清华MBA系列课件:产品开发-产品概念的产生、筛选和测试
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:489.26 KB
- 文档页数:47

第一章绪论1.1 技术创新对经济长期发展的影响(1)经济长波(长周期):繁荣—衰退—肖条—回升最早由俄国尼古拉?康德拉季耶夫于1926年提出,估计每一周期约50年,近200年来约有4个周期,现进入第5周期(2)创新与“长波”的关系关键要素突破(创新)—与新的生产组织结合—建立新“范式”—促进经济增长—作用趋缓(3)关键要素特征:①能大幅度降低成本②能长时间大量供应③具有广泛用途(4)新范式产生的变革:①出现企业内新的行为方式②要求新的劳动技术③出现利用新要素的新产品④出现充分利用新要素的根本、渐进的创新⑤出现新的投资模式、投资市场⑥形成新的基础设施投资波⑦新的小企业进入新生产部门⑧大企业集中于生产、使用关键要素密集的部门⑨出现新的消费服务模式⑩经济结构深层调整、制度变革1.2 中国产业、企业创新的必要性(1)国际人均GDP达到1000美元 ? 经济自动进入起飞阶段?20世纪80年代以来,先后16个国家人均GDP达到1000美元,现仍保持在1000美元以上的:7个;不升反降的:9个发展中国家的追赶多数都不成功泰国的反思:金融危机的背后——缺乏创新能力和战略(2)中国经济发展模式:高投入,高消耗,高污染,低产出〃能源—我国综合能源利用率33%,比发达国家低10个百分点主要产品单位能耗平均比国外先进水平高40%炼钢、水泥、乙烯综合能耗比国外高 21%,45%,31%—预计2020年我国能源消费总量约30亿吨标准煤:未来17年煤炭建设规模相当于美国目前的产煤能力;电力建设要再造两个日本电力工业;石油天然气对外依存度超过50%和40%〃矿产资源—森林资源为世界人均拥有量的1/545种主要矿产资源人均占有量不足世界人均水平的一半中国人均储量为世界人均储量的:石油 11%,天然气 4.5%,煤炭 79%,铜 18%,铁矿石 42%,铅7.3%—几十年来,GDP增长10多倍,矿产资源消费增长40多倍;如果照些下去,几十年后,我国资源需求量将接近全球消费总量〃水资源—全国目前缺水300 ~400亿米3—我国GDP约为美国的1/8,但用水总量和美国相当〃环境—每年工业固体废弃物产生量10亿吨—废水排放总量居世界之首(2003年453亿吨)— 2003年SO2排放2120万吨,大大超过环境自净能力,1/3国土受酸雨污染— CO2排放〃结论:我国目前的粗放发展方式难以持续,繁荣掩盖着危机出路:技术升级,产业升级我国企业面临的新的竞争形势〃告别短缺经济〃经济全球化〃科技进步加速〃与国外技术势差缩小北大方正:一项技术创新,导致新产业的出现和腾飞— 1974年第四代电子排版系统国外刚开始研究国内在研发第二、三代王选为主研发第四代— 1979. 华光 I,1983. 华光 II,1985. 华光 III 1987. 华光 IV商业化— 1988. 国外企业退出中国市场某电扇企业—国内最早大批量生产,第一个达亿元的乡镇企业—现在仍主要生产电扇,勉强生存美的—开始创业,生产电扇在其后—继而开发生产空调,新型家电,开拓其他领域—成长为大企业江阴兴澄特种钢铁有限公司— 1959年农具厂— 1970年仿造国外样机造工频炉炼第一炉钢— 1985年生产能力:6万吨普钢,3.4万吨钢材— 1986年钢产量21万吨,钢材17万吨— 1993年合资,成为国内最大的特钢厂,13项技术、经济指标全国第一江苏法尔胜股份有限公司:技术升级,产业升级— 1964年创建手摇麻绳小厂— 1968年生产钢丝绳—生产胶带钢丝绳市场占有率95%— 1985年国家机电产品出口基地— 1990年代初生产光缆,新材料— 2000年总资产21亿元,销售额19.9亿元,利税2.2亿元1.3.研究现状和方法从关注技术活动的某些阶段(研究开发阶段)向关注技术活动的全过程(技术创新过程)发展;从关注单项活动(技术开发活动)向关注多项活动集成(技术开发、组织变动、人力资源开发等)演进;从关注局部活动(技术性活动)向关注全局性活动(技术、生产、商业等)变化;从静态管理向动态管理推进,强调适应不断变化的环境并及时调整。








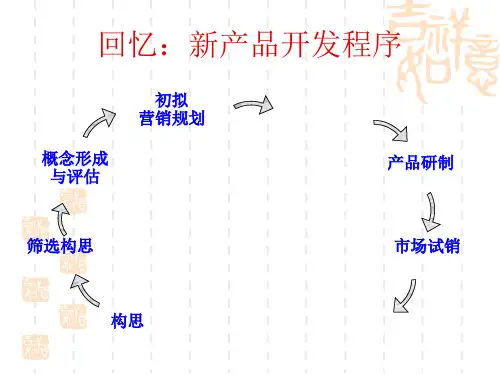
产品研发中的需求管理——《新产品开发》课堂演讲演讲提纲 开场白(自我介绍)5 分钟 产品生命周期流程简介10 分钟 需求管理关键概念、流程及工具45 分钟– Needs,Wants,Demands, Requirements– Project Chart– Customer Information– Customer Requirements– Internal Requirements– Product Definition– Templates & Tools 休息10 分钟 需求管理流程及工具work shop20 分钟 问答30 分钟Speech Objectives Walk through the product requirement management process of a real company, hence togive the audience some exposure of the RM implementation. Leaving the room, audience should have knowledge about,– What a real requirement management process looks like – What are key elements of this process – Some templates and tools And, Have Fun!What Is a Product?In this case, it is An instrument An accessory A software application A service An integrated system An upgrade to any of the aboveProduct Life Cycle OverviewDoc Config. ManagementISO 9001:2000Planning and TrackingRequirement ManagementConcept Investigation DefinitionDevelopmentSoftware QualificationHardwareFirstQualification ProductionShipmentDiscontinuance &Support LifeCONINVDEFDEVSHPDISPRCPCCPADDPricing PublicCorporate PriceCommitment & AvailabilityNew Product IntroductionWho Use PLC process?All people who are involved in the development, manufacture and support of products are affectedConcept Investigation DefinitionDevelopmentSoftware QualificationHardwareFirstQualification ProductionShipmentDiscontinuance &Support LifeProduct PlanningProduct Marketing Product Development (R&D)Manufacturing EngineeringQuestions to be answered:- Who is the customer? - What is the product? - Core competitive contribution - Product value proposition - Is it feasible? - How much resources areneeded to implement it? - ROI - Strategy fit? - ……Other Functions ------Business Management FinanceOther Marketing functions - Customer Support - Learning Product - Business developmentOther R&D / manufacturing Functions - Software Test Engineer - Quality Engineer - Procurement - Production - Reliability Engineer - Process Engineer - Transition SupervisorWhat Is a Requirement?我饿啦……鱼翅、熊掌……汉堡包……NeedsWantsDemands --Wants for specific products backed by an ability to pay- Opportunity Assessment - Project Charter - Customer Requirements - Internal Requirements - Product Definition热狗……RequirementsDDeeffiinniittiioonn ooff aa RReeqquuiirreemmeenntt:: AAnn eexxtteerrnnaallllyy oobbsseerrvvaabbllee cchhaarraacctteerriissttiicc ooff aa ddeessiirreedd ssyysstteemmProductsRequirements Examples The cellular phone shall have a color display of 256 colors or above The system's functions shall be activated and terminated by menu selections. The menu shall be localized into Chinese, Japanese and Korean.Why Manage Requirements?Project Failures Standish Group Survey 2000 found that:• 49% projects were “challenged” • 23% projects “failed” • 28% project “succeeded”Failed projects:• 5/8 attributed to requirements • 3/8 managerial • None were technical!Consequences of Poor Requirements?• Product nobody wants • Wasted effort • Burn-out • CynicismClassic ProblemsScope• feature creep • the boundary of the system is ill-defined • unnecessary design information may be givenUnderstanding• users have incomplete understanding of their needs • project team has poor understanding of problem domain • user and developer have different languages • ease of omitting “obvious” information • conflicting views for usersVolatility• requirements evolve over timeNO Requirements!Benefits of finding errors early¾Discovering requirements •requirements elicitation•data capture•analysis¾Documenting requirements •specifications¾Maintaining requirements •controlling changes•validating requirementsManaging ChangingRequirements Traceability and Validation 9Opportunity Assessment 9Project Charter9Customer Requirements 9Internal Requirements9Product DefinitionGather inputsGenerate the Opportunity Assessment Generate the Project CharterProduce a Customer Information Document (CI) Specify the Customer Requirements (CR) Determine the Minimum Viable Product Define the ProductGather the Internal Requirements (IR)Create a System DesignGenerate Sub System SpecificationsVerify the Product Definition Key deliverables:•Project Chart •Customer Information •Customer Requirements •Internal Requirements •Product DefinitionExamples of key deliverablesWriting Good Customer Requirements A “Good”requirement is9Necessary9Verifiable (Able to be tested -> not written subjectively)9Attainable9Technically feasible9Clear9Unambiguous, complete, expressing a single thought Common Problems9Making bad assumptions9Writing implementation (HOW) instead of requirements (WHAT) 9Describing operations instead of writing requirements9Using incorrect terms9Using incorrect sentence structure or bad grammar9Missing requirements9Over-specifying“Bad”Requirements•The user-interface shall be easy to use.•The system shall be 100ft2 in size.•The system shall support the training coordinator in defining training scenarios.•Have a unit calibration time commensurate with equivalent products.•The system’s power sensors will operate over various power and frequency ranges.•The ability for customers to download firmware on-site is required so that new features etc. can be added as they become available.•Minimize specified test equipment required to calibrate unit •The system (mobile test set) shall be capable of being connected to a mobile phone.Requirements Change ManagementNeeds喝水时,需要有盛水的容器Requirements写出满足以上需求的产品的RequirementsDe finition写出产品定义 Needs想知道手机上来电话时,对方是谁 Requirements写出满足以上需求的手机功能的RequirementsDe finition写出产品定义Other few key thingsTrade OffTailor it base on your needsCan not replace the true understanding of the customer needs, market dynamics and technologies needed to build the product。

课程介绍一、运筹学产生的和发展1. 运筹学产生的原因✓科学技术的发展,利用和改造自然的规模扩大,生产规模扩大,生产组织形式复杂,出现了更复杂的管理方面的问题。
管理方面的新问题:如何有效和合理地利用有限的或稀缺的资源,使系统的整体目标达到最优。
2. 运筹学的起源✓运筹学的三个来源:军事、经济、管理✓1981年美国军事运筹学会出版的“System analysis and modeling in defence”一书中称孙武子是世界上第一个军事运筹学家。
✓第二次世界大战期间英、美等国军事部门成立的一些研究小组的研究活动。
最初人们称这类研究为“运作研究”(operational research),或“运作分析”(operational analysis)。
✓研究的特点是集中一批跨多学科的研究人员,有组织地对一特定问题进行系统分析,提出提高某武器系统效率的操作方法和执行策略。
✓二战期间成功的运筹研究案例有:英国防空部门如何布置防空雷达,建立有效的空防预警系统;研究反潜飞机巡逻路线及深水炸弹引爆深度,击沉德军潜艇数提高4倍;研究如何使用机载雷达提高轰炸命中率,两年内使命中率提高3倍;研究船队在受敌机攻击时的躲避策略,使中弹率从47%下降到29%;✓数理经济对运筹学的影响Qusnay 的经济表Walras 提出的经济平衡问题V on Neumann 提出的广义经济平衡模型康托洛维奇(Kantorovich)发表的《生产组织和计划中的数学方法》✓管理科学-- 运筹学的关系✓管理理论中最有影响的三个学派中的两个(古典学派与系统学派)广泛应用定量分析与系统分析的方法。
✓古典学派的代表性人物Taylor, Gantt 等提出的动作分析、甘特图至今还在使用。
3. 运筹学的发展二战结束后运筹学在理论上得到全面的发展;线性规划、非线性规划、动态规划、网络分析、整数规划、对策论、排队论等分枝得到迅速的发展。
运筹学应用从军事部门迅速向工业部门转移。