2012届高考英语语法精讲精练-动词的时态和语态[教师版]
- 格式:doc
- 大小:870.00 KB
- 文档页数:49

2012年全国与各地高考英语分类精品解析系列简介单项选择题分类解析系列专题01单项选择题分类解析〔冠词、名词和主谓一致〕专题02单项选择题分类解析〔代词〕专题03单项选择题分类解析〔介词和介词短语〕专题04单项选择题分类解析〔形容词和副词〕专题05单项选择题分类解析〔动词和动词短语〕专题06单项选择题分类解析〔动词的时态和语态〕专题07单项选择题分类解析〔情态动词和虚拟语气〕专题08单项选择题分类解析〔非谓语动词〕专题09单项选择题分类解析〔定语从句〕专题10单项选择题分类解析〔连词和状语从句〕专题11单项选择题分类解析〔名词性从句〕专题12单项选择题分类解析〔特殊句式〕专题13单项选择题分类解析〔交际用语〕完形填空题分类解析系列专题01记叙文完形填空专题02夹叙夹议完形填空阅读理解题分类解析系列专题01人物传记、故事类阅读理解专题02新闻报道、广告类阅读理解专题03社会生活、说理议论类阅读理解专题04科普类阅读理解专题05新题型阅读理解书面表达题分类与选择讲评专题01书面表达题分类与选择讲评〔文字提纲式〕专题02书面表达题分类与选择讲评〔图画式〕专题03书面表达题分类与选择讲评〔开放式〕1.(2012课标卷)23. "Life is like walking in the snow", Granny used to say, "because every step 〞A. has shownB. is showingC. showsD. showed【答案】C【解析】考查动词的时态。
上下文讲的是哲理性的话,上文用的是一般现在时,下文回答时也用同样时态。
不要受“Granny used to say〞的影响,因为是直接引语。
句意:奶奶过去常常说:生活就像在雪地中行走,因为每一步都能看见。
2.(2012课标卷)33.I had been working on math for the whole afternoon and thenumbersbefore my eyes.A. swim B .swum C. swam D. had swum3.(2012大纲卷)14.—Did you ask Sophia for help ?—I ________ need to. I managed perfectly well on my own.A. wouldn’tB. don’tC. didn’tD. won’t【答案】C【解析】考查动词的时态。

2012年高考英语第二轮热点专题复习--动词的时态和语态教案教学设计(新课标版英语高考复习)内容解读1.高考考查的八种动词时态是:①一般现在时;②一般过去时;③一般将来时;④现在进行时;⑤过去进行时;⑥现在完成时;⑦过去完成时;⑧过去将来时。
2.容易混淆的三组动词时态是:①一般过去时和现在完成时;②一般过去时和过去完成时;③过去完成时与现在完成时。
3.各种时态及含情态动词的被动形式和应用。
能力解读1.了解动词时态的时、体概念;2.了解常考八种时态的基本用法并能够在真实的情景中恰当使用八种时态进行交际;3.能够区别容易混淆的时态的用法;4.掌握各种时态及含情态动词的被动语态的形式和应用;①分清动词的词性,熟悉并掌握常见的不及物动词happen, take place, occur, exist 等,它们不能用被动语态;② 分清主语与谓语之间的关系;③ 变被动语态的动词一般为及物动词,但有些不及物动词与介词所形成的短语动词也可有被动形式,此时,变被动语态后介词不能丢;④ 熟悉并掌握主动形式表被动意义的情况。
规律方法1.试题的立意由简单直接的“结构立意”(如状语从句、宾语从句等)转向了“情景立意”。
试题创设的语境明确,交际情景(对话形式占有一定比例)多是发生在学生学习或日常生活中的真实情况。
这样的情景设置实质上是对语法知识、语义理解和语言交际能力的综合考查,体现了高考试题由“知识立意”向“能力立意”转变人命题原则。
2.题干中的有效信息由“外显的”转向“隐藏的”。
3.试题的设问多以中学生普遍感到难以把握的几组时态来相互干扰。
命题趋势毫无疑问,对于动词时态的考查仍交进高考的测试重点。
试题将继续呈现“情景立意”和“能力立意”的原则,即在考查固定句式中的时态和语态的同时,注重在上下文中考查时态和语态,注重在语境中考查时态和语态。
突破方法1.学习动词的时态和语态时,切不可脱离实际运用的语言,一味死记硬背语法规则的条条框框。
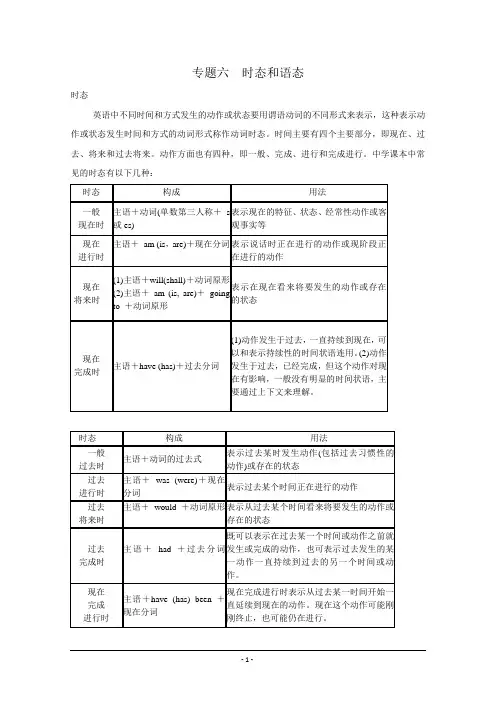
专题六时态和语态时态英语中不同时间和方式发生的动作或状态要用谓语动词的不同形式来表示,这种表示动作或状态发生时间和方式的动词形式称作动词时态。
时间主要有四个主要部分,即现在、过去、将来和过去将来。
动作方面也有四种,即一般、完成、进行和完成进行。
中学课本中常见的时态有以下几种:时态构成用法一般现在时主语+动词(单数第三人称+s或es)表示现在的特征、状态、经常性动作或客观事实等现在进行时主语+am (is,are)+现在分词表示说话时正在进行的动作或现阶段正在进行的动作现在将来时(1)主语+will(shall)+动词原形(2)主语+am (is, are)+goingto +动词原形表示在现在看来将要发生的动作或存在的状态现在完成时主语+have (has)+过去分词(1)动作发生于过去,一直持续到现在,可以和表示持续性的时间状语连用。
(2)动作发生于过去,已经完成,但这个动作对现在有影响,一般没有明显的时间状语,主要通过上下文来理解。
时态构成用法一般过去时主语+动词的过去式表示过去某时发生动作(包括过去习惯性的动作)或存在的状态过去进行时主语+was (were)+现在分词表示过去某个时间正在进行的动作过去将来时主语+would +动词原形表示从过去某个时间看来将要发生的动作或存在的状态过去完成时主语+had +过去分词既可以表示在过去某一个时间或动作之前就发生或完成的动作,也可表示过去发生的某一动作一直持续到过去的另一个时间或动作。
现在完成进行时主语+have (has) been +现在分词现在完成进行时表示从过去某一时间开始一直延续到现在的动作。
现在这个动作可能刚刚终止,也可能仍在进行。
语态语态是表示主语和动词之间语法关系及语义关系的动词形式,有主动语态和被动语态两种形式。
英语中的语态和时态是不可分割的,每种时态都有其相应的语态形式语态构成例句一般现在时的被动语态主语+am(is, are)+过去分词The lion is considered the king of the forest as it is a symbol of courage and power.现在进行时的被动语态主语+am(is, are)+being+过去分词My car is being repaired at present.现在将来时的被动语态主语+will(shall) be +过去分词/主语+am(is, are)+goingto be+过去分词The new bridge will be completedat the end of the year.现在完成时的被动语态主语+have(has) been+过去分词I am surprised that you should have beenfooled by such a simple trick.一般过去时的被动语态主语+was (were)+过去分词Marie Curie took little notice of the honorsthat were given to her in her later years.过去进行时的被动语态主语+was (were) +being +过去分词I had the distinct impression that I was beingfollowed.过去将来时的被动语态主语+would be+过去分词The workers scented changes that would bemade in the company.过去完成时的被动语态主语+had been +过去分词The new suspension bridge had beendesigned by the end of last month.一、时态动词的时态是英语语法的重中之重,因为它们与句子结构、句子表达、语言逻辑紧密相连,无论是单选、完形、阅读还是书面表达都离不开时态。

2012英语分类汇编----动词时态和语态动词时态和语态在高考中的考查重点:1.对下列十种时态的考查:一般现在时一般过去时一般将来时现在进行时过去进行时现在完成时现在完成进行时过去完成时将来完成时过去将来时2.既考查时态又考查语态;3.考查动词的及物与不及物;4.考查主动形式表示被动意义;5.考查动词词组在被动语态中的介词问题;6.对被动语态习惯句型的考查。
2012年时态1.(安徽高考,26)In order to find the missing child, villagers _____ all they can over the past five hours.A. didB. doC. had doneD. have been doing2.(安徽高考,33)Walmart, which is one of the largest American supermarket chains, _____ some of its stores open 20 hours on Mondays through Saturdays.A. keepsB. keepC. have keptD. had kept3.(全国高考I,23)“Life is like walking in the snow”, Granny used to say, “because every step _____.’A. has shownB. is showingC. showsD. showed4.(全国高考I,33)I had been working on math for the whole afternoon and the numbers _____ before my eyes.A. swimB. swumC. swamD. had swum5.(重庆高考,22)―Kevin, you look worried. Anything wrong?―Well, I _____ a test and I’m waiting for the result.A. will takeB. tookC. had takenD. take6.(重庆高考,27)Food supplies in the flood-stricken area _____. We must act immediately before there’s none left.A. have run outB. are running outC. have been run outD. are being run out7.(湖南高考,25)Close the door of fear behind you, and you _____ the door of faith open before you.A. sawB. have seenC. will seeD. are seeing8.(湖南高考,27)“The moment _____ soon,” he thought to himself, waiting nervously.A. cameB. has comeC. was comingD. is coming9.(湖南高考,33)―I remember you were a talented pianist at college. Can you play the piano for me?―Sorry, I _____ the piano for years.A. don’t playB. wasn’t playingC. haven’t playedD. hadn’t played10.(福建高考,24)─When did the computer crash?─This morning, while I _____ the reading materials downloaded from some websites.A. have sortedB. was sortingC. am sortingD. had sorted11.(北京高考,22)By the time you have finished this book, your meal _____ cold.A. getsB. has gotC. will getD. is getting12.(北京高考,30)Our friendship _____ quickly over the weeks that followed.A. had developedB. was developingC. would developD. developed13.(天津高考,12)The three of us _____ around Europe for about a month last summer.A. traveledB. have traveledC. had traveledD. travel(模块二第2单元grammar)14.(江西高考,26)—Look! Somebody _____ the sofa.—Well, it wasn’t me. I didn’t do it.A. is cleaningB. was cleaningC. has cleanedD. had cleaned15.(陕西高考,24)—Can I call you back at two o’clock this afternoon?—I’m sorry, but by then I _____ to Beijing. How about give.A. flyB. will flyC. will be flyingD. am flying16.(四川高考,3)—Goodbye, John. Come back again sometime.—Sure. _____.A. I didB. I doC. I shallD. I will17.(四川高考,9)—Did you catch what I said?—Sorry. I _____ a text message just now.A. had answeredB. have answeredC. would answerD. was answering18.(辽宁高考,31)I feel so excited! At this time tomorrow morning I _____ to Shanghai.A. will be flyingB. will flyC. have been flyingD. have flown19.(山东高考,28)After Jack had sent some e-mails, he _____ working on his project.A. had startedB. has startedC. startedD. starts20.(山东高考,34)The manager was concerned to hear that two of his trusted workers _____.A. will leaveB. are leavingC. have leftD. were leaving21.(江苏高考,32)The manager is said to have arrived back from Paris where he _____ some European business partners.A. would meetB. is meetingC. meetsD. had met22.(江苏高考,34)The president hopes that the people will be better off when he quits than when he _____.A. has startedB. startsC. startedD. will start23.(上海高考,30)—I hear that Jason is planning to buy a car.—I know. By next month, he _ enough for a used one.A. will have savedB. will be savingC. has savedD. saves24.(浙江高考,13)Peter had intended to take a job in business, but _____ that plan after the unpleasant experience in Canada in 2010.A. had abandonedB. abandonedC. abandonD. will abandon25.(浙江高考,16)—Alvin, are you coming with us?—I’d love to, but something unexpected _____.A. has come upB. was coming upC. had come upD. would come up26.(北京高考,25)George said that he would come to school to see me the next day, but he _____.A. wouldn’tB. didn’tC. hasn’tD. hadn’tDACCB BCDCB CDACC DDACD DCABA B语态1.(安徽高考,35)After school we went to the reading-room to do some reading, only to be told that it _____.A. was decoratedB. had decoratedC. had been decoratedD. was being decorated2.(湖南高考,22)Don’t worry. The hard work that you do now _____ later in life.A. will be repaidB. was being repaidC. has been repaidD. was repaid3.(北京高考,29)─Have you heard about that fire in the market?─Yes, fortunately no one _____.A. hurtB. was hurtC. has hurtD. had been hurt4.(上海高考,26)Is honesty the best policy? We _ that it is when we are little.A. will teachB. teachC. are taughtD. will be taught5.(天津高考,2)The letters for the boss _____ on his desk but he didn’t read them until three days later.A. were putB. was putC. putD. has put6.(四川高考,11)They are living with their parents for the moment because their own house _____.A. is being rebuiltB. has been rebuiltC. is rebuiltD. has rebuilt7.(辽宁高考,35)Mum, I was wondering if you could lend me a few dollars until I _____ on Friday.A. get paidB. got paidC. have paidD. had been paidDABCA AA虚拟语气1.(安徽高考,31)Grace doesn’t want to move to New York because she thinks if she _____ there, she wouldn’t be able to see her parents very often.A. livesB. would liveC. has livedD. were to live2.(湖南高考,29)Sorry, I am too busy now. If I _____ time, I would certainly go for an outing with you.A. have hadB. had hadC. haveD. had3.(福建高考,31)We lost our way in that small village, otherwise we _____ more places of interest yesterday.A. visitedB. had visitedC. would visitD. would have visited4.(天津高考,15)We would have called a taxi yesterday if Harold _____ us a ride home.A. didn’t offerB. wouldn’t offerC. hasn’t offeredD. hadn’t offered5.(陕西高考,17)If my car _____ more reliable, I would have driven to Lhasa instead of flying last summer.A. wasB. had beenC. should beD. would be6.(辽宁高考,33)Jaok is a great talker. It is high time that he _____ something instead of just talking.A. will doB. had doneC. doD. did7.(山东高考,30)If we _____ adequate preparations, the conference wouldn’t have been so successful.A. haven’t madeB. wouldn’t makeC. didn’t makeD. hadn’t made8.(浙江高考,19)Had they known what was coming next, they _____ second thoughts.A. may haveB. could haveC. must have hadD. might have had9.(北京高考,35)Don’t handle the vase as if it _____ made of steel.A. isB. wereC. has beenD. had beenDDDDB DDDB。
![2012届高考英语语法精讲精练-动词的时态和语态[学生版]](https://uimg.taocdn.com/565fa59edd88d0d233d46aba.webp)
2012届新课标高三第二轮专题讲解动词是英语中最灵活、最难掌握的词,在历年高考题中动词所占比例最大。
设题时给出四个不同的动词或短语来测试考生在具体语境中对动词及其短语意义的理解和运用能力。
主要出现在单项选择及完形填空中。
英语中的时态共有十六种,但是常考的或较常用的有十一种。
见下表:(一)一般现在时1.表示经常或习惯性的动作,多用行为动词,且常与表频率的时间状语连用We always care for each other and help each other.2.表示客观事实或普遍真理(不受主句时态的限制) The geography teacher told us the earth moves around the sun.1.表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,只用一般现在时;The plane takes off at 10:00 a.m.飞机上午10点起飞。
2.在时间、条件状语从句中常用一般现在时代替将来时。
但要注意由if 引导的条件状语从句中有时可以用shall或will表“意愿”,不表示时态;I’ll go there after I finish my work.If you will accept my invitation and come to our party, my family will be pleased.3.以here, there开头的句子里,go, come等少数动词的一般在时表示正在发生的动作。
There comes the bus.汽车来了。
Here she comes.她来了。
(二)一般过去时1.过去某一时间内经常发生或反复发生的动作或存在的状态He lived in Beijing when he was young. 他年轻时生活在北京。
2.表达过去发生的动作We visited the factory last Friday.上周五我们参观了那家工厂。

一、动词的语态的种类:主动语态和被动语态。
二、被动语态的构成方式:be + 过去分词一般现在时一般过去时一般将来时过去将来时现在进行时过去进行时现在完成时过去完成时should/would + be done情态动词情态动词 + be + 过去分词E.g. (1)一般现在时:Now English is taught in all middle schools in our country. (2)一般过去时:The Great hall of the People was built in 1959. (3)一般将来时: When will the work be finished? (4) )过去将来时:He told us that the work would be finished the next day. (5)现在进行时:Your tractor is being repaired now. (6)过去进行时:The child was being examined by the doctor when they came in. (7)现在完成时:The work hasn’t been finished yet. (8)过去完成: The new plan had been carried out before the second experiment began. (9)情态动词: Coal can be used to produce electricity for agriculture and industry. 三、主动语态转换为被动语态要注意的几点:1、带有双宾语(直接宾语和间接宾语)的主动句变为动句,若主动语态动词后又有直接宾语,又有间接宾语,.一般是将间接宾语改为被动语态句中的主语,将直接宾语保留在原处。
但若将直接宾语改为被动语态句中的主语,则将间接宾语保留在原处时,一般要在间接宾语前加介词to(此类动词为:bring,hand,leave,lend,read,pass,promise,refuse,return,send,shoe,tell,throw,write)或 for(此类动词为:buy,do,get,make,order,pay,play,sing)等。

动词是英语中最灵活、最难掌握的词,在历年高考题中动词所占比例最大。
设题时给出四个不同的动词或短语来测试考生在具体语境中对动词及其短语意义的理解和运用能力。
主要出现在单项选择及完形填空中。
根据意义和句法作用,英语动词可分为四类(一)实义动词1.按性质分实义动词又分成及物动词和不及物动词,表示动作或状态,在句中独立做谓语。
及物动词后须跟宾语;不及物动词不跟宾语。
例:—What did you think of her speech?—She _______for one hour but didn't ________ much.A. spoke; speakB. spoke; sayC. said; speakD. said; say注意:英语里及物动词和不及物动词不是截然分开的,有的动词既可以是及物动词也可以是不及物动词。
It is important for you to learn how to learn.第一个learn是及物动词,后面有宾语how to learn;第二个learn是不及物动词。
不及物动词向及物动词转化需要借助于介词、副词等构成短语动词。
He is working hard at English.2.按时限分实义动词又分成延续性动词和非延续性动词(短暂性动词)延续性动词动作可以延续,可以与一段时间连用。
如:live, study, work, stay, keep, have等。
非延续性动词(短暂性动词)动作瞬间完成,不能与一段时间连用。
如:finish, come,open, bring, buy等。
例:The evening news comes on at seven o' clock and ________ only thirty minutes.A. keepsB. continuesC. finishesD. lasts【解析】答案为D。
根据后面的时间状语“only thirty minutes”先排除“finish”为瞬间动词;keep“保留,保存”;continue意为“继续”; last意为“持续,继续”,根据题意“晚间新闻每天7:00开始,持续30分钟。
《动词的时态和语态(一)》教案一、教学目标1、动词时态的主要考点;2、各种时态的基本用法和特别用法;3、高考常考的时态的构成和时间状语。
二、教学重难点1、教学重点:各种时态的基本用法和特别用法;动词时态的主要考点。
2、教学难点:各种时态的特别用法。
三、教学过程(一)问题排行榜(Hit the charts)1.动词时态的主要考点是什么?2.各种时态的基本用法?特别用法?3.高考常考的时态?构成?时间状语?(二)攻克难点(Overcome difficulties)1.高考常考的时态?构成?时间状语?体一般体进行体完成体完成进行体2.各种时态的基本用法?特别用法?一、一般现在时态1.基本用法:1) 表示现阶段经常性、习惯性的动作或存在的状态、特征、客观真理。
常用的时间状语有often , usually , always , sometimes , every day/week 等。
提醒:当第三人称单数作主语时,谓语动词用单数形式。
e.g.They are both fine, too.The sun rises in the east.He gets up at six o’clock every day.2.特别用法:1)在条件状语从句和时间状语从句中,用一般现在时表示将来。
e.g.If you don’t go soon, you’ll be late.You mustn’t eat anything until you see the doctor.2) begin , come , go , leave , start , stop , arrive , return , open ,close等动词常用一般现在时表示按计划、规定将要发生的动作。
e.g. Class begins at eight in the morning.3)描述过去的事实,以求描绘的生动性。
The river rises higher and higher, breaks the banks and fills all low places.二、一般过去时态1.基本用法:1 )表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态。

《动词的时态和语态(二)》教案一、教学目标1、高考动词时态语态易错点;2、各种时态的被动语态的构成和用法;3、主动形式表被动意义;4、高考动词语态主要考点。
二、教学重难点1、教学重点:主动形式表被动意义;高考动词时态语态易错点。
2、教学难点:高考动词时态语态易错点。
三、教学过程(一)问题排行榜(Hit the charts)1、高考动词时态语态易错点有哪些?2、高考动词语态主要考点是什么?3、哪些情况下主动形式可以表被动意义?4、各种时态的被动语态的构成?用法?(二)攻克难点(Overcome difficulties)1、各种时态的被动语态的构成?用法?1.被动语态的构成: be/ get +及物动词的过去分词2. 英语中被动语态常用于下列几种场合:不知道动作的执行者;不必提到动作的执行者;强调或侧重动作的承受者;动作的执行者很模糊或是无生命的事物时;有些动词习惯上常用被动语态以及在文章标题、广告、新闻等中。
e.g.It’s suggested that we put the meeting off.The window glass was broken by a stone.Girls wanted.3. “It+be+过去分词+从句”结构的被动结构It is known that...众所周知It is suggested that...有人建议It is believed that...有人相信It is hoped that...大家希望It is thought that...大家认为4. 被动语态与系表结构的区别被动语态中的过去分词是动词,表示动作;系表结构中的过去分词相当于形容词,表示状态。
These things are sold quickly.(被动语态)These things are all sold out.(系表结构)常使用系表结构的词有:be seated坐着,be hidden躲藏,be lost迷路,be drunk喝醉,be dressed穿着,be devoted to致力于;献身,be determined决定,be compared比较。

Unit 2 How often do you exercise Section A课时训练 I.根据句意及首字母提示完成句子 1.—How often do you surf the Internet? —O_____ a week. 2.The young man e_____ every morning. Sometimes he runs, sometimes he plays basketball. 3.I often help with the h_____. 4.CCTV News is a popular p_____. We like it very much. 5.He sometimes u_____ the Internet. II.用所给词的适当形式填空 1.How often _____(do) she watch TV? 2.Millie usually watches TV _____(two) a week. 3.Would you like to do some _____(shop)on Saturday morning? 4.We do morning _____(exercise)every day. 5.He plays soccer at_____(little)three times a week. 6.We do _____(sport) four times a week. 7.I like _____(vegetable)for lunch. Ⅲ.根据汉语意思完成句子 1.她周末干什么? —_____ does she _____ on weekends? 她常常去看电影。
—She often _____ to the _____. 2.你多久锻炼一次? —_____ _____ do you _____? 一周三次。
—_____ _____ a week. 3.你最喜欢的节目是什么? _____ your_____ _____? 4.我爷爷每周锻炼两次。
动词是英语中最灵活、最难掌握的词,在历年高考题中动词所占比例最大。
设题时给出四个不同的动词或短语来测试考生在具体语境中对动词及其短语意义的理解和运用能力。
主要出现在单项选择及完形填空中。
英语中的时态共有十六种,但是常考的或较常用的有十一种。
见下表:(一)一般现在时1.表示经常或习惯性的动作,多用行为动词,且常与表频率的时间状语连用We always care for each other and help each other.2.表示客观事实或普遍真理(不受主句时态的限制)The geography teacher told us the earth moves around the sun.1.表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,只用一般现在时;The plane takes off at 10:00 a.m.飞机上午10点起飞。
2.在时间、条件状语从句中常用一般现在时代替将来时。
但要注意由if 引导的条件状语从句中有时可以用shall或will表“意愿”,不表示时态;I’ll go there after I finish my work.If you will accept my invitation and come to our party, my family will be pleased.3.以here, there开头的句子里,go, come等少数动词的一般在时表示正在发生的动作。
There comes the bus.汽车来了。
Here she comes.她来了。
(二)一般过去时1.过去某一时间内经常发生或反复发生的动作或存在的状态He lived in Beijing when he was young.他年轻时生活在北京。
2.表达过去发生的动作We visited the factory last Friday.上周五我们参观了那家工厂。
1.有些动词如:think, want, plan等用在一般过去时中常常译为“原来认为/以为,原来想,原计划”。
定额市鞍钢阳光实验学校专题06 动词时态及其语态动词的时态和语态是历年高考的重点,是高考的必考点。
应特别注意以下几点:要把握各种时态的特点,注意易混淆时态间的差异;准确理解具体语境下时态的正确意义,捕捉句子中所隐含的时间信息;要克服汉语式的惯性思维,排除误导,培养发散性思维。
高考中常考的时态有一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、过去将来时、现在完成时、过去完成时、将来进行时、现在完成进行时、过去完成进行时等等。
学习时要注意总结规律,灵活使用,特别要注意一些时态的特殊用法。
高考主要以单项填空、语法填空、短文改错等形式考查,动词的时态和语态在语法填空和短文改错中是必考点。
今后时态和语态还将是高考中的重点和难点所在。
【考点定位】2017考纲解读和近几年考点分布动词时态和语态是两个非常重要的语法范畴,构成了英语语法的基本框架,几乎所有动词的考查都必须要借助于时态和语态来完成。
试题在考查时态和语态的同时,还兼顾其它语法内容的测试,比如各种从句、强调、倒装等,其交叉式和复合式的特点尤为明显。
其考点主要包括:1、考查时态的基本概念。
如:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在完成时、将来进行时等。
2、考查各种时态之间的区别。
如:一般过去时和现在完成时;一般现在时与现在进行时;一般过去时和过去完成时等。
3、考查不能用被动语态的几种情况。
如:(1)所有的不及物动词或不及物动词词组不能用于被动语态之中。
(2)表示状态的谓语动词,如:last、hold、benefit、contain、equal、fit 等。
(3)表示归属的动词,如have、own、belong to等。
(4)表示“希望、意图”的动词,如:wish、want、hope、like、love、hate 等。
(5)宾语是反身代词或相互代词时谓语动词用主动语态,不能用被动语态。
4、考查主动形式表被动意义的情况。
(1)当feel、look、smell、taste、sound等后面接形容词时;(2)当cut,sell,read,write,fill,cook,lock,wash,drive,keep等词带状语修饰语时;(3)当break out、take place、shut off、turn off、work out等动词表示“发生、关闭、制定”等意思时;(4)want, require, need后面的动名词用主动表示被动含义。
动词的时态和语态一直是历年高考的必考点。
主要考查考生在特定语境下对时态和语态的理解,其中现在完成时、一般过去时、过去完成时的运用出现得最为频繁。
此外,为了增加试题的区分度,命题者还常常把动词的时态和语态以及主谓一致结合在一起考查。
在解题时要注意以下几个问题:1.这个动作可能发生在什么时间?题干中可参照的时间信息有哪些?2.这个动作处于什么状态?是进行中,还是已结束(完成)?限制或修饰这个动作的状语信息有哪些?3.这个动作与主语的关系,是主动还是被动?只要全面细致地考虑了这些问题,试题的答案也就水落石出了。
一、动词时态的基本结构和用法实用文档实用文档实用文档实用文档实用文档实用文档二、几种易混时态的辨析1.一般现在时与现在进行时一般现在时表示经常性的、习惯性的或状态性的行为。
而现在进行时则具有进行性、未完成性和暂时性的特点。
如:实用文档On the wall hangs a picture painted by Qi Baishi.This is not my coat. Mine is hanging behind the door.如:[2010·重庆卷] The palace caught fire three times in the last century,and little of the original building ________ now.A.remainsB.is remainedC.is remainingD.has been remained【解析】A 考查动词用法及时态。
remain作不及物动词用,表示“剩下,仍有”,只能用于主动语态,不可直接跟宾语。
结合语境应用一般现在时表示现状。
2.一般过去时和现在完成时一般过去时所表达的事件与现在无关。
而现在完成时则强调对现在的影响和结果。
如:I stayed in Beijing for five days. Then I went to America. (I am not in Beijing now. )I have stayed in Beijing for five days and haven't decided where to go next.(I am still in Beijing now and don't know where to go next.)实用文档[2010·北京卷] —I'm sorry,but I don't quite follow you. Did you say you wanted to return on September 20?—Sorry,I ________myself clear. We want to return on October 20.A.hadn't madeB.wouldn't makeC.don't makeD.haven't made【解析】D 本题考查时态和情景交际。
高考英语语法精讲与精练-动词时态与语态一、动词时态与语态讲前练:用所给单词的适当形式或用适当的单词(1个)填空I [1]_______ (have) dinner at a restaurant when Tony Steele came in. Tony [2]______ (work) in a lawyer's office years ago, but he [3]________ (work) at a bank now. He [4]______ (get) a good salary, but he always [5]_______ (borrow) money from his friends and never [6]______ (pay) it back. Tony [7]_____ (see) me and [8]_______ (sit) at the same table. He [9]___ never[10]__________ (borrow) money from me. While he[11]___________ (eat), I asked him to lend me twenty pounds. To my surprise, he [12]_____ (give) me the money immediately. 'I have never borrowed any money from you,' Tony said, 'so now you can pay for my dinner!'讲前练小结:1)有关时态的试题要重点关注时间状语、上下文体现的时间关系和句型中的时态问题,2)牢记不规则动词的变化。
Keys:1. was having 2. worked 3. is working 4.gets 5. borrows 6. pays 7. saw 8.. sat9. has 10. borrowed 11. was eating 12. gave二、动词时态与语态考点精讲:动词时态与语态考点1、主要的时态的形式及含义考点对练1:用所给动词的适当形式填空1.【2021·浙江高考卷】It doesn't impress like George Washington's plantation on the Potomac, but Lincoln's home in downtown Springfield, Illinois, 36(prove)irresistible to visitors since it opened to the public.Key:has proved/has proven 句意:它不像乔治华盛顿在波托马克河畔的种植园那样给人留下深刻印象,但林肯在伊利诺伊州斯普林菲尔德市中心的家,自从向公众开放以来,就被证明对游客来说是不可抗拒的。
2012高考英语语法:动词精讲精练(带答案)高考英语动词语态详解动词有两种语态:主动语态和被动语态。
1.当我们不知道谁是动作的执行者,2. 或者只需强调动作的承受者时,要用被动语态。
被动语态结构:be + 过去分词(PP) + (by …)在改写中应注意:1.把原来的宾语提到前面作被动语态的主语;2.把动词变成“be + 过去分词”;3.主动语态中的主语变为介词by的宾语。
时态被动语态结构一般现在时 am/is/are done一般过去时 was/were done现在进行时 am/is/are being done过去进行时 was/were being done一般将来时shall/will/be going to be done过去将来时 Would be done现在完成时 have/has been done过去完成时 had been doneEg.Some people attacked the towers.S V OThe towers were attacked by some people.S V1) A car knocked him down yesterday.-He was knocked down by a car yesterday.2)Two doctors and ten nurses make up the medical team. The medical team is made up of by two….3)When I got there, they were cutting up a fallen tree.A fallen tree was being cut up, when I got there.4)We’ll put on the play next Sunday.The play will be put on next Sunday.5)Workers are building a new teaching building in our school.A new teaching building is being built by workers in our school.6)They had completed the railway by the end of last year.The railway had been completed by the end of last year.7)We should protect the earth.The earth should be protected.8)You need to paint the wall.The wall needs to be painted.几种特殊结构1.My uncle gave me a gift on my birthday.I was given a gift on my birthday.A gift was given to me on my birthday.2.We often hear him play guitar.He is often heard to play guitar注意:see,watch,hear,notice,feel,make, listen to, look at等动词/短语后作宾语补语的不定式都不带to;但改成被动语态后必须带to。
高中英语语法复习学案教师版——动词的时态和语态动词的时态(一)一般现在时1.Thegeographyteachertoldusthattheearthmoves(move)aroundthesun.2.Waterboils(boil)at100 ℃.3.Thecarelessdriverhasjustbeenfined$10forstoppinghiscaratasignthatreads (read)“NOPARKING”.4.Whateveryousay(say),Iwillnotchangemymind. 6.12.3.定义:过去某一时间发生的动作或所处的状态。
含有“刚才,在过去”之意,暗示现在已经不这样。
时间状语:then;atthattime;justnow;threedaysago;yesterday;when 或while 引导的表示过去的时间状语从句【总结】1.定义:将来某一时刻要发生的动作或所处的状态。
时间状语:soon;nextweek;tomorrow等2.beto+动词原形的用法:(1)YouaretodoyourhomeworkbeforeyouwatchTV.=haveto/must“必须“(2)Youaretoreportthepolice.=should/oughtto“应该”7.Selectingamobilephoneforpersonaluseisnoteasytaskbecausetechnologyischanging(change)sorapidly.8.Idon’treallyworkhere.Iamjusthelping(help)outuntilthenewsecretaryarrives.【总结】1.定义1)现在进行时:说话时或现阶段正在发生的动作或存在的状态。
2)过去进行时:过去某个时刻或阶段正在发生的动作或存在的状态。
2.时间状语1)现在进行时:now;rightnow等2)过去进行时:atthistimeyesterday等3.一个长动作为背景,被一个短动作打断,长动作用进行体,短动作用一般体。
2012届新课标高三第二轮专题讲解动词是英语中最灵活、最难掌握的词,在历年高考题中动词所占比例最大。
设题时给出四个不同的动词或短语来测试考生在具体语境中对动词及其短语意义的理解和运用能力。
主要出现在单项选择及完形填空中。
英语中的时态共有十六种,但是常考的或较常用的有十一种。
见下表:(一)一般现在时1.表示经常或习惯性的动作,多用行为动词,且常与表频率的时间状语连用We always care for each other and help each other.2.表示客观事实或普遍真理(不受主句时态的限制)The geography teacher told us the earth moves around the sun.1.表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,只用一般现在时;The plane takes off at 10:00 a.m.飞机上午10点起飞。
2.在时间、条件状语从句中常用一般现在时代替将来时。
但要注意由if 引导的条件状语从句中有时可以用shall或will表“意愿”,不表示时态;I’ll go there after I finish my work.If you will accept my invitation and come to our party, my family will be pleased.3.以here, there开头的句子里,go, come等少数动词的一般在时表示正在发生的动作。
There comes the bus.汽车来了。
Here she comes.她来了。
(二)一般过去时1.过去某一时间内经常发生或反复发生的动作或存在的状态He lived in Beijing when he was young.他年轻时生活在北京。
2.表达过去发生的动作We visited the factory last Friday.上周五我们参观了那家工厂。
1.有些动词如:think, want, plan等用在一般过去时中常常译为“原来认为/以为,原来想,原计划”。
I thought the film would be interesting, but it isn't.我原以为这部电影是很有趣的,但是事实并非如此。
2.考生有时用现在完成时代替一般过去时Hello, I _______you were in London. How long _________here?A. don’t know; were youB. hadn’t known; are youC. haven’t known; areD. didn’t know; have you be en【解析】非常容易误选B。
其实答案为D,因为“didn’t know” 强调的是见面前不知道,即指过去不知道。
(三)一般将来时1.表示将来的动作和存在的状态The first time we’ll send you with an experienced reporter.第一次我们要派有经验的记者陪同你一起去。
2.表示一种倾向或习惯性动作Oil will float on water.油会浮在水面上。
Crops will die without water.没有水庄稼会死亡一般将来时几种特殊表达形式的区别1.be going to:表示打算做某事或有迹象表明即将发生某事I am going to visit my friend in hospital.我将去看望住在医院的朋友。
It looks as if it is going to rain.看起来好象要下雨了。
2.be about to:表示即时的将来。
一般不与时间状语连用Now ladies and gentleman, you’re about to hear the most incredible tale.女士们,先生们,你们马上就要听到一个难以置信的故事。
3.be to:可用来表示计划、安排(通常是正式的安排);指令;(表示可能)会做……,可能;必定会发生或已发生了某事;发布命令或告之规则Their daughter is to get married soon.他们的女儿可能不久就要结婚了。
(四)现在进行时1.表示现在正在进行的动作;It is raining heavily now, so we must stay inside.现在正下着大雨,因此我们必须呆在家里。
2.表示按计划安排即将发生的动作;My father is coming to see me this Saturday.这个星期六我爸爸要来看我。
现在进行时与always, often等频度副词连用,表经常反复的行动或某种感情色彩Why are always forgetting his name?为啥你总是记他的名字呢?(五)过去进行时1.表示按计划安排即将发生的动作My father is coming to see me this Saturday.这个星期六我爸爸要来看我。
2.表示过去某一时刻或某一段时间内正在进行的动作(这一过去时间须用时间状语表示)He was preparing his lecture all day yesterday.昨天一整天他都在准备他的演讲。
3.用在两个过去进行时动作同时发生I was writing while he was watching TV. 我在写东西而他在看电视。
4.表示过去将来动作He said she was arriving the next.day.他说他将在第二天到达。
考生有时用现在完成时或用一般过去时代替过去进行时。
①—Hey, look where you are going!—Oh, I’m terribly sorry._______.A. I’m not noticing.B. I wasn’t noticing.C. I haven’t noticed.D. I don’t notice.【解析】非常容易误选C。
其实答案为B。
因为对话的后者显然是在解释刚才不小心冒犯对方时正在做的事情,应该用过去进行时。
②He ______a book about China last year, but I don’t know if he _____it.A. wrote; has finishedB. was writing; has finishedC. was writing; had finishedD. wrote; will finish【解析】非常容易误选A。
其实答案为B。
从“I don’t know if he has finished it”推断,他去年一直在写,应该用过去进行时。
(六)将来进行时1.表示将来某一时间正在进行的动作,一般带状语When he comes to my house tomorrow, I will be writing the report.他明天来我家的时候,我将正在写报告。
2.表示现在正在进行的动作,但这个动作会延续到将来I think that she will be working on this experiment until next morning.我想她做这个实验将会一直做到明天早上。
3.表示预定的将来动作或对将来的预测Stop the child or he will be falling over.拦住那孩子,不然他会摔下去的。
将来进行时和一般将来时的区别1.一般将来时不仅表示“将来”,还含有“意志、意愿”等的意思I’ll try my best to hard work at English.我将尽全力努力学习英语。
(含意愿的意思)I’ll be studying English next term.下学期我将学习英语。
(表示单纯的将来)2.跟一般将来时连用的时间状语比较模糊,而跟进来进行时连用的时间状语非常具体I’ll write a letter to my father tomorrow.我明天要给父亲写信。
I’ll be writing a letter to my father this time tomorrow.明天这个时候,我会给父亲写信的。
(七)现在完成时表示过去发生的动作对现在产生的影响或结果,说话时已完成的动作。
I have finished the report. 我已经完成了这个报告。
She has cleaned the room.她已经打扫干净了这个房间。
1.表示从过去开始,持续到现在的动作或状态,往往和“for...”,“since...”表述的一段时间状语连用。
He has learned English for six years.他学英语已经六年了。
They have worked here since they left college.他们大学毕业以后就在这里工作。
2.表示“曾经到过某地(人已回来)”用“have/has been to”,表示“到某地去了(还未回来)”用“have/has gone to”。
—Where is Li Hua?—李华在哪里?-He has gone to the reading-room.—他去阅览室了。
—She knows a lot about Shanghai.—关于上海,她懂很多。
-She has been there.—她去过那里。
短暂动词(即瞬间动词),如:join,lose,buy,borrow,leave,go,come,arrive,die,marry,finish,complete,begin,start, break out等,在完成时态中,其肯定式不能和表示一段时间的状语连用。
要翻译“他已参军已经三年了”。
不能说:He has joined the army for three years.而要用以下三种方法:①“ago法”:He joined the army three years ago.②“延续法”:He has been in the army for three years.③“since法”:It is/has been three years since he joined the army.(八)过去完成时表示在过去某一时间以前已经完成的动作。
He had shut the door before the dog came up.在那狗走过来之前,他已将门关上了。
Everything had been all right up till this morning.直到今天上午为止,一切都正常。