kpi指标提取
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.35 MB
- 文档页数:17

关于KPI (Key Performance Indicator)的知识第一部分:KPI(Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia);Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is an industry jargon term for a type of Measure of Performance.KPIs are commonly used by an organization to evaluate its success or the success of a particular activity in which it is engaged. Sometimes success is defined in terms of making progress toward strategic goals, but often, success is simply the repeated achievement of some level of operational goal (zero defects, 10/10 customer satisfaction etc.). Accordingly, choosing the right KPIs is reliant upon having a good understanding of what is important to the organization. 'What is important' often depends on the department measuring the performance - the KPIs useful to a Finance Team will be quite different to the KPIs assigned to the sales force, for example. Because of the need to develop a good understanding of what is important, performance indicator selection is often closely associated with the use of various techniques to assess the present state of the business, and its key activities. These assessments often lead to the identification of potential improvements; and as a consequence, performance indicators are routinely associated with 'performance improvement' initiatives. A very common method for choosing KPIs is to apply a management framework such as the Balanced Scorecard.Categorization of indicatorsKey Performance Indicators define a set of values used to measure against.These raw sets of values, which are fed to systems in charge of summarizing the information, are called indicators. Indicators identifiable as possible candidates for KPIs can be summarized into the following sub-categories:∙Quantitative indicators which can be presented as a number.∙Practical indicators that interface with existing company processes.∙Directional indicators specifying whether an organization is getting better or not.∙Actionable indicators are sufficiently in an organization's control to effect change.∙Financial indicators used in performance measurement and when looking at an operating indexKey Performance Indicators, in practical terms and for strategic development, are objectives to be targeted that will add the most value to the business.These are also referred to as Key Success Indicators.Some Important AspectsKey performance indicators (KPIs) are ways to periodically assess the performances of organizations, business units, and their division, departments and employees. Accordingly, KPIs are most commonly defined in a way that is understandable, meaningful, and measurable. They are rarely defined in such a way such that their fulfillment would be hampered by factors seen as non-controllable by the organizations or individuals responsible. Such KPIs are usually ignored by organizations.In order to be evaluated, KPIs are linked to target values, so that the value of the measure can be assessed as meeting expectations or not.Identifying Indicators of OrganizationPerformance indicators differ from business drivers & aims (or goals).A school might consider the failure rate of its students as a Key Performance Indicator which might help the school understand its position in the educational community, whereas a business might consider the percentage of income from returning customers as a potential KPI.The key stages in identifying KPIs are:∙Having a pre-defined business process (BP).∙Having requirements for the BPs.∙Having a quantitative/qualitative measurement of the results and comparison with set goals.∙Investigating variances and tweaking processes or resources to achieve short-term goals.A KPI can follow the SMART criteria. This means the measure has a S pecific purpose for the business, it is M easurable to really get a value of the KPI, the defined norms have to be A chievable, the improvement of a KPI has to be R elevant to the success of the organization, and finally it must be T ime phased, which means the value or outcomes are shown for a predefined and relevant period.KPI ExamplesMarketingSome examples are:1.New customers acquired2.Demographic analysis of individuals (potential customers) applyingto become customers, and the levels of approval, rejections, and pending numbers.3.Status of existing customers4.Customer attrition5.Turnover (ie, Revenue) generated by segments of the customerpopulation.6.Outstanding balances held by segments of customers and terms ofpayment.7.Collection of bad debts within customer relationships.8.Profitability of customers by demographic segments andsegmentation of customers by profitability.Many of these customer KPIs are developed and managed with customer relationship management (CRM) software.Faster availability of data is a competitive issue for most organizations. For example, businesses which have higher operational/credit risk (involving for example credit cards or wealth management) may want weekly or even daily availability of KPI analysis, facilitated by appropriate IT systems and tools.ProblemsIn practice, overseeing Key Performance Indicators can prove expensive or difficult for organizations. Indicators such as staff morale may be impossible to quantify.Another serious issue in practice is that once a measure is created, it becomes difficult to adjust to changing needs as historical comparisons will be lost. Conversely, measures are often of dubious relevance, because history does exist.Furthermore, since businesses with similar backgrounds are often used as a benchmark for such measures, measures based only on in-house practices make it difficult for an organization to compare with these outside benchmarks.Measures are also used as a rough guide rather than a precise benchmark.第二部分:KPI (From IBIS)BackgroundThe term KPI has become one of the most over-used and little understood terms in business development and management. In theory it provides a series of measures against which internal managers and external investors can judge the business and how it is likely to perform over the medium and long term. Regrettably it has become confused with metrics – if we can measure it, it is a KPI. Against the growing background of noise created by a welter of such KPI concepts, the true value of the core KPI becomes lost.The KPI when properly developed should be provide all staff with clear goals and objectives, coupled with an understanding of how they relate to the overall success of the organisation. Published internally and continually referred to, they will also strengthen shared values and create common goals.What are the key components of a KPI?The KPI should be seen as:Only Key when it is of fundamental importance in gaining competitive advantage and is a make or break component in the success or failure of the enterprise. For example, the level of labour turnover is an important operating ratio, but rarely one that is a make or break element in the success and failure of the organisation. Many are able to operate on well below benchmark levels and still return satisfactory or above satisfactory results.Only relating to Performance when it can be clearly measured, quantified and easily influenced by the organisation. For example, weather influences many tourist related operations – but the organisation cannot influence the weather. Sales growth may be an important performance criteria – but targets must be set that can be measured.Only an Indicator if it provides leading information on future performance. A considerable amount of data within the organisation only has value for historical purposes – for example debtor and creditor length. By contrast rates of new product development provide excellent leading edge information. Obviously KPI's cannot operate in a vacuum. One cannot establish a KPI without a clear understanding of what is possible – so we have to be able toset upper and lower limits of the KPI in reference to the market and how the competition is performing (or in the absence of competition, a comparable measurement from a number of similar organisations). This means that an understanding of benchmarks is essential to make KPI's useful (and specific to the organisation), as they put the level of current performance in context –both for start ups and established enterprises – though they are more important for the latter. Benchmarks also help in checking what other successful organisations see as crucial in building and maintaining competitive advantage, as they are central to any type of competitive analysis.Start with what you need to measure and monitorDifferent organisations need to monitor different aspects of their environment. For example, the airline industry has a complex set of issues many of which (but not all) are different from the dairy farmer. Ibis has created a number of separate business monitoring modules for medium sized companies which we believe cover the majority of requirements for the development and maintenance of their organisation, that are part of a bottom up planning system based around k nowledge centres.第三部分:500强名企的KPI绩效管理案例500强名企的KPI绩效管理操作手册部分内容四、绩效指标的主要形式与内容(一)关键绩效指标(KPI)即用来衡量某一职位工作人员工作绩效表现的具体量化指标,是对工作完成效果的最直接衡量方式。

如何提取KPI指标关于如何提取KPI指标,首先需要明确KPI的概念,即关键绩效指标。
KPI是用来衡量和评估组织、团队或个人在达成既定目标过程中的绩效表现的重要指标。
在日常管理中,提取和定义合适的KPI指标对于监控和评估工作绩效具有重要意义。
下面将介绍如何有效地提取KPI指标。
首先,明确业务目标。
在提取KPI指标之前,需要明确所在组织或团队的具体业务目标和战略方向。
只有清晰了解业务目标,才能有针对性地选择和提取适合的KPI指标。
其次,确定衡量维度。
KPI指标通常包括衡量维度、目标值和监控方法等要素。
在确定KPI指标时,需要考虑到业务活动的各个方面,包括财务、客户、内部流程和学习与成长等多个维度,确保全面反映业务绩效表现。
接着,选择具体指标。
在每个衡量维度下,需要选择具体的KPI指标。
这些指标应该是可量化的,并能够直接反映业务活动的绩效水平。
同时,指标的选择应该符合SMART原则,即具有特定性、可衡量性、可达性、相关性和时限性。
然后,制定目标值。
为每个KPI指标设定合理的目标值是提取KPI指标的重要环节。
目标值应该既能够激励员工努力工作,又不至于过高造成无法实现。
同时,目标值应该具有一定的挑战性,可以促使员工不断提升绩效水平。
最后,建立监控机制。
一旦确定了KPI指标和目标值,就需要建立有效的监控机制来实时跟踪和评估绩效表现。
通过建立仪表盘、报表和定期评审会议等方式,确保KPI指标的监控和管理工作得以有效实施。
总的来说,提取KPI指标是一项重要的管理工作,需要结合业务目标和战略定位,明确衡量维度,选择具体指标,设定目标值,并建立有效的监控机制。
只有确保KPI指标的准确性和有效性,才能更好地引导和激励员工,实现组织绩效的持续提升。
提取KPI指标的四种方法
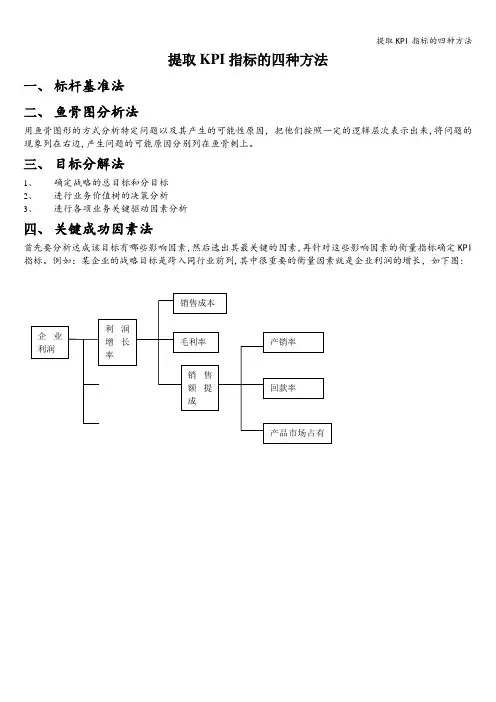
提取KPI指标的四种方法
一、标杆基准法
二、鱼骨图分析法
用鱼骨图形的方式分析特定问题以及其产生的可能性原因,把他们按照一定的逻辑层次表示出来,将问题的现象列在右边,产生问题的可能原因分别列在鱼骨刺上。
三、目标分解法
1、确定战略的总目标和分目标
2、进行业务价值树的决策分析
3、进行各项业务关键驱动因素分析
四、关键成功因素法
首先要分析达成该目标有哪些影响因素,然后选出其最关键的因素,再针对这些影响因素的衡量指标确定KPI 指标。
例如:某企业的战略目标是跨入同行业前列,其中很重要的衡量因素就是企业利润的增长,如下图:。

纵横分解提取部门绩效指标-—基于KPI的部门绩效指标选取一.什么是KPI?KPI(Key Performance Indicators)译为关键绩效指标,是指企业宏观战略目标决策经过层层分解产生的可操作性的战术目标,是宏观战略决策执行效果的监测指针。
KPI是衡量企业战略实施效果的关键指标,其目的是建立一种机制,将企业战略转化为内部过程和活动,以不断增强企业的核心竞争力,并持续取得高效益。
在具体的企业管理实践中,KPI指标体系的价值则是根据企业或部门战略,逐步分解与承接战略要项,并在此过程中帮助企业战略落地,同时确定部门和个人的责任和绩效标准。
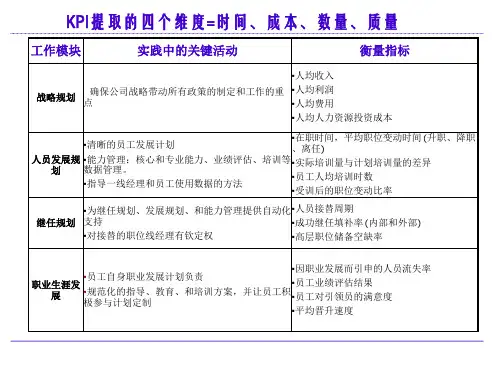
目前在国内外,大量公司采用KPI作为提取各个主体考核的基本指标来源.在进行绩效指标提取时,指标提取有四个维度:时间、成本、数量和质量。
由此引出KPI绩效指标制定的SMART五原则:•明确性(Specific):是指绩效考核要切中特定目标,不能笼统;•衡量性(Measurable):是指绩效指标是数量化或者行为化的,验证这些绩效指标的数据或者信息是可以获得的;•可接受性(Attainable):是指绩效指标在付出努力的情况下是可以实现的;•实际性(Realistic):是指实实在在的,可以证明和观察;•时限性(Time-bound):是指要注重完成绩效指标的特定期限.企业在提取KPI指标时,必须符合SMART原则,同时,在指标中还至少应当包含两种类型的KPI 指标-—常规KPI指标与改进KPI指标.常规KPI指标是面向阶段性战略目标的,反映战略实现状况;改进KPI指标是面向年度计划的,属战术性指标,反映年内经营管理中影响常规KPI指标达成的障碍因素改善情况.改进KPI指标的改善有利于常规KPI指标的达成,改进KPI指标随管理重点的变化而变化.常规KPI指标和改进KPI指标可以同时确保企业当前的战略目标顺利实现,同时改进KPI指标则保证了未来组织的弹性。
企业的KPI指标库也可以根据企业战略、外部市场等的变化而更新,这样就可以让KPI指标恰当地起到衡量、考核、牵引的作用。

如何进⾏KPI提炼如何进⾏KPI提炼KPI指标提炼是⼀个技术技巧活⼉,也是⼀个“争论”“谈判”活⼉。
到现在,也搞不清参加过多少次这样的“提炼”⼯作,什么应当遵守SMART原则,可以通过PAST⼯作流程分解法、鱼⾻图分解法、头脑风暴法等提炼指标。
可能有⼀部分卡卡对我⽐较了解:每天的打卡分享,对HR的理论说得不多,⽽对实际⼯作中的做法说得较多,对今天“如何提炼KPI指标”我仍然如此坚持认为:在我们这⽚⼟地上,不管是民营、国有还是机关事业单位,最适⽤的还是“专家意见法”,下⾯我简单分享⽤此法如何从上到下进⾏KPI指标提炼:1、公司级KPI指标提炼。
⾛过⼏家公司,每年在与⽼板制定来年的各项指标和⽬标时,最重要的就是纯利润这个指标,这是最主要的“纲”。
⽼板召集副总以上⼈员、法律顾问、⽼板⼏个最要好的朋友⼀起,利⽤周末或平时下班后的晚上,到咖啡厅、饭店、茶楼等,边吃边喝边聊,共同回顾过去⼏年取得的成绩和应当总结的教训,分析国内外政策、⾏业发展、企业机遇、⼈才发展等,最终都会落到由纯利润引开去:到底要做到哪些主要的事情才能保证此纯利润的实现?⼤家于轻松和谐的⽓氛中,你⼀⾔我⼀语,说出来了不少⼼中真实的想法,道出了许多⾃⼰的管理⼼得,从产品创新、成本控制、⽣产效率、物流控制、价格策略、促销⼿段、资⾦管理、⼈才管理、安全管理、社会责任等各⽅⾯进⾏了多次探讨,由于这些⽅⾯在他们的脑海中有清晰的数据和鲜活的事例,所以讨论都是层层深⼊、抽丝剥茧,每次都有⼀个结果。
经过以上专家们的多次民主协商后,由⽼板的秘书整理汇总后,呈⽼板修改,据了解,⽼板⼀般需要花上⼏天⼏夜才会有⼀个结果,据他介绍,那⼏天⼏夜是他最冷静也最痛苦的,指标定少了怕不能保证利润的实现,定多了怕⼤家有情绪,当然最磨⼈还是定各指标的⽬标了(不在今天讨论之列,以后再叙)。
⽼板有了初稿后,再召集各部门负责⼈、副总等⼀起开会讨论,基本修改的⽐较少,也是开会宣贯,定稿后让办公室和HR部门共同发布,并公布公司各显眼位置。


kpi指标提取方法嘿,咱今儿就来聊聊 KPI 指标提取这档子事儿!这可太重要啦,就好比是做菜得知道放啥调料一样。
你想想看,一个团队或者一个项目,要是没有明确的 KPI 指标,那不就像没头苍蝇一样乱撞嘛!那怎么提取 KPI 指标呢?首先得清楚目标吧,就像你要去一个地方,得知道目的地在哪儿呀。
比如说,我们要提高产品的销量,那销量不就是个关键指标嘛。
然后呢,把这个大目标分解成一个个小目标,就跟拆积木似的。
比如可以看看不同地区的销售情况,不同时间段的销售波动,这都是能提取出KPI 指标的地方呀。
再比如说,咱要是搞一个活动,那参与人数、活动效果、反馈意见这些不都是可以提取的指标嘛。
你说要是不关注这些,那活动搞了不就白搞啦?咱还可以从客户的角度出发呀。
客户满意度那绝对是个重要指标吧,那怎么衡量客户满意度呢?可以从客户的评价、投诉、重复购买率这些方面入手呀。
这就像你交朋友,朋友对你的评价很重要吧,总不能自己瞎感觉呀。
还有啊,成本也是个不能忽视的方面呢。
不能光顾着追求效果,把成本都抛到脑后啦。
那成本怎么提取成 KPI 指标呢?可以看看各项开支是不是合理呀,有没有浪费的地方呀。
你说这 KPI 指标提取是不是很有讲究?要是随便弄几个指标,那能有效果吗?那不是自欺欺人嘛!咱得认真对待,就像对待自己的宝贝一样。
提取 KPI 指标的时候,还得结合实际情况呀。
不能生搬硬套别人的方法,每个团队、每个项目都有自己的特点呀。
就像每个人的性格都不一样,你能拿对待张三的方法去对待李四吗?那肯定不行呀。
而且呀,提取了 KPI 指标还不算完,还得不断地去跟进、去调整。
这世界变化这么快,昨天合适的指标今天可能就不合适啦。
你不调整,那不就落后啦?总之呢,KPI 指标提取这事儿可得认真对待,要多思考、多分析。
别嫌麻烦,这可是为了咱能把事情做好呀。
你说是不是这个理儿?咱可不能稀里糊涂地就过去了,得把这事儿整明白咯,让咱的努力都有方向,都能出成果!你说呢?。

绩效考核管理之关键绩效指标体系一、关键绩效指标(KPI)基本概念KPI(关键绩效指标)是Key Performance Indicators的英文简写,是管理中“计划-执行—评价"中“评价”不可分割的一部分,反映个体/组织关键业绩贡献的评价依据和指标。
KPI是指标,不是目标,但是能够借此确定目标或行为标准:是绩效指标,不是能力或态度指标;是关键绩效指标,不是一般所指的绩效指标。
关键绩效指标是用于衡量工作人员工作绩效表现的量化指标,是绩效计划的重要组成部分.关键绩效指标具备如下几项特点:(一) 来自于对公司战略目标的分解这首先意味着,作为衡量各职位工作绩效的指标,关键绩效指标所体现的衡量内容最终取决于公司的战略目标.当关键绩效指标构成公司战略目标的有效组成部分或支持体系时,它所衡量的职位便以实现公司战略目标的相关部分作为自身的主要职责;如果KPI与公司战略目标脱离,则它所衡量的职位的努力方向也将与公司战略目标的实现产生分歧。
KPI来自于对公司战略目标的分解,其第二层含义在于,KPI是对公司战略目标的进一步细化和发展.公司战略目标是长期的、指导性的、概括性的,而各职位的关键绩效指标内容丰富,针对职位而设置,着眼于考核当年的工作绩效、具有可衡量性.因此,关键绩效指标是对真正驱动公司战略目标实现的具体因素的发掘,是公司战略对每个职位工作绩效要求的具体体现.最后一层含义在于,关键绩效指标随公司战略目标的发展演变而调整。
当公司战略侧重点转移时,关键绩效指标必须予以修正以反映公司战略新的内容。
(二)关键绩效指标是对绩效构成中可控部分的衡量企业经营活动的效果是内因外因综合作用的结果,这其中内因是各职位员工可控制和影响的部分,也是关键绩效指标所衡量的部分。
关键绩效指标应尽量反映员工工作的直接可控效果,剔除他人或环境造成的其它方面影响。
例如,销售量与市场份额都是衡量销售部门市场开发能力的标准,而销售量是市场总规模与市场份额相乘的结果,其中市场总规模则是不可控变量。

KPIKPI 绩效管理Key Performance Indicators 关键业绩指标企业旳生产过程是劳动者运用劳动工具变化劳动对象旳过程。
在企业生产旳三个基本要素(劳动力、劳动资料、劳动对象)中, 劳动力是最重要旳原因, 对旳旳记录、分析、预测劳动生产力指标, 对于企业有序地组织生产、充足开发、合理运用人力资源有着重要意义。
KPI指标体系建立流程KPI指标旳提取, 可以“十字对焦、职责修正”一句话概括。
但在详细旳操作过程中, 要做到在各层面都从纵向战略目旳分解、横向结合业务流程“十”字提取,也不是一件非常轻易旳事情。
分解企业战略目旳, 分析并建立各子目旳与重要业务流程旳联络。
企业旳总体战略目旳在一般状况下均可以分解为几项重要旳支持性子目旳, 而这些支持性旳更为详细旳子目旳自身需要企业旳某些重要业务流程旳支持才能在一定程度上到达。
因此,在本环节上需要完毕如下工作:(1)确定各支持性业务流程目旳。
在确认对各战略子目旳旳支持性业务流程后, 需要深入确认各业务流程在支持战略子目旳到达旳前提下流程自身旳总目旳, 并运用九宫图旳方式深入确认流程总目旳在不一样维度上旳详细分解内容。
(2) 确认各业务流程与各职能部门旳联络。
本环节通过九宫图旳方式建立流程与工作职能之间旳关联, 从而在更微观旳部门层面建立流程、职能与指标之间旳关联, 为企业总体战略目旳和部门绩效指标建立联络。
(3) 部门级KPI指标旳提取。
在本环节中要将从通过上述环节建立起来旳流程重点、部门职责之间旳联络中提取部门级旳KPI指标。
(4) 目旳、流程、职能、职位目旳旳统一。
根据部门KPI、业务流程以及确定旳各职位职责, 建立企业目旳、流程、职能与职位旳统一。
其重要内容包括:一)劳动力数量指标旳记录。
A. 按工作岗位分劳动力指标旳记录。
1. 工人: 基本生产工人旳(直接从事产品制造旳工人)、辅助生产工人(从事多种辅助性工作)2.学徒: 指在纯熟工指导下, 在生产劳动中学习生产技术, 享有徒工待遇旳人员;3. 营销人员: 指直接从事产品销售旳有关人员;4. 管理人员: 指在企业组织机构及生产车间从事行政、生产、经济管理工作旳人员;5. 工程技术人员:指肩负工程技术工作并具有工程技术能力并具有大专以上学历旳人员;KPI考核旳三大内容:月度工作计划考核表——一种月只需7天, 平常管理工作就轻松完毕;员工综合素质能力考核表——有助于主管权威旳树立;知识管理防错提醒单——防止员工反复出错。

kpi指标提取的五种方法
提取KPI(关键绩效指标)的五种方法如下:
1. 业务目标法:通过分析企业的业务目标和战略目标,确定关键绩效指标。
这种方法适用于需要从战略层面进行绩效管理的企业。
2. 顶层指标法:从企业层面选择一些关键指标,例如利润、市场份额、客户满意度等,作为评估企业绩效的指标。
这种方法适用于整体绩效评估或跨部门绩效管理。
3. 指标树法:通过将业务目标和战略目标逐级细化,建立指标树,从而找到合适的关键绩效指标。
这种方法适用于需要细分指标来监控绩效的企业。
4. 顾客驱动法:通过分析客户需求和期望,确定与客户价值相关的关键绩效指标。
这种方法适用于注重客户满意度和客户导向的企业。
5. 数据驱动法:通过收集和分析大量的数据,使用数据挖掘和分析工具,找到与业务目标和战略目标相关的关键绩效指标。
这种方法适用于数据丰富的企业,可以基于数据驱动的方式进行绩效管理。
MBAKPI(Key Performance Indicator,关键绩效指标)什么是关键绩效指标企业关键绩效指标(KPI:Key Performance Indicator)是通过对组织内部流程的输入端、输出端的关键参数进行设置、取样、计算、分析,衡量流程绩效的一种目标式量化管理指标,是把企业的战略目标分解为可操作的工作目标的工具,是企业绩效管理的基础。
KPI可以使部门主管明确部门的主要责任,并以此为基础,明确部门人员的业绩衡量指标。
建立明确的切实可行的KPI体系,是做好绩效管理的关键。
关键绩效指标是用于衡量工作人员工作绩效表现的量化指标,是绩效计划的重要组成部分。
KPI法符合一个重要的管理原理“八二原理”。
在一个企业的价值创造过程中,存在着“80/20”的规律,即20%的骨干人员创造企业80%的价值;而且在每一位员工身上“八二原理”同样适用,即80%的工作任务是由20%的关键行为完成的。
因此,必须抓住20%的关键行为,对之进行分析和衡量,这样就能抓住业绩评价的重心。
KPI相关概念KPA(Key Process Area )意为关键过程领域,这些关键过程域指出了企业</a>需要集中力量改进和解决问题的过程。
同时,这些关键过程域指明了为了要达到该能力成熟度等级所需要解决的具体问题。
每个KPA都明确地列出一个或多个的目标(Goal),并且指明了一组相关联的关键实践(Key Practices)。
实施这些关键实践就能实现这个关键过程域的目标,从而达到增加过程能力的效果。
我们也可以从人力资源管理角度意为(Key Performance Action)意为关键绩效行动,可以简单叫做关键行为指标,当一件任务暂时没有找到可衡量的KPI或一时难以量化的时候,可以对完成任务关键的几个分解动作进行要求,形成多个目标,对多个目标进行检查,达到考量的结果。
KPA是做好周计划和日计划的常用工具,通过KPA的检查考量统计可以将一个任务的KPI梳理出来。
关键绩效指标(KPI)(一)关键绩效指标(KPI)即用来衡量某一职位工作人员工作绩效表现的具体量化指标,是对工作完成效果的最直接衡量方式。
关键绩效指标来自于对企业总体战略目标的分解,反映最能有效影响企业价值创造的关键驱动因素。
设立关键绩效指标的价值在于:使经营管理者将精力集中在对绩效有最大驱动力的经营行动上,及时诊断生产经营活动中的问题并采取提高绩效水平的改进措施。
KPI指标并不一定能直接用于或适合所有岗位的人员考核,但因为KPI指标能在相当程度上反映组织的经营重点和阶段性方向,所以成为绩效考核的基础。
关于KPI指标的具体提取与分解方法在第三部分中予以详细说明。
(二)工作目标与过程设定即由上级领导与员工共同商议确定员工在考核期内应完成的主要工作及其效果,并在考核期结束时由上级领导根据期初所定目标是否实现,为员工绩效打分的绩效管理方式。
它是一种对工作职责范围内的一些相对长期性、过程性、辅助性、难以量化的主要工作任务完成情况的考核方法。
(三)KPI与工作目标的关系KPI与工作目标在绩效管理系统中互相配合、互为补充。
1.共同点在于:都是依据目标职位的工作职责和工作性质而设定,反映由公司战略目标分解得出的关键价值驱动因素,并且只反映目标职位的最主要经营活动效果,而非全部工作。
2.不同点在于:KPI可以用计算公式计算出员工经营活动的量化结果,侧重考察员工对经营成果有直接控制力的工作,它考察的是当期绩效和最终经营成果;工作目标是由上级领导以打分的形式,定性评价员工完成不易量化的主要工作情况,侧重考察员工对经营成果无直接控制力的工作,它考察的是长期性工作和工作的过程。
使用工作目标完成效果评价,可以弥补仅用完全量化的关键绩效指标来考核的不足,以便更加全面地反映员工的工作表现。
工作目标完成效果评价主要包括工作目标与目的的设定、评估标准的制定、权重的确定、评估级别的评定等。
什么是关键绩效指标(KPI)关键绩效指标(Key Performance Indicators,简称KPI),是在一般绩效评估指标(CPI)的基础上发展起来的,是对传统绩效评估理念的创新。
关键绩效指标是指以组织的战略目标为基础,通过对组织的战略目标进行层层分解,对组织运作过程中的关键成功要素进行归纳与提炼,最终得出能够用于衡量组织关键流程绩效以及监测组织的战略决策执行效果的,可量化或可行为化的一些关键指标。
确定关键绩效指标是绩效评估体系设计的基础。
关键绩效指标是从一般绩效指标的基础上发展而来的,是对传统绩效评估理念的创新;因此,基于关键绩效指标的绩效评估体系与一般的绩效评估体系,二者的具体比较请看表一:表一:关键绩效指标体系与一般绩效指标体系的区别表二是某企业的关键绩效指标体系实例,希望能够帮助读者更好地理解关键绩效指标的定义。
表二、某企业按部门建立的关键绩效指标体系关键绩效指标的分类:根据不同的维度,可以把关键绩效指标划分为不同的类型;但一般而言,常见的分类方法主要有以下几种:(1)根据提取指标的维度来区分,可以分为:①数量型指标:即用于评估在预先确定的条件下完成工作的数量多少的指标。
②质量型指标:即用于评估在预先确定的条件下完成工作的质量情况的指标。
③时间型指标:即用于评估在预先确定的条件下完成工作所需要时间的指标。
④成本型指标:即用于评估在预先确定的条件下完成工作所耗费成本的指标。
(2)依据在企业价值链中的贡献程度来划分,可以分为:①效益类指标:即位于企业价值链条的起点,衡量价值创造的指标,一般包括投资回报率、利润率、营业收入等财务指标。
②运营类指标:即在企业生产管理流程中,衡量实现价值增长的运营结果和控制变量的指标,如不良资产率、持续无故障时间、人均服务面积等都是常见的运营类指标。
③组织类指标:即为了实现改善企业的工作环境、提高员工满意度水平等目标,用于衡量内部管理流程的指标,如员工满意度、培训覆盖率等。
如何提取绩效考核的指标绩效考核的指标从哪里来呢?指标提取的依据主要有以下三个来源:一是企业发展战略以及相应的战略目标。
绩效考核不坚持战略导向,就很难保证绩效考核能有效支持企业战略。
企业的战略规划的实施实际上就是通过战略导向的绩效指标的设计来实现的。
二是工作分析。
工作分析是设计绩效考核指标的基础依据。
根据考核目的,对被考核者的岗位的工作内容、性质以及完成这些工作所具备的条件等进行研究和分析,以确定指标的各项要素。
三是企业业务流程。
绩效考核指标必须从业务流程中去把握。
根据被考核者在流程的扮演的角色、责任以及同上游、下游之间的关系,来确定其衡量工作成效的绩效指标。
那么,如何正确地提取绩效考核指标呢?首先,提取指标需要遵循相应的原则。
一是客观性原则:应以岗位特征为依据,不能一把尺子量所有的岗位。
二是明确性原则:应明确具体,即对工作数量和质量的要求、责任的轻重、业绩的高低做出明确的界定和具体的要求。
三是细分化原则:指标是对工作目标的分解过程,要使指标有较高的清晰度,必须对考核内容细分,直到指标可以直接评定为止。
四是可操作性原则:指标不宜定得过高,应最大限度地符合实际工作要求。
五是界限清楚原则:每项指标内涵和外延都应界定清楚,避免产生歧义。
六是可比性原则:对同一层次、同一职务或同一工作性质岗位的指标必须在横向上保持一致。
七是少而精原则:指标应能够反映出工作的主要要求,应当简单明了,容易被执行、被接受和理解。
简单的结构可以使考核信息处理和评估过程缩短,提高考核工作效益。
八是相对稳定性原则:指标选择后,要保持相对的稳定,不能随意更改。
其次,提取绩效考核指标必须有相应数量限制。
绩效考核指标并不是越多越好,因为绩效管理是有成本的,指标越多,企业投入绩效管理的成本相应也越多,所以在提取指标时,需要遵循20/80 原理,选取出最需要考核的指标。
对绩效考核指标的数量限制还与不同层次的岗位有关,越在基层,数量相对越少。
目前绩效考核主要是针对关键业绩指标(Key Performance Index,简称 KPI)进行,而所谓关键指标,当然就必须有一个数量限制了。