小学英语语法总汇精简版.doc
- 格式:doc
- 大小:57.50 KB
- 文档页数:5

小学英语语法大全一、名词复数规则1.一般情况下,直接加-s,如:book-books, bag-bags, cat-cats, bed-beds2.以s. x. sh. ch结尾,加-es,如:bus-buses, box-boxes, brush-brushes, watch-watches3.以“辅音字母y”结尾,变y为i, 再加-es,如:family-families, strawberry-strawberries4.以“f或fe”结尾,变f或fe为v, 再加-es,如:knife-knives ]Leaf——leaves5.不规则名词复数:man-men, woman-women, policeman-policemen, policewoman-policewomen,child-childrenfoot-feet,.tooth-teethfish-fish, people-people, Chinese-Chinese,Japanese-Japanese写出下列各词的复数I _________him _________this ___________her ______watch _______child _______photo ________diary ______day________ foot________ book_______ dress ________tooth_______ sheep ______box_______ strawberry _____peach______ sandwich ______dish_______bus_______man______ woman_______二、一般现在时一般现在时基本用法介绍【No. 1】一般现在时的功能1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。
如:The sky is blue.天空是蓝色的。
2.表示经常性或习惯性的动作。

小学英语语法大全第一章名词一、定义名词是表示人或事物名称的词。
它既可以表示具体的东西,也可以是表示抽象的东西。
二、分类1. 名词可以根据意义分为普通名词和专有名词如:john is a studentstudent是普通名词,john是专有名词普通名词前可以用不定冠词a/an, 定冠词the 或不加冠词,专有名词前一般不加冠词,专有名词的首字母要大写。
2. 普通名词又可以分为个体名词、集体名词、物质名词和抽象名词,其中个体名词与集体名词是可数名词,物质名词和抽象名称是不可数名词。
3. 专有名词专有名词是表示人名、地名、团体、机构、组织等的专有名词,多为独一无二的事物。
三、名词的数1、名词分为可数名词和不可数名词。
可数名词——可以数的名词不可数名词——数不清(没有复数)drink?milk tea water orange juice coke coffee porridgefood?rice bread meat fish fruit cake dumplings2、可数名词与不定冠词a(an)连用有数数形式,不可数名词不能与不定冠词a(an)连用,没有复数形式many+可数名词复数much/a little+不可数名词some, any , a lot of (lots of) 两者都可以修饰。
3、可数名词可以直接用数词来修饰不可数名词数词 +量词 +of + 名词对可数名词的数量提问用how many对不可数名词的数量提问用 how much4、不可数名词的量有以下两种表示方法:1) some, much ,a little ,a lot of ,a bit of , plenty of 用等表示多少。
注意既可以与可数名词复数,又可以与不可数名词连用的有:plenty of ,some ,a lot of ,lots of ,most of 等。
如there is much water in the bottle .瓶中有很多水。

小学英语语法大全第一章名词一、定义名词是表示人或事物名称的词。
它既可以表示具体的东西,也可以是表示抽象的东西。
二、分类1。
名词可以根据意义分为普通名词和专有名词如:john is a studentstudent是普通名词,john是专有名词普通名词前可以用不定冠词a/an, 定冠词the 或不加冠词,专有名词前一般不加冠词,专有名词的首字母要大写。
2。
普通名词又可以分为个体名词、集体名词、物质名词和抽象名词,其中个体名词与集体名词是可数名词,物质名词和抽象名称是不可数名词。
3。
专有名词专有名词是表示人名、地名、团体、机构、组织等的专有名词,多为独一无二的事物。
三、名词的数1、名词分为可数名词和不可数名词。
可数名词——可以数的名词不可数名词——数不清(没有复数)drink?milk tea water orange juice coke coffee porridgefood?rice bread meat fish fruit cake dumplings2、可数名词与不定冠词a(an)连用有数数形式,不可数名词不能与不定冠词a(an)连用,没有复数形式many+可数名词复数much/a little+不可数名词some, any , a lot of (lots of)两者都可以修饰.3、可数名词可以直接用数词来修饰不可数名词数词 +量词 +of + 名词对可数名词的数量提问用how many对不可数名词的数量提问用 how much4、不可数名词的量有以下两种表示方法:1) some, much ,a little ,a lot of ,a bit of , plenty of 用等表示多少.注意既可以与可数名词复数,又可以与不可数名词连用的有:plenty of ,some ,a lot of ,lots of ,most of 等。
如there is much water in the bottle 。
六年级英语语法知识汇总一、词类:1、动词:行为动词、be动词、神情动词。
〔1〕行为动词原形、 +s/es、+ed、+ing,详尽判断方法以下:(2〕be 动词a、Am--was Is --was Are--were 口诀:我用 am, 你用 are, is用在他她它,所有复数全用 are。
b、必然和否认句I am (not) from London. He /She is(not) a teacher.My hair is(not) long. Her eyes are(not) small.c、一般疑问句Am I ?Yes, you are.No,/ you aren .. ’tAre you/they ?Yes,we/ they are. No,we/ they aren . ’ t ’Is the cat fat?Yes, it is. No,/ it isn’ t.is 、am、are 为一类,一般用于一般现在时、现在进行时和一般将来时中。
was和 were 为另一类,一般用于一般过去时。
〔3〕神情动词can、must、could 、should 、would、may。
神情动词后动词总是用原形。
〔不受其他任何条件影响〕神情动词,没有第三人称单数,所有的神情动词都是这样,神情动词不受人称和数的影响,即无论主语是什么人称它都不变,神情动词,后边只能加动词原型。
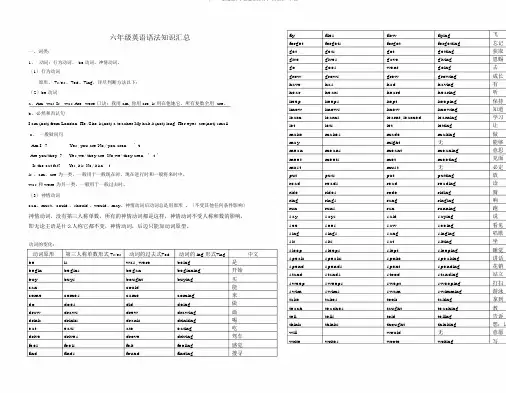
动词的变化:动词原形第三人称单数形式 +s/es动词的过去式+ed动词的 ing 形式+ing中文be is was, were being是begin begins began beginning开始buy buys bought buying买can could能come comes came coming来do does did doing做draw draws drew drawing画drink drinks drank drinking喝eat eats ate eating吃drive drives drove driving驾车feel feels felt feeling感觉find finds found finding搜寻fly flies flew flying飞forget forgets forgot forgetting忘记get gets got getting获取give gives gave giving恩赐go goes went going去grow grows grew growing成长have has had having有hear hears heard hearing听keep keeps kept keeping保持know knows knew knowing知道learn learns learnt, learned learning学习let lets let letting让make makes made making做may might无能够mean means meant meaning意思meet meets met meeting见面must must无必定put puts put putting放read reads read reading读ride rides rode riding骑ring rings rang ringing响run runs ran running跑say says said saying说see sees saw seeing看见sing sings sang singing唱歌sit sits sat sitting坐sleep sleeps slept sleeping睡觉speak speaks spoke speaking讲话spend spends spent spending花销stand stands stood standing站立sweep sweeps swept sweeping打扫swim swims swam swimming游泳take takes took taking拿到teach teaches taught teaching教tell tells told telling告诉think thinks thought thinking想;认will would无意愿write writes wrote writing写2、名词(1).专有名词和一般名词。

小学英语语法大全一、名词复数规则1.一般情况下,直接加 -s,如: book-books, bag-bags, cat-cats, bed-beds2.以 s. x. sh. ch 结尾,加 -es ,如:bus-buses, box-boxes,brush-brushes, watch-watches3.以“辅音字母 y ”结尾,变 y 为 i, 再加-es ,如:family-families, strawberry-strawberries4.以“f或 fe ”结尾,变 f 或 fe 为 v, 再加-es ,如:knife-knives ] Leaf —— leaves5.不规则名词复数:man-men, woman-women, policeman-policemen,policewoman-policewomen,child-childrenfoot-feet,.tooth-teethfish-fish, people-people, Chinese-Chinese,Japanese-Japanese写出下列各词的复数I _________him _________this ___________her ______watch _______child _______photo ________diary ______day________ foot________ book_______ dress ________tooth_______ sheep ______box_______ strawberry _____peach______ sandwich ______dish_______bus_______man______ woman_______二、一般现在时一般现在时基本用法介绍【No. 1 】一般现在时的功能1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。
如:The sky is blue. 天空是蓝色的。

小学英语语法大全第一章名词1.名词可以根据意义分为普通名词和专有名词如: john is a studentstudent 是普通名词, john 是专有名词普通名词前可以用不定冠词 a/an, 定冠词 the 或不加冠词,专有名词前一般不加冠词,专有名词的首字母要大写。
2.普通名词又可以分为个体名词、集体名词、物质名词和抽象名词,其中个体名词与集体名词是可数名词,物质名词和抽象名称是不可数名词。
3.专有名词专有名词是表示人名、地名、团体、机构、组织等的专有名词,多为独一无二的事物。
三、名词的数1、名词分为可数名词和不可数名词。
可数名词——可以数的名词不可数名词——数不清(没有复数)drink?milk tea water orange juice coke coffee porridge food?rice bread meat fish fruit cake dumplings2、可数名词与不定冠词 a(an) 连用有数数形式,不可数名词不能与不定冠词 a(an)连用,没有复数形式 many+ 可数名词复数 much/a little+ 不可数名词 some, any , a lot of (lots of) 两者都可以修饰。
3、可数名词可以直接用数词来修饰不可数名词数词 +量词 +of + 名词对可数名词的数量提问用 how many 对不可数名词的数量提问用 how much4、不可数名词的量有以下两种表示方法:1 ) some, much ,a little ,a lot of ,a bit of , plenty of 用等表示多少。
注意既可以与可数名词复数,又可以与不可数名词连用的有:plentyof ,some ,a lot of ,lots of ,most of如 there is much water in the bottle . 瓶中有很多水。
i'll tell you much good news. 我要告诉你许多好消息。

小学英语语法大全第一章名词一、定义名词是表示人或事物名称的词。
它既可以表示具体的东西,也可以是表示抽象的东西。
二、分类1.名词可以根据意义分为普通名词和专有名词如: john is a studentstudent是普通名词,john是专有名词普通名词前可以用不定冠词 a/an, 定冠词 the 或不加冠词,专有名词前一般不加冠词,专有名词的首字母要大写。
2.普通名词又可以分为个体名词、集体名词、物质名词和抽象名词,其中个体名词与集体名词是可数名词,物质名词和抽象名称是不可数名词。
3.专有名词专有名词是表示人名、地名、团体、机构、组织等的专有名词,多为独一无二的事物。
三、名词的数1、名词分为可数名词和不可数名词。
可数名词——可以数的名词不可数名词——数不清(没有复数)drink?milk tea water orange juice coke coffee porridgefood?rice bread meat fish fruit cake dumplings2、可数名词与不定冠词 a(an) 连用有数数形式,不可数名词不能与不定冠词a(an) 连用,没有复数形式many+可数名词复数much/a little+ 不可数名词some, any , a lot of (lots of) 两者都可以修饰。
3、可数名词可以直接用数词来修饰不可数名词数词 + 量词 +of + 名词对可数名词的数量提问用 how many对不可数名词的数量提问用how much4、不可数名词的量有以下两种表示方法:1) some, much ,a little ,a lot of ,a bit of , plenty of 用等表示多少。
注意既可以与可数名词复数,又可以与不可数名词连用的有: plenty of ,some ,a lot of ,lots of ,most of 等。
如 there is much water in the bottle . 瓶中有很多水。

小学英语语法总结全集小学英语语法汇总(一)可数名词与不可数名词“分家”一、可数名词与不可数名词的区别普通名词所表示的人或事物是可以按个数计算的,这类名词叫可数名词。
可数名词分为个体名词(表示某类人或事物中的个体,如worker,farmer, desk, fact ory 等)和集体名词(表示作为一个整体来看的一群人或一些事物,如people, famil y 等)。
如果普通名词所表示的事物是不能按个数来计算的,这类名词就叫不可数名词。
不可数名词分为物质名词(表示无法分为个体的物质,如meat,rice, water, milk, orange 等)和抽象名词(表示动作、状态、情况、品质等抽象概念,如work, homework, time, health, friendship 等)。
二、可数名词的家务事可数名词有单数和复数两种形式。
指一个人或一件事物时,用单数形式;指两个或多个人或事物时用复数形式。
名词由单数形式变成复数形式的规则如下:1.一般的名词词尾直接加-s 。
如:book → books room → roomshouse → houses day → days2.以s, ss, ch, sh, x 结尾的名词,在词尾加-es 。
如:bus → buses glass → glasseswatch →watchesdish → dishes box → boxes3.以"辅音字母+y"结尾的名词,要先将y 改为i 再加-es。
如:city → cities body → bodiesfactory → factories 等等。
4.以f 或fe 结尾的名词,要将f 或fe 改为v 再加-es。
如:half → halves leaf→ leavesknife → knives wife →wives5.特例[悄悄话:特例常常考,要记住。
]① child →children② man → men woman → womenpoliceman →policemen(规律:man → men)③ tomato →tomatoespotato →potatoes[悄悄话:初中英语以o 结尾的名词变复数时只有这两个词加-es,其余的当然加-s 喽!如:photo → photos ]④foot → feet tooth → teeth[悄悄话:oo 变成ee。

小学英语语法大全一、名词复数规则1.一般情况下,直接加-s,如:book-books, bag-bags, cat-cats, bed-beds2.以s. x. sh. ch结尾,加-es,如:bus-buses, box-boxes, brush-brushes, watch-watches3.以“辅音字母y”结尾,变y为i, 再加-es,如:family-families, strawberry-strawberries4.以“f或fe”结尾,变f或fe为v, 再加-es,如:knife-knives ]Leaf——leaves5.不规则名词复数:man-men, woman-women, policeman-policemen, policewoman-policewomen,child-childrenfoot-feet,.tooth-teethfish-fish, people-people, Chinese-Chinese,Japanese-Japanese写出下列各词的复数I _________him _________this ___________her ______watch _______child _______photo ________diary ______day________ foot________ book_______ dress ________tooth_______ sheep ______box_______ strawberry _____peach______ sandwich ______dish_______bus_______man______ woman_______二、一般现在时一般现在时基本用法介绍【No. 1】一般现在时的功能1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。
如:The sky is blue.天空是蓝色的。
2.表示经常性或习惯性的动作。

小学英语语法大全第一章名词一、定义名词是表示人或事物名称的词。
它既可以表示具体的东西,也可以是表示抽象的东西。
二、分类1. 名词可以根据意义分为普通名词和专有名词如:john is a studentstudent是普通名词,john是专有名词普通名词前可以用不定冠词a/an, 定冠词the 或不加冠词,专有名词前一般不加冠词,专有名词的首字母要大写。
2. 普通名词又可以分为个体名词、集体名词、物质名词和抽象名词,其中个体名词与集体名词是可数名词,物质名词和抽象名称是不可数名词。
3. 专有名词专有名词是表示人名、地名、团体、机构、组织等的专有名词,多为独一无二的事物。
三、名词的数1、名词分为可数名词和不可数名词。
可数名词——可以数的名词不可数名词——数不清(没有复数)drink?milk tea water orange juice coke coffee porridgefood?rice bread meat fish fruit cake dumplings2、可数名词与不定冠词a(an)连用有数数形式,不可数名词不能与不定冠词a(an)连用,没有复数形式many+可数名词复数much/a little+不可数名词some, any , a lot of (lots of) 两者都可以修饰。
3、可数名词可以直接用数词来修饰不可数名词数词 +量词 +of + 名词对可数名词的数量提问用how many对不可数名词的数量提问用 how much4、不可数名词的量有以下两种表示方法:1) some, much ,a little ,a lot of ,a bit of , plenty of 用等表示多少。
注意既可以与可数名词复数,又可以与不可数名词连用的有:plenty of ,some ,a lot of ,lots of ,most of 等。
如there is much water in the bottle .瓶中有很多水。

一、名词表示某一事物,有详尽的和抽象的之分。
分为可数名词和不能数名词。
重申:不能数名词都默认为单数,所以总是用is 也许 was;最好不要依照some、 any、 a lot of 等词去作判断,省得受误导。
1、可数名词怎样变“复数形式〞:a.一般情况下,直接加-s,如: book-books, bag-bags, cat-cats, bed-beds ;读音:清辅音后读[s] ,浊辅音和元音后读 [z] 。
b.以 s. x. sh. ch 结尾,加 -es,如: bus-buses, box-boxes, brush-brushes, watch-watches ;读音: [iz] 。
c.以“辅音字母 +y 〞结尾,变y 为i, 再加-es,如:family-families, strawberry-strawberries;读音:[z]。
d.以“f或 fe 〞结尾,变 f 或 fe 为 v, 再加 -es,如: knife-knives,thief-thieves;读音:[z]。
e.以“ o结〞尾的词,分两种情况1〕有生命的 +es读音:[z]如:mango-mangoes tomato-tomatoes hero-heroes2) 无生命的 +s读音:[z]如:photo-photos radio-radiosf. 不规那么名词复数: man-men, woman-women, policeman-policemen, policewoman-policewomen,snowman-snowmen, mouse-mice, child-children, foot-feet, tooth-teeth, fish-fish,people-people, Chinese-Chinese, Japanese-Japanese2、不能数名词没有复数。
若是要计算不能数名词所表达的数量,就得在数词和不能数名词之间加上“量词 +of 〞。
小学英语语法大全第一章名词一、定义名词是表示人或事物名称的词。
它既可以表示具体的东西,也可以是表示抽象的东西。
二、分类1. 名词可以根据意义分为普通名词和专有名词如:john is a studentstudent是普通名词,john是专有名词普通名词前可以用不定冠词a/an, 定冠词the 或不加冠词,专有名词前一般不加冠词,专有名词的首字母要大写。
2. 普通名词又可以分为个体名词、集体名词、物质名词和抽象名词,其中个体名词与集体名词是可数名词,物质名词和抽象名称是不可数名词。
3. 专有名词专有名词是表示人名、地名、团体、机构、组织等的专有名词,多为独一无二的事物。
三、名词的数1、名词分为可数名词和不可数名词。
可数名词——可以数的名词不可数名词——数不清(没有复数)drink?milk tea water orange juice coke coffee porridgefood?rice bread meat fish fruit cake dumplings2、可数名词与不定冠词a(an)连用有数数形式,不可数名词不能与不定冠词a(an)连用,没有复数形式many+可数名词复数much/a little+不可数名词some, any , a lot of (lots of) 两者都可以修饰。
3、可数名词可以直接用数词来修饰不可数名词数词 +量词 +of + 名词对可数名词的数量提问用how many对不可数名词的数量提问用 how much4、不可数名词的量有以下两种表示方法:1) some, much ,a little ,a lot of ,a bit of , plenty of 用等表示多少。
注意既可以与可数名词复数,又可以与不可数名词连用的有:plenty of ,some ,a lot of ,lots of ,most of 等。
如there is much water in the bottle .瓶中有很多水。
(完整版)小学最全英语语法汇总小学最全英语语法汇总一、时态1.普通如今时(1)表示经常发生的动作或情况,通常用“usually 通常, often 常常, every…每…, sometimes有时,always总是,”等词。
(2)基本结构:I / You / We /TheyHe / She / It确信句动词原形动词第三人称单数形式否定句don’t + 动原doesn’t + 动原普通疑咨询句(Yes/No) Do… ? Yes, Ido.Does…(动词原形)…?No,she doesn’t.特别疑咨询句What do …? How does she…(动词原形)…?(3) 动词第三人称单数形式(同名词单数变成复数办法相同)1 普通事情+s 如:walk-walks2. 辅音字母+y结尾去y +ies f ly-flies3. 结尾是 s, x, sh, ch +es watch-watches4.特别的do-does ,have-has, go-goes2.如今举行时,(1)表示正在发生的动作,通常用“now如今, look 看,linsen听”.(2)基本形式: be + 动词ingeg: I am(not) doing my homework.You/We/They are(not) reading.He/She/It is(not) eating.What are you doing?Is he reading?(3)动词的如今分词形式(动词+ing)普通事情+ing walk—walking结尾是别发音的 e -e +ingcome—coming重读闭音节双写最后一具字母+ing run-running swim-swimming3. 普通过去时(1)表示过去差不多发生的情况,通常用“last …上一具…, justnow刚刚, a moment ago刚刚,yesterday 昨天”等词。
小学英语语法大全第一章名词1、名词可以根据意义分为普通名词与专有名词如:john is a studentstudent就是普通名词,john就是专有名词普通名词前可以用不定冠词a/an, 定冠词the 或不加冠词,专有名词前一般不加冠词,专有名词得首字母要大写。
2、普通名词又可以分为个体名词、集体名词、物质名词与抽象名词,其中个体名词与集体名词就是可数名词,物质名词与抽象名称就是不可数名词。
3、专有名词专有名词就是表示人名、地名、团体、机构、组织等得专有名词,多为独一无二得事物。
三、名词得数1、名词分为可数名词与不可数名词。
可数名词——可以数得名词不可数名词——数不清(没有复数)drink?milk tea water orange juice coke coffee porridgefood?rice bread meat fish fruit cake dumplings2、可数名词与不定冠词a(an)连用有数数形式,不可数名词不能与不定冠词a(an)连用,没有复数形式many+可数名词复数much/a little+不可数名词some, any , a lot of (lots of) 两者都可以修饰。
3、可数名词可以直接用数词来修饰不可数名词数词+量词+of + 名词对可数名词得数量提问用how many对不可数名词得数量提问用how much4、不可数名词得量有以下两种表示方法:1) some, much ,a little ,a lot of ,a bit of , plenty of 用等表示多少。
注意既可以与可数名词复数,又可以与不可数名词连用得有:plenty of ,some ,a lot of ,lots of ,most of 等。
如there is much water in the bottle 、瓶中有很多水。
i'll tell you much good news、我要告诉您许多好消息。
小学英语语法总结一、时态小结定一般特征的化第三人称数的化情况:表示常性或性的作.在在表示在或在一段正在行的作.行一般表示去某生的作或情况.去一般将表示将要生的事情来everyday/morning/ ⋯usuallynow/look/listenyesterday morning/afternoon/eveninglastyear/monthaminuteago/anhouragothismorning/afternoon/eveningtomorrowthedayaftertomorrow/thenextday/Monday⋯attheweekend/tonighttomorrow 一般情况在尾直接加-s以ch,sh,s,x或o尾的加-es以音字母加y尾的,将y改成i再加-es在分的化情况:一般情况在尾直接加-ing以e尾的,去掉e再加-ing以重音尾的,双写最后一个字母加-ing去式的化情况:一般情况在尾直接加-ed以e尾的加-d以音字母加y尾的,将y改成i再加-ed以重音尾的,双写最后一个字母加-ed主要构成begoingto/will+ 原形be+ 形容night/morning/afternoon1.但凡在must,mustn’t,can,can’t,let’s,don,will’t,后may的一定要用动词的原形2.二、名词的复数。
3.名词按其数,可分两种:可数名词和不可数名词.4.可数名词的复数变化规那么:5.一般情况下,直接在词尾加-s,如:girl-girls,book-books,pen-pens6.以s,x,sh,ch结尾的词,在词后加-es,如:class-classes,box-boxes,match-matches,7.以辅音字母+y结尾的,变y为i再加-es,如:city-cities,family-families,country-countries8.以f或fe结尾的,变f或fe为v再加-es,如:knife-knives,wife-wives,life-lives,9.以o结尾的加-es或-s,如:radio-radios,tomato-tomatoes,potato-potatoes,zoo-zoos,photo-photos,4.6.man-men,woman-women,foot-feet,child-children,5.三、形容词的比拟级、最高级。
授课资料教育精品资料小学英语语法大全第一章一、定义名词是表示人或事物名称的词。
它既能够表示详尽的东西,也能够是表示抽象的东西。
二、分类1.名词能够依照意义分为一般名词和专有名词如: john is a studentstudent是一般名词,john是专有名词一般名词前能够用不定冠词 a/an, 定冠词 the 或不加冠词,专有名词前一般不加冠词,专有名词的首字母要大写。
2.一般名词又能够分为个体名词、集体名词、物质名词和抽象名词,其中个体名词与集体名词是可数名词,物质名词和抽象名称是不能足数名词。
3.专有名词专有名词是表示人名、地名、集体、机构、组织等的专有名词,多为独一无二的事物。
三、名词的数1、名词分为可数名词和不能足数名词。
可数名词——能足数的名词不能足数名词——数不清〔没有复数〕drink?milk tea water orange juice coke coffee porridgefood?rice bread meat fish fruit cake dumplingsa(an)连用,没有复数2、可数名词与不定冠词a(an)连用有数数形式,不能足数名词不能够与不定冠词形式many+可数名词复数much/a little+不能足数名词some, any , a lot of (lots of)两者都能够修饰。
3、可数名词能够直接用数词来修饰不能足数名词数词 + 量词 +of +名词对可数名词的数量提问用how many对不能足数名词的数量提问用how much4、不能足数名词的量有以下两种表示方法:1〕some, much ,a little ,a lot of,a bit of , plenty of用等表示多少。
of,most of等。
授课资料如there is much water in the bottle .瓶中有好多水。
i'll tell you much good news.我要告诉你好多好信息。
小学英语语法知识汇总一、词类:1、动词:行为动词、be动词、情态动词。
原形、+s/es单三、+ed过去式、+ing现在分词,具体判断方法如下:be动词a、Am--was Is --was Are--were 口诀:我用am, 你用are, is用在他她它,所有复数全用are。
b、肯定和否定句I am (not) from London. He /She is(not) a teacher. My hair is(not) long. Her eyes are(not) small. c、一般疑问句Am I …? Yes, you are. No, you aren’t. Are you/they…? Yes,we/ they are. No,we/ they aren’t. Is the cat fat? Yes, it is. No, it isn’t.is、am、are为一类,一般用于一般现在时、现在进行时和一般将来时中。
was和were为另一类,一般用于一般过去时。
(3)情态动词can、must、should、would、may。
情态动词后动词总是用原形。
(不受其他任何条件影响)2、名词这里强调两点:不可数名词都默认为单数,所以总是用is或者was。
如何加后缀:a.一般情况下,直接加-s,如:book-books, bag-bags, cat-cats, bed-bedsb.以s. x. sh. ch结尾,加-es,如:bus-buses, box-boxes, brush-brushes, watch-watches c.以“辅音字母+y”结尾,变y为i, 再加-es,如:family-families, strawberry-strawberries d.以“f或fe”结尾,变f或fe为v, 再加-es,如:knife-knivese.不规则名词复数:man-men, woman-women, policeman-policemen,policewoman-policewomen, mouse-mice child-children foot-feet ,.tooth-teeth fish-fish, people-people, Chinese-Chinese, Japanese-Japanese sheep-sheep deer-deer ox-oxen(注:动词第三人称单数形式规则与名词复数规则相同)3、形容词(包括副词)形容词表示某一事物或的特征,副词表示某一动作的特征。
规则变化如下:1) 单音节形容词的比较级和最高级形式是在词尾加-er 和-est 构成。
great (原级) greater(比较级) greatest(最高级)2) 以-e 结尾的单音节形容词的比较级和最高级是在词尾加-r 和-st 构成。
wide (原级) wider (比较级) widest (最高级)3)少数以-y, -er, -ow, -ble结尾的双音节形容词的比较级和最高级是在词尾加-er 和-est 构成。
clever(原级) cleverer(比较级) cleverest(最高级)4) 以-y 结尾,但-y 前是辅音字母的形容词的比较级和最高级是把-y 去掉,加上-ier 和-est 构成. happy (原形) happier (比较级) happiest (最高级)5) 以一个辅音字母结尾其前面的元音字母发短元音的形容词的比较级和最高级是双写该辅音字母然后再加-er和-est。
big (原级) bigger (比较级) biggest (最高级) hot(原级)hotter(比较级)hottest(最高级)6) 双音节和多音节形容词的比较级和最高级需用more 和most 加在形容词前面来构成。
beautiful (原级) more beautiful (比较级) the most beautiful(最高级)常用的不规则变化的形容词的比较级和最高级:原级比较级最高级good better best ,many more mostmuch more most ,bad worse worst ,little less least ,ill worse worst ,far farther(further)farthest(furthest)形容词前如加less 和lest 则表示"较不"和"最不"important 重要,less important 较不重要,lest important 最不重要三个重要特征:as……as中间一定用原形,有than的时候一定+er。
动词后接最高级中间不加the.人称代词:有主格和宾格之分。
一般动词前用主格,动词后用宾格。
物主代词:有两类:形容词性物主代词(短的,表示。
的)和名词性物主代词(长的,表示谁的东西)一般看后面有没有名词,如有,就用形容词性物主代词(短的);如无,就用名词性物主代词(长的)。
5、数量词我们学过两类:基数词和序数词。
基数用于表示数量多少,而基数词用于表示次序,常在日期中出现。
序数词的前面一般都加the。
例:the first ,the second ,the third ,the 14th 6、冠词有a、an、the。
a和an的区别:an用于元音音素(一般就是元音字母aeiou)前,a用于辅音音素前。
二、否定句:be动词(am、is、are、was、were)+not、情态动词(can、must、should)+ not、助动词(do、does、did)+ not如何将一个肯定的陈述句改为否定句:1、看句中有无be动词,如有,直接在be动词后+ not。
2、看句中有无情态动词,如有,直接在情态动词后+ not。
3、如上述二者都没有,就应用助动词+ not。
分四个步骤:(1)肯定陈述句中本来是没有助动词的,要加上去,位置在主语(某人或某物)后,动词前。
(2)确定助动词用do、does还是did,根据句中动词,动词是原形的助动词就用do,动词是第三人称单数的助动词就用does,动词用过去式的助动词就有did。
(3)在助动词后加not。
(4)原句中动词假如发生变化就要恢复成原形。
强调一点,有some的要考虑是否要用any。
三、一般疑问句。
如何将一个肯定的陈述句改为否定句:1、看句中有无be动词,如有,把be动词提到句首即可。
2、看句中有无情态动词,如有,把情态动词提到句首即可。
3、如上述二者都没有,就应把助动提到句首。
分四个步骤:(1)肯定陈述句中本来是没有助动词的,要加上去,位置在主语(某人或某物)后,动词前。
(2)确定助动词用do、does还是did,根据句中动词,动词是原形的助动词就用do,动词是第三人称单数的助动词就用does,动词用过去式的助动词就有did。
(3)把助动词后提到句首。
(4)原句中动词假如发生变化就要恢复成原形。
强调一点,有some的要考虑是否要用any。
四、特殊疑问句。
表示疑问,有疑问词(在开头),回答有很多种可能。
表示请求或命令别人做某事或不要做某事。
肯定祈使句一定是以动词原形开头(有时有please),否定的祈使句一定是don’t加动词原形开头(有时有please)。
把祈使句改为否定句只需在动词前加don’t即可。
六、时态1、一般现在时(1)一般现在时中的be动词:一般用原形:am is aream用于第一人称单数(I);is用于第三人称单数(he she it和其他人名或称谓,如:Ben his sister等);are用于第二人称单数(you)和所有复数(包括第一人称复数we、第二人称复数you;第三人称复数they和其他复数,如the children 、his parents等)。
(2)一般现在时中的动词:第一种情况:主语是第三人称单数(he she it 和其他,如Helen 、her cousin 等),动词后一般加s或es。
第二种情况:主语不是第三人称单数,动词都用原形。
(4)一般现在时判断依据(如何判断一个句子是一般现在时):△be动词是am、is、are△动词用原形或加s、es△没有时间状语或有usually、often、everyday、sometimes等不是具体的时间2、一般过去时(1)一般过去时中的be动词:一般用过去式:was werewas用于第一人称单数(I)和第三人称单数(he she it和其他人名或称谓,如:Ben 、his sister等);were用于第二人称单数(you)和所有复数(包括第一人称复数we、第二人称复数you;第三人称复数they和其他复数,如the children 、his parents等)。
(2)一般过去时中的动词:(助动词do/does统一变化为did)一般只有一种情况:+ed这里强调一点,和一般现在时不同的是这里不管主语是第几人称,也不管是单数和复数都加ed。
(4)一般过去时判断依据(如何判断一个句子是一般过去时):△be动词是was、were △动词加ed△有表示过去的时间状语现在学过的常用的表示过去的时间状语有:just now a moment ago yesterday last week last nightlast weekend last year last month three days ago two weeks ago five years ago this morning3、一般将来时:(1)构成形式:Be going to +动词原形, will + 动词原形(2)一般将来时表示动作即将发生或某人打算做某事。
(3)句中往往有tomorrow、soon、next week等词。
4、现在进行时:(1)构成形式:(规则:①+ing ,②去e加ing,③结尾辅元辅结构双写尾字母+ing)Be动词+动词的ing形式这里强调一点,两者缺少其中任何一种都不可以构成现在进行时。
(2)现在进行时表示动作正在进行或事情正在发生。
(3)有用的依据:一个句子中既有be动词,又有动词,且动词加了ing ←→该句是现在进行时(4)句中往往有now、look、listen等词。
动词过去式、现在分词的不规则变化:be 是——was, were——being begin 开始——began——beginning build 建筑——built——building buy 买——bought——buyingcan 能——could——无come 来——came——coming copy 拷贝——copied——copying do 做——did——doing draw 画——drew——drawing drink 喝——drank——drinking drive 驾车——drove——driving eat 吃——ate——eatingfeel 感觉——felt——feelingfind 找寻——found——findingfly飞——flew——flyingforget 忘记——forgot——forgettingget 得到——got——gettinggive 给予——gave——givinggo 去——went——goinggrow 成长——grew——growinghave 有——had——havinghear 听——heard——hearingkeep 保持——kept——keepingknow 知道——knew——knowing learn学习—learnt, learned——learning let 让——let——lettingmake 做——made——makingmay 可以——might——无mean 意思——meant-meaning meet 见面——met——meetingmust 必须——must——无put 放——put——puttingread 读——read——readingride 骑——rode——riding ring 响——rang——ringingrun 跑——ran——runningsay 说——said——sayingsee 看见——saw——seeingsing 唱歌——sang——singingsit 坐——sat——sittingsleep 睡觉——slept——sleeping speak 讲话——spoke——speaking spend 花钱——spent——spending stand 站立——stood——standing sweep 打扫——swept——sweeping swim 游泳——swam——swimming take 拿到——took——taking teach 教——taught——teaching tell 讲述——told——tellingthink 思考——thought——thinking will 意愿——would——无write 写——wrote——writ。