美国光伏产品认证规范-en61215
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:165.20 KB
- 文档页数:7

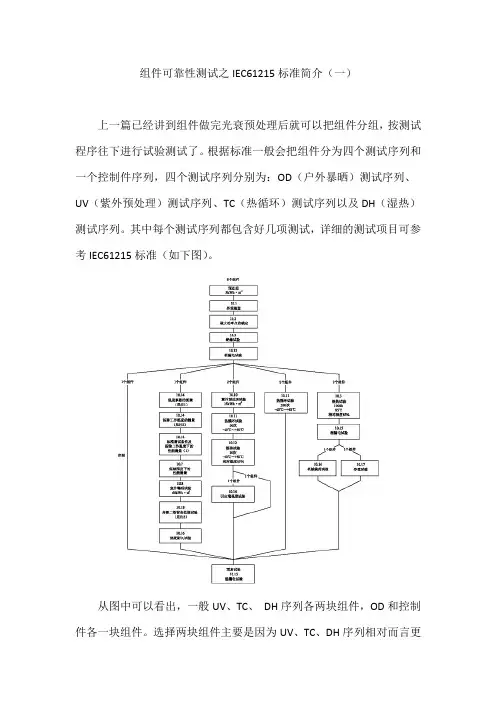
组件可靠性测试之IEC61215标准简介(一)上一篇已经讲到组件做完光衰预处理后就可以把组件分组,按测试程序往下进行试验测试了。
根据标准一般会把组件分为四个测试序列和一个控制件序列,四个测试序列分别为:OD(户外暴晒)测试序列、UV(紫外预处理)测试序列、TC(热循环)测试序列以及DH(湿热)测试序列。
其中每个测试序列都包含好几项测试,详细的测试项目可参考IEC61215标准(如下图)。
从图中可以看出,一般UV、TC、DH序列各两块组件,OD和控制件各一块组件。
选择两块组件主要是因为UV、TC、DH序列相对而言更容易测试失败,选择两块组件,当有一个组件未通过测试,还有机会,因为测试仅对样品负责,所以一块组件不合格不会影响整体测试。
标准中规定如果两个或两个以上组件测试失败,则该设计将视为达不到鉴定要求,也就是整体测试失败,或者是认证失败。
而当一个组件未通过测试时,可重新取另外两个组件从头进行全部相关试验程序的试验。
假如其中的一个或两个组件仍未通过试验,则该设计被判定达不到鉴定要求。
如果两个组件都通过了试验,则该设计被认为达到鉴定要求。
选择两块组件的序列,主要都是环境测试,也从另一方面说明IEC61215比较偏重于评估组件在室外长期使用过程中能否保持性能稳定和可靠性。
相对而言IEC61730和UL1703则较多的去评估组件在正常安装、使用和维护过程中,是否存在对相关人员及周边环境的危险,如电击、火灾等。
在详细介绍IEC61215环境测试之前,我们先了解一下IEC61215标准中的性能测试和安全测试。
之前我们介绍IEC61215标准的主要合格判断依据时,就说到几项非常重要的指标,无严重外观缺陷、功率衰减、湿漏电和绝缘试验等,其实这些都是基本测试,在组件完成每个关键的环境测试后,都会进行电性能及安全性能的评估测试,并会与样品的初始测试数据进行对比,以判断组件性能的稳定性和可靠性变化是否在标准接受的范围内。

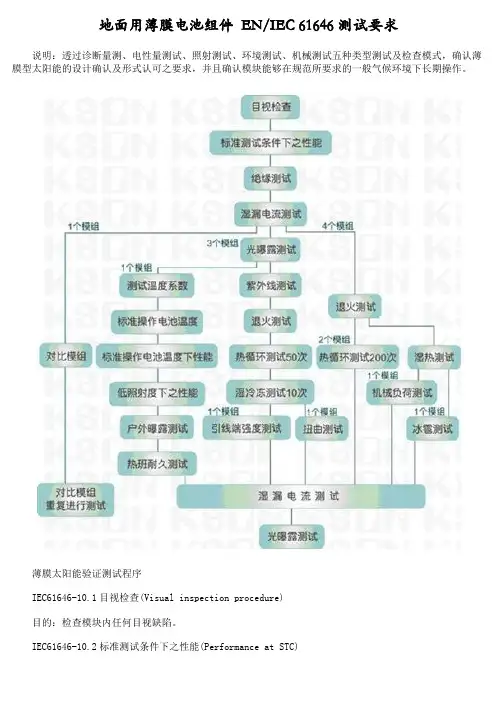
地面用薄膜电池组件EN/IEC 61646测试要求说明:透过诊断量测、电性量测试、照射测试、环境测试、机械测试五种类型测试及检查模式,确认薄膜型太阳能的设计确认及形式认可之要求,并且确认模块能够在规范所要求的一般气候环境下长期操作。
薄膜太阳能验证测试程序IEC61646-10.1目视检查(Visual inspection procedure)目的:检查模块内任何目视缺陷。
IEC61646-10.2标准测试条件下之性能(Performance at STC)目的:用自然光或是A级仿真器,在标准测试条件下(电池温度:25±2℃、照射度:1000wm^-2、标准太阳光谱照射分布符合IEC891规定),测试模块随负荷变化之电性能。
IEC61646-10.3绝缘测试(Insulation test)目的:欲测试模块中之载流零件与模块边框间是否有良好之绝缘IEC61646-10.4温度系数量测(Measurement of temperature coefficients)目的:由模块测试中测试其电流温度系数及电压温度系数,此测定之温度系数仅在测试中所使用之照射度下有效,对于线性模块,在此照射度±30%内是有效的。
IEC891规定了从具有代表性一批中之单体电池测量这些系数,本程序是对该标准之补充。
薄膜太阳能电池模块之温度系数依赖于召涉及模块所经历之热处理过程,当涉及温度系数时,热测试时之条件及照射结果等过程情况均应标明。
IEC61646-10.5标称操作电池温度[NOCT]之量测(Measurement of nominal operating cell temperature)目的:测试模块之NOCTIEC61646-10.6 NOCT下之性能(Performance at NOCT)目的:当标称操作电池温度与照射度为800Wm^-2时,在标准太阳光谱照射分布条件下,确定模块随负荷变化之电性能。

lid测试标准
LID测试是用于评估光伏组件性能的重要质量检测工作,以下是关于LID测试的几个标准:
1. IEC 61215:这是国际电工委员会发布的太阳能电池板和光伏组件的安全性能标准。
这个标准要求光伏组件在正常工作情况下,至少能够维持80%
的输出功率。
为达到此目标,光伏组件需要通过LID测试。
具体而言,该标准要求光伏组件在实验室环境下放置一天,然后进行测试,以评估其在实际工作条件下的性能。
此标准要求光伏组件的输出功率损失不能超过5%。
2. IEC 61646:这是针对薄膜光伏组件的标准,也包含了LID测试的要求。
这个标准要求光伏组件在曝光于一定光照条件下,需要放置72个小时以上,以模拟实际工作环境。
此标准规定,光伏组件的输出功率损失率应小于10%。
3. UL 1703:这是美国独立实验室UL发布的标准,规定了光伏组件在LID
测试中的要求。
这个标准要求光伏组件在实验室环境下曝光一定时间后,进行测试。
此标准要求,光伏组件的输出功率损失不能超过5%。
4. 《太阳能电池组件技术标准》:这是中国太阳能行业协会制定的标准,同样包含了LID测试的要求。
此标准规定,光伏组件经过LID测试后,其输出功率损失率应小于5%。
以上这些国际和国内标准为LID测试提供了详细的要求和方法。
通过LID测试可以有效评估光伏组件的实际性能,增强其质量和可靠性。
请注意,除了以上这些标准,还有一些其他的国际和国内标准可能涉及到光伏组件LID测试的要求和方法。
因此,在实际操作中,建议根据具体的标准和要求进行操作。

北美光伏产品的标准北美地区的光伏产品标准包括以下几个方面:1. 安全标准,北美光伏产品必须符合安全性要求,以确保其在使用过程中不会对人员或环境造成危害。
这些标准包括国家电气代码(NEC)和安全认证标准,如UL 1703(美国)和CSA C22.2 No. 61730(加拿大)。
2. 性能标准,光伏产品的性能标准主要包括功率输出、效率、可靠性和耐久性等方面。
在北美地区,光伏产品需要符合国家标准组织(NREL)和国际电工委员会(IEC)等组织制定的性能测试和认证标准,如IEC 61215和IEC 61730。
3. 网络接入标准,北美地区的光伏产品需要符合电力系统的要求,以实现与电网的安全和可靠连接。
这些标准包括IEEE 1547(美国)和CSA C22.3 No. 219(加拿大)等,确保光伏系统能够平稳地注入电网,并满足电网的稳定性和电能质量要求。
4. 环境标准,为了保护环境和可持续发展,北美地区的光伏产品需要符合相关的环境标准。
例如,美国环保署(EPA)的能源之星认证和加拿大环境部的能源效率认证等,这些标准要求产品在制造、使用和处理过程中减少对环境的影响。
5. 质量标准,为了确保光伏产品的质量和可靠性,北美地区的光伏产品需要符合ISO 9001质量管理体系标准和ISO 14001环境管理体系标准等。
这些标准要求制造商建立完善的质量控制和环境管理体系,以提供高质量的产品并减少负面影响。
总的来说,北美地区的光伏产品标准涵盖了安全性、性能、网络接入、环境和质量等多个方面。
这些标准的遵守和认证对于确保光伏产品的安全性、可靠性和可持续发展至关重要。
制造商和用户应当密切关注并遵守这些标准,以推动光伏产业的健康发展。


地面光伏组件——设计鉴定和定型第二部分:测试步骤1.范围和目的此国际标准系列基于IEC 规定了地面用光伏组件设计鉴定和定型的要求,该组件是在IEC 60721-2-1中所定义的一般室外气候条件下长期使用。
这部分IEC 61215适用于全部地面光伏组件材料,例如晶体硅光伏组件和薄膜组件。
本标准不适用于带聚光器的组件,尽管此项标准能可能用于低聚光组件(1-3个太阳光)。
对于低聚光组件,全部测试使用的电流,电压和功率等级均满足设计要求。
本试验程序的目的是在尽可能合理的经费和时间内确定组件的电性能和热性能,表明组件能够在规定的气候条件下长期使用。
通过此试验的组件的实际使用寿命期望值将取决于组件的设计以及它们使用的环境和条件。
2.引用标准下列标准所包含的条文,通过在本标准中全部或部分引用而构成了本标准的条文。
标注日期的标准,仅引用的版本有效。
未标注日期的标准,可使用最新版本标准(包括任何修订)。
IEC 60050,国际电工词汇(网址:)IEC 60068-1 环境测试-第一部分:总述和指导IEC 60068-2-21 环境测试-第2-21部分测试-测试U:引出端强度以及整体支架安装设备IEC 60068-2-78 环境测试-第2-78部分:测试Cab:湿热,稳定状态IEC 60721-2-1 环境状态的分类-第2-1部分:在自然条件下的环境状态-温度和湿度 IEC 60891 光伏设备-温度和辐照度的修正来测量I-V特性的步骤IEC 60904-1 光伏设备-第一部分:光电流-电压特性的测量IEC 60904-2 光伏设备-第二部分:光伏标准设备的要求IEC 60904-3 光伏设备-第三部分:地面光伏设备和标准光谱福照度数据的测量原则 IEC 60904-7 光伏设备-第七部分:光伏设备光谱错配修正的测量IEC 60904-8 光伏设备-第八部分:光伏设备光谱响应率的测量IEC 60904-9 光伏设备-第九部分:太阳光模拟器操作要求IEC 60904-10 光伏设备-第十部分:线性测试的方法IEC 61215-1 地面光伏组件-设计鉴定和定型-第一部分:测试要求IEC TS 61836 太阳光伏系统能量-术语,定义和符号IEC 61853-2 光伏组件测试结果和能量等级-第二部分:光谱响应,入射角,和组件操作测试温度IEC 62790 光伏组件的接线盒-安全要求和测试ISO 868 塑料和橡胶-通过硬度测验器测量压痕硬度(回跳硬度)3.术语和定义本文件的目的,术语和定义由IEC 60050和IEC TS 61836中给出,其他如下。



IEC 61215 地面用晶体硅光伏组件—设计鉴定和定型作者:广郡电子来源:未知人气:标签:IEC61215 光伏组件国标日期:2013-11-7 11:37:36导读:目次前言.I1.1.1.11 范围和目的.11.1.1.22 规范性引用文件.11.1.1.33 抽样.11.1.1.44 标志.11.1.1.55 试验.11.1.1.66 合格判据.11.1.1.77 严重外观缺陷.11.1.1.88 报告.1,目次前言1.1.1.1 1 范围和目的1.1.1.2 2 规范性引用文件1.1.1.3 3 抽样1.1.1.4 4 标志1.1.1.5 5 试验1.1.1.6 6 合格判据1.1.1.7 7 严重外观缺陷1.1.1.8 8 报告1.1.1.9 9 重新鉴定1.1.1.10 10 试验程序10.1 外观检查10.2 最大功率确定10.3 绝缘试验10.4 温度系数的测量10.5 电池标称工作温度的测量10.6 标准测试条件和标称工作温度下的性能10.7 低辐照度下的性能10.8 室外曝露试验10.9 热斑耐久试验10.10 紫外预处理试验10.11 热循环试验10.12 湿-冻试验10.13 湿-热试验10.14 引出端强度试验10.15 湿漏电流试验10.16 机械载荷试验10.17 冰雹试验10.18 旁路二极管热性能试验1.1.1.11 附录 A IEC 61215第二版对第一版修改图 1 鉴定试验程序图 2 标称工作温度校正因子图 3 参考平板图 4 用参考平板法测量标称工作温度图 5 风速校正因子图 6 A 类电池的热斑效应图7 反向特性图8 B 类电池的热斑效应图9 串联-并联连接方式图10 串联-并联-串联连接方式图11 热循环试验图12 湿-冻循环图13 冰雹试验设备图14 撞击位置示意图表 1 试验条件一览表表 2 冰球质量与试验速度表 3 撞击位置前言本标准等同采用IEC 61215ed2:2005 《地面用晶体硅光伏组件—设计鉴定和定型》。
TECHNOLOGY AND INFORMATION科学与信息化2023年6月下 43IEC 61215/61730标准在青藏高原地区的使用李中十上海让能新能源科技有限公司 上海 200000摘 要 结合青藏高原辐照度、紫外辐照环境、地区温度等历史观测资料和现有IEC标准,给出在青藏高原环境下使用IEC 61215和IEC 61730标准的方法[1-2]。
使得通过修改后标准检测和认证的晶体硅光伏组件,在青藏高原地区使用时,能够具有与一般气象条件下通过IEC 61215、IEC 61730标准检测认证的光伏组件具有大致相当的性能、安全可靠性和寿命期望。
关键词 光伏组件;青藏高原;辐照度;紫外;检测认证标准Application of IEC 61215/61730 Standard in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Region Li Zhong-shiShanghai Rangneng New Energy Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai 200000, ChinaAbstract Combined with the historical observation data such as irradiance, ultraviolet irradiation environment, regional temperature and the existing IEC standards, the method of using IEC 61215 and IEC 61730 standards in the environment of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is proposed [1-2]. So crystalline silicon photovoltaic modules that have passed the testing and certification as per the modified standards can have roughly the same performance, safety reliability and life expectations as photovoltaic modules that have passed the testing and certification as per IEC 61215 and IEC 61730 standards under general meteorological conditions when used in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Key words photovoltaic module; Qinghai-Tibet Plateau; irradiance; ultraviolet; testing and certification standards引言青藏高原地区具有得天独厚的日照条件、较低的年平均气温、较高的积雪和砾石地表反照率,因此在该地区安装无环境污染的光伏发电设备,具有较高的发电经济效益,亦具有很好的环保意义。
光伏组件认证标准
光伏组件的认证标准主要包括IEC 61215、IEC 61730、IEC 62716等。
1. IEC 61215是一个国际标准,用于测量太阳能电池板的性能和可靠性。
2. IEC 61730是一个安全标准,用于测试太阳能电池板和光伏电池组件的安全性能。
3. IEC 62716是一个环境测试标准,用于测试太阳能电池板和光伏电池组件的耐久性和性能在高温、多湿度和大气污染条件下的表现。
此外,TÜV认证也是一个重要的光伏组件认证标准,这是德国的认证机构,进行太阳能电池板和光伏电池组件的认证。
该认证旨在验证产品符合欧洲标准和质量标准。
IEC61215 标准(中文版)美国光伏检测室( ASU-PTL)中国全权代理Solspring International Energy Group太阳普林国际能源集团(加拿大)2005年中国目的1。
决定组件的电性能和热性能。
2。
表明组件在合理的成本和时间内,能够承受长时间的气候暴露。
取样根据 IEC 60410 标准,8块用于质量测试的组件应从一批或几批产品中任意抽取。
通过的标准:1。
最大输出 (The degradation of Max. output power does not exceedthe prescribed limit after each test nor 8% after each test sequence)2。
电路 (no sample has exhibited any open-circuit during the tests)3。
目测迹象(There is no visual evidence of a major defect) 4。
绝缘性(The insulation test requirements are met after the tests)5。
湿漏电 (The wet leakage current test requirements are met at thebeginning and the end of each sequence and after the damp heat test)6。
特殊要求(Specific requirements of the individual tests are met)5kWh/m2目测,电性能,绝缘,湿漏1 12 22热循环 200电性能紫外线湿热热循环 50户外暴二极管热试验湿冻机械强度雹击热斑终端试验目测,电性能,绝缘,IEC61215 (第二版)标签每一个组件的标签都应包括以下内容且清楚可读:1. 生产厂商名字或标志。
新版IEC 61215系列标准送样规则和合格判据解读摘要:IEC光伏标准及相关认证对于提高光伏产品质量、推动光伏市场健康有序发展起着不可忽视的作用。
新版IEC 61215标准与上一版相比,重新定义送样规则、引入新的合格判据。
对新版IEC 61215系列标准的全面理解,于组件认证意义重大。
关键词:光伏组件;送样规则;合格判据1.引言IEC标准在光伏组件可靠性和安全性测试方面始终扮演着国际权威角色,通过认证的组件产品象征着性能稳定、安全可靠,更容易被市场所接受。
从1993年IEC正式发布晶体硅质量测试标准——第1版IEC 61215开始,到2005年出版的第2版IEC 61215,再到2016版IEC 61215系列标准的诞生,61215标准不仅技术内容有较大变动,结构变动也非常大。
新版标准对IEC 61215晶体硅设计鉴定和IEC 61646薄膜组件设计鉴定进行了整合,变成了IEC 61215系列标准,采用一个通用的测试要求(IEC 61215-1)和一个通用的测试程序(IEC 61215-2),针对不同类型的组件,采用特殊要求加以说明,修改后的架构便于根据新兴技术的进步,及时对标准进行修订调整。
本文主要阐述了送样规则和合格判据这两个重要变更。
2.送样规则制造商进行产品认证时,必须根据IEC 61215-1:2016条款11中图1所示的要求,向实验室提供足够数量的样品。
在进行产品认证测试时,如果认证证书上覆盖多个功率等级的产品型号,那么制造商还需要从所覆盖型号的多个功率档位中,各选取至少2件组件送样,用于实验室验证各功率档位是否符合依据铭牌标示公差判定的标称值符合性要求(Gate No.1)。
目前常见的送样方式是制造商所送的用于加速老化试验的组件作为中间功率档位样品,另各送2件高功率档位和低功率档位样品。
同时,IEC 61215-1:2016建议提供额外的满足输出功率要求的备用样品,因为在该标准条款7中指出,如果一个组件未通过任一项试验,选取另外两件满足送样规则的样品完成该项试验所在测试序列的所有试验。
CTL PROVISIONAL DECISION SHEET ......Standard(s)-(year and edition):IEC 61215-2005 Ed.2 IEC 61646-1996 Ed.1Sub clause(s):See individual itemsSheet n°:PDSH 647Subject:Retest Guidelines for IEC61215 and IEC61646 Key words:PV module, modifications,retest guidelinesTo be approved by the45th CTL Plenary Meeting2008Question:How should a certified PV module be evaluated after changes are made to its design, materials, components or process in order to maintain its certification to IEC 61215 / IEC 61646?Decision:This Decision Sheet sets forth a uniform approach to maintain the certification of PV modules that have, or will, undergo modification from the articles originally certified. Changes in material selection, components and manufacturing process can impact electrical performance and reliability of the modified product. Those products meeting the requirements of the relevant standards after retesting are considered to be compliant and will be issued an amended CB Conformity Assessment Certificate and an Amended Test Report.The number of samples to be included in the retesting program and the pass/fail criteria is to be taken from the standard originally used to certify the product (either IEC 61215 or IEC 61646).This document is organized by major modification headings and specific supporting examples. Following this is the recommended retesting sequence with parenthetical reference to the specific clauses of the relevant IEC standards.For the modifications listed below, the Qualification Approval tests in IEC 61215 and IEC 61646 shall be used as a guideline by the National Certification Body (NCB), Certification Body Testing Laboratory (CBTL) and assessors.Any change in the design, materials, components or processing of the module may require a repetition of some or all of the qualification tests to maintain type approval. Each sample of the modified module shall be subjected to preconditioning and then checked against the STC power rating on the label.The following list provides guidance as to which tests should be repeated. Note 1: Tests 10.1, 10.2, 10.3 and 10.15 shall be performed before and after the specific tests listed below.Note 2: In case of IEC 61646 approval test:Specifics for thin film cell changes are under consideration;Final light soaking (10.19) test is compulsory for all test samples.a) Change in cell technologyFor modifications such as:—Metallization materials and/or process—Anti-reflective coating material—Type of diffusion process—Semiconductor layer materials—Order of cell process if the change involves the metallization system —Change of manufacturing site of the solar cells not under the same QA system, —Use of cells from a different manufacturer—Major reduction in cell thickness (greater than 25% for cell thickness > 200 μm and greater than 17.5% for cell thickness ≤ 200 μm )Repeat:—Thermal cycling, 200 cycles (10.11)—Damp heat (10.13), may be omitted if outer surface of cell is chemically identical (metallization and AR coating)—Hot spot endurance (10.9)—Mechanical Load test (10.16) for reduction of cell thickness onlyb) Modification to encapsulation systemFor modifications such as:—Different materials—Different additives—Different encapsulation process e.g. curing rateRepeat:—UV (10.10) / thermal cycling, 50 cycles (10.11) / humidity freeze sequence(10.12)—Damp heat (10.13)—Hail impact (10.17) if not tempered glass—Hot spot (10.9) if material composition changesc) Modification to superstrateFor modifications such as:—Different material—Different thickness, reduced by more than 10%—For glass, if there is a reduction in the heat strengthening process (for example, if a change is from tempered glass to heat strengthened or annealed) —Different surface treatments, adhesives or primers if they are in direct contact with encapsulate material—If the change is from glass to non-glass or vice-versa, it should be considered a new product altogetherRepeat:—UV (10.10) / thermal cycling, 50 cycles (10.11) / humidity freeze (10.12) sequence—Mechanical load test (10.16)—Hail test (10.17)—Damp heat (10.13) (if non-glass)—Hot spot (10.9) for non-glass if material changes or thickness is reduced —Outdoor exposure (10.8) if change in materiald)Increase in module size—For increase by more than 20% of length or widthRepeat:—Thermal cycling, 200 cycles (10.11)—Mechanical load (10.16)—Hail impact (10.17) (for size increases of more than 50%)e) Modification to backsheet/substrateFor modifications such as:—Different material—Reduction of thickness of more than 20 %—Different additives, surface treatments, adhesives and primersRepeat:—UV (10.10) / thermal cycling, 50 cycles (10.11) / humidity freeze (10.12) sequence—Robustness of terminations (10.14)—Damp heat (10.13) (if non-glass)—Hail impact (10.17) if rigidity depends on the backsheet—Mechanical load (10.16) if mounting depends on the backsheet/substrateIf there is a change from superstrate to substrate design or from substrate to superstrate design, the entire qualification test sequence in IEC 61215 shall be conducted.f) Modification to frame and/or mounting structureFor modifications such as:—Cross section of frame—Different framing material—Different mounting techniqueRepeat:—Mechanical load test (10.16)—Outdoor exposure (10.18) if plastic material is used—UV (10.10) / thermal cycling (10.11), 50 cycles / humidity freeze (10.12) sequence, if plastic material is used—Damp heat (10.13) if an adhesive system is used to mount the module —Thermal cycling (10.11), 200 cycles, if an adhesive system is used to mount the moduleg) Modification to junction box/electrical terminationFor modifications such as:—Different material—Different design—Different potting material—Different method of attachmentRepeat:—TC 50 (10.11), 10 HF (10.12)—Robustness of terminations (10.14)—Damp heat (10.13)—By-pass diode thermal test (10.18) (if bypass diode is in the box)h)Change in cell interconnect materials or techniqueFor modifications such as:—Different interconnect material,—Increased thickness of interconnect material (for thickness increases greater than 40 μm. If the new ribbon thickness is below 100 μm thickness no retest is required.)—Different bonding technique—Different number of interconnects—Different number of solder bonds per cell—Different solder material or fluxRepeat:—Temperature cycling, 200 cycles (10.11)—Damp heat (10.13) for changes in materials—Hot spot for changes in bonding technique or solder material (10.9)i)Change in electrical circuit of an identical packageFor modifications such as:—Modifications to the interconnection circuitry (for example more cells per bypass diode or re-routing of output leads)—Reconfiguration of voltage (i.e. 12V to 24V)Repeat:—Hot spot (10.9), only if more cells per by-pass diode—By-pass diode thermal test if the current in each diode increases (10.18) —Temperature cycling, 200 cycles (10.11) if there are internal conductors behind the cellsj)Higher or lower power output (by 10%) in an identical package including size and using identical cell processRepeat:—Hot spot (10.9)—Bypass diode thermal test (10.18) if greater than 10% higherk) Qualification of a frameless module after the design has received certification as a framed moduleRepeat the following tests with the laminate mounted using the manufacturers mounting instructions:—Damp heat (10.13) (If frame is part of the package seal)—Mechanical load (10.16)—Hail impact (unless superstrate is tempered glass) (10.17)l) Change in By-pass diode—Lower current rating or lower temperature rating—Different number of by-pass diodes per module—Different type or manufacturerRepeat:—Bypass diode thermal test (10.18)Modifications that do not require re-testingProvided that all structural components, materials used and processes (including cell process) remain the same, the following modifications shall not require re-testing: —Fewer cells in module—Smaller cells in module, as long as each cell has the same number or area of interconnects and equivalent numbers of solder bonds per unit area Explanatory Notes:Retest Guidelines is a very important and dynamic document. It is discussed and updated periodically by relevant NCBs, CBTLs, and IEC TC82 WG2.Before this PDSH, the Retest Guidelines was published on IECEE website under a special entry:File name: RetestGuideline_IEC61215_61646def.pdf.pdfDated: 2006-04-30Website location: /ctl/retest_guidelines/retest_guidelines.htmlBy transferring this document to the form of Decision Sheets, PV now only deals with IECEE normal procedures. It will be much easier for all users, especially for new laboratories and some assessors.With the publication of this Decision Sheet,RetestGuideline_IEC61215_61646def.pdf.pdf will be withdrawn fromthe above website .。