KS0066,SUNPLUS公司的SPLC78A01。
由其控制的液晶显示器可以提供若干个5×7或5×10点阵块组成的显示字符群,每个点阵块为一个字符位,字符间距和行距都为一个点的宽度,具有64 B的自定义字符RA M,可自定义8个5×8点阵字符或4个5×11点阵字符。
可以提供8×1~40×4(字符数×行数)各种显示屏规格,广泛应用于智能仪表、通讯、办公自动化及军工等领域。
1液晶显示模块的特点1.1 引脚功能表1是一种基于HD44780的液晶显示模块的引脚功能。
有些显示模块有2个使能端,这种器件可以提供多达4行的显示屏,一个使能端可以控制2行。
当RS和R/W都为低电平时可以写入指令或显示的地址;当RS为高电平、R/W为低电平时,可以写入要显示的数据;当RS为低电平、R/W 为高电平时,可以读出忙信号和地址计数器(CGRAM或DDRAM的值)。
当使能端E由高电平变为低电平时,液晶模块执行写操作(写入命令或要显示的数据、地址);D0~D7为双向数据线。
真值表如表2所示。
1.2 指令集(1)清屏功能:清显示屏,光标回到00H处。
(2)归位功能:光标复位回到00H处。
(3)输入模式设置功能:设置光标和显示模式。
其中:I/D=1时光标向右移,I/D=0时光标向左移;S=1屏幕上的文字可以移动,S=0屏幕上的文字不可以移动。
(4)显示开关控制功能:设置显示、光标及闪烁开、关。


LCD1602数据手册1602采用标准的16脚接口,其中:第1脚:VSS为地电源第2脚:VDD接5V正电源第3脚:V0为液晶显示器对比度调整端,接正电源时对比度最弱,接地电源时对比度最高,对比度过高时会产生“鬼影”,使用时可以通过一个10K的电位器调整对比度第4脚:RS为寄存器选择,高电平时选择数据寄存器、低电平时选择指令寄存器。
第5脚:RW为读写信号线,高电平时进行读操作,低电平时进行写操作。
当RS和RW共同为低电平时可以写入指令或者显示地址,当RS为低电平RW为高电平时可以读忙信号,当RS为高电平RW为低电平时可以写入数据。
第6脚:E端为使能端,当E端由高电平跳变成低电平时,液晶模块执行命令。
第7~14脚:D0~D7为8位双向数据线。
第15~16脚:空脚1602液晶模块内部的字符发生存储器(CGROM)已经存储了160个不同的点阵字符图形,如表1所示,这些字符有:阿拉伯数字、英文字母的大小写、常用的符号、和日文假名等,每一个字符都有一个固定的代码,比如大写的英文字母“A”的代码是01000001B(41H),显示时模块把地址41H中的点阵字符图形显示出来,我们就能看到字母“A”1602液晶模块内部的控制器共有11条控制指令,如表2所示,它的读写操作、屏幕和光标的操作都是通过指令编程来实现的。
(说明:1为高电平、0为低电平)指令1:清显示,指令码01H,光标复位到地址00H位置指令2:光标复位,光标返回到地址00H指令3:光标和显示模式设置 I/D:光标移动方向,高电平右移,低电平左移 S:屏幕上所有文字是否左移或者右移。
高电平表示有效,低电平则无效指令4:显示开关控制。
D:控制整体显示的开与关,高电平表示开显示,低电平表示关显示 C:控制光标的开与关,高电平表示有光标,低电平表示无光标 B:控制光标是否闪烁,高电平闪烁,低电平不闪烁指令5:光标或显示移位 S/C:高电平时移动显示的文字,低电平时移动光标指令6:功能设置命令 DL:高电平时为4位总线,低电平时为8位总线 N:低电平时为单行显示,高电平时双行显示 F: 低电平时显示5x7的点阵字符,高电平时显示5x10的点阵字符指令7:字符发生器RAM地址设置指令8:DDRAM地址设置指令9:读忙信号和光标地址 BF:为忙标志位,高电平表示忙,此时模块不能接收命令或者数据,如果为低电平表示不忙。

hd44780组成和使用方法宝子!今天咱们来唠唠HD44780这个超有趣的东西。
先说说它的组成吧。
HD44780呀,它内部结构就像是一个小小的智能世界。
它有控制器部分,这个就像是大脑,指挥着整个显示的运作呢。
还有显示数据存储器,就像是个小仓库,把要显示的字符或者图形的数据都妥妥地存起来。
再加上字符发生器,这个可厉害啦,能把那些存好的数据变成咱们能看到的字符形状。
那这个HD44780咋使用呢?要是你想让它显示点东西,就像让它给你说句温馨的小话。
你得先把它和你的电路连接好,就像是给它搭好舞台一样。
一般来说,有数据总线要连好,这就像是在它和你的控制设备之间建了个信息高速公路,数据就在这上面跑来跑去的。
然后呢,你得给它发送指令。
这指令就像是你对它下的小命令。
比如说你想让它显示个“你好”,你得先告诉它要在哪个位置显示,是第一行呢还是第二行。
这就好比你告诉一个小助手,把这个东西放在哪个架子上一样。
在发送数据的时候呀,你得按照它的规矩来。
它就像个有点小脾气的小伙伴,数据的格式、顺序都得对。
要是弄错了,它可能就会给你显示个乱码,就像小朋友调皮地做个鬼脸,告诉你“你错啦”。
还有哦,它的电源供应也很重要。
就像人要吃饭一样,它得有合适的电压来维持它的活力。
如果电压不稳,它可能就会表现得怪怪的,就像人饿了没力气干活一样。
你要是想调整显示的样式,比如让字变大一点或者变个颜色(这得看它外接的显示模块有没有这个功能啦),那也得通过发送特定的指令来实现。
这就像是给它打扮一样,你得告诉它今天要穿什么样的衣服,是漂亮的裙子(某种显示样式)还是帅气的裤子(另一种显示样式)。
总的来说呢,HD44780虽然看起来有点复杂,但只要你耐心地去了解它的小脾气,按照它的规则来,就能让它乖乖地为你显示出各种有趣的东西啦。
就像和一个新认识的朋友慢慢磨合,最后成为超棒的搭档一样。
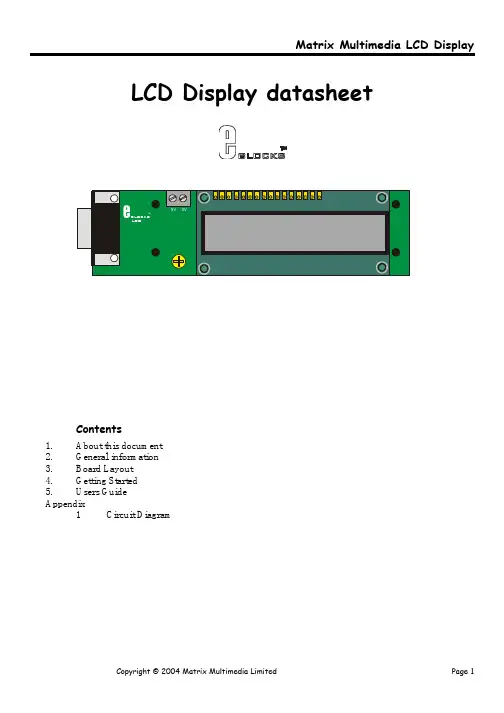
LCD Display datasheetContents1.About this document2.General information3.Board Layout4.Getting Starteders GuideAppendix1Circuit Diagram1 About this documentThis document concerns the Matrix LCD Display code EB-005-00-1.Trademarks and CopyrightPIC, PICmicro are registered trademarks of Arizona Microchip Inc.E-blocks is a trademark of Matrix Multimedia Limited.EB-005-00-1 and associated software and documentation are Copyright ©2004 Matrix Multimedia Limited. Other sources of informationThere are various other documents and sources that you may find useful:Getting started with E-Blocks.pdfThis describes the E-blocks system and how it can be used to develop complete systems for learning electronics and for PICmicro programming.PPP Help fileThis describes the PPP software and its functionality. PPP software is used for transferring hex code to a PICmicro microcontroller.DisclaimerThe information in this document is correct at the time of going to press. Matrix Multimedia reserves the right to change specifications from time to time.Technical supportIf you have any problems operating this product then please refer to the troubleshooting section of this document first. You will find the latest software updates, FAQs and other information on our web site: . If you still have problems please email us at:***************************.uk.Whenemailingpleasestatetheoperatingsystem,theversionofPPPyou are using.2 General informationDescriptionThis is an LCD Display designed for E-blocks. It is a 16 character, 2-line alphanumeric LCD display connected to a single 9-way D-type connector. This allows the device to be connected to most E-Block I/O ports.The LCD display requires data in a serial format, which is detailed in the user guide below. The display also requires a 5V power supply. Please take care not to exceed 5V, as this will cause damage to the device. The 5V is best generated from the E-blocks Multipogrammer or a 5V fixed regulated power supply.The potentiometer RV1 is a contrast control that should be used to adjust the contrast of the display for the environment it is being used in.Features•E-blocks compatible•Low cost•Compatible with most I/O ports in the E-Block range (requires 5 I/O lines via 9 way D-type connector)•Ease to develop programming code using Flowcode icons.3 LCD Board Layout1)9 Way D-type Plug2)16 character, 2-line alphanumeric LCD display3)9 Screw terminal4)Contrast Control4 Getting StartedAs can be seen the circuit diagram (Appendix 1) consists of a simple LCD circuit. To test this board you will need to apply 5V to the LCD Board via the screw terminal and then set the appropriate bits using the 9-Way D-type connector. The details off the LCD configuration are stated in the Chapter 4 Users’ guide. Testing the LED Board – LCD.hexThe following instructions explain the steps to test and use your LCD Board. The instructions assume that PPP is installed and functional. It also assumes that you are confident in sending a program to the PIC via the multiprogrammer.The LCD.hex program will place a counter on to the LCD Board1)Ensure power is supplied to all the necessary boards.2)Insert the LCD board into Port B of the Multiprogrammer3)Ensure that the Multiprogrammer is in correct configuration-Fast mode (SW1 towards the centre of the board)-Ensure that a 19.6608MHz crystal is inserted in the Multiprogrammer boardSW2 is not used when in Xtal mode so it doesn’t matter it’s position4)Program the a PIC16F88 with the test program LCD.hex5)Press the reset button on the Multiprogrammer.6)Adjust contrast accordingly.This should satisfy that the LCD Board is fully functional!4 Users’ guideThe LCD is a 16 character x 2 lines module. Internally it is 40 characters x 2 lines. Line 1 ranges from H’00’ to H’27’ and Line 2 ranges from H’40’ to H’67’.The LCD Module uses a Samsung KS0066U controller, which is similar to the Hitachi HD44780 controller. The PICmicro board uses pins 1 - 6 on the 9-way D-type connector to program the LCD, as shown in the circuit diagram below. When the LCD board is turned on, data can only be sent to it after 30ms, this is the time taken for the LCD to initialize [as it clears all the RAM and sets up the Entry Mode].LCD Block DiagramTo 9-way D-type ConnectorTo send a command to the LCD, data must be sent in two steps, the MSB followed by the LSB [byte is data on pins 1 - 4]. As each byte is sent to the LCD, B5 must be go high then low, for the LCD to acknowledge the byte. After the second byte has been acknowledged the LCD executes the command. The PICmicro board must wait for at least the length of the execution time for that command, before the next command can be sent. A timing diagram of this process is shown below.LSB MSB LSBMSB Pin 6Pins 1- 4LCD BusyTimingDiagramThe first command to be sent to the LCD must be ‘Function Set’ [to setup the LCD], this is usually followed by ‘Display Control’ and then ‘Clear Display’. According to ‘Entry Mode Set’ after each character is sent to the LCD, the position of the cursor changes [by default it is incremented].Bit Name01I/D SH D C B S/C R/L Decrement cursor position Increment cursor positionCursor blink onCursor blink offMove cursor Shift displayShift left Shift rightCursor onCursor offDisplay onDisplay offDisplay shiftNo display shiftDDRAM is Display Data RAM DDRAM address is location of cursor CGRAM is Character Generator RAM X is Don t CareMatrix Multimedia LCD DisplayAppendix 1 – Circuit DiagramCopyright © 2004 Matrix Multimedia Limited Page 7。


ST Sitronix ST7066Dot Matrix LCD Controller/Driver Features!"5 x 8 and 5 x 11 dot matrix possible!"Low power operation support:-- 2.7 to 5.5V!"Wide range of LCD driver power-- 3.0 to 11V!"Correspond to high speed MPU bus interface -- 2 MHz (when V CC = 5V)!"4-bit or 8-bit MPU interface enabled!"80 x 8-bit display RAM (80 characters max.) !"9,920-bit character generator ROM for a total of 240 character fonts-- 208 character fonts (5 x 8 dot)-- 32 character fonts (5 x 11 dot)!"64 x 8-bit character generator RAM-- 8 character fonts (5 x 8 dot)-- 4 character fonts (5 x 11 dot) !"16-common x 40-segment liquid crystal display driver!"Programmable duty cycles-- 1/8 for one line of 5 x 8 dots with cursor-- 1/11 for one line of 5 x 11 dots & cursor-- 1/16 for two lines of 5 x 8 dots & cursor !"Wide range of instruction functions:Display clear, cursor home, display on/off,cursor on/off, display character blink, cursorshift, display shift!"Pin function compatibility with HD44780, KS0066 and SED1278!"Automatic reset circuit that initializes the controller/driver after power on!"Internal oscillator with external resistors !"Low power consumption!"QFP80 and Bare Chip availableDescriptionThe ST7066 dot-matrix liquid crystal display controller and driver LSI displays alphanumeric, Japanese kana characters, and symbols. It can be configured to drive a dot-matrix liquid crystal display under the control of a 4- or 8-bit microprocessor. Since all the functions such as display RAM, character generator, and liquid crystal driver, required for driving a dot-matrix liquid crystal display are internally provided on one chip, a minimal system can be interfaced with this controller/driver.The ST7066 has pin function compatibility with the HD44780, KS0066U and SED1278 that allows the user to easily replace it with an ST7066. The ST7066 character generator ROM is extended to generate 208 5 x 8 dot character fonts and 32 5 x 11 dot character fonts for a total of 240 different character fonts. The low power supply (2.7V to 5.5V) of the ST7066 is suitable for any portable battery-driven product requiring low power dissipation.The ST7066 LCD driver consists of 16 common signal drivers and 40 segment signal drivers which can extend display size by cascading segment driver ST7065 or ST7063. The maximum display size can be either 80 characters in 1-line display or 40 characters in 2-line display. A single ST7066 can display up to one 8-character line or two 8-character lines.Product Name Support Character ST7066-0A English / JapanST7066-0B English / EuropeanCharacter Generator ROM (CGROM)The character generator ROM generates 5 x 8 dot or 5 x 11 dot character patterns from 8-bit character codes. It can generate 208 5 x 8 dot character patterns and 32 5 x 11 dot character patterns. User-defined character patterns are also available by mask-programmed ROM.Character Generator RAM (CGRAM)In the character generator RAM, the user can rewrite character patterns by program. For 5 x 8 dots, eight character patterns can be written, and for 5 x 11 dots, four character patterns can be written.Write into DDRAM the character codes at the addresses shown as the left column of Table 4 to show the character patterns stored in CGRAM.See Table 5 for the relationship between CGRAM addresses and data and display patterns. Areas that are not used for display can be used as general data RAM.Timing Generation CircuitThe timing generation circuit generates timing signals for the operation of internal circuits such as DDRAM, CGROM and CGRAM. RAM read timing for display and internal operation timing by MPU access are generated separately to avoid interfering with each other. Therefore, when writing data to DDRAM, for example, there will be no undesirable interference, such as flickering, in areas other than the display area.LCD Driver CircuitLCD Driver circuit has 16 common and 40 segment signals for LCD driving. Data from CGRAM/CGROM is transferred to 40 bit segment latch serially, and then it is stored to 40 bit shift latch. When each common is selected by 16 bit common register, segment data also output through segment driver from 40 bit segment latch. In case of 1-line display mode, COM1 ~ COM8 have 1/8 duty or COM1 ~ COM11 have 1/11duty , and in 2-line mode, COM1 ~ COM16 have 1/16 duty ratio.Cursor/Blink Control CircuitIt can generate the cursor or blink in the cursor/blink control circuit. The cursor or the blink appears in the digit at the display data RAM address set in the address counter.Table 4 Correspondence between Character Codes and Character Patterns (ROM Code: 0A)Table 4(Cont.) (ROM Code: 0B)!"Read Busy Flag and AddressWhen BF = “High”, indicates that the internal operation is being processed.So during this time the next instruction cannot be accepted.The address Counter (AC) stores DDRAM/CGRAM addresses, transferred from IR.After writing into (reading from) DDRAM/CGRAM, AC is automatically increased (decreased) by 1. !"Write Data to CGRAM or DDRAMWrite binary 8-bit data to DDRAM/CGRAM.The selection of RAM from DDRAM, CGRAM, is set by the previous address set instruction : DDRAM address set, CGRAM address set. RAM set instruction can also determine the AC direction to RAM.After write operation, the address is automatically increased/decreased by 1, according to the entry mode.!"Read Data from CGRAM or DDRAMRead binary 8-bit data from DDRAM/CGRAM.The selection of RAM is set by the previous address set instruction. If address set instruction of RAM is not performed before this instruction, the data that read first is invalid, because the direction of AC is not determined. If you read RAM data several times without RAM address set instruction before read operation, you can get correct RAM data from the second, but the first data would be incorrect, because there is no time margin to transfer RAM data.In case of DDRAM read operation, cursor shift instruction plays the same role as DDRAM address set instruction : it also transfer RAM data to output data register. After read operation address counter is automatically increased/decreased by 1 according to the entry mode. After CGRAM read operation, display shift may not be executed correctly.* In case of RAM write operation, after this AC is increased/decreased by 1 like read operation. In this time, AC indicates the next address position, but you can read only the previous data by read instruction.111D7 D7 D6 D6 D5 D5 D4 D4 D3 D3 D2 D2 Code Code RS RS RW RW DB7 DB7 DB6 DB6 DB5 DB5 DB4 DB4 DB1 DB1 DB2 DB2 DB3 DB3 D1 D1 D0D0DB0DB00 1 BF AC6 AC5 AC4 AC3 AC2 CodeRSRWDB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB1 DB2 DB3 AC1 AC0DB0Reset FunctionInitializing by Internal Reset CircuitAn internal reset circuit automatically initializes the ST7066 when the power is turned on. The following instructions are executed during the initialization. The busy flag (BF) is kept in the busy state until the initialization ends (BF = 1). The busy state lasts for 10 ms after VCC rises to 4.5 V.1. Display clear2. Function set:DL = 1; 8-bit interface dataN = 0; 1-line displayF = 0; 5 ´ 8 dot character font3. Display on/off control:D = 0; Display offC = 0; Cursor offB = 0; Blinking off4. Entry mode set:I/D = 1; Increment by 1S = 0; No shiftNote:If the electrical characteristics conditions listed under the table Power Supply Conditions Using Internal Reset Circuit are not met, the internal reset circuit will not operate normally and will fail to initialize the ST7066. For such a case, initialization must be performed by the MPU asexplain by the following figure.。

LCD选型指南—我选择、我喜欢现在LCD市场上的产品可谓琳琅满目,但如何快速方便地选择一款我们所需的LCD 产品,我想这个问题一定困扰着许多的读者、工程项目设计者。
一块LCD真正可以工作起来,最主要的两个部分就是液晶显示部分以及液晶驱动部分,本文便以这两个部分作为出发点,带领大家一起进去LCD的选型世界。
指导读者如何快速方便地选择自己需要的LCD器件。
首先我们先来认识一下如何选择所需的液晶显示屏。
在这里笔者再啰嗦一下,本文没有探讨深奥的理论,也没有分析复杂的原理以及复杂的物理结构、材料结构,而是就使用者最最关心的如何用的方面来做一些归纳和总结,希望会给读者带来一些帮助。
好了闲话休提,让我们来进入本文的重点。
第一部分如何选择所需的液晶显示屏?第一招:确定显示屏类型液晶显示屏的类型按照显示种类不外乎以下几大类:数显型液晶显示屏、点阵字符型液晶显示屏、图形点阵型液晶显示屏、高档液晶显示屏:如彩色液晶显示屏、接触式液晶显示屏(1)数显型液晶显示屏顾名思义,数显就是主要用来显示数字和一些常用的表示符号,显示部分为段式显示,常见的有八段式数字显示。
如下图1所示。
(2)点阵字符型液晶屏点阵字符型液晶模块主要可以用来显示数字、汉字、中西文字符。
当然模块中通常带有数字、汉字、字符库。
它的显示与数显液晶显示屏比较的类似,只不过显示的过程中把“段”用“点”来代替,当然其显示的功能也更加的齐全。
如下图2所示。
(3)图形点阵型液晶屏图形点阵型液晶模块可以用来实现点阵字符型模块的几乎所有功能,同时其还可以显示任意的图形。
其功能与前面介绍的两种相比已经相当的齐全。
其显示的过程也是由“点”来构成。
只不过点阵字符型液晶模块是由“离散的点”来构成,而图形点阵型液晶模块是由“连续的点”构成。
如下图3所示:(4)高档液晶显示屏彩色以及触摸式液晶显示屏的价格比较的昂贵,一般用于比较复杂的场合和环境下。
如下图4所以。
通过以上的分析我想您对于LCD显示屏的类型一定是十分的清楚了,通过第一步直接的观察,可以直观地选择所需要的器件是属于哪一个大类,然后再根据具体的特性要求再进一步地缩小范围。
HD44780U的使用(C语言)字符型液晶显示模块的接口技术字符型液晶显示模块的外接口信号实际上就是HD44780U与计算机接口部的信号,信号时序为M6800系列时序。
当使用8080时序的A T89C51系列的计算机与其连接时,关键就是注意E信号的使用。
计算机与字符型液晶显示模块的连接方法有两种,一种为直接访问方式,另一种为间接控制方式。
本书将分别详细地介绍这两种方法的接口技术。
1 直接访问方式直接访问方式是计算机把字符型液晶显示模块作为存储器或I/O设备直接挂在计算机的总线上。
在这种方式下,控制信号由AT89C51的读操作信号RD和写操作信号WR与地址信号合成产生。
本文推荐的直接访问方式的实用接口电路如图1所示。
图1 直接访问方式的接口电路上图所示的电路,对于完成液晶显示模块的显示来说,所用的硬件是相对比较少的,但是如果计算机需要进行扩展的话,使用上图的话不是很经济(浪费了太多的地址空间)。
这个时候,可以考虑使用全地址译码或者部分地址译码的方式。
在上图所示的电路中:●8位数据总线与A T89C51的数据总线连接●E信号由WR和RD信号逻辑与非后产生,然后由地址A15选通控制●R/W由地址A14提供●RS信号由地址A13提供这样就确定了AT89C51操作字符型液晶显示模块的唯一地址选择。
图中的电位器为V0提供了可调的驱动电压,用以实现显示对比度的调节。
同时,上图所示的电路不经过任何改变就可以仿真出4位计算机对字符型液晶显示模块的接口,主要是驱动软件的改变。
以下将给出直接访问方式的8位和4位接口的驱动程序。
(1)地址定义#include <reg51.h>#include <intrins.h>#include <stdio.h>#define uchar unsigned char#define uint unsigned int#define nop() _nop_()xdata uchar WC_ADD _at_ 0x8000;xdata uchar RC_ADD _at_ 0xC000;xdata uchar WD_ADD _at_ 0xA000;xdata uchar RD_ADD _at_ 0xE000;(2)读入BF与AC的值8位接口:uchar RdBFAC(void){uchar status;status=RC_ADD&0x80; /*屏蔽低7位*/return status;}4位接口:uchar RdBFAC(void){uchar status,temp;status=RC_ADD;temp=RC_ADD;status=status&0x80; /*屏蔽低7位*/ return status;}(3)写指令代码8位接口:void WRCMD(uchar CMD){uchar temp;do{temp=RdBFAC();}while(temp>=0x80);WC_ADD=CMD;}4位接口:void WRCMD(uchar CMD){uchar temp;do{temp=RdBFAC();}while(temp>=0x80);WC_ADD=CMD;CMD<<=4;WC_ADD=CMD;}(4)写显示数据8位接口:void WRDAT(uchar DAT) {uchar temp;do{temp=RdBFAC();}while(temp>=0x80); WD_ADD=DAT;}4位接口:void WRDAT(uchar DAT) {uchar temp;do{temp=RdBFAC();}while(temp>=0x80); WD_ADD=DAT;DAT<<=4;WD_ADD=DAT;}(5)读显示数据8位接口:uchar RdDAT(void){uchar DAT,temp;do{temp=RdBFAC();}while(temp>=0x80);DAT=RD_ADD;return DAT;}4位接口:uchar RdDAT(void){uchar DAT,DATtemp,temp;do{temp=RdBFAC();}while(temp>=0x80);DAT=RD_ADD;DATtemp=RD_ADD;DAT=DAT|(DATtemp>>=4);return DAT;}2 间接控制方式间接控制方式是计算机把字符型液晶显示模块作为终端与计算机的并行接口连接,计算机通过对该并行接口的操作间接的实现对字符型液晶显示模块的控制。
摘要设计了一款智能浇水系统,以实现花卉的自动浇水。
本次设计的盆花自动浇水系统分为两大模块:空气温湿度的检测与控制和实时时间的显示与定时控制。
其中空气温湿度的检测与控制部分又分为空气温湿度的检测和显示、自动浇水系统。
空气温湿度的检测和显示以温湿度传感器DHT11为感应部件,将检测到的空气温湿度值送入STC89C51单片机,再将其数值输出到LCD液晶显示屏上显示。
并通过单片机程序设定浇水的上下限值与DHT11送入单片机的空气湿度值相比较,当低于下限值时,单片机输出一个信号控制电磁阀打开,开始浇水,高于上限值时由单片机输出一个信号控制电磁阀关闭,停止浇水。
实时时间的显示与定时控制是由单片机从时钟芯片DS1302读入时间与每天的实时时间,通过程序设定的定时浇水的时间与浇水的量进行浇水。
关键词:STC89C51单片机;DHT11温湿度传感器;LCD;DS1302时钟芯Abstract: The design of an intelligent watering system, to realize the automatic watering flower. Potted plant automatic watering system of this design is divided into two modules: the air temperature and humidity detection and control and real-time display and timing control. The detection and control of air temperature and humidity is divided again for detection of air temperature and humidity and display, automatic watering system.Detection of air temperature and humidity and display of temperature and humidity sensor DHT11 as the sensing component, air temperature and humidity will detect the value into the STC89C51 microcontroller, and then display the numerical output to LCD LCD screen. And through the MCU program set the upper and lower limits of water compared to air humidity and DHT11 into the single value, when less than the lower limit, the SCM output a signal to control the electromagnetic valve is opened, the beginning of watering, higher than the limit value by SCM outputs a signal to control the electromagnetic valve is closed, stop watering. The real time display and timing control by the SCM from the real-time clock chip DS1302 read and time of day, time andwatering watering them through the program setting the amount of watering.Keywords: STC89C51; DHT11 temperature and humidity sensor; LCD; DS1302 clock core目录1.绪论 (1)1.1选题的目的与意义 (1)1.2自动浇花器目前的发展现状 (1)1.3设计方案 (1)2.系统的总体设计 (3)2.1 应用场所 (3)2.2 系统预期功能 (3)2.3 系统总体设计方案 (3)2.3.1主题分类 (3)2.3.2.流程图 (3)3.系统的核心器件 (5)3.1 STC89C51单片机 (5)3.1.1 STC89C51的内部结构 (5)3.1.2 STC89C51单片机引脚功能 (6)3.1.3单片机存储器结构 (6)3.2 DHT11数字温湿度传感器 (7)3.2.1 DHT11的性能指标和特性 (8)3.2.2 DHT11的引脚说明 (8)3.3 DS1320时钟芯片 (8)3.3.1 DS1302的性能指标和特性 (8)3.3.2 DS1302的引脚说明 (8)3.3.2 DS1302的控制字节 (9)3.4 LCD1602液晶显示屏 (9)3.4.1 LCD液晶显示器简介 (9)3.4.2 液晶显示的主要技术参数 (9)3.4.3 LCD1602的引脚说明 (10)4.系统的硬件电路设计 (12)4.1空气式温度的采集于显示 (12)4.2 定时器部分 (12)4.3 系统原理图 (12)5.软件部分设计 (14)6.总结 (15)参考文献 (16)致谢........................................................................................................................ 错误!未定义书签。