英语时态8种基本时态讲解
- 格式:doc
- 大小:35.00 KB
- 文档页数:10



下面就英语中常见的八种基本时态进行阐述,其它的时态都是在这八种时态的基础上结合而成的。
一、一般现在时:1.概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。
2.时间状语:always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays,3.基本结构:动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要加(e)S)4.否定形式:am/is/are+not;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。
5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
6.例句:. It seldom snows here.He is always ready to help others.Action speaks louder than words.二、一般过去时:1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。
2.时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc.3.基本结构:be动词;行为动词4.否定形式:was/were+not;在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。
5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。
6.例句:She often came to help us in those days.I didn't know you were so busy.三、现在进行时:1.概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
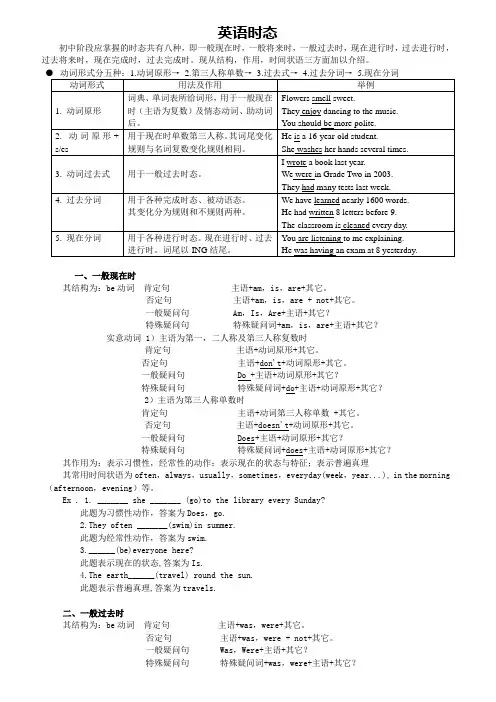
英语时态初中阶段应掌握的时态共有八种,即一般现在时,一般将来时,一般过去时,现在进行时,过去进行时,过去将来时,现在完成时,过去完成时。
现从结构,作用,时间状语三方面加以介绍。
一、一般现在时其结构为:be动词肯定句主语+am,is,are+其它。
否定句主语+am,is,are + not+其它。
一般疑问句 Am,Is,Are+主语+其它?特殊疑问句特殊疑问词+am,is,are+主语+其它?实意动词1)主语为第一,二人称及第三人称复数时肯定句主语+动词原形+其它。
否定句主语+don't+动词原形+其它。
一般疑问句 Do +主语+动词原形+其它?特殊疑问句特殊疑问词+do+主语+动词原形+其它?2)主语为第三人称单数时肯定句主语+动词第三人称单数 +其它。
否定句主语+doesn't+动词原形+其它。
一般疑问句 Does+主语+动词原形+其它?特殊疑问句特殊疑问词+does+主语+动词原形+其它?其作用为:表示习惯性,经常性的动作;表示现在的状态与特征;表示普遍真理其常用时间状语为often,always,usually,sometimes,everyday(week,year...), in the morning (afternoon,evening)等。
Ex . 1. _______ she _______ (go)to the library every Sunday?此题为习惯性动作,答案为Does,go.2.They often _______(swim)in summer.此题为经常性动作,答案为swim.3.______(be)everyone here?此题表示现在的状态,答案为Is.4.The earth______(travel) round the sun.此题表示普遍真理,答案为travels.二、一般过去时其结构为:be动词肯定句主语+was,were+其它。


英语的8种时态一)动词的时态时态是谓语动词所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式.英语动词有16种时态,但是常见的只有九种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时,过去将来时,现在完成进行时。
常用的时态只有八种。
1.一般现在时的用法1)表示经常性、习惯性的动作;表示现在的状态、特征和真理.句中常用often,usually, every day等时间状语。
例如:He goes to school every day.(经常性动作)He is very happy.(现在的状态)The earth moves around the sun.(真理)2)在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,用一般现在时表示将来.例如:If you come this afternoon,we' ll have a meeting.When I graduate,I’ll go to the countryside.3)有时这个时态表示按计划、规定要发生的动作,(句中都带有时间状语)但限于少数动词如begin,come,leave,go,arrive,start,stop,return,open,close等.例如:The meeting begins at seven.The train starts at nine in the morning.4)表示状态和感觉的动词,如be,like,hate,think,remember,find,sound等常用一般现在时.例如:I like English very much.The story sounds very interesting.5)书报的标题,小说等情节介绍常用一般现在时.2.一般过去时的用法l)表示过去某时间发生的事、存在的状态或过去反复发生的动作.He saw Mr Wang yesterday.He worked in a factory in 19862)表示过去经常发生的动作,也可用“used to”和“would +动词原形”。

英语时态8种基本时态
英语时态:8种基本时态
引言:
英语是世界上最广泛使用的语言之一,掌握英语的时态对于正确表达和理解英语句子至关重要。
英语时态可以用来表示动作的发生时间、持续时间和完成程度。
本文将介绍英语中的8种基本时态,分别是一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、将来进行时、现在完成时和过去完成时。
一、一般现在时(Simple Present Tense):
一般现在时是用来描述经常性的、普遍性的事实或习惯动作。
句子中的主语与动词原形保持一致。
例如:“I eat breakfast every morning”(我每天早上吃早餐)。
二、一般过去时(Simple Past Tense):
一般过去时用来描述过去发生的具体事情或经历。
常用的过去式形式是动词的过去式。
例如:“She watched a movie last night”(她昨晚看了一部电影)。
三、一般将来时(Simple Future Tense):
一般将来时用于表示将来发生的动作或事件。
常用的表达方式是使用助动词\。

语中常见的时态有8种--- 一般现在时/一般过去时;现在进行时/过去进行时;一般将来时/过去将来时;现在完成时/过去完成时。
另外还有现在完成进行时/过去完成进行时,将来完成时,将来进行时。
一关于一般现在时(第三人称动词后加” s” 或“es” )(1)表示经常性、习惯性动作。
(2)普遍真理、自然现象,谚语、报刊标题等(3)代替将来时(主从句均为将来时时,代替从句中的将来时)(4)以here ,there 开头的句子中,动词go come 等用现在时代替进行时Here comes the bus. There goes the bell.二关于一般过去时(谓语构成: V +ed, 注意不规则动词的构成)(1)表过去经常性、习惯性动。
(注意比较would do/ used to do )She often came to visit us when she was there.Whenever I went to Beijing, he would come to guide me.(2) 过去某一时刻发生的动作。
三关于现在进行时(am/is/are + ving)(1) 表示此时此刻或现阶段正在进行的动作。
How are getting along with your studies these days?More and more people are giving up smoking.(2) 表将来,用于从句中,可代替将来时。
常用于瞬间动词,如come, go, leave, arrive, die 等,常表示渐进或安排要进行的动作。
If she is doing her homew ork, don’t interrupt her.He is dying.注意:系动词look, feel, taste, smell, sound, prove,等及心理活动的动词want, mean, mind, hope, understand, know, like, dislike ,love, prefer, hate ,doubt等一般不用进行时。

英语八大基本时态和被动语态要点指南英语八大基本时态一、一般现在时定义:经常、反复发生的动作、行为及现在的某种状况。
结构:①am(第一人称单数)/is(第三人称单数)/are(其他人称);②has (第三人称单数)have(其他人称)③行为动词,除了第三人称单数要由动词原形词尾-s /-es /y变为i,-es;其他概用动词原形时间状语:always(“总是,一直”,反义词为never), usually(“通常如此,很少例外”,反义词为unusually), often(“经常、常常,动作重复,但中有间断”,反义词为never),sometimes(“有时、不时,动作偶然,常有间断”), seldom(“很少,不常”), never(“从不,未曾”), forever(永远), every week (day, year, month…)(每周,每天,每年,每月…), once a week(一周一次), on Sundays(在每个星期天),now andthen(时常) from time to time (不时地),in the morning(afternoon, evening…)(在上午,在下午,在晚上…) etc.Tips:(频度副词频率由高到低)always> usually > often > sometimes >Seldom >never 通常说来,always表示100%,usually表示80%,often表示60%,sometimes表示40%,seldom表示20%,never表示0%。
否定式:①am/is/are+ not;②谓语动词若为行为动词,则在动词前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。
(即后边的行为动词用原形)一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首,且用be动词回答;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。

英语八大时态讲解
英语的八大时态包括:一般现在时,一般过去时,现在进行时,过去进行时,一般将来时,过去将来时,现在完成时,过去完成时。
以下是每个时态的详细讲解:
一般现在时:表示经常性或习惯性动作,常与表频度的时间状语连用,如She often speaks English。
也可以表示现在的状态、特征、职业、能力、感觉等,如He seems to feel a bit down today。
此外,它还可以表示真理、客观存在、科学事实或用于格言警句中,如Shanghai lies in the east of China。
一般过去时:表示发生在过去的动作或存在的状态,通常与表示过去的时间状语yesterday,last night,some years ago,in 1990等连用。
现在进行时:表示正在进行的动作或存在的状态,如I am studying now。
过去进行时:表示在过去某个时间点正在进行的动作或存在的状态,如She was studying at 8 o’clock yesterday。
一般将来时:表示将来要发生的动作或存在的状态,如I will go to school tomorrow。
过去将来时:表示在过去某个时间点看来将要发生的动作或存在的状态,如She said she would come to see me the next day。
现在完成时:表示过去发生的动作持续到现在,并可能继续下去,如I have studied English for 5 years。
过去完成时:表示在过去某个时间点之前已经完成的动作或存在的状态,如He said he had finished his homework。

英语最常用的8种时态英语最常用的8种时态:一般现在时、一般现过去时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、—般将来时、过去将来时。
1、一般现在时一般现在时,是一种英语语法形式。
表示通常性、规律性、习惯性、真理性(即事实)的动作或状态,或者动作有时间规律发生的事件的一种时间状态。
在英语语法中,“时“指动作发生的时间,”态“指动作的样子和状态。
2、一般现过去时一般过去将来时表示从过去的某一时间来看将来要发生的动作或呈现的状态。
在英语时态中,“时“指动作发生的时间,”态“指动作的样子和状态。
一般过去将来时的出发点是过去,即从过去某一时刻看以后要发生的动作或状态。
3、现在进行时现在进行时,专业术语,是英语的一种时态,表示现在进行的动作或存在的状态。
在英语时态中,“时“指动作发生的时间,”态“指动作的样子和状态。
现在进行时表示动作发生的时间是“现在”,动作目前的状态是“正在进行中”。
4、过去进行时过去进行时,表示过去在某一时间段或某一段时间内正在发生或进行的动作或状态。
在英语时态中,“时“指动作发生的时间,”态“指动作的样子和状态。
5、现在完成时由“have/has+过去分词”构成,主要有两个含义:表示动作发生在过去,但与现在的情况有联系,有时无时间状语,有时和一些表示不确定的过去时间状语连用,如:many times,just,yet,ever,never,already,before,so far, by now等连用。
6、过去完成时过去完成时:表示过去某一时间或动作以前已经发生或完成了的动作,对过去的某一点造成的某种影响或是结果,用来指在另一个过去行动之前就已经完成了的事件。
在英语时态中,“时“指动作发生的时间,”态“指动作的样子和状态。
它表示动作发生的时间是“过去的过去”,侧重事情的结果。
7、—般将来时一般将来时表示将来某一时段的动作或状态,或将来某一段时间内经常的动作或状态。
在英语时态中,“时“指动作发生的时间,”态“指动作的样子和状态。
初中英语动词时态1、一般现在时主要用于下面几情况:1) 描述当前时间内经常出现、反复发生的动作或存在的状态。
在这种情景中,句子常带有表示频率的时间状语:always , everyday , often , once a week (month , year , etc.) , sometimes , seldom , usually等等,以表示句中的动作或状态是习惯性的、经常性的。
例如:They raise ducks as a sideline .他们以养鸭为副业。
She doesn't often write to her family, only once a month. 她不常给家里写信,仅一月一封而已。
I cycle to work every day .我每天骑自行车上班。
It seldom rains here .这儿很少下雨。
2)仅为了描述状态、性质、特征、能力等等。
这里的目的是为了"描述现阶段的动作或状态",其重点"不是强调动作发生的时间、或进行的状态"。
例如:He can speak five foreign languages .他能说五种外语。
That is a beautiful city .那是座美丽的城市。
Changjiang River is one of the longest rivers in the world. 长江是世界上最长的河流之一。
She majors in music .她主修音乐。
All my family love football .我全家人都喜欢足球。
My sister is always ready to help others . 我妹妹总是乐于助人。
3) 陈述客观事实、客观真理。
顾名思义,客观的情况是"没有时间概念"的;也"不会在意动作进行的状态"。
初中英语语法八种基本时态归纳阶段是学英语的黄金期,学生到底该怎么学英语才最有效呢?下面是小偏整理的初中英语语法八种基本时态归纳,感谢您的每一次阅读。
初中英语语法八种基本时态归纳1.一般现在时概念:表示经常发生的动作或经常存在的状态。
常和always,often,usually,sometimes,everyday等表时间的状语连用。
如:1)Igotoschooleveryday.我每天都去学校。
(表经常)2)Heisalwayslikethat.他总是那样。
(表状态)构成:1)主语+be(am/are/is)+……2)主语+实义动词/三单动词+…2.一般过去时概念:1)表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态.常和表示过去的时间状语连用.如:yesterday,lastweek,in1998,twodaysago等.如:Iwenttoamovieyesterday.我昨天去看了一场电影.2)也可表示过去经常或反复发生的动作.如:Healwayswenttoworkbybikelastweek.构成:1)主语+be(was/were)+……2)主语+实义动词过去式+3.现在进行时概念:表示现在(说话瞬间)正在进行或发生的动作.如:Heissinging.TheyarewatchingTVnow.构成:主语+助动词be(am/are/is)+动词-ing形式构成.4.过去进行时概念:表示过去某一时刻或某一段时间正在进行的动作.这一特定的过去时间除了有上下文暗示外,一般用时间状语来表示.如:1)---Whatwereyoudoing?---Iwasjumping.2)---WhatwastheboydoingwhentheUFOarrived?---Hewassleeping.构成:主语+助动词be(was/were)+动词-ing形式构成.5.一般将来时概念:表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示将来经常或反复发生的动作,常与表示将来的时间状语连用,如:tomorrow,nextweek,nextyear,inthefuture等.如:Hewillgoshoppingtomorrow.Theyaregoingtoplaybasketballnextweek.构成:1)主语+助动词will+动原+…2)主语+begoingto+动原+….6.过去将来时概念:表示在过去将来的某一时间发生的动作或存在的状态.构成:1)主语(第一人称)+助动词should+动原+…2)主语+would+动原+….3)主语+was/weregoingto+动原…用法:过去将来时除了上下文暗示外,一般常用在间接引语中,主句谓语动词为过去时态.如:1)Ishouldgo.2)YouknewIwouldcome.3)TheyweregoingtoNaning.7.现在完成时构成:主语+助动词(have/has)+动词过去分词+…用法例句表示过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果.---Haveyouhadyourlunchyet?---Yes,Ihave.(现在我不饿了)8.过去完成时构成:主语+助动词had+动词过去分词+…用法例句表示过去在过去某一时间或动作之前已经发生或完成了的动作.它表示的动作发生的时间是”过去的过去”.表示过去某一时间可用by,before等构成的短语,也可用when,before,等引导的从句或者通过上下文表示.Ihadfinishedmyhomeworkwhenmymomcamebackhome.怎么学英语进步快阶段是学英语的黄金期,小学生到底该怎么学英语才最有效呢?为了家长和孩子们少走弯路,给大家支一招:学英语,从家庭环境的角度,有两个方法非常有效。
英语的8种时态1. 简单现在时 (Simple Present Tense): 表示经常性或习惯性的动作,或客观事实。
例句: He works in a company.(他在一家公司工作。
)2. 现在进行时 (Present Continuous Tense): 表示现在正在进行的动作。
例句: She is studying for her exams.(她正在为考试而学习。
)3. 现在完成时 (Present Perfect Tense): 表示过去发生的动作对现在产生的影响或结果。
例句: I have finished my homework.(我已经完成了我的作业。
)4. 现在完成进行时 (Present Perfect Continuous Tense): 表示过去一直延续到现在的动作。
例句: They have been playing football for two hours.(他们已经踢了两个小时的足球。
)5. 简单过去时 (Simple Past Tense): 表示过去发生的动作或状态。
例句: She visited her grandparents last weekend.(她上周末去看望了她的祖父母。
)6. 过去进行时 (Past Continuous Tense): 表示过去某个时刻正在进行的动作。
例句: We were watching a movie when the power went out.(当停电时,我们正在看电影。
)7. 过去完成时 (Past Perfect Tense): 表示过去某个时间之前已经发生的动作。
例句: He had already left when I arrived.(我到达时,他已经离开了。
)8. 过去完成进行时 (Past Perfect Continuous Tense): 表示过去一直延续到过去某个时间的动作。
例句: She had been working in that company for 10 years before she retired.(她在退休前已经在那家公司工作了10年。
英语时态8种基本时态结构英语中有8种基本时态结构:简单现在时、进行时、完成时、过去时、过去进行时、过去完成时、将来时和将来完成时。
1. 简单现在时 (Simple Present)简单现在时用来表示经常性、习惯性或普遍真相的动作或状态。
在句子中,主语是第三人称单数,谓语动词要加上“-s”或“-es”。
例如:- He goes to work every day. (他每天上班。
)- Cats like to chase mice. (猫喜欢追逐老鼠。
)- The sun rises in the east. (太阳从东方升起。
)2. 进行时 (Present Continuous)进行时用来表示目前正在进行的动作或状态。
在句子中,谓语动词由“be”动词的不同形式加上动词的现在分词构成。
例如:- She is watching TV now. (她现在正在看电视。
)- We are studying for the exam. (我们正在为考试学习。
)- They are playing soccer in the park. (他们在公园里踢足球。
)3. 完成时 (Present Perfect)完成时用来表示过去已经发生但与现在相关的动作或状态。
在句子中,谓语动词由“have/has”+过去分词构成。
例如:- I have finished my homework. (我已经完成作业。
)- She has lived in London for five years. (她在伦敦住了五年。
)- They have traveled to many countries. (他们去过许多国家。
)4. 过去时 (Simple Past)过去时用来表示过去一些时间发生的动作或状态。
在句子中,谓语动词用动词的过去式形式。
例如:- I visited my grandparents last weekend. (上周末我去看望了我的祖父母。
英语时态8种基本时态讲解一.概念:英语中表示不同时间发生的动作或存在的状态,需用不同的动词形式表示,这种不同的动词形式称为时态。
二.种类:(基本时态)一般现在时一般过去时现在进行时过去进行时一般将来时过去将来时现在完成时过去完成时三.用法:(1)一般现在时表示经常发生或习惯性的动作或状态及客观现实和普遍真理。
一般现在时常以动词原形表示,但当主语是第三人称单数时,动词词尾加-s或-es。
(2)句型结构:主语+V.(包括be动词)+宾语+…She is an engineer.He has breakfast at 6:00every day.(3)注意:1)一般现在时通常与always , often , usually , every day , sometimes , once a week 等时间状语连用。
I always watch TV at 8:00 in the evening .They go home once a week .We usually do our homework at home .2)表客观现实或普遍真理。
The sun always rises in the east .The light travels faster than the sound .3)表永远性的动作或状态。
He lives in the country .(4)否定句和疑问句。
1)-----He is an engineer.-----He isn’t an engineer.-----Is he an engineer?-----Y es, he is ./ No, he isn’t.2)----We get up at 7:30 in the morning .-----We don’t get up at 7:30 in the morning .-----Do you get up at 7:30 in the morning ?-----Yes, we do. / No, we don’t.3)----He likes music.-----He doesn’t like music.-----Does he like music?-----Yes ,he does./ No, he d oesn’t .(1)一般过去时表示发生在过去的动作或存在的状态,通常与表示过去的时间状语yesterday, last night ,some years ago, in 1990,in those days.等连用。
I was a student 6years ago.I went to Beijing last year.They saw a film last night .(2)句型结构:主语+V.过去时+宾语+…例句:昨天他很忙。
去年他抽烟了。
两年前他去参军了。
他在1990年去世了。
(3)否定句和疑问句。
a)----He was busy yesterday.-----He wasn’t busy.-----Was he busy?-----Yes, he was./ No, he wasn’t.b)----He smoked last year.-----He didn’t smoke last year.-----Did he smoke last year?-----Yes ,he did ./No ,he didn’t.c)----He joined the army in 1990.-----He didn’t joined the army in 1990.-----Did he join the army in 1990?-----Yes ,he did ./No ,he didn’t.(4)动词不规则变化:do----did go----went come----came run----ran write----wrote begin----began drink----drank keep----kept leave----left sleep----slept make----made lie----lay dig----dug eat----ate know----knew cut----cut set----set let----let read----read hurt----hurt(1)表示将来发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表将来的时间状语tomorrow, the day after tomorrow, next Sunday, soon, in a few days等连用。
(2)句型结构:主语+will/shall+V.原形+…(第一人称用shall)I shall go to Shanghai tomorrow.They will have a meeting next week.----She will be 20 years old.----Will she be 20 years old?----Yes, she wil l./ No, she won’t .(3)主语+will/shall+V.原形+…be(am, is, are)going toThey will have a meeting next Sunday.(will=are going to )----What will they do next Sunday ?----When will they have a meeting?(4)be about to+V.原形I am about to leave school.不能与表示时间的副词连用。
They are about to set out.(√)They are about to set out soon.(×)复习题:1.He (do) his homework at school every day.2.They (finish) their work yesterday.3.We (visit) their farm next year.4.我半小时后要吃午饭。
5.他将骑自行车去学校。
6.他们下周日将去买汽车。
(1)过去将来时是立足于过去某时,从过去的观点看将要发生的动作或状态。
主要用于宾语从句中。
(2)基本结构:主语+would/should was/were going to +V.原形+…He said that he would have a meeting next week.(He says that he will nave a meeting next week.)They said we should leave school tomorrow.(They say we shall leave school tomorrow.)(1)现在进行时表示现在或现在这段时间正在进行的动作。
通常与now, at present 等时间状语连用。
(2)基本结构:主语+be(am, is, are)+ v-ing +…You are listening to me carefully now.She is writing a letter this year.Look! They are dancing.We are studying English at present .It’s raining hard now.(1)表示过去某一时刻或某阶段时间正在进行的动作,通常与at 6:00 yesterday, at this/ that time yesterday, when 引导的时间状语等连用。
(2)基本结构:主语+be (was/were) +v- ing +…It was raining at 7:00 the day before yesterday.They were building a reservoir at this time last winter.We were reading when the teacher came in.We weren’t reading…Were you reading…What were you doing when the teacher came in.(1)表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或表示过去某时间已经开始一直持续到现在的动作或状态。
通常与下列时间状语连用:up to now, in the past, recently, by… , for 5 years, since 1994, so far, already, yet, ever, just…(2)基本结构:主语+ have/has + P.P(动词过去分词)I’ve finished this work.He has ever been to Australia.I have not heard from her recently.I have already read this book.Have you read…?Yes, I have. No, I haven’t.What have you read?(3)过去分词的不规则变化do did donego went goneeat ate eatencome came comehave had hadwrite wrote writtenbe was/were beensee saw seenhear heard heardswim swam swumdrink drank drunkgive gave givenforget forgot forgotten take took takenkeep kept keptsleep slept sleptteach taught taughtbuy bought boughttell told toldmake made madecut cut cuthurt hurt hurtread read readlet let let(4)注意1)含有终止意义或暂短意义的动词不能与for, since 引导的一般时间状语连用。
(buy, begin, die, come, go , join, leave 等)I have bought a book.I have had a book for 3 years.继续阅读。