计算机体系结构试题及答案版本
- 格式:docx
- 大小:25.37 KB
- 文档页数:16

1.某台主频为1GHz的计算机执行标准测试程序,程序中指令类型、执行数量和平均时钟周期数如下:求该计算机的有效CPI、MIPS和程序执行时间。
(10分)2.将计算机系统中某一功能的处理速度加快15倍,但该功能的处理时间仅占整个系统运行时间的40%,则采用此增强功能方法后,能使整个系统的性能提高多少?3.如果某计算机系统有3个部件可以改进,则这3个部件进改进后达到的加速比分别为:S1=30,S2=20,S3=10。
(1)如果部件1和部件2改进前的执行之间占整个系统执行的时间比例都为30%,那么,部件3改进前的执行时间占整个系统执行时间的比例为多少,才能使3个部件都改进后的整个系统的加速比Sn达到10?(2)如果3个部件改进前执行时间占整个系统执行时间的比例分别是30%,30%和20%,那么,3个部件都改进后系统的加速比是多少?未改进部件执行时间在改进后的系统执行时间中占的比例是多少?(10分)4.假设某应用程序中有4类操作,通过改进,各操作获得不同的性能提高。
具体数据如下表所示:(1)改进后,各类操作的加速比分别是多少?(2)各类操作单独改进后,程序获得的加速比分别是多少?(3)4类操作均改进后,整个程序的加速比是多少?5.一台模型机的9条指令的使用频度如下:(10分)ADD(加):26%SHR(右移):2%SUB(减):17%CLL(循环左移):5%JOM(按页转移):11%CLA(累加器清零):15%STO(存):2%STP(停机):12%JMP(转移):10%试设计这9条指令的Huffman编码的操作码表示以及其等长扩展操作码表示,并计算这两种表示的平均操作码长度。
6.有一个“Cache-主存”存储层次。
主存共分为8个块(0~7),Cache为4个块(0~3),采用直接映像方式。
(1)对于如下主存块地址流:0、2、6、1、3、7、0、1、4、5、4、6、0、7、2,如主存中内容一开始未装入Cache,请列出每次访问后Cache中各块的分配情况;(2)对于(1),指出既发生块失效又发生块争用的时刻;(3)对于(1),求出此期间的Cache命中率。

计算机组织架构考试题库及答案计算机组织架构是计算机科学的一个重要分支,它研究的是计算机系统中硬件和软件的组成、结构、操作和设计方法。
以下是计算机组织架构的考试题库及答案,供您参考。
一、选择题1. 计算机组织架构主要研究的是计算机系统中硬件和软件的( )。
A. 组成B. 结构C. 操作D. 设计方法答案:A、B、C、D2. 计算机的中央处理器(CPU)主要由( )两部分组成。
A. 控制器和运算器B. 控制器和内存C. 运算器和内存D. 控制器和输入输出设备答案:A3. 下列哪种存储器是计算机的主要存储设备?( )A. 只读存储器(ROM)B. 随机访问存储器(RAM)C. 磁盘存储器D. 光盘存储器答案:B4. 计算机的指令包括操作码和( )。
A. 地址码B. 操作数C. 寄存器D. 指针答案:B5. 计算机的输入输出设备中,属于输入设备的是( )。
A. 打印机B. 鼠标C. 显示器D. 键盘答案:B、D二、填空题1. 计算机的中央处理器(CPU)主要由控制器和______两部分组成。
答案:运算器2. 计算机的存储器分为内存和外存,其中内存主要包括______和______。
答案:随机访问存储器(RAM)、只读存储器(ROM)3. 计算机的指令由操作码和______组成。
答案:操作数4. 计算机的______负责将指令译码,并控制计算机的运行。
答案:控制器5. 计算机的______用于存储正在运行的程序和数据。
答案:内存三、简答题1. 请简述计算机组织架构的主要研究内容。
答案:计算机组织架构主要研究计算机系统中硬件和软件的组成、结构、操作和设计方法,包括计算机的中央处理器(CPU)、内存、输入输出设备、指令系统等方面的设计和技术。
2. 请简述中央处理器(CPU)的主要功能。
答案:中央处理器(CPU)是计算机的核心部件,主要负责执行计算机指令、控制计算机运行、进行数据运算和处理等功能。
它主要由控制器和运算器两部分组成,通过控制器的控制,协调运算器和其他硬件设备的工作,完成对指令的执行和数据的处理。

计算机体系结构基础知识试题及答案解析一、选择题1. B2. A3. D4. C5. B6. C7. A8. D9. B 10. C二、填空题1. 互联网2. 中央处理器3. 存储器4. 输入/输出设备三、简答题1. 计算机体系结构是指计算机硬件与软件之间的逻辑结构和功能关系,即计算机的整体结构和组成方式。
2. CPU(中央处理器)是计算机体系结构的核心,它负责执行计算机的指令并控制计算机的运行。
3. 存储器是计算机中用于存储数据和程序的部件,包括主存储器(RAM)和辅助存储器(硬盘、固态硬盘等)。
4. 输入/输出设备用于实现计算机与外部设备之间的数据交换,包括显示器、键盘、鼠标、打印机等。
四、论述题计算机体系结构是计算机科学中的重要组成部分,它对于计算机的设计和开发具有重要意义。
计算机体系结构的基本原理可以通过一系列试题来进行检测和考察。
下面是一套基础的计算机体系结构试题及其答案解析。
首先是选择题部分,这部分试题主要考察对计算机体系结构基础知识的理解和应用能力。
通过选择正确的答案来判断考生对相关知识的掌握情况。
根据试题解析,我们可以得出正确的答案和解释。
接下来是填空题部分,这部分试题主要考察考生对计算机体系结构相关术语的理解和记忆能力。
通过填写正确的术语来补全句子,从而测试考生对相关知识的熟悉程度。
最后是简答题部分,这部分试题通过提出开放式问题,要求考生对计算机体系结构的相关概念和原理进行简要的叙述。
考生需要用清晰、准确的语言来回答问题,展示自己对知识的理解和运用能力。
综上所述,计算机体系结构基础知识试题及答案解析是一套用于考察计算机科学学习者对计算机体系结构基本原理的掌握程度的试题。
通过做题和解析,考生可以检测自己的学习效果,并加深对相关知识的理解。
希望这套试题能为广大学习者提供帮助,推动计算机科学的进一步发展。

第3章计算机网络体系结构一、填空题1.协议主要由(语法)、(语义)和(同步)三个要素组成。
2.OSI模型分为(物理层)、(数据链路层)、(网络层)、(传输层)、(会话层)、(表示层)和(应用层)七个层次。
3.OSI模型分为(资源子网)和(通信子网)两个部分。
4.物理层定义了(机械特性)、(电气特性)、(功能特性)和(规程特性)四个方面的内容。
5.数据链路层处理的数据单位称为(帧)。
6.数据链路层的主要功能有(链路管理)、(成帧)、(信道共享)、(帧同步)、(流量控制)、(差错控制)、(透明传输)和(寻址)。
7.在数据链路层中定义的地址通常称为(硬件地址)或(物理地址)。
8.网络层所提供的服务可以分为两类:(面向连接的)服务和(无连接的)服务。
9.传输层的功能包括(服务选择)、(连接管理)、(流量控制)、(拥塞控制)和(差错控制)等。
二、名词解释同步协议实体对等层对等层通信服务 CIDR 协议数据单元服务数据单元同步同步指的是广义的、在一定条件下发生什么事情的特性,而且条件和时间有关,具有时序的含义。
协议计算机网络中意图进行通信的结点必须要遵守一些事先约定好的规则。
这些为进行数据交换而建立的规则、标准或约定即称为协议,也称为网络协议。
实体任何接收或者发送数据的硬件单元或者软件进程模块都可以称为通信实体,简称实体。
对等层不同的网络结点,若它们遵循的是同一种网络体系结构的话,那么在不同结点上完成同样功能的层次称为对等层。
对等层通信在分层的网络体系结构中,每个层次只知道自己从上层接收来数据并处理后再传递给下一层,结果通信目的方该层次的对等层就收到与己方处理的一模一样的数据。
就好像在两个对等层之间有一条“通道”直接把数据传送过去一样,这种情况就称为对等层通信。
服务下一层能被上一层看见的功能称为服务。
协议数据单元、服务数据单元对等层上传送的数据单位称为协议数据单元,而直接相邻的两个层次之间交换的数据单位称为服务数据单元。

(完整版)计算机系统结构考试题目及参考答案.doc一:名词解释1:虚拟机:由软件实现的机器。
2:CPI :是衡量CPU 执行指令效率的重要标志,指执行每条指令所需的平均时钟周期数。
3:摩尔定律:当价格不变时,集成电路上可容纳的晶体管数目,约每隔18 个月便会增加一倍,性能也将提升一倍。
4:并发性:指两个或多个事件在同一时间间隔内发生的并行性。
5:程序局部性原理:是指程序在执行时呈现出局部性规律,即在一段时间内,整个程序的执行仅限于程序中的某一部分。
相应地,执行所访问的存储空间也局限于某个内存区域。
局部性原理又表现为:时间局部性和空间局部性。
6: CISC/RISC : CISC :即复杂指令系统计算机,指在系统中增加更多和复杂的指令,来提高操作系统效率的计算机。
RISC :即精简指令系统计算机,指在系统中选取使用一些频率最高的、长度固定的、格式种类少的简单指令的计算机。
7:计算机系统结构:指对机器语言计算机的软、硬件功能的分配和对界面的定义。
8:系列机:指先设计好一种系统结构,而后就按这种系统结构设计它的系统软件,按器件状况和硬件技术研究这种结构的各种实现方法,并按照速度、价格等不同要求,分别提供不同速度、不同配置的各档机器。
9:模拟:用机器语言程序解释实现程序移植的方法。
10:仿真:用微程序直接解释另一种机器的指令系统。
11:寻址方式:寻找操作数或指令的有效地址的方式。
12:替换算法:在存储体系中,当出现页面失效时或者主存的所有页面已经全部被占用而又出现页面失效时,按照某种算法来替换主存中某页。
[ 由于主存中的块比Cache 中的块多,所以当要从主存中调一个块到Cache 中时,会出现该块所映象到的一组(或一个)Cache 块已全部被占用的情况。
这时,需要被迫腾出其中的某一块,以接纳新调入的块。
]二:选择题1,直接执行微指令的是( C )A 汇编程序B 编译程序C 硬件D 微指令程序2,对汇编语言程序员不透明的是( C )A 程序计数器B 主存地址寄存器C 条件码寄存器D 指令寄存器3,最早的冯·诺依曼型计算机是以( B )为中心的A 运算器B 控制器C 存储器D I/O 设备4,计算机系统结构的角度的结构来看,机器语言程序员看到的机器属性是( C )A 计算机软件所要完成的功能B 计算机硬件的全部组成C 编程要用到的硬件组织D 计算机各部分硬件的实现5,不同系列计算机之间实现可移植性的途径,不包括( B )A 采用统一的高级语言B 采用统一的汇编语言C 模拟D 仿真6,利用时间重叠原理,实现并行处理的是( A )A 流水处理机B 多处理机C 阵列处理机D 集群系统7,多处理机实现的并行主要是(B)A 指令级并行B 任务级并行C 操作级并行D 操作步骤的级并行8 计算机系统结构不包括( B )A 信息保护B 存储速度C 数据表示D 机器工作状态9,不需要编址的数据存储空间( D )A CPU 通用寄存器B 主存储器C I/O 寄存器D 堆栈10, RISC 执行程序的速度比CISC 快的原因是( C )A RISC 指令系统中条数较少B 程序在 RISC 编译生成的目标程序较短C RISC 指令平均执行周期数较少D RISC 中只允许 LOAD 和 STORE 指令存储11,程序员在编写程序时,使用的访存地址是( B )A 主存地址B 逻辑地址C 物理地址D 有效地址12,虚拟存储器主要是为了( A )A 扩大存储器系统容量B 提高存储器系统速度C 扩大存储器系统容量和提高存储器系统速度D 便于程序的访存操作13,与全相联映像相比,组相联映像的优点是( B )A 目录表小B 块冲突概率低C 命中率高D 主存利用率高14,输入输出数据不经过CPU 内部寄存器的输入输出方式是( C )A 程序控制方式B 中断C DMA 方式D 上述三种方式15,在配置了通道的计算机系统中,用户程序需要输入输出时引起的中断是( A )A 访管中断B I/O 中断C 程序性中断D 外部中断16,当计算机系统通过执行通道程序,完成输入输出工作时,执行通道程序的是(B)A CPUB 通道C CPU 和通道D 指定的外设三:填空1,常见的计算机系统结构的分类法有两种:Flynn 分类法,冯氏分类法冯氏分类法是根据系统的最大并行度对计算机系统结构进行分类,大多数的位并行的单处理机属于字串位并的处理机方式2,由软件实现的机器称为:虚拟机3,在一个计算机系统中,低层机器的属性往往对高层机器的程序员是透明的。

一填空题(每空1分,共30分)1、系列机是指具有相同的体系结构,但具有不同组织和实现的一系列不同型号的机器。
2、存储程序计算机结构上的主要特点之一是以运算器为中心。
3、从计算机系统结构的多级层次结构可知,通常情况下,第1、2、3级用解释方法实现,第4或更高级用翻译方法实现。
4、对于最常见的事件,通常赋予它优先的处理权和资源使用权,这是计算机体系结构设计中的大概率事件优先原则。
5、容量为64块的Cache采用组相联方式映像,字块大小为128字节,每4块为一组,若主存容量为4096块,且以字编址,那么主存地址为 19 位,主存区号为 6 位。
6、可改进比例的值总是小于等于1 。
7、一般有两种策略来保存寄存器的内容,即:调用者保存和被调用者保存。
8、DLX指令集提供了立即数寻址、寄存器寻址、偏移寻址和寄存器间接寻址4种寻址方式。
9、对某流水线处理器测试时发现其存在结构冲突,通常可采用资源重复和流水化功能单元方法解决该问题。
10、编译器通过重新组织代码顺序消除暂停的技术被称为指令调度。
11、按照流水的级别可以把流水线分为部件级流水线、处理机级流水线和处理机间流水线。
12、为解决流水线使用非流水数据通路的寄存器引起冲突,在流水线设计中采用寄存器文件技术解决该问题。
13、Cache的替换算法常见的有 FIFO 、LRU 和随机法。
14、改进Cache性能的方法主要有降低失效率、减少失效开销和减少Cache命中时间。
15、减少流水线处理分支暂停时钟周期数的途径包括尽早判断分支转移是否成功和尽早计算出分支成功转移的PC值。
二、选择题(1—15题,每题1分,共15分)1、下面的指令中, A 不属于RISC处理器指令集。
A.ADD R4,[1000] B.LD R3,(R4) C.SUB R4,R3 D.SD 0(R3),R42. 在其它部件性能保持不变的情况下,对CPU性能的不断改进并没有获得期望的结果,这主要是受到了 A 的影响。

计算机系统结构试题及答案一、选择题(50分,每题2分,正确答案可能不只一个,可单选或复选)1.(CPU周期、机器周期)是内存读取一条指令字的最短时间。
2.(多线程、多核)技术体现了计算机并行处理中的空间并行。
3.(冯•诺伊曼、存储程序)体系结构的计算机把程序及其操作数据一同存储在存储器里。
4.(计算机体系结构)是机器语言程序员所看到的传统机器级所具有的属性,其实质是确定计算机系统中软硬件的界面。
5.(控制器)的基本任务是按照程序所排的指令序列,从存储器取出指令操作码到控制器中,对指令操作码译码分析,执行指令操作。
6.(流水线)技术体现了计算机并行处理中的时间并行。
7.(数据流)是执行周期中从内存流向运算器的信息流。
8.(指令周期)是取出并执行一条指令的时间。
9.1958年开始出现的第二代计算机,使用(晶体管)作为电子器件。
10.1960年代中期开始出现的第三代计算机,使用(小规模集成电路、中规模集成电路)作为电子器件。
11.1970年代开始出现的第四代计算机,使用(大规模集成电路、超大规模集成电路)作为电子器件。
12.Cache存储器在产生替换时,可以采用以下替换算法:(LFU算法、LRU算法、随机替换)。
13.Cache的功能由(硬件)实现,因而对程序员是透明的。
14.Cache是介于CPU和(主存、内存)之间的小容量存储器,能高速地向CPU提供指令和数据,从而加快程序的执行速度。
15.Cache由高速的(SRAM)组成。
16.CPU的基本功能包括(程序控制、操作控制、时间控制、数据加工)。
17.CPU的控制方式通常分为:(同步控制方式、异步控制方式、联合控制方式)反映了时序信号的定时方式。
18.CPU的联合控制方式的设计思想是:(在功能部件内部采用同步控制方式、在功能部件之间采用异步控制方式、在硬件实现允许的情况下,尽可能多地采用异步控制方式)。
19.CPU的同步控制方式有时又称为(固定时序控制方式、无应答控制方式)。
1、简述:1)计算机体系结构研究的目的;2)计算机系统中并行性的层次划分。
目的是:研究计算机体系结构的目的是提高计算机系统的性能。
所谓并行性(parallelism)是指在同一时刻或是同一时间间隔内完成两种或两种以上性质相同或不相同的工作。
只要时间上互相重叠,就存在并行性。
从执行程序的角度看,并行性等级从低到高可分为:(1) 指令内部并行:指令内部的微操作之间的并行。
(2) 指令级并行:并行执行两条或多条指令。
(3) 任务级或过程级并行:并行执行两个或多个过程或任务(程序段)。
(4) 作业或程序级并行:在多个作业或程序间的并行。
从处理数据的角度,并行性等级从低到高可以分为:(1) 字串位串:同时只对一个字的一位进行处理。
(2) 字串位并:同时对一个字的全部位进行处理。
(3) 字并位串:同时对许多字的同一位(称位片)进行处理。
(4) 全并行:同时对许多字的全部或部分位进行处理。
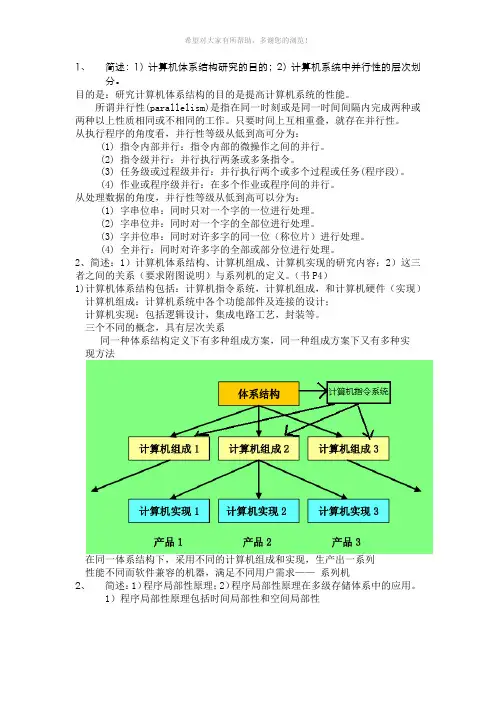
2、简述:1)计算机体系结构、计算机组成、计算机实现的研究内容;2)这三者之间的关系(要求附图说明)与系列机的定义。
(书P4)1)计算机体系结构包括:计算机指令系统,计算机组成,和计算机硬件(实现)计算机组成:计算机系统中各个功能部件及连接的设计;计算机实现:包括逻辑设计,集成电路工艺,封装等。
三个不同的概念,具有层次关系同一种体系结构定义下有多种组成方案,同一种组成方案下又有多种实现方法在同一体系结构下,采用不同的计算机组成和实现,生产出一系列性能不同而软件兼容的机器,满足不同用户需求——系列机2、简述:1)程序局部性原理;2)程序局部性原理在多级存储体系中的应用。
1)程序局部性原理包括时间局部性和空间局部性时间局部性:如果被访问过的存储器地址在较短时间内被再次访问,则程序具有良好的时间局部性。
在一定的时间内,重复访问同一个地址的次数越多,时间局部性越好。
空间局部性:如果程序访问某个存储器地址后,又在较短时间内访问临近的存储器地址,则程序具有良好的空间局部性。

体系测试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 体系结构中,以下哪一项不是基本构件?A. 处理器B. 总线C. 存储器D. 打印机2. 在计算机体系结构中,下列哪个选项是衡量性能的关键指标?A. 内存大小B. CPU频率C. 硬盘容量D. 显示器分辨率3. 以下哪个不是计算机体系结构的分类?A. 冯·诺依曼体系结构B. 哈佛体系结构C. 网络体系结构D. RISC体系结构4. 计算机体系结构中的流水线技术主要用于:A. 提高内存访问速度B. 减少数据传输延迟C. 提高指令执行效率D. 增强图形处理能力5. 以下哪个不是计算机体系结构中的并行技术?A. 指令级并行B. 数据级并行C. 线程级并行D. 磁盘阵列6. 在计算机体系结构中,缓存的目的是:A. 存储操作系统B. 存储临时文件C. 减少CPU与内存之间的速度差异D. 存储用户数据7. 以下哪个是衡量计算机体系结构性能的指标?A. 像素B. 分辨率C. 时钟频率D. 硬盘转速8. 计算机体系结构中的多核处理器技术主要用于:A. 减少能耗B. 提高计算速度C. 增加存储容量D. 改善图形显示9. 以下哪个是计算机体系结构中的虚拟化技术?A. 多任务处理B. 多线程处理C. 多核处理D. 虚拟内存10. 在计算机体系结构中,以下哪个技术可以提高系统的可靠性?A. 冗余设计B. 电源管理C. 热插拔技术D. 网络通信答案:1.D 2.B 3.C 4.C 5.D 6.C 7.C 8.B 9.D 10.A二、填空题(每空1分,共10分)1. 计算机体系结构中的______是指将指令和数据分开存储和处理。
2. 计算机体系结构中的______技术可以提高指令的执行速度。
3. 计算机体系结构中的______技术允许多个指令在不同的阶段同时执行。
4. 计算机体系结构中的______是指使用多个处理器来提高计算能力。
5. 计算机体系结构中的______是指通过软件来模拟硬件的功能。

计算机系统结构试题及答案⼤全计算机系统结构试题模拟试卷(有答案)⼀、名词解释1.系统结构:是对计算机系统中各机器级之间界⾯的划分和定义,以及对各级界⾯上、下的功能进⾏分配。
2.SIMD:单指令流多数据流计算机系统。
3.资源共享4.Cache:⾼速缓冲存储器5.模拟:是对真实事物或者过程的虚拟⼆、选择1.Cache是介于CPU和( C )之间的⼩容量存储器,能⾼速地向CPU提供指令和数据,从⽽加快程序的执⾏速度。
A.寄存器B.DRAMC.主存D.硬盘2.并⾏性开发的途径为时间重叠、资源共享和( C )等。
A.时间并⾏B.资源分布C.资源重复D.时间并发3.冯?诺依曼型计算机的设计思想是( C )。
A.存储数据并按地址顺序执⾏B.存储程序并按地址逆序执⾏C.存储程序并按地址顺序执⾏D.存储程序并乱序执⾏4.在计算机系统的层次结构中,属于硬件级的是( D )。
A.应⽤语⾔级B.⾼级语⾔级C.汇编语⾔级D.机器语⾔级5.消除流⽔线性能瓶颈的⽅法:瓶颈段细分和( B )。
A.瓶颈段串联B.瓶颈段并联C.瓶颈段拆分D.瓶颈段流⽔三、简答1.试述现代计算机系统的多级层次结构。
2.试述RISC设计的基本原则和采⽤的技术。
3.试述全相联映像与直接映像的含义及区别。
直接映像: 指主存的⼀个字块只能映像到Cache的⼀个准确确定的字块中。
直接映象是⼀种最简单的地址映像⽅式,它的地址变换速度快,⽽且不涉及其他两种映像⽅式中的替换策略问题。
但是这种⽅式的块冲突概率较⾼,当称序往返访问两个相互冲突的块中的数据时,Cache的命中率将急剧下降,因为这时即使Cache中有其他空闲块,也因为固定的地址映像关系⽽⽆法应⽤。
全相联映像:指主存的⼀个字块可以映像到整个Cache的任何⼀个字块中。
这种⽅式只有当Cache中的块全部装满后才会出现块冲突,所以块冲突的概率低,可达到很⾼的Cache命中率;但实现很复杂。
当访问⼀个块中的数据时,块地址要与Cache块表中的所有地址标记进⾏⽐较已确定是否命中。

一.名词解释计算机系统结构:传统机器程序员所看到的计算机属性,即概念性结构与功能特性。
在计算机技术中,把这种本来存在的事物或属性,但从某种角度看又好像不存在的概念称为透明性。
系列机:由同一厂家生产的具有相同系统结构、但具有不同组成和实现的一系列不同型号的计算机。
同构型多处理机系统:由多个同类型或至少担负同等功能的处理机组成,它们同时处理同一作业中能并行执行的多个任务。
堆栈型机器:CPU 中存储操作数的单元是堆栈的机器。
累加器型机器:CPU 中存储操作数的单元是累加器的机器。
通用寄存器型机器:CPU 中存储操作数的单元是通用寄存器的机器。
数据相关:考虑两条指令i和j,i在j的前面,如果下述条件之一成立,则称指令j与指令i数据相关:(1)指令j使用指令i产生的结果;(2)指令j与指令k数据相关,而指令k又与指令i数据相关。
定向:用来解决写后读冲突的。
在发生写后读相关的情况下,在计算结果尚未出来之前,后面等待使用该结果的指令并不见得是马上就要用该结果。
如果能够将该计算结果从其产生的地方直接送到其它指令需要它的地方,那么就可以避免停顿。
向量处理机:指令级并行:简称ILP。
是指指令之间存在的一种并行性,利用它,计算机可以并行执行两条或两条以上的指令。
指令的动态调度:是指在保持数据流和异常行为的情况下,通过硬件对指令执行顺序进行重新安排,以提高流水线的利用率且减少停顿现象。
是由硬件在程序实际运行时实施的。
指令的静态调度:是指依靠编译器对代码进行静态调度,以减少相关和冲突。
它不是在程序执行的过程中、而是在编译期间进行代码调度和优化的。
失效率:CPU访存时,在一级存储器中找不到所需信息的概率。
失效开销:CPU向二级存储器发出访问请求到把这个数据调入一级存储器所需的时间。
强制性失效:当第一次访问一个块时,该块不在Cache中,需要从下一级存储器中调入Cache,这就是强制性失效。
容量失效:如果程序在执行时,所需要的块不能全部调入Cache中,则当某些块被替换后又重新被访问,就会产生失效,这种失效就称作容量失效。
可编辑修改精选全文完整版《计算机系统结构》练习题一一、单项选择题1.页式虚拟存储器的地址变换对于 D 是透明的.A. 操作系统设计者B. 任何程序员C. 系统结构设计者D. 应用程序员2.以下各类中断中,属于自愿中断的是 C .A. 外部中断B. I/O中断C. 执行“访管”指令D. 机器校验中断3. 高速外部设备磁盘机适合连接于 C .4. 页式虚拟存储器页表的作用是 A .A. 反映虚页在主存的存储情况B. 仅反映虚页是否调入主存C. 反映主存实页与Cache的对应关系D. 反映虚页在辅存的存储情况5.软件和硬件的功能在逻辑上是 C 的.D.软件优于固件6. 计算机中最优化的操作码编码方法是 D .码码C.扩展操作码 D.哈夫曼编码7. 从计算机系统执行程序的角度看,并行性等级由低到高分为四级 A .A.指令内部——指令之间——进程之间——程序之间B.指令之间——指令内部——进程之间——程序之间C.进程之间——指令之间——指令内部——程序之间D.程序之间——进程之间——指令之间——指令内部8. 计算机系统多级层次结构中,操作系统机器级的直接上层是 D .A.传统机器级B.高级语言机器C.应用语言机器级D.汇编语言机器级9.全相联地址映像是指 A .A.任何虚页都可装入主存中任何实页的位置B.一个虚页只装进固定的主存实页位置C.组之间是固定的,而组内任何虚页可以装入任何实页位置D.组间可任意装入,组内是固定装入10.对于同一系列机,必须保证软件能够 C .A.向前兼容,并向上兼容B.向前兼容,并向下兼容C.向后兼容,力争向上兼容D.向后兼容,力争向下兼容11.设有16个处理单元的并行处理机系统, 采用共享主存的方式. 若同时存取16个数据, 为避免存储器访问冲突, 共享主存的多体数量应该为 C 才合理.A. 15B. 16C. 17D. 1912. 软件兼容的根本特征是 C .A. 向前兼容B. 向后兼容C. 向上兼容D. 向下兼容13.在下列机器中,能够实现软件兼容的机器是 B .A. 完全不同种类的机型B. 系统结构相同的机器C. 宿主机和目标机D. 虚拟机14.输入输出系统硬件的功能对 C 是透明的。
计算机体系结构试题及答案【篇一:计算机体系结构习题(含答案)】1、尾数用补码、小数表示,阶码用移码、整数表示,尾数字长p=6(不包括符号位),阶码字长q=6(不包括符号位),为数基值rm=16,阶码基值re=2。
对于规格化浮点数,用十进制表达式写出如下数据(对于前11项,还要写出16进值编码)。
(1)最大尾数(8)最小正数(2)最小正尾数(9)最大负数(3)最小尾数(10)最小负数(4)最大负尾数(11)浮点零(5)最大阶码(12)表数精度(6)最小阶码(13)表数效率(7)最大正数(14)能表示的规格化浮点数个数2.一台计算机系统要求浮点数的精度不低于10-7.2,表数范围正数不小于1038,且正、负数对称。
尾数用原码、纯小数表示,阶码用移码、整数表示。
(1) 设计这种浮点数的格式(2) 计算(1)所设计浮点数格式实际上能够表示的最大正数、最大负数、表数精度和表数效率。
3.某处理机要求浮点数在正数区的积累误差不大于2-p-1 ,其中,p是浮点数的尾数长度。
(1) 选择合适的舍入方法。
(2) 确定警戒位位数。
(3) 计算在正数区的误差范围。
4.假设有a和b两种不同类型的处理机,a处理机中的数据不带标志符,其指令字长和数据字长均为32位。
b处理机的数据带有标志符,每个数据的字长增加至36位,其中有4位是标志符,它的指令数由最多256条减少到不到64条。
如果每执行一条指令平均要访问两个操作数,每个存放在存储器中的操作数平均要被访问8次。
对于一个由1000条指令组成的程序,分别计算这个程序在a处理机和b处理机中所占用的存储空间大小(包括指令和数据),从中得到什么启发?5.一台模型机共有7条指令,各指令的使用频率分别为35%,25%,20%,10%,5%,3%和2%,有8个通用数据寄存器,2个变址寄存器。
(1) 要求操作码的平均长度最短,请设计操作码的编码,并计算所设计操作码的平均长度。
6.某处理机的指令字长为16位,有双地址指令、单地址指令和零地址指令3类,并假设每个地址字段的长度均为6位。
填空题1.从2002年以来,计算机性能的年增长率下降到了约30%。
其主要原因是:①大功耗问题;②可以进一步有效地开发的指令级并行性已经很少;③存储器访问速度的提高缓慢。
2. 可移植性是指一个软件可以不经修改或者只需少量修改就可以由一台计算机移植到另一台计算机上运行。
实现可移植性的常用方法有3种:系列机,模拟和仿真,统一高级语言。
2.通用寄存器型指令集结构计算机在灵活性和提高性能方面有明显的优势。
主要体现在①寄存器的访问速度比存储器快;②对编译器而言,能更加容易有效地分配和使用寄存器;③寄存器可以用来存放变量。
3.MIPS的数据寻址方式只有立即数寻址和偏移量寻址。
4.向量处理机的结构由所采用的向量处理方式决定。
有两种典型的结构;存储器-存储器型结构和寄存器-寄存器型结构。
5.Cache-主存层次的工作由硬件实现,对系统程序员是透明的。
6.降低Cache不命中率最直接的方法是增加Cache的容量。
不过,这种方法不但会增加成本,而且还可能增加命中时间,这种方法在片外Cache中用得比较多。
7.大多数磁盘阵列的组成可以由以下两个特征来区分:数据交叉存放的粒度、冗余数据的计算方法以及在磁盘阵列中的存放方式。
8.时延和带宽是用来评估互连网络性能的两个基本指标。
时延包括通信时延和网络时延。
9.计算机系统可分为SISD、SIMD、MISD和MIMD四类,许多早期并行处理机是SIMD计算机,近年来,MIMD已经成为通用多处理机系统结构的选择。
这是因为MIMD具有灵活性,并且MIMD能充分利用现有微处理器的性价比优势。
判断题1.从计算机语言的角度,系统结构把计算机系统按功能划分成多级层次结构,其中,第2级是操作系统虚拟机,第3级是汇编语言虚拟机。
(错)2.计算机系统中提高并行性的3种途径中,资源重复是在并行性概念中引入时间因素,加快硬件周转而赢得时间。
(错)3.指令集结构中采用多种寻址方式可能会增加实现的复杂度和使用这些寻址方式的指令的CPI。
计算机体系结构试题及答案(Computer architecture questions andanswers)Questions and answers of computer architecture1, benefiting from the development of high performance computer: (1) the development of circuit technology; (2) the development of computer architecture technology.2, structure: computer systems can be classified by function of language as a multilevel structure, each layer in different language features. Sixth: the application of virtual machine language - > fifth: high-level language virtual machine assembly language - > Fourth: - > Third: virtual machine operating system virtual machine - level second: machine language (traditional machine level) - > Level 1: micro machine level program.3, computer architecture: see computer programmer attribute, namely the general structure and functional properties.4, transparency: in computer technology, the things or properties already exists, the concept from a point of view and have called transparency.5, the proposed architecture Amdahl attribute refers to the computer machine language level programmers see.The essence of 3 6, a classic computer architecture concept is to determine the computer system hardware and software interface, which is the instruction set design, above theinterface by software function realization, interface by hardware and firmware functions to achieve.7, computer organization is the logic of the computer system; computer is a physical computer system to achieve.The difference and connection between the 8, computer architecture, computer organization, computer?Answer: a system structure can have a variety of components, a component can have a variety of physical implementation, including system structure research on organization and implementation.9, a series of machine: refers to a system of the same structure but with different organization and implementation of a series of different types of machines.10, software compatibility: the same software can be run without change on the machine system of the same structure, and the results they get the same, the only difference is the different running time.11, compatible machine: different manufacturers, has the same computer architectures.12, backward compatibility is the basic characteristics of software compatibility, is the fundamental characteristics of series machine.13, in the field of computer market can be divided into threemajor areas: servers, desktop systems, embedded computing.14, Moore: integrated circuit density approximately doubled every two years.Technology based analysis of 15 quantitative performance evaluation: (1) (a) response time: from the beginning to the end of the time between events; all the time spent on the computer to complete a task. (b): the complete flow in unit time and workload. (c) x, y assumed two computers; X faster than y means: for a given task, the response time of X is less than y. The performance of X is several times the Y refers to the response time of X / y = n response time, response time and performance is inversely proportional to.16, the probability of event priority principle: (basic idea) for the probability of events (the most common event), giving priority to use it right and resource rights, to obtain the global optimal results.17, Amdahl Law: accelerate the execution speed of a component system performance obtained speedup, the importance is limited by the components in the system of. System acceleration ratio = total execution time (improved) / total execution time (improved) =......18, Amdahl law corollary: if only for a part of the computer in the performance improvement is more improved, the effect of the system. If only a part of the whole task is optimized, so much the acceleration ratio is not greater than 1 / (1- improvement ratio).19, the performance of CPU: Cpu time = total number of clock cycles / clock frequency Cpi = total number of clock cycles (IC / CPI: the number of clock cycles per instruction; the average IC implementation process: the number of instructions.)The performance of Cpu formula: total CPU time = CPI * IC / CPI clock frequency which reflects the computer architecture and computer technology, computer instruction set; Ic reflects the structure and technology of computer programming instruction set; clock frequency: reflect the implementation of computer technology, production technology and computer organization.20, parallelism refers to at the same time or two or more than two kinds of properties of the same or different work in the same time interval.The second chapter1, according to the CPU internal storage unit type of instruction set architecture for classification, can be divided into the stack based instruction set architecture, instruction set architecture and accumulator type general register type instruction set architecture.2, general register type instruction set machine is further subdivided into 3 types:Register to register type (R-R), register memory type (R-M), a memory register.3, addressing: (1) register addressing: example: ADD R4 R3, meaning Regs[R4]<-Regs[R4]+Regs[R3](2) immediate values: example: ADD R4, addressing 3 meanings: Regs[R4]<-Regs[R4]+3(3): offset cases: ADD R4, 100 (R1) meaning:Regs[R4]+Mem[100+Regs[R1]](4) register indirect addressing: example: ADD R4 (R1) meaning: Regs[R4]<-Regs[R4]+Mem[Regs[R1]](5) index addressing: example: ADD R3 (R1+R2) meaning:Regs[R3]<-Regs[R3]+Mem[Regs[R1]+Regs[R2]](6) direct addressing or absolute addressing: for example: ADD R1, (1001): Regs[R1]<-Regs[R1]+Mem[1001] meaning(7) memory indirect addressing: example: ADD R1, a (R3) meaning: Regs[R1]<-Regs[R1]+Mem[Mem[Regs[R3]]](8) the increment addressing: example: ADD R1 (R2) + meaning: Regs[R1]<-Regs[R1]+Mem[Regs(9) decrement addressing(10) zoom addressingThe function of structure design of the instruction set, 4:The instruction set classification structure in operationThe type of operation example(1) arithmetic and logical operations on integer arithmetic and logic operations: addition, subtraction, and, or etc.(2) data transmission LOAD/STORE(3) control branch, jump, procedure call and return, trap(4) operating system calls, virtual memory management.(5) floating point addition and subtraction operation(6) is converted to decimal decimal decimal decimal add, multiply, to characters(7) string string comparison, mobile(8) the pixel operation, compression operation5, complex instruction machine (CISC): refers to strengthen the instruction function, realize the function of software to hardware design, computer system to realize the instruction set architecture based on.The shortcomings of the CISC instruction set:(1) in the command system, the frequency of use of all kinds of orders is different.(2) the CISC instruction set architecture complexity brings complexity of computer architecture, which not only increases the development time and cost, but also easy to cause the design error.(3) the CISC instruction set architecture complexity brings great burden to the VLSI design, is not conducive to the monolithic integration.(4) in the CISC instruction set architecture, many complex instructions require very complex operation, so slow.(5) in the CISC instruction set architecture, because of the directive function is not balanced, not conducive to the use of computer architecture technology (such as advanced water technology) to improve the performance of the system.In 1980s 6, reduced instruction set computer developed: its purpose is to reduce the instruction set of the complexity of the structure as far as possible, in order to simplify the realization of the goal of improving performance, but also in today's instruction set is a main trend of the structure and function of design.Follow the design principles:(1) choose to use the highest frequency of instruction, and added some of the most useful instructions.(2) the function of each instruction is as simple as possible, and completed in one machine cycle.(3) all have the same length as the instruction.(4) only the LOAD and STORE operating instructions to access memory and other instruction operation is performed in the register between.(5) in a simple and effective way to support advanced language.7 operand types: integer, decimal, floating point (point), characters, strings, vectors, stack etc..There are two ways to express 8, operand types: (1) specified by the operation code encoding. (2) data can be a mark by the hardware to explain the type of the operand specified by these tags, so as to choose the appropriate operation.9, the operand type size: byte (8), the word (16b), the word (32b), double word (64b)The third chapter1, pipeline technology: refers to a repeat of the timing process is decomposed into several sub processes, and each process can be effective in its special function with other processes executing at the same time.2, pipeline classification: (1) according to the function of the number of points: single function pipeline, multifunctional pipeline;(2) according to the connection between the same time segments to static and dynamic pipeline pipeline(3) according to the line level: component level pipeline (operation line), pipelined processor (instruction pipelining), inter processor pipeline (macropipeline)(4) according to whether there is water between each section of a feedback loop: linear and nonlinear pipeline pipeline(5) according to the data representation: scalar processor, vector processor3, the first processor controller structure comprises three independent controllers and four buffer stack. The three controller: memory controller, controller, controller operation instruction. Four: the first instruction buffer buffer stack stack, linear buffer stack, stack current readings, then write the number of stack.4, the throughput is the number: the number of tasks or output per unit time of the pipeline. TP = n / TkThe actual throughput rate is less than the maximum throughput of Tk = (k+n-1) t5, speedup: refers to the speed of the line and the function of non line speed ratio (s);Efficiency: refers to the utilization rate of pipeline equipment (E).6, if the line segment is equal to the time: throughput rate: TP=n/ (k+n-1) t TPmax=1/ tIf each execution time is not equal, complete several tasks: TP=n (sigma / Ti + (n-1) max (delta T1, Delta t2... Delta TK)7, the speedup and efficiency of the relationship: E = s/m or S = mE8, efficiency and throughput of the relationship: E = TP t0 TP = E/ or T11, efficiency: K E = n a task flow segment occupied area of the total space / time zones = T0 / K Tk?E = n/ (k+n-1) S = k? N / TP / (k+n-1) = n (k+n-1) t12, single function pipeline stack: refers to only perform one fixed function pipeline stack.13, multi functional water: water each stack stack to achieve different functions through different connections.14, nonlinear pipeline scheduling task: to find a minimum cycle, according to a new task to the input line cycle, each function section line are not in conflict, and the pipeline throughput and maximum efficiency.15, nonlinear pipeline: between some water section of feedback loop or feed-forward loop.16, start distance: continuous input even intervals between tasks.17, pipeline conflict: several tasks competing for the same water section.18, forbidden vector: distance between sets of appointments each row in the table of any of the two "x".19, conflict vector: C = (Cm? Cm-1?... C1? C2? M) which allowed maximum value in the vector20, the relevant data: in the process of execution of the instructions, if the instructions used, the number of variables, such as the operation is in front of the results of the implementation of the relevant instructions, called data.21, control: caused by conditional branch instructions, rotor program instructions, the relevant interrupt.22, three kinds of data: limit write, read after write, write.The fourth chapter1, ILP: when there are correlation between instructions in the pipeline, they can overlap parallel execution, the potential parallelism is called instruction level parallelism exists in this sequence of instructions.2, in a variety of technical development loop level parallelismin the most basic techniques are: instruction scheduling, loop unrolling technique and technical change.The fifth chapter (storage system)1, the definition method of memory storage system: two or more than two speed, capacity and price vary with hardware, software or hardware and software combination connected into a storage system. And the memory system is transparent to application programmers, and to the application programmer, it is a memory, the memory of the memory close to the speed of the fastest, the storage capacity and the storage capacity of the largest equal unit capacity price close to the lowest memory.2, the storage system is divided into two categories: (1): Cache storage system composed of Cache and main memory, the purpose is to improve the speed of memory. (2) virtual storage system consists of a main memory and hard disk, to expand memory capacity.3, the price of storage system: C = (C1S1+C2S2) / (S1+S2)4, the storage system speed: Representation: access cycle, access cycle, storage period, access time, etc..5, the hit rate of definition: probability in M1 memory access toU = N1 / (N1+N2) N1 of M1 memory access times, N2 is on the M2 memory access times.6, the efficiency of access:T1 1E = T1/T = = = f (U, T2/T1)U? T1+ (1-u) T2 u+ (1-u) T2/T1?7, using prefetching to improve the hit rate (method).Do not hit, a block of data in a plurality of adjacent M2 memory units taken out into the M1 memory.U (u+n-1 / N) = 'U' is the pre shooting technique after u is the original hit rate;The product of n as the data block size and the number of data reuse.8, accelerate the internal address transformation method: (1) the table of contents: with a small capacity high speed memory storing the page table; (2): fast and slow speed of table table table to form a two level storage system; (3): the hash function associative access into the access address access.9, the page replacement algorithm: (1) random algorithm (RAND);(2) FIFO algorithm (FIFO); (3) least recently used (LFV); (4) LRU (LRV); (5) the optimal replacement algorithm (OPT).10, "bump" phenomenon: a page is just out of the main memory, but also to be transferred.11, the stack type replacement algorithm: for an arbitrary program page address stream for the two main memory page number distribution, a memory allocated m page and n a memory page, and M = n. If at any time t, main memory page number set Bt satisfy the relation: Bt (m) = Bt (n) is a type of this kind of algorithm stack replacement algorithm.12, Cache address mapping method: (1) fully associative mapping;(2) direct mapping; (3) set associative mapping;(4) choose a set associative mapping mapping section (5).13, Cache memory replacement algorithm: (1) rotation method (2) LRV algorithm (3) comparing (4) stack method.The consistency of Cache 14, single processor:Direct method: [including write write through method, CPU writes data to Cache, while the page is written to main memory.And write back: "conflict modify method, CPU data into Cache, do not write memory, only when the replacement when the modified Cache block write back to main memory.Comparing the advantages and disadvantages of the two:(1) reliability: write direct method is better than the write back.(2) the amount of memory and communication, write back and writeless than direct method.(3) the complexity of control, direct write back write is simple.(4) the hardware implementation cost is written back to the write through law.The consistency of 15, multiprocessor: (1) the directory protocol (2) and listen to the agreementThe sixth chapter (input / output system)1, measure the performance index of I/O system mainly has the response time and reliability.Data transmission, 2 disk external transfer rate and internal transfer rate.3, the external transmission rate (burst data transmission rate): computer read from the cache data into the hard disk by disk interface, to the corresponding speed controller.4, internal transfer rate (sustained transfer rate): hard disk data from disk read, to buffer memory on the hard disk speed.5, reliable performance parameters reflecting storage peripherals are reliability, availability and credibility.6, reliability measure: mtbf.7, availability metrics: mean time between failure.8, bus: bus communication link between each subsystem shared, the two has the advantages of low cost and diversity.The main disadvantage of the 9 bus: it has exclusive use, causing the bottleneck equipment information exchange, thus limiting the total throughput of I/O system.10, split transaction bus: there is a plurality of devices, available through the packaging technology to improve the bus bandwidth, so that each I/O operation will not have to occupy the bus in the transmission process, the basic idea of the bus transaction is divided into two parts of requests and responses, such as the bus idle time interval to request and response in the a bus transaction between other bus transaction is used. (also known as water bus, bus, bus suspension packet switching)11, the control of external equipment input / output mode is divided into: direct transfer procedures, query, interrupt, DMA, channel mode.Addressing mode 12, I/O equipment: (1) memory mapped I/O or unified addressing (2) I/O addressing individual equipment13, channel: to perform limited I/O instruction, and can be a plurality of peripheral devices share a small dedicated DMA processor.14, channel function: (1) received from the CPU I/O command, and according to the peripheral equipment and the channelinstruction requires the selection of the specified connection.(2) CPU channel organization channel program, remove channel instructions from the main memory, decode the channel command, and issued a command to the device controller is selected according to the needs of. (3) as the main memory and peripheral assembly and disassembly information, data transmission and memory I/O control equipment and provide a transmission path, indicating the data memory address and send byte number. (4) specify the transfer at the end of the operation to be carried out. (5) check the peripheral equipment working state, normal or fault.(6) complete the format conversion required in data transmission process.15, types of channels: (1) channel multiplexer (2) selects the channel (3) multi channel array.The working process, 16 channels: (1) using SVCI into management program in the user program by CPU, through the management procedures to organize a channel program, and start the channel. (2) channel processor implementation of CPU for which the organization's channel program, complete the assigned work data I/O. Channel processor execute channel program was performed with the CPU user program in parallel.(3) channel program after the end to the CPU interrupt request, CPU responding to an interrupt request after second times to enter the operating system, call management program of the I/O interrupt request processing.The seventh chapter (multiprocessor)1, Cache coherence protocol: (1) the directory protocol and listen to the agreement; (2) laterally divided into: write Invalid Protocol and write update protocol; (3) longitudinally divided into single treatment protocol and single data stream protocol.2, the classification of parallel computer architecture: single instruction single data stream (SISD), single instruction multiple data stream (SIMD) and multiple instruction single data stream (MISD) and multiple instruction multiple data stream (MIMD).3, the directory protocol is divided into three categories: full map directory, the directory, the directory chain co..4, the chain Directory: by maintaining a directory pointer chain to track shared data copy.Thought: when P1 read x memory, X sent to cachel, a chain and write cachel end pointer CT also holds a pointer to a cachel in memory, P2 to read x, memory holds a pointer to a cachel2, a processor need to write x, he must be along the whole a directory even send a data information in the received signal to answer the invincible, all processors, memory to allow the processor to write rightThe cachel data block in need of replacement, to delete the cache directory from the chain, there are solutions;(1) the cachei+1 pointer to cachei+1, store the new data blockin cachel (2) cachel and cachel in the chain seat all subsequent units in X is invalid (3) using two-way chain, when replacing the no longer need to traverse the entire chain, but the pointer has doubled, agreement more perfectAdvantages: B does not limit the sharing of copy number data blocks while maintaining scalability, pointer length has the number of processors on the relation between growth, the number of processors and the number of pointers for each block of data is independent of the cacheDisadvantages: complex chain directory in Chengdu more than two directory5 definition: Internet; is symmetric systems or distributed system nodes may like processor, memory module or other devices, they exchange information through the Internet, in the topology, the Internet provides a set of interconnected or image as input and output between two groups of nodes6 (1) the number of nodes is called the network scale(2) the number of edges and nodes interconnected to the maximum value of the node is called the network diameter(3) any network nodes even the maximum length of the shortest path is called the network diameter(4) equal width (b) in the network into a two phase digestion method, the minimum number of edges cut along the road is called channel bisection width(5): refers to the designation of the routing path selection in network communication7 function: if the Internet Interconnection Network N a end and N end respectively with the integer 0, 1,...... .N algebra, is said to work with the interconnection function number and number of symmetric relations such asSaid method 8 interconnection network(1) the interconnection function representation (2) graphical representation (3) input and output the corresponding representation9 common data routing (or interconnection function) function:(1) the replacement cycle (2) (3) (4) uniform shuffle hypercube routing function (5) broadcasting and communication。
计算机体系面试题及答案一、选择题1. 在计算机体系结构中,冯·诺依曼体系结构的主要特点是:A. 程序存储B. 程序控制C. 程序和数据分开存储D. 以上都是答案:D2. 以下哪个不是计算机体系结构的分类?A. 单片机B. 微处理器C. 微控制器D. 操作系统答案:D3. 计算机的指令周期包括以下哪些阶段?A. 取指B. 译码C. 执行D. 所有以上答案:D二、填空题1. 计算机体系结构中,______是指计算机硬件和软件的组织和功能特性。
答案:体系结构2. 在计算机体系结构中,______是指计算机硬件的物理实现,包括CPU、存储器、输入输出设备等。
答案:硬件3. 计算机体系结构中的______是指计算机的逻辑功能和操作方式,它决定了计算机如何执行指令和处理数据。
答案:软件三、简答题1. 简述计算机体系结构的发展历程。
答案:计算机体系结构的发展历程可以分为几个阶段:最初的电子管计算机,随后的晶体管计算机,再到集成电路计算机,以及现在的大规模集成电路计算机。
每个阶段都伴随着计算速度的显著提升和体积的缩小。
2. 什么是并行计算机体系结构?它有哪些优点?答案:并行计算机体系结构是指在单个计算机系统中使用多个处理单元(如CPU或GPU)来同时执行多个任务或同一任务的不同部分。
它的优点包括提高计算速度、增强处理能力以及更有效地利用资源。
四、论述题1. 论述现代计算机体系结构面临的主要挑战及其可能的解决方案。
答案:现代计算机体系结构面临的主要挑战包括能源效率、散热问题、性能瓶颈、安全性和可扩展性。
可能的解决方案包括使用更高效的处理器架构、采用先进的散热技术、优化软件以提高并行处理能力、加强安全措施以及设计可扩展的系统架构。
五、案例分析题1. 某公司计划开发一款新的高性能计算机系统,要求能够处理大量数据并具备高扩展性。
请分析该公司在设计计算机体系结构时应考虑的因素。
答案:在设计新的高性能计算机系统时,公司应考虑以下因素:选择合适的处理器架构以满足性能需求;设计高效的内存管理和存储系统以处理大量数据;确保系统的可扩展性,以便未来能够添加更多的处理单元或存储资源;考虑能源效率和散热问题,以降低运行成本并确保系统的稳定运行;最后,还应考虑系统的安全性,以保护数据不被未授权访问。
计算机体系结构试题及答案1、计算机高性能发展受益于:(1) 电路技术的发展;(2) 计算机体系结构技术的发展。
2、层次结构:计算机系统可以按语言的功能划分为多级层次结构,每一层以不同的语言为特征。
第六级:应用语言虚拟机-> 第五级:高级语言虚拟机-> 第四级:汇编语言虚拟机-> 第三级:操作系统虚拟机->第二级:机器语言(传统机器级) -> 第一级:微程序机器级。
3、计算机体系结构:程序员所看到的计算机的属性,即概括性结构与功能特性。
4、透明性:在计算机技术中,对本来存在的事物或属性,从某一角度来看又好像不存在的概念称为透明性。
5、Amdahl 提出的体系结构是指机器语言级程序员所看见的计算机属性。
6、经典计算机体系结构概念的实质3是计算机系统中软、硬件界面的确定,也就是指令集的设计,该界面之上由软件的功能实现,界面之下由硬件和固件的功能来实现。
7、计算机组织是计算机系统的逻辑实现;计算机实现是计算机系统的物理实现。
8、计算机体系结构、计算机组织、计算机实现的区别和联系?答:一种体系结构可以有多种组成,一种组成可以有多种物理实现,体系结构包括对组织与实现的研究。
9、系列机:是指具有相同的体系结构但具有不同组织和实现的一系列不同型号的机器。
10、软件兼容:即同一个软件可以不加修改地运行于系统结构相同的各机器,而且它们所获得的结果一样,差别只在于运行时间的不同。
11、兼容机:不同厂家生产的、具有相同体系结构的计算机。
12、向后兼容是软件兼容的根本特征,也是系列机的根本特征。
13、当今计算机领域市场可划分为:服务器、桌面系统、嵌入式计算三大领域。
14、摩尔定律:集成电路密度大约每两年翻一番。
15、定量分析技术基础(1)性能的评测:(a)响应时间:从事件开始到结束之间的时间;计算机完成某一任务所花费的全部时间。
(b)流量:单位时间内所完成的工作量。
(c )假定两台计算机x 、y;x 比y 快意思为:对于给定任务,x 的响应时间比y少。
x的性能是y的几倍是指:响应时间x / 响应时间y = n ,响应时间与性能成反比。
16、大概率事件优先原则:(基本思想)对于大概率事件(最常见的事件),赋予它优先的处理权和资源使用权,以获得全局的最优结果。
17、Amdahl定律:加快某部件执行速度所获得的系统性能加速比,受限于该部件在系统中所占的重要性。
系统加速比= 总执行时间(改进前)/ 总执行时间(改进后)= ,,18、Amdahl定律推论:如果仅仅对计算机中的一部分做性能改进,则改进越多,系统获得的效果越小。
如果只针对整个任务的一部分进行优化,那么多获得的加速比不大于1 / (1- 可改进比例)。
19、cpu 性能:Cpu时间= 总时钟周期数/ 时钟频率Cpi =总时钟周期数/ ic (cpi :平均每条指令的时钟周期数;ic :执行过程当中的指令条数。
)Cpu性能公式:总cpu 时间= cpi × ic / 时钟频率其中:cpi 反映了计算机实现技术、计算机指令集的结构和计算机组织;Ic 反映了计算机指令集的结构和编程技术;时钟频率:反映了计算机实现技术,生产工艺和计算机组织。
20、并行性:是指在同一时刻或是同一时间间隔内完成两种或两种以上性质相同或不相同工作。
第二章1、根据cpu 内部存储单元类型对指令集结构进行分类,般可分为堆栈型指令集结构、累加器型指令集结构和通用寄存器型指令集结构。
2、通用寄存器型指令集机进一步细分为3种类型:寄存器-寄存器型(R-R)、寄存器-存储器型(R-M)、存储器-寄存器型。
3、寻址方式:(1)寄存器寻址:例:ADD R4, R3 含义:Regs[R4]<-Regs[R4]+Regs[R3](2)立即值寻址:例:ADD R4,#3含义:Regs[R4]<-Regs[R4]+3(3 )偏移寻址:例:ADD R4, 100(R1)含义:Regs[R4]+Mem[100+Regs[R1]](4 )寄存器间接寻址:例:ADD R4, (R1)含义:Regs[R4]<-Regs[R4]+Mem[Regs[R1]](5 )索引寻址:例:ADD R3, (R1+R2)含义:Regs[R3]<-Regs[R3]+Mem[Regs[R1]+Regs[R2]](6)直接寻址或绝对寻址:例:ADD R1, (1001)含义:Regs[R1]<-Regs[R1]+Mem[1001](7 )存储器间接寻址:例:ADD R1,a(R3)含义:Regs[R1]<-Regs[R1]+Mem[Mem[Regs[R3]]]8)自增寻址:例:ADDR 1, (R2)+ 含义:Regs[R1]<-Regs[R1]+Mem[Regs9)自减寻址10)缩放寻址4、指令集结构的功能设计:指令集结构中操作的分类操作类型(1)算术与逻辑运算算术和逻辑运算:加、减、与、或等(3)控制支、跳转、过程调用和返回、自陷等(4)系操作系统调用、虚拟存储器管理。
(5)浮点加、减等操作(6)十十进制加、十进制乘、十进制到字符的转换实例整数的(2)LOAD/STORE数据传(7 )字符串字符串移比较动、(8 )图形像素操作,压缩操作5、复杂指令机(CISC):是指强化指令功能,实现软件功能向硬件功能转移,基于这种指令集结构而设计实现的计算机系统。
CISC指令集存在的缺点:(1)在这种指令系统中,各种指令的使用频率相差悬殊。
(2)CISC 指令集结构的复杂性带来了计算机体系结构的复杂性,这不仅增加了研制时间和成本,而且还容易造成设计错误。
(3)CISC 指令集结构的复杂性给VLSI 设计带来了很大负担,不利于单片集成。
(4)在CISC指令集结构中,许多复杂指令需要很复杂的操作,因而运行速度慢。
(5)在CISC指令集结构中,由于各条指令功能的不均衡,不利于采用先进的计算机体系结构技术(如流水技术)来提高系统的性能6、20世纪80年代发展起来的精简指令集计算机:其目的是尽可能地降低指令集结构的复杂性,以达到简化实现,提高性能的目的,也是当今指令集结构功能设计的一个主要趋势。
其设计时遵循的原则:选取使用频率最高的指令,并补充一些最有用的指令。
(1)(2每条指令的功能尽可能简单,并在一个机器周期内完成。
)(3所有指令长度均相同。
)(4只有LOAD和STORE操作指令才访问存储器,其它指令)操作均在寄存器之间进行。
(5以简单有效的方式支持高级语言。
)7、操作数类型:整数(定点)、浮点、十进制、字符、字符串、向量、堆栈等。
8、操作数类型的表示有两种方法:(1)由操作码的编码指定。
(2)数据可以附上由硬件解释的标记,由这些标记指定操作数的类型,从而选择适当运算。
9、操作数类型大小有:字节(8)、半字(16b)、单字(32b)、双字(64b)第三章1、流水线技术:是指将一个重复的时序过程,分解为若干个子过程,而每一个子过程都可有效地在其专用功能段上与其它子过程同时执行。
2、流水线分类:(1)按功能的多少来分:单功能流水线、多功能流水线;(2)按同一时间内各段之间的连接方式来分:静态流水线、动态流水线(3)按流水线的级别来分:部件级流水线(运算操作流水线)、处理机级流水线(指令流水线)、处理机间流水线(宏流水线)(4)按各个流水段之间是否有反馈回路来分:线性流水线、非线性流水线(5)按数据表示分:标量流水处理机、向量流水处理机3、先行控制器处理机结构:包括三个独立的控制器和四个缓冲栈。
其中三个控制器为:存储控制器、指令控制器、运算控制器。
四个缓冲栈:先行指令缓冲栈、线性读数缓冲栈、现行操作栈,后行写数栈。
4、吞吐率:是指单位时间内流水线所完成的任务数或输出结果的数量。
TP = n / Tk实际吞吐率小于最大吞吐率Tk = (k+n-1) △t5、加速比:是指流水线的速度与等功能非流水线的速度之比( s);效率:是指流水线的设备利用率( E)。
6、若流水线各段的时间相等:吞吐率:TP=n/(k+n-1) △t TPmax=1/ △t若各段执行时间不相等时,完成几个任务:TP=n /( ∑ti + (n-1)max( △t1, △t2,△ tk)7、加速比和使用效率的关系:E = s/m 或S = mE8、效率和吞吐率的关系:E = TP △t0或TP = E/ △t11、效率:E = n个任务占用的时空区/ k个流水段的总的时空区= T0 / K ·TkE = n/(k+n-1) S = k · n /(k+n-1) TP = n / (k+n-1)△t12、单功能流水栈:是指只能完成一种固定功能的流水栈。
13、多功能流水栈:流水栈的各段通过不同连接实现不同功能。
14、非线性流水线调度:任务时要找出一个最小的循环周期,按照个周期向流水线输入新任务,流水线的各个功能段都不会发生冲突,而且流水线的吞吐率和效率最高15、非线性流水线:某些流水段之间有反馈回路或前馈回路。
16、启动距离:连续输入连个任务之间的时间间隔。
17、流水线冲突:几个任务争用同一个流水段。
18、禁止向量:预约表中每一行任意两个“ x”之间距离的集合。
19、冲突向量:C = (Cm·Cm-1·, · C2·C1)其中m时禁止向量中的最大值20、数据相关:在执行本条指令的过程中,如果用到的指令、操作数、变量等是前面指令的执行结果,这种相关称为数据相关。
21、控制相关:由条件分支指令、转子程序指令、中断等引起的相关。
22、三种数据相关:限度后写相关、先写后读相关、写写相关。
第四章1、指令级并行:当指令之间不存在相关时,它们在流水线中时可以重叠起来并行执行的,这种指令序列中存在的潜在并行性称为指令级并行。
2、在开发循环级并行的各种技术中,最基本的技术有:指令调度技术、循环展开技术和换名技术。
第五章(存储系统) 1、存储系统定义:两个或两个以上速度、容量和价格各不相同的存储器用硬件、软件或软件与硬件相结合的方法连接起来成为一个存储系统。
这个存储器系统对应用程序员时透明的,并且,以应用程序员看,它是一个存储器,这个存储器的速度接近最快的那个存储器,存储容量与容量最大的那个存储器相等,单位容量的价格接近最便宜的那个存储器。
2、存储系统分为两类:( 1)Cache 存储系统:由 Cache 与主存储器构成,目的是提高存储器速度。
(2)虚拟存储系统:由主存储器和硬盘构成,目的是扩大存储器容量。
3、存储系统的价格: C =( C1S1+C2S2) /( S1+S2)4、存储系统的速度:表示方法:访问周期、存取周期、存储周期、存取时间等。