DHCP协议抓包实验
- 格式:doc
- 大小:2.90 MB
- 文档页数:7

华为⽹络实验-利⽤DHCP服务(中继⼝)⾃动获取IP⽬录实验原理第⼀步:客户端通过⼴播发送DHCP Discover 报⽂寻找服务器端第⼆步:服务器端通过单播发送DHCP Offer 报⽂向客户端提供IP地址等⽹络信息第三步:客户端通过⼴播DHCP Request 报⽂告知服务器端本地选择使⽤哪个IP地址第四步:服务器通过单播DHCP Ack报⽂告知客户端IP地址是合法可⽤的即客户端两次⼴播,服务器端两次单播实验⽬的通过DHCP服务(中继⼝)来⾃动获取IP具体操作1.SW1的命令1)进⼊系统界⾯并重命名为SW12)把e0/0/1⼝变为access⼝,同理e/0/0/2,e/0/0/3,e/0/0/4.3)把g0/0/1⼝变为trunk⼝2.R1的命令1)进⼊系统界⾯并重命名为R12)添加g/0/0/0和g/0/0/2的IP和⼦⽹掩码3)开通DHCP全局服务,添加单臂路由并让g/0/0/1成为中继⼝转到14.0.0.24)设置默认路由3.R2的命令1)进⼊系统界⾯并重命名为R2并添加g/0/0/2的IP和⼦⽹掩码,这边就不截图了,直接开始下⾯命令2)开始DHCP全局服务,添加g/0/0/1IP和⼦⽹掩码并让这个⼝也成为中继⼝转到14.0.0.23)添加3条静态路由4.R3的命令1)命名R2并添加⼝的IP和⼦⽹掩码2)开始DHCP服务,在接⼝处声明服务池3)第⼀个服务池R2那边的中继⼝(⽹络号、⼦⽹掩码、ip、dns)注:excluded-ip-address+IP ------排除IPstatic-bind ip-address+ip mac-address+mac地址 -----绑定ip和主机mac4)第⼆个服务池R1单臂路由的⼦接⼝5)第三个服务池R1单臂路由的另⼀个⼦接⼝6)设置⼀条静态路由即可(处于末梢端,并且是R2的直连路由)实验结果1)配置界⾯改为⾃动获取DHCP并抓包2)输⼊ipconfig /renew-----获取ip注:ipconfig /release----释放ip ⼀般不⽤同理,其他4台pc也能获取⾃⼰的ip,因为PC5我给它配了⼀个固定ip15.0.0.88并且与之mac绑定了3)全⽹互通(ping)实验总结DHCP服务的报⽂可以总结为两次客户端⼴播+两次服务器单播。
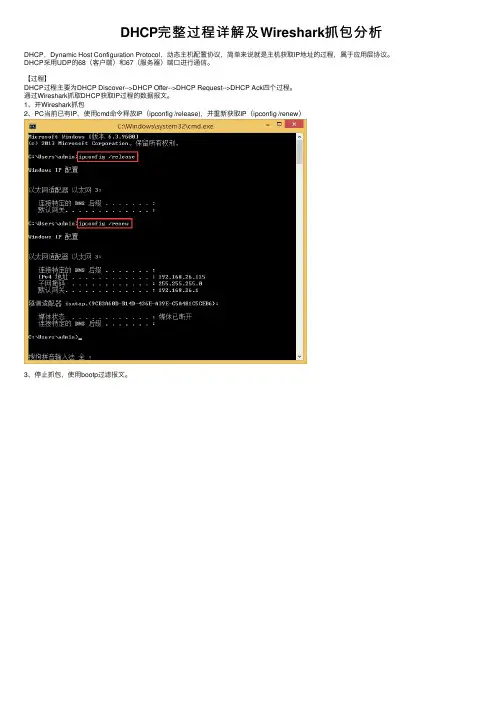
DHCP完整过程详解及Wireshark抓包分析DHCP,Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol,动态主机配置协议,简单来说就是主机获取IP地址的过程,属于应⽤层协议。
DHCP采⽤UDP的68(客户端)和67(服务器)端⼝进⾏通信。
【过程】DHCP过程主要为DHCP Discover-->DHCP Offer-->DHCP Request-->DHCP Ack四个过程。
通过Wireshark抓取DHCP获取IP过程的数据报⽂。
1、开Wireshark抓包2、PC当前已有IP,使⽤cmd命令释放IP(ipconfig /release),并重新获取IP(ipconfig /renew)3、停⽌抓包,使⽤bootp过滤报⽂。
4、可以看到图中的5个报⽂,其中DHCP Release报⽂为PC释放IP时发出的报⽂。
获取IP时,PC会发送DHCP Discover⼴播报⽂,由于当前PC没有IP,故源IP为0.0.0.0;特别要注意到的是,PC会随机出⼀个Transaction ID,如果之后收到的Offer报⽂中的Transaction ID与PC模拟出的不同,PC会将该Offer报⽂直接丢弃。
DHCP Offer报⽂DHCP Request报⽂DHCP Ack报⽂【模拟服务器发送Offer报⽂的过程及注意事项】1、保证服务器与客户端的连通性2、准备好⼀个Offer报⽂(可编辑)3、使⽤Wireshark抓取客户端发出的Discover报⽂,确定当前客户端随机出的Transaction ID4、更改Offer报⽂中的Transaction ID与Discover报⽂中⼀致5、使⽤发包软件发送Offer报⽂注:Transaction ID【地址租期】DHCP服务器提供的每个IP地址都有相应的租⽤期,在Offer报⽂中的IP Address Lease Time中可以看到。

实验7_使用Wireshark分析DHCP协议DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)是一种网络协议,用于动态分配IP地址、子网掩码、默认网关、DNS服务器等网络配置信息给计算机设备。
在本实验中,我们将使用Wireshark工具来分析DHCP协议的工作流程和数据包的结构。
首先,我们需要准备一个局域网环境,并在其中设置一个DHCP服务器和至少一个客户端设备。
DHCP服务器负责为客户端设备分配IP地址和其他网络配置信息。
客户端设备在启动时会发送DHCP请求,以获取分配给它的IP地址和其他配置信息。
使用Wireshark进行DHCP协议分析的步骤如下:1. 打开Wireshark软件,并选择适当的网络接口进行抓包。
在“捕获”选项卡中,选择正确的网络接口,然后点击“开始”按钮开始抓包。
2.在客户端设备上,启动DHCP服务发现过程。
客户端将发送一个DHCP发现广播消息,以寻找可用的DHCP服务器。
3. 在Wireshark中,我们可以看到DHCP发现消息的数据包。
可以通过在过滤器栏中输入“bootp”或“dhcp”来过滤只显示与DHCP相关的数据包。
4.DHCP服务器接收到DHCP发现消息后,会回复一个DHCP提供消息。
该消息包含了DHCP服务器可以提供给客户端的IP地址和其他配置信息。
5.客户端接收到DHCP提供消息后,会发送一个DHCP请求消息,以确认接受DHCP服务器提供的配置信息。
6.DHCP服务器接收到DHCP请求消息后,会发送一个DHCP确认消息,将IP地址和其他配置信息分配给客户端。
7. 在Wireshark中,我们可以查看这些DHCP消息的详细信息。
可以看到每个消息的源IP地址、目的IP地址、消息类型、配置选项等。
8.客户端设备在接收到DHCP确认消息后,将使用分配给它的IP地址和其他配置信息来配置自己的网络连接。
通过分析DHCP协议的数据包,我们可以了解到DHCP协议的工作流程和数据包的结构。

实验15 DHCP服务器配置及原理实验1 实验目的通过实验,掌握DHCP服务器配置及工作原理。
2 实验环境VMware及windows 2003系统WireShark3 实验原理3.1 DHCP简介DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)提供了一种简便的方法,能够自动地为网络中没有IP地址的主机分配IP地址、子网掩码等信息,不再需要手动进行配置,大大减轻了网络管理员的工作量,因此得到了广泛的应用。
3.2 DHCP客户端获得IP地址的过程客户机从DHCP服务器获得租约的简要步骤是:初始化→选择→请求→绑定。
1、初始化当DHCP客户计算机启动时,其IP地址并没有任何设置。
然后它将DHCP DISCOVER 消息发送给本地子网。
DHCP DISCOVER包含客户介质访问控制(MAC)地址及客户系统名称。
MAC地址是所有网卡保存的唯一地址。
通过在消息中使用MAC地址,客户确保能在网络上唯一地被识别。
2、选择DHCP服务器从客户计算机收到DHCP DISCOVER消息后,将通过DHCP OFFER信息作出反应。
DHCP OFFER信息包含有客户计算机的MAC地址,提供了TCP/IP地址,子网掩码以及DHCP服务器的IP地址,它以广播的方式送到客户计算机。
DHCP服务器发送DHCP OFFER 信息之后仍暂时保留发送给客户计算机的地址,并等待要获得该地址的客户的确认信息。
如果在引导期间DHCP客户没有从DHCP服务器接收到DHCP OFFER消息,它将每隔五分钟与DHCP服务器试着进行五次通信。
其中四次重试间隔时间分别为2、4、8、16秒,另一次则在0-100毫秒之间的任意间隔。
3、请求当DHCP客户接收到DHCP OFFER消息时,要决定使用哪一条消息,因为网络上有可能有多个DHCP服务器,客户可能收到不止一条DHCP OFFER消息。
一般情况下,客户计算机使用第一条接到的信息。

dhcp配置实验报告DHCP配置实验报告引言:网络通信在现代社会中扮演着至关重要的角色。
为了实现网络连接,IP地址分配是必不可少的一步。
动态主机配置协议(DHCP)是一种常用的自动分配IP 地址的协议,它简化了网络管理和配置的过程。
本实验旨在通过配置DHCP服务器和客户端,深入理解DHCP的工作原理和应用。
一、DHCP简介动态主机配置协议(DHCP)是一种网络协议,用于自动分配IP地址、子网掩码、网关和其他网络参数给计算机。
DHCP服务器负责分配IP地址,而客户端则通过与DHCP服务器的通信来获取所需的网络配置信息。
二、实验环境本实验使用了一台运行Windows操作系统的计算机作为DHCP服务器,另外两台计算机作为客户端,它们都连接在同一个局域网中。
三、DHCP服务器配置1. 安装DHCP服务器软件在Windows计算机上,我们可以使用Windows Server操作系统自带的DHCP 服务器软件,也可以选择第三方软件。
本实验使用了Windows Server自带的DHCP服务器软件。
2. 配置IP地址池打开DHCP服务器管理工具,配置IP地址池,即可用于分配的IP地址范围。
我们设置了一个起始IP地址和一个结束IP地址,以及子网掩码。
3. 配置其他网络参数除了IP地址,DHCP服务器还可以分配其他网络参数,如默认网关、DNS服务器等。
我们在DHCP服务器管理工具中设置了这些参数,并将其与IP地址池关联。
四、DHCP客户端配置1. 设置网络适配器在Windows客户端上,我们需要将网络适配器的配置方式改为自动获取IP地址。
这样,客户端将通过DHCP协议与DHCP服务器通信,获取所需的网络配置信息。
2. 获取网络配置信息客户端启动后,会自动发送DHCP发现报文,以寻找可用的DHCP服务器。
一旦找到DHCP服务器,客户端将与其进行通信,获取所需的网络配置信息。
3. 应用网络配置信息客户端收到DHCP服务器发送的网络配置信息后,将自动应用这些配置,包括IP地址、子网掩码、网关等。

Using WireShark for DHCP capture andDNS capture0921282109B04The configuration of the WireSharkThe WireShark interface in Linux is as above.The capture is done in the lab, in an café house as well as in the dorm. The connection to cafe is wireless connection, in the lab thelaptop is allocated to a public IP address and in dorm, where it iswired connection, the laptop is allocated to a private IP address, while the router’s IP is 192.168.1.1.While with wired connection, the interface selected is eth0,with wireless connection, the interface selected is eth 2.When capturing DHCP packet, the configuration of capture is as follows:When capturing DNS message, the configuration is as follows:●The procedure of captureClick on the third button to While capturing, click thethird start capture. button to stop.●DHCP analysisAfter input and in cmd ,,Release the link and rebuild the link using DHCP protocol.The five messages that the Wireshark packed are release, discover, offer, request and ACK. It can be inferred from the picture above that the source port number is 68 and the destination port number is 67. And the destination is a DHCP server as well as a router. The server’s IP address is 192.168.1.1(which is a private IP address used by a router) and the host’s IP address is 192.168.1.100(which is also a private IP address).1.Discover messageThe client broadcasts messages on the physical subnet to discover available DHCP servers. Network administrators can configure a local router to forward DHCP packets to a DHCP server from a different subnet. This client-implementation creates a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packet with the broadcast destination of 255.255.255.255 or the specific subnet broadcast address.field value meaning2.Transaction ID an integer For client to match response4.Your IPaddress 0.0.0.0 The client is waiting to beassigned for an IP address, so thisis all 0.5.Next serverIP address 0.0.0.0 The server’s IP address isunknown.6.t=53 DHCP type =DHCP discoveryCompare with the example in the lectureExcept for the mac address and the transaction ID all fields are the same.2.Offer messageWhen a DHCP server receives an IP lease request from a client, it reserves an IP address for the client and extends an IP lease offer by sending a DHCPOFFER message to the client. This message contains the client's MAC address, the IP address that the server is offering, the subnet mask, the lease duration, and the IP address of the DHCP server making the offer.The server determines the configuration based on the client's hardware address as specified in the CHADDR (Client Hardware Address) field. Here the server, 192.168.1.1, specifies the IP address in the YIADDR (Your IP Address) field.field value meaning2 Transaction ID an integer For client to match response3 Client IP address 0.0.0.0 Only field if the client isBOUND, REVEW, orREBIND, so it’s all 0.4 Your IP address 192.168.1.100 The client is offered with anIP address5 Next server IP address 0.0.0.0 The server’s IP address is inoption 546 t=53 DHCP type =DHCP offer Compare with the example in the lectureExcept for the mac address, the next server IP address and the transaction ID all fields are the same. The next IP address that captured is all zero because the server IP is in the 54 flag.3.Request messageIn response to the offer Client requests the server. The client replies DHCP request, unicast to the server, requesting the offered address. A client can receive DHCP offers from multiple servers, but it will accept only one DHCP offer. Based on the Transaction ID field in the request, servers are informed whose offer the client has accepted. When other DHCP servers receive this message, they withdraw any offers that they might have made to the client and return the offered address to the pool of available addresses. In some cases DHCP request message is broadcast, instead of being unicast to a particular DHCP server, because the DHCP client has still not received an IP address. Also, this way one message can let all other DHCP servers know that another server will be supplying the IP address without missing any of the servers with a series of unicast messages.field value meaning2 Transaction IDan integerFor client to match response4 Your IP address0.0.0.0The client is still waiting for an IP address so it is all 05 Next server IP address 0.0.0.0 The server’s IP address is in option 546 t=53DHCP type =DHCP request 7 t=54 Server’s identifier is 192.168.1.1 8 t=50 Re quested IP address is 192.168.1.100Compare with the example in the lectureExcept for the mac address and the transaction ID all fields are the same.4.ACK messageWhen the DHCP server receives the DHCPREQUEST message from the client, the configuration process enters its final phase. The acknowledgement phase involves sending a DHCPACK packet to the client. This packet includes the lease duration and any other configuration information that the client might have requested. At this point, the IP configuration process is completed.field value meaning2 TransactionIDan integer For client to match response3 Client IPaddress 0.0.0.0 Only field if the client isBOUND, REVEW, orREBIND, so it’s all 0.4 Your IPaddress 192.168.1.100 The client is allocated withthe address6 t=53 DHCP type =DHCP request7 t=54 Server’s identifier is 192.168.1.18 t=1 Subnet mask 255.255.255.09 t=3 Router is 192.168.1.110 T=6 Domain name serverThe server’s IP address is in option 54Compare with the example in the lecturecomparefield12 3 4f8fdea2e f8fdea2e f8fdea2e f8fdea2e TransactionID0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Client IPaddress0.0.0.0 192.168.1.100 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.100 Your IPaddress●DHCP sequenceThe Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical distributed naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities.A Domain Name Service translates queries for domain names (which are meaningful to humans) into IP addresses for the purpose of locating computer services and devices worldwide.Input in the broserThere are 2 DNS messages, the host asks for and the server send back the address of server.1.query1 Frame address3 Port number DNS port: 53 src port: 48376The DNS port is 53 and the port of the host is a random number. 4 DNS ID 4a 36Correlate querieswithresponses.5 Flags 01 00 This is a message that the host send to server, so it is a quire.6 Question section1 The number of availablequestion is 1 (the question is at the end of the message)7 Answer section 0These three ars in answer section. This is a query message, so the three are all 0.8Authority section9 Additional section2.answer1 Frame address2 Destination ipaddress 192.168.1.112 The private IP in the localnetwork that the router allocatedit to the laptop. Which is also thehost.3 Port number src port: 53dst port: 48376 The DNS port is 53 and the port of the host is a random number.4 DNS ID 4a 36 Correlate queries withresponses.5 Flags 81 80 The server can de recursivequery and the message is aresponce.6 Questionsection 1 The number of availablequestion is 1 (the question is atthe end of the message)7 Questionsection 1 The same as the previousmessage sent.8 Answer section 7 There are 7 IPAddress for google server.9 Authoritysection0 No Authority section。


dhcp配置实验报告
DHCP配置实验报告
实验目的:通过实验掌握DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)的配置和使用方法,了解DHCP在网络中的作用和原理。
实验内容:
1. 确定网络拓扑:在实验环境中,我们使用了一台路由器和多台计算机,路由器连接到互联网,计算机连接到路由器的局域网端口。
2. 配置DHCP服务器:在路由器上配置DHCP服务器,设置IP地址池、子网掩码、网关和DNS服务器等参数。
3. 配置DHCP客户端:在计算机上配置DHCP客户端,将网络设置改为自动获取IP地址和DNS服务器。
4. 测试DHCP功能:通过在计算机上查看IP地址、子网掩码、网关和DNS服务器等信息,验证DHCP服务器是否成功分配了IP地址和其他网络参数。
实验结果:
经过配置和测试,我们成功实现了DHCP服务器和客户端的正常工作。
在计算机上查看网络设置,发现它们成功获取了IP地址、子网掩码、网关和DNS服务器等信息。
这表明DHCP服务器成功地为计算机分配了IP地址和其他网络参数,实现了自动网络配置的功能。
实验总结:
通过本次实验,我们深入了解了DHCP的配置和使用方法,掌握了DHCP在网络中的作用和原理。
DHCP能够自动分配IP地址和其他网络参数,简化了网络管理工作,提高了网络的灵活性和可靠性。
在实际网络环境中,合理配置和使
用DHCP能够提高网络的效率和管理水平,是网络管理员必须掌握的重要技能之一。
我们将继续深入学习和实践,不断提升自己的网络技术水平。

一、实验目的及要求:1、分析IP协议,熟知IP协议数据包各个字段的含义与作用;2、分析IP数据报分片,熟悉IP数据包的传递方式。
二、实验设备:与因特网连接的计算机,操作系统为Windows,安装有Wireshark、IE浏览器等软件。
三、实验原理:1、DHCP(动态主机配置协议)报文说明:(1)DHCP-DISCOVER:DHCP客户端广播发送的,用来查找网络中可用的DHCP服务器。
(2)DHCP-OFFER:DHCP服务器用来响应客户端的DHCP-DISCOVER请求,并为客户端指定相应配置参数。
(3)DHCP-REQUEST:DHCP客户端广播发送DHCP服务器,用来请求配置参数或者续借租用。
(4)DHCP-ACK:DHCP服务器通知客户端可以使用分配的IP地址和配置参数。
(5)DHCP-NAK:DHCP服务器通知客户端地址请求不正确或者租期已过期,续租失败。
(6)DHCP-RELEASE:DHCP客户端主动向DHCP服务器发送,告知服务器该客户端不再需要分配的IP地址。
(7)DHCP-DECLINE:DHCP客户端发现地址冲突或者由于其它原因导致地址不能使用,则发送DHCP-DECLINE报文,通知服务器所分配的IP地址不可用。
(8)DHCP-INFORM:DHCP客户端已有IP地址,用它来向服务器请求其它配置参数2、pingPING(Packet Internet Groper),因特网包探索器,用于测试网络连接量的程序。
Ping是工作在TCP/IP网络体系结构中应用层的一个服务命令,主要是向特定的目的主机发送ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol因特网报文控制协议)Echo请求报文,测试目的站是否可达及了解其有关状态。
四、实验内容和步骤:1、用300字左右,描述你对IP协议的认识;IP协议,即互联网协议(Internet Protocol),是互联网技术的核心组成部分,它定义了数据如何在互联网中传输。

计算机网络——实验一DHCP⚫ 学号:⚫班级:⚫姓名:一、为了观察DHCP运行情况,执行相关命令,捕获DHCP相关信息。
执行命令前相关信息如下:具体操作如下:1、打开Windows命令提示符应用程序,输入“ipconfig /release”,该命令将释放当前IP地址,这样主机IP地址就变成0.0.0.0。
2、启动Wireshark数据包嗅探器,开始捕获数据包。
3、返回Windows命令提示符,输入“ipconfig /renew”。
这将指示主机获取网络配置,包括新的IP地址。
本次实验中,主机获取的IP地址为192.168.1.161。
4、等待“ipconfig /renew”结束,再次输入相同命令“ipconfig /renew”。
5、第二个“ipconfig /renew”命令结束后,输入“ipconfig /release”命令将先前分配的IP地址释放给计算机。
6、最后,输入“ipconfig /renew”,再次为计算机分配IP地址。
7、停止Wireshark数据包捕获。
二、相关问题1、DHCP信息是通过UDP还是TCP发送的?UDP2、绘制一个定时数据报,说明客户机和服务器之间第一个由四个数据包组成的 Discover/Offer/Request/ACK DHCP 交换的顺序。
指出每个数据包的源端口号和目的端口号。
这些端口号是否与本实验作业中给出的示例相同?顺序为:Discover——Offer——Request——ACK3、主机的链路层地址是什么?4、DHCP Discover报文与 DHCP Requst报文有何不同?同时Discover报文没有以下两项:5、在前四组(发现/提供/请求/返回)DHCP 报文中,每组的事务标识(Transaction-ID)值是什么?第二组(请求/ACK)DHCP 信息中的事务标识(Transaction-ID)值是什么?事务标识(Transaction-ID)字段的作用是什么?区分不同组的DHCP,避免不同组的DHCP信息接受混乱。

dhcp实验报告总结
本次dhcp实验旨在探究dhcp协议的工作原理和应用,通过对实验过程的观察和数据分析,得出以下结论:
1. DHCP是一种自动分配IP地址和其他网络配置信息的协议,
它可以大大简化网络管理工作。
在实验中,我们通过配置dhcp服务
器和客户端,成功实现了IP地址的自动分配和网络配置的自动获取。
2. 在dhcp服务器的配置中,需要设置IP地址池、网关、DNS
服务器等基本信息,以及dhcp分配的IP地址的租期、子网掩码等网络参数。
在客户端配置中,只需要启用dhcp协议,即可自动获取IP 地址和其他网络配置信息。
3. 在实验中,我们还学习了dhcp协议的工作流程和报文格式。
DHCP协议使用4种报文类型:DHCPDISCOVER、DHCPOFFER、DHCPREQUEST、DHCPACK。
当客户端需要获取IP地址时,它会广播DHCPDISCOVER报文,dhcp服务器会回复DHCPOFFER报文,客户端再发送DHCPREQUEST 报文确认,并最终收到DHCPACK报文。
4. 在实验过程中,我们发现dhcp协议可以帮助网络管理员更好地管理IP地址和网络配置信息,避免了手动配置的繁琐和错误。
但是,如果dhcp服务器故障或配置不当,会给网络带来严重影响,因
此在实际应用中需要仔细考虑dhcp协议的可靠性和安全性。
综上所述,本次dhcp实验让我们更深入地了解了dhcp协议的工作原理和应用,对于今后网络管理和配置工作有很大帮助。
- 1 -。
DHCP:Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol 给主机动态的分配IP地址DHCP Server :UDP67DHPC Client:UDP68DHCP服务器分配IP的过程:1.DHCP客户端发送DHCP Discover消息,广播,请求分配IP2.DHCP服务器提供DHCP Offer消息,回应,表示可提供IP3.DHCP客户端发送DHCP Request消息,选定一个服务器,并请求IP租用4.DHCP服务器发送ACK消息,确认地址租用给客户端Wireshark过滤命令:bootp技巧:1.采用断开网络再连接2.win+R——CMD——输入ipconfig /release断开连接,输入ipconfig /renew重连Wireshark抓包对DHCP IP分配过程进行分析:1.DHCP客户端以广播的形式发送Discover请求IP租用2.范围内的DHCP服务器接收到discover请求后,会向客户端发出DHCP Offer报文作为回应,该报文包含该DHCP服务器可向DHCP客户端提供的IP地址以及该DHCP服务器自己的IP地址信息3.DHCP客户端会选择最先接收到的DHCP Offer进行处理,并以广播的形式发送DHCP Request报文,该报文会加入对应DHCP服务器的地址以及所需要的IP4.DHCP服务器接收到DHCP Request报文后,会判断报文中的服务器IP是否与自己相同。
如果不同,不做任何处理,只清除相应的IP分配记录;如果相同,服务器会向客户端发送ACK报文,确认可以使用,并且附上相应的租期。
5.DHCP客户端接收到ACK信息后,会检查该IP是否能够使用,如果可以就直接使用该IP并使用租期自动启用延续过程。
如果发现IP已被使用,则发送DHCP Decline报文告知服务器禁用该IP然后重新发起Discover。
6.当租期不到1/2左右时候,如果还要继续使用该IP,客户端会自动向服务器发起续租请求报文Request报文,服务器会向客户端发送ACK报文确认。
dhcp服务器实验报告DHCP服务器实验报告一、引言在计算机网络中,DHCP(动态主机配置协议)是一种常用的网络协议,用于自动分配IP地址和其他网络配置参数给网络中的设备。
本实验旨在通过搭建和配置DHCP服务器,探索其工作原理和应用。
二、实验目的1. 理解DHCP协议的基本原理和作用;2. 学会搭建和配置DHCP服务器;3. 掌握DHCP服务器的运行机制和常见问题的排查方法。
三、实验环境本次实验使用了一台运行Linux操作系统的服务器和若干台客户端设备。
四、实验步骤1. 安装和配置DHCP服务器软件首先,在Linux服务器上安装DHCP服务器软件,例如ISC DHCP Server。
然后,通过编辑配置文件,设置DHCP服务器的参数,包括IP地址池范围、租约时间、网关、DNS服务器等。
2. 启动DHCP服务器在配置完成后,启动DHCP服务器,使其开始监听网络中的DHCP请求。
3. 客户端设备获取IP地址在客户端设备上,设置网络接口为自动获取IP地址。
然后,重启设备或执行DHCP请求命令,以获取DHCP服务器分配的IP地址和其他配置参数。
4. 验证IP地址分配情况在DHCP服务器上,查看租约列表,确认每个客户端设备是否成功获取了IP地址。
同时,可以通过ping命令测试客户端设备是否能够与其他设备正常通信。
五、实验结果与分析通过实验,我们观察到以下现象和结果:1. DHCP服务器成功分配了IP地址给客户端设备,并提供了其他网络配置参数,如网关和DNS服务器。
2. 客户端设备可以通过获取的IP地址与其他设备进行正常通信。
3. 在租约过期前,客户端设备可以一直使用分配到的IP地址。
一旦租约过期,客户端设备需要重新向DHCP服务器请求新的IP地址。
六、实验问题与解决方法在实验过程中,我们遇到了一些问题,并通过以下方法解决:1. DHCP服务器无法启动:检查配置文件是否正确,确保IP地址池范围和其他参数设置正确。
dhcp服务配置实验报告DHCP服务配置实验报告概述:在计算机网络中,DHCP(动态主机配置协议)是一种用于自动分配IP地址和其他网络参数的协议。
通过使用DHCP,网络管理员可以更有效地管理大量计算机设备的IP地址分配,同时减少了手动配置的工作量。
本实验旨在探索和配置DHCP服务,以实现自动分配IP地址的功能。
实验环境:本次实验使用了一台运行Ubuntu操作系统的虚拟机作为DHCP服务器,同时还有几台运行不同操作系统的虚拟机作为客户端。
所有虚拟机都连接到同一个虚拟网络中。
实验步骤:1. 安装和配置DHCP服务器:首先,我们在Ubuntu虚拟机上安装了ISC DHCP服务器软件包。
然后,通过编辑DHCP服务器的配置文件,指定了DHCP服务器的IP地址范围、默认网关、DNS服务器等参数。
接下来,我们启动了DHCP服务器并确保其正常运行。
2. 客户端配置:在客户端虚拟机上,我们将网络配置设置为自动获取IP地址。
这样,当客户端启动时,它会自动向DHCP服务器发送一个DHCP请求,并从服务器获取一个可用的IP地址。
3. IP地址分配测试:一旦客户端启动并发送了DHCP请求,DHCP服务器将为其分配一个可用的IP地址。
我们使用命令行工具ping来测试客户端是否成功获取了IP地址,并且能够与其他设备进行通信。
4. IP地址续约:DHCP协议还提供了IP地址续约机制,以确保客户端在租约到期之前能够保持与DHCP服务器的通信。
我们通过修改DHCP服务器的配置文件,将租约时间设置为较短的值,并观察客户端是否能够在租约到期前成功完成续约。
实验结果:通过本次实验,我们成功配置了DHCP服务器,并实现了自动分配IP地址的功能。
客户端能够根据需要动态获取IP地址,并能够与其他设备进行通信。
在IP地址续约测试中,我们观察到客户端能够在租约到期前成功完成续约,确保了网络连接的稳定性。
实验总结:DHCP服务的配置对于大规模网络管理非常重要。
DHCP报文分析一、环境搭建:DHCP获取IP的过程中需要有服务器提供IP地址,所以我在虚拟机中装了windows server2003服务机,然后配置DCHP服务。
搭建DHCP步骤:1、打开开始菜单-选择控制面板;2、然后打到一个名为添加或删除程序的文件;3、用鼠标左键双击打开添加或删除程序,打开添加或删除程序之后选择添加/删除Windows组件(A);4、单击选择添加/删除windows组件之后会弹出一个Windows组件添加向导;5、在拉动下拉列表框,找到网络服务这一项,再单击窗口中的详细信息按钮,打开网络服务属性窗口;6、在网络服务窗口中的下拉列表中找到一个名为动态主机配置协议(DHCP)前勾选前面的小勾,单击确定按钮之后回到Windows组件向导对话框中;7、单击下一步按钮执行DCHP安装,安装过程中会弹出一个可选网络组件窗口,单击确定按钮;8、单击确定按钮之后弹出一个选择链接窗口,选择本地链接,然后单击属性选项;9、打开本地链接属性窗口,选择TCP/IP协议;10、单击属性之后打开TCP/IP协议属性窗口,根据你网络情况为其配置一个IP地址;11、配置好IP地址之后单击确定按钮,回到本地链接属性窗口,单击关闭按钮,回到选择连接窗口,单击确定按钮;12、单击确定之后继续执行安装过程,安装完成之后会提示完成Windows组件向导窗口,单击完成按钮即可;13、接下来打开开始菜单-管理工具,可以看到DHCP,即搭建成功,下面就要配置了。
然后就是DHCP服务器的配置了,步骤如下:1、打开开始菜单-管理工具中的DHCP,右键点击新建作用域,出现新建作用域向导;2、点击下一步,输入名称和描述,点击下一步;3、设置起始IP地址和结束IP地址,形成地址池,即用于分配的IP地址空间,长度和子网掩码一般默认,然后点击下一步;4、输入排除范围,即DHCP不分配的IP地址(如果是单一的IP地址,可以直接添加),点击下一步;5、配置租约期限(默认是8天),点击下一步;6、配置DHCP选项,当然你可以选择稍后配置直接完成操作;7、配置客户端使用的路由器IP地址,然后点击下一步:8、配置域名称和DNS服务器:9、配置WINS服务器,点击下一步:10、激活作用域,完成配置。
一、请以文字列举对主机192.168.1.11进行ARP攻击的方法,并说明达到的效果。
对主机进行ARP攻击主要有两种方法:1、伪装为主机,向网关发送ARP包,以告诉网关主机的IP地址和MAC地址,但IP地址为真,MAC地址为假。
这样,主机192.168.1.11发送的请求都能发送到网关,但网关查找ARP表得到了错误的主机MAC地址,而向错误的主机发送了回应,因此得不到网关的回应而无法连网。
2、伪装为网关,向主机发送ARP包,以告诉主机网关的IP地址和MAC地址,但IP地址为真,MAC地址为假。
这样主机192.168.1.11向网关发送请求时,会发送到错误MAC地址对应的另一台主机,而真正网关没法收到主机192.168.1.1的请求,自然主机192.168.1.11无法联网。
二、主机A有两个IP,分别为192.168.1.11和192.168.2.22,主机B为192.168.1.123,请用主机B去ping主机A,并根据所抓数据包说明ping的结果是否正确。
1、主机B ping 192.168.1.11图1、ping 192.168.1.11结果图2、ping 192.168.1.11数据包可以看到数据包结果和ping的结果是相同的,均是4次请求,4次回应。
2、主机B ping 192.168.2.22图2、ping 192.168.2.22结果图4、ping 192.168.2.22数据包可以看到数据包结果和ping的结果是相同的,均是4次请求,但无回应,请求超时。
分析原因主机A的IP 192.168.2.22和主机B的IP 192.168.1.123属于不同网段。
主机B向网关发送请求数据后,网关知道此IP192.168.2.22和主机B属于不同网段,不会回应。
三、家庭网络接入方式是DHCP,请抓包分析哪些数据包为客户与局端的握手协商过程。
、图5、数据包结果。
1.DHCP协议简介:DHCP,全称是Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol,中文名为动态主机配置协议,它的前身是BOOTP,他工作在OSI的应用层,是一种帮助计算机从指定的DHCP服务器获取它们的配置信息的自举协议【DHCP工作在三层,但是它也有二层协议的部分,使用udp协议,客户机使用端口为68,服务器使用端口为67】DHCP使用客户端/服务器模式,请求配置信息的计算机叫做DHCP客户端,而提供信息的叫做DHCP的服务器。
DHCP为客户端分配地址的方法有三种:手工配置,自动配置,动态配置DHCP最重要的功能就是动态分配,除了IP地址,DHCP分组还为客户端提供其他的配置信息,比如子网掩码,这使得客户端无需用户手动就能自动配置网络2.DHCP的工作流程:(1)DHCP Discover阶段:DHCP客户机以广播方式(因为DHCP服务器的IP地址对于客户机来说是未知的)发送DHCP Discover发现信息来寻找DHCP服务器,即向地址255.255.255.255发送特定的广播信息。
网络上每一台安装了TCP/IP协议的主机都会接收到这种广播信息,但只有DHCP服务器才会做出响应【广播】(2)DHCP Offers阶段:在网络中接收到DHCP discover发现信息的DHCP服务器都会做出响应,它从尚未出租的IP地址中挑选一个分配给DHCP客户机,向DHCP客户机发送一个包含出租的IP地址和其他设置的DHCP offer提供信息【单播】(3)DHCP Request阶段:如果有多台DHCP服务器向DHCP客户机发来的DHCP offer 提供信息,则DHCP客户机只接受第一个收到的DHCP offer提供信息,然后它就以广播方式回答一个DHCP request请求信息,该信息中包含向它所选定的DHCP服务器请求IP地址的内容。
之所以要以广播方式回答,是为了通知所有的DHCP服务器,它将选择某台DHCP服务器所提供的IP地址,并确认以网络中并没有其他客户机使用该IP地址【广播】(4)DHCP ACK(NACK)阶段:当DHCP服务器收到DHCP客户机回答的DHCP request 请求信息之后,它便向DHCP客户机发送一个包含它提供的IP地址和其他设置的DHCP ACK确认信息,告诉DHCP客户机可以使用它所提供的IP地址,然后DHCP 客户机便将其TCP/IP协议与网卡绑定,另外,除DHCP客户机选中的服务器外,其他的DHCP服务器都将收回曾提供的IP地址【单播】重新登录:以后DHCP客户机每次重新登陆网络时,就不需要再发送DHCP Discover 发现信息了,而是直接发送包含前一次所分配的IP地址的DHCP request请求信息。
网络抓包实验
之
利用WireShark分析DHCP协议
—1116120209夏丽一.实验目的
学习使用网络抓包软件WireShark,掌握Dhcp协议。
二.实验内容
分析Dhcp协议请求及响应过程。
三.实验工具
WireShark抓包软件
四.实验步骤
使用DHCP获取IP地址
(1)打开命令窗口,启动Wireshark。
(2)输入“ipconfig /release”。
这条命令会释放主机目前的IP地址,此时,主机IP地址会变为0.0.0.0
(3)然后输入“ipconfig /renew”命令。
这条命令让主机获得一个网络配置,包括新的IP 地址。
(4)等待,直到“ipconfig /renew”终止。
然后再次输入“ipconfig /renew”命令。
(5)当第二个命令“ipconfig /renew”终止时,输入命令“ipconfig /release”释放原来的已经分配的IP地址
(6)停止分组俘获。
如下图:
五.实验分析
1.发现
由截图可知,本机发起DHCP Discover包,用来寻找DHCP服务器,源ip是0.0.0.0,因为刚开始还不知道,目的地址是255.255.255.255的广播地址,广播到整个网段。
Message type为1表明是请求包,由客户端发出。
Hardware address length为6表示本机的网络硬件地址长度为6bytes
Hops为0表示跳数,此处为0 表示没有经过网关。
此字段表示DHCP报文类型
此字段表示DHCP客户端的报文类型。
这是UDP上的DHCP,本机发起的端口是68,目标端口是67.
2.提供
DHCP服务器收到客户端发的DHCP Discover之后,会在自己的地址池中拿出一个没有分配的地址以及配套的参数(如:掩码、DNS、网关、域名、租期……),然后以一个DHCP
Offer包发送出去。
此时源IP是DHCP服务器的IP,目的IP是255.255.255.255的广播。
这时候本机还无法获得IP,所以DHCP服务器只能用广播来回应。
此截图表明通过UDP传输,客户端端口号68,服务器是67。
Message type为2表明是回复包。
Hops为1不标明经过了一个中继。
表明给客户端的IP地址,但是现在还没有确认。
这是中断的地址,就是网关
DHCP服务器地址3.选择
客户端收到这个DHCP Offer后,会再发出一个DHCP Request给服务器来申请这个Offer 中包含的地址。
这个时候,客户端还没有正式拿到地址,所以还需要向DHCP服务器申请。
此时客户端的源IP还是0.0.0.0,目的IP还是255.255.255.255。
将这些都广播出去,告诉其他DHCP服务器和分配给本机的服务器。
4.确认
被客户机选择的DHCP服务器在收到DHCPREQUEST广播后,会广播返回给客户机一个DHCPACK消息包,表明已经接受客户机的选择,并将这一IP地址的合法租用以及其他的配置信息都放入该广播包发给客户机。
六.实验小结
通过本次试验,自己更加了解了DHCP的获取过程,以及中间的数据包传递。