2018年第五届浙江大学生工程训练综合能力竞赛
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:791.59 KB
- 文档页数:12

第二章工程材料+热处理(16/18)×1. 低碳钢为了达到硬而耐磨,可采用淬火热处理工艺。
2. 在碳素钢中,为提高其性能,加入一种或多种合金元素,即成为合金钢。
(正确)3. 热处理工艺中淬硬性和淬透性的含义是一样的。
(错)4. 正火比退火过冷度大(冷却速度较快),获得的组织较细,因此正火的强度和硬度比退火高。
(错误)5. 焊接后为消除焊接应力,可采用退火工艺。
(正确)6. 造成热处理变形的主要原因,是淬火冷却时工件内部产生的内应力所致。
(正确)7. 为了获得优良的淬火质量,细而长的轴类零件、薄而平的零件,应垂直淬入冷却液中。
(错误)8. 金属材料的塑性,随温度的升高而降低。
(错误)9. 淬火加高温回火的工艺称为调质处理。
(正确)10. W18Cr4V是()。
A、工具钢 B、弹簧钢 C、不锈钢 D、耐热钢11.调质的目的是()。
A、提高硬度 B、降低硬度 C、改善切削性能D、获得良好综合力学性能12.钳工实习时做的小锤头,热处理应采用()。
A、淬火+低温回火 B、正火 C、退火 D、淬火+高温回火13.以下哪些不属于金属材料及热处理实践所需的仪器或设备A、箱式电炉B、邵氏硬度计C、洛氏硬度计D、维氏硬度计14.铸造机床床身一般采用的材料是() A、铸钢 B、可锻铸铁C、灰铸铁 D、球墨铸铁15.制造轴、齿轮、连杆、曲轴等机械零件,一般应选用。
A、耐磨钢 B、低碳钢C、中碳钢 D、高碳钢16.以下硬度值标示中,哪一项的写法是正确的。
A、HBS240 B、HRA80 C、55HRC D、HV80017.选择材料时,应考虑哪些原则()。
A、力学性能B、使用性能和工艺性能 C、化学性能18.用碳素工具钢制造的刀具能否用于高速切削为什么A、能,因硬度高B、不能,因硬度低C、能,因红硬性好D、不能,因红硬性差19.淬火后零件立即进行回火处理的目的是()。
A、提高硬度 B、提高强度C、降低脆性,提高韧性第三章铸造(/20)1. 在造型时,舂砂太松(紧),则会产生气孔。
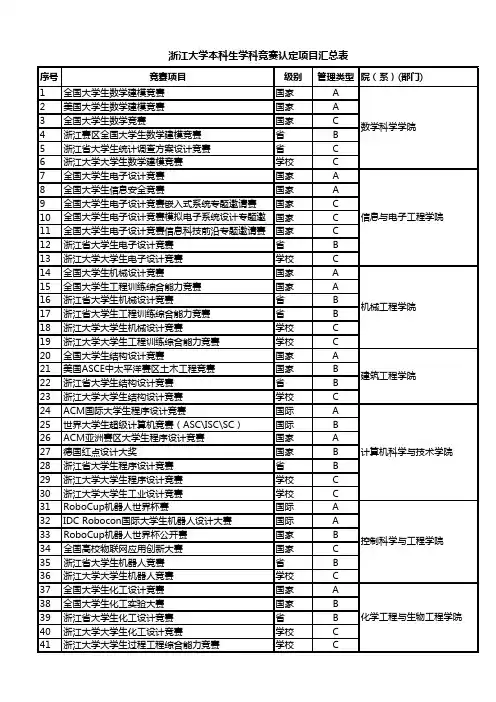

A类学科竞赛
一、“挑战杯”大学生课外学术科技作品竞赛
二、全国大学生数学建模竞赛
三、浙江省大学生电子商务竞赛
四、浙江省大学生电子设计竞赛
五、浙江省大学生力学竞赛
六、全国大学生机械设计竞赛
七、浙江省大学生多媒体作品设计竞赛
八、浙江省大学生工业设计竞赛
九、浙江省大学生财会信息化竞赛
十、浙江省第八届大学生程序设计竞赛
十一、浙江省第三届大学生生命科学竞赛
十二、浙江省大学生英语演讲竞赛
十三、浙江省大学生智能车竞赛
十四、浙江省大学生统计调查竞赛
十五、浙江省大学生服务外包竞赛
十六、浙江省大学生工程训练综合能力竞赛
十七、浙江省大学生职业生涯规划大赛
十八、国际大学生数学建模竞赛
十九、全国航空航天模型锦标赛
B类学科竞赛
一、全国大学生节能减排社会实践与科技竞赛
二、浙江省高校管理案例分析大赛
三、“创意杭州”工业设计大赛
四、浙江省大学生物理科技创新竞赛
五、白金创意平面设计学生作品大赛
六、第四届中国大学生公共关系策划大赛
七、2012年CCTV“希望之星”英语风采大赛杭州市决赛
八、2012年CCTV“希望之星”英语风采大赛浙江省决赛
九、2012年全国口译大赛浙江省决赛
十、第18届中国日报社“全国英语演讲比赛浙江省决赛十一、浙江省大学生高等数学竞赛。

关于举办浙江省第五届工程造价技能竞赛活动的通知根据省住房和城乡建设厅、省发展改革委、省财政厅联合印发的《关于颁发浙江省建设工程计价依据(2018版)的通知》(浙建建[2018]61号)要求,浙江省2018版计价依据从2019年1月1日起正式执行实施,为强化我市工程造价执(从)业人员专业能力、提高业务水平、选拔优秀人才、提供优秀人才展示平台。
经研究,决定举办“品茗杯”台州市第五届工程造价技能大赛。
现将有关事项通知如下:一、组织机构主办单位:台州市建设工程造价事务中心、台州市建筑工会承办单位:台州市建设工程造价管理协会协办单位:杭州品茗安控信息技术股份有限公司二、参赛对象全市工程造价执(从)业人员。
三、比赛内容(2018版)浙江省建设工程计价依据的应用。
四、比赛方式本次比赛线上线下相结合,分网络初赛和现场决赛二阶段。
1、网络初赛报名时间和方式:(1)报名时间:2019年12月9日-12月12日。
(2)报名方式:登录台州造价网(www。
tzzj。
cn),填写报名信息。
报名成功以后,可登陆竞赛系统熟悉初赛规则和初赛题型。
(3)初赛时间:2019年12月13-14日。
(4)初赛规则:比赛共60分钟,100分制,50道单选题。
参赛人员登录电脑端进行比赛,每位参赛者有2次考试机会,以2次中的最高分为依据,按分数排名,前60名选手进入下一轮决赛。
2、决赛时间和方式:(1)竞赛时间:2019年12月21日下午。
(2)决赛形式:现场竞答,不分专业,总时间预计90分钟。
利用手机的形式进行答题,共分为四个环节。
(3)地点:台州市(具体待定)。
(4)决赛规则:竞赛时长为60分钟,每位参赛选手只有一次答题机会。
可提早交卷,在规定时间内未完成比赛,系统自动提交试卷。
试卷提交,系统自动评分。
五、奖项设置1、本次比赛按照决赛总分排名情况设特等奖1名(奖金3000元)、一等奖3名(奖金各1500元)、二等奖5名(奖金各1000元)、三等奖7名(奖金各500元),以上获奖人员同时获得台州市“造价技能拔尖人员”荣誉。


关于参与第五届全国大学生工程训练综合能力竞赛的通知各学院:由全国大学生工程训练综合能力竞赛两委会(组委会、专家委员会)负责并报请教育部批准,第五届全国大学生工程训练综合能力竞赛国赛段将在沈阳航空航天大学和合肥工业大学两所高校各举办一场。
在沈阳航空航天大学举办的是“无碳小车越障竞赛”,命题及竞赛内容与第四届全国大学生工程训练综合能力竞赛国赛段相同。
在合肥工业大学举办的是“重力势能驱动的自控行走小车越障竞赛”。
学校决定在全校范围内选拔参赛队员,欢迎同学们积极参与。
本次参赛选手初选、复选及参赛指导等工作由工程训练中心负责组织实施。
现将有关事项通知如下:一、沈阳赛区的比赛命题与竞赛内容1.竞赛主题竞赛主题为“无碳小车越障竞赛”。
要求经过一定的前期准备后,在比赛现场完成一台符合本命题要求的可运行的机械装置,并进行现场竞争性运行考核。
每个参赛作品需要提交相关的设计、工艺、成本分析和工程管理4个文件及长度为3分钟的关于参赛作品设计及制作过程的汇报视频。
2.竞赛命题本届竞赛命题为“以重力势能驱动的具有方向控制功能的自行小车”。
设计一种小车,驱动其行走及转向的能量是根据能量转换原理,由给定重力势能转换而得到的。
该给定重力势能由竞赛时统一使用质量为1Kg的标准砝码(¢50×65 mm,碳钢制作)来获得,要求砝码的可下降高度为400±2mm。
标准砝码始终由小车承载,不允许从小车上掉落。
图1为小车示意图。
图1 无碳小车示意图要求小车在行走过程中完成所有动作所需的能量均由此给定重力势能转换而得,不可以使用任何其他来源的能量。
要求小车具有转向控制机构,且此转向控制机构具有可调节功能,以适应放有不同间距障碍物的竞赛场地。
要求小车为三轮结构。
具体设计、材料选用及加工制作均由参赛学生自主完成。
3.竞赛安排每个参赛队由3名在校本科大学生和1名指导教师及1名领队组成,参加校、省及全国竞赛。
3.1 本校制作参赛队按本竞赛命题的要求,在各自所在的学校内,自主设计,独立制作出一台参赛小车。

The 15th Zhejiang Provincial Collegiate Programming ContestSponsored byContest SectionApril 29, 2018Problem ListThis problem set should contain 13 (thirteen) problems on 17 (seventeen) numbered pages. Please inform a runner immediately if something is missing from your problem set.Prepared by Zhejiang University ACM/ICPC Problem Setter Team.Problem A.PeakDescriptionA sequence of n integers a1,a2,...,a n is called a peak,if and only if there exists exactly one integer k such that1<k<n,and a i<a i+1for all1≤i<k,and a i−1>a i for all k<i≤n.Given an integer sequence,please tell us if it’s a peak or not.InputThere are multiple test cases.Thefirst line of the input contains an integer T,indicating the number of test cases.For each test case:Thefirst line contains an integer n(3≤n≤105),indicating the length of the sequence.The second line contains n integers a1,a2,...,a n(1≤a i≤2×109),indicating the integer sequence. It’s guaranteed that the sum of n in all test cases won’t exceed106.OutputFor each test case output one line.If the given integer sequence is a peak,output“Yes”(without quotes), otherwise output“No”(without quotes).Examplestandard input standard output7515732 512121 41234 44321 31213212512312Yes No No No Yes No NoProblem B.King of KaraokeDescriptionIt’s Karaoke time!DreamGrid is performing the song Powder Snow in the game King of Karaoke.The song performed by DreamGrid can be considered as an integer sequence D1,D2,...,D n,and the standard version of the song can be considered as another integer sequence S1,S2,...,S n.The score is the number of integers i satisfying1≤i≤n and S i=D i.As a good tuner,DreamGrid can choose an integer K(can be positive,0,or negative)as his tune and add K to every element in D.Can you help him maximize his score by choosing a proper tune? InputThere are multiple test cases.Thefirst line of the input contains an integer T(about100),indicating the number of test cases.For each test case:Thefirst line contains one integer n(1≤n≤105),indicating the length of the sequences D and S. The second line contains n integers D1,D2,...,D n(−105≤D i≤105),indicating the song performed byDreamGrid.The third line contains n integers S1,S2,...,S n(−105≤S i≤105),indicating the standard version of the song.It’s guaranteed that at most5test cases have n>100.OutputFor each test case output one line containing one integer,indicating the maximum possible score. Examplestandard input standard output24123423465-5-4-3-2-1 543213 1NoteFor thefirst sample test case,DreamGrid can choose K=1and changes D to{2,3,4,5}.For the second sample test case,no matter which K DreamGrid chooses,he can only get at most1match.Problem C.Magic12MonthsDescriptionIt’s New Year’s Eve,and it’s also the best time of the year to play the card game Magic12Months to pray for good luck of the coming year.BaoBao has just found a deck of standard52playing cards(without Jokers)in his pocket and decides to play the game.The rules are as follows:1.Setup1.1.Remove the four‘K’s from the52cards.1.2.Shuffle the remaining48cards and divide them face down into12piles(4cards per pile)withequal probability.2.Gameplay2.1.Let p=1.2.2.Flip the card on the top of the p-th pile,check its rank r,and discard the card.2.3.If r is a number,let p=r;If r=‘A’,let p=1;If r=‘J’,let p=11;If r=‘Q’,let p=12.2.4.If the p-th pile is empty,the game ends;Otherwise go back to step2.2.When the game ends,having all the4cards of rank mflipped and discarded indicates that the m-th month in the coming year is a lucky month.BaoBao is in the middle of the game and has discarded n cards.He wants to know the probability that the i-th month of the coming year is a lucky month for all1≤i≤12when the game ends.Given these n cards,please help him calculate the answer.InputThere are multiple test cases.Thefirst line of input contains an integer T(about100)–the number of test cases.For each test case:Thefirst and only line contains an integer n(0≤n≤48)–the number offlipped cards,followed by the rank of the n cards r1,r2,...,r n(r i∈{A,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,J,Q})separated by a space in the order they areflipped.It’s guaranteed that the input describes a valid and possible situation of the game.OutputFor each test case output one line containing12numbers separated by a space,where the i-th number indicates the probability that the i-th month of the coming year is a lucky month.You should output a probability in its simplest fraction form A/B where A and B are coprime.Specifically, if the probability equals0,you should output0;If the probability equals1,you should output1. Please,DO NOT output extra spaces at the end of each line,or your answer may be considered incorrect! Examplestandard input3309Q10J Q10J10J J85765767663A24A2424472A3A4A Astandard output12/32/511/212/32/52/52/311/211/21/21/21/21/21/21/21/21/21/21/2100000000000Problem D.Sequence SwappingDescriptionBaoBao has just found a strange sequence{<s1,v1>,<s2,v2>,...,<s n,v n>}of length n in his pocket. As you can see,each element<s i,v i>in the sequence is an ordered pair,where thefirst element s i in the pair is the left parenthesis‘(’or the right parenthesis‘)’,and the second element v i in the pair is an integer.As BaoBao is bored,he decides to play with the sequence.At the beginning,BaoBao’s score is set to 0.Each time BaoBao can select an integer k,swap the k-th element and the(k+1)-th element in the sequence,and increase his score by(v k×v k+1),if and only if1≤k<n,s k=‘(’and s k+1=‘)’. BaoBao is allowed to perform the swapping any number of times(including zero times).What’s the maximum possible score BaoBao can get?InputThere are multiple test cases.Thefirst line of the input contains an integer T,indicating the number of test cases.For each test case:Thefirst line contains an integer n(1≤n≤103),indicating the length of the sequence.The second line contains a string s(|s|=n)consisting of‘(’and‘)’.The i-th character in the string indicates s i,of which the meaning is described above.The third line contains n integers v1,v2,...,v n(−103≤v i≤103).Their meanings are described above. It’s guaranteed that the sum of n of all test cases will not exceed104.OutputFor each test case output one line containing one integer,indicating the maximum possible score BaoBao can get.Examplestandard input standard output46)())()135-132 6)())()135-10032 3())1-1-13())-1-1-124 21 0 2NoteFor thefirst sample test case,the optimal strategy is to select k=2,3,5,4in order. For the second sample test case,the optimal strategy is to select k=2,5in order.Problem E.LISDescriptionDreamGrid is learning the LIS(Longest Increasing Subsequence)problem and he needs tofind the longest increasing subsequence of a given sequence a1,a2,...,a n of length n.Recall that•A subsequence b1,b2,...,b m of length m is a sequence satisfying b1=a k1,b2=a k2,...,b m=a kmand1≤k1<k2<···<k m≤n.•An increasing subsequence b1,b2,...,b m is a subsequence satisfying b1<b2<···<b m. DreamGrid defines the helper sequence f1,f2,...,f n where f i indicates the maximum length of the increasing subsequence which ends with a i.In case you don’t know how to derive the helper sequence,he provides you with the following pseudo-code which calculates the helper sequence.procedure lis_helper(a:original sequence){Let n be the length of the original sequence,f(i)be the i-th element in sequence f,and a(i)be the i-th element in sequence a}for i:=1to nf(i):=1for j:=1to(i–1)if a(j)<a(i)and f(j)+1>f(i)f(i):=f(j)+1return f{f is the helper sequence}DreamGrid has derived the helper sequence using the program,but the original sequence a1,a2,...,a n is stolen by BaoBao and is lost!All DreamGrid has in hand now is the helper sequence and two range sequences l1,l2,...,l n and r1,r2,...,r n indicating that l i≤a i≤r i for all1≤i≤n.Please help DreamGrid restore the original sequence which is compatible with the helper sequence and the two range sequences.InputThere are multiple test cases.Thefirst line of the input contains an integer T,indicating the number of test cases.For each test case:Thefirst line contains an integer n(1≤n≤105),indicating the length of the original sequence.The second line contains n integers f1,f2,...,f n(1≤f i≤n)seperated by a space,indicating the helper sequence.For the following n lines,the i-th line contains two integers l i and r i(0≤l i≤r i≤2×109),indicating the range sequences.It’s guaranteed that the original sequence exists,and the sum of n of all test cases will not exceed5×105. OutputFor each test case output one line containing n integers separated by a space,indicating the original sequence.If there are multiple valid answers,print any of them.Please,DO NOT print extra spaces at the end of each line,or your solution may be considered incorrect!Examplestandard input standard output46123243 052433123515512131 100200 200300 200400 400500 10050071231142 030303030303032111223123253 200300200500200 012003122Problem F.Now Loading!!!DescriptionDreamGrid has n integers a1,a2,...,a n.DreamGrid also has m queries,and each time he would like toknow the value of∑1≤i≤n ⌊ai⌈log p a i⌉⌋for a given number p,where⌊x⌋=max{y∈Z|y≤x},⌈x⌉=min{y∈Z|y≥x}.InputThere are multiple test cases.Thefirst line of input is an integer T indicating the number of test cases. For each test case:Thefirst line contains two integers n and m(1≤n,m≤5×105)–the number of integers and the number of queries.The second line contains n integers a1,a2,...,a n(2≤a i≤109).The third line contains m integers p1,p2,...,p m(2≤p i≤109).It is guaranteed that neither the sum of all n nor the sum of all m exceeds2×106.OutputFor each test case,output an integer(m ∑i=1i·z i)mod109,where z i is the answer for the i-th query. Examplestandard input standard output232 100100010000 1001045 2323223123123 123232423511366 45619Problem G.JUMPin’JUMP UP!!!DescriptionTired of solving mathematical equations,DreamGrid starts to solve equations related to strings:for two strings x and y with the same length consisting of lowercase English letters,calculate f(x,y,n),which is defined as the number of nonempty strings z consisting of lowercase English letters such that xz=zy and the length of z does not exceed n.DreamGrid has two strings s=s1s2...s n and t=t1t2...t m.He would like to ask several questions about the value of f(t,s[x..(x+m−1)],y),where s[x..(x+m−1)]is the substring of s starting from s x with length m and y is a given number.InputThere are multiple test cases.Thefirst line of input contains an integer T,indicating the number of test cases.For each test case:Thefirst line contains three integers n and m and q(1≤n,m,q≤105,m≤n)–the length of s,the length of t and the number of questions.The second line contains n lowercase English letters denoting the string s.The third line contains m lowercase English letters denoting the string t.Each of the next q lines contains two integers x i and y i(1≤x i≤n+1−m,1≤y i≤1018)denoting the i-th question.It is guaranteed that neither the sum of all n nor the sum of all q exceeds106.OutputFor each question,output an integer denoting the answer.Examplestandard input standard output1 423 abcd ba12 22 321 0 0Problem H.Game on a TreeDescriptionBaoBao is playing a game on a rooted tree with n vertices and(n−1)weighted edges.At the beginning of the game,a chess piece is placed on the root of the tree,which is vertex1.In each step,BaoBao can perform one of the four operations:1.Move the chess piece along an edge from its current vertex to a child vertex.This operation willcost BaoBao w units of value,where w is the weight of the edge.2.Jump the chess piece back to vertex1.This operation is free and won’t cost BaoBao any unit ofvalue.3.Set a“save point”on the current vertex of the chess piece.If a save point has been set on someother vertex before,the save point on the old vertex will be removed(so there will be at most one save point on the tree at the same time).This operation is free and won’t cost BaoBao any unit of value.4.Jump the chess piece back to the save point(the save point must be set before this operation).Thisoperation is free and won’t cost BaoBao any unit of value.The goal of the game is to visit every leaf vertex of the tree using the chess piece.Please help BaoBao calculate the minimum units of value he has to spend to achieve the goal.Recall that a leaf vertex of a tree is a vertex with no child.InputThere are multiple test cases.Thefirst line of the input contains an integer T,indicating the number of test cases.For each test case:Thefirst line contains one integer n(2≤n≤200),indicating the size of the tree.The following(n−1)lines each contains three integers u i,v i and w i(1≤u i,v i≤n,1≤w i≤109), indicating an edge connecting vertex u i and vertex v i with weight w i in the tree.It’s guaranteed that the given graph is a tree,and the sum of n over all test cases will not exceed2000. OutputFor each test case output one line containing one integer,indicating the minimum units of value BaoBao has to spend to achieve the goal.Example standardinputstandard output 381213112425426223738338121231341351261671681812100231341351261671681148107NoteThe trees of the sample test cases are shown above.For the first sample test case,BaoBao should perform the following operations:go to 2,save on 2,go to 4,go to 5,back to save (2),go to 6,back to root (1),go to 3,save on 3,go to 7,back to save (3),go to 8.For the second sample test case,BaoBao should perform the following operations:go to 2,go to 3,save on 3,go to 4,back to save (3),go to 5,back to root (1),go to 2,go to 6,save on 6,go to 7,back to save(7),go to 8.For the third sample test case,BaoBao should perform the following operations:go to 2,save on 2,go to 3,go to 4,back to save (2),go to 3,go to 5,back to save (2),go to 6,save on 6,go to 7,back to save (6),go to 8.Problem I.Magic PointsDescriptionGiven an integer n ,we say a point (x,y )on a 2D plane is a magic point,if and only if both x and y are integers,and exactly one of the following conditions is satisfied:•0≤x <n and y =0;•0≤x <n and y =n −1;•x =0and 0≤y <n ;•x =n −1and 0≤y <n .It’s easy to discover that there are 4n −4magic points in total.These magic points are numbered from 0to 4n −5in counter-clockwise order starting from (0,0).DreamGrid can create n magic lines from these magic points.Each magic line passes through exactly two magic points but cannot be parallel to the line x =0or y =0(that is to say,the coordinate axes).The intersections of the magic lines are called dream points,and for some reason,DreamGrid would like to make as many dream points as possible.Can you tell him how to create these magic lines?InputThere are multiple test cases.The first line of input contains an integer T (about 100),indicating the number of test cases.For each test case,there is only one integer n (2≤n ≤1000).OutputFor each case output 2n integers p 1,p 2,...,p 2n in one line separated by one space,indicating that in your answer,point p 2k −1and point p 2k is connected by a line for all 1≤k ≤n .If there are multiple answers,you can print any of them.Example standard inputstandard output32340213142536061938410NoteThe sample test cases are shown as follow:Problem J.CONTINUE...?DescriptionDreamGrid has n classmates numbered from1to n.Some of them are boys and the others are girls.Each classmate has some gems,and more specifically,the i-th classmate has i gems.DreamGrid would like to divide the classmates into four groups G1,G2,G3and G4such that:•Each classmate belongs to exactly one group.•Both G1and G2consist only of girls.Both G3and G4consist only of boys.•The total number of gems in G1and G3is equal to the total number of gems in G2and G4.Your task is to help DreamGrid group his classmates so that the above conditions are satisfied.Note that you are allowed to leave some groups empty.InputThere are multiple test cases.Thefirst line of input is an integer T indicating the number of test cases. For each test case:Thefirst line contains an integer n(1≤n≤105)–the number of classmates.The second line contains a string s(|s|=n)consisting of0and1.Let s i be the i-th character in the string s.If s i=1,the i-th classmate is a boy;If s i=0,the i-th classmate is a girl.It is guaranteed that the sum of all n does not exceed106.OutputFor each test case,output a string consists only of{1,2,3,4}.The i-th character in the string denotes the group which the i-th classmate belongs to.If there are multiple valid answers,you can print any of them;If there is no valid answer,output“-1”(without quotes)instead.Examplestandard input standard output5112103101400007 1101001-1-1314 1221 3413214Problem K.Mahjong SortingDescriptionDreamGrid has just found a set of Mahjong with3M suited tiles and a White Dragon tile in his pocket. Each suited tile has a suit(Character,Bamboo or Dot)and a rank(ranging from1to M),and there is exactly one tile of each rank and suit combination.Character tiles whose rank ranges from1to9Bamboo tiles whose rank ranges from1to9Dot tiles whose rank ranges from1to9White Dragon tileAs DreamGrid is bored,he decides to play with these tiles.Hefirst selects one of the3M suited tiles as the“lucky tile”,then he picks N tiles from the set of(3M+1)tiles and sorts these N tiles with the following rules:•The“lucky tile”,if contained in the N tiles,must be placed in the leftmost position.•For two tiles A and B such that neither of them is the“lucky tile”,if–A is a Character tile and B is a Bamboo tile,or–A is a Character tile and B is a Dot tile,or–A is a Bamboo tile and B is a Dot tile,or–A and B have the same suit and the rank of A is smaller than the rank of B, then A must be placed to the left of B.White Dragon tile is a special tile.If it’s contained in the N tiles,it’s considered as the original(not-lucky)version of the lucky tile during the sorting.For example,consider the following sorted tiles,where “3Character”is selected as the lucky tile.White Dragon tile,in this case,is considered to be the original not-lucky version of“3Character”and should be placed between“2Character”and“4Character”.As DreamGrid is quite forgetful,he immediately forgets what the lucky tile is after the sorting!Given N sorted tiles,please tell DreamGrid the number of possible lucky tiles.InputThere are multiple test cases.Thefirst line of the input contains an integer T,indicating the number of test cases.For each test case:Thefirst line contains two integers N and M(1≤N,M≤105,N≤3M+1),indicating the number of sorted tiles and the maximum rank of suited tiles.For the next N lines,the i-th line describes the i-th sorted tile counting from left to right.The line begins with a capital letter s i(s i∈{C,B,D,W}),indicating the suit of the i-th tile:•If s i=C,then an integer r i(1≤r i≤M)follows,indicating that it’s a Character tile with rank r i;•If s i=B,then an integer r i(1≤r i≤M)follows,indicating that it’s a Bamboo tile with rank r i;•If s i=D,then an integer r i(1≤r i≤M)follows,indicating that it’s a Dot tile with rank r i;•If s i=W,then it’s a White Drangon tile.It’s guaranteed that there exists at least one possible lucky tile,and the sum of N in all test cases doesn’t exceed106.OutputFor each test case output one line containing one integer,indicating the number of possible lucky tiles. Examplestandard input standard output439 C2 WC4 69 C2 C7 WB3 B4 D2 3100 C2 WC9 39 C1 B2 D32 4 7 25NoteFor thefirst sample,“2Character”and“3Character”are possible lucky tiles.For the second sample,“8Character”,“9Character”,“1Bamboo”and“2Bamboo”are possible lucky tiles.Problem L.Doki Doki Literature ClubDescriptionDoki Doki Literature Club!is a visual novel developed by Team Salvato.The protagonist is invited by his childhood friend,Sayori,to join their high school’s literature club.The protagonist then meets the other members of the club:Natsuki,Yuri,and the club president Monika.The protagonist starts to participate in the club’s activities such as writing and sharing poetry,and grows close to the four girls.What a lovely story!A very important feature of the game is its poetry writing mechanism.The player is given a list of various words to select from that will make up his poem.Each girl in the Literature Club has different word preferences,and will be very happy if the player’s poem is full of her favorite words.The poem writing mini-game(from wikipedia)BaoBao is a big fan of the game and likes Sayori the most,so he decides to write a poem to please Sayori.A poem of m words s1,s2,...,s m is nothing more than a sequence of m strings,and the happiness of Sayori after reading the poem is calculated by the formulaH=m∑i=1(m−i+1)·f(s i)where H is the happiness and f(s i)is Sayori’s preference to the word s i.Given a list of n words and Sayori’s preference to each word,please help BaoBao select m words from the list andfinish the poem with these m words to maximize the happiness of Sayori.Please note that each word can be used at most once!InputThere are multiple test cases.Thefirst line of input contains an integer T(about100),indicating the number of test cases.For each test case:Thefirst line contains two integers n and m(1≤m≤n≤100),indicating the number of words and the length of the poem.For the following n lines,the i-th line contains a string consisting of lowercased English letters w i (1≤|w i|≤15)and an integer f(w i)(−109≤f(w i)≤109),indicating the i-th word and Sayori’s preference to this word.It’s guaranteed that w i=w j for all i=j.OutputFor each test case output one line containing an integer H and m strings s1,s2,...,s m separated by one space,indicating the maximum possible happiness and the corresponding poem.If there are multiple poems which can achieve the maximum happiness,print the lexicographically smallest one.Please,DO NOT output extra spaces at the end of each line,or your answer may be considered incorrect!A sequence of m strings a1,a2,...,a m is lexicographically smaller than another sequence of m strings b1,b2,...,b m,if there exists a k(1≤k≤m)such that a i=b i for all1≤i<k and a k is lexicographically smaller than b k.A string s1=a1a2...a x is lexicographically smaller than another string s2=b1b2...b y,if there exists a k(1≤k≤min(x,y))such that a i=b i for all1≤i<k and a k<b k,or a i=b i for all1≤i≤min(x,y) and x<y.Examplestandard input standard output4108hello0world0 behind0far1be2spring10can15comes20 winter25if20055collegiate0 programming-5 zhejiang10 provincial5 contest-4532bcda1bcd1bbbbb132a1aa1aaa12018if winter comes can spring be far behind15zhejiang provincial collegiate programming contest 3bbbbb bcd3a aaProblem M.Lucky7DescriptionBaoBao has just found a positive integer sequence a1,a2,...,a n of length n from his left pocket and another positive integer b from his right pocket.As number7is BaoBao’s favorite number,he considers a positive integer x lucky if x is divisible by7.He now wants to select an integer a k from the sequence such that(a k+b)is lucky.Please tell him if it is possible.InputThere are multiple test cases.Thefirst line of the input is an integer T(about100),indicating the number of test cases.For each test case:Thefirst line contains two integers n and b(1≤n,b≤100),indicating the length of the sequence and the positive integer in BaoBao’s right pocket.The second line contains n positive integers a1,a2,...,a n(1≤a i≤100),indicating the sequence. OutputFor each test case output one line.If there exists an integer a k such that a k∈{a1,a2,...,a n}and(a k+b) is lucky,output“Yes”(without quotes),otherwise output“No”(without quotes).Examplestandard input standard output4374563747652 25252 426 100124No Yes Yes YesNoteFor thefirst sample test case,as4+7=11,5+7=12and6+7=13are all not divisible by7,the answer is“No”.For the second sample test case,BaoBao can select a7from the sequence to get7+7=14.As14is divisible by7,the answer is“Yes”.For the third sample test case,BaoBao can select a5from the sequence to get5+2=7.As7is divisible by7,the answer is“Yes”.For the fourth sample test case,BaoBao can select a100from the sequence to get100+26=126.As 126is divisible by7,the answer is“Yes”.。

第二章工程材料+热处理(16/18)×1. 低碳钢为了达到硬而耐磨,可采用淬火热处理工艺。
2. 在碳素钢中,为提高其性能,加入一种或多种合金元素,即成为合金钢。
(正确)3. 热处理工艺中淬硬性和淬透性的含义是一样的。
(错)4. 正火比退火过冷度大(冷却速度较快),获得的组织较细,因此正火的强度和硬度比退火高。
(错误)5. 焊接后为消除焊接应力,可采用退火工艺。
(正确)6. 造成热处理变形的主要原因,是淬火冷却时工件内部产生的内应力所致。
(正确)7. 为了获得优良的淬火质量,细而长的轴类零件、薄而平的零件,应垂直淬入冷却液中。
(错误)8. 金属材料的塑性,随温度的升高而降低。
(错误)9. 淬火加高温回火的工艺称为调质处理。
(正确)10. W18Cr4V是()。
A、工具钢 B、弹簧钢 C、不锈钢 D、耐热钢11.调质的目的是()。
A、提高硬度 B、降低硬度 C、改善切削性能D、获得良好综合力学性能12.钳工实习时做的小锤头,热处理应采用()。
A、淬火+低温回火 B、正火 C、退火 D、淬火+高温回火13.以下哪些不属于金属材料及热处理实践所需的仪器或设备A、箱式电炉B、邵氏硬度计C、洛氏硬度计D、维氏硬度计14.铸造机床床身一般采用的材料是() A、铸钢 B、可锻铸铁C、灰铸铁 D、球墨铸铁15.制造轴、齿轮、连杆、曲轴等机械零件,一般应选用。
A、耐磨钢 B、低碳钢C、中碳钢 D、高碳钢16.以下硬度值标示中,哪一项的写法是正确的。
A、HBS240 B、HRA80 C、55HRC D、HV80017.选择材料时,应考虑哪些原则()。
A、力学性能B、使用性能和工艺性能 C、化学性能18.用碳素工具钢制造的刀具能否用于高速切削为什么A、能,因硬度高B、不能,因硬度低C、能,因红硬性好D、不能,因红硬性差19.淬火后零件立即进行回火处理的目的是()。
A、提高硬度 B、提高强度C、降低脆性,提高韧性第三章铸造(/20)1. 在造型时,舂砂太松(紧),则会产生气孔。
关于举办浙江省第五届大学生力学竞赛选拔赛通知为了培养大学生的创新思维和实践动手能力,激发大学生学习力学与相关专业知识的热情,活跃校园学术氛围,培养团队协作精神,促进浙江省高校大学生相互交流与学习,将于2016 年11 月25 日-26 日在宁波大学举行浙江省第五届大学生力学竞赛。
为选拔优秀学生参赛,学校将举办浙江省第五届大学生力学竞赛选拔赛。
现将选拔赛具体事项通知如下:一、组织机构主办单位:教务处承办单位:机械工程学院二、参赛对象杭州电子科技大学在读本科生均可报名参加。
三、报名方式及截止日期1、填写报名表,在2016年7月15日前发送到,详见附件1。
2、根据附件2:浙江省第五届力学竞赛的通知中理论方案设计要求,撰写理论设计方案,于2016年9 月20 日前发送到联系人:王老师,联系电话:四、竞赛方式和时间安排举行时间:2016年10 月10日本次选拔赛包括理论方案设计、实物制作、飞行试验和答辩等环节, 具体比赛内容见附件。
校内选拔赛选出三队选手,经过集训代表学校参加浙江省第五届大学生力学竞赛。
五、项设置和评奖原则(1)评奖原则公平、公正、公开(2)奖项设置本次竞赛设置一等奖三名、二等奖五名,三等奖若干名附件1:第五届省大学生力学竞赛校选拔赛报名表附件2 :关于举行浙江省第五届大学生力学竞赛的通知关于举行浙江省第五届“宁工检测杯”大学生力学竞赛的通知各有关高校:浙江省大学生力学竞赛是以培养大学生的创新思维和实践动手能力,激发大学生学习力学与相关专业知识的热情,活跃校园学术氛围,培养团队协作精神,促进浙江省高校大学生相互交流与学习为目的省级竞赛。
经研究决定2016年举行浙江省第五届大学生力学竞赛。
现将竞赛具体事项通知如下:一、组织机构主办单位:浙江省教育厅承办单位:宁波工程学院赞助单位:宁波科捷建筑工程技术服务中心竞赛委员会:有关高校的教授、专家组成,主要负责竞赛的总体组织、指导、命题和评奖等工作。
首届浙江省大学生工程训练综合能力竞赛无碳小车设计说明书参赛者:潘沿龙韩昌吴总荣指导老师:张广海冯仁专2012-12-10目录摘要 (3)一绪论 (4)1.1本届竞赛命题主题 (4)1.2小车功能设计要求 (4)1.3小车整体设计要求 (4)二方案设计 (5)2.1车架 (5)2.2原动机构 (5)2.3传动机构 (6)2.4转向机构 (6)2.5行走机构 (7)2.6微调机构 (7)三技术设计 (8)3.1零部件设计 (8)3.2三维装配图 (9)四评价分析 (11)4.1小车优缺点 (11)4.2自动行走比赛时的前行距离估计 (11)4.3改进方向 (11)五参考文献 (11)六附录 (11)摘要第三届全国大学生工程训练综合能力竞赛命题主题为“无碳小车越障竞赛”。
在设计小车过程中特别注重设计的方法,力求通过对命题的分析得到清晰开阔的设计思路;作品的设计做到有系统性规范性和创新性;设计过程中综合考虑材料、加工、制造成本等给方面因素。
我们借鉴了优化设计、系统设计等现代设计发发明理论方法;采用了AutoCAD、SolidWorks等软件辅助设计。
我们把小车的设计分为三个阶段:方案设计、技术设计、制作调试。
通过每一阶段的深入分析、层层把关,使我们的设计尽可能向最优设计靠拢。
方案设计阶段根据小车功能要求我们根据机器的构成(原动机构、传动机构、执行机构、控制部分、辅助部分)把小车分为车架、原动机构、传动机构、转向机构、行走机构、微调机构六个模块,进行模块化设计。
分别针对每一个模块进行多方案设计,通过综合对比选择出最优的方案组合。
我们的方案为:车架采用分开式铝板、原动机构采用了阶梯轴、传动机构采用两级齿轮、转向机构采用凸轮滑杆、行走机构采用差速器、微调机构采用微调螺母螺钉。
技术设计阶段我们在实体建模的基础上对每一个零件进行了详细的设计,综合考虑零件材料性能、加工工艺、成本等。
小车部分零件是标准件,可以购买,同时除部分要求加工精度高的部分需要特殊加工外,大多数都可以通过手工加工出来。
2018年第五届浙江省大学生工程训练综合能力竞赛暨第六届全国大学生工程训练综合能力竞赛预赛的通知(第二轮)浙科竞〔2018〕21号各高校:为了推动高等教育内涵式发展,促进大学生工程实践和创新能力的提升,促进浙江省高校创客教育工作,根据教育部《关于开展全国大学生工程训练综合能力竞赛的通知》(教高司函﹝2009)78号)和省教育厅《关于公布2018年浙江省大学生科技竞赛赛项的通知》文件要求,经研究,定于2018年11月30日-12月2日在杭州电子科技大学(下沙)举行2018年第五届浙江省大学生工程训练综合能力竞赛暨第六届全国大学生工程训练综合能力竞赛预赛,第一轮具体事项通知如下:一、组织机构主办单位: 浙江省大学生科技竞赛委员会秘书处单位:浙江大学承办单位: 杭州电子科技大学二、竞赛主题1.竞赛主题:智能物流本主题主要是模拟离散制造业的智能物流小车,小车具有车间作业中的物料扫码识别、搬运、码垛和循迹等功能。
学生通过前期准备完成一套符合本命题要求的可运行装置,进行现场竞争性运行、现场拆改调试和现场加工的考核。
每个参赛作品根据项目不同提交结构设计方案、加工工艺方案、电路设计方案和创业企划书等报告。
以培养学生的实践动手能力和创新能力。
2.竞赛命题:智能物流小车(1)关于小车:自主设计制作智能物流小车,该小车应具有赛道自主行走、物料扫码识别、规避障碍、轨迹判断、自动转向和制动等功能。
这些功能可由机械或电控装置自动实现,不允许使用人工交互遥控,在指定场地完成规避障碍物并抓取目标物料放置到指定地点。
具体设计、材料选用及加工制作均由参赛学生自主完成。
行走车体、抓取执行机构件可由激光切割、3D打印、数控及雕刻等机加工方式自行设计制作,也可使用建议套件组;电控器件、主控板、检测元器件、电机和电池可使用建议套件组,或采用标准件,其中整车电池最大供电电压不超过9V。
(验车时提供相关电控部件规格及技术指标说明文档,验车不合格取消参赛资格。