物流技术概论outcome
- 格式:doc
- 大小:75.00 KB
- 文档页数:6





第一篇物流总论第一章物流概述第二章物流的分类与形式第一章物流概述本章关键词:物流、商流、物品、物流学、第三利润源、现代物流理念。
复习思考题:1。
举例说明流通产业在社会经济中的地位. P2-32.如何理解商流与物流之间的关系?P43.如何理解物流的概念与内涵?P6-104。
请简要说明物流活动的构成。
P11—125.什么是物流的生产性和社会性?P136.请简要说明“物流学"的课程定位。
P157。
结合实际说明物流的地位与作用。
P15-168。
“黑暗大陆”和“第三利润源”的内涵是什么?P17-189。
为什么说“物流是市场的延伸”?P1810。
物流系统与物流一体化理念的区别在哪里?P19—21第一节商流与物流一、流通产业在社会经济中的地位1。
流通是连接生产和消费的纽带;2。
流通对生产的反作用;3.流通是国民经济现代化的支柱.二、流通的内容1.商流;2.物流;3.信息流和资金流。
三、商流与物流的关系1。
商流与物流的统一;2。
商流与物流的分离;四、商流与物流分离的表现形式1。
结算程序引起的商流与物流分离;”信汇“、”电汇“;”托收承付“;”三角结算“2。
购销方式引起的商流与物流的分离;预购;赊销;分项付款3。
期货市场形成引起的商流与物流的分离;4.电子商务环境下商流与物流的分离。
第二节物流的概念一、物流概念的起源;1915年阿奇·萧《市场流通中的若干问题》1974年鲍尔索克斯《后勤管理》等二、“物流”称谓的由来;1956年早稻田大学宇野正雄PD”物的流通”,,于70年代末直接引入二战期间,美军建立了“运筹学”丰富了“后勤学”,于80年代初引入三、物流的定义;1。
历史上的物流定义:日本通商省物流调查会;日本早稻田大学西泽修;日本专家汤浅和夫;1976美国物流管理委员1/ 10会;美国察尔斯·塔夫;1985加拿大物流管理协会CALM;1985美国物流管理协会CLM;1994欧洲物流协会;1998美国物流管理协会2.对物流的通俗解释:“物流”泛指手持资料实体在进行社会再生产过程中,在空间有目的的(从供应地向接收地)实体流动过程。

Explanation of inventory decisions.ZK currently make use of two specialist dedicated international logistics organizations to deal with their international deliveries and to help them meet their customer service and expansion targets.Control the inventory means that correct amount of shares has been sent to the right place at the right time, so as to ensure the cost savings and maintain the balance between demand and supply or inventory decisions can consider from the Product depreciation and Stock levels.Distribution center of the inventory the goods. Order point depends on demand and safety stock lead time. Stock levels are concerned with how many stocks are stored at a certain period of time. The company spends a large amount of capital on inventory to stock the products in order to supply enough goods for customers to meet their demands. If the stock levels are too low, it may lead to break the supply chain and fail to meet customers’ needs.Just the opposite, if the stock level is too high, the products will be overstocked and unmarketable. So ZK need know safety stock to maintain the normal operation of the company, and get the profit maximization.Consumption of fixed capital is a term used in business accounts, tax assessments and national accounts for depreciation of fixed assets. Production of new product and product mold or processing fee will let the product to devalue.Pull systems refer to a group of techniques that aim to ensure that when stock is used it is replaced. Pull systems do not plan, they react. They will work fine if processes and logistics are infinitely flexible, do not vary and are uncomplicated. I suggest the company with push system, because of the production of the toys of The Times ZK epidemic periods is so transient state, pull systems can reduce the cost of inventory increase.Considerations for choosing transport modes identified.The choices of transport methods, ZK would consider about factors such as cost, routing, speed, safety, the nature of cargos and customer needs.Cost is important factor that ZK would like to be taken into account firstly. Different modes have different levels of cost. The cost of rail cargo transportation is relatively low because ZK just need charge fee of usage and tax while the high establishment cost is charged by the government. Air transportation always has disadvantage of high cost because the cost is high with the fee of fuel and maintenance, depreciation of equipment and labor force.Yet, the cost of ocean and road transport might be lower than rail and air. So I suggest ZK use by sea. But ZK need to a reliable shipping company. E.g. UPS; MAERSK; APL;No matter what the transport can have certain risk, in order to avoid these risks, the company can buy insurance. They are stable to carry large amount of fragile and dangerous cargoes, so ZK could choose container to prevent the cargos from bump, shake, losses and accidents in long distance transportation.Anyway which modes are selected to use, the purpose of the transportation is to send the right cargo at right time to meet the need of customers. If the location of customers is near the ocean, ZK could choose shipping to transport. If foreign customers order the products urgently, ZK might choose airplane to deliver the cargos quickly. Depending on various customer needs, ZK could choose the suitable transport modes to save the cost and finish the task with high quality so that they could increase the customer trust and company reputation.Considerations for choosing warehousing facilities.When it comes to the factors influencing warehouse location, there is no doubt that the location of warehouse would link to the transportation system. So the warehouse location must be close to the traffic hub of the major road, rail and air freight linksand it could also be near the ocean ports.ZK have my own warehouse can supply to domestic customers. So ZK in a foreign country, ZK can choose to be recognized international storage company, the goods stored in there, to facilitate the supply foreign customers. ZK have security inventory, can continuous supply to customers, and to ensure that the development of the company.Evidence of additional research and answers linked to the case materialPush systems:Push systems are systems in which orders are made for everything likely to be needed. The obvious disadvantage is that is it difficult to forecast all of the time.ZK can use the push system production enough products, directly through the form of promotion and advertising to capture market share.Technological development: Technology is the making, modification, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems, methods of organization, in order to solve a problem, improve a preexisting solution to a problem, achieve a goal or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, modifications, arrangements and procedures. Technologies significantly affect human as well as other animal species' ability to control and adapt to their natural environments.ZK can develop technical advantage to expand the market, to win market share.ConclusionZK should take into account many factors to do inventory decision, transportation decision and warehousing decision. The services provided by the international logistics firms could help ZK fulfill its distribution strategies. The above statement ismy own idea, if I do this will improve the company's development in the future.6.0Reference1.‘Enterprise resource planning’, From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia/wiki/Enterprise_resource_planning , Access Date: Dec.4, 20122.‘Green Logistics’, From Baidupedia/view/138559.htm, Access Date: Dec.5, 20123.MBALib, ‘What is stock level’, July.5, 2012/201007/051035451002100100021074128.shtmlAccess Date: Dec.5, 20124.Iyouyou, ‘How to operate the management of product packaging’, Aug.4, 2010/content/2010/08/04/35948.html, Access Date: Dec.5, 20105.‘The advantages of international multimode transportation’:88/jzxyssw/mymain.aspx?cid=147&articleID=528, Access Date: Dec.5, 20106.KOFAX, ‘Sales Order Processing’, 2010/solutions/sales-order-processing.asp, Access Date: Dec.5, 20107.Alan McKinnon, Sharon Culliane, Michael Browne, and Anthony Whiteing, Green Logistics:Improving the Environmental Sustainability of Logistics, the United Stated: Kogan Page Limited,20108.Lutz Preuss, The Green Multiplier: A Study of Environmental Protection and the Supply Chain,New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2005。


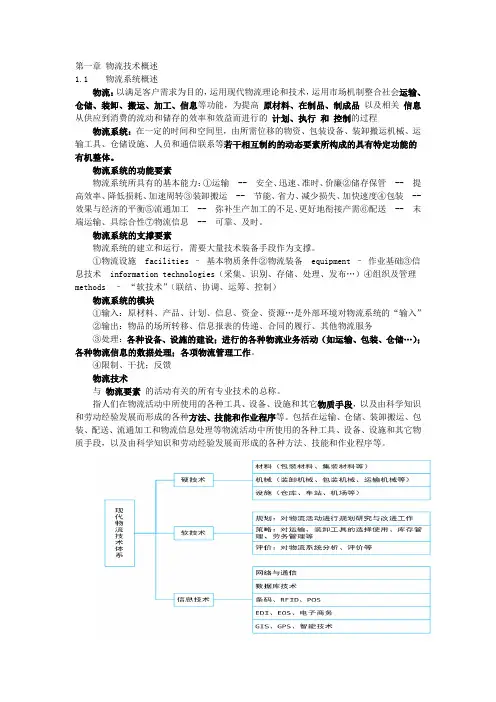
第一章物流技术概述1.1 物流系统概述物流:以满足客户需求为目的,运用现代物流理论和技术,运用市场机制整合社会运输、仓储、装卸、搬运、加工、信息等功能,为提高原材料、在制品、制成品以及相关信息从供应到消费的流动和储存的效率和效益而进行的计划、执行和控制的过程物流系统:在一定的时间和空间里,由所需位移的物资、包装设备、装卸搬运机械、运输工具、仓储设施、人员和通信联系等若干相互制约的动态要素所构成的具有特定功能的有机整体。
物流系统的功能要素物流系统所具有的基本能力:①运输 -- 安全、迅速、准时、价廉②储存保管 -- 提高效率、降低损耗、加速周转③装卸搬运 -- 节能、省力、减少损失、加快速度④包装 -- 效果与经济的平衡⑤流通加工 -- 弥补生产加工的不足、更好地衔接产需⑥配送 -- 末端运输、具综合性⑦物流信息 -- 可靠、及时。
物流系统的支撑要素物流系统的建立和运行,需要大量技术装备手段作为支撑。
①物流设施 facilities –基本物质条件②物流装备 equipment –作业基础③信息技术 information technologies(采集、识别、存储、处理、发布…)④组织及管理methods –“软技术”(联结、协调、运筹、控制)物流系统的模块①输入:原材料、产品、计划、信息、资金、资源…是外部环境对物流系统的“输入”②输出:物品的场所转移、信息报表的传递、合同的履行、其他物流服务③处理:各种设备、设施的建设;进行的各种物流业务活动(如运输、包装、仓储…);各种物流信息的数据处理;各项物流管理工作。
④限制、干扰;反馈物流技术与物流要素的活动有关的所有专业技术的总称。
指人们在物流活动中所使用的各种工具、设备、设施和其它物质手段,以及由科学知识和劳动经验发展而形成的各种方法、技能和作业程序等。
包括在运输、仓储、装卸搬运、包装、配送、流通加工和物流信息处理等物流活动中所使用的各种工具、设备、设施和其它物质手段,以及由科学知识和劳动经验发展而形成的各种方法、技能和作业程序等。

《物流学概论》讲义物流学概论是一门关于物流管理的学科,主要研究货物的流动和供应链的管理。
物流学概论涵盖了物流管理的基本原理、流程和技术等方面的内容。
下面是一份《物流学概论》的讲义,介绍了物流管理的基本概念、作用和发展趋势等内容。
一、物流管理的基本概念1.物流的定义:物流是指在产品生命周期中,为满足用户需求,将从原材料采购到产品销售的过程中,所涉及到的物流资源、活动、信息和服务等有机结合在一起,通过适当的计划、组织、指挥和控制,使物流资源得以合理配置和有效利用的一种管理活动。
2.物流管理的目标:物流管理的目标是通过最佳的物流组织和流程,实现产品的及时和安全交付,并提供满足用户需求的物流服务,同时最大程度地降低物流成本。
3.物流系统:物流系统由物流组成要素、物流环境和物流技术三个方面组成。
其中,物流组成要素包括物流资源、物流活动、物流信息和物流服务等;物流环境包括政府政策、市场需求、经济环境等;物流技术包括物流信息技术、物流设备技术和物流管理技术等。
二、物流管理的作用1.降低物流成本:通过合理的物流组织和流程管理,降低物流成本,提高企业物流效益。
例如,合理安排运输路线,优化运输方式,减少运输时间和成本。
2.提高产品服务水平:物流管理能够实现产品的及时和安全交付,提高产品的服务水平。
例如,合理安排库存,确保货物及时供应,避免缺货现象。
3.改善供应链效能:物流管理通过整合供应链各个环节,优化供应链流程,提高供应链效能。
例如,建立供应链信息管理系统,实现信息的及时共享和协调配合。
4.提高企业竞争力:物流管理能够提高企业运作效率和管理水平,提高企业在市场上的竞争力。
例如,合理安排生产计划,减少生产周期,提高企业响应市场变化的能力。
三、物流管理的发展趋势1.信息化:随着物流信息技术的快速发展,物流管理正不断向信息化方向发展。
例如,建立物流信息系统,实现物流信息的实时监控和管理。
2.网络化:物流管理正向网络化方向发展,通过建立网络化的合作伙伴关系,实现物流资源的共享和协同管理。

SummaryThe report in order to introduce about the need for up-to date ICT applications in international logistics, the effect of technological changes in security and how ZK could benefit from them, environmentally friendly logistics and relate this to the international toy industry, .the impact of reverse logistics on ZK and its customers and the reasons ZK or similar company might develop into a global logistics company. 1. An Introduction about EDI.Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is utilized for the automated exchange and transfer of document between various operations.And EDI is an exchange of structured information from one computer to another electronically with a minimum of human input.It can allow all partners in a supply chain to exchange their invoices, purchase orders, information requests and other important business documents from one business system to another one.There are lots of benefits of utilizing EDI for ZK. For example, EDI can help ZK company to transfer information or document in a high speed, which is quite time saving for this enterprise. On the other hand, ZK can also establish an EDI transfer from the customs to make some cooperations and this kind of transfer method has excellent security for ZK.However, the shortcoming about EDI is obvious, too. Founding an EDI path means that ZK should spend a high cost on the initial setup, for example, the purchasing and installing of the electric cable. Of course, using EDI can not help ZK to realize the transfer of "one to many", which is another obvious disadvantage.2. An introduction about reverse logisticsReverse logistics means “taking things back”, where goods are returned from a end customer or a wholesaler to the original producer, which involves a large amount of work in logistics industry. And reverse logistics are 'activities involved in removing a product or service after the original point of sale.' The overall aim is to maximize thevalue of the products. By the way, reverse logistics can deal with out-of date merchandise, returns from consumers, redistribution of merchandise, Overstocked goods.The reverse logistics can help ZK company to avoid some unnecessary losses. E.g, returning outdated toys in warehouse to original producer can let this firm not to face the dull sale of those outdated toys. Another example is that the recall can limit possibility of company being sued for negligence about its products, limiting bad publicity for this enterprise.3. An introduction about green logisticsGreen logistics are becoming increasingly important in at least 50% of the world, with the implementation of the Kyoto treaty. Increasing oil prices according to high consumption are also adding to distribution costs being already high for lots of products. The use of road, air freight and fossil fuels adds to pollution.For ZK the green logistics can help this company to recover a large amount of resources which may be wasted in the process of logistics just as some scrap materials of toys. Then almost all the sources can be utilized effectively by ZK company.The green logistics can be also used by some industries like food industry. For example, the "green packaging" of food can obviously improve the recovery rate of packaging material, which can control the unnecessary consuming of resources, to make the enterprise be more efficient.Of course, green logistics is a good choice for the paper industry, too. As is known to all the paper industry may cause serious pollution in the process of production or logistics, which means that if the green logistics can be utilized by paper industry the environment pollution in logistics process will be solved. For example, paper enterprise can recover the dumped pulp in order to utilize for the next production.4. impactFor ZK, the green logistics can reduce the cost of time and capital. Because in greenlogistics the transportation method can be changed from highway, railway to air freight and truck, which is a door to door service and this kind of service can save much time for ZK. On the other hand the green logistics can help ZK to realize a better warehousing management than before, which means that the spending of managing warehouse will be cut down.In the reverse logistics, ZK company should choose the appropriate transport channel to make sure its logistics process very efficient. Besides if ZK has its own motorcade, for example, a fleet of delivery lorries. Then there should be a reasonable distribution for these lorries. Because ZK must consider that how many lorries should be utilized for reverse logistics.5. Be a global logistics companyThey can make this enterprise save more cost than before, and the logistic process will be more effective and environmental by using these methods. However, there may be some difficulties in implementing these logistics measures just as the distribution of limited resources. Therefore, if ZK can solve these problems, it will be easier for this company to utilize EDI, reverse logistics and green logistics, which is an obvious advantage for the development of ZK in the future.Summary (3)1.An Introduction about EDI (3)2.An introduction about reverse logistics (3)3.An introduction about green logistics (4)4.impact (4)5.Be a global logistics company (5)。
物流学概论(共五则)第一篇:物流学概论物流学概论第一章物流概念的内涵与外延第一节物流的概念一国外经典的物流概念物流理念的发展经过了一个漫长而曲折的过程,有关物流的概念朔源的探究从1978年物流概念传入我国后,从来就没有停止过。
尤其自20世纪60年代后,各种物流的概念更是层出不穷。
虎骨物流的发展过程和理解历史上经典的物流概念,不仅有利于我们了解物流的发展规律,更有利于我们全面、深入理解物流的内涵。
1935年,美国销售协会对物流进行了定义;‘物流是包含于销售之中的物质资料和服务,从生产地点到销售地点流动过程中伴随的种种经济活动。
’此概念是在物流时代最具代表性的定义。
50年代中叶,日本在经济恢复中,十分重视学习西方科学技术。
1956年,日本生产性本部向美国派出了‘搬运专业考察团’,此举动对日本未来物流的发展起到了积极的推动作用。
日本于60年代正是引进了‘物流’这一概念,并将其解释为‘物的流通’,‘实物流通’的简称。
日本通产省的物流调查会的定义;‘物流是制品从生产地道最终消费者的物理性转移活动。
具体是由包装、装卸、运输、保管以及信息等活动组成。
美国物流协会1963年对物流管理的定义为;‘物流管理是为了计划、执行和控制原材料、在制品库存机制成品从起源地到消费地的有效流动而进行的两种或多种活动的集成。
这些活动可能包括但不仅限于;顾客服务、需求预测、交通、库存控制、物料搬运、订货处理、零件及服务支持、工厂及仓库的选择、采购、包装、退货处理、废弃物回收、运输及仓储管理。
这是从管理角度审视物流的经典。
美国物流工程是学会19947年的物流定义是;‘物流是与需求、设计、资源供给与维护有关,以支持目标、计划及运作的科学、管理、工程及技术活动的艺术。
‘这是从工程视角对物流的省视。
1981年,美国空军的建议;‘物流是计划执行军队的调动与维护的科学。
’奥找最全面的定义,物流与军队活动有诸方面的联系1.军队物资的设计与研发2,军事人员的运输与疏散。
物流概论期末重点总结归纳一、物流概论的定义与基本概念物流是指在市场经济活动中,通过计划、组织、指挥、协调和控制物资、信息等流程,实现物品从供应商到消费者的有序流动和转化,以满足市场需求的经济活动。
物流的基本概念包括:1. 供应链管理:是基于一定的战略规划和组织架构,通过对供应商、制造商、分销商以及用户之间的物流活动的整体规划协调,实现物流成本最小化与效率最大化的管理。
2. 物流网络:是指由供应商、生产商、分销商及用户相互联系形成的物流网络,包括材料供应、生产制造、仓储配送等一系列环节,以实现物流活动的有机组合和协同运作。
3. 物流成本:包括采购成本、生产成本、运输成本、仓储成本、库存成本等一系列与物流活动有关的费用,在物流管理中,降低物流成本是一个重要的目标。
二、物流的发展历程物流的发展经历了三个阶段:1. 物流的前期:20世纪40年代,随着工业化的发展,物资流动的问题日益凸显,传统的个体经济模式难以满足经济的发展需求。
此时物流被人们意识到并开始进行研究。
2. 物流的初级阶段:20世纪60年代至80年代,国际上开始形成物流学科,物流开始成为一门独立的学科。
以西方国家为代表的整个工业界开始重视物流的重要性,并进行了大量的研究和实践。
3. 物流的成熟阶段:20世纪80年代至今,随着信息技术和物流技术的不断推进,物流发展迅速。
物流转型为供应链管理,强调整个供应链中各个环节的协同作业,以提高整体物流效率和降低成本。
三、物流的作用与重要性1. 降低生产成本:物流通过合理的流通方式和供应链管理,可以降低生产成本,提高企业竞争力。
2. 提高服务质量:物流通过及时的配送和高效的供应链管理,可以提高产品和服务的品质,从而提高顾客满意度。
3. 减少库存风险:物流通过合理的库存控制和仓储管理,可以减少库存风险,降低企业的资金占用和存货关税成本。
4. 缩短供应链周期:物流通过合理的运输和物资流动安排,可以缩短供应链周期,提高产品的市场反应速度。
Section2- AssessmentThe assessment example below can be used by centre, or alternatively centre can develop their own assessment.Assessment 1Outcome covered 1Assessment instructionsPrepare a report/response which answers the following question.1.Identify two sources of finance available to private and public sector organizations andexplain the advantages and disadvantages associated with each.Private sector organization:1)Use share to raise money:Advantage:The capital provided by the owner of a business is long-term capital, because in the normal course of events it will not be repaid to owner.Disadvantage:Control a certain percentage shares, will be control the organization’s lifeblood. And it leads much assets and profits flow into the shareholders pocket.2)Loan:Advantage:It is the easiest and the most effective way to raise money.Disadvantage:1.Business risk, i.e. the risk inherent in the project. If the project is risky, a provider offinance will be less certain of recovering its investment, and will charge a higher rateof interest to compensate for that danger.2.Financial risk, if the borrower is already heavily dependent on outside finance, theinterest and repayments will consume much of its profits.Public sector organization:1)Use charity to raise finance:It is depend on the donors who support the work of the charity, special events to collect donations from a wide range of people. However, it has uncertainty, which easily lead to insufficient funding.2)Through the government allocate the funding:Advantage:This finance way is use the money from the government revenue received from taxpayers.Disadvantage:The funds must be used to the projects have benefit for the taxpayers, unless the government did not give the money to the public sector organization.2.Define two alternative methods of funding a capital purchase, e.g. a forklift truck. Considerthe financial benefits or disadvantage of each method.Bank overdraft: the bank allows the business to spend more cash than it actually owns, the bank itself making up the shortfall, it usually charge an arrangement fee for setting up the overdraft facility, and it will charge interest on the amount of cash that has been “overspent” by the businessBenefits:1)Allows a firm to draw check to a greater value than the actual balance in the bankaccount of company.2)Bank overdrafts are a fairly cheap form of finance with the added advantage of flexibility.In some cases a small overdraft facility may be offered free of charge.Disadvantage:1)The bank will take a close interest in the affairs of the business until the overdraft isrepaid.2)An overdraft is need repayable on demand; therefore, the bank can withdraw the facilityat a moment’s notice and require the business to pay the amount owing.Credit from suppliers: A supplier provides goods or services to a purchase with an arrangement for payment at a later date. Their suppliers have in effect-probably unwillingly-“loaned” goods to the business.Advantage:This can be cheapest form of finance.Disadvantage:1)Prices may be adjusted to allow for credit.2)Delayed payments can lead to poor relations with suppliers3.Describe the differences between revenue and capital purchasing and why they areaccounted for in separate ways.Revenue expenditure refers to obtain the benefits of financial services and only those expenditures that occur in the current period. These expenditures as current expenses should be credited to the appropriate expense account. The effectiveness of expenditures associated with the current fiscal year, should be treated as revenue expenditureCapital expenditure refers to the benefits of obtaining property or services and those expenses that can occur multiple accounting periods. Therefore, these expenses should be capitalized and included in the asset class subjects first, and then restaging by the benefits obtained, transferred to the appropriate expense account.Generally, an expense is part of revenue expenditure or capital expenditure, usually the length of the period by the expenditure benefits prevail.Different:1)Revenue expenditure included in the current expense account; capital expendituresnecessary to transfer assets, included in fixed asset accounts, according to the useful life of the future amortization expense.2)Revenue expenditure is to bring benefits to the current period, generally less than oneyear; while capital expenditures not only bring benefits to the current period will also bring benefits to the future business activities, usually in more than one year.3)Revenue expenditure and capital expenditure accounting processes and methods ofdifferent financially.4)Revenue expenditure is the expenditure of simple reproduction management aspects ofthe enterprise, it has liquidity, the final form of current assets or current expenses;capital expenditures expanded reproduction corporate spending, it has a relatively fixity, the final form of fixed assets.4.Explain a decision making process that is relevant to the purchase of a capital item. Detailthe steps taken and what the considerations are for the managers.For example by forklift truck:1.Initial request for capital item: Identifying the need for the purchase, and then formalizethe need.2.Sourcing: Investigate the circumstance of market.Know all information about the forklift truck. And according to the enterprise need choose the suitable forklift struck.3.Authorization: build a business budget.Consider how to raise the finance to buy the forklift truck.4.Investigation: seek a supplier which can be authorization from the enterprise.The manager should find more than 3 suppliers and compare their product and the conditions they give.5.Appraisal and evaluation: evaluation and appraisal.In this item the manager should consider its total life cycle costs.6.Buying decision: approval to purchase.The manager should give the company about the forklift information, supplier requirements, full life-cycle costs and payment ways and deliver information.7.Purchase and contract: purchase and acquireCoordination and communication, reminders, purchase acceptance, organize payment.5.Calculate the life cycle cost for a specific capital purchase using two alternative sources ofsupply. You may use the purchase identified in question 2. Contrast the final costing of each example, show the benefits/savings accrued and comment on your results.Forklift truck purchase:From this life cycle cost table, plan A (the forklift track purchase from company A) have to cost much net cost than B (the forklift track from company B), however, the plan A’s NPV(net present value)is less than 0, and plan B’s NPV is greater than 0, which means the enterprise should priority consider the plan A, so if this purchase has a high risk and it cannot use for 2 years, it is means the plan A cost less than plan B. But if the forklift truck purchase can be use more than 2 years, because the fund cost, maintenance and repair and overhauls, the plan A have to cost much fund than plan B. From this we can conclude that if this purchase has a low risk, the enterprise should buy the forklift from company B, if it has a high risk, the enterprise should buy it from company A.6.Explain two methods of investment appraisal fromPaybackDiscounted cash flowAccounting rate of returnPaybackThe great virtue of this method is its simplicity. The idea is to assess how long a project willtake to pay back the initial investment. Suppose that a company proposes to purchase a replacement machine for £200 000. In the company A, the new machine will lead to financial benefits of £50 000 per annum for each of the five years that the machine is expected to be in use.The net cash flow of company AIn the company B, An alternative project offers financial benefits of £20 000 per annum in years in one to three and £80 000 per years in four to six. The cash flow profile looks like this:The net cash flow of company BIn company A, this project finished the pay back in the fourth year, by the time the machine’s useful life is finished the cumulative net cash flow has reached a positive figure of £50 000.In company B, it finished the pay back need 4 years and 9 months, but overall, this project generates a positive cash flow of £100 000.The effect of using the payback criterion is clear: it gives preference to projects which pay back quickly, even if other projects offer better returns in the long term. For this reason it should be used only as a supplement to more sophisticated methods.The Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) MethodThe idea is simply to calculate the average rate of return earned by the money invested. The decision rule is: A project is acceptable if its rate of return is greater than management ’s minimum rate of return.1)investmentinitial Estimated prof itaverage Estimated =ARR2)projectthe of life useful expected projectthe of profit ve Accumulati =Average profitsAccording to the calculate, the company A average annual returns of £10 000are expected on an investment of £200 000, a 5 per cent rate return, in company B, averageannual returns of £16 667 are expected on an investment of £200 000, a rate of return of 8.3 per cent per annum. Therefore, the company B ’s project is preferable.。