实验04 Java输入输出流报告
- 格式:doc
- 大小:229.00 KB
- 文档页数:8

java输入输出流实验报告总结Java输入输出流是Java中非常重要的概念,也是Java程序设计的基础。
在Java 程序中,输入输出流用于处理与设备之间的数据传输,例如键盘、鼠标、文件等。
Java的输入输出流主要包含两种类型:字节流和字符流。
字节流以字节为最小读写单位,而字符流以字符为最小读写单位。
Java的输入流有很多种类型,例如:InputStream、ByteArrayInputStream、FileInputStream等。
这些输入流的共同特点是读取外部数据到程序中。
Java的输出流也有多种类型,例如:OutputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream、FileOutputStream等。
这些输出流的共同特点是将程序中的数据输出到外部。
下面将以实验报告的形式进行总结,详细介绍Java输入输出流的原理和使用方法。
实验一:字节流输入输出1. 实验目的:掌握字节流输入输出的基本使用方法。
2. 实验内容:编写一个程序,实现从文件中读取数据,然后将数据输出到另一个文件中。
3. 实验步骤:a. 创建一个输入流对象,用于读取原始文件的数据。
b. 创建一个输出流对象,用于将读取到的数据输出到目标文件中。
c. 循环读取输入流中的数据,直到读取到文件末尾。
d. 将读取到的数据写入输出流中。
e. 关闭输入流和输出流。
4. 实验结果:成功读取原始文件中的数据,并将数据输出到目标文件中。
实验二:字符流输入输出1. 实验目的:掌握字符流输入输出的基本使用方法。
2. 实验内容:编写一个程序,实现从键盘输入文字,然后将文字输出到屏幕上。
3. 实验步骤:a. 创建一个字符输入流对象,用于读取键盘输入的文字。
b. 创建一个字符输出流对象,用于将读取到的文字输出到屏幕上。
c. 循环读取输入流中的文字,直到读取到换行符。
d. 将读取到的文字写入输出流中。
e. 关闭输入流和输出流。
4. 实验结果:成功从键盘输入文字,并将文字输出到屏幕上。
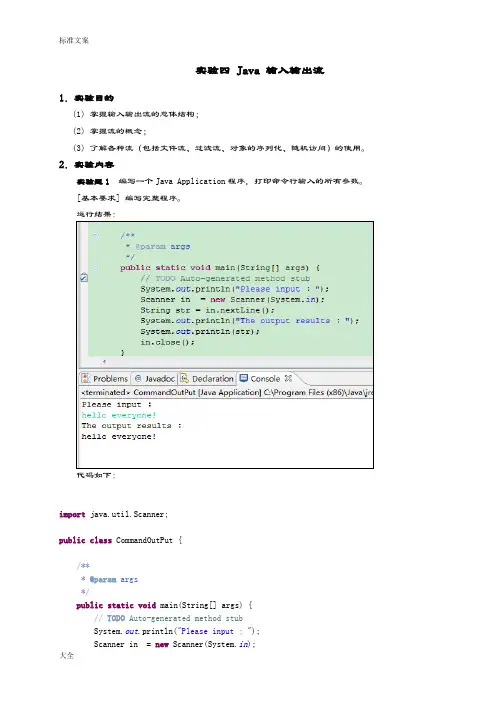
实验四 Java 输入输出流1.实验目的(1) 掌握输入输出流的总体结构;(2) 掌握流的概念;(3) 了解各种流(包括文件流、过滤流、对象的序列化、随机访问)的使用。
2.实验内容实验题1 编写一个Java Application程序,打印命令行输入的所有参数。
[基本要求] 编写完整程序。
运行结果:代码如下:import java.util.Scanner;public class CommandOutPut {/*** @param args*/public static void main(String[] args) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.out.println("Please input :");Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);String str = in.nextLine();System.out.println("The output results :");System.out.println(str);in.close();}}实验题2 通过键盘输入路径,搜索指定路径下的全部内容。
运行结果:代码如下:package .output;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.IOException;public class Output {/*** @param args* @throws IOException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stubString fileName = "d:\\xxx.txt";File file = new File(fileName);byte[] b=new byte[(int)file.length()];FileInputStream out=new FileInputStream(file);out.read(b);out.close();String s=new String(b);//将字节流转换为字符串System.out.println(s);}}实验题3设计一个类FileRWTest,实现从input.txt文件中读入数据到字符数组cBuffer中,然后再写入到文件“output.txt”中。
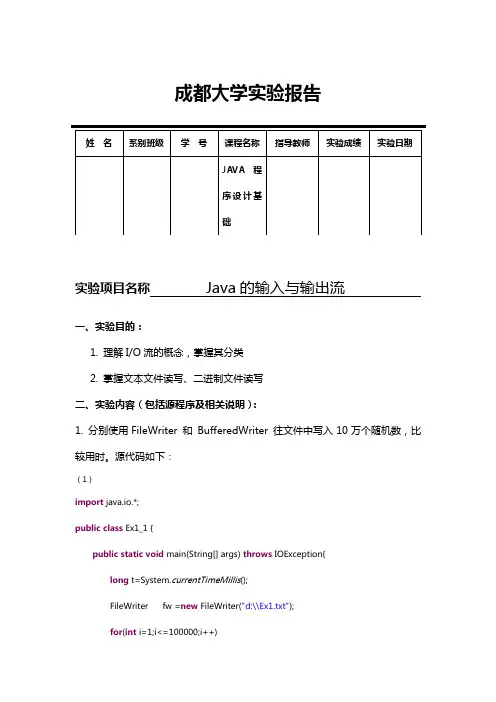
成都大学实验报告实验项目名称Java的输入与输出流一、实验目的:1. 理解I/O流的概念,掌握其分类2. 掌握文本文件读写、二进制文件读写二、实验内容(包括源程序及相关说明):1. 分别使用FileWriter 和BufferedWriter 往文件中写入10万个随机数,比较用时。
源代码如下:(1)import java.io.*;public class Ex1_1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{long t=System.currentTimeMillis();FileWriter fw =new FileWriter("d:\\Ex1.txt");for(int i=1;i<=100000;i++){fw.write((int)(Math.random()*10000)+" \n");}fw.close();t=System.currentTimeMillis()-t;System.out.println("The elapsed: "+t);}}(2)import java.io.*;public class Ex1_1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{long t=System.currentTimeMillis();BufferedWriter fw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("d:\\Ex1.txt"));for(int i=1;i<=100000;i++){fw.write((int)(Math.random()*10000)+"\n");}fw.close();t=System.currentTimeMillis()-t;System.out.println("The elapsed: "+t);}}2. 生成一个html文件,使其能显示2的幂次(0~9)的表格如下:代码如下:import java.io.*;public class Ex1_1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("d:\\Ex2.html"));bw.write("<table border=1 align=center width=200 height=250>");bw.newLine();bw.write("<tr><td align=center>Power of 2<td align=center>Value</tr>");for(int i=0;i<=9;i++){bw.write("<tr><td align=center>"+i+"<td align=center>"+Math.pow(i, 2)+"</tr>");}bw.write("</table>");bw.newLine();bw.close();}}3. 在文本文件bigbook.txt中包含有很长篇幅的英语短文,编写程序要求统计文件的所有短文中包含英文字母“A”的个数,并显示统计的时间。


JAVA程序设计实验报告专业:班级:学号:姓名:2015-2016第二学期信息工程学院实验名称:输入输出流实验地点:_鹤琴102__实验目的:(1)掌握输入输出流的概念和分类;(2)掌握输入输出流的使用。
实验内容:1、建立文件TestInputStream.java,将该文件的内容输出在控制台,同时对该文件做一个备份backup.java。
package IO;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;import javax.swing.JOptionPane;class TestInputStream {FileInputStream fin = null;FileOutputStream fout = null;byte[] bb ;File file = new File("E:13131425/TestInputStream.java");File copy = new File("E:13131425/backup.java");TestInputStream() throws Exception{Taking();}public void Taking() throws Exception {//FileInputStream fis= new FileInputStream(newFile("E:13131425/TestInputStream.java")); 有效fin = new FileInputStream(file); //有效toobyte[] bb=new byte[65560];int bytes = fin.read(bb);String str = new String(bb, 0, bytes);System.out.println(str);fout = new FileOutputStream(copy);fout.write(bb);JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "成功复制到 backup.java");fin.close();fout.close();}}2、将Unicode编码为0~50000的字符保存在文件中(d:/test/unicode.txt)。

实验项目四Java 高级编程第2部分 Java输入/输出流[实验目的]1、掌握java 常用输入、输出流类及其各自方法。
2、能够灵活使用java 常用输入、输出流类及其各自方法解决实际应用问题。
[实验要求]1、复习理论教学中所学的内容。
2、认真进行实验预习,查阅参考书,书写源程序,书写实验预习报告。
3、认真总结实验并书写实验报告。
[实验课时] 2学时[实验教学方式] 学生上机实验,教师随堂指导。
[实验内容]输入输出流实验1学读汉字1.模板代码//ChineseCharacters.javaimport java.io.*;importjava.util.StringTokenizer;public class ChineseCharacters{ publicStringBuffergetChinesecharacters(File file){ StringBufferhanzi=new StringBuffer();try{ FileReaderinOne=【代码1】 //创建指向文件f的inOne 的对象BufferedReaderinTwo=【代码2】 //创建指向文件inOne的inTwo 的对象String s=null;int i=0;while((s=【代码3】)!=null) //inTwo读取一行{ StringTokenizertokenizer=new StringTokenizer(s," ,'\n' ");while(tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()){ hanzi.append(tokenizer.nextToken());}}}catch(Exception e) {}returnhanzi;}}//StudyFrame.javaimportjava.awt.*;importjava.awt.event.*;import java.io.*;importjavax.sound.sampled.*;public class StudyFrame extends Frame implements ItemListener,ActionListener,Runnable { ChineseCharacterschinese;Choice choice;Button getCharacters,voiceCharacters;Label showCharacters;StringBuffertrainedChinese=null;Clip clip=null;Thread voiceThread;int k=0;Panel pCenter;CardLayoutmycard;TextAreatextHelp;MenuBarmenubar;Menu menu;MenuItem help;publicStudyFrame(){ chinese=new ChineseCharacters();choice=new Choice();choice.add("training1.txt");choice.add("training2.txt");choice.add("training3.txt");showCharacters=new Label("",Label.CENTER);showCharacters.setFont(new Font("宋体",Font.BOLD,72));showCharacters.setBackground(Color.green);getCharacters=new Button("下一个汉字");voiceCharacters=new Button("发音");voiceThread=new Thread(this);choice.addItemListener(this);voiceCharacters.addActionListener(this);getCharacters.addActionListener(this);Panel pNorth=new Panel();pNorth.add(new Label("选择一个汉字字符组成的文件"));pNorth.add(choice);add(pNorth,BorderLayout.NORTH);Panel pSouth=new Panel();pSouth.add(getCharacters);pSouth.add(voiceCharacters);add(pSouth,BorderLayout.SOUTH);pCenter=new Panel();mycard=new CardLayout();pCenter.setLayout(mycard);textHelp=new TextArea();pCenter.add("hanzi",showCharacters);pCenter.add("help",textHelp);add(pCenter,BorderLayout.CENTER);menubar=new MenuBar();menu=new Menu("帮助");help=new MenuItem("关于学汉字");help.addActionListener(this);menu.add(help);menubar.add(menu);setMenuBar(menubar);setSize(350,220);setVisible(true);addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){ public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){ System.exit(0);}});validate();}public void itemStateChanged(ItemEvent e){ StringfileName=choice.getSelectedItem();File file=new File(fileName); trainedChinese=chinese.getChinesecharacters(file); k=0;mycard.show(pCenter,"hanzi") ;}public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){ if(e.getSource()==getCharacters){ if(trainedChinese!=null){ char c=trainedChinese.charAt(k);k++;if(k>=trainedChinese.length())k=0;showCharacters.setText(""+c);}else{ showCharacters.setText("请选择一个汉字字符文件");}}if(e.getSource()==voiceCharacters){ if(!(voiceThread.isAlive())){ voiceThread=new Thread(this);}try{voiceThread.start();}catch(Exception exp){}}if(e.getSource()==help){ mycard.show(pCenter,"help") ;try{ File helpFile=new File("help.txt");FileReaderinOne=【代码4】 //创建指向文件helpFile的inOne 的对象BufferedReaderinTwo=【代码5】 //创建指向文件inOne的inTwo 的对象String s=null;while((s=inTwo.readLine())!=null){ textHelp.append(s+"\n");}inOne.close();inTwo.close();}catch(IOExceptionexp){}}}public void run(){ voiceCharacters.setEnabled(false);try{ if(clip!=null){ clip.close()}clip=AudioSystem.getClip();File voiceFile=new File(showCharacters.getText().trim()+".wav");clip.open(AudioSystem.getAudioInputStream(voiceFile));}catch(Exception exp){}clip.start();voiceCharacters.setEnabled(true);}}//StudyMainClass.javapublic class StudyMainClass{ public static void main(String args[]){ newStudyFrame();}}实验2统计英文单词字//模板代码//WordStatistic.javaimport java.io.*;importjava.util.Vector;public class WordStatistic{ VectorallWorsd,noSameWord;WordStatistic(){ allWorsd=new Vector();noSameWord=new Vector();}public void wordStatistic(File file){ try{RandomAccessFileinOne=【代码1】 //创建指向文件file的inOne 的对象RandomAccessFileinTwo=【代码2】 //创建指向文件file的inTwo 的对象longwordStarPostion=0,wordEndPostion=0;long length=inOne.length();int flag=1;int c=-1;for(int k=0;k<=length;k++){ c=【代码3】 //inOne调用read()方法boolean boo=(c<='Z'&&c>='A')||(c<='z'&&c>='a');if(boo){ if(flag==1){ wordStarPostion=inOne.getFilePointer()-1;flag=0;}}else{ if(flag==0){if(c==-1)wordEndPostion=inOne.getFilePointer();elsewordEndPostion=inOne.getFilePointer()-1;【代码4】//inTwo调用seek方法将读写位置移动到wordStarPostionbyte cc[]=new byte[(int)wordEndPostion-(int)wordStarPostion];【代码5】//inTwo调用readFully(byte a)方法,向a传递ccString word=new String(cc);allWorsd.add(word);if(!(noSameWord.contains(word)))noSameWord.add(word);}flag=1;}}inOne.close();inTwo.close();}catch(Exception e){}}public Vector getAllWorsd(){ returnallWorsd;}public Vector getNoSameWord(){ returnnoSameWord;}}//RandomExample.javaimportjava.awt.*;importjava.awt.event.*;importjava.util.Vector;importjava.io.File;public class StatisticFrame extends Frame implements ActionListener { WordStatistic statistic;TextAreashowMessage;Button openFile;FileDialogopenFileDialog;Vector allWord,noSameWord;publicStatisticFrame(){ statistic=new WordStatistic();showMessage=new TextArea();openFile=new Button("Open File");openFile.addActionListener(this);add(openFile,BorderLayout.NORTH);add(showMessage,BorderLayout.CENTER);openFileDialog=new FileDialog(this,"打开文件话框",FileDialog.LOAD);allWord=new Vector();noSameWord=new Vector();setSize(350,300);setVisible(true);addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){ public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){ System.exit(0);}});validate();}public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){ noSameWord.clear();allWord.clear();showMessage.setText(null);openFileDialog.setVisible(true);String fileName=openFileDialog.getFile();if(fileName!=null){ statistic.wordStatistic(new File(fileName));allWord=statistic.getAllWorsd();noSameWord=statistic.getNoSameWord();showMessage.append("\n"+fileName+"中有"+allWord.size()+"个英文单词"); showMessage.append("\n其中有"+noSameWord.size()+"个互不相同英文单词"); showMessage.append("\n按使用频率排列:\n");int count[]=new int[noSameWord.size()];for(int i=0;i<noSameWord.size();i++){ String s1=(String)noSameWord.elementAt(i);for(int j=0;j<allWord.size();j++){ String s2=(String)allWord.elementAt(j);if(s1.equals(s2))count[i]++;}}for(int m=0;m<noSameWord.size();m++){ for(int n=m+1;n<noSameWord.size();n++){ if(count[n]>count[m]){ String temp=(String)noSameWord.elementAt(m);noSameWord.setElementAt((String)noSameWord.elementAt(n),m); noSameWord.setElementAt(temp,n);int t=count[m];count[m]=count[n];count[n]=t;}}}for(int m=0;m<noSameWord.size();m++){ showMessage.append("\n"+(String)noSameWord.elementAt(m)+":"+count[m]+"/"+allWord.size()+"="+(1.0*count[m])/allWord.size()); }}}}RandomExample.javapublic class StatisticMainClass{ public static void main(String args[]){ newStatisticFrame();}}3.完成实验指导书P98上机实验10 的实验题目1“分析成绩单”以及P103 实验3“读取压缩文件”。


java中输入输出总结一、数据流的基本概念流一般分为输入流(Input Stream)和输出流(Output Stream)两类,但这种划分并不是绝对的。
比如一个文件,当向其中写数据时,它就是一个输出流;当从其中读取数据时,它就是一个输入流。
当然,键盘只是一个数人流,而屏幕则只是一个输出流。
java的标准数据流:标准输入输出指在字符方式下(如DOS),程序与系统进行交互的方式,分为三种:标准输入studin,对象是键盘。
标准输出stdout,对象是屏幕。
标准错误输出stderr,对象也是屏幕。
二、java.io包中的数据流和文件类字节流:从InputStream和OutputStream派生出来的一系列类。
这类流以字节(byte)为基本处理单位。
InputStream、OutputStreamFileInputStream、FileOutputStreamPipedInputStream、PipedOutputStreamByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStreamFilterInputStream、FilterOutputStreamDataInputStream、DataOutputStreamBufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream字符流:从Reader和Writer派生出的一系列类,这类流以16位的Unicode码表示的字符为基本处理单位。
Reader、WriterInputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriterFileReader、FileWriterCharArrayReader、CharArrayWriterPipedReader、PipedWriterFilterReader、FilterWriterBufferedReader、BufferedWriterStringReader、StringWriter三、字节流方法InputStream 和OutputStreamread():从流中读入数据skip():跳过流中若干字节数available():返回流中可用字节数mark():在流中标记一个位置reset():返回标记过得位置markSupport():是否支持标记和复位操作close():关闭流int read() :从输入流中读一个字节,形成一个0~255之间的整数返回(是一个抽象方法)。

实验四Java输入、输出和异常处理一、实验目的1.了解I/O流的使用;2.掌握常见的输入/输出流类及其主要方法。
3.熟悉S y s t e m类,掌握标准输入/输出。
4.学会利用Tr y-c a t c h-f i n a l l y语句来捕获和处理异常;5.掌握自定义异常类的方法。
二、实验要求1.使用标准数据流的应用程序。
2.使用文件输入输出流的应用程序。
3.通过编程理解系统异常处理的机制和创建自定义异常的方法。
三、实验内容(一)使用标准数据流的应用程序标准数据流指在字符方式下(如D O S提示符)程序与系统进行输入输出的方式,键盘和显示器屏幕是标准输入输出设备,数据输入的起点为键盘,数据输出的终点是屏幕,输出的数据可以在屏幕上显示出来。
1.程序功能:将键盘上输入的字符在屏幕上显示出来。
2.编写S Y4_1.j a v a程序文件,源代码如下:c l a s s S Y4_1{p u b l i c s t a t i c v o i d m a i n(S t r i n g[]a rg s)t h r o w s j a v a.i o.I O E x c e p t i o n {b y t e b u ff e r[]=n e w b y t e[10];S y s t e m.o u t.p r i n t l n("从键盘输入不超过10个字符,按回车键结束输入:");i n t c o u n t=S y s t e m.i n.r e a d(b u f f e r);//读取输入的字符并存放在缓冲区b u ff e r中S y s t e m.o u t.p r i n t l n("保存在缓冲区b u ff e r中元素的个数为:"+c o u n t);S y s t e m.o u t.p r i n t l n("b u f f e r中各元素的值为:");f o r(i n t i=0;i<c o u n t;i++){S y s t e m.o u t.p r i n t(""+b u ff e r[i]);//在屏幕上显示b u ff e r 元素的值}S y s t e m.o u t.p r i n t l n();S y s t e m.o u t.p r i n t l n("输出b u ff e r字符元素:");S y s t e m.o u t.w r i t e(b u ff e r,0,b u f f e r.l e n g t h);}}3.编译、运行S Y4_1.j a v a文件。
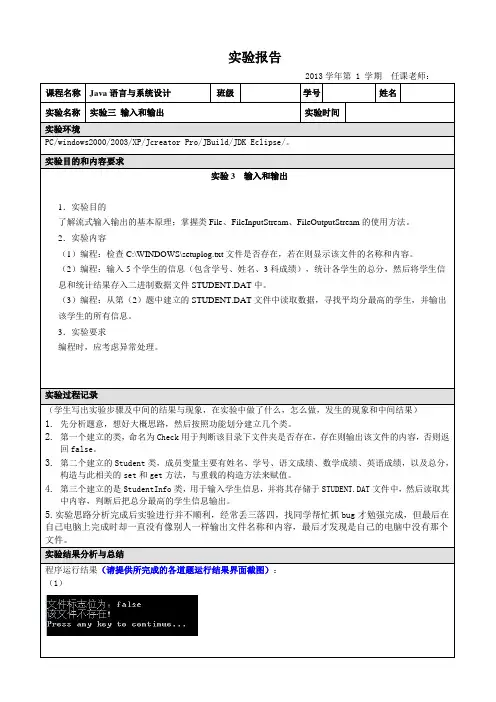
实验报告2013学年第 1 学期任课老师:课程名称Java语言与系统设计班级学号姓名实验名称实验三输入和输出实验时间实验环境PC/windows2000/2003/XP/Jcreator Pro/JBuild/JDK Eclipse/。
实验目的和内容要求实验3输入和输出1.实验目的了解流式输入输出的基本原理;掌握类File、FileInputStream、FileOutputStream的使用方法。
2.实验内容(1)编程:检查C:\WINDOWS\setuplog.txt文件是否存在,若在则显示该文件的名称和内容。
(2)编程:输入5个学生的信息(包含学号、姓名、3科成绩),统计各学生的总分,然后将学生信息和统计结果存入二进制数据文件STUDENT.DAT中。
(3)编程:从第(2)题中建立的STUDENT.DAT文件中读取数据,寻找平均分最高的学生,并输出该学生的所有信息。
3.实验要求编程时,应考虑异常处理。
实验过程记录(学生写出实验步骤及中间的结果与现象,在实验中做了什么,怎么做,发生的现象和中间结果)1.先分析题意,想好大概思路,然后按照功能划分建立几个类。
2.第一个建立的类,命名为Check用于判断该目录下文件夹是否存在,存在则输出该文件的内容,否则返回false。
3.第二个建立的Student类,成员变量主要有姓名、学号、语文成绩、数学成绩、英语成绩,以及总分,构造与此相关的set和get方法,与重载的构造方法来赋值。
4.第三个建立的是StudentInfo类,用于输入学生信息,并将其存储于STUDENT.DAT文件中,然后读取其中内容,判断后把总分最高的学生信息输出。
5.实验思路分析完成后实验进行并不顺利,经常丢三落四,找同学帮忙抓bug才勉强完成,但最后在自己电脑上完成时却一直没有像别人一样输出文件名称和内容,最后才发现是自己的电脑中没有那个文件。
实验结果分析与总结程序运行结果(请提供所完成的各道题运行结果界面截图):(1)(制作了一个相应文件后检测到的截图)(2)指导老师评阅意见指导老师:年月日填写内容时,可把表格扩大。

实验报告课程名称: Java语言程序设计姓名:学号:班级:数学与计算机科学学院数学与计算机科学学院实验报告实验名称:输入与输出指导教师:日期:}private static void writeFile() throws Exception{String s;while(true){System.out.println("输入字符串:");System.out.flush();s=keyread.readLine();if(s.length()==0) break;bwrite.write(s);bwrite.newLine();}}public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{String filename="E:\\project_java\\src\\file";file=new File(filename);if(!file.exists()){System.out.println("文件不存在");return;}fwrite=new FileWriter(file);bwrite=new BufferedWriter(fwrite);keyread=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));writeFile();keyread.close();bwrite.close();fread=new FileReader(file);bread=new BufferedReader(fread);readFile();bread.close();}}第2题代码:import java.io.*;public class MyFile{public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {String filename="E:\\project_java\\src\\file";File file=new File(filename);if(!file.exists()){System.out.println("文件不存在");return;}FileReader fread=new FileReader(file);BufferedReader bread=new BufferedReader(fread);String s=bread.readLine();while(s!=null) {System.out.println(s);s=bread.readLine();}fread.close();System.out.println("文件路径:"+file.getAbsolutePath());System.out.println("修改时间:"+stModified());System.out.println("文件长度:"+file.length());System.out.println("文件可读:"+file.canRead());System.out.println("文件可写:"+file.canWrite());}}实验结果第1题:第2题:。
实验四Java 输入输出流import java.util.Scanner;public class CommandOutPut {/*** @param args*/public static void main(String[] args) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.out.println("Please input :");Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);String str = in.nextLine();System.out.println("The output results :");System.out.println(str);in.close();}}实验题2 通过键盘输入路径,搜索指定路径下的全部内容。
package .jp;import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.File;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStreamReader;public class alldir {public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub//打印指定路径下所有的文件String path = null;System.out.println("please input path: ");BufferedReader in = null;in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));path=in.readLine();File file = new File(path);System.out.println(path+"路径下的所有文件如下:\n");File[] allfile = file.listFiles();for(File f : allfile)System.out.println(f.getName());}}实验题3设计一个类FileRWTest,实现从input.txt文件中读入数据到字符数组cBuffer中,然后再写入到文件“output.txt”中。
java输入输出流实验报告总结】Java输入输出流实验报告总结在本次实验中,我们学习了Java的输入输出流的概念和用法。
输入输出流是Java中用于处理输入和输出操作的工具。
通过输入流,我们可以将外部数据输入到程序中进行处理,通过输出流,我们可以将程序中的数据输出到外部文件或设备上。
在本次实验中,我们通过几个具体的示例来探索输入输出流的不同用法和特性,以期更好地理解和掌握它们的使用。
首先,我们学习了如何使用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream这两个类来进行字节流的输入和输出操作。
这两个类分别用于从指定文件中读取字节数据和将字节数据写入到指定文件中。
通过这两个类,我们可以实现文件的拷贝、移动、创建等功能。
同时,我们还了解了如何使用BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream这两个类来提高读写效率。
这两个类可以通过缓存数据来减少对底层系统的IO操作次数,从而提高读写速度。
接下来,我们学习了如何使用FileReader和FileWriter这两个类进行字符流的输入和输出操作。
这两个类与字节流的输入输出类似,但它们处理的是字符数据。
通过这两个类,我们可以读取和写入文本文件中的字符数据。
我们还了解了字符编码和字符集的概念,并学习了如何使用InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter来进行字符流和字节流之间的转换。
除了字节流和字符流,我们还学习了对象流的使用。
对象流可以将Java 对象直接写入到文件中,也可以从文件中读取Java对象。
这在处理一些复杂的对象数据时非常有用。
我们通过使用ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream这两个类,实现了对象的读写操作。
需要注意的是,被写入和读取的对象必须实现Serializable接口,否则会抛出NotSerializableException异常。
在实验过程中,我们还探索了如何使用标准输入输出流。
java输入输出实验报告Java输入输出实验报告引言:Java是一种广泛应用的编程语言,其输入输出(Input/Output,简称I/O)功能对于程序的交互和数据处理至关重要。
本实验旨在通过实际操作,探索Java中的输入输出机制,并深入了解其原理和应用。
一、实验目的通过本次实验,我们的目标是:1. 理解Java中的输入输出概念和基本原理;2. 掌握Java中的标准输入输出流(System.in和System.out)的使用;3. 学会使用Java中的文件输入输出流,实现对文件的读写操作;4. 熟悉Java中的异常处理机制,处理输入输出过程中的异常情况。
二、实验环境本次实验所需的环境和工具如下:1. Java开发工具(如Eclipse、IntelliJ IDEA等);2. 一台配置良好的计算机。
三、实验过程1. 标准输入输出流的使用在Java中,标准输入流(System.in)用于接收用户的输入,标准输出流(System.out)用于向屏幕输出信息。
我们可以通过Scanner类来实现对标准输入流的读取,通过System.out.println()方法实现对标准输出流的输出。
下面是一个示例代码:```javaimport java.util.Scanner;public class StandardIOExample {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("请输入您的姓名:");String name = scanner.nextLine();System.out.println("您好," + name + "!欢迎使用Java输入输出功能。
"); }}```2. 文件输入输出流的使用除了标准输入输出流,Java还提供了FileInputStream和FileOutputStream类,用于实现对文件的读写操作。
实验4:输入输出流一、实验目的1.理解I/O流的概念,掌握其分类,掌握Java I/O基本原理。
2.掌握对硬盘上的文件和目录进行操作的基本方法。
3.掌握FileInputStream、FileOutputStream类的基本使用方法。
4.掌握FileReader类、FileWriter类的使用。
5.掌握BufferedWriter类、BufferedWriter类的使用。
6.掌握RandomAccessFile类的使用。
7.掌握对象序列化的方法及ObjectInputStream、ObjectOutputStream类的基本使用方法。
二、实验要求本次实验要求以Eclipse为开发平台。
三、实验内容与步骤1.编写一个Java Application程序,实现如下的设计功能:运行该程序可以列出当前目录下的所有文件。
import .*;public class sy1 {public static void main(String args[]){File file= new File("D:\\");();File[]f1=();for(int i=0;i<;i++){if(f1[i].isDirectory()){"dirctory is"+f1[i].getName());}else{"flie is"+f1[i].getName());}}}}2.编写一个Java Application程序(文件名为),要求通过字节流从该文件中读取数据并写入到“”文件中去,实现该文件的复制。
import .*;public class CopyFile {public static void main(String args[]){int a;byte[] b="你好吗,逗比".getBytes();try{FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("D:\\新建文件夹\\zzj\\src\\zzj\\");(b);();}catch(IOException e){"error"+e);}}}3.编写一个程序(文件名为),将程序文件本身的内容每行开头添加上行号拷贝到另一个文件中。
java输入输出实验报告《Java输入输出实验报告》摘要:本实验主要通过使用Java编程语言进行输入输出实验,通过实验对Java的输入输出功能进行了深入了解和学习。
实验结果表明,Java具有强大的输入输出功能,能够满足不同场景下的输入输出需求。
一、实验目的1. 了解Java的输入输出功能2. 掌握Java中输入输出的基本方法和技巧3. 熟练运用Java输入输出进行实际编程二、实验内容1. 使用Java的标准输入输出流进行输入输出操作2. 使用Java的文件输入输出流进行文件的读写操作3. 使用Java的网络输入输出流进行网络数据的读写操作三、实验步骤1. 编写Java程序,使用标准输入输出流进行简单的输入输出操作2. 编写Java程序,使用文件输入输出流进行文件的读写操作3. 编写Java程序,使用网络输入输出流进行网络数据的读写操作四、实验结果1. 使用标准输入输出流进行输入输出操作的程序能够正常运行,能够实现对用户输入的数据进行输出并进行相应的处理。
2. 使用文件输入输出流进行文件的读写操作的程序能够正常运行,能够实现对文件的读取和写入操作。
3. 使用网络输入输出流进行网络数据的读写操作的程序能够正常运行,能够实现对网络数据的读取和写入操作。
五、实验总结通过本次实验,我对Java的输入输出功能有了更深入的了解和掌握。
Java具有丰富的输入输出功能,能够满足不同场景下的输入输出需求。
同时,我也学会了如何使用Java进行标准输入输出、文件输入输出和网络输入输出的操作,这些知识对我今后的编程工作将会有很大的帮助。
六、实验感想本次实验让我对Java的输入输出功能有了更深入的了解,也让我对Java编程语言有了更深的认识。
通过实验,我不仅学会了如何使用Java进行输入输出操作,还学会了如何处理各种输入输出异常情况,这对我今后的编程学习和工作都将会有很大的帮助。
希望今后能够继续深入学习Java编程,提升自己的编程能力。
实验四 Java 输入输出流1.实验目的(1) 掌握输入输出流的总体结构;(2) 掌握流的概念;(3) 了解各种流(包括文件流、过滤流、对象的序列化、随机访问)的使用。
2.实验内容实验题1 编写一个Java Application程序,打印命令行输入的所有参数。
[基本要求] 编写完整程序。
运行结果:代码如下:import java.util.Scanner;public class CommandOutPut {/*** @param args*/public static void main(String[] args) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.out.println("Please input :");Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);String str = in.nextLine();System.out.println("The output results :");System.out.println(str);in.close();}}实验题2 通过键盘输入路径,搜索指定路径下的全部内容。
运行结果:代码如下:package .output;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.IOException;public class Output {/*** @param args* @throws IOException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stubString fileName = "d:\\xxx.txt";File file = new File(fileName);byte[] b=new byte[(int)file.length()];FileInputStream out=new FileInputStream(file);out.read(b);out.close();String s=new String(b);//将字节流转换为字符串System.out.println(s);}}实验题3设计一个类FileRWTest,实现从input.txt文件中读入数据到字符数组cBuffer中,然后再写入到文件“output.txt”中。
运行结果:代码:package .fileRWTester;import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.BufferedWriter;import java.io.FileReader;import java.io.FileWriter;import java.io.IOException;public class FileRWTest {/*** @param args* @throws IOException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// TODO Auto-generated method stubBufferedReader source = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("d:\\input.txt"));BufferedWriter target = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("d:\\output.txt"));//byte[] cBuffer = new byte[(int)((CharSequence) source).length()];String temp = null;////将字节流转换为字符串while ((temp = source.readLine()) != null) {target.write(temp);target.newLine();target.flush();}source.close();target.close();}}实验题 4 建立一个书籍信息的文本文件,其中包括编号、书籍名称、版本、价格、销售额字段及5本书籍的记录。
编写程序读入书籍信息文件并将第3本、第4本书籍价格分别增加20和30,再将修改后的书籍信息文件输出到另一个文本文件中(文件名称为book.txt)。
文本文件book.txt内容如下:编号名称版本价格销售额1001 Java程序设计第2版56.9 5601002 Java开发实战第1版98.9 8201003 C++程序设计指南第3版62.5 3621004 EJB3.0入门经典第1版59.8 12801005 Spring3.0 in Action 第3版95.8 1189设计思路:首先建立一个Book类,定义属性private String num,private String name,private String edition,private Float price,private Float slaes,在主函数中创建5个实例,并把值赋给String text,然后调用target.write()函数写入文件book里。
运行结果:检测是否写入,用read()函数读出:代码:package .Input.tester;import java.io.BufferedWriter;import java.io.FileWriter;import java.io.IOException;import .Input.clas.Book;public class InputTester {/*** @param args* @throws IOException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// TODO Auto-generated method stubBook b1 = new Book("1001", "Java程序设计", "第2版", 56.9F, 560f);Book b2 = new Book("1002", "Java开发实战", "第1版", 98.9f, 820f);Book b3 = new Book("1003", "C++程序设计指南", "第3版", 62.5f, 362f);Book b4 = new Book("1004", "EJB3.0入门经典", "第1版", 59.8f, 1280f);Book b5 = new Book("1005", "Spring3.0 in Action", "第3版 ", 95.8f, 1189f);Book[] books = { b1, b2, b3, b4, b5 };String text = null;for (int index = 0; index < books.length; ++index) {text += books[index];text += '\n';}BufferedWriter target = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("d:\\book.txt"));target.write(text);target.flush();}}问题:忘记在Book类中些toString函数,故导致每次写入都不是想要写入的东西。
实验题5 有四个类,主类Store在包.nwsuaf.jp.p4中,Mobile、Mp3Player、Product在包.nwsuaf.jp.p4.data中,Mobile、Mp3Player是Product类的子类, Product类实现Seralizable 接口。
基本要求:(1)在Store类中用ObjectOutputStream类的对象把Mobile、Mp3Player类对象输出到文件“product.txt”中。
(2)在Store类中用ObjectInputStream类的对象从文件“product.txt”输入数据并将其输出。
实验设计:在product中重写writeObject和raedObject函数,并在主函数中调用writeObject和raedObject 函数对文件读写。
实验结果:写入文件的从文件中读出的:代码:Product中的writeObject和raedObject函数:private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream oos) throws IOException { oos.defaultWriteObject();oos.writeBytes(getName());oos.writeFloat(getPrice());}private void readObject(ObjectInputStream ois) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {ois.defaultReadObject();}主函数:package .nwsuaf.jp.p4;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import .nwsuaf.jp.p4.data.Mobile;import .nwsuaf.jp.p4.data.Mp3Player;public class Store {/*** @param args*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException {try {Mp3Player p1 = new Mp3Player("Meizo X3 (256MB)", 399.0f);Mp3Player p2 = new Mp3Player("Meizo E5 (512MB)", 580.0f);Mp3Player p3 = new Mp3Player("Xlive XM Mp3Play(256MB)", 930.0f);Mobile m1 = new Mobile("E365 on China Mobile", 1780.0f);Mobile m2 = new Mobile("E3330 on China Mobile", 1450.0f);ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d:\\product.txt"));oos.writeObject(p1);oos.writeObject(p2);oos.writeObject(p3);oos.writeObject(m1);oos.writeObject(m2);oos.close();ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream( "d:\\product.txt"));while ((ois.readObject()) != null) {System.out.println(ois.readObject());}ois.close();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}三、实验总结:通过本次试验,掌握了输入输出流的简单用法,但运用不是很熟练,不看书很难编写下去。