整数规划及美赛题目-数模第二次培训
- 格式:pptx
- 大小:422.90 KB
- 文档页数:28

数学建模美赛2024题目全文共四篇示例,供读者参考第一篇示例:今年的题目是关于气候变化和环境保护的议题。
题目涉及到了全球变暖对气候和环境的影响,以及如何通过有效的政策和措施来减缓这种影响。
参赛者需要结合大量的气象数据、环境数据和经济数据,建立数学模型来分析不同政策对环境的影响,并提出具体的政策建议。
题目要求参赛者首先了解全球变暖的背景和影响,包括气候变化对冰川、海平面和生态系统的影响。
然后需要收集大量的数据,包括气温、降水、二氧化碳排放量等信息,建立数学模型来模拟气候变化的趋势和影响。
在此基础上,参赛者需要分析不同政策对气候和环境的影响,比如减排政策、再生能源政策、森林保护政策等。
最终,他们需要提出具体的政策建议,用数学模型来验证这些政策的有效性和可行性。
这道题目不仅考验参赛者的数学建模能力,还要求他们具备丰富的跨学科知识和分析能力。
参赛者需要深入了解气候变化和环境问题的本质,同时还需要掌握大量的数据处理和模型建立技巧。
他们需要运用数学、统计学、计算机科学等知识,同时还要具备创新思维和团队合作能力。
通过参与这项挑战性的比赛,大学生们不仅可以提升自己的数学建模能力,还可以培养跨学科的综合能力和团队合作精神。
这对于他们未来从事科研、工程或管理等领域的工作都将大有裨益。
这也是一次展示自己才华和创造力的绝佳机会,可以让他们在学术界和工业界获得更多的认可和机会。
2024年美国大学生数学建模竞赛的题目涉及到了气候变化和环境保护这一全球性议题,要求参赛者建立数学模型来分析不同政策对环境的影响,并提出具体的政策建议。
这是一项极具挑战性和实践意义的比赛,将为参赛者提供一个全面发展和展示自己才华的平台。
希望所有参赛者都能在这场比赛中收获满满的成绩和经验!第二篇示例:2024年美国大学生数学建模竞赛(MCM/ICM)是一个全球性的高水平数学建模比赛。
在这个比赛中,参赛队伍需要在72小时内利用自己的数学建模技能解决提出的真实世界问题。

2024美赛数学建模题目
2024年美国大学生数学建模竞赛(MCM/ICM)赛题包括以下六道题目:
MCM A(环境类)题目:遭受旱灾的植物群落。
题目要求建立预测模型,预测植物群落未来随时间的变化。
MCM B(环境类、政策类)题目:重新想象马赛马拉。
题目难度主要在数据不好找,预测动物和人们相互作用的模型。
MCM C(数图、图论优化类知识)题目:预测单词结果。
可以采用神经网络模型,利用隶属度函数进行分类,用聚类模型转换为不同的类,再用神经网络作为输出。
ICM D 题目:联合国可持续发展目标的优先顺序。
关键在数据层面,构建
各个指标之间的关系网络,各个指标之间存在限制。
ICM E(环境类)题目:光污染。
难度系数主要还是在获取光污染的数据上。
ICM F 题目:绿色GDP。
择某个标准来计算绿色GDP,基于水资源安全的模型来构建它对全球气候变化的影响。
以上就是2024年美国大学生数学建模竞赛的六道赛题,每道题目的主题和要求均已给出。
如需更多信息,可以登录美赛官网进行查询。

2021数学建模美赛题目摘要:一、引言1.介绍2021 年数学建模美赛2.分析赛题背景及挑战性二、赛题概述1.题目一:疫苗分配1.1 问题背景1.2 问题描述1.3 问题分析2.题目二:航空碳排放2.1 问题背景2.2 问题描述2.3 问题分析3.题目三:交通网络优化3.1 问题背景3.2 问题描述3.3 问题分析三、建模思路与方法1.针对题目一的建模思路2.针对题目二的建模思路3.针对题目三的建模思路四、案例分析与讨论1.针对题目一的案例分析2.针对题目二的案例分析3.针对题目三的案例分析五、总结与展望1.总结2021 年数学建模美赛的特点2.对未来数学建模竞赛的展望正文:一、引言2021 年数学建模美赛是美国数学及其应用联合会(MAA)举办的一场面向全球大学生的数学建模竞赛。
该竞赛旨在通过对现实世界问题的抽象和建模,提高参赛者的创新思维、团队协作和数学应用能力。
2021 年的赛题涵盖了疫苗分配、航空碳排放和交通网络优化等热点问题,为参赛者带来了全新的挑战。
二、赛题概述1.题目一:疫苗分配1.1 问题背景在全球抗击新冠病毒的过程中,疫苗的分配成为了关键因素。
如何合理地将有限的疫苗分配到各个国家和地区,以最大程度地保护人们的生命安全和减少疫情对社会经济的影响,是一个亟待解决的问题。
1.2 问题描述给定一定数量的疫苗,以及各国家和地区的人口、接种意愿、疫情严重程度等信息,需要建立一个模型来预测不同分配策略下的接种效果,并为决策者提供优化建议。
1.3 问题分析本问题涉及多目标优化、动态规划、模拟仿真等多种数学方法,需要参赛者灵活运用数学工具解决实际问题。
2.题目二:航空碳排放2.1 问题背景随着航空业的快速发展,碳排放问题日益受到关注。
为了减缓气候变化,需要制定合理的航空碳排放政策。
2.2 问题描述给定一定时期内的航班计划、机型、航线等信息,需要建立一个模型来预测碳排放量,并为政策制定者提供优化建议。

第二套培训题A 题:在自身仓库容量有限条件下的随机存贮策略工厂生产需定期地定购各种原料,商家销售要成批地购进各种商品。
无论是原料或商品,都有一个怎样存贮的问题。
存得少了无法满足需求,影响利润;存得太多,存贮费用就高,也影响利润。
因此说存贮管理是降低成本、提高经济效益的有效途径和方法。
问题一:某商场销售的某种商品。
市场上这种商品的销售速率假设是不变的,记为r ;每次进货的订货费为常数1c 与商品的数量和品种无关;使用自己的仓库存贮商品时,单位商品每天的存贮费用记为2c ,由于自己的仓库容量有限,超出时需要使用租借的仓库存贮商品,单位商品每天的存贮费用记为3c ,且32c c ≤;允许商品缺货,但因缺货而减少销售要造成损失,单位商品的损失记为4c ;每次订货,设货物在X 天后到达,交货时间X 是随机的;自己的仓库用于存贮该商品的最大容量为0Q ,每次到货后使这种商品的存贮量q 补充到固定值Q 为止,且Q Q <0;在销售过程中每当存贮量q 降到L 时即开始订货。
请你给出求使总损失费用达到最低的订货点*L (最优订货点)的数学模型。
问题二:以下是来自某个大型超市的关于三种商品的真实数据: 商品一:康师傅精装巧碗香菇炖鸡面r =12盒/天;1c =10元;2c =0.01元/盒.天;3c =0.02元/盒.天;4c =0.95元/盒.天; 0Q =40盒;Q =60盒,共有连续的36次订货后到达时间天数记录如下:3 3 7 1 2 3 3 0 34 6 3 1 4 3 3 25 2 3 2 5 3 2 3 3 0 3 4 3 1 4 5 4 3 1商品二:心相印手帕纸10小包装r =15盒/天;1c =10元;2c =0.03元/盒.天;3c =0.04元/盒.天;4c =1.50元/盒.天; 0Q =40盒;Q =60盒。
共有连续的43次订货后到达天数记录如下:4 2 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 2 1 2 4 3 2 3 2 2 4 2 3 4 3 3 2 3 2 3 2 2 1 3 25 3 2 4 2 2 商品三:中汇香米5KG 装r =20袋/天;1c =10元;2c =0.06元/袋.天;3c =0.08元/袋.天;4c =1.25元/袋.天; 0Q =20袋;Q =40袋,共有连续的61次订货后到达天数记录如下:3 4 4 2 3 3 2 2 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 5 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 2 2 3 3 1 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 3 2 5 6 3 4 3 1。

Problem A Rotating Grill Design for oscillating fanOne common type of oscillating directional electronic fan is a rotate grill fan. The key technology is the shape and speed of the rotating grill. The special-designed grill rotates to direct air for wide circulation. The clockwise and counter clockwise motion changes airflow direction.Please consider the factors of natural breeze, and build a breeze mode to design the grill to make the air from the fan to be comfortable.一种用于振动风机的旋转格栅设计问题一种常见的振动定向电子风机是一种旋转式格栅风机。
关键技术是旋转格栅的形状和速度。
特别设计的烧烤炉旋转,以直接空气流通。
顺时针和逆时针方向运动改变气流方向。
请考虑自然因素的微风,并建立风模式设计的格栅,使空气从风扇舒适。
Problem B Red Sun in the Morning: find an exit strategyRed sun at night, sailors' delight. Red sun in the morning, sailors take warning.Ten years ago hurricane Katrina had a devastating effect on the economies of several states, causing many deaths and much suffering. Comprehensive evacuation plans have been developed since then, but the authorities still want to improve their effectiveness. Your team has been hired by the Mississippi Emergency Management Administration (MSEMA) to review their current evacuation strategies.Things to keep in mind: All hurricanes are assigned a category: from 1 (the weakest) to 5 (the strongest, like Katrina). The category and the location of landfall are first predicted about 4 days in advance. Predictions are revised using updated information 48 hours later, and the final (most accurate) predictions become available 24 hours ahead of the expected landfall. The category of the hurricane and the actual location of the landfall determine which counties will be flooded. In addition, driving conditions in surrounding counties might be seriously affected by the size of the hurricane.Build a model to advise MSEMA on an optimal strategy: which counties should be ordered to evacuate, when, and where to. The first page of your manuscript should be a one page non-technical, executive summary for the governor of Mississippi. It should describe your main recommendations, the criteria you used to evaluate their effectiveness, and any caveats you believe are important to mention.%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%Time permitting, your model should also account for the fact that evacuations initiated in Louisiana, Alabama, and Mississippi affect each other. For example, a large portion of the New Orleans population will likely evacuate through Jackson, MS using highways 59 and 55. If the population of Jackson needs to evacuate, much of it will be directed North within MS or West toward Monroe, LA. Parts of coastal counties in MS will evacuate through Mobile, AL.Despite these interdependencies, the decisions in each state are rarely made collaboratively. So, if you are a governor in one of these states and you order the evacuation later than the others, the population of your state might be at disadvantage since the roads will be already clogged by then. If thehurricane turns out to be stronger than expected, your constituents might end up stuck in traffic in affected areas. On the other hand, if you order the evacuation too early, this disruption carries a high economic cost –coastal areas generate much revenue for your state and early predictions about the expected hurricane strength/landfall time/location might be inaccurate.夜晚的红太阳,水手们的喜悦。

Problem A Warmer Days or Sour Grapes ?The high quality of wines(葡萄酒)produced in the Finger Lakes Region(五指湖区)of upstate (北部)New York is widely known. Proximity(接近)to lakes tempers the climate and makes it more suitable for growing several varieties of premium(独特)grapes: R iesling(雷司令), G ewürztraminer(琼瑶浆),C hardonnay(霞多丽), M erlot(梅洛), P inot Noir(黑比诺), and CabernetF ranc(品丽珠). (There are many more, but we will restrict(限制)the discussion to these six to simplify(简化)the modeling.) Each variety has its own preferred “average temperature” range but is also different in its susceptibility(感受性)to diseases and ability to withstand(抵抗)short periods of unusually cold temperature.As our local climate changes, the relative suitability of these varieties will be changing as well. A forward-looking winery(酒厂)has hired your team to help with the long-term planning. You will need to recommenda) the proportion(比例)of the total vineyard(葡萄园)to be used for growing each of the above six varieties;b) and when should these changes be implemented (实施)(based on observed temperatures and/or current market prices for each type of wine).Naturally, the winery is interested in maximizing its annual profit. But since the latter (后者)is weather-dependent, it might vary a lot year-to-year. You are also asked to evaluate the trade-offs (权衡)between optimizing the expected/average case versus the worst(-realistic-)scenario(情景).Things to keep in mind:Climate modeling is complicated(复杂)and predicting the rate of “global warming” is a hotly debated area. For the purposes of this problem, assume that the annual average temperature in Ithaca(伊萨卡), NY will increase by no more than 4°C by the end of this century.It is not all about the average temperature – a short snap(临时)of sub- zero(零度)temperature in late Ferburay or early March (after the vines already started getting used to warmer weather) is far more damaging than the same low temperature would be in the middle of the winter.It takes at least 3 years for a newly planted vine to start producing grapes suitable for winemaking.Problem B Outlook of Car-to-Car TechSAN FRANCISCO -- After more than a decade of research into car-to-car communications, U.S. auto safety regulators took a step forward today by unveiling their plan for requiring cars to have wireless gear that will enable them to warn drivers of danger.These vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) transmitters and software could save thousands of lives and prevent hundreds of thousands of crashes each year by providing cars with information they never will be able to gather simply from cameras and sensors. “Safety is our top priority, and V2V technology represents the next great advance in saving lives,” Transportation Secretary Anthony Foxx said in an announcement. “This technology could move us from helping people survive crashes to helping them avoid crashes altogether.”Requirement 1: Present a mathematical model to discuss the reduction of the number of traffic accidents and road fatalities/injuries in San Francisco by V2V technology. Requirement 2: Determine the maximum number of cars in San Francisco due to the V2V technology.Requirement 3: Discuss the benefits of V2V technology to alleviate road congestion. Requirement 4: Provide your recommendation to the government.Prblem C Forest FiresOne major environmental concern is the occurrence of forest fires (also called wildfires), which affect forest preservation, bring economical and ecological damage and endanger human lives. Such phenomenon is due to multiple causes (e.g. human negligence and lightnings). Despite an increasing of state expenses to control this disaster, each year millions of forest hectares (ha) are destroyed all around the world.Fast detection is an important element for successful firefighting. Traditional human surveillance is expensive and affected by subjective factors, there has been an emphasis to develop automatic solutions, such as satellite-based, infrared/smoke scanners and local sensors (e.g. meteorological). Propagation models try to describe the future evolution of the forest fire given an initial scenario and certain input parameters. Modeling the dynamical behavior of fire propagation in a forest is helpful for creating scheme to control and fight fire.Requirement 1 Describe several different metrics that could be used to evaluate the effectiveness of fire detection. Could you combine your metrics to make them even more useful for measuring quality?Requirement 2 Model the dynamical behavior of fire spread in a forest. Requirement 3 Discuss the factors to affect fire occurrence. Which factors are the most critical in causing fires. Build mathematical models to predict the burned area of fires using Meteorological Data.Requirement 4 Give y our suggestion for preventing from forest fire and fighting against it.Problem D Wearable Activity RecognitionThe percentage of EU citizens aged 65 years or over is projected to increase from 17.1% in 2008 to 30.0% in 2060. In particular, the number of 65 years old is projected to rise from 84.6 million to 151.5 million, while the number of people aged 80 or over is projected to almost triple from 21.8 million to 61.4 million (EUROSTAT: New European Population projections 2008–2060). It has been calculated that the purely demographic effect of an ageing population will push up health-care spending by between 1% and 2% of the gross domestic product (GDP) of most member states. At first sight this may not appear to be very much when extended over several decades, but on average it would in fact amount to approximately a 25% increase in spending on health care, as a share of GDP, in the next 50 years (European Economy Commission, 2006). The effective incorporation of technology into health-care systems could therefore be decisive in helping to decrease overall public spending on health. One of these emerging health-care systems is daily living physical activity recognition.Daily living physical activity recognition is currently being applied in chronic disease management (Amft & Troter, 2008; Zwartjes, Heida, van Vugt, Geelen, & Veltink, 2010), rehabilitation systems (Sazonov, Fulk, Sazonova, & Schuckers, 2009) and disease prevention (Sazonov, Fulk, Hill, Schutz, & Browning, 2011; Warren et al., 2010), as well as being a personal indicator to health status (Arcelus et al., 2009). One of the principal subjects of the health related applications being mooted is the monitoring of the elderly. For example, falls represent one of the major risks and obstacles to old people’s independence (Najafi, Aminian, Loew, Blanc, & Robert, 2002; Yu, 2008). This risk is increased when some kind of degenerative disease affects them. Most Alzheimer’s patients, for exa mple, spend a long time every day either sitting or lying down since they would otherwise need continuous vigilance and attention to avoid a fall.The registration of daily events, an important task in anticipating and/or detecting anomalous behavior patterns and a primary step towards carrying out proactive management and personalized treatment, is normally poorly accomplished by patients’ families, healthcare units or auxiliary assistants because of limitations in time and resources. Automatic activity-recognition systems could allow us to conduct a completely detailed monitoring and assessment of the individual, thus significantly reducing current human supervision requirements.Most wearable activity recognition systems assume a predefined sensor deployment that remains unchanged during runtime. However, this assumption does not reflect real-life conditions. During the normal use of such systems, users may place the sensors in a position different from the predefined sensor placement. Also, sensors may move from their original location to a different one, due to a loose attachment. Activity recognition systems trained on activity patterns characteristic of a given sensor deployment may likely fail due to sensor displacements.Your task is as follows.(1) Build models to recognize daily living activities.(2) Explore the effects of sensor displacement induced by both the intentionalmisplacement of sensors and self-placement by the user.(3) Verify your recognition models’ toleranc e to sensor displacement.Data Set Information:The REALDISP (REAListic sensor DISPlacement) dataset has been originally collected to investigate the effects of sensor displacement in the activity recognition process in real-world settings. It builds on the concept of ideal-placement, self-placement and induced- displacement. The ideal and mutual-displacement conditions represent extreme displacement variants and thus could represent boundary conditions for recognition algorithms. In contrast, self-placement reflects a users perception of how sensors could be attached, e.g., in a sports or lifestyle application. The dataset includes a wide range of physical activities (warm up, cool down and fitness exercises), sensor modalities (acceleration, rate of turn, magnetic field and quaternions) and participants (17 subjects). Apart from investigating sensor displacement, the dataset lend itself for benchmarking activity recognition techniques in ideal conditions.Dataset summary:#Activities: 33#Sensors: 9#Subjects: 17#Scenarios: 3ACTIVITY SET:A1: WalkingA2: JoggingA3: RunningA4: Jump upA5: Jump front & backA6: Jump sidewaysA7: Jump leg/arms open/closedA8: Jump ropeA9: Trunk twist (arms outstretched)A10: Trunk twist (elbows bent)A11: Waist bends forwardA12: Waist rotationA13: Waist bends (reach foot with opposite hand)A14: Reach heels backwardsA15: Lateral bend (10_ to the left + 10_ to the right)A16: Lateral bend with arm up (10_ to the left + 10_ to the right)A17: Repetitive forward stretchingA18: Upper trunk and lower body opposite twistA19: Lateral elevation of armsA20: Frontal elevation of armsA21: Frontal hand clapsA22: Frontal crossing of armsA23: Shoulders high-amplitude rotationA24: Shoulders low-amplitude rotationA25: Arms inner rotationA26: Knees (alternating) to the breastA27: Heels (alternating) to the backsideA28: Knees bending (crouching)A29: Knees (alternating) bending forwardA30: Rotation on the kneesA31: RowingA32: Elliptical bikeA33: CyclingSENSOR SETUP:Each sensor provides 3D acceleration (accX,accY,accZ), 3D gyro (gyrX,gyrY,gyrZ), 3D magnetic field orientation (magX,magY,magZ) and 4D quaternions (Q1,Q2,Q3,Q4). The sensors are identified according to the body part on which is placed respectively:。

2015数学建模美赛试题编辑整理:尊敬的读者朋友们:这里是精品文档编辑中心,本文档内容是由我和我的同事精心编辑整理后发布的,发布之前我们对文中内容进行仔细校对,但是难免会有疏漏的地方,但是任然希望(2015数学建模美赛试题)的内容能够给您的工作和学习带来便利。
同时也真诚的希望收到您的建议和反馈,这将是我们进步的源泉,前进的动力。
本文可编辑可修改,如果觉得对您有帮助请收藏以便随时查阅,最后祝您生活愉快业绩进步,以下为2015数学建模美赛试题的全部内容。
地球资源的消耗速度快,越来越多的人关注人类社会的未来.自1960年以来,已经有许多专家研究可持续发展.然而大多数人的研究对象是整个世界,一个国家或一个地区。
几乎没有人选择48个最不发达国家(LDC)在联合国为研究对象列表。
然而,LDC国家集团共享许多相同的点。
他们的发展道路也有法律的内涵。
本文选择这些国家为研究对象针对发现常规的可持续发展道路。
本文组织如下.第二部分介绍研究的背景和本研究的意义。
第三节描述了我们对可持续发展的理解细节和显示我们的评估系统的建立过程和原理,那么我们估计每一个国家的LDC和获得可持续发展的能力和等级。
第四节提供了一个最糟糕的国家毛里塔尼亚计划指数在第三节。
第五节演示了在第四节的合理性和可用性计划。
最后在第六节总结本文的主要结论和讨论的力量和潜在的弱点。
地球上的资源是有限的。
三大能源石油、天然气和煤炭可再生。
如何避免人类的发展了资源枯竭和实现可持续发展目标是现在的一个热门话题.在过去的两个世纪,发达国家已经路上,先污染,再控制和达到高水平的可持续发展。
发展中国家希望发展和丰富。
然而,因为他们的技术力量和低水平的经济基础薄弱,浪费和低效率的发展在这些国家是正常的.所以本文主要关注如何帮助发展中国家特别是48在联合国最不发达国家实现可持续发展是列表可持续发展的理解是解决问题的关键.可持续发展的定义经历了一个长期发展的过程.在这里,布伦特兰可持续发展委员会的简短定义的"能力发展可持续- — - — - -以确保它既满足现代人的需求又不损害未来的能力代来满足自己的需求"[1]无疑是最被广泛接受的一个在各种内吗定义.这个定义方面发挥了重要作用在很多国家的政策制定的过程.然而,为了证明一个国家的现状是否可持续不可持续的,更具体的定义是必要的更具体的概念,我们认为,如果一个国家的发展是可持续的,它应该有一个基本的目前的发展水平,一个平衡的国家结构和一个光明的未来。

启航系列之数学建模培训资料(第二次)专题1:线性规划在人们的生产实践中,经常会遇到如何利用现有资源来安排生产,以取得最大经济效益的问题。
此类问题构成了运筹学的一个重要分支—数学规划,而线性规划(Linear Programming 简记LP)则是数学规划的一个重要分支。
自从1947年G . B. Dantzig 提出求解线性规划的单纯形方法以来,线性规划在理论上趋向成熟,在实用中日益广泛与深入。
特别是在计算机能处理成千上万个约束条件和决策变量的线性规划问题之后,线性规划的适用领域更为广泛了,已成为现代管理中经常采用的基本方法之一。
1.1 线性规划的实例与定义例1 某机床厂生产甲、乙两种机床,每台销售后的利润分别为4000元与3000元。
生产甲机床需用B A 、机器加工,加工时间分别为每台2小时和1小时;生产乙机床需用C B A 、、三种机器加工,加工时间为每台各一小时。
若每天可用于加工的机器时数分别为A 机器10小时、B 机器8小时和C 机器7小时,问该厂应生产甲、乙机床各几台,才能使总利润最大?上述问题的数学模型:若设该厂生产1x 台甲机床和2x 乙机床时总利润最大,则21,x x 应满足(目标函数)2134maxx x z += (1)s.t.(约束条件)⎪⎪⎩⎪⎪⎨⎧≥≤≤+≤+0,781022122121x x x x x x x (2)这里变量21,x x 称之为决策变量,(1)式被称为问题的目标函数,(2)中的几个不等式是问题的约束条件,记为s.t.(即subject to)。
上述即为一规划问题数学模型的三个要素。
由于上面的目标函数及约束条件均为线性函数,故被称为线性规划问题。
总之,线性规划问题是在一组线性约束条件的限制下,求一线性目标函数最大或最小的问题。
在解决实际问题时,把问题归结成一个线性规划数学模型是很重要的一步,但往往也是困难的一步,模型建立得是否恰当,直接影响到求解。
而选取适当的决策变量,是我们建立有效模型的关键之一。
2006数学建模培训第二阶段题目要求:两题都做,层次是由简入繁。
用LINGO软件编程求解。
A生产计划问题某公司用两种原油(A和B)混合加工成两种汽油(甲和乙)。
甲、乙两种汽油含原油A的最低比例分别为50%和60%,每吨售价分别为4800元和5600元。
该公司现有原油A 和B的库存量分别为500t,还可以从市场上买到不超过1500t的原油A。
原油A的市场价为:购买量不超过500t时的单价为10000元/t;购买量超过500t但不超过1000t时,超过500t的部分8000元/t;购买量超过1000t时,超过1000t的6000元/t。
该公司应如何安排原油的采购和加工。
B有瓶颈设备的多级生产计划问题有制造企业的中期生产计划管理中,常常要考虑如下的生产计划优化问题:在给定的外部需求和生产能力等限制条件下,按照一定的生产目标编制未来若干生产周期的最优生产计划,这种问题一般称为批量问题。
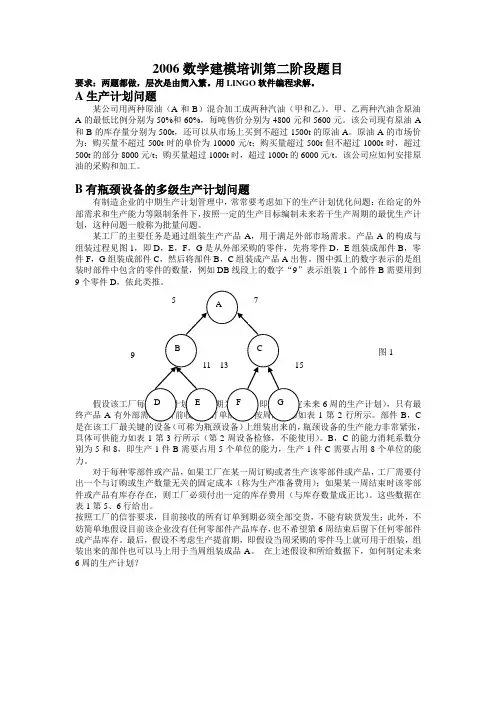
某工厂的主要任务是通过组装生产产品A,用于满足外部市场需求。
产品A的构成与组装过程见图1,即D,E,F,G是从外部采购的零件,先将零件D,E组装成部件B,零件F,G组装成部件C,然后将部件B,C组装成产品A出售。
图中弧上的数字表示的是组装时部件中包含的零件的数量,例如DB线段上的数字“9”表示组装1个部件B需要用到9个零件D,依此类推。
图16周的生产计划),只有最终产品A第2行所示。
部件B,C具体可供能力如表1第3行所示(第2周设备检修,不能使用)。
B,C的能力消耗系数分别为5和8,即生产1件B需要占用5个单位的能力,生产1件C需要占用8个单位的能力。
对于每种零部件或产品,如果工厂在某一周订购或者生产该零部件或产品,工厂需要付出一个与订购或生产数量无关的固定成本(称为生产准备费用);如果某一周结束时该零部件或产品有库存存在,则工厂必须付出一定的库存费用(与库存数量成正比)。
这些数据在表1第5、6行给出。
按照工厂的信誉要求,目前接收的所有订单到期必须全部交货,不能有缺货发生;此外,不妨简单地假设目前该企业没有任何零部件产品库存,也不希望第6周结束后留下任何零部件或产品库存。


实验05 数学规划模型㈡(2学时)(第4章数学规划模型)1.(求解)汽车厂生产计划(LP,整数规划IP)p101~102(1) (LP)在模型窗口中输入以下线性规划模型max z = 2x1 + 3x2 + 4x3s.t. 1.5x1 + 3x2 + 5x3≤ 600280x1 + 250x2 + 400x3≤ 60000x1, x2, x3≥ 0并求解模型。
★(1) 给出输入模型和求解结果(见[101]):(2) (IP)在模型窗口中输入以下整数规划模型max z = 2x1 + 3x2 + 4x3s.t. 1.5x1 + 3x2 + 5x3≤ 600280x1 + 250x2 + 400x3≤ 60000x1, x2, x3均为非负整数并求解模型。
LINGO函数@gin见提示。
★(2) 给出输入模型和求解结果(见[102]模型、结果):2.(求解)原油采购与加工(非线性规划NLP ,LP 且IP )p104~107模型:已知 ⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧≤≤+≤≤+≤≤=)15001000(63000)1000500(81000)5000(10)(x x x x x xx c注:当500 ≤ x ≤ 1000时,c (x ) = 10 × 500 + 8( x – 500 ) = (10 – 8 ) × 500 + 8x112112221112212211112112122211122122max 4.8() 5.6()()500100015000.50.6,,,,0z x x x x c x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x =+++-+≤++≤≤≥+≥+≥2.1解法1(NLP )p104~106将模型变换为以下的非线性规划模型:1121122212311122122111121121222123122312311122122max4.8()5.6()(1086)50010000.50.6(500)0(500)00,,500,,,,0z x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x =+++-+++≤++≤≥+≥+=++-=-=≤≤≥LINGO 软件设置:局部最优解,全局最优解,见提示。
Mathematical model of commensal and host speciesMathematical modeling of ecological unit was started by Lotka [1] and V olterra [2] and laterseveral mathematicians and ecologists Meyer [3], Kushing [4], kapur [5-6] contributed to the growth of this area ofacquaintance. The Ecological dealings can be broadly classified as Ammensalism, Competition, Commensalism,Neutralism,Mutualism, Predation and Parasitism.Here we shall consider a model of a distinctive two species commensal, host system. Commensalism is a syn biotic interaction between two populations where one population 1S is benefited by the otherpopulation 2S , while the other population 2S is neither harmed nor benefited due to interaction with the population 1S .The benefited population 1S is called the commensal and the other population 2S is called the host. For a real life example with photographs is given belowA Squirrel in an oak tree gets a place to live and food for its survival, while the tree remains neither benefited nor harmed.Consider and answer the following: Build a mathematical model to describe the two species commensal, host system. Please consult the related literature and data to complete the simulation calculation of your mathematical model.Study your model of commensalism with stochastic term which is invented and investigated the effect of environmental fluctuations around the positive equilibrium due to additive white noise.REFERENCES[1] Lotka AJ, “Elements of Physical Biology”, Williams and Wilking, Baltimore, 1925.[2] V olterra V, “Leconssen La Theorie Mathematique De La Leitte Pou Lavie”, Gauthier-Villars, Paris, 1931.[3] Meyer WJ, “Concepts of Mathematical Modeling” ,Mc. Grawhill, 1985.[4] Cushing JM, “Integro-Differential Equations and Delay Models in Population Dynamics”, Lecture Notes in Bio- Mathematics, Springerverlag,1977.[5] Kapur JN, “Mathematical Modelling in Biology and Medicine”, Affiliated East West, 1985.[6] Kapur JN, “Mathematical Modelling”, Wiley Easter, 1985.。
Prblem C Forest FiresOne major environmental concern is the occurrence of forest fires (also called wildfires), which affect forest preservation, bring economical and ecological damage and endanger human lives. Such phenomenon is due to multiple causes (e.g. human negligence and lightnings). Despite an increasing of state expenses to control this disaster, each year millions of forest hectares (ha) are destroyed all around the world.Fast detection is an important element for successful firefighting. Traditional human surveillance is expensive and affected by subjective factors, there has been an emphasis to develop automatic solutions, such as satellite-based, infrared/smoke scanners and local sensors (e.g. meteorological). Propagation models try to describe the future evolution of the forest fire given an initial scenario and certain input parameters. Modeling the dynamical behavior of fire propagation in a forest is helpful for creating scheme to control and fight fire.Requirement 1Describe several different metrics that could be used to evaluate the effectiveness of fire detection. Could you combine your metrics to make them even more useful for measuring quality?Requirement 2Model the dynamical behavior of fire spread in a forest.Requirement 3 Discuss the factors to affect fire occurrence. Which factors are the most critical in causing fires. Build mathematical models to predict the burned area of fires using Meteorological Data.Requirement 4 Give y our suggestion for preventing from forest fire and fighting against it.。
2015年峨眉校区数学建模培训第二次实战训练题 请先认真阅读下列注意事项:(1) 实战训练题为A ,B 两题,每队根据自己的情况选择一题完成;(2) 做题时间:公布时间起至8月24日下午开始检查报告;期间的上课照常进行,请随时关注我们在群里的通知。
(3) 要求必须按照国家正式比赛的要求编号和程序打包压缩,见第一次训练题目里面的要求,注意峨眉校区编号033,无需打印;A 题 深空探测电磁波是无线通信中或雷达探测目标时传递信息的载体,它在传播过程中会碰到各种各样的障碍物或待探测的目标,形成电磁散射,影响通信质量或给雷达探测目标提供信息,因此研究电磁波与障碍物或目标的相互作用过程具有广泛的应用。
电磁散射的强度与电磁波所碰到的物体或目标的几何形状和材料性质相关,一般可用雷达横截面积来度量。
(1)假定某雷达发射一束电磁波,经过长距离传播后在空中碰到一球形目标,请建立数学模型计算以下情况的电磁散射雷达横截面积。
计算时假定来波是一频率为300兆赫兹的平面波(经过长距离传播后可用平面波近似), 以球心为原点建立坐标系, 入射波的极化方向沿x +方向,入射方向沿z +方向,球形目标半径为0.5米,其周围没有其它物体。
假定球形目标是一个无损耗的介质体,相对介电常数为3.0,相对磁导率为1.0。
请提供相关数学模型公式、计算程序及结果显示图形。
结果只要显示沿纬度方向观察且角度在0到180度之间的极化分量雷达横截面积曲线。
(2)如果我们使用这一模型来探测太空中有无天体快速靠近地球,那么需要几个探测雷达,以及如何测定该可疑天体的速度,地球到该天体运行轨迹的距离。
B题:DNA序列的k-mer index 问题这个问题来自 DNA序列的k-mer index问题。
给定一个DNA序列,这个系列只含有4个字母ATCG,如 S =“CTGTACTGTAT”。
给定一个整数值k,从S的第一个位置开始,取一连续k个字母的短串,称之为k-mer(如k= 5,则此短串为CTGTA),然后从S的第二个位置,取另一k-mer (如k= 5,则此短串为TGTAC),这样直至S的末端,就得一个集合,包含全部k-mer 。
Airline OverbookingYou're all packed and ready to go on a trip to visit your best friend in New York City. After you check in at the ticket counter, the airline clerk announces that your flight has been overbooked. Passengers need to check in immediately to determine if they still have a seat.Historically, airlines know that only a certain percentage of passengers who have made reservations on a particular flight will actually take that flight. Consequently, most airlines overbook-that is, they take more reservations than the capacity of the aircraft. Occasionally, more passengers will want to take a flight than the capacity of the plane leading to one or more passengers being bumped and thus unable to take the flight for which they had reservations.Airlines deal with bumped passengers in various ways. Some are given nothing, some are booked on later flights on other airlines, and some are given some kind of cash or airline ticket incentive.Consider the overbooking issue in light of the current situation:●Less flights by airlines from point A to point B.●Heightened security at and around airports.●Passengers' fear.●Loss of billions of dollars in revenue by airlines to date.Build a mathematical model that examines the effects that different overbooking schemes have on the revenue received by an airline company in order to find an optimal overbooking strategy, i.e., the number of people by which an airline should overbook a particular flight so that the company's revenue is maximized.Insure that your model reflects the issues above, and consider alternatives for handling “bumped” passengers. Additionally, write a short memorandum to the airline's CEO summarizing your findings and analysis.。
【最新整理,下载后即可编辑】数学建模任意两个城市之间的最廉价路线参与人员信息:2012 年 6 月 6 日一、问题提出某公司在六个城市C1、C2、C3、C4、C5、C6中都有分公司,从Ci到Cj的直达航班票价由下述矩阵的第i行、第j列元素给出(∞表示无直达航班),该公司想算出一张任意两个城市之间最廉价路线表,试做出这样的表来。
0 50 ∞40 25 1050 0 15 20 ∞25∞15 0 10 20 ∞40 20 10 0 10 2525 ∞20 10 0 5510 25 ∞25 55 0二、问题分析若网络中的每条边都有一个数值(长度、成本、时间等),则找出两节点(通常是源节点和阱节点)之间总权和最小的路径就是最短路问题。
最短路问题是网络理论解决的典型问题之一,可用来解决管路铺设、线路安装、厂区布局和设备更新等实际问题。
最短路问题,我们通常归属为三类:单源最短路径问题、确定起点终点的最短路径问题、全局最短路径问题———求图中所有的最短路径。
题中要求算出一张任意城市间的最廉价路线表,属于全局最短路问题,并且使得该公司总经理能够与各个子公司之间自由往返。
(此两点为主要约束条件)Floyd 算法,具体原理如下:(1) 我们确定本题为全局最短路问题,并采用求距离矩阵的方法根据路线及票价表建立带权矩阵W ,并把带权邻接矩阵我w 作为距离矩阵的初始值,即(0)(0)()ij v v D d W ⨯==(2)求路径矩阵的方法在建立距离矩阵的同时可建立路径矩阵R ,()ij v v R r ⨯=,ij r 的含义是从i v 到j v 的最短路径要经过点号为ij r 的点。
(3)查找最短路径的方法若()1v ij r p =,则点1p 是点i 到j 的最短距离的中间点,然后用同样的方法再分头查找。
三、 模型假设: 1.各城市间的飞机线路固定不变2.各城市间飞机线路的票价不改变3.忽略乘客除票价以外的各项开销费用4.不考虑雷雨云、低云、大风、雷暴、冰雹等主要天气因素对飞行的影响。
数学建模知识——之参考资料一、数学建模竞赛中应当掌握的十类算法1.蒙特卡罗算法该算法又称随机性模拟算法,是通过计算机仿真来解决问题的算法,同时可以通过模拟可以来检验自己模型的正确性,是比赛时必用的方法。
2.数据拟合、参数估计、插值等数据处理算法比赛中通常会遇到大量的数据需要处理,而处理数据的关键就在于这些算法,通常使用Matlab作为工具。
3.线性规划、整数规划、多元规划、二次规划等规划类问题建模竞赛大多数问题属于最优化问题,很多时候这些问题可以用数学规划算法来描述,通常使用Lindo、Lingo软件实现。
4.图论算法这类算法可以分为很多种,包括最短路、网络流、二分图等算法,涉及到图论的问题可以用这些方法解决,需要认真准备。
5.动态规划、回溯搜索、分治算法、分支定界等计算机算法这些算法是算法设计中比较常用的方法,很多场合可以用到竞赛中。
6.最优化理论的三大非经典算法:模拟退火法、神经网络、遗传算法这些问题是用来解决一些较困难的最优化问题的算法,对于有些问题非常有帮助,但是算法的实现比较困难,需慎重使用。
7.网格算法和穷举法网格算法和穷举法都是暴力搜索最优点的算法,在很多竞赛题中有应用,当重点讨论模型本身而轻视算法的时候,可以使用这种暴力方案,最好使用一些高级语言作为编程工具。
8.一些连续离散化方法很多问题都是实际来的,数据可以是连续的,而计算机只认的是离散的数据,因此将其离散化后进行差分代替微分、求和代替积分等思想是非常重要的。
9.数值分析算法如果在比赛中采用高级语言进行编程的话,那一些数值分析中常用的算法比如方程组求解、矩阵运算、函数积分等算法就需要额外编写库函数进行调用。
10.图象处理算法赛题中有一类问题与图形有关,即使与图形无关,论文中也应该要不乏图片的,这些图形如何展示以及如何处理就是需要解决的问题,通常使用Matlab进行处理。
二、数学软件的主要分类有哪些?各有什么特点?数学软件从功能上分类可以分为通用数学软件包和专业数学软件包,通用数学包功能比较完备,包括各种数学、数值计算、丰富的数学函数、特殊函数、绘图函数、用户图形届面交互功能,与其他软件和语言的接口及庞大的外挂函数库机制(工具箱)。