2012年外贸业务员考试:《基础理论》模拟试题及答案解析
- 格式:docx
- 大小:26.19 KB
- 文档页数:11



全国外贸业务员试考基础理论考试试题一、选择题(每题2分,共30分)1.以下哪个不属于国际贸易的支付方式?A. 信用证B. 电汇C. 托收D. 凭证支付2. 下列哪种国际贸易方式可以实现双边结算和相互放贷?A. 私人对外贸易B. 工厂贸易C. 国际转口贸易D. 商品贸易3. 在国际采购中,以下哪种采购方式属于批量采购?A. 定点采购B. 竞争性谈判C. 协议采购D. 比价采购4. 在国际贸易中,一般情况下,在合同中约定的交割港是指货物的A. 起运港B. 运输港C. 中转港D. 目的港5. 出口内销是指将计划内出口商品在国内市场上销售的贸易方式。
以下哪种条件不需要满足?A. 出口内销必须控制出口商品的质量和成本B. 出口内销必须遵循出口政策和法律法规的规定C. 出口内销必须按照国内的市场需求来调整出口商品的规格和品牌D. 出口内销必须满足国内市场的消费者需求6. 在国际贸易中,以下哪种信用证是最常见的一种?A. 电汇信用证B. 可撤销信用证C. 不可撤销信用证D. 过期信用证7. 以下哪项不属于国际物流的主要业务范畴?A. 运输B. 仓储C. 包装D. 人力资源8. 在国际贸易中,以下哪一项不属于知识产权的保护形式?A. 专利B. 商标C. 版权D. 信用证9. 关税是国家对进口和出口商品课征一定比例的税款。
以下哪项不属于关税的种类?A. 进口关税B. 出口关税C. 过境关税D. 销售税10. 以下哪项不属于国际贸易中经常出现的贸易壁垒?A. 关税B. 非关税壁垒C. 证据不足壁垒D. 制度性壁垒11. 以下哪个属于保护主义的贸易政策?A. 自由贸易B. 关税配额C. 投资自由D. 扩大开放12. 对于外贸人员来说,以下哪项不属于专业素质和能力?A. 商务英语熟练B. 贸易政策了解C. 人际交往能力D. 物流管理知识13. 以下哪种情况不属于依据国际商事规则处理纠纷的机制?A. 国际贸易谅解程序B. 仲裁C. 法院判决D. 调解14. 在国际贸易中,随货的商业发票是A. 商业合同的补充条款B. 汇票的补充条款C. 押汇的补充条款D. 托收单据的补充条款15. 以下哪项不属于国际结算方式?A. 托收C. 承兑D. 汇兑二、问答题(每题10分,共40分)1. 国际贸易的基本步骤有哪些?2. 请简述信用证的作用和流程。

外贸跟单员基础理论模拟试卷30(题后含答案及解析) 题型有:1. 单选题 2. 多选题 3. 判断题单项选择题在下列试题的几种答案中选出一个正确答案。
1.以下哪些不是属于供应商因在管理方面原因造成原材料供应不及时( )。
A.质量管理不到位B.对再转包管理不严C.交货期责任意识不强D.超过产能接单正确答案:D2.以下哪些不是属于原材料供应商在生产能力方面出现的问题( )。
A.生产交货时间计算错误B.临时急单插入C.小批量订单需合起来生产D.需调度的材料、零配件采购延迟,生产量掌握不准确E.不合格品产生较多正确答案:A3.适当的交货地点是指( )。
A.供应商企业的仓库B.采购商仓库C.供应商企业的生产线上D.只要离企业最近、方便企业装卸运输的地点都是适当的交货地点正确答案:D4.跟单员花费精力最多的跟单环节是( )。
A.制作采购单B.内部报批C.采购单跟踪D.原材料检验正确答案:C5.跟单员跟踪采购单的最后环节是( )。
A.跟踪原材料供应商的生产加工工艺B.跟踪原材料C.跟踪加工过程D.跟踪包装人库正确答案:D6.营业执照企业注册地与企业经营办公地不一致的原因,不可能的是( ).A.企业近期搬新址,还来不及进行工商变更B.有的老企业,在当时注册时就存在住所、办公场所、生产场所分处三地或多地的情况C.企业违法经营,有意搬离注册地D.企业注册地与企业经营办公地不一致是我国法律允许的行为正确答案:D7.对于注册资本与注册资金的关系,以下正确的是( ).A.注册资本就是注册资金,两者含义相同B.注册资本随着企业经营效益的变化而变化C.注册资本是所有的股东投人的资本,一律不得抽回D.注册资金反映的是公司法人财产权正确答案:C多项选择题在下列试题的几种答案中选出两个或两个以上的正确答案。
错选、少选或多选都不得分。
8.以下对出口退税理解正确的是( )A.避免了本国出口产品受到国际双重征税B.可以使出口货物以不含税的价格进入国际市场C.是根据我国国情制定的有别于其他国家的一项特殊税收制度D.可以增强出口产品的国际竞争力正确答案:A,B,D9.我国《合同法》规定:合同的书面形式是指( )。

外贸业务基础理论考试试卷第一部分选择题(共40题,每题1分,共40分)1.外贸业务的定义是什么?– A. 指企业与外国进行的经济交流活动– B. 指企业与国内进行的经济交流活动– C. 指企业与国际组织进行的经济交流活动– D. 指企业与政府进行的经济交流活动2.以下哪个不属于外贸业务环节?– A. 采购– B. 生产– C. 销售– D. 人力资源管理3.下列哪个是外贸业务的基本流程?– A. 市场调研、签订合同、制定方案、生产、发货、售后– B. 市场调研、签订合同、生产、装运、运输、售后– C. 市场调研、签订合同、运输、报关、售后– D. 市场调研、签订合同、生产、发货、运输、售后4.在外贸业务中,FOB是指什么意思?– A. Free On Board (装运港)价– B. Free Out of Bounds (交货地)价– C. Free Over Border (运输方式)价– D. Free On Border (报关口岸)价5.以下哪个不是外贸公司的主要职能?– A. 市场开拓– B. 合同签订– C. 资金管理– D. 税务申报6.以下哪种货币不属于国际贸易结算的主要货币?– A. 美元– B. 欧元– C. 日元– D. 人民币7.CIF是指什么意思?– A. Cost, Insurance and Financing– B. Cost, Insurance and Freight– C. China Import and Financing– D. China Import and Freight8.在外贸业务中,L/C是指什么?– A. 账期付款– B. 现金付款– C. 信用证付款– D. 提货付款9.以下哪种贸易方式是指不使用中间商,由生产商直接出口给买家?– A. 找短工– B. 找代理– C. 找批发商– D. 直销10.国际贸易中,OECD是指什么组织?– A. 欧洲经济合作组织– B. 亚洲经济合作组织– C. 北美经济合作组织– D. 南美经济合作组织11.在国际贸易中,贸易壁垒是指什么?– A. 限制贸易的措施– B. 促进贸易的措施– C. 促进外资流入的措施– D. 促进经济发展的措施12.以下哪个不是国际贸易中常见的贸易壁垒?– A. 关税– B. 配额– C. 逆差– D. 汇率13.以下哪个不属于国际贸易中常见的贸易形式?– A. 平行贸易– B. 间接贸易– C. 直接贸易– D. 紧密贸易14.WTO是指什么组织?– A. 世界贸易组织– B. 世界旅游组织– C. 世界金融组织– D. 世界卫生组织15.贸易术语中的DAP是指什么?– A. Delivery At Port (港口交货)– B. Delivered At Place (指定地点交货)– C. Delivered Duty Paid (完税后交货)– D. Delivery After Payment (支付后交货)16.外贸经理的主要职责是什么?– A. 协助市场调研工作– B. 签订合同和报关– C. 拓展市场和管理团队– D. 财务管理和税务申报17.外贸合同中的INCOTERMS指的是什么?– A. 贸易壁垒– B. 国际贸易准则– C. 货物品质标准– D. 国际贸易条款18.在国际贸易中,关税是指什么?– A. 货物运输费用– B. 进出口税– C. 税收补贴– D. 保险费用19.外贸业务中的HS编码是什么?– A. 车辆识别号– B. 货物品质标准– C. 货物分类编号– D. 进出口许可证号码20.外贸业务中,以下哪个不属于国际贸易中的主要支付方式?– A. 信用证– B. 托收– C. 货到付款– D. 转账汇款第二部分填空题(共10题,每题2分,共20分)21.国际贸易的发展利于 __________ 的提高。

2012年外贸业务员《外贸业务基础理论(含英语)》真题及详解一、单项选择题(请将答案填涂在答题卡上,答在试卷上无效。
每小题1分,共40分)1.根据《INCOTERMS® 2010》的规定,CFR贸易术语下,买卖双方风险的分界点是()。
A.装运港船舷B.装运港船上C.目的港船舷D.目的港船上【答案】A【解析】CFR是指当货物在指定装运港越过船舷时,卖方即完成交货,卖方必须支付将货物运至指定目的港所必需的费用和运费,但交货后货物灭失或损坏的风险,以及由于发生事件而引起的任何额外费用,自卖方转移至买方。
因此,买卖双方风险的分界点是装运港船舷。
2.我国海关法规定,进口货物完税价格是指()。
A.FOBB.CFRC.CIFD.FCA【答案】C【解析】从价税计算公式:进口货物应纳关税税额=完税价格×适用的进口关税税率其中,这里完税价格=CIF价格。
3.根据《UCP600》的规定,开证行的合理审单时间是收到单据次日起的()工作日之内。
A.4个B.5个C.6个D.7个【答案】B【解析】《UCP600》第十四条(b):“按照指定行事的被指定银行、保兑行(如有)以及开证行,自其收到提示单据的翌日起算,应各自拥有最多不超过五个银行工作日的时间以决定提示是否相符。
该期限不因单据提示日适逢信用证有效期或最迟提示期或在其之后而被缩减或受到其它影响。
4.在国际货物运输保险中,下列风险属于一般外来风险的是()。
A.战争B.罢工C.失火D.串味【答案】D【解析】AB两项,战争和罢工都属于特殊外来风险;C项,失火属于意外事故。
5.根据我国有关规定,对外贸易经营者应于取得出口经营权之日起()内,向所在地的主管退税机关申请办理出口退税认定。
A.15天B.30天C.45天D.60天【答案】B6.从2011年12月1日开始,国家外汇管理局在()省市开展出口收汇核销制度试点改革,取消现场核销。
A.5个B.6个C.7个D.8个【答案】C【解析】自2011年12月1日起,在江苏、山东、湖北、浙江(不含宁波)、福建(不含厦门)、大连、青岛等省(市)进行试点。

2012年全国外贸跟单员岗位专业考试外贸跟单基础理论试题册A卷(含英语)(考试时间:2012年11月18日上午9:00—11:00)一、单项选择题(共50小题,每小题1分,共计50分。
请将答案填涂在答题卡上,答在试题册上无效。
)1.按UCP 600规定,信用证上如出现“约”字,应解释为允许有不超过()的增减幅度。
A.2.5% B.5%C.10% D.不一定2.出口货物木质包装标识中,若其中YY为HT,则HT表示()。
A.检验检疫局代码B.溴甲烷熏蒸C.热处理D.出境货物木质包装企业登记号3.如果出口货物包装上有标识,以下表述正确的是()。
A.塑料可回收标识B.铝制品可回收标识C.纸制品可回收标识D.绿点标识4.()是生产技术准备工作的核心内容,是直接影响产品生产质量的主要体系要素。
A.工艺准备B.生产质量C.工艺方法D.工艺过程5.当采用CIP、CPT、FCA贸易术语成交时,就卖方承担的费用多少而言,下列排列顺序正确的是()。
A.CIP﹥CPT﹥FCA B.CPT﹥FCA﹥CIPC.FCA﹥CIP﹥CPT D.CIP﹥FCA﹥CPT6.在国内运输跟单中,货物托运后,外贸跟单员将已托运的信息及时告知收货人,请他注意()的到货通知,也就是货物已运达、且已具备提货条件的通知。
A.发货人B.承运人C.收货人D.托运人外贸跟单基础理论试题册A卷(含英语)第1页(共28页)7.某商品单价是每台750美元CFR汉堡,外商要求改报为CIFC3%汉堡价,按照CIF 金额的110%投保一切险和战争险,费率分别为0.8%和0.5‰,则CIFC3%价格为()美元/台。
A.757.30 B.780.72C.755.30 D.780.498.在国际航空运输中,货物抵达目的地后,承运人向收货人发出到货通知,收货人凭()提取货物,并在货运单上签收。
A.货运单B.到货通知C.物权凭证D.发货人授权书9.按我国海关有关规定,收货人必须在运输工具进境申报之日起()日内向海关申报,否则将被征收滞报金。
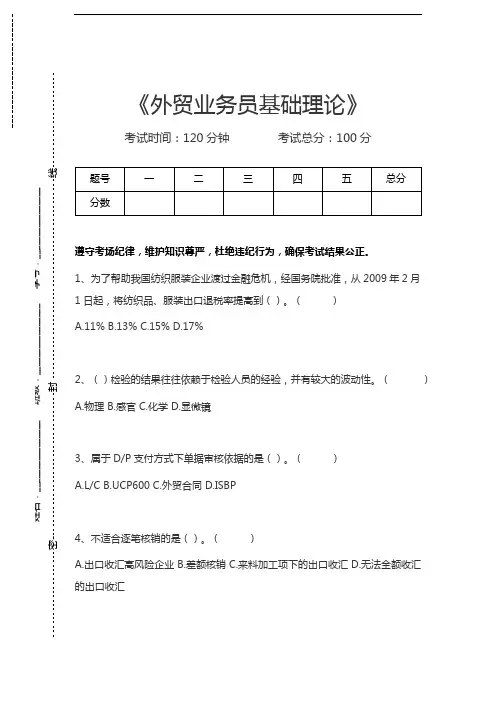
《外贸业务员基础理论》考试时间:120分钟 考试总分:100分遵守考场纪律,维护知识尊严,杜绝违纪行为,确保考试结果公正。
1、为了帮助我国纺织服装企业渡过金融危机,经国务院批准,从2009年2月1日起,将纺织品、服装出口退税率提高到()。
( ) A.11% B.13% C.15% D.17%2、()检验的结果往往依赖于检验人员的经验,并有较大的波动性。
( ) A.物理 B.感官 C.化学 D.显微镜3、属于D/P 支付方式下单据审核依据的是()。
( ) A.L/C B.UCP600 C.外贸合同 D.ISBP4、不适合逐笔核销的是()。
( )A.出口收汇高风险企业B.差额核销C.来料加工项下的出口收汇D.无法全额收汇的出口收汇姓名:________________ 班级:________________ 学号:________________--------------------密----------------------------------封 ----------------------------------------------线-------------------------5、《欧洲经济共同体产品责任指令》对产品责任实行()。
()A.过失责任原则B.无过失责任原则C.公平责任原则D.过错推定责任原则6、注册商标的专用权,是以核准注册的商标和核定使用的商品为限,有限期为()年。
()A.3B.6C.10D.157、根据进出口贸易风险的性质划分,分为静态风险和动态风险,前者属于()风险,后者属于()风险。
()A.不可回避/可回避B.不可回避/不可回避C.可回避/可回避D.可回避/不可回避8、假远期信用证中贴现费用由()支付。
()A.开证申请人B.受益人C.开证行D.通知行9、空运货物的货物体积÷体积重量=()m<sup>3</sup>/kg。
()A.6B.0.6C.0.06D.0.00610、<p> When the seller pays for all charges up to an including the loading of a consignment on board the carrying vessel, the term is ().</p>()A.DDUB.FCAC.FOBD.CIF11、Financial documents include the following except ().()A.promissory notesB.bills of ladingC.checksD.draft12、A bank opens an L/C at the request of the importer. It is a (an)().()A.issuing bank.B.applicantC.sellerrming bank13、The basic functions of a bill of lading is (are)().()A.a receipt for the goods which evidences the taking-over or loading by the carrierB.an evidence of contract of carriage between the carrier and the shipper.C.a document of title to goods.D.All of the above.14、If the seller finds any discrepancies in the letter of credit, whom does he write to asking for an amendment?().()A.The issusing bankB.The advising bankC.The applicantD.The negotiating bank15、Bank of China informs the beneficiary, a Chinese import and export company that a foreign bank has opened a letter of credit in his favor. The bank does not add its engagement by informing the beneficiary. The Bank of China ia acting as ().()A.The issusing bankB.The advising bankC.The confirming bankD.The negotiating bank16、<p> <strong>Questions from 31 to 35 are based on the following passage:</strong><br /> The exporter, as drawer of a draft (bill of exchange), hands the draft to his bank, the remitting bank, who in turn forwards it to the buyer through a collecting bank in the buyer’s country. A draft (also called a bill) is a written order to a bank or a customer to pay someone on demand or at a fixed time in the future a certain sum of money. If shipping documents accompany the draft, the collection is called “documentary collection.”<br /> Documentary collection falls into two major categories: one is documents against payment(D/P); the other, documents against acceptance (D/A).<br /> Documents against payment, as the term suggests, is that the collecting bank will only give the shipping documents representing the title to the goods on the condition that the buyer makes payment.<br />Where the paying arrangement is D/A, the collecting bank will only give the buyer the shipping documents after buyer’s acceptance of the bill drawn on him, i.e. the buyer signs his name on the bill promising to pay the sum when it matures. In return he gets what he needs – the shipping documents.<br /> Under D/A, the seller gives up the title to the goods – shipping documents before he gets payment of the goods. Therefore, an exporter must think twice before he accepts such paying arrangement.</p> Under D/P , the importer can obtain the goods only by().()A.showing the bill of ladingB.signing on the bill of exchangeC.paying in cashD.paying or accepting the bill of exchange17、<p> <strong>Questions from 31 to 35 are based on the following passage:</strong><br /> The exporter, as drawer of a draft (bill of exchange), hands the draft to his bank, the remitting bank, who in turn forwards it to the buyer through a collecting bank in the buyer’s country. A draft (also called a bill) is a written order to a bank or a customer to pay someone on demand or at a fixed time in the future a certain sum of money. If shipping documents accompany the draft, the collection is called “documentary collection.”<br /> Documentary collection falls into two major categories: one is documents against payment(D/P); the other, documents against acceptance (D/A).<br /> Documents against payment, as the term suggests, is that the collecting bank will only give the shipping documents representing the title to the goods on the condition that the buyer makes payment.<br />Where the paying arrangement is D/A, the collecting bank will only give the buyer the shipping documents after buyer’s acceptance of the bill drawn on him, i.e. the buyer signs his name on the bill promising to pay the sum when it matures. In return he gets what he needs – the shipping documents.<br /> Under D/A, the seller gives up the title to the goods – shipping documents before he gets payment of the goods. Therefore, an exporter must think twice before he accepts such paying arrangement.</p> Under D/A , the importer can gets what he needs – the shipping documents only by().()A.showing the bill of ladingB.paying in cashC.making acceptance of the bill of exchangeD.paying the bill of exchange18、<p> <strong>Questions from 31 to 35 are based on the following passage:</strong><br /> The exporter, as drawer of a draft (bill of exchange), hands the draft to his bank, the remitting bank, who in turn forwards it to the buyer through a collecting bank in the buyer’s country. A draft (also called a bill) is a written order to a bank or a customer to pay someone on demand or at a fixed time in the future a certain sum of money. If shipping documents accompany the draft, the collection is called “documentary collection.”<br /> Documentary collection falls into two major categories: one is documents against payment(D/P); the other, documents against acceptance (D/A).<br /> Documents against payment, as the term suggests, is that the collecting bank will only give the shipping documents representing the title to the goods on the condition that the buyer makes payment.<br />Where the paying arrangement is D/A, the collecting bank will only give the buyer the shipping documents after buyer’s acceptance of the bill drawn on him, i.e. the buyer signs his name on the bill promising to pay the sum when it matures. In return he gets what he needs – the shipping documents.<br /> Under D/A, the seller gives up the title to the goods – shipping documents before he gets payment of the goods. Therefore, an exporter must think twice before he accepts such paying arrangement.</p> A draft can be described as followings except ().()A.a bill of exchangeB.a kind of shipping documentsC.a billD.a written paying order19、<p> <strong>Questions from 31 to 35 are based on the following passage:</strong><br /> The exporter, as drawer of a draft (bill of exchange), hands the draft to his bank, the remitting bank, who in turn forwards it to the buyer through a collecting bank in the buyer’s country. A draft (also called a bill) is a written order to a bank or a customer to pay someone on demand or at a fixed time in the future a certain sum of money. If shipping documents accompany the draft, the collection is called “documentary collection.”<br /> Documentary collection falls into two major categories: one is documents against payment(D/P); the other, documents against acceptance (D/A).<br /> Documents against payment, as the term suggests, is that the collecting bank will only give the shipping documents representing the title to the goods on the condition that the buyer makes payment.<br />Where the paying arrangement is D/A, the collecting bank will only give the buyer the shipping documents after buyer’s acceptance of the bill drawn on him, i.e. the buyer signs his name on the bill promising to pay the sum when it matures. In return he gets what he needs – the shipping documents.<br /> Under D/A, the seller gives up the title to the goods – shipping documents before he gets payment of the goods. Therefore, an exporter must think twice before he accepts such paying arrangement.</p> In a transaction, if payment is made by collection, then the remitting bank is always located in()()A.Seller’s country B.Buyer’s country C.Either A or B D.None of the above20、<p> <strong>Questions from 31 to 35 are based on the following passage:</strong><br /> The exporter, as drawer of a draft (bill of exchange), hands the draft to his bank, the remitting bank, who in turn forwards it to the buyer through a collecting bank in the buyer’s country. A draft (also called a bill) is a written order to a bank or a customer to pay someone on demand or at a fixed time in the future a certain sum of money. If shipping documents accompany the draft, the collection is called “documentary collection.”<br /> Documentary collection falls into two major categories: one is documents against payment(D/P); the other, documents against acceptance (D/A).<br /> Documents against payment, as the term suggests, is that the collecting bank will only give the shipping documents representing the title to the goods on the condition that the buyer makes payment.<br />Where the paying arrangement is D/A, the collecting bank will only give the buyer the shipping documents after buyer’s acceptance of the bill drawn on him, i.e. the buyer signs his name on the bill promising to pay the sum when it matures. In return he gets what he needs – the shipping documents.<br /> Under D/A, the seller gives up the title to the goods – shipping documents before he gets payment of the goods. Therefore, an exporter must think twice before he accepts such paying arrangement.</p> The meaning of D/A is().()A.documents against acceptanceB.documents against paymentC.delivery after paymentD.cash against payment21、<p> <strong>Questions from 36 to 40 are based on the following passage:</strong><br /> Against this background, the WTO facesseveral daunting challenges. The first is to continue bringing down tariffs on traded goods. Average penalties have fallen steadily since the GATT’s formation but even the most open economies retain lofty barriers: for instance, America still charges a tariff of 14.6% on import of clothing, five times higher than its average levy.<br /> Resistance to tariff cuts is strongest in agriculture. According to Tim Josling, a trade expert at Stanford University, tariffs and other barriers on farm goods average a crippling 40% worldwide and create distortions that “destroy huge amounts of value”. A new set of global farm talk is planned to start in 1999. At the least, you might think, these could lock in impressive reforms in Latin America and encourage further watering-down of the European Union’s Common Agricultural Policy. But they will prove difficult: squabbles over agriculture almost sank the Uruguay round.</p> What does the WTO face?()()A.fair trade rules.B.free tradeC.export tax reduction.D.several challenges.22、<p> <strong>Questions from 36 to 40 are based on the following passage:</strong><br /> Against this background, the WTO faces several daunting challenges. The first is to continue bringing down tariffs on traded goods. Average penalties have fallen steadily since the GATT’s formation but even the most open economies retain lofty barriers: for instance, America still charges a tariff of 14.6% on import of clothing, five times higher than its average levy.<br /> Resistance to tariff cuts is strongest in agriculture. According to Tim Josling, a trade expert at Stanford University, tariffs and other barriers on farm goodsaverage a crippling 40% worldwide and create distortions that “destroy huge amounts of value”. A new set of global farm talk is planned to start in 1999. At the least, you might think, these could lock in impressive reforms in Latin America and encourage further watering-down of the European Union’s Common Agricultural Policy. But they will prove difficult: squabbles over agriculture almost sank the Uruguay round.</p> Where does impressive reforms lock in according to the passage?().()A.Americatin AmericaD.Africa23、当发现进口货物与合同不符时,代理进口的外贸企业有权直接对国外出口商起诉。



第五章出口还价核算与还盘操作一、单项选择题(以下各小题所给出的4个选项中,只有1项最符合题目要求,请将正确选项的代码填入括号内)如果外贸业务员对国外客户的发盘内容(),则不属于还盘。
[2012年真题,2010年真题]A.有条件接受B.部分接受C.实质性更改D.非实质性更改【答案】D【解析】如果对国外客户的发盘内容有实质性更改,则属于还盘。
二、多项选择题(以下各小题给出的4个选项中,有2个或者2个以上的选项符合题目要求,请将符合题目要求选项代码填入括号内)1.在出口业务中,若流通型外贸企业的外贸业务员接受国外客户略低于我方发盘的还盘价,却还要实现预期的总利润,可以采取的措施包括()。
[2015年真题] A.要求国内供应商降低价格B.要求国外客户增加订单量C.节约业务定额费D.缩短付款时间【答案】ABC【解析】D项,缩短付款时间只能使我方提早收到货款,却不能实现预期的总利润。
2.如果外贸业务员对国外客户的发盘内容(),则属于还盘。
[2014年真题] A.有条件接受B.部分接受C.实质性更改D.非实质性更改【答案】ABC【解析】接受必须与发盘相符,只接受发盘中的部分内容,或对发盘条件提出实质性的更改,或提出有条件的接受,均不构成接受,而只能视作还盘。
3.在出口谈判过程中,出口商提高价格让进口商接受的理由包括()。
[2011年真题]A.延长付款时间B.劳动力成本上涨C.原材料价格上涨D.缩短付款时间【答案】ABC【解析】D项,缩短付款时间,出口商应该降低价格。
4.在进口谈判过程中,让出口商降低价格的理由包括()。
[2012年真题]A.减少订单量B.增加订单量C.原材料价格上涨D.缩短付款时间【答案】BD【解析】AC两项都会使得出口商提升价格。
三、判断题(判断以下各小题的对错,正确的打“√”,错误的打“×”)1.在外贸谈判中,采用较多的是高一低一高让步方式。
()【答案】×【解析】在外贸谈判中,采用较多的是小幅递减让步和大幅递减让步方式。
2012年外贸业务员考试:《基础理论》模拟试题试卷总分:100答题时间:120分钟一、单项选择题1.进出口贸易磋商是( )的一项重要工作。
[1分]-----正确答案(A)A外贸业务员外贸单证员BC外贸跟单员D报关员2.签订出口合同是( )的一项重要工作。
[1分]-----正确答案(A)A外贸业务员B外贸单证员外贸跟单员CD报关员3.以下哪项不属于生产型外贸企业的经营范围?( )[1分]-----正确答案(D)出口本企业自产产品AB进口本企业所需的原辅材料C进口本企业所需的机械设备、零配件出口其他企业生产产品D4.由拍卖人宣布预定的最低价格,然后由买主竞相加价,直至出价最高时由拍卖人接受并以击槌动作宣告达成交易的拍卖方式是( )。
[1分]-----正确答案(D)A密封递价拍卖减价拍卖BC荷兰式拍卖D买主叫价拍卖5.关于代理和寄售的区别表述错误的是( )。
[1分]-----正确答案(B)A代理商与代销商与委托人的关系都是委托代理或者代销的关系B代理商是零售商的一种,代销商一般是批发商,两者处于不同的流通环节C代理行为产生的法律后果由委托人负责,而代销商有权以自己的名义订立合同,自己处理相应的法律事务代理商一般不设仓库,商品销售的费用由代理人来承担。
代销商一般有自设店面和仓库,以便顾客看样买D货、及时成交6.卖期保值(Se11ing Hedging)是指( )。
[1分]-----正确答案(A)A经营者在实货市场买进一批实物,为避免转卖时价格下跌,就在期货市场卖出同等数量的同一时期交货的期货合同经营者在期货市场买进一批实物,为避免转卖时价格下跌,就在现货市场卖出同等数量的同一时期交货的期B货合同C经营者在实货市场卖出一批实物,为避免转卖时价格下跌,就在期货市场买进同等数量的同一时期交货的期货合同D经营者在实货市场买进一批实物,为避免转卖时价格下跌,就在期货市场买进同等数量的同一时期交货的期货合同下列关于对销贸易的说法正确的是( )。
外贸业务基础理论试卷(含英语)(A 卷) 第1页 (共12页)总分复查人2012年全国外贸业务员考试外贸业务基础理论试卷(含英语)(A 卷)(考试时间:2012年5月13日 上午9:00—11:00)题 号一二三四五总 分阅卷组长得 分一、单项选择题(请将答案填涂在答题卡上,答在试卷上无效。
每小题1分,共40分)1.根据《INCOTERMS ®2010》的规定,CFR 贸易术语下,买卖双方风险的分界点是()。
A .装运港船舷B .装运港船上C .目的港船舷D .目的港船上2.我国海关法规定,进口货物完税价格是指()。
A .FOB B .CFR C .CIFD .FCA3.根据《UCP600》的规定,开证行的合理审单时间是收到单据次日起的()工作日之内。
A .4个B .5个C .6个D .7个4.在国际货物运输保险中,下列风险属于一般外来风险的是()。
A .战争B .罢工C .失火D .串味5.根据我国有关规定,对外贸易经营者应于取得出口经营权之日起()内,向所在地的主管退税机关申请办理出口退税认定。
A .15天B .30天C .45天D .60天6.从2011年12月1日开始,国家外汇管理局在()省市开展出口收汇核销制度试点改革,取消现场核销。
A .5个B .6个得 分评卷人复查人座位号C.7个D.8个7.开证行授权指定银行向受益人预付全部或部分信用证金额,由开证行保证偿还利息的信用证是()。
A.可转让信用证B.红条款信用证C.背对背信用证D.对开信用证8.我国对于国家鼓励发展产业的外商投资项目,在投资总额内进口的自用设备,除《外商投资项目不予免税的进口商品目录》所列商品外,可以免征()。
A.进口关税和进口报关费用B.进口环节消费税和进口环节增值税C.进口关税和进口环节增值税D.进口关税和进口环节消费税9.以下采用哪种信用证支付方式时受益人一般不出具汇票?()A.即期付款信用证 B.延期付款信用证C.议付信用证 D.承兑信用证10.以下哪种保险单据称为“小保单”?()A.保险单B.保险凭证C.预约保险单D.保险批单11.如果外贸业务员对国外客户的发盘内容(),则不属于还盘。
外贸跟单员基础理论模拟试卷23(题后含答案及解析) 题型有:1. 单选题 2. 多选题 3. 判断题单项选择题在下列试题的几种答案中选出一个正确答案。
1.绿色包装材料是指( )。
A.术质包装B.纸质包装C.塑料包装D.所有可回收再利用包装材料正确答案:D2.相对而言,( )作为包装材料使用不是很普遍。
A.木材B.纸C.塑料D.陶瓷正确答案:D3.以下说法错误的是( )。
A.椴木是食品包装箱的忌用材料B.杉木是茶叶包装箱的忌用材料C.马尾树适合用作机电产品等重型包装箱D.A和B都正确正确答案:C4.瓦楞纸板有各种瓦楞形状,其中( )能适应大多数瓦楞包装要求,使用较为普遍。
A.U型B.V 型C.UV型D.VV型正确答案:C5.瓦楞纸箱依据瓦楞纸板种类、内装物重量和纸箱综合尺寸可分为三类,第1类适用于( )。
A.短途运输包装B.一般运输包装C.出口运输包装D.内销商品运输包装正确答案:C6.班轮运输的运费应该包括( )。
A.装卸费,不计滞期费、速遣费B.装卸费,但计滞期费、速遣费C.卸货费和滞期费,不计速遣费D.卸货费和速遣费,不计滞期费正确答案:A7.签发多式联运提单的承运人的责任是( )。
A.只对第一程运输负责B.必须对全程运输负责C.对运输不负责D.只对最后一程运输负责正确答案:B8.开展( )是实现“门到门”运输的有效途径,它有利于简化手续,减少中间环节、快速低成本地提高运输质量。
A.航空运输B.邮包运输C.铁路运输D.多式联运正确答案:D9.我国检验检疫管制的入境货物,必须向海关提交出入境检验检疫机构签发的的单证是( )。
A.进口货物报关单B.入境货物通关单C.进口许可证D.进口收汇核销单正确答案:B10.法定检验检疫又称( )。
A.强制性检验检疫B.非强制性检验检疫C.贸易合同规定的检验检疫D.强迫性检验检疫正确答案:A11.入境货物的检验检疫工作程序是( )。
A.先放行通关后进行检验检疫B.先进行检验检疫后放行通关C.检验检疫与放行通关同时进行D.不进行检验检疫就放行通关正确答案:B12.海关最基本的任务是( )。
第一章外贸与外贸业务员一、单项选择题1.()又称为有形贸易。
A.知识产权贸易B.服务贸易C.货物贸易D.技术贸易【答案】C【解析】货物贸易又称为有形贸易,是指物质商品的进出口。
2.出入境旅游是属于()。
A.知识产权贸易B.服务贸易C.货物贸易D.技术贸易【答案】B【解析】《服务贸易总协定》把服务贸易分为十二大类,即商业性服务、销售服务、金融服务、娱乐服务、通讯服务、教育服务、卫生服务、运输服务、建筑服务、环境服务、旅游服务和其他服务。
3.进出口贸易磋商是()的一项重要工作。
A.外贸业务员B.外贸单证员C.外贸跟单员D.报关员【答案】A【解析】外贸业务员是指在进出口业务中,从事寻找客户、贸易磋商、签订合同、组织履约、核销退税、处理争议等进出口业务全过程操作和管理的综合性外贸从业人员。
4.签订出口合同是()的一项重要工作。
A.外贸业务员B.外贸单证员C.外贸跟单员D.报关员【答案】A【解析】外贸业务员是指在进出口业务中,从事寻找客户、贸易磋商、签订合同、组织履约、核销退税、处理争议等进出口业务全过程操作和管理的综合性外贸从业人员。
5.以下哪项不属于生产型外贸企业的经营范围?()A.出口本企业自产产品B.进口本企业所需的原辅材料C.进口本企业所需的机械设备、零配件D.出口其他企业生产产品【答案】D【解析】生产型外贸企业经营本企业自产产品的出口业务和本企业所需的机械设备、零配件、原辅材料的进口业务,不包括出口其他企业生产产品。
二、判断题1.生产型外贸企业与流通型外贸企业一样,既能经营自营进出口业务,又能经营代理进出口业务。
()【答案】×【解析】生产型外贸企业只能经营自营进出口业务,不能经营代理进出口业务;而流通型外贸企业两者均可经营。
2.外贸单证员完成的是若干个业务点的工作;外贸跟单员完成的是其中一条业务线的工作;外贸业务员完成的是一个业务面的工作。
()【答案】√3.购买国外某一项专利是属于服务贸易。
2012年外销员考试《国际贸易理论与实务》模拟试题及答案一、单项选择题1、下列术语中卖方不负责办理出口手续及支付相关相关费用的是()。
A、FCAB、FASC、FOBD、EXW2、象征性交货指卖方的交货义务是()。
A、不交货B、即交单又实际性交货C、凭单交货D、实际性交货3、CIF Ex Ship’s Hold 属于()。
A、内陆交货类B、装运港船上交货类C、目的港交货类D、目的地交货4、我出口大宗商品,按CIF新加坡术语成交,合同规定采用租船运输,如我方不想负担卸货费用,我方应采用的贸易术语变形是()。
A、CIF Liner Terms SingaporeB、CIF Landed SingaporeC、CIF Ex Ship’s Hold SingaporeD、CIF EX Tackle Singapore5、在以CIF和CFR术语成交的条件下,货物运输保险分别由卖方和买方办理,运输途中货物灭失和损坏的风险()。
A、前者由卖方承担,后者由买方承担B、均由卖方承担C、均由买方承担D、前者由买方承担,后者由卖方承担6、按照《2000通则》的规定,以FOBST贸易术语的变形成交,买卖双方风险的划分界限是()。
A、货交承运人B、货物在装运港越过船舷C、货物在目的港卸货后D、装运港码头7、《1932年华沙——牛津规则》是国际法协会专门为解释()合同而制定的。
A、FOBB、CFRC、CIFD、FCA8、CIF Ex Ship’s Hold与DES相比,买方承担的风险()。
A、前者大B、两者相同C、后者大D、买方不承担任何风险9、在交货地点上,《1941年美国对外贸易定义修订本》中对()的解释与《2000年通则》中对FOB的解释相同。
A、FOB Under TackleB、FOBC、FOB VesselD、FOB Liner Terms10、根据《2000年通则》的解释,CFR术语仅适用于水上运输,如果卖方先将货物交到货站或使用滚装与集装箱运输时,应采用()为宜。
2012年外贸业务员外贸业务基础理论模拟试卷[大] [中] [小]发布日期:2012-01-04 09:32 一、单项选择题(每小题1分,共40分) 1.UCP600规定,承付(Honor)不包括( )。
A.即期付款 B.延期付款 C.承兑 D.议付 2.UCP600规定,开证行的合理审单时间是收到单据次日起的( )个工作日之内。
A.5 B.6 C.7 D.8 3.( )是票据的主票据行为。
A.背书 B.承兑 C.出票 D.付款 4.出口完税价格是指( )。
A.FOB B.CFR C.CIF D.FCA 5.根据《联合国国际货物销售合同公约》规定,卖方无需承担( )的义务。
A.交付货物 B.移交一切与货物有关的单据 C.支付价款 D.移交货物所有权给买方 6.在( )市场,“CE”标志属于强制性认证标志。
A.新加坡 B.日本 C.欧盟 D.美国 7.采用( )支付方式时,无需投保出口信用保险。
A.前T/T B.D/P C.D/A D.O/A 8.打包贷款一般用于( )的贸易融资。
A.装运前 B.装运后 C.交单时 D.议付时 9.根据INCOTERMS 2000规定,采用( )术语时,由买方办理出口报关。
A.EXW B.FAS C.FOB D.DDP 10.根据CIC条款,空运险负“仓至仓”责任,自被保险货物运离保险单所载明的起运地仓库或储存处所开始运输时生效,直至该项货物到达保险单所载明目的地收货人的最后仓库或储存处所。
如未抵达上述仓库或储存处所,则以被保险货物在最后卸载地点全部卸离运输工具后满( )为止。
A.20天 B.30天 C.60天 D.90天 11.对出口商而言,以下支付方式风险从小到大的排列顺序是( )。
A.L/C B.L/C<前T/T C.前T/T D.前T/T 12.UCP600规定,遇节假日不可顺延的期限是( )。
A.信用证效期 B.装运期 C.交单期 D.汇票到期日 13.( )是当今世界上最大的检验鉴定公司。