modal auxiliaries 情态动词
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:698.00 KB
- 文档页数:40

谈谈情态动词(Modal Verbs)(⼀) 我们常见的英⽂动词有:及物动词(Transtive Verbs)、不及物动词(Intranstive Verbs)、助动词(Axiliary Verbs)、联系动词(Link Verbs /Copula)和情态动词(Modal Verbs)。
其他还有:⾮谓语动词,如:动词不定式、动名词。
这回我们就来谈谈情态动词(Modal Verbs 注意Modal 不是 Model 喔)。
* 情态动词也可称为"情态助动词(Modal Auxiliaries)",因为它和基本助动词(be,do, have)都属于助动词类。
* 情态动词和其他动词连⽤,可表⽰说话⼈的语⽓。
* 情态动词可表达建议、要求、可能和意愿等。
* 情态动词没有⼈称和数的变化。
* 常⽤的情态动词有:can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would这九⼤情态动词;其他的还有ought to, need, dare 等。
其实我们这⾥谈的情态动词,它的特征⽤法,有许多⽅⾯和助动词是⼀样的(请参阅《英⽂语法拉杂谈》助动词);但为了⽅便阅读,因此即使相同的部份,这⾥也同样列出。
⼀、情态动词的变化:(情态动词could,动词 to work) 1.1 简单型(Simple):表⽰现在或将来的状态 I could work (动词不可加 to ,如:to work.下同) you could work he could work she could work it could work we could work they could work 1.2 完成式型(Perfect):表⽰过去的状态 I could have worked (动词是 have + v-ed 过去分词。
下同) you could have worked he could have worked she could have worked it could have worked we could have worked they could have worked 1.3 进⾏式型(Continuous):表⽰现在或将来还在进⾏的状态 I could be working (动词是be + v-ing 现在分词。


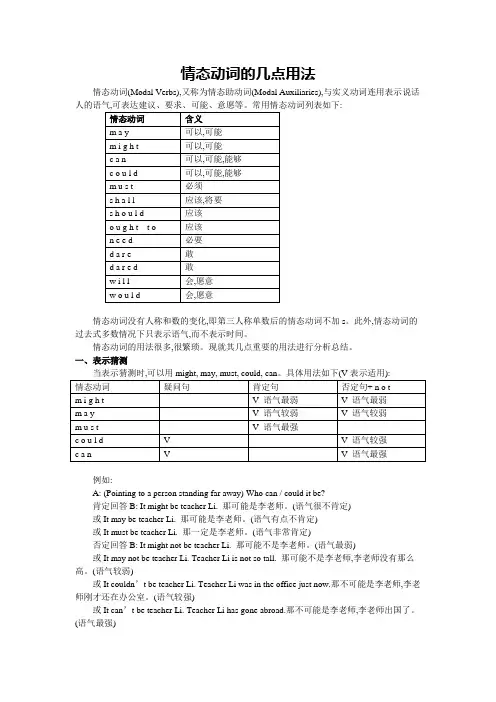
情态动词的几点用法情态动词(Modal Verbs),又称为情态助动词(Modal Auxiliaries),与实义动词连用表示说话人的语气,可表达建议、要求、可能、意愿等。
常用情态动词列表如下:情态动词没有人称和数的变化,即第三人称单数后的情态动词不加s。
此外,情态动词的过去式多数情况下只表示语气,而不表示时间。
情态动词的用法很多,很繁琐。
现就其几点重要的用法进行分析总结。
一、表示猜测例如:A: (Pointing to a person standing far away) Who can / could it be?肯定回答B: It might be teacher Li. 那可能是李老师。
(语气很不肯定)或It may be teacher Li. 那可能是李老师。
(语气有点不肯定)或It must be teacher Li. 那一定是李老师。
(语气非常肯定)否定回答B: It might not be teacher Li. 那可能不是李老师。
(语气最弱)或It may not be teacher Li. Teacher Li is not so tall. 那可能不是李老师,李老师没有那么高。
(语气较弱)或It couldn’t be teacher Li. Teacher Li was in the office just now.那不可能是李老师,李老师刚才还在办公室。
(语气较强)或It can’t be teacher Li. Teacher Li has gone abroad.那不可能是李老师,李老师出国了。
(语气最强)注意:如果表示对过去发生的事情的猜测,可用以上情态动词+ have +过去分词来表示。
例如:The ground is so wet. It must have rained last night. 地这么湿。
昨晚一定是下雨了。
二、表示许可、必须和必要当用情态动词表示许可、必须和必要时,可以用may, might, can ,could, must, need。

情态动词⏹英语助动词(auxiliaries)主要有两类,基本助动词(primary auxiliaries)和情态动词(modal auxiliaries)。
⏹基本助动词有三个,即do, have 和be。
⏹情态动词有九个,它们是:can, may, must, ought to, shall, will, need, dare, used to等等。
加上过去式共十三个,could,might,should,wouldCan 能,可能固定搭配:cannot (help) but do=can`t help doing 不得不,只能can’t/couldn't+不定式完成体”结构1. “can’t/can have done”结构表示以“现在”为出发点,推侧过去某种“动作”发生了,多用于否定句和疑问句中,意为“很可能……了’,“不太可能……”等。
如:Her interference can have done a great deal of harm. 她的干涉可能已造成巨大伤害.She can’t have written this because it is in French and she doesn't know French. 这不可能是她写的,因为这是用法文写的,而她不懂法文2.在疑问句或否定句中,”can +不定式完成体”结构表示语气很强的猜侧或推断。
如:Can he have made a mistake? 他会弄错了吗?(含义是:他不可能搞错的)比较:Could he have made a mistake?他会弄错了吗? (一般性推测)He can' t have made a mistake.他肯定不会弄错。
Can和could同样用于比较的时候,can的语气更强烈3. “could/couldn`t+不定式完成体”表示以“过去”为起点Could have done 虚拟语气用法:本来可以,本来会,本来能(事实上没有)推测:有可能Couldn`t have done 虚拟语气用法:本不会,本不能(实际上已经做了)推测:不会,不可能Tom could have broken the glass. He was the only one at home yesterday. 汤姆可能打破了这个玻璃杯Mary couldn`t have bolded the door.玛丽不可能把门闩上。
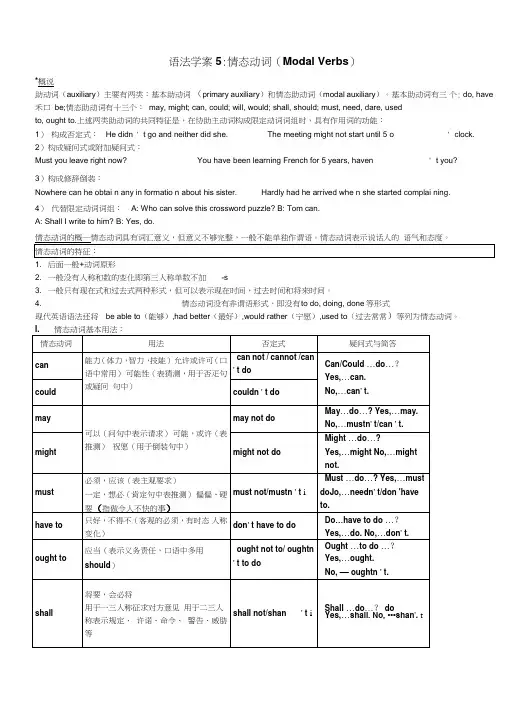
语法学案5:情态动词(Modal Verbs)*概说助动词(auxiliary)主要有两类:基本助动词(primary auxiliary)和情态助动词(modal auxiliary)。
基本助动词有三个: do, have 禾口be;情态助动词有十三个:may, might; can, could; will, would; shall, should; must, need, dare, usedto, ought to.上述两类助动词的共同特征是,在协助主动词构成限定动词词组时,具有作用词的功能:1)构成否定式:He didn ' t go and neither did she. The meeting might not start until 5 o ' clock.2)构成疑问式或附加疑问式:Must you leave right now? You have been learning French for 5 years, haven ' t you?3)构成修辞倒装:Nowhere can he obtai n any in formatio n about his sister. Hardly had he arrived whe n she started complai ning.4)代替限定动词词组:A: Who can solve this crossword puzzle? B: Tom can.A: Shall I write to him? B: Yes, do.1. 后面一般+动词原形2. 一般没有人称和数的变化即第三人称单数不加-s3. 一般只有现在式和过去式两种形式,但可以表示现在时间,过去时间和将来时间。
4. 情态动词没有非谓语形式,即没有t o do, doing, done等形式现代英语语法还将be able to(能够),had better(最好),would rather(宁愿),used to(过去常常)等列为情态动词。



情态动词英语语法知识精讲情态动词(modal verb)本身有词义,表示说话人的语气或情态,但词义不完全,不能单独用作谓语动词,一般只能和动词原形一起构成谓语动词。
小编在这里整理了相关资料,希望能帮助到您。
情态动词概述特征1)情态动词(modal verb)本身有词义,表示说话人的语气或情态,但词义不完全,不能单独用作谓语动词,一般只能和动词原形一起构成谓语动词。
2)情态动词所表示的情态有:命令、允诺、请求、拒绝、愿望、愿意、义务、必要、可能、能力、敢于、需要等。
3)情态动词(ought除外)和助动词shall,will,should,would 一样,后面的动词不定式一般皆不带。
形式变化1)没有人称和数的变化,第三人称单数的现在时也无变化。
如:I can We canYou can You canHeThey canShe canIt2)有些情态动词有过去式,有少数过去式和它的原形相同。
a)有过去式的情态动词有:may -- wouldcan ―― couldmay―― nightshall -- shouldhave to -- had tob)过去式不变的情态动词有:must - must (或had to)ought to - ought toneed---needdare - dare(亦可用dared)3)大多数情态动词后面可用动词的进行式、完成式和被动形式,如:can(may,must)be doing,can(may,must) have done,can(may,must)be done等。
否定式情态动词和助动词一样,后面可直接跟否定词not。
现将情态动词的否定式及其否定式的简略式(简略式用于口语中)列举如下:shall not--shan't [FB:nt]will not---won't [wEunt]can not-can't [kB:nt]must not-mustn't [5mQsnt]should not-- shouldn'twould not-- wouldn'tcould not-- couldn'tdare not- daren't [dZEnt]need not-- needn't在疑问句中的用法情态动词在疑问句中的用法和助动词相同。

Modal Auxiliaries ([情态]助动词)Choose the answer that best completes each sentence.1. We ____________ be more strict with ourselves. We should not overlook our shortcomings.A. willB. couldC. mustD. need2. You need not thank us. This is what we ____________ do.A. ought toB. mightC. should be able toD. had better3. “You _____ a bit more helpful when we arrested you.” The policeman said to the young man.A. might beB. would have beenC. could have beenD. must have been4. “You ____________ lead a horse to the water, but you _____ not make it drink.”A. can, mightB. will, mayC. can, mayD. may, can5. There are twenty minutes to go. We ___________ here so early.A. need not have comeB. could not have comeC. might not have comeD. must not have come6. Tom is not in the room now. He _____ in the library. He will have an examination next Monday.A. would studyB. must studyC. must be studyingD. could have studied7. You __________ that if you don’t want to.A. don’t need to doB. needn’t to doC. needn’t to have doneD. don’t need to8. “Must I hand in my paper now?” “No, you _________. You can hand it in tomorrow.”A. must notB. do not have toC. had not betterD. can not9. No one will eat this food; it _________ away.A. had to throwB. had better to throwC. had better to be thrownD. might as well be thrown10. Mr. Smith __________ pass an examination before he could get his promotion.A. needsB. had toC. is able toD. must11. __________ to have lunch with us today?A. Will you likeB. Would you mindC. Would you likeD. May you like12. She _________ fifty or so when I first met her at a conference.A. had beenB. must beC. has beenD. must have been13. “Did you blame him for his mistakes?” “Yes, but _____ it.”A. I’d rather not to doB. I’d rather not have doneC. I’d better not to doD. I’d better not to have done14. The room is in a terrible mess; it _____ cleaned.A. can’t have beenB. shouldn’t have beenC. mustn’t have beenD. wouldn’t have been15. You should try to speak slowly and clearly when you give your speech. If you don’t, some ofyour words ________.A. may be misunderstoodB. may have been misunderstoodC. would be misunderstoodD. would have been misunderstood。
情态动词(modal auxiliary)助动词主要分为两种,基本助动词(do、have和be)、情态助动词(may、might、can、could、must、will、would、ought to、dare、shall、should、need、used to、had better)。
助动词主要是⽤来协助主动词构成限定动词词组,具有作⽤词的功能。
个别情态动词有现在式和过去式两种形式,过去式可⽤于过去、现在或将来。
情态动词表推测:1.对于将来情况的推测:情态动词+动词原形can、could、may、might语⽓依次递减,其中may不能⽤于疑问句2.对现在或⼀般情况的推测:情态动词+动词原形、情态动词+be+doing、情态动词+bemust、ought to、would、will、must表推断,语⽓递增can、could、may、might⽤于否定句时can/could not 表⽰不可能may/might not 表⽰可能不不3.对过去的推测:情态动词+have+donemust have done ⼀定曾can/could not have done ⼀定不会只能⽤于否定句和疑问句 could可能性⼩于canshould/ought to have done 本该 ought to ⽐should⼝⽓强烈may/might have done 应该已经 might have done ⽤于主语是第⼆⼈称时表⽰本可以...⽽没may have done 只能⽤于肯定句或否定句疑问句⽤can两者均可⽤于现在时,过去时只能⽤mightneedn't have done 本可不必情态动词表能⼒:can表⽰现在或将来的能⼒;could表⽰过去或过去将来的能⼒;be able to 表⽰好不容易才,有时态变化,主语只能是有⽣命的物体,不能变被动式,be可以改为某些系动词(seem、turn、look)can't help doing 忍不住征求意见:can、may、could、might⽤于主语为第⼀⼈称的句⼦,can i...⾮正式⽤法 may i..正式⽤法can、could⽤于主语为第⼆⼈称的句⼦⾥,不能⽤may或mightwould、could⽐⽤will、can语⽓更委婉,更客⽓shall、should⽤于第⼀⼈称和第三⼈称,表⽰征求对⽅的意见eg:when shall we meet again?表意志:shall表⽰说话⼈的意志,will表⽰句⼦主语的意志;eg:I shan't/won't lend you the moneyshould、would⽤于表⽰委婉的愿望would rather(not)do 宁愿(不)must 表⽰必须,其否定式⽤needn't表⽰不必做某事,mustn't表⽰禁⽌做某事;have to 表⽰不得不,有时态的变化,否定式don't have toought to、should表⽰应该做某事,ought to⽐should语⽓强,否定式为ought not to、shouldn'thad better(not)do 最好(别)做某事,有⾃⼰的被动语态,had better be donedare表⽰敢过去的习惯:used to 过去经常做某事would do 含有主观的感情⾊彩,过去的不规则习惯。
英语情态动词表示可能性浅谈
周求知
【期刊名称】《教学与管理》
【年(卷),期】1990(000)001
【摘要】英语中,may,might,can,could,should,ought,will,would,must等情态动词(Modal auxiliaries)都可以用来表示对事情推测的可能性(Possibility),而它们在词义、色彩及用法等方面都有所不同。
本文按其表示可能性程度从小到大的顺序,分述如下: 一、may或might表示的可能性往往具有怀疑和把握性不大的意味。
用might时可能性比may小,但在语气上比较委婉,是表示客气的虚拟式。
may或might与动词不定式连用,表示现在或将来的可能性。
例如: He may be in the classroom now.
【总页数】5页(P35-39)
【作者】周求知
【作者单位】
【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】G420
【相关文献】
1.浅谈法律英语文书中情态动词“shall”和“may”的翻译 [J], 苏晓娜
2.浅谈历届NMET中表示推测的情态动词的用法 [J], 成文辉
3.情态动词表示可能性与高考考点 [J], 邹国如
4.浅谈任务型模式在英语情态动词教学上的应用 [J], 呼亮
5.历年高考英语情态动词表示“推测性”考例透析 [J], 王福祯
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。