英语时态8种基本时态讲解()
- 格式:doc
- 大小:34.00 KB
- 文档页数:8

英语必考八大时态结构及用法详解一、一般现在时1。
概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况.2。
基本结构:①is/am/are;②do/does否定形式:①am/is/are+not;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don’t,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn’t,同时还原行为动词。
3. 一般疑问句:①把is/am/are动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
4. 用法1)经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。
例如:I leave home for school at 7 every morning。
每天早上我七点离开家。
2) 客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。
例如:The earth moves around the sun. 地球绕太阳转动.Shanghai lies in the east ofChina. 上海位于中国东部.3) 表示格言或警句。
例如:Pride goes before a fall。
骄者必败。
注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。
例如:Columbus proved that the earth is round。
哥伦布证实了地球是圆的。
4) 现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性.例如:I don't want so much。
我不要那么多。
Ann writes good English but does not speak well。
安英语写得不错,讲的可不行.5)一般现在时表示将来含义a。
下列动词come, go,arrive,leave,start,begin, return的一般现在时可以表示将来,主要用来表示在时间上已确定或安排好的事情。
例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning。
火车明天上午六点开。


英语时态8种基本时态讲解()English Tenses: An n of the 8 Basic TensesI。
n:In English。
different verb forms are used to express ns or states that occur at different times。
These different verb forms are called tenses.II。
Types: (Basic Tenses)1.Simple Present Tense2.Simple Past Tense3.Present Continuous Tense4.Past Continuous Tense5.Simple Future Tense6.Future Continuous Tense7.Present Perfect Tense8.Past Perfect TenseIII。
Usage:1.Simple Present Tense:1) The Simple Present Tense is used to express habitual or repeated ns or states。
as well as objective reality and universal truths。
The Simple Present Tense is often expressed in the base form of the verb。
but when the subject is third-person singular。
the verb ending is -s or -es.2) Sentence structure: Subject + V。
(including the be verb) + Object +。
Examples:She is an engineer.He has breakfast at 6:00 every day.3) Notes:1) The Simple Present Tense is often used with time ns such as always。

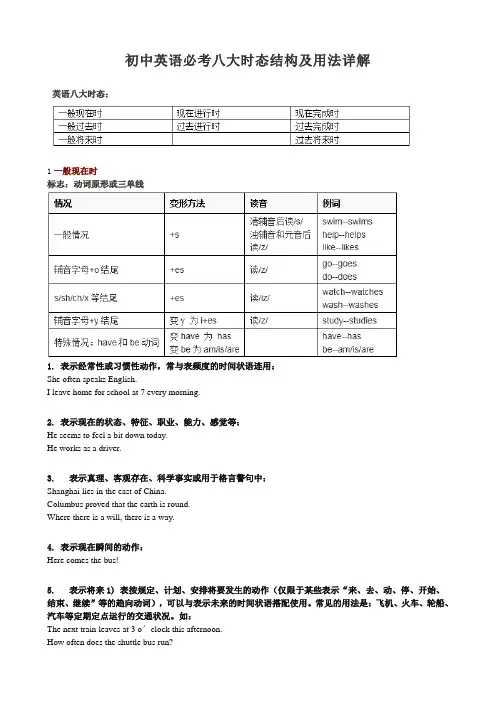
初中英语必考八大时态结构及用法详解英语八大时态:1一般现在时标志:动词原形或三单线1. 表示经常性或习惯性动作,常与表频度的时间状语连用:She often speaks English.I leave home for school at 7 every morning.2. 表示现在的状态、特征、职业、能力、感觉等:He seems to feel a bit down today.He works as a driver.3. 表示真理、客观存在、科学事实或用于格言警句中:Shanghai lies in the east of China.Columbus proved that the earth is round.Where there is a will, there is a way.4. 表示现在瞬间的动作:Here comes the bus!5. 表示将来1) 表按规定、计划、安排将要发生的动作(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的趋向动词),可以与表示未来的时间状语搭配使用。
常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通状况。
如:The next train leaves at 3 o’clock this afternoon.2) 在时间和条件状语从句中常使用一般现在时表示将来发生的事情:When Bill comes (不用will come), ask him to wait for me.I shall go there tomorrow unless I’m too busy.2一般过去时标志:动词过去式*闭音节:元音字母a, e, i, o, u如果发字母本来的音则称为开音节,否则称为闭音节。
1. 表示过去某时所发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示过去的时间状语连用(e.g. yesterday, this morning, just now, a moment ago, in May, last night / year / week, once upon a time, the other day, before …, when …, in the past等)。

初中英语时态8种基本时态讲解初中英语中,常见的有8种基本时态,分别是:一般现在时、现在进行时、现在完成时、一般过去时、过去进行时、过去完成时、一般将来时和过去将来时。
以下是这8种基本时态的详细讲解:1. 一般现在时:表示经常发生的动作或存在的状态。
结构为“动词原形/动词的第三人称单数形式”。
例如:“I have a cat.”2. 现在进行时:表示正在进行的动作。
结构为“be动词+动词的现在分词”。
例如:“She is reading a book.”3. 现在完成时:表示过去的动作对现在造成的影响或完成的动作。
结构为“have/has+动词的过去分词”。
例如:“I have finished my homework.”4. 一般过去时:表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态。
动词形式为“动词的过去式”。
例如:“She was at the park yesterday.”5. 过去进行时:表示在过去某一时刻正在进行的动作。
结构为“was/were+动词的现在分词”。
例如:“They were having dinner at 6 o’clock.”6. 过去完成时:表示过去的过去,即某个过去的动作之前已经完成的动作。
结构为“had+动词的过去分词”。
例如:“By the end of last year, they had built 500 houses.”7. 一般将来时:表示将来要发生的动作或存在的状态。
结构为“will+动词原形”或“am/is/are going to+动词原形”。
例如:“We will visit the museum next week.”8. 过去将来时:表示从过去的某一时刻看,将来要发生的动作或存在的状态。
结构为“would+动词原形”或“was/were going to+动词原形”。
例如:“He said he would come back soon.”以上就是初中英语8种基本时态的讲解,希望对你有帮助!。

初中英语必考八大时态结构及用法详解一.一般现在时1. 概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。
2. 基本结构:①is/am/are;②do/does否定形式:①am/is/are+not; ②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。
3. 一般疑问句:①把is/am/are 动词放于句首;②用助动词do 提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
4. 用法1)经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。
例如:I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 每天早上我七点离开家。
2)客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。
例如:The earth moves around the sun. 地球绕太阳转动。
Shanghai lies in the east ofChina. 上海位于中国东部。
3)表示格言或警句。
例如:Pride goes before a fall 骄者必败。
注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。
例如:Columbus proved that the earth is round. 哥伦布证实了地球是圆的。
4)现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。
例如:I don't want so much. 我不要那么多。
Ann writes good English but does not speak well.安英语写得不错,讲的可不行。
5)一般现在时表示将来含义。
a. 下列动词come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return 的一般现在时可以表示将来,主要用来表示在时间上已确定或安排好的事情。
例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. 火车明天上午六点开。



现在完成时态现在完成时由“have/has + 过去分词”构成1.现在完成时的肯定式、否定式和疑问式以及简略回答:肯定式:I / We / You / They have cleaned the room .He / She has cleaned the room .否定式:I / We / You / They have not / havn’t cleaned the room .He / She has not / hasn’t cleaned the room .疑问式:Have I / we / you / they cleaned the room ?Has he / she cleaned the room ?简略回答:肯定Yes, I / we / you / they have . 否定No, I / we / you / they have not / havn’t .肯定Yes, he / she has . 否定No, he / she has not / hasn’t .1.现在完成时表示过去发生或已经完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果。
这种用法有时不带时间状语,有时同just, already, yet, recently, never, ever, before 等表示不确定时间的副词连用。
I’ve just sent a fax to them. 我刚刚给他们发了一份传真。
The film hasn’t started yet. 电影还没有开始。
---Have you typed my letter already ?---Yes, I have. 你已经把我的信打好了吗?已经打好了。
We’ve bought a new house. 我们已经买了座新房子。
注意:在有表示过去的时间状语(last…, yesterday, …ago, when等)时,不能用现在完成时。

英语八大基本时态和被动语态要点指南英语八大基本时态一、一般现在时定义:经常、反复发生的动作、行为及现在的某种状况。
结构:①am(第一人称单数)/is(第三人称单数)/are(其他人称);②has (第三人称单数)have(其他人称)③行为动词,除了第三人称单数要由动词原形词尾-s /-es /y变为i,-es;其他概用动词原形时间状语:always(“总是,一直”,反义词为never), usually(“通常如此,很少例外”,反义词为unusually), often(“经常、常常,动作重复,但中有间断”,反义词为never),sometimes(“有时、不时,动作偶然,常有间断”), seldom(“很少,不常”), never(“从不,未曾”), forever(永远), every week (day, year, month…)(每周,每天,每年,每月…), once a week(一周一次), on Sundays(在每个星期天),now andthen(时常) from time to time (不时地),in the morning(afternoon, evening…)(在上午,在下午,在晚上…) etc.Tips:(频度副词频率由高到低)always> usually > often > sometimes >Seldom >never 通常说来,always表示100%,usually表示80%,often表示60%,sometimes表示40%,seldom表示20%,never表示0%。
否定式:①am/is/are+ not;②谓语动词若为行为动词,则在动词前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。
(即后边的行为动词用原形)一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首,且用be动词回答;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
初中英语八大时态讲解英语中,时态是英语语法中重要的组成部分,它表示的是在某个时间段内动作的状态。
初中英语中,时态主要包括八大时态,分别是:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、过去将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时和过去完成时。
一、一般现在时一般现在时表示的是经常性或习惯性的动作或状态,也可以表示现在的状态或特征。
例如,“I eat breakfast every morning.”这句话中,“eat”这个动作就是经常性的动作,所以使用一般现在时。
二、一般过去时一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的事情或存在的状态。
例如,“I went to the park yesterday.”这句话中,“went”这个动作发生在过去,所以使用一般过去时。
三、一般将来时一般将来时表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态。
例如,“I will go to the park tomorrow.”这句话中,“go”这个动作将在明天发生,所以使用一般将来时。
四、过去将来时过去将来时表示从过去某个时间看,将要发生的动作或存在的状态。
例如,“He said he would go to the park.”这句话中,“he”认为“he would go to the park”是未来要发生的事情,所以使用过去将来时。
五、现在进行时现在进行时表示正在进行的动作或存在的状态。
例如,“I am eating an apple.”这句话中,“eating”这个动作正在进行,所以使用现在进行时。
六、过去进行时过去进行时表示过去某个时间正在进行的动作或存在的状态。
例如,“She said she was watching TV at 8 o’clock last night.”这句话中,“watching TV”这个动作在昨晚8点正在进行,所以使用过去进行时。
七、现在完成时现在完成时表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,也可以表示持续到现在的动作或状态。
英语八大时态讲解
英语的八大时态包括:一般现在时,一般过去时,现在进行时,过去进行时,一般将来时,过去将来时,现在完成时,过去完成时。
以下是每个时态的详细讲解:
一般现在时:表示经常性或习惯性动作,常与表频度的时间状语连用,如She often speaks English。
也可以表示现在的状态、特征、职业、能力、感觉等,如He seems to feel a bit down today。
此外,它还可以表示真理、客观存在、科学事实或用于格言警句中,如Shanghai lies in the east of China。
一般过去时:表示发生在过去的动作或存在的状态,通常与表示过去的时间状语yesterday,last night,some years ago,in 1990等连用。
现在进行时:表示正在进行的动作或存在的状态,如I am studying now。
过去进行时:表示在过去某个时间点正在进行的动作或存在的状态,如She was studying at 8 o’clock yesterday。
一般将来时:表示将来要发生的动作或存在的状态,如I will go to school tomorrow。
过去将来时:表示在过去某个时间点看来将要发生的动作或存在的状态,如She said she would come to see me the next day。
现在完成时:表示过去发生的动作持续到现在,并可能继续下去,如I have studied English for 5 years。
过去完成时:表示在过去某个时间点之前已经完成的动作或存在的状态,如He said he had finished his homework。
英语时态8种基础时态道解之阳早格格创做一.观念:英语中表示分歧时间爆收的动做或者存留的状态,需用分歧的动词汇形式表示,那种分歧的动词汇形式称为时态.二.种类:(基础时态)普遍当前时普遍往日时当前举止时往日举止时普遍将去时往日将去时当前完毕时往日完毕时三.用法:1)普遍当前时表示常常爆收或者习惯性的动做或者状态及客瞅现真战一致真理.普遍当前常常以动词汇本形表示,但是当主语是第三人称单数时,动词汇词汇尾加-s或者-es.2)句型结构:主语+V.(包罗be动词汇)+宾语+…She is an engineer.He has breakfast at 6:00every day.3)注意:a)普遍当前常常常取always , often , usually , every day , sometimes ,once a week 等时间状语连用.I always watch TV at 8:00 in the evening.They go home once a week.We usually do our homework at home.b)表客瞅现真或者一致真理.The sun always rises in the east.The light travels faster than the sound.c)表永近性的动做或者状态.He lives in the country.4)第三人称单数变更形式.a)普遍情况动词汇正在词汇尾加-s .come---comes speak---speaks work---works live---lives b)以o, s, x, ch, sh末端的单词汇正在词汇后加-es.do---does go---goes finish---finishes brush---brushes fix---fixes pass---passes watch---watchesc)以“辅音字母+y”末端的单词汇变y为i加-es.Study---studies carry-carries cry---criesd)以“元音字母+y”末端的单词汇曲交加-s.play---plays stay---stays例句:咱们每天早上九面制做业.尔正在早上七面半起床.他每天七面去上班.咱们常常下午挨篮球.他喜欢音乐.天球盘绕太阳转.火车六面出收.5)可定句战疑问句.a)-----He is an engineer.-----He isn’t an engineer.-----Is he an engineer?-----Yes, he is ./ No, he isn’t.b)----We get up at 7:30 in the morning .-----We don’t get up at 7:30 in the morning .-----Do you get up at 7:30 in the morning ?-----Yes, we do. / No, we don’t.c)----He likes music.-----He doesn’t like music.-----Does he like music?-----Yes ,he does./ No, he doesn’t .1)普遍往日时表示爆收正在往日的动做或者存留的状态,常常取表示往日的时间状语yesterday, last night ,some years ago, in 1990,in those days.等连用.I was a student 6years ago.I went to Beijing last year.They saw a film last night .2)句型结构:主语+V.往日时+宾语+…例句:今天他很闲.去年他抽烟了.二年前他去从军了.他正在1990年去世了.3)可定句战疑问句.a)----He was busy yesterday.-----He wasn’t busy.-----Was he busy?-----Yes, he was./ No, he wasn’t.b)----He smoked last year.-----He didn’t smoke last year.-----Did he smoke last year?-----Yes ,he did ./No ,he didn’t.c)----He joined the army in 1990.-----He didn’t joined the army in 1990.-----Did he join the army in 1990?-----Yes ,he did ./No ,he didn’t.4)动词汇往日式变更准则.a)普遍情况下的词汇加-ed.work---worked call----called laugh----laughedExplain----explained finish----finished knock----knockedb)以没有收音的字母e末端的单词汇曲交加-d .live----lived change----changed smoke----smoked die----died graduate----graduated drive----drovec)以“辅音字母+y”末端的单词汇,变y为i加-ed.study----studied carry----carried cry----criedtry----tried marry----marriedd)以“元音字母+y”末端的单词汇曲交加-ed.play----played stay----stayede)以“一个元音字母+一个辅音字母”末端的单词汇应先单写那个辅音字母而后再加-ed.stop----stopped plan----planned pat----pattedf)动词汇没有准则变更:do----did go----went come----came run----ran write----wrotebegin----began drink----drank keep----kept leave----left sleep----sleptmake----made lie----lay dig----dug eat----ate know----knew cut----cut set----set let----let read----read hurt----hurt例句:尔前天拿走了那本书籍.去年尔购了一辆自止车.每天早上尔听音乐.她常常待正在家里.二天前尔完毕了那项处事.复习:1) I (be) a teacher 2 years ago.2) He (be) a student now.3) He (do) his homework at home every day.4) They (join) the Party in 1998.5) We (not eat) apples yesterday.6) We (not play) basketball every day.7) He (not go ) home once a week.8) I am 16 years old. (划线部分提问)9) I go to work at 8:00 every morning. (划线部分提问)10) They joined the Party in 1990. (划线部分提问)11) I went to Beijing last year. (划线部分提问)1)表示将去爆收的动做或者存留的状态,常取表将去的时间状语tomorrow, the day after tomorrow, next Sunday, soon, in a few days等连用.2)句型结构:主语+will/shall+V.本形+…(第一人称用shall)I shall go to Shanghai tomorrow.They will have a meeting next week.----She will be 20 years old.----Will she be 20 years old?----Yes, she will./ No, she won’t .3)主语+will/shall+V.本形+…be(am, is, are)going toThey will have a meeting next Sunday.(will=are going to )----What will they do next Sunday ?----When will they have a meeting?I am about to leave school.没有克没有及取表示时间的副词汇连用.They are about to set out.(√)They are about to set out soon.(×)复习题:1.He (do) his homework at school every day.2.They (finish) their work yesterday.3.We (visit) their farm next year.4.尔半小时后要吃午饭.5.他将骑自止车去书籍院.6.他们下周日将去购汽车.1)往日将去时是坐脚于往日某时,从往日的瞅面瞅将要爆收的动做或者状态.主要用于宾语从句中.2)基础结构:主语+would/should was/were going to +V.本形+…He said that he would have a meeting next week.(He says that he will nave a meeting next week.)They said we should leave school tomorrow.(They say we shall leave school tomorrow.)1)当前举止时表示当前或者当前那段时间正正在举止的动做.常常取now, at present 等时间状语连用.2)基础结构:主语+be(am, is, are)+ v-ing +…You are listening to me carefully now.She is writing a letter this year.Look! They are dancing.We are studying English at present .It’s raining hard now.3)动词汇当前分词汇的形成①普遍动词汇曲交正在词汇后加-ingdo – doing read - readingwork – working think – thinkingstudy – studying go – goingwatch – watching jump - jumping②以没有收音的字母e 末端的动词汇,应先去掉 e 而后加– inglike – liking take – takingleave – leaving live – livingreceive – receiving dance – dancingcome – coming smoke – smokingwrite - writing③以“一个元音字母+ 一个辅音字母”末端的动词汇,应先单写那个辅音字母而后再加-ingstop – stopping begin – beginningdig – digging swim – swimmingrun – running sit – sitting(注意:listen – listening open – opening eat – eatingrain – raining sleep - sleeping)1)表示往日某一时刻或者某阶段时间正正在举止的动做,常常取at 6:00 yesterday, at this/ that time yesterday, when 带领的时间状语等连用.2)基础结构主语+be (was/were) +v- ing +…1.It was raining at 7:00 the day before yesterday.2.They were building a reservoir at this time last winter.3.We were reading when the teacher came in.We weren’t reading…Were you reading…What were you doing when the teacher came in.3)例句 1. 前天那个时间Tom 正正在瞅影戏.2. 上周日四面咱们正正在游泳.3.师瞅睹咱们时咱们正正在玩扑克.4.I ____ (do) my homework yesterday.5.He ____ (do) his homework at 5:00 yesterday.6.He ____ (do) his homework now.1)1. 表示往日爆收的动做对于当前制成的做用2.表示往日某时间已经启初向去持绝到当前的动做或者状态常常取下列时间状语连用up to now, in the past, recently, by… , for 5 years, since 1994, so far, already, yet, ever, just…2)基础结构主语+ have/has + P.P(动词汇往日分词汇)1.I’ve finished this work.2.He has ever been to Australia.3.I have not heard from her recently.4. I have already read this book.Have you read…?Yes, I have. No, I haven’t.What have you read?3)往日分词汇的形成(准则变更共往日式的形成)没有准则变更如下do did donego went goneeat ate eatencome came comehave had hadwrite wrote writtenbe was/were beensee saw seenhear heard heardswim swam swumdrink drank drunkgive gave givenforget forgot forgottentake took takenkeep kept keptsleep slept sleptteach taught taughtbuy bought boughttell told toldmake made madecut cut cuthurt hurt hurtread read readlet let let4)注意1.含有终止意思或者久短意思的动词汇没有克没有及取 for, since带领的普遍时间状语连用.(buy, begin, die, come, go , join, leave 等)A)I have bought a book.I have bought a book for 3 day. (wrong)I have had a book for 3 years.B)He have joined the army for 3 years. (wrong)He has been in the army for 3 years.He joined the army 3 years ago.C)He has been dead for 3 years.He died 2 years ago.It is 2 years since he died.He has died for 2 years. (wrong)D)He has gone to Australia.He has been to Australia.2.当前完毕时取普遍往日时的辨别(时间状语的辨别)I ___ (hear) form her recently / yesterday.3.例句:他已经阅读了那本书籍.咱们到久时为止已教习了二千个单词汇.他们居住正在华夏三年了.他瞅那部影戏二次了.Bob 自从 1997 年正在那所书籍院教教.1)表示动做爆收正在往日某一时间之前已经完毕的动做或者状态,强调“往日的往日”,常取by the time, by the end of…,before , by 等带领时间的状语连用.2)基础结构主语+ had + 动词汇往日分词汇 + …When I got to the cinema yesterday the film had begun already.今天当尔到达影戏院时影戏已经启初了.He had learned English before he came here.他去那女之前已经教会英语了.He had aught this class for 3 years by the time I left the school.当尔离启那个书籍院为止他已教那个班级三年了.By the end of last term I had learned 2000 English words.到那教期终尔已教会了2000 个英语单词汇.时态部分总复习题I. Fill in the blanks.1.We usually ___ (get ) up at 7:00 every morning.2.She ___ (watch) TV when she heard a loud knock at the door this timeyesterday.3.My mother ___ (come) here tomorrow.4.Look ! Some one ___ (dance) there.5.Wei Hua’s brother ___ (join) the army in 1995.6.He ___ (write) a letter this afternoon.7.Rice ___ (grow) in the south of China.8.She said ___ (go) to Japan next year.9.We ___ (study) 2,000 words since we came to the school.10. By the end of last term he ___ (teach) that class for 2 years.II. Translation(1)尔每天早上7 面常常挨篮球.(2)今天尔去游泳了.(3)今天他道他们将于后天去瞅赏少乡.(4)咱们将正在下教期教习俄语.(5)他当前正正在玩游戏.(6)去年冬天那个时间他们正正在盖房子.(7)尔居住正在山东20 年了.(8)到上月终为止他处事十年了.。
英语时态8种基本时态讲解一.概念:英语中表示不同时间发生的动作或存在的状态,需用不同的动词形式表示,这种不同的动词形式称为时态。
二.种类:(基本时态)一般现在时一般过去时现在进行时过去进行时一般将来时过去将来时现在完成时过去完成时三.用法:(1)一般现在时表示经常发生或习惯性的动作或状态及客观现实和普遍真理。
一般现在时常以动词原形表示,但当主语是第三人称单数时,动词词尾加-s或-es。
(2)句型结构:主语+V.(包括be动词)+宾语+…She is an engineer.He has breakfast at 6:00every day.(3)注意:1)一般现在时通常与always , often , usually , every day , sometimes , once a week 等时间状语连用。
I always watch TV at 8:00 in the evening .They go home once a week .We usually do our homework at home .2)表客观现实或普遍真理。
The sun always rises in the east .The light travels faster than the sound .3)表永远性的动作或状态。
He lives in the country .(4)否定句和疑问句。
1)-----He is an engineer.-----He isn’t an engineer.-----Is he an engineer?-----Yes, he is ./ No, he isn’t.2)----We get up at 7:30 in the morning .-----We don’t get up at 7:30 in the morning .-----Do you get up at 7:30 in the morning ?-----Yes, we do. / No, we don’t.3)----He likes music.-----He doesn’t like music.-----Does he like music?-----Yes ,he does./ No, he d oesn’t .(1)一般过去时表示发生在过去的动作或存在的状态,通常与表示过去的时间状语yesterday, last night ,some years ago, in 1990,in those days.等连用。
I was a student 6years ago.I went to Beijing last year.They saw a film last night .(2)句型结构:主语+V.过去时+宾语+…例句:昨天他很忙。
去年他抽烟了。
两年前他去参军了。
他在1990年去世了。
(3)否定句和疑问句。
a)----He was busy yesterday.-----He wasn’t busy.-----Was he busy?-----Yes, he was./ No, he wasn’t.b)----He smoked last year.-----He didn’t smoke last year.-----Did he smoke last year?-----Yes ,he did ./No ,he didn’t.c)----He joined the army in 1990.-----He didn’t joined the army in 1990.-----Did he join the army in 1990?-----Yes ,he did ./No ,he didn’t.(4)动词不规则变化:do----did go----went come----came run----ran write----wrote begin----began drink----drank keep----kept leave----left sleep----sleptmake----made lie----lay dig----dug eat----ate know----knewcut----cut set----set let----let read----read hurt----hurt(1)表示将来发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表将来的时间状语tomorrow, the day after tomorrow, next Sunday, soon, in a few days等连用。
(2)句型结构:主语+will/shall+V.原形+…(第一人称用shall)I shall go to Shanghai tomorrow.They will have a meeting next week.----She will be 20 years old.----Will she be 20 years old?----Yes, she wil l./ No, she won’t .(3)主语+will/shall+V.原形+…be(am, is, are)going toThey will have a meeting next Sunday.(will=are going to )----What will they do next Sunday ?----When will they have a meeting?(4)be about to+V.原形I am about to leave school.不能与表示时间的副词连用。
They are about to set out.(√)They are about to set out soon.(×)复习题:1.He (do) his homework at school every day.2.They (finish) their work yesterday.3.We (visit) their farm next year.4.我半小时后要吃午饭。
5.他将骑自行车去学校。
6.他们下周日将去买汽车。
(1)过去将来时是立足于过去某时,从过去的观点看将要发生的动作或状态。
主要用于宾语从句中。
(2)基本结构:主语+would/should was/were going to +V.原形+…He said that he would have a meeting next week.(He says that he will nave a meeting next week.)They said we should leave school tomorrow.(They say we shall leave school tomorrow.)(1)现在进行时表示现在或现在这段时间正在进行的动作。
通常与now, at present 等时间状语连用。
(2)基本结构:主语+be(am, is, are)+ v-ing +…You are listening to me carefully now.She is writing a letter this year.Look! They are dancing.We are studying English at present .It’s raining hard now.(1)表示过去某一时刻或某阶段时间正在进行的动作,通常与at 6:00 yesterday, at this/ that time yesterday, when 引导的时间状语等连用。
(2)基本结构:主语+be (was/were) +v- ing +…It was raining at 7:00 the day before yesterday.They were building a reservoir at this time last winter.We were reading when the teacher came in.We weren’t reading…Were you reading…What were you doing when the teacher came in.(1)表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或表示过去某时间已经开始一直持续到现在的动作或状态。
通常与下列时间状语连用:up to now, in the past, recently, by… , for 5 years, since 1994, so far, already, yet, ever, just…(2)基本结构:主语+ have/has + P.P(动词过去分词)I’ve finished this work.He has ever been to Australia.I have not heard from her recently.I have already read this book.Have you read…?Yes, I have. No, I haven’t.What have you read?(3)过去分词的不规则变化do did donego went goneeat ate eatencome came comehave had hadwrite wrote writtenbe was/were beensee saw seenhear heard heardswim swam swumdrink drank drunkgive gave givenforget forgot forgottentake took takenkeep kept keptsleep slept sleptteach taught taughtbuy bought boughttell told toldmake made madecut cut cuthurt hurt hurtread read readlet let let(4)注意1)含有终止意义或暂短意义的动词不能与for, since 引导的一般时间状语连用。
(buy, begin, die, come, go , join, leave 等)I have bought a book.I have had a book for 3 years.I have bought a book for 3 day. (wrong)He has been in the army for 3 years.He joined the army 3 years ago.He have joined the army for 3 years. (wrong)He has been dead for 3 years.He died 2 years ago.It is 2 years since he died.He has died for 2 years. (wrong)He has gone to Australia.He has been to Australia.(5)现在完成时与一般过去时的区别(时间状语的区别)1)现在完成时和一般过去时所表示的动作都发生在过去,但它们所强调的重点不同:现在完成时侧重于对现在的影响;而一般过去时侧重于某一动作发生在过去某个时间或某段时间。