数据库原理英文简介
- 格式:pptx
- 大小:1.78 MB
- 文档页数:8
![[数据库原理]【英文版】Chapter05](https://uimg.taocdn.com/8b2bc028b4daa58da0114a0a.webp)


结构化查询语言SQL(Structured Query Language)是结构化查询语言的缩写。
SQL是在关系数据库上执行数据操作、检索及维护所使用的标准语言,可以用来查询数据,操作数据、定义数据、控制数据,所有数据库都使用相同或者相似的语言。
SQL可分为:1.数据定义语言(DDL):Data Definition Language用于建立、修改、删除数据库对象,包括创建语句(create)、修改语句(alter)、删除语句(drop),比如使用 create table创建表,使用alter table修改表,使用drop table删除表等动作。
这类语言不需要事务的参与,自动提交。
2.数据操作语言(DML):Data Manipulation Language用于改变数据库,包括insert、update、delete三条语句,分别用于对数据库数据的插入、更新、删除。
DML语言和事务是相关的,执行完DML操作后必须经过事务控制语句提交后才能真正的将改变引用到数据库中。
3.事务控制语言(TCL):Transaction Control Language用来维护数据一致性的语句,包括提交commit、回滚rollback,保存点savepoint三条语句,其中commit用来确认已经进行的数据库改变, rollback语句用来取消已经进行的数据库改变,当执行DML操作后(也就是上面说的增加、修改、删除等动作),可以使用commit语句来确认这种改变,或者使用rollback取消这种改变。
savepoint语句用来设置保存点,使当前的事务可以回退到指定的保存点,便于取消部分改变。
4.数据查询语言(DQL):Data Query Language用来查询所需要的数据,例如select。
5.数据控制语言(DCL):Data Control Language用于执行权限的授予和收回操作、创建用户等,包括授予grant语句、收回revoke语句、create user语句,其中grant用于给用户或角色授予权限,revoke 用于回收用户或角色已有的权限。

数据库系统原理,github1.数据库系统原理是数据库技术的基础理论。
Database system principle is the fundamental theory of database technology.2.通过学习数据库系统原理,可以深入了解数据库的存储、管理和优化。
Studying the principles of database system can help us understand the storage, management and optimization of databases in depth.3.数据库系统原理涉及到数据结构、算法、操作系统等多方面知识。
The principles of database system involve various knowledge such as data structure, algorithms, and operating systems.4.学习数据库系统原理可以帮助我们设计高效的数据库系统。
Studying the principles of database system can help us design efficient database systems.5.了解数据库系统原理能够提升我们在数据库领域的专业能力。
Understanding the principles of database system can enhance our professional skills in the field of databases.6. 《数据库系统原理》是一本经典的数据库教材。
"Database System Principles" is a classic textbook on databases.7.该书详细介绍了数据库系统的各个方面。
The book provides a detailed introduction to various aspects of database systems.8.通过阅读该书,可以系统地学习数据库系统原理。

数据库原理与应用英语Database Principles and ApplicationsIntroduction:Database principles and applications play a crucial role in managing and organizing large volumes of data efficiently. With the advent of technology and the increasing reliance on data for decision-making, understanding the principles behind databases is essential. This article aims to discuss the fundamental concepts of database principles and their applications.1. Database Principles:A database is a structured collection of data that is organized and managed to provide efficient access and retrieval. The principles underlying databases include data modeling, data integrity, and transaction management.1.1 Data Modeling:1.2 Data Integrity:Data integrity ensures the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data in the database. It is maintained through various integrity constraints such as Primary Key, Foreign Key, Unique Key, and Check constraints. These constraints enforce rules that prevent the entry of invalid or inconsistent datainto the database.1.3 Transaction Management:Transaction management ensures the atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability (ACID) properties of database operations. Transactions represent a logical unit of work that can consist of multiple database operations. The database management system (DBMS) ensures that transactions are executed reliably and with proper concurrency control.2. Database Applications:2.1 Online Transaction Processing (OLTP):2.2 Decision Support Systems (DSS):2.3 Customer Relationship Management (CRM):CRM databases are used to store customer-related information such as contact details, purchase history, and preferences. CRM systems help organizations to manage customer interactions and improve customer satisfaction. They are widely used in sales, marketing, and customer service departments.2.4 Data Warehousing:Data warehousing involves the collection, integration, and storage of data from various sources for analysis and reporting. Data warehouse databases are designed to support decision-making processes by providing a consolidated and historical view of data. They are used in business intelligence, reporting, and data analytics.2.5 Geographic Information Systems (GIS):GIS databases store spatial data such as maps, satellite images, and geospatial information. They enable the integration and analysis of spatial data in various domains like urban planning, environment management, and logistics. GIS databases use specialized spatial indexing techniques to optimize queries based on location.Conclusion:In conclusion, database principles and applications form the foundation of efficient data management. Understanding the principles of data modeling, data integrity, and transaction management is crucial for designing and maintaining robust databases. Moreover, the applications of database principles are diverse, ranging from online transaction processing to decision support systems and customer relationship management. Mastering database principles and their applications is essential for professionals working in the field of data management and analytics.。

![[数据库原理]【英文版】Chapter01](https://uimg.taocdn.com/64df49c008a1284ac850430a.webp)

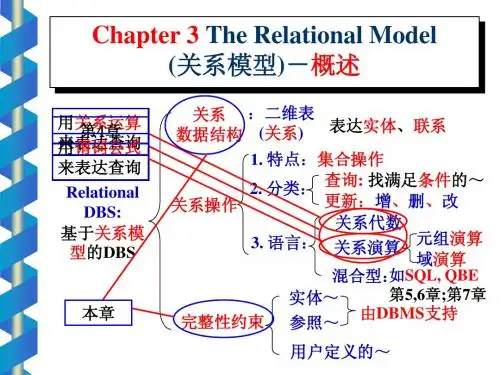


数据库原理基本概念Basic concepts of database theory一、数据---DataData is everything.Data can exist in a variety of forms -- as digital numbers, text, image, sound, video and etc.二、数据库---DatabaseA database is a repository for a collection of computerized data files.A database is an organized collection of data for one or more purposes, usually in digital form. The data are typically organized to model relevant aspects of reality (for example, the availability of rooms in hotels), in a way that supports processes requiring this information (for example, finding a hotel with vacancies). The term "database" refers both to the way its users view it, and to the logical and physical materialization of its data, content, in files, computer memory, and computer data storage.三、数据库系统---DBS(Database System)A database system is a term that is typically used to encapsulate the constructs of a data model, database Management system (DBMS) and database.四、数据库管理系统---DBMS(Database ManagementSystem)A database management system (DBMS) is a software package with computer programs that control the creation, maintenance, and the use of a database. It allows organizations to conveniently develop databases for various applications by database administrators (DBAs) and other specialists.A collection of programs that enables you to store, modify, and extract information from a database.五、数据库管理员---DBA(Database Administrator)A database administrator is a person responsible for the design, implementation, maintenance and repair of an organization's database.六、模式---SchemaA database schema of a database system is its structure described in a formal language supported by the database management system (DBMS) and refers to the organization of data to create a blueprint of how a database will be constructed.In other words, schema is the structure of the database that defines the objects in the database.七、内模式---Internal SchemaInternal Schema: storage schema– Describes how data is stored and what the physical structureof data is.– Totally dependent on particular implementation.– There is only one internal schema in a DB.八、外模式---External SchemaExternal Schema: user schema or subschema– Interface between users and DBS– Describes the logical structure of some local data oriented tosome applications and users– There may be many external schemata in a DB.九、三级模式---Three Levels of Schema-Physical level: describes how a record (e.g., customer) is stored.-Logical level: describes data stored in database, and therelationships among the data.-View level: application programs hide details of data types. Views can also hide information (such as an e mployee’s salary)for security purposes.十、映像---MappingData mapping is the process of creating data element mappings between two distinct data models. Data mapping is used as a first step for a wide variety of data integration tasks including:●Data transformation or data mediation between a data source anda destination●Identification of data relationships as part of data lineageanalysis●Discovery of hidden sensitive data such as the last four digitssocial security number hidden in another user id as part of a datamasking or de-identification project●Consolidation of multiple databases into a single data base andidentifying redundant columns of data for consolidation orelimination十一、逻辑独立性---Logical Independence When schema changes (e.g., new relation/new attribute added), DBA changes the Ex-schema/schema mapping, so the external schema can stay unchanged, i.e. applications needn’t be changed.十二、物理独立性---Physical Independence When internal schema changes ,DBA changes the schema/internal schema mapping, so the schema can stay unchanged . Thus, the external schema also keeps the same.十三、数据模型---Data ModelA data model in software engineering is an abstract model, that documents and organizes the business data for communication between team members and is used as a plan for developing applications, specifically how data is stored and accessed.A data model can be sometimes referred to as a data structure, especially in the context of programming languages. Data models are often complemented by function models, especially in the context of enterprise models.。
数据库原理英文Database PrinciplesIntroduction:Database principles are fundamental concepts that govern the design, management, and use of databases. A database is a structured collection of data that is organized and stored in a manner that allows for efficient retrieval, manipulation, and analysis.Data Models:Data models are used to represent how data is organized and structured within a database. These models determine the relationships between data elements and define the rules for how data is stored and manipulated. Common data models include hierarchical, network, relational, and object-oriented.Relational Model:The relational model is the most widely used data model in modern databases. It organizes data into relations, which are tables with rows and columns. Each row represents a record, and each column represents a characteristic or attribute of that record. Relationships between tables are established through primary keys and foreign keys.Normalization:Normalization is the process of designing database tables to reduce redundancy and improve data integrity. It involves breaking down large tables into smaller ones and creating relationships between them. The goal is to eliminate data anomalies and ensure that eachpiece of data is stored in one place only.Query Languages:Query languages allow users to retrieve, manipulate, and update data in a database. The most common query language is Structured Query Language (SQL), which is used to interact with relational databases. SQL provides a set of commands and functions that enable users to perform operations such as data retrieval, insertion, deletion, and modification.Indexing and Query Optimization:Indexes are data structures that improve the speed of data retrieval operations. They provide a way to locate data quickly based on specific criteria. Query optimization involves analyzing and rearranging queries to execute them in the most efficient way possible. Techniques such as storing intermediate results, using parallel processing, and selecting appropriate indexing strategies are commonly employed.Transaction Management:A transaction is a unit of work that consists of one or more operations performed on a database. Transaction management ensures the atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability of database operations. Transactions are usually managed by a database management system (DBMS) through the use of transaction logs and concurrency control mechanisms. Concurrency Control:Concurrency control prevents conflicts when multiple users try to access or modify the same data simultaneously. Techniques suchas locking, timestamping, and optimistic concurrency control are used to manage concurrent access and ensure data consistency. Backup and Recovery:Backup and recovery involve creating copies of a database to protect against data loss and ensuring that data can be restored in the event of a failure. Backups can be performed at different levels (database, table, or file) and can be either full or incremental. Recovery mechanisms restore the database to a consistent state after a failure, using backup copies and transaction logs. Conclusion:Understanding database principles is essential for designing efficient and robust databases. Data modeling, normalization, query languages, indexing, transaction management, concurrency control, and backup and recovery are key concepts that form the foundation of database systems. By applying these principles, database professionals can optimize data storage, retrieval, and manipulation, leading to better performance and data integrity.。
Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (BUPT)School of Computer Science and Technology Syllabus for Database System Principles 1. OverviewsCourse No.:323•04105Course Title:Database System Principles Course Credit: 3 Credits, required courseSemester and Year: Spring 2007Class: 04411—04415Teaching hours:●Class teaching: 51 hours●After-class experiments: 17 hours●Course design, or professional practice for this course:(数据库系统综合课程设计), 30 hours, 1 credits,conducted in the 3rd semester.Prerequisites:●Data Structures●Discrete Mathematics●Operating Systems●Algorithms Design and Analysis2. Lecture MeetingsTime: Tuseday AM: 8:00 – 10:00Friday AM: 8:00 – 10:00, only odd weeksLocation: Room 539, 3th Teaching Building3. FacultyInstructor●Name: Dr. Wen YE (叶文)●Office: Room 918, 3rd Teaching Building●Office Hours: Wednesday 3:00 to 4:30 PM,I am also available by appointment at a time more convenientfor you, especially at the end of this semester●Phone: 86-10-62282633 (O)●E-mail: gryew@, yewen@Experiments Directors:●Name: ???●Responsibility: directing experiments●Office: Room 913, Main Building●Office Hours: Friday 14:00 to 17:00 PM, or by appointmentGraduate Teaching Assistant:●Name: ?? ( )●Responsibility: checking homework●Office: Room 918, 3rd Teaching Building●Office Hours: Wednesday 13:30 to 15:00 PM, or by appointment●E-mail:4. Text Book1. Abraham Silberschatz, Henry F.Korth, S. Sudarshan, Database System Concepts(Forth Edition, Fifth Edition), Higher Education Press and McGraw-Hill Companies, Beijing, May, 2002. References1.中国计算机科学与技术学科教程2002研究组,中国计算机科学与技术学科教程2002,清华大学出版社,北京,2002年8月。
Database Principles and Applications IntroductionThe purpose of this document is to provide an overview of database principles and their applications. The document will discuss the fundamental concepts of databases, including data models, relational databases, and various database management systems. It will also explore the practical applications of databases in different industries and highlight their significance in modern data-driven environments.Table of Contents1.Data Models2.Relational Databases3.Database Management Systems4.Database Applications5.Conclusion1. Data ModelsData models serve as the foundation for organizing and representing data in a structured manner. They define the structure, relationships, and constraints of the data. There are several types of data models, including:•Hierarchical Model: Represents data in a tree-like structure with parent-child relationships.•Network Model: Represents data using a graph structure, allowing more complex relationships.•Relational Model: Represents data as tables or relations, with rows and columns.•Object-Oriented Model: Represents data as objects, with attributes and methods.•Entity-Relationship Model: Represents data using entities, attributes, and relationships.2. Relational DatabasesRelational databases are based on the relational model, which organizes data into tables, each with its own columns and rows. The relationships between tables are defined using primary and foreign keys. Key concepts in relational databases include:•Tables: Organized collections of data, with each column representinga specific attribute and each row representing a record.•Primary Key: A unique identifier for each record in a table.•Foreign Key: A field in one table that refers to the primary key in another table, establishing a relationship between the two.•Normalization: The process of organizing data to eliminate redundancy and improve data integrity.•SQL: Structured Query Language used for managing and querying relational databases.3. Database Management SystemsA Database Management System (DBMS) is software that allows users to create, manage, and manipulate databases. It provides an interface to interact with the underlying database and includes features such as:•Data Definition Language (DDL): Allows users to create, modify, and delete database structures, tables, and constraints.•Data Manipulation Language (DML): Enables users to insert, update, delete, and retrieve data from a database.•Transaction Management: Ensures the integrity and consistency of database operations.•Security: Provides mechanisms for authentication, authorization, and access control.•Query Optimization: Automatically optimizes queries for better performance.Some popular DBMSs include Oracle, MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, and PostgreSQL.4. Database ApplicationsDatabases have various applications across industries, playing a crucial role in managing and analyzing large amounts of data. Here are a few examples of database applications:•E-commerce: Databases are used to store product information, customer data, and manage orders.•Healthcare: Databases store patient records, medical history, and facilitate efficient healthcare management.•Finance: Databases are used for storing financial transactions, managing accounts, and processing payments.•Education: Databases manage student records, course information, and enable online learning platforms.•Logistics: Databases help in tracking inventory, managing supply chains, and optimizing logistics operations.The applications of databases are diverse and extend to almost every industry that deals with data management and analysis.ConclusionDatabase principles and applications are essential in modern data-driven environments. Understanding data models, relational databases, and database management systems is crucial for effective data organization and retrieval. The practical applications of databases span across industries and demonstrate their significance in today’s digital world. By leveraging databases, organizations can efficiently manage and analyze vast amounts of data, enabling informed decision-making and improving overall efficiency.。