语言学文本
- 格式:doc
- 大小:63.50 KB
- 文档页数:5

文本与本文的名词解释引言:文本是人们在日常生活中经常遇到的一个概念,但它的定义和含义并不是人们普遍理解和掌握的。
在本文中,我将解释和探讨文本的含义以及它与本文的关系。
一、文本的定义与背景文本是指呈现在纸面、屏幕、书籍等媒介上的语言与信息的书写形式。
它可以是一个段落、一篇文章、一本小说,也可以是电影的剧本、歌词、广告宣传语等等。
文本凭借着语言和符号的力量,表达作者的思想、传达信息,从而与读者进行交流和沟通。
文本一词最早出现在语言学中,用于描述语言学研究中抽象的语言单位。
在当代语言学领域,文本的概念也得到了广泛的应用和发展。
文本不再仅仅指书面的文字,它可以是口头表达、图片、影像、音频等多种形式的表达。
这种扩大的定义使得文本更加多样化和丰富,而不仅仅局限于书面传统的文字表达。
二、文本的特点与重要性1. 多样性与复杂性文本的形式和类型非常多样,可以是科学论文、故事小说、新闻报道等等。
它们涵盖了生活中的方方面面,并且常常以多元化的方式进行表达。
文本可以凭借着巧妙的语言技艺、形象的比喻和具体的描述,将作者的思想和情感生动地传递给读者。
2. 意义与沟通文本是人与人之间沟通交流的桥梁。
通过文本,作者可以将思想、知识、经验传递给读者,而读者也可以通过阅读文本获得信息、启发思考并与作者进行互动。
无论是教育、娱乐还是各种形式的社交媒体,都以文本作为主要的传播工具。
3. 公共领域与个人表达文本不仅存在于公共领域,如新闻报道、政府文件等,也贯穿于个人生活中的各个方面,例如个人日记、信件、社交媒体上的状态更新等。
通过文本,个人可以表达自己的思想、情感和观点,与他人分享并建立联系。
三、文本与本文的关系本文是针对特定主题或问题进行撰写的文章,是一种具体的文本形式。
本文的目的是对文本的定义、特点和重要性进行阐述,以促使读者对此有更深入的理解。
本文紧扣主题,使用文字和语言来构建一个结构完整、思路清晰的文本。
通过分类、定义、分析等手法,以逻辑的方式呈现信息,从而使读者对文本这个概念有更清晰的认识。

叙事文本分析的语言学模式罗钢当代叙事学受到结构主义语言学极为深刻的影响,本文拟介绍一种叙事学家们在文本分析中惯常采用的语言学模式。
一过去,人们在分析叙事作品时,注重的是作品的情节、人物、主题等等,而叙事学的文本分析,是从文本语言的有机构成开始的。
在语言中,有一种对于确定其诗歌功能意义深远的对立,这就是隐喻与转喻的对立。
1956年,雅各布森在《语言学基础》一书中对二者的关系作了系统的阐发。
在这方面,雅各布森吸取了索绪尔结构主义语言学的一个基本观念。
索绪尔认为,语言,就像人类其它符号行为一样,具有双重性质,分别涉及两种行为,这就是选择和组合,这种选择和组合构成符号行为的基础。
举例来说,如果我们看见一位少女身着T恤和牛仔短裤,穿白色网球鞋,少女的这身装束便构成一个信息,依据特定的语境,它可以告诉我们少女的性格,她此时此刻的心情以及她将要去作什么。
这个信息的构成便不可避免地要涉及选择与组合两种行为,少女先从她的各种上装如大衣,衬衫等中选择了T恤;又从各种裙子和裤子里面选择了牛仔短裤;再从她的各种鞋里选择了白色网球。
这种选择依赖于她对自己的服装的了解,同时也依赖于她对自己的需要的认识。
选择之后紧接着便是组合,组合的过程依赖于她对各种服装搭配的知识和公众的服装惯例的了解。
例如,身着深色西装再穿白色网球鞋使显然是不符合服装惯例的(尽管这种惯例在不断变化),这种服装的正确搭配,就类似我们根据语法正确地组成一个句子。
一句中国古诗,例如“僧敲月下门”,它的构成也要涉及类似的选择和组合的行为。
首先:诗人要从一系列具有同样语法功能(名词),和属于同一语义域的词汇(如和尚、僧、道、尼等)中选出“僧”这个词,然后从意义接近的系列动词,如“敲”“打”“拍”“推”中选出“敲”这个动词,最后再从另一系列名词,如“扉”、“门”“闼”等中选出“门”这个词,然后将这些个别的词汇单位根据中文的语法规则组合起来,例如我们不能说,“门敲月下僧”,就如我们不能把裤子笼到身上,衣服套在腿上一样,如果这样作,就违反了语言和服装的惯例。



第一章语言学导论Chapter1 Invitations to LinguisticsLinguistics is nowadays coming into wide use with combination of theories and practice as wellas linguistics and other disciplines.Linguistics is of great use with very wide application. —人工智能,人机对话,机器翻译The research of linguistics has already gone beyond language itself.Definition of LinguisticsHow do you define linguistics? What is linguistics?—— Linguistics can be defined as the scientific or systematic study of language. It is a sciencein the sense that it scientifically studies the rules, systems and principles of human language.What are we going to learn about linguistics?1.It is generally agreed that linguistics should include at least five parameters, namely, phonological, morphological, syntactic, semantic and pragmatic. These can be called microlinguistics.语音学 (phonetics); 音系学 (phonology); 形态学 (morphology); 句法学 (syntax) — Schools of Modern Linguistics 现代语言学流派; 语义学 (semantics) ; 语用学 (pragmatics) (chapter2-6) 2. Macrolinguistics —— interdisciplinary learningSaussure, father of modern linguistics( 现代语言学之父) were intended to establish the autonomy of linguistics, giving it a well-defined subject of study and freeing it from reliance onother disciplines. However, the interactive links between linguistics and other sciences are developing fast.尽管索绪尔的目的是给予语言学自主性,给它定义明确的研究对象,将它从对其他学科的依赖中解放出来。

英语语言学大全英语是全球通用的语言之一,许多人都学习英语,但并不了解英语语言学的深层次内容。
本文将为您介绍英语语言学的基本概念和主要分支,希望帮助您更好地了解和学习英语。
一、语言学基础概念语言学是研究语言的学科,它涉及语言的形态、结构、意义、使用和历史等方面。
在语言学中,有一些基础概念需要了解:1.语音学语音学是研究语音的学科,包括语音的产生、听觉和声学特征等方面。
在学习英语时,我们需要掌握它的基本音素、音标和发音规则,才能有效地进行听、说、读、写等活动。
2.语法学语法学是研究语言结构和组织的学科,有时也称为句法学。
它研究语言的词类、句子结构、语法关系等方面。
通过学习英语的语法,我们可以正确使用语言,避免出现语法错误。
3.语义学语义学是研究语言意义的学科,它探究词汇、短语和句子意义的形成和变化。
在英语学习中,我们需要理解单词和短语的意义,以及句子的含义,以便正确理解和表达内容。
4.语用学语用学是研究语言使用的学科,包括口语和书面语言的使用场合、对话方式、说话人的语言目标和对听者的影响等方面。
在英语学习中,我们需要了解不同场合和对象的语言使用规范,以便与人交流时更加得心应手。
二、英语语言学的主要分支除了以上基础概念外,英语语言学还有一些重要的学术分支,能够帮助我们更深入地了解和掌握英语。
1.语音学英语语音学探究的是英语中的音素、音标和发音规则等方面,以及与其他语音系统的比较和差异。
2.语法学英语语法学研究的是英语的句法结构、语法关系和句子意义等方面,以及与其他语言的比较和翻译问题。
3.词汇学英语词汇学是研究英语词汇的学科,包括单词的来源、组成和意义等方面,以及与其他语言的比较和词汇翻译问题。
4.语用学英语语用学研究的是英语在语言使用中的实际应用,包括语言交际、言语行为、语境和语言目的等方面。
5.文本语言学英语文本语言学是研究英语文本的结构、组织和语言特点等方面的学科,包括语篇分析和修辞分析等内容。

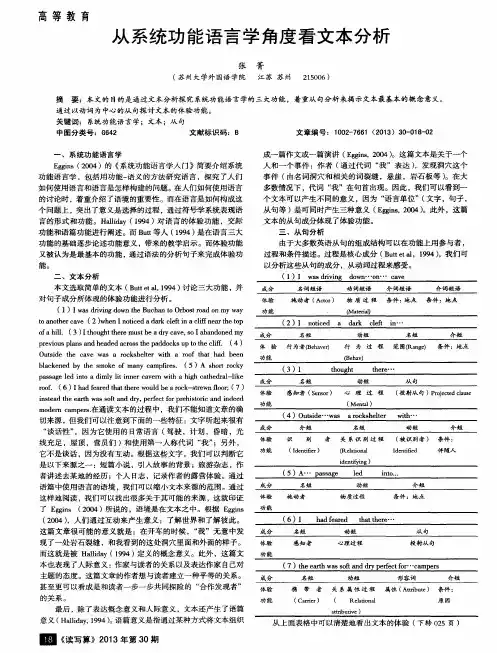

“系统功能语言学”框架下文本分析与散文翻译作者:宋杨来源:《今日湖北·下旬刊》2014年第12期摘要以系统功能语言学为基础的翻译研究主要体现在语篇翻译理论的建立,从分析语篇功能及内在特征出发阐述翻译中的一系列问题。
本文以散文翻译为例阐述语篇功能和语篇意向对散文翻译的整体连贯的影响。
关键词语篇意向语篇功能散文翻译一、引言20世纪后半叶以Halliday为代表的系统功能语言学派影响巨大,它根植于伦敦学派并吸收其他学派的精华形成了相当完整的思想体系、理论体系和研究方法。
国内从80年代末才开始系统的研究介绍系统功能语言学,其后一直处于上升势头,在语篇分析和翻译研究方面应用广泛。
篇章语言学与翻译相结合,将文本类型对比分析运用在翻译实践中,通过对不同体裁的文本进行分析提出相应的翻译方法,或通过英汉类似文本的对比分析提出翻译策略。
对语言的研究从句扩展至篇,语言功能重新释义为语篇功能。
The largest quantity of translation in a text is done at the level of the word, the lexical unit,the collocation, the group, the clause and the sentence—rarely the paragraph, never the text—probably in that order. 语篇指任何不完全受句子语法约束的在一定语境下表示完整语义的自然语言单位。
语篇是广义的,既包括话语(discourse),也包括篇章(text)。
它可以是一个词……也可以是一个短语或词组……它可以是一个小句……它可以是一幅对联、一首小诗、一篇散文、一则日记、一部小说(三步曲或其中的章节)……;它也可以是一句口号、一首歌曲、一次对话、一场口角、一次长达三个小时的演讲……。
由于人们说话写文章都要表达较为复杂的思想,非一言两语能够了事,因此多数场合下要动用好多句子,于是更多的人把语篇看成是大于句子的单位,尽管这样的理解并不很精确。

语言学讲稿08级尊敬的评委,亲爱的同学们:大家好!我是来自08级的XXX,在这里非常荣幸能够为大家带来一场有关语言学的讲稿。
语言学作为一门独特且广泛应用的学科,涉及到人类语言的各个方面,对于我们理解语言现象有着巨大的帮助。
在接下来的演讲中,我将从语言的定义、语言的结构、语言的变化以及语言的应用等几个方面来展开讲述。
希望通过这次演讲,能够为大家带来一些对语言学的简单了解。
首先,让我们从语言的定义入手。
语言这一概念是十分广泛和抽象的,因此在语言学中有着多个不同的定义。
一般来说,语言是人类交流和表达意义的一种符号系统。
在我们生活中,语言扮演着非常关键的角色,无论是口头交流还是书面文字,都离不开语言的运用。
同时,语言也是人类思维的重要媒介,它的发展和变化与人类文化、社会的演进密不可分。
接下来,让我们来了解一下语言的结构。
语言的结构包括两个层面,即语音层面和语法层面。
语音是指语言的语音系统。
不同的语言中,语音的组织方式也不尽相同。
例如,汉语是一种声调语言,意思可以通过声调的不同来表达。
而英语则是一种重音语言,意思可以通过重读音节的不同来表达。
语法是指语言的句法和词法系统。
语法规定了单词和句子的结构和用法,是语言的骨架。
语法可以分为词法和句法两个层面,词法负责研究单词的构成和变化规律,句法则负责研究句子的组织和句法关系。
除了语言的结构,语言的变化也是语言学的一个重要研究方向。
语言是一种活的交流工具,它不断演变和发展。
语言的变化可以分为语音变化、词汇变化和语法变化几个方面。
语音变化是指语言中的音位、音韵规则以及发音方式的改变。
词汇变化是指语言中单词的意义、形式和用法的变化。
语法变化是指语言中句法结构和语法规则的变化。
语言的变化是一个复杂而多元化的过程,它受到各种因素的影响,包括文化、社会、地理等等。
因此,研究语言的变化对于我们理解语言发展的规律和背后的因素具有重要意义。
最后,让我们来看一下语言学的应用。
语言学的应用范围非常广泛,它涉及到教育、翻译、语音识别、信息检索、人工智能等许多领域。

genre语言学名词解释英文genre语言学名词解释英文1. Genre (文类) - a category of artistic composition, characterized by similarities in form, style, or subject matter.2. Register (语体) - a variety of language used in a particular social setting or for a specific purpose.3. Discourse (话语) - written or spoken communication or debate.4. Text (文本) - a piece of written or printed material regarded as conveying meaning.5. Cohesion (连贯性) - the quality of being united or connected in a logical or natural way.6. Intertextuality (互文性) - the relationship between different texts, often seen as a way in which they comment on or refer to each other.7. Paratext (旁文) - elements in a text that are outside the main body, such as titles, subtitles, or footnotes.8. Style (文体) - the way in which something is written or spoken, characterized by its vocabulary, syntax, and tone.9. Rhetoric (修辞) - the art of using language effectively and persuasively.10. Pragmatics (语用学) - the branch of linguistics concerned with language use in context, and how it is affected by the speaker's intentions and the listener's interpretation.。
纽马克的文本类型理论及翻译方法探究纽马克的文本类型理论及翻译方法探究引言:语言是人类交流的重要工具,而翻译作为语言传递的桥梁,在跨文化交流中起到至关重要的作用。
翻译不仅仅是简单的将一种语言转换成另一种语言,更重要的是要传递原文的含义和文化内涵。
在翻译过程中,理解原文所属的文本类型对于翻译者来说尤为重要。
本文将探究纽马克的文本类型理论以及在翻译过程中的实际应用方法。
一、纽马克的文本类型理论纽马克是德国语言学家,他提出了四种基本的文本类型:记叙文、说明文、议论文和应用文。
这四种文本类型都具有不同的语言特点和表达方式。
1. 记叙文:记叙文是描述故事、事件或情境的文本类型。
记叙文常用的语言特点是用情感色彩明显的动词、形容词和副词,以及人物的内心独白和描写。
翻译记叙文时,翻译者需要保持原文的故事性和连贯性,尽可能地传达原文中的情感。
2. 说明文:说明文是介绍和解释事物性质、原因和特征的文本类型。
说明文常用的语言特点是客观、中立,以及使用事实、数据和逻辑推理来支持论述。
翻译说明文时,翻译者需要确保准确传达原文中的论述和解释,避免主观感情的插入。
3. 议论文:议论文是阐述观点、辩论和争辩的文本类型。
议论文的语言特点是使用辩证性的词汇和句子结构,以及常见的修辞手法和辩证论证。
在翻译议论文时,翻译者需要注意理解原文中的逻辑关系,准确传达原文中的观点和论证。
4. 应用文:应用文主要是用于实际应用的文本类型,如邮件、广告、手册等。
应用文的语言特点是简洁明了,以行动和结果为导向。
翻译应用文时,需要确保准确地传达原文中的指示、操作和信息。
二、翻译方法探究纽马克的文本类型理论为翻译提供了指导,翻译者可以根据原文所属的文本类型选择合适的翻译方法。
1. 记叙文的翻译方法:记叙文强调故事性和情感,翻译者可以采用较为自由的方式进行翻译,以保持故事的连贯性和情感的传达。
重点是理解和传达原文中的情感色彩和描写。
2. 说明文的翻译方法:说明文强调客观、中立的描述,翻译者应该尽量准确地传达原文中的事实和解释。
语言学研究中的文本分析工具使用教程引言语言学研究通过分析语言的各种特征和结构来探索它们背后的规律和机制。
文本分析是语言学研究中常用的工具之一,它可以帮助我们深入理解语言的结构、语用和语境等方面。
本文将介绍一些常用的文本分析工具和它们的使用方法,帮助读者更好地利用这些工具进行语言学研究。
一、词频分析工具1. AntConcAntConc是一款免费的词频分析工具,它可以帮助研究者分析语料库中的词频、词汇搭配等信息。
使用AntConc进行词频分析的步骤如下:a. 导入语料首先,在AntConc中选择“File”菜单,点击“Open...”,然后选择要分析的语料文件。
b. 设置分析参数在“Profile”选项卡中,设置分析参数,如选择要分析的文本范围、忽略的词汇等。
c. 进行词频分析点击“Start”按钮开始分析,AntConc会自动计算并显示出词频统计结果。
2. WordSmith ToolsWordSmith Tools是一款功能强大的文本分析软件,包含了多种工具和功能,其中包括词频分析。
使用WordSmith Tools进行词频分析的步骤如下:在WordSmith Tools中选择“File”菜单,点击“Open Text...”,然后选择要进行分析的语料文件。
b. 进行词频分析在“Tools”选项卡中选择“WordList”,WordSmith Tools会自动计算文本中的词频信息,并将结果显示在新的窗口中。
二、共现分析工具1. GephiGephi是一款开源的网络分析工具,可以用于分析文本中词语的共现关系。
使用Gephi进行共现分析的步骤如下:a. 准备数据首先,将要分析的文本转换成Gephi支持的格式,例如CSV或GEXF。
b. 导入数据打开Gephi软件,在“File”菜单中选择“Import Spreadsheet”,然后选择要导入的数据文件。
c. 进行共现分析在“Data Laboratory”选项卡中选择“Statistics”菜单,点击“Network Analysis”,然后选择“Co-occurrence”,设置共现分析参数。
Chapter 1 Language and Linguistics1. Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.2. Properties of LanguageA. Language is symbolic.B. Language is arbitrary and conventional.C. Language is systematic.D. Language is human specific.E. Language is socio-culturalF. Language is dynamicG. Language is habitual behaviorH. Language is functional3. Design features of human languageThe defining properties of human language that tell the difference between human languages and any system of animal communication.A. DualityIt is also termed “double articulation”, referring to the fact that language isorganized at two levels or layers simultaneously: speech sound and meaning.B. ArbitrarinessThere is no intrinsic or inherent connection between a sound and a meaning; asound doesn’t have to mean a particular thing, and the same thing can beexpressed by different sounds.C. ProductivityThis feature is also called creativity or open-endedness. By this feature,we refer to the fact that we are making and hearing new sentences all the time and the potential number of sentences in a language is infinite.D. Displacementlanguage can be used to refer to things that are removed from the immediate situation of speaking. People can communicate about things and events happening here and there, and now and then. E. Cultural transmissionA person acquires a language in a culture with other speakers and not from parental genes.A human baby doesn’t speak any la nguage at birth. A Chinese baby is not born to speak Chinese.F. InterchangeabilityThe speaker has the ability to receive and also send the message.G. SpecializationSpeech is produced for communication, not chiefly for some other function, such as echolocation. And when people communicate, they have purpose and intention.H. DiscretenessLanguage elements can be broken into segments.4. Functions of human language4.1 From a learner’s pragmatic point of viewA.means of communicationB. B. a tool of learningC. a vehicle of thoughtD. a weapon for survival & career4.2 From an interactive point of viewA. phatic: language is used for setting up a certain atmosphere or maintaining social contact rather than for exchanging information or ideas. Greetings, farewells or comments on the weather or clothing.B. directive: language is used to get the hearer to do something. Tell me the result when you finish.C. informative: language is used to tell something, characterized by the use of declarative sentences.D. interrogative : language is used to obtain information.E. expressive: language is used to indicate the speaker’s feeling or attitude .F. evocative: language is used to create certain feeling in the hearer. The aim is to amuse, startle, worry or please.G. Performative: people speak to do things or perform. I’m sorry. Thank you. I promise not to be late again.5. Definition and branches of linguisticsLinguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language.Phonetics (语音学) ----The study of sounds which are used in linguistic communication is called phonetics .( articulatory phonetics, acoustic phonetics, auditory phonetics.)Phonology (音位学)---- The study of how sounds are put together and used in communication is called phonology.Morphology (形态学,构词学) and lexicology (词汇学)----Morphology is the study of the structure of words, and lexicology is the study of vocabulary of a language.Semantics (语义学)---- The study of meaning in language is called semantics.Syntax (句法学)----The study of the structure and production of clauses and sentences. Pragmatics (语用学)----The study of meaning in context of use is called pragmatics Psycholinguistics (心理语言学)---- The study of language with reference to the workings of mind.Sociolinguistics (社会语言学)---- Sociolinguistics is often defined as the study of language and society. It refers to the study of language in relation to social factors, that is , social class, educational level and type of education, age, sex, and ethnic origin, etc.Applied linguistics (应用语言学)---- Findings in linguistic studies can often be applied to the solution of such problems as the recovery of speech ability. The study of such applications is generally known as applied linguistics.Langue (语言) and parole (言语) ---- Langue refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all members of the speech community. Parole is the realization of langue in actual use. Competence (语言能力) and performance (语言运用,语言行为) ---- Competence is the ideal user’s knowledge of the rules o f his language. Performance is the actual realization of this knowledge in linguistic communicationDescriptive (描写性研究) and prescriptive (规定性研究)----If a linguistic study aims to describe and analyze the language people actually use, it is said to be descriptive.If the linguistic study aims to lay down rules for correct and standard behavior in using language, it is prescriptive.Chapter 2 Semantics1. Situational context (情景语境)refers to the particular spatiotemporal situation in which an utterance occurs, the main components of which include, apart from the place and time of the utterance, the speaker and the hearer, the actions they are performing at the time, the various objects and events existing in the situation.2. Linguistic context, (语言语境)the words, clauses, sentences,paragraphs, a whole chapter and even the entire book form a linguistic context where a word or structure exists.3.Lexical meaning (词汇意义)---meaning expressed by different parts of speech of words。