智能可穿戴设备市场白皮书
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:1.13 MB
- 文档页数:38

智能穿戴行业的机遇与挑战随着科技的不断发展和人们对智能化生活的需求增长,智能穿戴设备在近几年迅速崛起,成为了全球科技市场的一个热门领域。
智能穿戴行业涵盖了各种智能手表、智能眼镜、智能手环等产品,为用户提供了更方便、更智能化的生活体验。
然而,智能穿戴行业虽然面临着巨大的市场机遇,但也面临着一系列的挑战。
一、机遇1. 科技的不断进步随着科技的不断进步,智能穿戴设备的功能和性能得到了大幅提升。
比如,智能手表能够连接手机,实现电话、短信等功能,同时还能监测用户的运动、心率等数据。
这种科技的发展为智能穿戴设备提供了更多的应用场景,为行业带来了巨大的机遇。
2. 消费者对智能生活的追求现在的消费者日益重视健康、便捷、智能化的生活方式,智能穿戴设备能够满足这些需求,因此受到了越来越多消费者的欢迎。
智能穿戴设备的市场需求不断增长,给行业带来了巨大的机遇。
3. 应用领域不断扩大智能穿戴设备的应用领域正在不断扩大,不仅仅局限于个人消费市场。
例如,医疗领域可以利用智能手环监测患者的健康状况,提供个性化的医疗服务;工业领域可以利用智能眼镜提高工作效率和安全性;体育领域可以利用智能手表追踪运动员的训练数据。
这些应用领域的不断扩大,为智能穿戴行业带来了更多的机遇。
二、挑战1. 技术问题智能穿戴设备的技术要求非常高,需要在小巧的体积中集成多个传感器和功能模块。
因此,技术上的挑战是智能穿戴行业面临的一个重要问题。
比如,延长电池续航时间、提高屏幕显示效果、改善传感器的精度等,这些都是技术上的难题。
2. 隐私和安全问题智能穿戴设备搜集到的用户数据非常庞大,其中包含了用户的个人隐私信息。
如果这些数据泄露或被滥用,将给用户带来巨大的风险和损失。
因此,智能穿戴行业需要加强对数据的保护和安全,确保用户的隐私不受侵犯。
3. 市场竞争随着智能穿戴行业的发展,竞争也越来越激烈。
许多科技公司和传统制造商都加入到智能穿戴设备领域,推出了自己的产品。
这就意味着市场上供应过剩,竞争压力不断增加。

目录P1P2P12P17P24P26P36P39P45P47引言无人机应用场景和通信需求4G网络能力5G网络能力网联无人机终端通信能力5G应用案例无人机安全飞行标准进展趋势,总结和展望贡献单位IMT-2020(5G)推进组于2013年2月由中国工业和信息化部、国家发展和改革委员会、科学技术部联合推动成立,组织架构基于原IMT-Advanced推进组,成员包括中国主要的运营商、制造商、高校和研究机构。
推进组是聚合中国产学研用力量、推动中国第五代移动通信技术研究和开展国际交流与合作的主要平台。
引言无人驾驶航空器(Unmanned Aerial Vehicle,以下简称UAV)简称为无人机,其全球市场在过去十年中大幅增长,现在已经成为商业、政府和消费应用的重要工具。
无人机能够支持诸多领域的解决方案,可以广泛应用于建筑、石油、天然气、能源、公用事业和农业等领域。
当前,无人机技术正在朝军民融合的方向高速发展,无人机产业已经是国际航空航天最具活力的新兴市场,成了各国经济增长的亮点。
无线通信在过去20 年经历了突飞猛进的发展,从以话音为主的2G 时代,发展到以数据为主的3G 和4G 时代,目前正在步入万物互联的5G 时代。
移动网络在继续丰富人们的沟通和生活的同时,也向全行业数字化转型提供能力,提高各行业的运作效率和服务质量。
5G 以全新的网络架构,提供10Gbps 以上的带宽、毫秒级时延、超高密度连接,实现网络性能新的跃升。
ITU 定义了5G 三大场景:增强移动带宽(Enhanced Mobile Broadband,以下简称eMBB)、超高可靠低时延通信(Ultra-Reliable Low-latency C o m m u n i c a t i o n s,以下简称u R L L C)、大规模机器类通信(M a s s i v e M a c h i n e-Ty p e Communications,以下简称mMTC)。


Table of Contents1.Emerging Market for Low Power Services and Applications 41.1IoT development & Growing Demand for LPWA 41.2NB-IoT Use Cases & Market Potential 5 2Emerging Low Power Technologies 62.1Introduction to NB-IOT (Best Solution For LPWA ) 62.2The NB-IOT deployment scenarios 72.3Low band, an excellent choice for fast deployment 83.Shaping the Business model 93.1Value Chain and Partnerships 93.2Business Potential & Revenue model 103.3Summary 10 4IOT Use case 114.1IOT Public 114.2IOT Industry 134.3IOT Appliance 154.4IOT Personal 16 5Operator Reference Cases 185.1Smart Parking 185.2Smart Metering 195.3Pet Tracking 20 6Glossary 22Executive SummaryThe LPWA market has existed for about 10 years; it’s not a new thing. The current technologies (solutions) supporting this market are fragmented and non-standardized, therefore there are shortcomings like poor reliability, poor security, high operational and maintenance costs. Furthermore, the new overlay network deployment is complex.NB-IOT overcomes the above defects, with all the advantages like wide area ubiquitous coverage, fast upgrade of existing network, low-power consumption guaranteeing 10 year battery life, high coupling, low cost terminal, plug and play, high reliability and high carrier-class network security, unified business platform management. Initial network investment may be quite substantial and superimposed costs are very little. NB-IOT perfectly matches LPWA market requirements, enabling operators to enter this new field.NB-IOT enables operators to operate traditional businesses such as Smart Metering, Tracking, by virtue of ultra-low-cost ($ 5 ) modules and super connectivity (50K / Cell), also opens up more industry opportunities, for example, Smart City, eHealth.NB-IOT makes it possible for more things to be connected, but also managing the commercial value of the resulting Big Data is a big task, operators can carry out cooperation with related industries, in addition to selling connections, they can also sell data.1.Emerging Market for Low Power Services and Applications1.1IoT development & Growing Demand for LPWAThe Internet of Things – IoT – has moved from fiction to reality. By 2020, there will be over 14 billion network-enabled devices, according to the International Energy Agency. This compares to approximately 3.2 billion people using the internet. IoT dramatically widens the internet’s scope from people-operated computers towards autonomous smart devices. Often, these devices are connected to the internet for remote diagnostics & control, leading to cost savings. In addition, innovative IoT hardware & services can generate new revenues – for example, connected glasses used for industrial applications, more efficient logistics serving new market segments, or industrial appliances sold in a per-usage business model. In many cases, business users & private users can control their IoT application through existing smartphones and tablets, through mobile applications that interact with web servers which the connected objects connect to.Many mobile operators have set up dedicated IoT/M2M business units in order to serve the growing number of companies looking to embrace the business benefits that mobile IoT brings. Larger operators have even made acquisitions so that they can serve a wider part of the value chain and capture revenues beyond pure connectivity. As the market grows, it is becoming obvious that there are many mobile IoT use cases for which existing cellular networks are not suitable.The reasons are simple: Coverage, battery life and device cost. First, coverage: Existing cellular networks already offer very good area coverage in mature markets. However, many potential “connected objects” are located in vast remote areas, far away from the next cellular base station. If there is coverage, it is often weak which requires the device transmitter to operate at high power, draining the battery. In addition, cellular networks are not optimized for applications that occasionally transmit small amounts of data. A battery life of several years combined with an inexpensive device cannot be realized on existing cellular standards, as they do not support the required power saving mechanisms.The third aspect is device cost: Mobile devices working on GSM, 3G and LTE are designed for a variety of services, including mobile voice, messaging and high-speed data transmission. However, NB-IoT applications do not utilize any of this; they just require low-speed but reliable data transfer, and an appropriate level of reliability. Therefore, using cellular devices for NB-IoT applications means using devices that are too expensive for the application. Many of the NB-IoT use cases require a low device price, not just in order to have a positive business case for the service operation, but also due to practical aspects such as ease of installation or risk of theft.In summary, there are strong market trends pointing at growing demand for NB-IoT applications, while the networks that can efficiently serve such applications are not in place yet. This whitepaper examines trends in the market for NB-IoT applications and discusses technology options that operators can choose from in order to enter this new business.1.2 NB-IoT Use Cases & Market PotentialThe strong growth in the NB-IoT market has motivated many analyst firms to create forecasts showing the expected numbers of connections as well as the revenue potential. Generally, the global IoT market is expected to be worth trillions of dollars by 2020. The NB-IoT market is a subset of this, and it is important for operators to understand the revenue potential in the countries they operate in. Before looking into specific countries, we need to identify the industries or verticals where NB-IoT can add value. Figure 1 below shows nine industries where we see major market potential for NB-IoT services:Figure 1: Target Industries for NB-IoT Services Huawei’s business case analytics is designed to evaluate the NB -IoT business for specificindustries, countries or regions. Based on our deep country-specific research which includes social and demographic data evaluation, we have modeled how the adoption rates for different NB-IoT applications will develop during the next five years.Our forecasts are based on use cases; distinct NB-IoT applications that will often be deployed in more than one industry. The model currently includes over fifty use cases, covering many service categories such as:∙Smart metering (electricity, gas and water) ∙Facility management services ∙Intruder alarms & fire alarms for homes & commercial properties ∙Connected personal appliances measuring health parameters ∙ Tracking of persons, animals or objectsAgriculture Health Care /E-Health Retail Safety and SecurityAutomotive &LogisticsEnergy &Utilities Manufacturing Smart City Smart Home∙ Smart city infrastructure such as street lamps or dustbins∙ Connected industrial appliances such as welding machines or air compressors.Figure 2 below shows as one output example of five-year revenue forecast (connectivity only) by Huawei for Germany divided by nine industries: Figure 2: Five-year NB-IoT revenue forecast for GermanyThe overall sum of 1.67 billion USD for five years equals a per-year NB-IoT revenue of 334 million USD. This would equal to a revenue uplift of 2.2% for the existing German operators thanks to the launch of NB-IoT services. This show, just as starting point, that already with conservativeassumptions, NB-IoT is a promising new business area which operators should invest into now, if they do not want other players to capture this attractive market. 2 Emerging Low Power Technologies2.1 Introduction to NB-IOT (Best Solution For LPWA )As mentioned earlier services that leverage low power wide area networks mainly require deep / wide coverage, low power consumption and massive connections. There are several inherent characteristics of the NB-IOT technology that makes it the best for LPWA deployment.15922518011778175227276233Overall Revenues:1.67 bn USDFigure 3: Inherent capabilities of NB-IOTMoreover low power consumption is a prerequisite for almost 80% of all LPWA use cases, ranging from applications like smart meter, smart parking, and wearables to smart grid. Additionally, with the availability of massive connections it is possible to make everything around us smart.To realize this, it’s ideal to have about 50K devices per cell; this is possible assuming there are the household density per every sq m is 1500 with 40 devices in every household.When we compare inherent capabilities of NB-IOT with other LPWA technologies like e-MTC, SigFox and Lora, NB-IOT offers better performance. Furthermore, when we look at all the technologies in terms of network investment, coverage scenario, uplink and downlink traffic and network reliability we realize that NB-IOT is the most suitable technology.Additionally from a performance point of view, NB-IOT guarantees 20+dB coverage, ~1000x connections, ~10 years using only 200 KHz bandwidth whereas the other technologies like eMTC, SigFox offers far less in terms of performance.NB-IOT has quite an extensive ecosystem mainly because of its support from many global top operators. Most importantly unlicensed solutions can’t guarant ee reliability and security.2.2The NB-IOT deployment scenariosThe recently 3GPP agreed technology for LPWA deployment NB-IOT will offer three deployment scenarios; these are, Guard Band, In Band and Stand Alone.Standalone deployment is mainly utilizes new bandwidth where as guard band deployment is done using the bandwidth reserved in the guard band of the existing LTE network, In Band on the other hand makes use of the same resource block in the LTE carrier of the existing LTE network.Figure 4: Three deployment scenarios of NB-IOTIn summary, it becomes clear that the Standalone and Guard band deployment options tend to offer the best performance in terms of improved indoor coverage, FDMA (GMSK) also offers about 20% power consumption saving and lower cost.2.3Low band, an excellent choice for fast deploymentLow band is quite known for its excellent performance in terms of coverage; furthermore leveraging the inherent characteristics of this frequency band in deploying NBIOT offers several benefits. It is widely known that several operators around the globe use the 900MHz frequency band for GSM voice deployments because of its extensive coverage capability. This is possible because such low frequency bands have excellent propagation characteristics and this generally improves the indoor penetration.Deploying NB-IOT in frequency bands like 700MHz, 800MHz, and 900MHz is a great choice because they provide an already large and established ecosystem since quite a number of operators select them; it also offers benefits in terms of site number. There is quite a substantial number of commercial networks both UMTS and LTE that are currently running on the 900MHz frequency band. Analyst firms recently confirmed that there are about 14 LTE 900MHz commercial networks as at July 2015.A few examples of such operators can be found in the Czech Republic and Sweden. There are other operators in South Korea with commercial LTE networks on the 800MHz frequency band. For mobile operators who are already running GSM 900MHz, it is possible to just upgrade, some operators might also be running on LTE 800MHz, there is a clear upgrade pathway to NB-IOT for such operators too.3.Shaping the Business model3.1Value Chain and PartnershipsAs shown in the NB-IoT business study for Germany, already connectivity is a valuable contributor to the operator’s bottom line. Partnerships with IoT technology providers and alliances with chipset manufacturers are helping the operators to secure this part of the value chain as we see it today for some of the NB-IoT solutions, e.g. smart metering, smart parking and pet tracking. At the moment we see connectivity platforms already in the cloud in many markets where operators have deployed IoT services.But there is more in than just connectivity. Operators have a chance to go further up the value chain by taken over more responsibilities than pure connectivity.Figure 5 : Telco business models for NB-IoT along the value chain Consequently the next step towards an integrated offer would be the incorporation of more functionality which points towards a setup, where the operators can offer the full NB –IoT Network as a service in the cloud to end to end service providers which are either private or governmental entities, according to the addressed industries or verticals .This will create for the operator the opportunity to lever its asset as security, billing and big data into that domain. Quality of service assurance and service level agreements are common in the telco space and could be leveraged into the NB-IoT Network as a service business model Following this idea even more, operators themselves can enter the IoT business as an end to end service provider by adding customer management and system integration functionalities on top. The operator as e2e business owner can also outsource certain parts of the e2e domain to its partners, sharing effort and revenues, and to expand the operators own experience in the OTT domain. However competing in the OTT domain is not comm on to most of the today’s opera tors and could be quite challenging.3.2 Business Potential & Revenue modelThe business is scalable and can be grown by demands by orienting the service introduction and go to market strategy on use cases which are profitable at a given point of time and contributing to the operator’s bottom line allowing further business expansion. As the operator can reuse his exi sting sites, no specific investment in towers or acquisition of sites are needed.Figure 6 : NB-IoT “time to market” and number of primary use casesThe selection of use cases can be different per operator, country and region or per addressed market. Huawei’s business modeling framework is able to address those challenges and advise on the right mix of investment, use case deployment and business model selection.3.3 SummaryThe opportunities for operators to enter business in NB-IoT domain are reflecting the huge potential of NB-IoT. Operators can choose from three basic setups according to their strategy per country or region:Connectivity: For the Internet of Things a reliable connectivity is required, but there are more business opportunities as just to engage in connectivityNB-IoT networks can be deployed by usingthe existing sites 1 Year 3 Year5 YearSmart ElectricitySmart WaterMeteringAlarms in Single-Family Houses Motor VehicleTrackingConnected StreetLamp………..Connected BloodPressure Meter Smart GasNB- IoT NW as a Service: Carrier grade solutions with security, billing, big data integration and QoS assurance allow the creation of new businesses and improvements to existing ones on a solid technological basis. NB-IoT Network as a service is supporting the global trends of network virtualization and cloud based service provision.End to End service provision: Operators may choose to extend into the e2e service provider domain for specific IoT solutions, but this needs careful planning, technology and business partnerships with players in the industry, including outsourcing and revenue sharing models.4IOT Use CaseIn this section, the various services and applications supported by LPWA has been classified under four categories; IOT Appliance, Personal, Public and Industry.Figure 7: Four use case categories for NB-IOT4.1IOT PublicAs the name suggests, IOT public focuses on LPWA applications that serves the general public; below are a few examples.i.Smart meteringSmart metering helps saves manpower by remotely collecting electricity, water and gas meter data over the cellular network. This is gaining quite an amount of momentum with most of the top European MNOs taking an interest in this topic mainly due to the market opportunity it presents. Smart metering will consequently help cut down cost generated from manual meter reading andchanging of meter batteries, which seems to be the two major cost drivers for conventional metering. Smart metering includes smart meters for water, gas and electricity.Figure 8: Smart metering use caseii.Alarms & Event DetectorsSecurity has always been a very important aspect of human living , people at all times want to be guaranteed of home safety. Alarms and event detection will help to rapidly inform that user about a detected home intrusion. This system will not only offer inteligent protection from intrusion but will also offer intelligence for detected events that can lead to a fire outbreak like a sudden increase in home temperature or smoke. Alarms and events detectors will make use of sensors placed devices in ideal locations in the home that constantly communicates with the LPWA network, this use case will make use of a very low data throughput and battery life of the devices will be ultra critical.Figure 9: Alarm & Event Detectorsiii. Smart garbage binsGarbage bins in city are not built by demand, and most of time the collecting trucks routes and schedule are fixed which is not optimal for a smooth collection. Smart garbage cans can signal to the waste management agent when the garbage can is full and in need of service, the best collection route will be calculated and delivered to the drivers. Historical collection data can provide optimized routes and guide on the right-size garbage can for each location. Charging for this service can be done on sensor amount or on monthly fee basis.Figure 10: Smart garbage bin4.2IOT INDUSTRYIOT Industry mainly delivers low power wide area applications that help to improve general enterprise and industrial efficiency; here are a few examples;iv.Logistics trackingLarge volumes of sensor data sent from tracking devices on shipping containers are aggregated and taken into an analysis to ensure that real time tracking of the location of shipments can be made possible. Alerts and optimized service recommendations are sent to technicians on their iPads, so that they can take preemptive actions in -real time. Charging model for this application can be done on a monthly payment or postpaid basis.Figure 11: Logistics tracking use casev. Asset trackingAsset tracking mainly deals with monitoring methods of physical assets made possible by a module on the asset broadcasting its location. Assets are usually tracked using GPS technology. This service is best leveraged in the logistics and transportation management industry, where through the use of sensors in modules sending information over the cellular network it is possible to gather and manage data relating to the current geographical location of assets. Asset tracking helps the owners of the assets to detect and preemtively react to unexpected events.Figure 12: Asset tracking use casevi. Smart agriculture NB-IOTTracking ApplicationSatelliteFarming industry is a sector with slim margins, and the way to survive in this industry is to optimize the general agriculture production including crops and livestock.Developing a sensor function to ensure the feeding of cattle has an optimized mix of nutritions to improve the yields from farming, and to reduce the waste of cattle feed. Installing sensors in the farming equipment that mix the cattle’s feed, through sensors measurements the variation in the cattle diet can quickly be identified, assessed and corrected. Charging model for this application can be done on a monthly payment or postpaid basis.Figure 13: Smart agriculture4.3IOT ApplianceConventionally, smart home application are deployed on short range technologies like Z-Wave, Zigbee but a home gateway is needed. In the case, where the appliance is embedded with an NB-IOT chipset the benefits are surprising. For example, management becomes more efficient through improvements in big data analysis. IOT appliance mainly comprises of LPWA applications that aims to provide intelligence for the user through sensors and devices that are found in the local area. Below are a few examples;Figure 14: IOT Appliance use cases4.4IOT PersonalIOT personal largely features LPWA applications that create a personal area network for the purposes of information exchange for the user. Below are a few examples;vii.WearablesConnected wearables in the past few years have taken center stage and increasingly becoming a lucrative industry as it is an application that mainly revolves around health, fitness and wellness. According to Cisco, there will be 177M connected wearables by 2018. Its market value is estimated at $250M in 2015 and is set to rise to $1.6B in 2022. A report released by Research&Markets and Berg Insight also estimated that global shipments of connected wearables in 2014 was 19 million and this figure is set to hit 168.2million by 2019 growing at a CAGR of 74.8%. Some of the few products that are making inroads in this industry are JawBone, GoPro & Nike just to name a few. While smartphone giants like Apple, Sony and Samsung are more linked to smartwatches.Figure 15: Wearables use caseviii. Smart bicycleFor bike rental companies it is vital to keep track of where the bike is at the moment, especially if it gets stolen. A bike rental company in Holland has embedded an M2M SIM card into the bike’s frame, and in this way the bike rental company can always find the bike. The M2M SIM is embedded into the bike in a non visible placeIf the bike is not returned to the rental company then the bike is positioned via the SIM. The rental cost for bikes can be reduced since the number of stolen bikes dramatically decrease. Stolen bikes can easily and quickly be located by the police via the SIM. Charging model can be done on a monthly payment or postpaid basis.Figure 16: Smart bicyclei.Kids monitoring use caseThe world’s population is aging, and senior people living alone at home need care in an easy and affordable way. Also parents have a great interest in being assured about their wellbeing andactivities. This use case provides realtime tracking of kids and the elderly. The information about their activities to the cloud. Real-time insights about the their status can be received on the users smartphone or other device.Figure 17: Kids monitoring use case5Operator Reference Cases5.1Smart ParkingParking can be a challenging issue, especially in urban areas where 30 % of all traffic congestion is caused by drivers circling around to find a parking space. Smart parking provides parking information to citizens in real time to enable better parking management. Huawei and a top operator are working on a smart parking project. Operator expects tens of millions of devices to be connected with this smart parking service. Another collaborator in this project is Neul, who provides the platform.Figure 18: Smart Parking reference caseIn this service, sensors that are placed under cars will communicate with the parking server through the cellular network to gain parking information. The operator and Huawei completed field trials for the smart parking project in July 2015 with Proof of Concepts already done. The commercialization of this project is expected in the second quarter of 2016.5.2Smart MeteringSmart metering as mentioned earlier enable the automated collection of utility meter data (Electricity, Water & Gas). Huawei and another operator are collaborating on an end to end smart metering solution. During Mobile World Congress 2015, Huawei and the operator unveiled this partnership on end to end smart metering project. Other players like Neul, Veolia, Kamstrup and Ublox are all collaborating efforts on this project that is planned to be launched in the first half of 2016.Figure 19: Smart metering reference caseProof of Concept for the smart metering project have already been completed, Huawei and the operator are looking forward to conducting field trials in November mercialization of the smart metering project is expected in the third quarter of 2016.5.3Pet TrackingHumans and their pets share a good bond, unfortunately many users often face issues regarding lost or stolen pets. Pet tracking use case is one application that helps the user to keep track of its pets activities and most importantly location at all times. A small lightweight device placed around the neck of the pet embedded with an NB-IOT chipset helps to send tracking information to its user’s device. This NB-IOT devices collects and sends location information leveraging GPS and Location Based Services and this can be done either periodically or in real time based on the users’ preferences.Figure 20: Pet tracking reference caseThe user can then receive the information with a tracking route that is already integrated with the map. Furthermore, this device is embedded with several forms of alarms that can alert the user when the device battery is running low .Huawei is collaborating with other industry players and another operator on the pet tracking application.6GlossaryNBIOT- Narrow Band Internet of ThingsPSD – Power Spectral DensityLPWA-Low Power Wide AreaGMSK – Gaussian Minimum Shift KeyingCAGR – Compound Annual Growth RateSC FDMA – Single Carrier Frequency Division Multiple Access DL – DownlinkUL – UplinkeHealth – Electronic Health3GPP – Third Generation Partnership ProjectTTM – Time to MarketdB – DecibelGPRS – General Packet Radio ServiceMNO – Mobile Network OperatorPoC – Proof of ConceptKHz – Kilohertz2017。

人工智能发展白皮书近年来,人工智能技术的快速发展和广泛应用,已经成为推动经济社会发展和提高生产力的重要力量。
为了深入探讨人工智能的发展趋势和未来方向,本白皮书梳理了相关领域的最新研究成果和经验分享,提出了一些具有前瞻性和可操作性的建议,旨在为我国人工智能行业的高质量发展提供科学依据和战略指导。
一、人工智能发展现状人工智能是一种通过计算机模拟人类智能行为的技术,包括机器学习、自然语言处理、计算机视觉等多个方向。
随着计算机算力和数据量的不断增加,人工智能在许多领域已经取得了显著成果,涉及金融、医疗、交通、制造、安防等多个领域。
在图像识别方面,人工智能已经能够识别出猫、狗等复杂图像,并在人脸识别、安防监控等领域得到广泛应用;在语音识别方面,人工智能可以实现自然语言交互、语音翻译等功能,拓展了人机交互的范畴;在自动驾驶领域,人工智能的应用也让无人驾驶成为了可能。
二、人工智能发展趋势1.多学科交叉融合。
人工智能需要信息学、数学、物理学等多个领域的知识支持,未来人工智能的发展将更加强调多学科交叉融合。
2.大数据为支撑。
人工智能需要大量的数据进行学习和训练,未来随着大数据的不断积累,人工智能将更加强大。
3.智能硬件普及。
未来智能硬件将逐渐普及,人工智能将在更多的场景中得到应用。
4.深度学习成为主流。
深度学习是目前最有效的机器学习方法之一,未来将成为人工智能领域的主流。
三、人工智能发展面临的挑战1.数据隐私和安全。
大数据的应用需要关注数据隐私和安全保护。
2.算法公正性和道德伦理。
人工智能的算法可能存在偏见,需要加强算法公正性和道德伦理建设。
3.人才短缺。
目前人工智能领域的高端人才相对稀缺,需要加强人才培养和引进。
四、人工智能发展战略建议1.加强人才培养和引进。
提高人工智能领域的科研人员和技术工人素质,加强国际人才引进与合作,提高人工智能领域的人才储备。
2.加强数据安全和隐私保护。
完善数据采集、存储、传输和使用的法律法规规范,加大数据安全和隐私保护力度。

智能穿戴白皮书报告导读2015年之后智能穿戴设备市场遭遇了几年的冷遇期,用户的高期待和产品的实用价值之间产生了明显落差,市场增速也从300%、200%突然掉落至不到30%。
2015年,曾经风光一时的Google Glass项目被叫停,2017年转型至行业应用2015年9月,Apple Watch Series2上市,而当时还未找到产品方向的苹果智能手表的一项噱头是提供配套的爱马仕表带2016年,曾经的行业宠儿Jawbone宣布停产智能手环,行业进入寒冬。
明星项目Pebble则被过去的竞争对手Fitbit收购,而Fitbit自己也是股价一路下坡。
2015年之后智能穿戴设备市场遭遇了几年的冷遇期,用户的高期待和产品的实用价值之间产生了明显落差,市场增速也从300%、200%突然掉落至不到30%。
2015年,曾经风光一时的Google Glass项目被叫停,2017年转型至行业应用2015年9月,Apple Watch Series2上市,而当时还未找到产品方向的苹果智能手表的一项噱头是提供配套的爱马仕表带2016年,曾经的行业宠儿Jawbone宣布停产智能手环,行业进入寒冬。
明星项目Pebble则被过去的竞争对手Fitbit收购,而Fitbit自己也是股价一路下坡。
关于我们全行业报告圈旗下全行业报告库是一家专注于分享国内外各类行业研究报告/专题热点行业报告/白皮书/蓝皮书/年度报告等各类优质研究报告分享平台。
所有报告来源于国内外数百家机构,包含零售消费、金融领域、互联网+、机械制造、新能源产业等专题研究.....目前已累积收集近43000+份行业报告,涉及11大板块,305个细分领域。
免责声明本平台仅收集分享内容,报道版权归原撰写发布机构所有,由全行业报道圈的社区朋友通过公开合法的渠道获得。
如涉及侵权,请联系我们删除;如果您对报告内容有疑问,请联系撰写和出版机构。

可穿戴智能设备市场分析及未来趋势预测随着科技的不断进步,可穿戴智能设备市场随之崛起。
在过去几年中,可穿戴设备市场一直在持续增长,预计在未来几年中仍将继续保持强劲的增长态势。
本文旨在对可穿戴智能设备市场进行分析,并预测其未来趋势。
一、市场概况可穿戴智能设备市场包括手环、智能手表、智能眼镜、智能耳机等多种产品。
据市场研究公司IDC数据显示,2019年全球可穿戴设备出货量达到了1.732亿台,同比增长89.0%。
其中,智能手表和运动手环占可穿戴设备市场出货量的大多数。
中国是可穿戴设备市场的一个重要国家,据悉,2019年中国可穿戴设备出货量约为8080万台。
这主要得益于国内消费者对健康生活的重视和科技创新的不断进步。
二、市场亮点A. 健康需求推动市场增长随着人们生活水平提高和健康意识增强,健康监测成为了可穿戴设备的一大亮点。
一些可穿戴设备具有健康数据监测、睡眠监测、运动监测等功能,有效促进用户身体健康。
B. 适应多种场景需求可穿戴智能设备在适应多种场景需求上有不错的表现。
比如,智能手表通过立体语音通话、短信审核、音乐等功能,满足用户在户外、商务场合等多种场景下的需求。
C. 通过AI实现个性化定制人工智能技术的运用,有效推动了可穿戴设备市场的个性化定制。
根据用户的身体数据、运动习惯等个性需求,可穿戴设备可以提供更加贴心的服务和个性化的应用。
三、未来趋势预测A. 多元化定制未来的可穿戴设备将会更加注重多元化定制。
比如,针对老年人、儿童等特殊人群,可穿戴设备将会提供更加适配的功能和服务,为用户提供更加便捷贴心的体验。
B. 5G和云计算应用5G和云计算的发展将进一步推动可穿戴设备市场的发展。
5G 技术将促进设备之间的互联互通,而云计算则可提供更加丰富和高效的数据应用,从而为用户提供更加优质的服务和体验。
C. 生态化发展未来可穿戴设备市场将更加注重生态化发展。
通过构建生态系统,可穿戴设备可以与智能家居、汽车、医疗保健等领域进行有机结合,为用户提供更加智能、高效、便捷的生活服务。

智能硬件产业发展白皮书作者:来源:《中国计算机报》2018年第49期为加快推进智能硬件产业发展,在工业和信息化部电子信息司指导下,赛迪智库电子信息产业研究所编写了《智能硬件产业发展白皮书》。
本书全面梳理了全球和我国智能硬件产业的规模现状、产业链结构和主要特点,对虚拟现实产业的创新进展、应用推进、政策环境、主要企业、投融资的发展现状等做了详细的总结,对产业未来发展趋势进行了展望,并提出了若干建议,以期为我国虚拟现实产业发展和行业管理提供决策参考和依据。
发展状况市场规模随着万物互联时代的到来,硬件智能化成为全社会的共识,在此背景下,智能硬件成为全球发展最快、市场潜力最大的行业之一。
由于政府、科技企业的高度重视和大力投入,智能硬件产业得到了快速发展,出货量、装机量和市场规模显著提升。
据市场调研机构艾媒咨询发布和赛迪智库整理的数据显示,2015年全球智能硬件出货量为13.9亿部,2016年达到18.8亿部,同比增长33%,2017年达到25.6亿部,2020年达到64亿部,年复合增长率在30%以上,在电子信息领域保持领先水平。
全球智能硬件产业初步形成了包括智能可穿戴设备、智能医疗健康设备、智能汽车、无人机、智能服务机器人、智能车载设备等规模化产品领域,呈现出蓬勃发展态势,推动着传统行业的智能化升级。
从细分产品来看,2016年全球智能手表出货量达到2010万块左右,较2015年的1940万块同比增长3.9%。
预计到2020年,全球智能手表出货量将超过5000万块,年复合增长率达到23.0%。
智能手机方面。
IDC数据显示,2016年全球智能手机出货量达到15.1亿部,同比增长5.7%,增速低于2015年的两位数。
其中,基于安卓操作系统的智能手机出货量达到12.5亿部,同比增长7.6%,市场占有率达到82.6%。
预计2020年,全球智能手机出货量将达到19.2亿部,同比增长4.3%,年复合增长率为6%。
智能服务机器人方面。
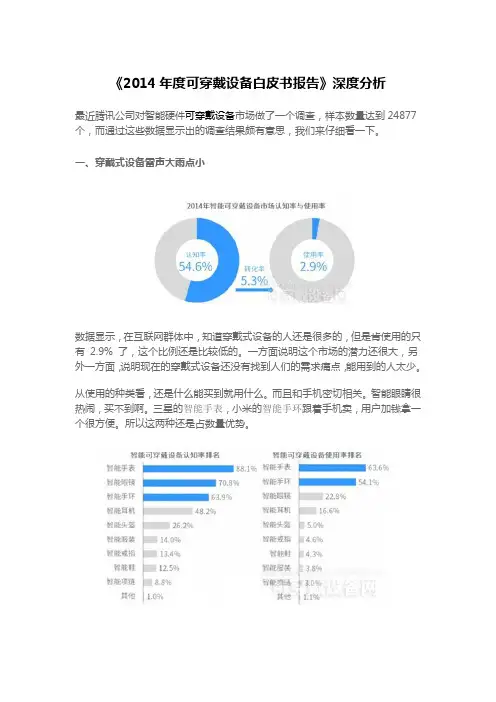
《2014年度可穿戴设备白皮书报告》深度分析最近腾讯公司对智能硬件可穿戴设备市场做了一个调查,样本数量达到24877个,而通过这些数据显示出的调查结果颇有意思,我们来仔细看一下。
一、穿戴式设备雷声大雨点小数据显示,在互联网群体中,知道穿戴式设备的人还是很多的,但是肯使用的只有2.9% 了,这个比例还是比较低的。
一方面说明这个市场的潜力还很大,另外一方面,说明现在的穿戴式设备还没有找到人们的需求痛点,能用到的人太少。
从使用的种类看,还是什么能买到就用什么。
而且和手机密切相关。
智能眼睛很热闹,买不到啊。
三星的智能手表,小米的智能手环跟着手机卖,用户加钱拿一个很方便。
所以这两种还是占数量优势。
二、尝鲜,新奇是卖点从获知渠道看,科技网站是用户知道穿戴式设备的主要渠道,然后是产品官网和购物网站,网络媒体,特别是专业媒体对于穿戴式设备的宣传有重要作用。
算了一下用户自己购买的比率,大约有四分之三是自己掏钱的,如果算上前面2.9% 的使用率,只有2.17% 的用户掏钱买了穿戴式设备。
从渠道看,官网和实体店也是手机购买的重要渠道,说明穿戴式设备目前和智能手机的关系很密切。
产品使用率也很可怜,有58% 的人还在用,其余基本放弃,说明手环的实用性不高,尝鲜过后扔掉的不少。
满意率和还在用的比例差不多,功能太少,电池续航差,连接手机麻烦是三大原因。
体验差,没啥用是穿戴式设备的主要问题。
从这些数据看,穿戴式设备还在玩具阶段,大家看到科技媒体介绍,买手机的时候顺便拿来玩玩,用用不好用就不玩了。
真正找到痛点被广泛接受的产品还没出现。
三、什么人在用穿戴式设备?调查里面有个很有意思的数字,学生比例是20%,收入不愿意透露是18.1%。
无收入的学生在穿戴式设备中占得比例并不小。
从人群看,初中到大学文化,20-40 岁的社会中坚力量也是穿戴式设备消费的主力军。
穿戴式设备乐于被社会中坚力量所接受,但是这表明了它的潜力,而目前没有普及,是产品本身的问题,而非用户的问题。

海克斯康发布智能制造白皮书作者:来源:《智能制造》2020年第08期近日,海克斯康《慧心智造》白皮书正式发布。
全书共计13.5万字,以制造业发展变革、智能制造关键技术、智能工厂策略架构,以及智能工厂实证方案与解决方案应用实例五大章节全方位地呈现了智能工厂图景。
24项综合解决方案、30家标杆企业成功案例,旨在全方位呈现海克斯康智能工厂解决方案,凭借以质量为核心的生态系统,推动不同业务类型、不同智能化程度的制造企业实现智能制造。
同时,白皮书的发布也希望为践行智能制造、推动企业数字化转型的企业管理者、专业技术人员和各界专家学者提供参考和借鉴。
海克斯康《慧心智造》白皮书在深入分析市场发展和制造业趋势的基础上,阐明数字化、网络化和智能化为中国创新驱动发展所带来的新动力。
沿着制造业的流程主线,从概念设计、虚拟仿真验证、制造工艺仿真、工装设计制造、加工编程、加工仿真、过程控制、计量辅助制造、在线与离线计量检测、质量优化和设备管理等环节,白皮书力图以扎实的理论基础、前沿的制造技术、完善的策略架构、实操可行的方案与全球优秀实践经验,全方位剖析智能制造。
白皮书在深入了解和分析全球制造业发展与技术趋势的基础上,指出智能制造不是一蹴而就的,它是一个渐进式的成就过程。
同时智能工厂也更像是一场旅程,任何一家制造型企业均有能力结合自身组织特点与技术优势切入智能制造的潮流中。
它有可能是从一个产品、一组方案或一套系统开始的,点点相连、线线成面,逐步辐射,形成企业专属的智能工厂。
近20年来,海克斯康聚焦于助推全球化的数字变革浪潮,先后将全球200余家领先技术公司纳入麾下,成为较为完整的数字化信息技术解决方案的领导者。
面向制造业,凭借独特的智能制造技术组合、200年制造业专业积淀以及服务全球客户所积累的宝贵经验,为不同规模、不同技术基础的企业提供了漸进式的智能工厂切入路径。

Ibot8.0产品白皮书第 1 页共47 页目录1.前言 (6)1.1.目的范围 (6)1.2.产品定位 (6)1.3.名词术语 (6)2.公司简介 (8)2.1.小I简介 (8)2.2.小I发展历程 (8)3.产品概述 (11)3.1.智能机器人 (11)3.2.产品架构 (11)3.1.1.机器人前端平台 (12)3.1.2.智能服务引擎平台 (12)3.1.3.机器人统一管理平台 (14)3.1.4.知识库组织说明 (14)3.3.产品演进路径 (17)3.4.技术特点 (17)3.5.技术指标 (18)3.6.扩展接口 (19)3.7.优势特性 (19)4.产品主要功能 (22)4.1.基础智能问答 (22)4.2.前端用户功能 (23)4.2.1 Web机器人功能 (23)4.2.2微信机器人功能 (28)4.2.3IM机器人功能 (31)4.2.4短信机器人功能 (33)4.3.后台主要管理功能 (35)4.3.1知识管理功能 (35)4.3.2服务管理功能 (36)4.3.3渠道管理功能 (36)4.3.4素材管理功能 (37)4.3.5语音管理功能 (38)4.3.6运维管理功能 (38)4.3.7系统管理功能 (39)5产品实施 (39)5.1.实施流程 (39)5.2.知识建设 (39)5.2.1 语言知识库构建 (40)5.2.2 业务知识库构建 (41)5.3.二次开发 (42)5.4.系统部署 (44)5.4.1 常规部署 (45)5.4.2 扩展部署 (45)5.4.3 集群部署 (47)版权声明版权所有© 2013-2015上海智臻网络科技有限公司。
本文档的内容,所有文本全部或部分均受版权保护,上海智臻网络科技有限公司是本文档所有版权作品的拥有者。
除非预先得到本公司的书面授权,否则严禁对本文档进行复制、改编、翻译、发布等等。
本文信息如有变动,恕不另行通知。
人工智能与可穿戴设备智能化穿戴的未来趋势随着科技的迅猛发展,人工智能和可穿戴设备正成为未来科技领域的热点。
人们对于这两个技术的结合产生了浓厚的兴趣,并且对其未来趋势充满了期待。
本文将探讨人工智能与可穿戴设备智能化穿戴的未来趋势,展望其在各领域的应用前景。
一、智能化穿戴设备的快速发展近年来,随着智能手机、智能手表等可穿戴设备的普及,人们对于智能化穿戴设备的需求不断增加。
这些设备通过感知人体的生理参数、监测环境的变化等方式,提供个性化的信息服务和数据分析,极大地方便了人们的生活。
而人工智能作为一种具有智能学习和决策能力的技术,更进一步增强了可穿戴设备的智能化程度。
二、人工智能与可穿戴设备的结合人工智能与可穿戴设备的结合可以实现对用户行为的准确识别、分析以及智能推荐等功能。
例如,通过对用户的步态分析,结合人工智能的模式识别技术,可以精准判断用户的行走状态,进而提供个性化的健身锻炼方案。
此外,结合人工智能的语音识别和自然语言处理技术,可穿戴设备还可以实现智能助手的功能,为用户提供语音交互、信息查询等服务。
三、可穿戴设备智能化穿戴的未来趋势1. 健康监测方向:可穿戴设备可以实时监测用户的心率、血压等健康指标,并通过人工智能技术进行数据分析和提醒。
未来可穿戴设备有望更加精准地预测用户的健康状况,并提供相应的健康建议。
2. 智能物流领域:可穿戴设备可以帮助物流从业人员进行智能化管理。
结合人工智能和传感技术,可监测货物的温度、湿度等环境指标,并实时反馈给相关人员。
这将有助于提高物流效率和货物安全。
3. 智能交通方向:可穿戴设备可以提供导航、事故预警、交通管制等功能。
用户通过智能眼镜或智能手环等设备,可以实时获得路况信息,并获得最佳行车路线。
这对于缓解交通拥堵和提高行车安全具有重要意义。
4. 智能家居应用:人工智能与可穿戴设备的结合将为智能家居带来更多可能。
通过智能手环或智能手表等设备,用户可以实现对家里灯光、电器等智能设备的控制。
i版权所有© 华为技术有限公司2020。
保留一切权利。
非经本公司书面许可,任何单位和个人不得擅自摘抄、复制本文档内容的部分或全部,并不得以任何形式传播。
商标声明和其他华为商标均为华为技术有限公司的商标。
本文档提及的其他所有商标或注册商标,由各自的所有人拥有。
注意您购买的产品、服务或特性等应受华为公司商业合同和条款的约束,本文档中描述的全部或部分产品、服务或特性可能不在您的购买或使用范围之内。
除非合同另有约定,华为公司对本文档内容不做任何明示或暗示的声明或保证。
由于产品版本升级或其他原因,本文档内容会不定期进行更新。
除非另有约定,本文档仅作为使用指导,本文档中的所有陈述、信息和建议不构成任何明示或暗示的担保。
华为技术有限公司地址:深圳市龙岗区坂田华为总部办公楼邮编:518129网址:客户服务邮箱:support@客户服务电话:4008302118FTTR技术白皮书目录目录1 什么是FTTR(Fiber to The Room/Request) (1)2 FTTR的应用场景 (3)2.1 光纤到房间:全屋千兆覆盖 (3)2.2 基于FTTR的创新业务:Wi-Fi感知 (5)3 FTTR技术方案 (9)3.1 架构 (9)3.2 FTTR光网关 (10)3.3 边缘ONT (11)3.4 家庭光纤组件 (11)4 实践案例 (13)4.1 广州电信FTTR实践案例 (13)4.2 东莞溪村公寓FTTR实践项目 (14)5 FTTR产业发展初探 (15)1 什么是FTTR(Fiber to The Room/Request)通信行业一直在持续加快光纤带宽升级,当前,接入网络已大部分实现光纤接入,光纤到户渗透率全球平均水平已达到65%。
在中国,光纤宽带发展保持全球领先地位,据国家互联网信息办公室发布的《2019年通信业统计公报》,截至2019年12月底,全国互联网宽带接入端口数量达到9.16亿个,其中,光纤接入端口占比达91.3%,远高于全球平均水平。
智能体白皮书2020
来源 | 华为、IDC、中国信通院等
IDC、中国信息化百人会、中国信息通信研究院、中国人工智能产业发展联盟与华为联合编撰的《智能体白皮书》指出,在第四次工业革命爆发前的历史拐点,“智能体”的新理念将推动城市、行业、企业在智能升级中合理运用这一参考架构,从而加快整个社会的高质量发展。
白皮书显示,在智慧社会,数据作为重要的生产要素,需要通过“任意对象和信息的数字化”“任意信息的普遍联接”以及“海量信息的存储和计算”的关键共性数字基础设施,把数据资源变成“智源”,才能有力支撑各行各业的数字化转型走向智能升级,重构体验、优化流程和使能创新。
这需要多种ICT关键技术形成一体化协同发展,以智能交互为感知系统、以高速联接为神经传导系统、以云上部署的AI为中枢系统,形成具备立体感知、全域协同、精确判断和持续进化的、开放的智能系统,成为一个类似人的智能体。
智能体把联接、计算、云、AI、行业应用一体化协同发展,形成开放兼容、稳定成熟的基础支撑技术体系,是智能升级的参考架构。
根据不同的需求提供场景化解决方案,帮助企业客户实现商业成功,帮助政府实现兴业、惠民、善政。
同时,白皮书强调,智能体建设是一项系统性工程,需要进行体系化规划和长期投入,多数项目需要3-5年甚至更长时间才能取得显著成果。
经过对大量行业及企业数字化转型
实践的分析,业界已经积累了一套具有通用性、普适性的实施框架,包含咨询、规划、实施、运维、持续运营、配套生态体系建设等多个模块。
以及,从先建联接,再优化,最后到智能的三阶段实施路径。
以下为全文。
人工智能安全白皮书(2018年)中国信息通信研究院安全研究所2018年9月版权声明本白皮书版权属于中国信息通信研究院(工业和信息化部电信研究院)安全研究所,并受法律保护。
转载、摘编或利用其它方式使用本白皮书文字或者观点的,应注明“来源:中国信息通信研究院安全研究所”。
违反上述声明者,本单位将追究其相关法律责任。
前言人工智能作为引领未来的战略性技术,日益成为驱动经济社会各领域从数字化、网络化向智能化加速跃升的重要引擎。
近年来,数据量爆发式增长、计算能力显著性提升、深度学习算法突破性应用,极大地推动了人工智能发展。
自动驾驶、智能服务机器人、智能安防、智能投顾等人工智能新产品新业态层出不穷,深刻地改变着人类生产生活,并对人类文明发展和社会进步产生广泛而深远的影响。
然而,技术的进步往往是一把“双刃剑”,人工智能作为一种通用目的技术,为保障国家网络空间安全、提升人类经济社会风险防控能力等方面提供了新手段和新途径。
但同时,人工智能在技术转化和应用场景落地过程中,由于技术的不确定性和应用的广泛性,带来冲击网络安全、社会就业、法律伦理等问题,并对国家政治、经济和社会安全带来诸多风险和挑战。
世界主要国家都将人工智能安全作为人工智能技术研究和产业化应用的重要组成部分,大力加强对安全风险的前瞻研究和主动预防,积极推动人工智能在安全领域应用,力图在新一轮人工智能发展浪潮中占得先机、赢得主动。
本白皮书从人工智能安全内涵出发,首次归纳提出了人工智能安全体系架构,在系统梳理人工智能安全风险和安全应用情况的基础上,进一步总结了国内外人工智能安全的管理现状,研究提出了我国人工智能安全风险应对与未来发展建议。
目录一、人工智能安全内涵与体系架构 (1)(一)人工智能基本概念与发展历程 (1)(二)人工智能安全内涵 (2)(三)人工智能安全体系架构 (3)二、人工智能安全风险分析 (6)(一)网络安全风险 (6)(二)数据安全风险 (8)(三)算法安全风险 (9)(四)信息安全风险 (12)(五)社会安全风险 (13)(六)国家安全风险 (15)三、人工智能安全应用情况 (16)(一)网络信息安全应用 (17)(二)社会公共安全应用 (20)四、人工智能安全管理现状 (23)(一)主要国家人工智能安全关注重点 (23)(二)主要国家人工智能安全法规政策制定情况 (26)(三)国内外人工智能安全标准规范制定情况 (29)(四)国内外人工智能安全技术手段建设情况 (31)(五)国内外人工智能重点应用的安全评估情况 (33)(六)国内外人工智能人才队伍建设情况 (34)(七)国内外人工智能产业生态培育情况 (36)五、人工智能安全发展建议 (37)(一)加强自主创新,突破共性关键技术 (37)(二)完善法律法规,制定伦理道德规范 (38)(三)健全监管体系,引导产业健康发展 (39)(四)强化标准引领,构建安全评估体系 (40)(五)促进行业协作,推动技术安全应用 (40)(六)加大人才培养,提升人员就业技能 (41)(七)加强国际交流,应对共有安全风险 (42)(八)加大社会宣传,科学处理安全问题 (43)一、人工智能安全内涵与体系架构(一)人工智能基本概念与发展历程1、人工智能基本概念计算机之父阿兰·图灵在1950年的论文《计算机器与智能》中提出了“机器智能”以及著名的“图灵测试”:如果有超过30%的测试者不能确定出被测试者是人还是机器,那么这台机器就通过了测试,并被认为具有人类智能。
一、前言
随着移动互联网技术的发展,在2024年会出现更加发达的移动互联
网技术,为消费者提供更优质的服务。
移动互联网可以满足消费者的需求,让他们随时随地想要什么就可以获得什么,更好地满足他们的日常需求,
从而增强用户体验。
本白皮书将详细介绍移动互联网在2024年发展的趋势。
二、移动互联网技术
1、5G无线网络
2024年,5G无线网络将成为移动互联网发展的重要基础,提供更大
的带宽、更快的网络速度、更安全的信息传输以及更低的延迟等功能。
2、智能语音技术
智能语音识别技术可以让用户更轻松的与智能设备进行交流,具有中
文语音识别、国际语音识别等功能,以及更友好的用户体验,处理复杂的
任务,可以为智能家居、智能安全和社交、电子商务等提供更优质的服务。
3、虚拟现实技术
2024年,虚拟现实技术将得到进一步发展,可以为消费者提供更多
有趣的体验。
它支持多种形式的虚拟现实体验,更好地满足移动互联网的
消费者需求,可以更加有效地推动消费者行为,提高消费者的购买满意度。
4、跨屏技术
2024年,跨屏技术将获得进一步发展。
腾讯ISUX :2015 智能可穿戴设备市场白皮书
5
腾讯 ISUX 在两天前发布了《2015 智能可穿戴设备市场白皮书》,其中有不少数据值得关注。
根据介绍,本次数据总样本量 8083 人,主要受访对象为 QQ 用户,调研时间为今年 5 月。
值得注意的一点是,虽然售价亲和力存在明显差异,但智能手表的品类认知率依然整体高于智能手环 10% 左右。
过半数用户对“智能手表”概念有认知,这可能得益于 Apple Watch 的发布和上市。
不过,后续的数据也表明:2014 年 11 月至 2015 年 5 月期间,可穿戴设备在中国网民中的渗透率从 2.9% 增长至 8.4%,其中手环的渗透率达到 4.6%,明显高于智能手表的 3.1% 和运动相机的 0.7%。
不出意外的话,可能跟手环方案的标准化和伴随其实现的入门级售价相关。
穿戴式设备用户中,男性用户暂时呈现主导状态,占比为 85%,与大学以上学历比例相同。
(这一数据可能与后面的用户外观方面诉求相关)
报告称:Apple Watch、小米手环和 GoPro 三个知名强势品牌分别引领了各自细分市场。
市占率方面,Apple Watch 因为处于发货初期未被计入腾讯报告数据。
而国产品牌的表现则超过我们能的预期。
根据 Canalys 今年初的分析数字,Android Wear 2014 年总出货量为 72 万台。
有趣的是,Moto 360 在国内无法正常使用的情况下占比达到 8%,而线上推广声量不大的 360 儿童手表凭借品牌认知度在线下取得了不错的成绩。
此前传出产能问题的 InWatch 和 Geak 则分列第三和第七。
手环方面则与普遍认知没有明显偏差,售价合理、供货稳定的小米手环占据绝对主导地位,三星 Gear 系列因为手机产品份额在适配机型独占的情况下排到第二。
后续几名除
了咕咚之外并无国产品牌出现。
余下国内品牌之间,因为实际存量数字不高,具体量差应该不大。
ISUX 这篇报告还提到,用户主要认知和购买产品的渠道是各品牌官网。
认知方面科技媒体和朋友推荐列二三位,购买上排在官网和授权网店之后的是电商和实体渠道。
实用性是目前穿戴式设备遇到的最主要问题。
和我们此前报道各机构下调 Apple Watch 出货预期反映出来的趋势相符,穿戴式设备作为一个凭空创造出来的“需求”,在产品性能、功能都未符合广泛预期的时候,用户粘性并不理想。
腾讯报告显示,穿戴式设备三月流失率 30%,三月以上流失率高达 41%。
用户流失的主要原因均分布在基础功能和体验方面。
需求方面则以健康为主。
近半年内对此类商品的购买意愿达到 24%,增长了整一倍。
总体而言,国内用户对在苹果、小米和三星等主流品牌的影响下,对智能可穿戴设备的认知和认可度都在逐渐提高。
但因为基础功能和交互缺陷,在售价普遍走低(小米手环售价 99 元起,促销期间 79 元;Apple Watch 起售价不足 2000 元)的情况下仍然没能实现理想的渗透率和留存率。
另一方面,穿戴式设备产品缺乏明确的目标人群画像 —— 没能满足占比最大的高学历深度/专业男性工作者及玩家需要的专业监测和方便交互,外观和配对稳定/便捷性上也没能满足一般女性电子产品用户的需求。
以下为报告全文:
::__IHACKLOG_REMOTE_IMAGE_AUTODOWN_BLOCK__::2 ::__IHACKLOG_REMO
TE_IMAGE_AUTODOWN_BLOCK__::3。