生物信息学-课堂练习生物信息学蛋白质序列分析-课堂练习
- 格式:doc
- 大小:144.50 KB
- 文档页数:4
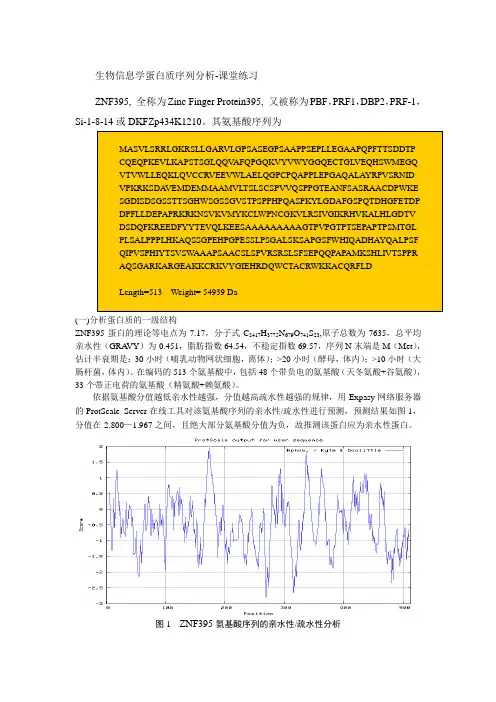
生物信息学蛋白质序列分析-课堂练习ZNF395, 全称为Zinc Finger Protein395, 又被称为PBF ,PRF1,DBP2,PRF-1,Si-1-8-14或DKFZp434K1210。
其氨基酸序列为(一)分析蛋白质的一级结构ZNF395蛋白的理论等电点为7.17,分子式C 2417H 3775N 679O 741S 23,原子总数为7635,总平均亲水性(GRA VY )为-0.451,脂肪指数64.54,不稳定指数69.57,序列N 末端是M (Met ),估计半衰期是:30小时(哺乳动物网状细胞,离体);>20小时(酵母,体内);>10小时(大肠杆菌,体内)。
在编码的513个氨基酸中,包括48个带负电的氨基酸(天冬氨酸+谷氨酸),33个带正电荷的氨基酸(精氨酸+赖氨酸)。
依据氨基酸分值越低亲水性越强,分值越高疏水性越强的规律,用Expasy 网络服务器的ProtScale Server 在线工具对该氨基酸序列的亲水性/疏水性进行预测,预测结果如图1,分值在-2.800—1.967之间,且绝大部分氨基酸分值为负,故推测该蛋白应为亲水性蛋白。
图1 ZNF395氨基酸序列的亲水性/疏水性分析(二)分析蛋白质的二级结构利用SOPMA在线工具对二级结构进行预测,如图2,α螺旋99个占19.30%,延伸链66个占12.87%,β-转角18个占3.51%,无规卷曲330个占64.33%,其二级结构主要由无规卷曲组成。
图2 ZNF395蛋白二级结构预测注:蓝色表示α螺旋;红色表示延伸链;紫色表示无规则卷曲(三)分析膜蛋白质利用在线分析工具TMHMM Server 2.0,对ZNF395氨基酸跨膜结构域进行在线预测和分析,结果表明,该序列编码的蛋白非跨膜蛋白(见图3)。
利用Signal P 3.0 Server在线预测工具对ZNF395蛋白质进行信号肽预测,无信号肽存在(图4)。

绪论1、生物信息学的概念及其组成部分生物信息学(Bioinformatics):是一门交叉学科,包含了生物信息的获取、处理、储存、分析、解释和应用在内的所有方面,它综合运用了生物学、计算机科学和数学等多方面的知识和方法,来阐述和理解大量生物学数据所包含的生物学意义,并应用于解决生命科学研究和生物技术相关产业中的各种问题。
生物信息学的三个组成部分:①建立可以存放和管理大量生物信息学数据的数据库②研究开发可用于有效分析与挖掘生物学数据的方法、算法和软件工具③使用这些工具去分析和解释不同类型的生物学数据2、生物信息学的主要研究领域①生物数据的建立与搜索②序列比较与相似性搜索③基因组结构注释④蛋白质结构与功能的预测⑤基因组数据分析⑥比较基因组合系统发生遗传学分析⑦功能基因组和蛋白质组学数据分析⑧信号传导、代谢和基因调节途径的构建与描述3、初级数据库二级数据库的概念说出几个数据并说明包含什么数据一级数据库(primary database):数据直接来源于实验获得原始数据,只经过简单的归类、整理和注释。
例如GenBank、EMBL、DDBJ、SWISSPORT、PDB二级数据库(secondary database):在一级数据库、实验数据和理解分析的基础上针对特定的目标衍生而来,是对生物学知识和信息的进一步整理。
例如human genome databases GDB转录因子数据库等4、简述核酸序列的测序①DNA测序一般原理DNA测序一般采用全自动的荧光标记链终止反应完成,该法利用了DNA聚合酶能从脱氧核糖核苷酸(dNTP)延伸但不能从双脱氧核糖核苷酸(ddNTP)延伸的特性,通过加入限量的荧光标记过的双脱氧核苷酸来产生有特定终止碱基的嵌套DNA片段,然后通过聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(PAGE)分离并通过扫描仪读取序列(300-800bp)②基因组测序策略—分而治之---shortgun因为测序反应每次只能测300-800bp故先将基因组分割成一定大小的片段,然后对这些片段分别测序,测完后再将这些片段拼接起来—鸟枪法(shortgun)③一次性测序例如:表达序列标签(EST)是其中的代表,它对随机挑选的cDNA克隆进行两端一次测序得到300-500bp的片段,代表cDNA的一部分。

一:名词解释1.生物信息学2.NCBI3.PubMed4.生物芯片5.BLAST6.UniProt7.电子克隆8.EMBL二:填空题1.基因芯片可以分为2. 人类基因组全序列分析分两大步骤即制图和测序,并最终绘制出四张图谱:3. 分子系统发生分析主要分为三个步骤即4. 国际上最主要的三大核酸序列数据库分别是5. 蛋白质得分矩阵有7. 文献是掌握科研进展的最直接方式,目前由NCBI维护的大型文献资源是。
3. 用于核酸序列比对中常见的三种得分矩阵,分别为4. 根据生物芯片探针分子类型的不同,可以将生物芯片哪三种,5. 核酸序列分析所获得的信息主要有(举例说明四个)6. 限制性酶切分析是分子生物学实验中的日常工作之一,这方面最好的限制酶数据库是三:选择题1、如果试图确定一个新蛋白质序列属于哪一个蛋白质家族,或该序列可能包含何种结构域或功能位点,应使用:()A: PROSITE数据库 B: DDBJ数据库C: PIR数据库 D: PDB数据库2、构建序列进化树的一般步骤不包括:()A:建立DNA文库 B:建立数据模型 C:建立取代模型 D:建立进化树3、BLAST教案所程序中,哪个方法是不存在的?()A:BLASTP B:BLASTN C:BLASTX D:BLASTQ4. 以下常见的几个物种,哪一个目前还没有完成全基因组测序:()A: 茶树 B: 玉米 C: 水稻 D: 小鼠5、向核酸序列数据库(GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ)提交数据,应该使用下面哪个软件:()。
A: Blast B:Sequin C:SRS D:Swiss-Model6、在蛋白质序列数据库中比较查询手头未知的蛋白质序列,应使用Blast中哪个具体的算法:()。
A:BLASTX B:tBLASTN C:BLASTP D:BLASTN7、下列中属于一级蛋白质结构数据库的是:()A:EMBL B:DDBJ C:PDB D:SWISS-PROT8、下面不属于SWISS-PROT蛋白质数据库的注释范畴的是:()A: 与其它蛋白质的相似性 B: 蛋白质的二级结构C: 由于缺乏该蛋白质而引起的疾病 D: 核酸的功能描述9、下列属于蛋白质二级结构预测的软件程序是()A: BLASTX B:SOPMA C:DNAstar D:GO10. 如果做DNA结构分析,应该考虑用下面哪个数据库:()A:GenBank B: PIR C:NDB D:UniProt四:简单题1.简述Entrez的设计概念和使用方法?2. 简述生物大分子PDB存储的生物分子种类和数据结构特点?3.简述生物信息学的研究意义?4 简述蛋白质序列分析的基本内容以及常用的软件?5. 简述Swiss-Prot的数据结构?6、简述序列多重比对的意义?7、简述生物信息学的发展历史?五:论述题1.论述蛋白质相互作用研究的意义,传统的实验方法和计算预测方法的应用?2.论述后基因组时代生物信息学面临的挑战和研究策略?3.论述生物信息学的应用?4. 论述如何利用基因芯片数据做聚类分析。



生物信息学中的蛋白质序列分析与预测研究蛋白质是生命体中至关重要的分子,它们在细胞功能和结构的调控中发挥着重要的作用。
蛋白质的序列决定了其结构和功能,因此蛋白质序列的分析和预测成为生物信息学研究的重要方向之一。
本文将重点介绍蛋白质序列分析和预测的方法与技术,以及在生物学研究中的应用。
蛋白质序列的分析是指根据蛋白质的氨基酸序列,通过一系列的计算和分析方法,对其结构和功能进行研究的过程。
蛋白质序列分析的方法有很多,其中最常用的包括:比对分析、同源建模、序列特征分析和亚细胞定位预测。
首先,比对分析是蛋白质序列分析的基础方法之一。
通过将待分析的蛋白质序列与已知的蛋白质序列数据库进行比对,可以找到与之相似的序列,进而推测蛋白质的结构和功能。
比对分析常用的工具有BLAST和PSI-BLAST等,它们通过比较序列之间的相似性和一致性,确定序列的保守区域和结构域,从而揭示蛋白质的功能。
其次,同源建模是一种根据已知蛋白质的结构来预测未知蛋白质的结构的方法。
在同源建模中,通过比对已知蛋白质的结构与待预测蛋白质的序列,找到与之相似的蛋白质结构作为模板,并利用模板的结构信息,预测待预测蛋白质的结构。
同源建模的常用工具有SWISS-MODEL和Phyre2等。
同源建模不仅可以预测蛋白质的三维结构,还可以提供结构功能的启示,从而推测其功能。
另外,序列特征分析也是蛋白质序列分析的重要方向之一。
序列特征分析通过对蛋白质序列中的特定模式、保守区域和功能位点进行分析,揭示蛋白质的结构和功能。
常用的序列特征分析方法包括信号肽预测、跨膜区域识别、功能位点预测和蛋白质域识别等。
这些方法通过分析蛋白质序列中的特定特征,揭示蛋白质的功能和结构。
最后,亚细胞定位预测是蛋白质序列分析的一个重要方向。
蛋白质在细胞中的定位决定了其在细胞内发挥的功能,因此准确预测蛋白质的亚细胞定位对于理解其功能至关重要。
亚细胞定位预测通过分析蛋白质序列中的亚细胞定位信号和保守区域,预测蛋白质的亚细胞定位位置。
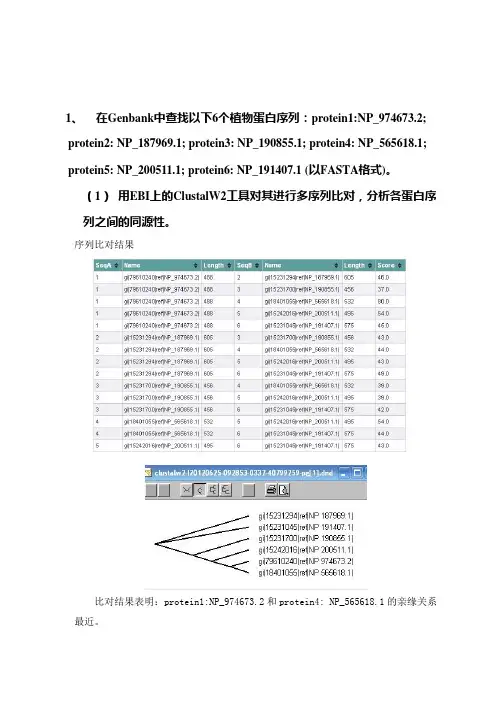
1、在Genbank中查找以下6个植物蛋白序列:protein1:NP_974673.2; protein2: NP_187969.1; protein3: NP_190855.1; protein4: NP_565618.1; protein5: NP_200511.1; protein6: NP_191407.1 (以FASTA格式)。
(1)用EBI上的ClustalW2工具对其进行多序列比对,分析各蛋白序列之间的同源性。
序列比对结果比对结果表明:protein1:NP_974673.2和protein4: NP_565618.1的亲缘关系最近。
(2)利用Phylip软件,选择距离法构建其进化树(要求写出具体的建树步骤)。
1.将蛋白序列保存为FASTA格式,存于txt文档;2.用Clustalx打开txt文本,保存为*.phy文件;3.用seqboot程序打开phy文件,输出结果文件*_seqboot4.用protdist程序打开*_seqboot文件,输出为*_protdist文件5. 用neighbor程序打开*_protdist文件,输出为*_neighbor文件6. 用consense程序打开*_neighbor文件,输出为*_consense文件7.用dratree程序打开*_consense文件得到进化树。
(注:由于seqboot软见无法正常运行,因此进化树无法显示)(3)任意选取其中的一个蛋白进行蛋白质一级序列分析、二级结构预测及三维结构的模拟。
选择protein3: NP_190855.1一级结构网址:/tools/protparam.htmlNumber of amino acids: 456 氨基酸数目Molecular weight: 51154.5 相对分子质量Theoretical pI: 8.69 理论 pI 值Amino acid composition 氨基酸组成Ala (A) 30 6.6%Arg (R) 28 6.1%Asn (N) 15 3.3%Asp (D) 27 5.9%Cys (C) 5 1.1%Gln (Q) 18 3.9%Glu (E) 28 6.1%Gly (G) 37 8.1%His (H) 16 3.5%Ile (I) 16 3.5%Leu (L) 42 9.2%Lys (K) 32 7.0%Met (M) 5 1.1%Phe (F) 17 3.7%Pro (P) 16 3.5%Ser (S) 46 10.1%Thr (T) 21 4.6%Trp (W) 8 1.8%Tyr (Y) 19 4.2%Val (V) 30 6.6%Pyl (O) 0 0.0%Sec (U) 0 0.0%(B) 0 0.0%(Z) 0 0.0%(X) 0 0.0%正/负电荷残基数Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu): 55Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys): 60Atomic composition: 原子组成Carbon C 2270Hydrogen H 3531Nitrogen N 645Oxygen O 686Sulfur S 10Formula: C2270H3531N645O686S10 分子式Total number of atoms: 7142 总原子数Extinction coefficients: 消光系数Extinction coefficients are in units of M-1 cm-1, at 280 nm measured in water.Ext. coefficient 72560Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 1.418, assuming all pairs of Cys residues form cystines Ext. coefficient 72310Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 1.414, assuming all Cys residues are reducedEstimated half-life: 半衰期The N-terminal of the sequence considered is M (Met).The estimated half-life is: 30 hours (mammalian reticulocytes, in vitro).>20 hours (yeast, in vivo).>10 hours (Escherichia coli, in vivo).Instability index: 不稳定系数The instability index (II) is computed to be 48.99This classifies the protein as unstable.Aliphatic index: 75.26 脂肪系数Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY): -0.554 总平均亲水性/tools/protscale.html蛋白质亲疏水性分析所用氨基酸标度信息Ala: 1.800 Arg: -4.500 Asn: -3.500 Asp: -3.500 Cys: 2.500 Gln: -3.500 Glu: -3.500 Gly: -0.400 His: -3.200 Ile: 4.500 Leu: 3.800 Lys: -3.900 Met: 1.900 Phe: 2.800 Pro: -1.600 Ser: -0.800 Thr: -0.700 Trp: -0.900 Tyr: -1.300 Val: 4.200 : -3.500 : -3.500 : -0.490分析所用参数信息Weights for window positions 1,..,9, using linear weight variation model:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 91.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00edge center edge跨膜结构预测结果(没有跨膜结构)信号肽分析:二级结构预测三级结构预测网站/~phyre2、在拟南芥基因组数据库中(/)查找编号分别为At4G33050, At3G13600,At3G52870或At2G26190基因,针对所查找的基因进行初步的生物信息学分析(每人任选其中一个基因)。

1、在Genbank中查找以下6个植物蛋白序列:protein1:NP_974673.2; protein2: NP_187969.1; protein3: NP_190855.1; protein4: NP_565618.1; protein5: NP_200511.1; protein6: NP_191407.1 (以FASTA格式)。
(1)用EBI上的ClustalW2工具对其进行多序列比对,分析各蛋白序列之间的同源性。
序列比对结果比对结果表明:protein1:NP_974673.2和protein4: NP_565618.1的亲缘关系最近。
(2)利用Phylip软件,选择距离法构建其进化树(要求写出具体的建树步骤)。
1.将蛋白序列保存为FASTA格式,存于txt文档;2.用Clustalx打开txt文本,保存为*.phy文件;3.用seqboot程序打开phy文件,输出结果文件*_seqboot4.用protdist程序打开*_seqboot文件,输出为*_protdist文件5. 用neighbor程序打开*_protdist文件,输出为*_neighbor文件6. 用consense程序打开*_neighbor文件,输出为*_consense文件7.用dratree程序打开*_consense文件得到进化树。
(注:由于seqboot软见无法正常运行,因此进化树无法显示)(3)任意选取其中的一个蛋白进行蛋白质一级序列分析、二级结构预测及三维结构的模拟。
选择protein3: NP_190855.1一级结构网址:/tools/protparam.htmlNumber of amino acids: 456 氨基酸数目Molecular weight: 51154.5 相对分子质量Theoretical pI: 8.69 理论 pI 值Amino acid composition 氨基酸组成Ala (A) 30 6.6%Arg (R) 28 6.1%Asn (N) 15 3.3%Asp (D) 27 5.9%Cys (C) 5 1.1%Gln (Q) 18 3.9%Glu (E) 28 6.1%Gly (G) 37 8.1%His (H) 16 3.5%Ile (I) 16 3.5%Leu (L) 42 9.2%Lys (K) 32 7.0%Met (M) 5 1.1%Phe (F) 17 3.7%Pro (P) 16 3.5%Ser (S) 46 10.1%Thr (T) 21 4.6%Trp (W) 8 1.8%Tyr (Y) 19 4.2%Val (V) 30 6.6%Pyl (O) 0 0.0%Sec (U) 0 0.0%(B) 0 0.0%(Z) 0 0.0%(X) 0 0.0%正/负电荷残基数Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu): 55Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys): 60Atomic composition: 原子组成Carbon C 2270Hydrogen H 3531Nitrogen N 645Oxygen O 686Sulfur S 10Formula: C2270H3531N645O686S10 分子式Total number of atoms: 7142 总原子数Extinction coefficients: 消光系数Extinction coefficients are in units of M-1 cm-1, at 280 nm measured in water.Ext. coefficient 72560Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 1.418, assuming all pairs of Cys residues form cystines Ext. coefficient 72310Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 1.414, assuming all Cys residues are reducedEstimated half-life: 半衰期The N-terminal of the sequence considered is M (Met).The estimated half-life is: 30 hours (mammalian reticulocytes, in vitro).>20 hours (yeast, in vivo).>10 hours (Escherichia coli, in vivo).Instability index: 不稳定系数The instability index (II) is computed to be 48.99This classifies the protein as unstable.Aliphatic index: 75.26 脂肪系数Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY): -0.554 总平均亲水性/tools/protscale.html蛋白质亲疏水性分析所用氨基酸标度信息Ala: 1.800 Arg: -4.500 Asn: -3.500 Asp: -3.500 Cys: 2.500 Gln: -3.500 Glu: -3.500 Gly: -0.400 His: -3.200 Ile: 4.500 Leu: 3.800 Lys: -3.900 Met: 1.900 Phe: 2.800 Pro: -1.600 Ser: -0.800 Thr: -0.700 Trp: -0.900 Tyr: -1.300 Val: 4.200 : -3.500 : -3.500 : -0.490分析所用参数信息Weights for window positions 1,..,9, using linear weight variation model:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 91.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00edge center edge跨膜结构预测结果(没有跨膜结构)信号肽分析:二级结构预测三级结构预测网站/~phyre2、在拟南芥基因组数据库中(/)查找编号分别为At4G33050, At3G13600,At3G52870或At2G26190基因,针对所查找的基因进行初步的生物信息学分析(每人任选其中一个基因)。
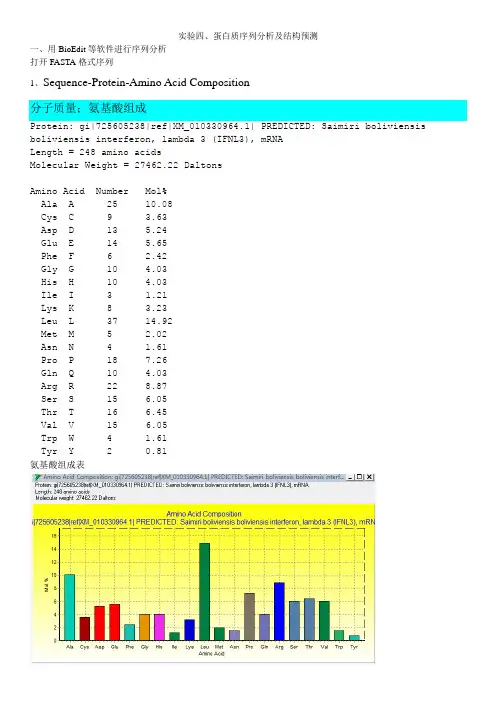
实验四、蛋白质序列分析及结构预测一、用BioEdit等软件进行序列分析打开FASTA格式序列1、Sequence-Protein-Amino Acid Composition分子质量;氨基酸组成Protein: gi|725605238|ref|XM_010330964.1| PREDICTED: Saimiri boliviensis boliviensis interferon, lambda 3 (IFNL3), mRNALength = 248 amino acidsMolecular Weight = 27462.22 DaltonsAmino Acid Number Mol%Ala A 25 10.08Cys C 9 3.63Asp D 13 5.24Glu E 14 5.65Phe F 6 2.42Gly G 10 4.03His H 10 4.03Ile I 3 1.21Lys K 8 3.23Leu L 37 14.92Met M 5 2.02Asn N 4 1.61Pro P 18 7.26Gln Q 10 4.03Arg R 22 8.87Ser S 15 6.05Thr T 16 6.45Val V 15 6.05Trp W 4 1.61Tyr Y 2 0.81氨基酸组成表2、helical wheel diagram3、Hydrophobic Moment matrix with Eisenberg consensus scale 疏水性4、Kyte&Doolittle Mean Hydrophobicity Profile5、Eisenberg Scale Mean Hydrophobicity Profile6、Cornette Scale Mean Hydrophobicity Profile7、Parker HPLC Scale Mean Hydrophobicity Profile8、Boyko Scale Mean Hydrophilicity Profile9、Hopp%Woods Scale Mean Hydrophilicity10、ProtParam tool /protparam/ProtParam (References / Documentation) is a tool which allows the computation of various physical and chemical parameters for a given protein stored in Swiss-Prot or TrEMBL or for a user entered sequence. The computed parameters include the molecular weight, theoretical pI, amino acid composition, atomic composition, extinction coefficient, estimated half-life, instability index, aliphatic index and grand average of hydropathicity (GRA VY) (Disclaimer).输入FASTA格式序列等电点11、跨膜区分析进入CBS 依次进入TMHMMWelcome to CBS http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/index.shtml CBS Prediction Servers http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/ TMHMM /protparam/输入FASTA格式序列结果Data 部分数据# WEBSEQUENCE# AA inside membr outside 1 A 0.00271 0.00000 0.99729 2 T 0.00267 0.00004 0.99729 3 G 0.00265 0.00006 0.99729 4 A 0.00265 0.00008 0.99727 5 A 0.00252 0.00022 0.99726 6 A 0.00252 0.00023 0.99726 7 C0.001720.001020.997268 T 0.001720.001020.99726………… ………… 1403 C 0.00059 0.00002 0.99939 1404 G 0.00059 0.00002 0.99939 1405 C 0.00059 0.00002 0.99939 1406 G 0.00059 0.00002 0.99939 1407 A0.000590.000020.999391408 G 0.00059 0.00002 0.99939 1409 A 0.00059 0.00002 0.99939 1410 C 0.00059 0.00002 0.99939 1411 C 0.00059 0.00002 0.99938 1412 T 0.00060 0.00005 0.99935 1413 G 0.00060 0.00009 0.99932 1414 A 0.00060 0.00012 0.99928 1415 A 0.00060 0.00014 0.99926 1416 T 0.00060 0.00016 0.99924 1417 T 0.00060 0.00018 0.99922 1418 G 0.00060 0.00019 0.9992 1419 T 0.00060 0.00023 0.99917 1420 G 0.00060 0.00023 0.99917 1421 T 0.00060 0.00023 0.99918 1422 T 0.00060 0.00023 0.99918 1423 G 0.00059 0.00024 0.99917 1424 C 0.00059 0.00024 0.99917 1425 C 0.00059 0.00024 0.99917 1426 A 0.00059 0.00024 0.99917 1427 G 0.00059 0.00024 0.99917 1428 C 0.00060 0.00024 0.99917 1429 G 0.00060 0.00024 0.99917 1430 G 0.00060 0.00024 0.99917 1431 G 0.00060 0.00023 0.99917 1432 G 0.00060 0.00023 0.99917 1433 A 0.00061 0.00023 0.99917 1434 C 0.00062 0.00021 0.99917 1435 C 0.00066 0.00017 0.99917 1436 T 0.00070 0.00013 0.99917 1437 G 0.00072 0.00011 0.99917 1438 T 0.00075 0.00009 0.99917 1439 G 0.00076 0.00008 0.99917 1440 T 0.00078 0.00006 0.99917 1441 G 0.00079 0.00004 0.99917 1442 T 0.00082 0.00001 0.99917 1443 C 0.00082 0.00001 0.99917 1444 T 0.00082 0.00001 0.99917 1445 G 0.00083 0.00000 0.99917 1446 A 0.00083 0.00000 0.9991712、信号肽及亚细胞定位进入SignalP 4.1 Server http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/输入FASTA格式序列结果:亚细胞定位: 进入:TargetP 1.1 Server http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TargetP/ 输入序列提交:结果:13、功能分析1)基于序列同源性分析的蛋白质功能预测NCBI----blast 找到吻合相对高的序列查看详情序列同源性蛋白质功能分析NCBI---GENE进入相关文献了解功能2)基于motif、结构位点、结构功能域数据库的蛋白质功能预测Motif:PROSITE//cgi-bin/prosite/ScanView.cgi?scanfile=806498321699.scan.gz结构域基序My Hits:http://hits.isb-sib.ch/cgi-bin/PFSCAN 输入序列结果:http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/二、蛋白质二级结构预测1)NetTurnP - Prediction of Beta-turns in proteinsNetTurnP 1.0 - Prediction of Beta-turn regions in protein sequenceshttp://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetTurnP/输入序列结果:NetTurnP - Prediction of Beta-turns in proteinsTechnical University of Denmark# For publication of results, please cite:# NetTurnP - Neural Network Prediction of Beta-turns by Use of Evolutionary Information and Predicted Protein Sequence Features.# Petersen B, Lundegaard C, Petersen TN (2010)# PLoS ONE 5(11):e15079 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015079## Column 1: Amino acid# Column 2: Sequence name# Column 3: Amino acid number# Column 4: Prediction for Beta-turn# Column 5: Class assignment - "T" for Beta-turn#V Sequence 1 0.287 .T Sequence 2 0.363 .A Sequence 3 0.403 .S Sequence 4 0.482 .E Sequence 5 0.495 .W Sequence 6 0.493 .G Sequence 7 0.552 TP Sequence 8 0.527 TS Sequence 9 0.564 TA Sequence 10 0.572 TD Sequence 11 0.643 TE Sequence 12 0.631 TD Sequence 13 0.620 TQ Sequence 14 0.612 TR Sequence 15 0.497 .S Sequence 16 0.518 TE Sequence 17 0.515 TM Sequence 18 0.557 TK Sequence 19 0.582 TR Sequence 20 0.555 TG Sequence 21 0.561 TM Sequence 22 0.552 TS Sequence 23 0.559 TR Sequence 24 0.560 TG Sequence 25 0.533 TC Sequence 26 0.486 .L Sequence 32 0.179 . M Sequence 33 0.184 .A Sequence 34 0.210 . T Sequence 35 0.236 . V Sequence 36 0.269 . L Sequence 37 0.319 . T Sequence 38 0.396 . V Sequence 39 0.448 . T Sequence 40 0.475 .G Sequence 41 0.505 T A Sequence 42 0.480 . V Sequence 43 0.449 . P Sequence 44 0.455 . V Sequence 45 0.463 . T Sequence 46 0.456 . R Sequence 47 0.467 . P Sequence 48 0.523 T P Sequence 49 0.504 T R Sequence 50 0.492 .A Sequence 51 0.488 . L Sequence 52 0.526 T P Sequence 53 0.568 T D Sequence 54 0.612 T A Sequence 55 0.650 T R Sequence 56 0.585 T G Sequence 57 0.497 .C Sequence 58 0.452 .H Sequence 59 0.380 .I Sequence 60 0.425 .A Sequence 61 0.452 . Q Sequence 62 0.457 .F Sequence 63 0.558 T K Sequence 64 0.524 T S Sequence 65 0.494 . L Sequence 66 0.482 . S Sequence 67 0.347 . P Sequence 68 0.280 . Q Sequence 69 0.259 .E Sequence 70 0.254 . L Sequence 71 0.181 . Q Sequence 72 0.153 .A Sequence 73 0.152 .F Sequence 74 0.167 . K Sequence 75 0.187 .L Sequence 81 0.362 .E Sequence 82 0.382 .E Sequence 83 0.373 . S Sequence 84 0.401 . L Sequence 85 0.373 . L Sequence 86 0.414 . L Sequence 87 0.555 T K Sequence 88 0.547 T D Sequence 89 0.559 T C Sequence 90 0.576 T R Sequence 91 0.414 .C Sequence 92 0.424 . R Sequence 93 0.443 . S Sequence 94 0.442 . R Sequence 95 0.522 T L Sequence 96 0.531 T F Sequence 97 0.572 T P Sequence 98 0.632 T R Sequence 99 0.596 T T Sequence 100 0.572 T W Sequence 101 0.535 TD Sequence 102 0.394 . L Sequence 103 0.416 . R Sequence 104 0.404 . Q Sequence 105 0.398 . L Sequence 106 0.414 . Q Sequence 107 0.371 . V Sequence 108 0.453 . R Sequence 109 0.475 .E Sequence 110 0.472 . R Sequence 111 0.481 . P Sequence 112 0.371 . V Sequence 113 0.271 .A Sequence 114 0.240 . L Sequence 115 0.188 .E Sequence 116 0.182 .A Sequence 117 0.175 .E Sequence 118 0.164 . L Sequence 119 0.168 .A Sequence 120 0.150 . L Sequence 121 0.141 . T Sequence 122 0.142 . L Sequence 123 0.143 .E Sequence 124 0.151 .A Sequence 130 0.479 .D Sequence 131 0.576 T N Sequence 132 0.572 T D Sequence 133 0.541 T M Sequence 134 0.512 T A Sequence 135 0.329 . L Sequence 136 0.275 .G Sequence 137 0.255 .D Sequence 138 0.253 . V Sequence 139 0.278 . L Sequence 140 0.373 .D Sequence 141 0.400 . R Sequence 142 0.395 . P Sequence 143 0.383 . L Sequence 144 0.308 .H Sequence 145 0.244 . T Sequence 146 0.202 . L Sequence 147 0.173 .H Sequence 148 0.152 .H Sequence 149 0.151 . V Sequence 150 0.149 . L Sequence 151 0.152 . S Sequence 152 0.162 . Q Sequence 153 0.173 . L Sequence 154 0.233 . R Sequence 155 0.280 .A Sequence 156 0.306 .C Sequence 157 0.354 . V Sequence 158 0.366 . Q Sequence 159 0.405 . P Sequence 160 0.406 . Q Sequence 161 0.403 . P Sequence 162 0.466 . T Sequence 163 0.517 T A Sequence 164 0.541 T G Sequence 165 0.588 T P Sequence 166 0.540 T R Sequence 167 0.493 . P Sequence 168 0.503 T W Sequence 169 0.433 .G Sequence 170 0.397 . R Sequence 171 0.341 . L Sequence 172 0.232 .H Sequence 173 0.198 .L Sequence 179 0.253 . Q Sequence 180 0.273 .E Sequence 181 0.290 .A Sequence 182 0.447 . P Sequence 183 0.494 . K Sequence 184 0.517 T K Sequence 185 0.554 T E Sequence 186 0.472 . S Sequence 187 0.628 T S Sequence 188 0.604 T G Sequence 189 0.595 T C Sequence 190 0.593 T L Sequence 191 0.334 .E Sequence 192 0.306 .A Sequence 193 0.286 . S Sequence 194 0.243 . V Sequence 195 0.230 . T Sequence 196 0.194 .F Sequence 197 0.177 . N Sequence 198 0.185 . L Sequence 199 0.180 .F Sequence 200 0.181 . R Sequence 201 0.199 . L Sequence 202 0.191 . L Sequence 203 0.249 . T Sequence 204 0.462 . R Sequence 205 0.469 .D Sequence 206 0.466 . L Sequence 207 0.491 . K Sequence 208 0.304 .C Sequence 209 0.311 . V Sequence 210 0.393 .A Sequence 211 0.467 . S Sequence 212 0.554 T G Sequence 213 0.630 T D Sequence 214 0.634 T L Sequence 215 0.593 T C Sequence 216 0.566 T A Sequence 217 0.554 T P Sequence 218 0.579 T S Sequence 219 0.573 T H Sequence 220 0.577 T L Sequence 221 0.544 T P Sequence 222 0.483 .I Sequence 228 0.362 .D Sequence 229 0.326 .F Sequence 230 0.303 .I Sequence 231 0.312 .Y Sequence 232 0.343 .T Sequence 233 0.420 .S Sequence 234 0.480 .T Sequence 235 0.499 .T Sequence 236 0.491 .C Sequence 237 0.509 TL Sequence 238 0.459 .N Sequence 239 0.472 .L Sequence 240 0.475 .L Sequence 241 0.412 .P Sequence 242 0.594 TP Sequence 243 0.599 TN Sequence 244 0.612 TR Sequence 245 0.650 TY Sequence 246 0.368 .Explain the output. Go back.2)GOR - Garnier et al, 1996NPS@ : GOR4 secondary structure predictionhttps://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa_gor4.html结果:3)NetSurfP-1.1 - Protein secondary structure and surface accessibility server http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetSurfP/结果:NetSurfP - Protein Surface Accessibility andSecondary Structure PredictionsTechnical University of Denmark# For publication of results, please cite:# A generic method for assignment of reliability scores applied to solvent accessibility predictions.# Bent Petersen, Thomas Nordahl Petersen, Pernille Andersen, Morten Nielsen and Claus Lundegaard# BMC Structural Biology 2009, 9:51 doi:10.1186/1472-6807-9-51## Column 1: Class assignment - B for buried or E for Exposed - Threshold: 25% exposure, but not based on RSA# Column 2: Amino acid# Column 3: Sequence name# Column 4: Amino acid number# Column 5: Relative Surface Accessibility - RSA# Column 6: Absolute Surface Accessibility# Column 7: Z-fit score for RSA prediction# Column 8: Probability for Alpha-Helix# Column 9: Probability for Beta-strand# Column 10: Probability for CoilE A Sequence 3 0.434 47.882 -1.297 0.113 0.087 0.800 E S Sequence 4 0.585 68.527 -0.812 0.113 0.087 0.800 E E Sequence 5 0.613 107.109 0.159 0.113 0.087 0.800 B W Sequence 6 0.249 59.981 -0.639 0.052 0.084 0.864 E G Sequence 7 0.338 26.577 -0.814 0.053 0.043 0.903 E P Sequence 8 0.410 58.207 -1.117 0.053 0.043 0.903 E S Sequence 9 0.584 68.410 -1.020 0.053 0.043 0.903 E A Sequence 10 0.367 40.388 -1.062 0.058 0.017 0.925 E D Sequence 11 0.536 77.238 -0.648 0.053 0.043 0.903 E E Sequence 12 0.644 112.542 -0.710 0.184 0.043 0.773 E D Sequence 13 0.581 83.708 -1.977 0.184 0.043 0.773 E Q Sequence 14 0.508 90.693 -0.589 0.268 0.043 0.689 E R Sequence 15 0.464 106.302 -0.355 0.354 0.048 0.598 E S Sequence 16 0.414 48.533 -1.835 0.354 0.048 0.598 E E Sequence 17 0.592 103.370 -0.492 0.354 0.048 0.598 E M Sequence 18 0.400 80.020 -1.980 0.354 0.048 0.598 E K Sequence 19 0.526 108.198 -0.605 0.278 0.093 0.628 E R Sequence 20 0.472 108.180 -0.949 0.113 0.087 0.800 B G Sequence 21 0.272 21.391 -2.226 0.113 0.087 0.800 B M Sequence 22 0.197 39.440 -0.962 0.118 0.150 0.732 B S Sequence 23 0.281 32.875 -1.279 0.118 0.150 0.732 E R Sequence 24 0.291 66.593 -1.665 0.191 0.086 0.723 B G Sequence 25 0.158 12.458 -1.360 0.268 0.043 0.689 B C Sequence 26 0.026 3.678 -0.098 0.502 0.102 0.396 B M Sequence 27 0.143 28.634 0.257 0.725 0.163 0.112 B A Sequence 28 0.104 11.483 -0.200 0.725 0.163 0.112 B V Sequence 29 0.048 7.454 0.791 0.807 0.137 0.056 B L Sequence 30 0.041 7.507 0.219 0.870 0.077 0.053 B V Sequence 31 0.081 12.465 -0.059 0.886 0.090 0.024 B L Sequence 32 0.067 12.213 0.544 0.870 0.077 0.053 B M Sequence 33 0.073 14.667 0.432 0.870 0.077 0.053 B A Sequence 34 0.072 7.901 -0.058 0.831 0.044 0.125 B T Sequence 35 0.115 16.020 -0.434 0.831 0.044 0.125 B V Sequence 36 0.128 19.735 -0.312 0.831 0.044 0.125 B L Sequence 37 0.130 23.730 0.063 0.751 0.050 0.199 B T Sequence 38 0.266 36.964 -0.231 0.660 0.049 0.291 E V Sequence 39 0.339 52.104 -1.218 0.354 0.048 0.598 E T Sequence 40 0.409 56.770 -2.017 0.184 0.043 0.773 B G Sequence 41 0.313 24.625 -1.553 0.053 0.043 0.903 E A Sequence 42 0.370 40.752 -2.039 0.018 0.088 0.893 B V Sequence 43 0.186 28.542 -0.494 0.020 0.205 0.775 E P Sequence 44 0.337 47.806 -1.325 0.020 0.205 0.775 B V Sequence 45 0.170 26.206 -1.051 0.018 0.088 0.893 E T Sequence 46 0.381 52.803 -1.502 0.018 0.047 0.935 E R Sequence 47 0.526 120.362 -0.292 0.018 0.019 0.964 B P Sequence 48 0.241 34.127 -1.181 0.018 0.019 0.964 E P Sequence 49 0.395 56.079 -1.454 0.018 0.019 0.964E L Sequence 52 0.335 61.265 -0.180 0.018 0.047 0.935 E P Sequence 53 0.340 48.232 -0.691 0.018 0.047 0.935 E D Sequence 54 0.732 105.424 0.275 0.018 0.019 0.964 E A Sequence 55 0.475 52.301 -1.315 0.018 0.019 0.964 E R Sequence 56 0.514 117.660 -0.150 0.018 0.047 0.935 E G Sequence 57 0.466 36.698 -0.497 0.019 0.141 0.840 B C Sequence 58 0.061 8.578 -0.417 0.021 0.279 0.699 E H Sequence 59 0.342 62.283 0.151 0.022 0.359 0.619 B I Sequence 60 0.110 20.368 -0.560 0.022 0.359 0.619 E A Sequence 61 0.325 35.848 -1.172 0.020 0.205 0.775 E Q Sequence 62 0.503 89.872 0.409 0.019 0.141 0.840 BF Sequence 63 0.126 25.348 -0.199 0.018 0.088 0.893 E K Sequence 64 0.564 116.077 0.135 0.018 0.088 0.893 E S Sequence 65 0.482 56.444 -1.479 0.018 0.047 0.935 B L Sequence 66 0.207 37.902 -0.776 0.018 0.019 0.964 E S Sequence 67 0.392 45.966 0.122 0.018 0.019 0.964 E P Sequence 68 0.386 54.802 -1.124 0.858 0.002 0.139 E Q Sequence 69 0.509 90.872 -0.427 0.923 0.002 0.076 B E Sequence 70 0.213 37.159 -0.370 0.923 0.002 0.076 B L Sequence 71 0.196 35.961 0.420 0.970 0.001 0.030 E Q Sequence 72 0.476 84.960 0.319 0.970 0.001 0.030 B A Sequence 73 0.118 13.048 -0.154 0.970 0.001 0.030 B F Sequence 74 0.061 12.263 0.168 0.970 0.001 0.030 E K Sequence 75 0.402 82.630 1.003 0.923 0.002 0.076 E R Sequence 76 0.407 93.249 1.034 0.923 0.002 0.076 B A Sequence 77 0.046 5.047 0.102 0.858 0.002 0.139 E K Sequence 78 0.339 69.732 0.957 0.858 0.002 0.139 E D Sequence 79 0.535 77.122 0.100 0.858 0.002 0.139 B A Sequence 80 0.222 24.497 0.325 0.858 0.002 0.139 B L Sequence 81 0.086 15.783 0.088 0.802 0.014 0.185 E E Sequence 82 0.421 73.479 0.113 0.802 0.014 0.185 E E Sequence 83 0.579 101.064 -0.635 0.717 0.014 0.269 B S Sequence 84 0.234 27.437 -1.170 0.622 0.015 0.363 B L Sequence 85 0.140 25.726 -0.141 0.522 0.016 0.462 B L Sequence 86 0.258 47.203 -0.156 0.455 0.046 0.498 B L Sequence 87 0.251 45.976 -0.887 0.268 0.043 0.689 E K Sequence 88 0.591 121.651 -0.038 0.191 0.086 0.723 E D Sequence 89 0.577 83.160 -0.834 0.052 0.084 0.864 B C Sequence 90 0.214 29.989 0.573 0.056 0.142 0.802 E R Sequence 91 0.462 105.752 0.703 0.066 0.296 0.638 B C Sequence 92 0.092 12.945 -0.868 0.066 0.296 0.638 E R Sequence 93 0.441 100.897 -0.588 0.064 0.216 0.721 E S Sequence 94 0.347 40.668 -1.463 0.019 0.141 0.840 E R Sequence 95 0.456 104.538 -0.134 0.020 0.205 0.775 B L Sequence 96 0.213 39.055 -1.115 0.021 0.279 0.699 B F Sequence 97 0.137 27.576 0.398 0.019 0.141 0.840 E P Sequence 98 0.373 52.957 -0.918 0.018 0.088 0.893B W Sequence 101 0.197 47.354 0.333 0.125 0.227 0.648 E D Sequence 102 0.408 58.850 0.628 0.125 0.227 0.648 B L Sequence 103 0.135 24.664 0.252 0.216 0.235 0.548 E R Sequence 104 0.493 112.989 0.612 0.216 0.235 0.548 E Q Sequence 105 0.460 82.102 0.772 0.321 0.252 0.427 B L Sequence 106 0.109 19.995 0.672 0.216 0.235 0.548 E Q Sequence 107 0.423 75.548 0.333 0.199 0.152 0.649 B V Sequence 108 0.126 19.428 0.026 0.307 0.165 0.527 E R Sequence 109 0.384 88.005 0.285 0.278 0.093 0.628 E E Sequence 110 0.570 99.527 -0.787 0.354 0.048 0.598 B R Sequence 111 0.242 55.487 0.547 0.561 0.047 0.393 B P Sequence 112 0.212 30.111 -0.237 0.717 0.014 0.269 E V Sequence 113 0.264 40.608 0.527 0.831 0.044 0.125 B A Sequence 114 0.129 14.216 -0.416 0.911 0.033 0.057 B L Sequence 115 0.071 13.073 0.588 0.911 0.033 0.057 E E Sequence 116 0.312 54.576 0.365 0.938 0.007 0.055 B A Sequence 117 0.118 12.982 -0.203 0.938 0.007 0.055 B E Sequence 118 0.226 39.395 0.183 0.911 0.033 0.057 B L Sequence 119 0.058 10.638 0.730 0.911 0.033 0.057 E A Sequence 120 0.387 42.614 0.935 0.911 0.033 0.057 B L Sequence 121 0.109 20.013 0.598 0.831 0.044 0.125 B T Sequence 122 0.078 10.846 0.183 0.918 0.063 0.019 B L Sequence 123 0.077 14.117 0.561 0.911 0.033 0.057 E E Sequence 124 0.439 76.623 1.894 0.950 0.028 0.022 B V Sequence 125 0.081 12.388 0.564 0.950 0.028 0.022 B L Sequence 126 0.069 12.579 0.437 0.879 0.010 0.111 E E Sequence 127 0.476 83.210 0.447 0.879 0.010 0.111 E A Sequence 128 0.489 53.833 -0.563 0.622 0.015 0.363 B T Sequence 129 0.204 28.281 -0.526 0.339 0.016 0.645 E A Sequence 130 0.424 46.714 -0.865 0.109 0.005 0.886 E D Sequence 131 0.581 83.664 0.009 0.053 0.005 0.942 E N Sequence 132 0.499 73.112 -1.368 0.053 0.005 0.942 E D Sequence 133 0.550 79.255 -1.082 0.176 0.004 0.820 E M Sequence 134 0.529 105.773 0.296 0.502 0.002 0.495 E A Sequence 135 0.313 34.548 0.985 0.802 0.014 0.185 B L Sequence 136 0.053 9.778 0.183 0.923 0.002 0.076 B G Sequence 137 0.212 16.669 -0.022 0.970 0.001 0.030 E D Sequence 138 0.544 78.390 0.415 0.970 0.001 0.030 B V Sequence 139 0.096 14.755 0.975 0.938 0.007 0.055 B L Sequence 140 0.041 7.489 0.162 0.879 0.010 0.111 E D Sequence 141 0.490 70.609 0.135 0.600 0.003 0.397 E R Sequence 142 0.403 92.241 0.602 0.502 0.002 0.495 B P Sequence 143 0.092 12.984 0.209 0.600 0.003 0.397 B L Sequence 144 0.084 15.325 0.131 0.782 0.003 0.216 E H Sequence 145 0.361 65.630 -0.192 0.923 0.002 0.076 B T Sequence 146 0.132 18.336 -0.058 0.923 0.002 0.076 B L Sequence 147 0.038 6.958 0.485 0.970 0.001 0.030 E H Sequence 148 0.348 63.247 0.498 0.970 0.001 0.030 E H Sequence 149 0.331 60.136 0.839 0.970 0.001 0.030B V Sequence 150 0.041 6.348 0.473 0.970 0.001 0.030 B L Sequence 151 0.173 31.676 0.458 0.970 0.001 0.030 E S Sequence 152 0.550 64.472 0.552 0.970 0.001 0.030 B Q Sequence 153 0.280 49.954 0.494 0.970 0.001 0.030 B L Sequence 154 0.060 11.023 0.197 0.923 0.002 0.076 E R Sequence 155 0.443 101.378 1.090 0.858 0.002 0.139 E A Sequence 156 0.519 57.216 0.794 0.694 0.003 0.303 BC Sequence 157 0.076 10.727 -0.397 0.600 0.003 0.397 B V Sequence 158 0.214 32.846 -0.023 0.430 0.016 0.555 E Q Sequence 159 0.581 103.749 0.558 0.181 0.016 0.803 E P Sequence 160 0.372 52.815 -0.699 0.053 0.043 0.903 E Q Sequence 161 0.518 92.479 -0.120 0.018 0.019 0.964 B P Sequence 162 0.229 32.552 -1.009 0.018 0.019 0.964 E T Sequence 163 0.558 77.381 -0.839 0.018 0.019 0.964 E A Sequence 164 0.573 63.101 -1.965 0.018 0.019 0.964 E G Sequence 165 0.501 39.429 -1.447 0.018 0.019 0.964 E P Sequence 166 0.502 71.234 -1.690 0.018 0.019 0.964 E R Sequence 167 0.404 92.424 -0.216 0.018 0.047 0.935 B P Sequence 168 0.281 39.916 -1.411 0.115 0.016 0.868 E W Sequence 169 0.443 106.638 -0.546 0.339 0.016 0.645 E G Sequence 170 0.290 22.847 -2.131 0.522 0.016 0.462 B R Sequence 171 0.219 50.128 0.487 0.802 0.014 0.185 B L Sequence 172 0.041 7.562 -0.568 0.938 0.007 0.055 E H Sequence 173 0.310 56.334 0.581 0.923 0.002 0.076 E H Sequence 174 0.347 63.156 0.424 0.970 0.001 0.030 B W Sequence 175 0.066 15.753 0.456 0.970 0.001 0.030 B L Sequence 176 0.068 12.414 0.160 0.970 0.001 0.030 E H Sequence 177 0.394 71.760 0.246 0.970 0.001 0.030 E R Sequence 178 0.303 69.364 1.450 0.923 0.002 0.076 B L Sequence 179 0.055 10.052 0.711 0.858 0.002 0.139 E Q Sequence 180 0.443 79.120 0.982 0.782 0.003 0.216 E E Sequence 181 0.620 108.314 1.492 0.600 0.003 0.397 B A Sequence 182 0.100 10.998 -0.174 0.176 0.004 0.820 E P Sequence 183 0.519 73.618 0.665 0.109 0.005 0.886 E K Sequence 184 0.729 149.894 0.904 0.181 0.016 0.803 E K Sequence 185 0.619 127.267 0.262 0.115 0.016 0.868 E E Sequence 186 0.510 89.062 -0.518 0.115 0.016 0.868 E S Sequence 187 0.407 47.689 -0.749 0.115 0.016 0.868 E S Sequence 188 0.454 53.185 -0.258 0.257 0.016 0.727 E G Sequence 189 0.289 22.744 -0.967 0.354 0.048 0.598 B C Sequence 190 0.064 9.014 -0.312 0.502 0.102 0.396 B L Sequence 191 0.115 21.075 -0.202 0.649 0.163 0.188 E E Sequence 192 0.325 56.830 0.201 0.701 0.107 0.192 B A Sequence 193 0.086 9.488 -0.828 0.779 0.100 0.120 B S Sequence 194 0.136 15.927 0.029 0.779 0.100 0.120 B V Sequence 195 0.065 9.914 -0.429 0.779 0.100 0.120 B T Sequence 196 0.085 11.817 -0.319 0.870 0.077 0.053 B F Sequence 197 0.072 14.511 0.097 0.911 0.033 0.057 B N Sequence 198 0.150 21.989 -0.346 0.879 0.010 0.111B L Sequence 199 0.057 10.492 0.062 0.938 0.007 0.055B F Sequence 200 0.081 16.176 0.103 0.938 0.007 0.055E R Sequence 201 0.258 59.013 1.046 0.938 0.007 0.055B L Sequence 202 0.082 14.959 0.208 0.879 0.010 0.111B L Sequence 203 0.067 12.249 0.337 0.879 0.010 0.111B T Sequence 204 0.240 33.343 0.112 0.717 0.014 0.269E R Sequence 205 0.489 112.050 0.481 0.430 0.016 0.555E D Sequence 206 0.433 62.366 -0.416 0.257 0.016 0.727B L Sequence 207 0.084 15.399 0.517 0.191 0.086 0.723E K Sequence 208 0.501 103.159 1.207 0.231 0.330 0.439B C Sequence 209 0.097 13.675 0.387 0.268 0.505 0.227B V Sequence 210 0.137 21.057 0.261 0.268 0.505 0.227B A Sequence 211 0.306 33.699 -0.976 0.135 0.317 0.548E S Sequence 212 0.529 61.987 -0.462 0.056 0.142 0.802E G Sequence 213 0.427 33.636 -1.328 0.018 0.047 0.935E D Sequence 214 0.636 91.705 -1.310 0.018 0.047 0.935B L Sequence 215 0.288 52.660 -0.493 0.052 0.084 0.864B C Sequence 216 0.088 12.327 -0.952 0.056 0.142 0.802E A Sequence 217 0.282 31.032 -0.158 0.052 0.084 0.864E P Sequence 218 0.369 52.304 -0.980 0.053 0.043 0.903E S Sequence 219 0.571 66.909 -1.224 0.053 0.043 0.903E H Sequence 220 0.419 76.125 -1.162 0.053 0.043 0.903B L Sequence 221 0.149 27.264 0.307 0.053 0.043 0.903E P Sequence 222 0.336 47.622 -0.813 0.113 0.043 0.844B A Sequence 223 0.295 32.520 -1.323 0.113 0.087 0.800E T Sequence 224 0.276 38.309 -0.522 0.191 0.086 0.723B H Sequence 225 0.267 48.640 -0.426 0.199 0.152 0.649B H Sequence 226 0.283 51.514 -0.300 0.216 0.235 0.548B A Sequence 227 0.115 12.695 -0.606 0.231 0.330 0.439B I Sequence 228 0.062 11.507 0.198 0.252 0.423 0.325B D Sequence 229 0.222 32.033 -0.360 0.252 0.423 0.325B F Sequence 230 0.088 17.762 0.207 0.273 0.587 0.140B I Sequence 231 0.071 13.154 -0.244 0.273 0.587 0.140B Y Sequence 232 0.153 32.717 0.494 0.268 0.505 0.227B T Sequence 233 0.215 29.793 -0.735 0.252 0.423 0.325B S Sequence 234 0.254 29.804 -1.090 0.216 0.235 0.548B T Sequence 235 0.277 38.475 -0.682 0.307 0.165 0.527B T Sequence 236 0.258 35.785 -0.222 0.199 0.152 0.649B C Sequence 237 0.072 10.067 -0.863 0.216 0.235 0.548B L Sequence 238 0.158 28.875 -0.255 0.216 0.235 0.548E N Sequence 239 0.462 67.564 -0.902 0.216 0.235 0.548B L Sequence 240 0.189 34.661 -0.397 0.113 0.087 0.800B L Sequence 241 0.210 38.451 0.093 0.053 0.043 0.903E P Sequence 242 0.379 53.752 -0.085 0.018 0.019 0.964E P Sequence 243 0.466 66.125 -1.303 0.018 0.019 0.964E N Sequence 244 0.670 98.132 -2.145 0.018 0.047 0.935E R Sequence 245 0.568 130.095 -0.533 0.018 0.019 0.964E Y Sequence 246 0.734 156.941 -1.908 0.003 0.003 0.994Explain the output. Go back.5)PORTERhttp://distill.ucd.ie/porter/结果:Subject: Porter response toQuery_name:Query_length: 248Prediction: VTASEWGPSADEDQRSEMKRGMSRGCMAVLVLMATVLTVTGAVPVTRPPRALPDARGCHICCCCCCCCCCCHHHHHHHHCCCCCCCHHHHHHHHHHHHHCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCHAQFKSLSPQELQAFKRAKDALEESLLLKDCRCRSRLFPRTWDLRQLQVRERPVALEAELA HHHCCCCHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHCECCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCHHHHHHHHHHHHHLTLEVLEATADNDMALGDVLDRPLHTLHHVLSQLRACVQPQPTAGPRPWGRLHHWLHRLQ HHHHHHHHHHHHCHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHCCCCCCCCCCHHHHHHHHHHHHHCEAPKKESSGCLEASVTFNLFRLLTRDLKCVASGDLCAXPSHLPATHHAIXDFIYTSTTCL CCCCCCCHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHCCCCCCCCCCCCHHHHHHHCCCHHHNLLPPNRYCCCCCCCCPredictions based on PDB templates (seq. similarity up to 58.5%)Query served in 59 secondsMultiple queries to multiple servers at:http://distill.ucd.ie/distill/Access individually Porter, Porter+, PaleAle, BrownAle, X-Stout , XX-Stout, 3Distill at: http://distill.ucd.ie/porter/http://distill.ucd.ie/porter+/http://distill.ucd.ie/paleale/http://distill.ucd.ie/brownale/http://distill.ucd.ie/xstout/http://distill.ucd.ie/xxstout/Prediction of protein disorder by Spritz:http://distill.ucd.ie/spritz/For an explanation of the output formats, refer to:http://distill.ucd.ie/distill/explanation.html#output_formats Please cite one or more of the following:G.Pollastri, A.McLysaght."Porter: a new, accurate server for protein secondary structure prediction". Bioinformatics, 21(8):1719-1720, 2005./cgi/content/abstract/21/8/1719C.Mooney, Y.Wang, G.Pollastri."SCLpred: Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction by N-to-1 Neural Networks", Bioinformatics, 27 (20), 2812-2819, 2011./content/27/20/2812D.Bau, A.J.M.Martin, C.Mooney, A.Vullo, I.Walsh, G.Pollastri. "Distill: Asuite of web servers for the prediction of one-, two- and three-dimensional structural features of proteins" BMC Bioinformatics, 7:402, 2006./1471-2105/7/402/abstractC. Mooney, G.Pollastri "Beyond the Twilight Zone: Automated prediction of structural properties of proteins by recursive neural networks and remote homology information" Proteins, 77(1), 181-90, 2009. /journal/122274852/abstract G.Pollastri, A.J.M.Martin, C.Mooney, A.Vullo. "Accurate prediction of protein secondary structure and solvent accessibility by consensus combiners of sequence and structure information" BMC Bioinformatics, 8:201, 2007. /1471-2105/8/201/abstract I.Walsh,D.Bau, .M.Martin, C. Mooney, A.Vullo, G.Pollastri "Ab initio and template-based prediction of multi-class distance maps by two-dimensional recursive neural networks" BMC Structural Biology, 9:5, 2009. /1472-6807/9/5A.Vullo, I.Walsh, G.Pollastri."A two-stage approach for improved prediction of residue contact maps"BMC Bioinformatics, 7:180, 2006. /1471-2105/7/180/abstractG. Pollastri, A. Vullo, P . Frasconi, P . Baldi."Modular DAG-RNN Architectures for Assembling Coarse Protein Structures".Journal of Computational Biology, 13:3, 631-650, 2006.A. Vullo, O. Bortolami, G. Pollastri, S. Tosatto."Spritz: a server for the prediction of intrinsically disordered regions in protein sequences using kernel machines"Nucleic Acids Research, 34:W164-W168, 2006. 6)TUAT Kuroda Lab's Programb.tuat.ac.jp/dlpsvm.html结果:部分数据Sequence position Prob. by SVM-ALL Prob. by SVM-Long Prob. by SVM-Short Li 1 0 A2 0 T3 0 G4 0 A5 -0.973539 0 0 A6 -1.086915 0 0 A7 -0.891253 0 0 C8 -0.644379 0 0 T9 -0.378074 0 0 A。

生物信息学中的蛋白质序列分析随着生物技术的不断发展,人们对于生物体内各种蛋白质的研究愈发深入。
而蛋白质序列分析则是生物信息学中重要的一环,可以用于蛋白质结构预测、功能分析、进化研究等方面。
在这篇文章中,我们将探讨蛋白质序列分析在生物信息学中的应用以及涉及到的技术和算法。
一、蛋白质序列的组成蛋白质由氨基酸组成,而蛋白质序列指的是氨基酸连接的线性序列。
氨基酸是构成蛋白质的基本单元,不同的氨基酸组合构成不同的蛋白质。
目前已知的氨基酸有20种,它们由不同的侧链和碳氮骨架组成,这种多样性导致了蛋白质具有丰富多样的结构和功能。
二、蛋白质序列分析的应用1、预测蛋白质结构蛋白质结构与其功能息息相关,因此对于蛋白质结构的预测一直是研究的热点问题。
蛋白质序列是进行蛋白质结构预测的重要依据之一。
一般来说,蛋白质结构预测可分为二级结构和三级结构预测。
二级结构指的是蛋白质中α-螺旋、β-折叠和无规则卷曲等局部的结构。
目前,常用的二级结构预测方法有Chou-Fasman算法、GOR算法等。
而三级结构预测指的是蛋白质整体的三维结构,其预测难度更大,目前还没有完全解决。
但是,针对蛋白质结构的许多研究都是基于蛋白质序列的分析和预测。
2、鉴定蛋白质功能蛋白质的功能与其序列和结构有关,因此通过分析蛋白质序列也可以预测蛋白质的功能。
一般来说,蛋白质的功能可以分为三类:催化、结构和调节。
催化作用指的是酶类蛋白质对化学反应的促进作用。
结构作用指的是蛋白质形成结构,对于细胞和组织的形态和机能具有重要作用。
调节作用指的是蛋白质对细胞、胚胎、发育和免疫系统等的调节作用。
对于蛋白质功能的鉴定,目前的方法主要有以下几种:1)基于序列的比对方法;2)结构基因学方法;3)基于基因组的方法。
三、蛋白质序列分析的技术和算法1、BLAST算法BLAST(Basic Local Alignment Search Tool)算法是常用的序列比对算法之一,它通过比对两条序列后,计算两个序列之间的相似性得分。

生物信息学作业题生物信息学作业题绪论1.什么是生物信息学?2.生物信息学有哪些主要研究领域?第一章生物信息学的分子生物学基础1.DNA的双螺旋结构要点是什么?2.什么是基因组和蛋白质组?对它们的研究有何意义?第二章生物信息学的计算机基础1.简述网络操作系统的类型。
第三章核酸序列分析1.什么是全局比对?2.什么是局部比对?有哪些优点?第四章分子进化分析1.分子进化分析具有哪些优点?2. 简述分子进化的中性学说。
第五章基因组分析1. 什么是基因组学?其主要研究内容是什么?2.简述基因预测分析的一般步骤。
第六章蛋白质组分析1. 蛋白质组学的概念和主要研究的大致方向是什么?2. 蛋白质组功能预测的程序是怎样的?第七章生物芯片数据分析1. 什么是生物芯片?2. 生物芯片有哪些方面的应用?第八章核酸与蛋白质结构预测1. RNA二级结构典型的预测方法有哪些?2. 基于统计学的预测蛋白质二级结构的方法有哪些?第九章生物信息学平台与工具软件1. 请利用Clustal X软件对下列6条蛋白质序列进行多重比对(比对结果用BioEdit软件打开,用“截图”方式显示比对结果)。
>1mqngkvkwfn sekgfgfiev eggedvfvhf saiqgegfkt leegqevtfe veqgnrgpqatnvnkk>2mqgkvkwfnn ekgfgfieie gaddvfvhfs aiqgegykal eegqevsfdi tegnrgpqaanvvkl>3mqngkvkwfn sekgfgfiev eggedvfvhf saiqgegfkt leegqevtfe veqgnrgpqatnvnkk>4mqgkvkwfnn ekgfgfieie gaddvfvhfs aiqgegykal eegqevsfdi tegnrgpqaanvvkl>5mqngkvkwfn sekgfgfiev eggedvfvhf saiqgegfkt leegqevtfe veqgnrgpqatnvnkk>6mqgkvkwfnn ekgfgfieie gaddvfvhfs aiqgegykal eegqevsfdi tegnrgpqaanvvkl2. 现有一ZmPti1b蛋白质序列,请用DNAMAN软件分析其二级结构,给出分析结果。
一、序列(1)从NCBI网站中查找人类钙网蛋白的基因序列,登录号为AY047586.1,序列长度为1402 bp,CDS区为54..1307bp。
序列如图3。
图1. NCBI网站中查找人类钙网蛋白序列图2. 人类钙网蛋白序列的相关信息图3 人类钙网蛋白的FASTA格式序列(2)通过blast比对获得相似性前6条的序列:白犀牛钙网蛋白(XM_004442548.1 )、野猪胸腺克隆(AK398467.1)、鼠的钙网蛋白(X53363.1)、小家鼠钙网蛋白( NM_007591.3)、褐家鼠钙网蛋白( NM_022399.2)、现代人互补DNA克隆( BC107102.2),对7条序列的CDS区进行比对分析,并构建系统进化树。
图4 进行BLAST的界面图5 BLAST之后的结果图6 BLAST之后的结果图7 MAGA的运行结果图8 MEGA的运行结果图9 系统进化树二、对人类钙网蛋白的蛋白质进行一级结构的预测从NCBI中搜索人类钙网蛋白的蛋白序列,其登录号为AAL13126.1,序列如图所示:图10 人类钙网蛋白的蛋白序列通过protparam(/tools/protparam.html)对人类钙网蛋白的蛋白质的基本理化性质进行预测,结果显示该蛋白编码氨基酸数目为417,相对分子质量为48141.5 Da,理论pI值4.29。
图11 protparam的首页图12 蛋白质的氨基酸数目.相对分子质量.理论pI值.氨基酸组成图13 蛋白质的正/负电荷残基数.分子式.总原子数图14 蛋白质的消光系数.半衰期.不稳定系数.脂肪系数.总平均亲水性三、对该蛋白质二级结构进行预测(亲疏水性、跨膜区、结构域等)(1)通过protscale (/tools/protscale.html)网站进行亲疏水性预测。
图15 亲疏水性工具protscale首页图16 亲疏水性预测的结果图17 亲疏水性预测的结果(2)通过http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM-2.0这个网站,对该蛋白质进行跨膜区预测图19 跨膜区工具TMHMM首页图19 跨膜区预测结果(3)通过(http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/)这个网站,对该蛋白质进行结构域预测图19 结构域工具smart页面图20 结构域预测结果四、通过(/)这个网站,对该蛋白质三级结构进行预测图21 三维工具swiss-modle页面图22 三级结构预测结果个人收获生物信息学通俗的说法就是利用数学和计算机知识来处理生物数据,在这一个学期内的学习中,不仅学习到了有关生物信息学的一些理论知识,而且也使我们接触到了怎样用现代技术来处理得到的数据,每一步做出来的东西都让我们很惊讶也很惊喜,原来生物世界是这么美妙。
⽣物信息学课程复习题(南医⼤)⽣物信息学课程习题第⼀章绪论⼀、填空1、在年,美国国会批准启动⼈类基因组计划,拟⽤年时间测定⼈类全部条染⾊体上共个碱基序列的测定。
2、是遗传信息的携带者。
3、蛋⽩质三维结构测定主要⽅法有和。
4、理想的抗⽣素靶标应为微⽣物细胞所必须,在病原体中⾼度,且在⼈体中或与⼈类基因有。
5、下图例举了⼀个计算机辅助药物设计的实例,从a图中我们得到了配体上R基团附近的受体上有和残基,具有性,因此可以将R基团设计为性基团,如图b中所⽰的基团,使得抑制活性⽐改造前提⾼了近5000倍。
⼆、名词HGP(human genome project),EST(expressed sequence tag), SNP(single nucleotide polymorphism),⽣物信息学(Bioinformatics),药物基因组学(Pharmacogenomics),intron,“Junk DNA”,⽐较基因组学,蛋⽩质组学,分⼦进化树(evolutionary tree),基因组,基因组药物三、简答1、简述⽣物信息学在药物研究开发领域的应⽤可体现在哪些⽅⾯?2、如何利⽤基因组信息寻找新的药物作⽤靶标?3、如何利⽤⼈类基因组信息实现个性化治疗,其基于的原理是什么?4、试叙述基因芯⽚⽤于疾病诊断的原理,并说明其优缺点。
5、最近甲型流感流⾏,请设计甲型流感的分⼦诊断⽅法,说明其原理。
第⼆、三章数据库⼀、单选题1、以下数据库不能⽤于检索核酸序列的是( B )A. GenBankB. PDBC. EMBLD.DDBJ2、蛋⽩质结构数据常保存为下⾯哪⼀种格式为后缀的⽂件()A. PDBB. txtC. SeqD. mdb3、下列格式属于FASTA格式的是()A. >seq1B.C. ATGCCATAD. > ATGCCATAATGCCATA ATGCCATA⼆、填空题1、阅读以下数据格式,写出以下标注的含义:LOCUS是,DEFINITION是,ACCESSION是,VERSION是,SOURCE是在论⽂中使⽤了NCBI数据库中的该序列,应标注该序列的编号,应填。
生物信息学答题卷考题一:到蛋白质序列数据库中查询一条杆状病毒(Baculovirus)DNA聚合酶(DNA polymerase)的完整序列,写出序列名称、登录号及来源物种的分类情况,然后用Blast(注意:写出所用程序及所搜索的数据库名称)搜索到数据库中和它相似程度较高的10条序列(写出这些序列的名称和登陆号及来源物种的分类情况。
要求至少包括3-4个属,每个属中选择1-2个种),对这10条序列进行多序列比对后(写出比对所用程序及比对结果),使用phylip软件,用距离法对它们进行分子进化分析(包括对进化树进行统计评估),说明这种蛋白质的进化历程(60分)。
答:(1)到蛋白质序列数据库中查询一条杆状病毒(Baculovirus)DNA聚合酶(DNA polymerase)的完整序列如下:完整序列(ORIGIN):1 mastdsldtr tfdyasdssf eviiitnaph dydgyielga aarllapfqk nisalwtnaa61 pshkltrnnk nylhvfglfk ylqnynlntk khppeyytik svicdlmmga qgktfdplce121 iktqlcaiqe slneaivtln ghaaadpapr tearelvesl hseyskkltf atdtildhvk181 sikdlvclnk序列名称: capsid protein [Choristoneura fumiferana MNPV]即:云杉卷叶蛾(虎尾松卷叶蛾)颗粒体病毒具体信息:LOCUS NP_848433 190 aa linear VRL06-MAY-2009登录号(ACCESSION): NP_848433来源物种的分类情况SOURCE Choristoneura fumiferana MNPVORGANISM Choristoneura fumiferana MNPVViruses; dsDNA viruses, no RNA stage; Baculoviridae;Alphabaculovirus.FEATURES Location/Qualifierssource 1..190/organism="Choristoneura fumiferana MNPV"/db_xref="taxon:208973"/country="Ireland"(2)然后用Blast搜索和它相似程度较高的10条序列如下:说明:所用程序:blosum62所搜索的数据库名称:swissprot数据库中和它相似程度较高的10条序列1、RecName: Full=Capsid protein p24名称:RecName: Full=Capsid protein p24LOCUS VP24_NPVOP 192 aa linear VRL 11-JAN-2011登录号:P24078来源物种的分类情况:SOURCE Orgyia pseudotsugata MNPVORGANISM Orgyia pseudotsugata MNPVViruses; dsDNA viruses, no RNA stage; Baculoviridae;Alphabaculovirus.FEATURES Location/Qualifierssource 1..192/organism="Orgyia pseudotsugata MNPV"/host="Orgyia pseudotsugata (Douglas fir tussock moth)"/db_xref="taxon:262177"2、RecName: Full=Capsid protein p24名称:RecName: Full=Capsid protein p24LOCUS VP24_NPVAC 198 aa linear VRL 11-JAN-2011登录号:P41678来源物种的分类情况:SOURCE Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirusORGANISM Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirusViruses; dsDNA viruses, no RNA stage; Baculoviridae;Alphabaculovirus.FEATURES Location/Qualifierssource 1..198/organism="Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus"/host="Lepidoptera (butterflies and moths)"/db_xref="taxon:46015"3、RecName: Full=Flagellar motor switch phosphatase FliY; AltName: Full=CheY-P phosphatase FliY; AltName: Full=Flagellar motor switch protein FliY名称:RecName: Full=Flagellar motor switch phosphatase FliY; AltName: Full=CheY-P phosphatase FliY; AltName: Full=Flagellar motor switch protein FliYLOCUS FLIY_BACSU 378 aa linear BCT 08-FEB-2011登录号:P24073来源物种的分类情况:SOURCE Bacillus subtilisORGANISM Bacillus subtilisBacteria; Firmicutes; Bacillales; Bacillaceae; Bacillus.FEATURES Location/Qualifierssource 1..378/organism="Bacillus subtilis"/db_xref="taxon:1423"4、RecName: Full=Uncharacterized protein YjeA名称:RecName: Full=Uncharacterized protein YjeALOCUS YJEA_HAEGA 322 aa linear BCT 30-NOV-2010登录号:Q9ZIY0来源物种的分类情况:SOURCE Avibacterium paragallinarumORGANISM Avibacterium paragallinarumBacteria; Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Pasteurellales;Pasteurellaceae; Avibacterium.FEATURES Location/Qualifierssource 1..322/organism="Avibacterium paragallinarum"/db_xref="taxon:728"5、RecName: Full=Protein YOP1名称:RecName: Full=Protein YOP1LOCUS YOP1_USTMA 172 aa linear PLN 08-MAR-2011 登录号:Q4P0H0来源物种的分类情况:SOURCE Ustilago maydisORGANISM Ustilago maydisEukaryota; Fungi; Dikarya; Basidiomycota; Ustilaginomycotina;Ustilaginomycetes; Ustilaginales; Ustilaginaceae; Ustilago. FEATURES Location/Qualifierssource 1..172/organism="Ustilago maydis"/db_xref="taxon:5270"6、RecName: Full=Protein anon-37Cs名称:RecName: Full=Protein anon-37CsLOCUS A37C_DROLE 544 aa linear INV 10-AUG-2010 登录号:O96570来源物种的分类情况:SOURCE Scaptodrosophila lebanonensisORGANISM Scaptodrosophila lebanonensisEukaryota; Metazoa; Arthropoda; Hexapoda; Insecta; Pterygota;Neoptera; Endopterygota; Diptera; Brachycera; Muscomorpha;Ephydroidea; Drosophilidae; Scaptodrosophila.FEATURES Location/Qualifierssource 1..544/organism="Scaptodrosophila lebanonensis"/db_xref="taxon:7225"7、RecName: Full=Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A1; Short=PsaA名称:RecName: Full=Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A1; Short=PsaA LOCUS PSAA_SYNPW 767 aa linear BCT 08-FEB-2011登录号:Q9R6U0来源物种的分类情况:SOURCE Synechococcus sp. WH 7803ORGANISM Synechococcus sp. WH 7803Bacteria; Cyanobacteria; Chroococcales; Synechococcus.FEATURES Location/Qualifierssource 1..767/organism="Synechococcus sp. WH 7803"/db_xref="taxon:32051"8、RecName: Full=UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvoylglucosamine reductase; AltName:Full=UDP-N-acetylmuramate dehydrogenase名称:RecName: Full=UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvoylglucosamine reductase; AltName:Full=UDP-N-acetylmuramate dehydrogenaseLOCUS MURB_CAMJE 258 aa linear BCT 08-FEB-2011登录号:Q9PM01来源物种的分类情况:SOURCE Campylobacter jejuniORGANISM Campylobacter jejuniBacteria; Proteobacteria; Epsilonproteobacteria; Campylobacterales;Campylobacteraceae; Campylobacter.FEATURES Location/Qualifierssource 1..258/organism="Campylobacter jejuni"/db_xref="taxon:197"9、RecName: Full=UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvoylglucosamine reductase; AltName:Full=UDP-N-acetylmuramate dehydrogenase名称:RecName: Full=UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvoylglucosamine reductase; AltName:Full=UDP-N-acetylmuramate dehydrogenaseLOCUS MURB_CAMJR 258 aa linear BCT 08-FEB-2011登录号:Q5HSB7来源物种的分类情况:SOURCE Campylobacter jejuni RM1221ORGANISM Campylobacter jejuni RM1221Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Epsilonproteobacteria; Campylobacterales;Campylobacteraceae; Campylobacter.FEATURES Location/Qualifierssource 1..258/organism="Campylobacter jejuni RM1221"10、RecName: Full=Probable molybdopterin-guanine dinucleotide biosynthesis protein A 名称:RecName: Full=Probable molybdopterin-guanine dinucleotide biosynthesis protein A LOCUS MOBA_METAC 225 aa linear BCT 03-MAY-2011登陆号:Q8TPD6来源物种的分类情况:SOURCE Methanosarcina acetivorans C2AORGANISM Methanosarcina acetivorans C2AArchaea; Euryarchaeota; Methanomicrobia; Methanosarcinales;Methanosarcinaceae; Methanosarcina.FEATURES Location/Qualifierssource 1..225/organism="Methanosarcina acetivorans C2A"/db_xref="taxon:188937"搜索过程附图:(3)对这10条序列进行多序列比对:写出比对所用程序:clustalx比对结果分析:比对所得的以phy为后缀的文件用写字板格式打开后得如下结果: 10 771P24078.1 ---------- ---------- ------MANA DSLDAR-AFS YAPDASFEVIP41678.1 ---------- ---------- ---------- ----TR-NFM YSPDSSLEVVQ9R6U0 ---------- TAKTQVEKVD NPATFELFGK PGHFDR-ALA KGPKTTTWVWQ3AMS5.1 MTISPPERGS DAKSQVEKVD NPATFELFGK PGHFDR-ALA KGPKTTTWVWQ9PM01.1 ------MIID FKKYSSVRIG NEFEVLVLDQ ICDFDG-FLI GGANN----LQ4P0H0 ---------- ---------- -KVEYFVAQI DKELSRYPAL KKFEQTVPVPQ9ZIY0.1 ------SIQT LLSRAKIIAE IRQFFSERGL LEVETPILSE FGVTDVHLSTP24073.2 --IDALLNGT GSTLDEPEIP EVDDLSEMER DAIGEIGNIS FGSSATALSTO96570 ---------E SLSFSGYKLT RRNLYNAPAL KVMGRSVNNS SSNNNDQQQYQ8TPD6.1 ---------- ---------- MSGKTELKPG RTKSRSAIVL AGGRGRRMGMIITNAPNDHD GY---LELNA AARL-LAPFQ KN-ISALWTS ----------IITNSDGDHD GY---LELTA AAKV-MSPFL SNGSSAVWTN ----------NLHANAHDFD SHTSDLEEVS RKIF-SAHFG HLAVIFIWLS GAFFHGARFSNLHANAHDFD AHTSDLQEVS RRIF-SAHFG HLAVIFIWLS GAFFHGARFSLVSPKPKNIG ILGDGFNFIQ ILDR-NKDFI HLRIGCKTKS S---------KAYAALGAFG IFTLFVFFNI AAGF-LTNLL GFFVPAYFS- ----------FSTKLISPFQ KKEKTLWLST SPEYPMKRLL SAGSGAIFQL CKVFRN---ELLNQKVDITT PSVTVIPRSK ISDAFPEPYV AIEVNYTEGF SG--------NLESAKQNTQ IVVIGAGLAG LSAAQHLLRH GFRSTIVLEA TDRYGG---RVEKALLEFEG KTILERLLEN LFRVVDEVIL SVRDIPQKEK ----------……(此处省略约9KB的数据分析结果)以上是多序列比对的纯数据结果,部分数据省略,因为可以从下面的进化树得到具体的分析。
生物信息学课堂操作练习一、生物信息学科的发展和研究内容通过下列internet上的自教课程,初步了解不同的数据库和分析工具/2can/Education二、生物数据库1. 熟悉各种数据库。
2. 重点了解GenBank和SWISS-PROT所包含的各种功能和适用范围。
三、关键词或词组为基础的数据库检索1. 熟练掌握Entrez检索体系。
2. 查找与水稻抗病基因Xa21有关的资料(1) 由多少碱基构成?编码多少个氨基酸?(2) exon和intron的位置?(3) 是否有3-D structure数据?1) 由多少碱基构成?编码多少个氨基酸?4623b.p., 1025A.a.;2) exon和intron的位置?Exon: 24~2700,3543~3943 intron: remaining;3) 是否有3-D structure数据?没有.3. 查找C. elegans基因组的资料。
(1) chromosome I的测序是否已完成?(2) 已知的chromosome I的序列有多少碱基?序列发表在哪份杂志上?期号和页码?1) chromosome I的测序是否已完成?完成.2) 已知的chromosome I的序列有多少碱基? 序列发表在哪份杂志上? 期号和页码? 15.0724Mb.p.(15072421b.p.), Science 1999 Jan 1;283(5398):35.4. 查看人类基因组第1染色体上基因的分布。
/mapview/maps.cgi?ORG=hum&MAPS=ideogr,est,loc&LINKS= ON&VERBOSE=ON&CHR=15. 查看Arabidopsis的系谱树,以及Arabidopsis第1染色体上的序列。
比较Arabidopsis基因组的资料提供形式与人类基因组有什么不同(/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?id=3701,/mapview/maps.cgi?taxid=3702&chr=1)貌似没什么区别……比较Arabidopsis基因组的资料提供形式与人类基因组有什么不同。
生物信息学蛋白质序列分析-课堂练习
ZNF395, 全称为Zinc Finger Protein395, 又被称为PBF,PRF1,DBP2,PRF-1,Si-1-8-14或DKFZp434K1210。
其氨基酸序列为
结构域分析:http://www.expasy.ch/prosite/
(一)分析蛋白质的一级结构
分析蛋白质的pI、Mw、氨基酸组成:Tools and software packages------Identification and characterization-----ProtParam
http://www.expasy.ch/tools/protparam.html
分析蛋白质的疏水性:Primary structure analysis-----ProtScale
http://www.expasy.ch/tools/protscale.html
分析蛋白质的重复序列:Primary structure analysis-----REP
http://www.embl-heidelberg.de/~andrade/papers/rep/search.html
(二)分析蛋白质的二级结构
预测蛋白质的?-螺旋和?-折叠结构:Secondary structure prediction-----nnPredict
/~nomi/nnpredict.html
蛋白质的其它二级结构:Secondary structure prediction-----SOPMA
(三)分析蛋白质的三级结构
molecular modeling:“tertiary structure prediction ”栏目选择选择一个分析工具,email服务
(四)分析膜蛋白质
预测膜整合蛋白的跨膜区: Topology prediction------SOSUI
http://bp.nuap.nagoya-u.ac.jp/sosui/
分析膜锚定蛋白的GPI位点:Post-translational modification------big-PI Predictor
http://mendel.imp.ac.at/sat/gpi/gpi_server.html
(五)分析蛋白质的翻译后修饰
分析信号肽及其剪切位点: Post-translational modification prediction----SignalIP
http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/
分析糖链连接点:分析O-连接糖蛋白,Post-translational modification prediction----NetOGlyc
http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetOGlyc/
分析N-连接糖蛋白,Post-translational modification prediction----NetNGlyc
(六)分析蛋白质的亚细胞定位
Topology prediction----PSORT-----WoLF PSORT
/
(七)分析化学因子作用蛋白质的位点
“Identification and characterization ”------“Other prediction or characterization tools”栏目选择“PeptideCutter” 软件
http://www.expasy.ch/tools/peptidecutter/
1.蛋白基本理化性质分析
利用Expasy 软件包中的ProtParam工具(http://www.expasy.ch/tools/protparam.htmL) 进行蛋白的氨基
酸组成、分子质量、等电点及疏水性等理化性质的分析。
2. 利用PROF法(/)网站工具和(http://npsa-pbil.ibcp.fr)网站HNN软件预测蛋白的二级结构。
利用Scan Prosite(/)网站工具对蛋白进行结构域分析。
利用Swiss-Model数据库软件预测该蛋白的三级结构,结果用蛋白质三维图象软件Rasmol2.7查看。
3.蛋白亚细胞定位与功能分析
利用CBS(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM-2.0/)网站工具对蛋白进行跨膜分析。
采用PredictNLS (/predictNLS/) 对蛋白进行核定位信号分析,预测利用(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/)网站工具预测蛋白的信号肽。
利用PSORT(http: //psort.nibb.ac.jp/form2.htmL)网站工具进行蛋白亚细胞定位预测。
利用CBS (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/ProtFun/)网站工具预测蛋白的功能。