CH01-案例及习题
- 格式:doc
- 大小:93.00 KB
- 文档页数:3


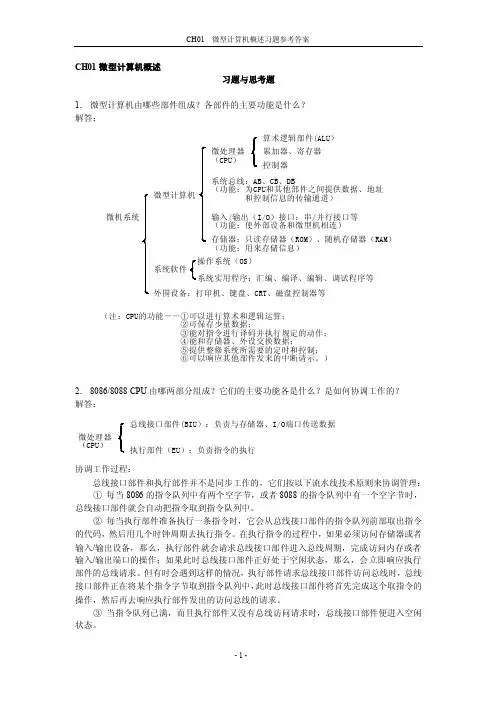
CH01微型计算机概述习题与思考题1. 微型计算机由哪些部件组成?各部件的主要功能是什么? 解答:微机系统微型计算机系统软件外围设备:打印机、键盘、CRT 、磁盘控制器等微处理器(CPU )系统总线:AB 、CB 、DB(功能:为CPU 和其他部件之间提供数据、地址 和控制信息的传输通道)存储器:只读存储器(ROM )、随机存储器(RAM )(功能:用来存储信息)输入/输出(I/O )接口:串/并行接口等(功能:使外部设备和微型机相连)算术逻辑部件(ALU )累加器、寄存器控制器操作系统(OS )系统实用程序:汇编、编译、编辑、调试程序等(注:CPU 的功能--①可以进行算术和逻辑运算; ②可保存少量数据; ③能对指令进行译码并执行规定的动作; ④能和存储器、外设交换数据;⑤提供整修系统所需要的定时和控制; ⑥可以响应其他部件发来的中断请示。
)2. 8086/8088 CPU 由哪两部分组成?它们的主要功能各是什么?是如何协调工作的? 解答:微处理器(CPU )总线接口部件(BIU ):负责与存储器、I/O 端口传送数据执行部件(EU ):负责指令的执行协调工作过程:总线接口部件和执行部件并不是同步工作的,它们按以下流水线技术原则来协调管理: ① 每当8086的指令队列中有两个空字节,或者8088的指令队列中有一个空字节时,总线接口部件就会自动把指令取到指令队列中。
② 每当执行部件准备执行一条指令时,它会从总线接口部件的指令队列前部取出指令的代码,然后用几个时钟周期去执行指令。
在执行指令的过程中,如果必须访问存储器或者输入/输出设备,那么,执行部件就会请求总线接口部件进入总线周期,完成访问内存或者输入/输出端口的操作;如果此时总线接口部件正好处于空闲状态,那么,会立即响应执行部件的总线请求。
但有时会遇到这样的情况,执行部件请求总线接口部件访问总线时,总线接口部件正在将某个指令字节取到指令队列中,此时总线接口部件将首先完成这个取指令的操作,然后再去响应执行部件发出的访问总线的请求。




【Lua程序设计第四版练习题答案】ch01Lua语⾔⼊门
联系1.1: 运⾏阶乘的⽰例并观察,如果输⼊负数,程序会出现什么问题?试着修改代码来解决问题。
-- 定义⼀个计算阶乘的函数
function fact (n)
if n == 0 then
return 1
else
return n * fact(n-1)
end
end
print("enter a number:")
a = io.read("*n") -- 读取⼀个数字
print(fact(a))
这是本章最开始提到的阶乘⽰例程序,通过实际的运⾏,我们了解到由于程序没有对负数形式进⾏校验的逻辑,因此程序会⼀直迭代递归下去,没有终⽌条件lua编译器报出堆栈溢出的错误才结束。
在进⾏修改之后的代码如下:
opefunction fact(n)
n = n or 0
if n < 0 then
error("Cannot calculate the factorial of a negative number")
elseif n == 0 then
return 1
else
return n * fact(n-1)
end
end
print("Enter a number: ")
a = io.read("*n")
print("Answer is: ", fact(a))
这⾥加⼊对输⼊负数的终⽌条件的判断,因此不会再出现堆栈溢出的错误。

Chapter 1The Demand for Audit and Other Assurance Services Review Questions1-1The relationship among audit services, attestation services, and assurance services is reflected in Figure 1-3 on page 13 of the text. An assurance service is an independent professional service to improve the quality of information for decision makers. An attestation service is a form of assurance service in which the CPA firm issues a report about the reliability of an assertion that is the responsibility of another party. Audit services are a form of attestation service in which the auditor expresses a written conclusion about the degree of correspondence between information and established criteria.The most common form of audit service is an audit of historical financial statements, in which the auditor expresses a conclusion as to whether the financial statements are presented in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles. An example of an attestation service is a report on the effe ctiveness of an entity’s internal control over financial reporting. There are many possible forms of assurance services, including services related to business performance measurement, health care performance, and information system reliability. 1-2 An independent audit is a means of satisfying the need for reliable information on the part of decision makers. Factors of a complex society which contribute to this need are:1.Remoteness of informationa.Owners (stockholders) divorced from managementb.Directors not involved in day-to-day operations ordecisionsc.Dispersion of the business among numerous geographiclocations and complex corporate structures2.Biases and motives of providerrmation will be biased in favor of the providerwhen his or her goals are inconsistent with thedecision maker's goals.3.Voluminous dataa.Possibly millions of transactions processed daily viasophisticated computerized systemsb.Multiple product linesc.Multiple transaction locationsplex exchange transactionsa.New and changing business relationships lead toinnovative accounting and reporting problemsb.Potential impact of transactions not quantifiable,leading to increased disclosures1-3 1. Risk-free interest rate This is approximately the rate the bank could earn by investing in U.S. treasury notes for thesame length of time as the business loan.2.Business risk for the customer This risk reflects thepossibility that the business will not be able to repay itsloan because of economic or business conditions such as arecession, poor management decisions, or unexpectedcompetition in the industry.rmation risk This risk reflects the possibility thatthe information upon which the business risk decision wasmade was inaccurate. A likely cause of the information riskis the possibility of inaccurate financial statements.Auditing has no effect on either the risk-free interest rate or business risk. However, auditing can significantly reduce information risk.1-4The four primary causes of information risk are remoteness of information, biases and motives of the provider, voluminous data, and the existence of complex exchange transactions.The three main ways to reduce information risk are:er verifies the information.er shares the information risk with management.3.Audited financial statements are provided.The advantages and disadvantages of each are as follows:1-5 To do an audit, there must be information in a verifiable form and some standards (criteria) by which the auditor can evaluate the information. Examples of established criteria include generally accepted accounting principles and the Internal Revenue Code. Determining the degree of correspondence between information and established criteria is determining whether a given set of information is in accordance with the established criteria. The information for Jones Company's tax return is the federal tax returns filed by the company. The established criteria are found in the Internal Revenue Code and all interpretations. For the audit of Jones Company's financial statements the information is the financial statements being audited and the established criteria are generally accepted accounting principles.1-6The primary evidence the internal revenue agent will use in the audit of the Jones Company's tax return include all available documentation and other information available in Jones' office or from other sources. For example, when the internal revenue agent audits taxable income, a major source of information will be bank statements, the cash receipts journal and deposit slips. The internal revenue agent is likely to emphasize unrecorded receipts and revenues. For expenses, major sources of evidence are likely to be cancelled checks, vendors' invoices and other supporting documentation.1-7This apparent paradox arises from the distinction between the function of auditing and the function of accounting. The accounting function is the recording, classifying and summarizing of economic events to provide relevant information to decision makers. The rules of accounting are the criteria used by the auditor for evaluating the presentation of economic events for financial statements and he or shemust therefore have an understanding of generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), as well as auditing standards. The accountant need not, and frequently does not, understand what auditors do, unless he or she is involved in doing audits, or has been trained as an auditor.1-81-9Five examples of specific operational audits that could be conducted by an internal auditor in a manufacturing company are:1.Examine employee time cards and personnel records todetermine if sufficient information is available to maximizethe effective use of personnel.2.Review the processing of sales invoices to determine if itcould be done more efficiently.3.Review the acquisitions of goods, including costs, todetermine if they are being purchased at the lowest possiblecost considering the quality needed.4.Review and evaluate the efficiency of the manufacturingprocess.5.Review the processing of cash receipts to determine if theyare deposited as quickly as possible.1-10 When using a strategic systems auditing approach in an audit of historical financial statements, an auditor must have a thorough understanding of the client and its environment. This knowledge should include the client’s regulatory and operating environment, business strategies and processes, and measurement indicators. The strategicsystems approach is also useful in other assurance or consulting engagements. For example, an auditor who is performing an assurance service on information technology would need to understand the client’s business strategies and processes related to information technology, including such things as purchases and sales via the Internet. Similarly, a practitioner performing a consulting engagement to evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of a cli ent’s manufacturing process would likely start with an analysis of various measurement indicators, including ratio analysis and benchmarking against key competitors.1-11 The major differences in the scope of audit responsibilities are:1.CPAs perform audits in accordance with auditing standards ofpublished financial statements prepared in accordance withgenerally accepted accounting principles.2.GAO auditors perform compliance or operational audits inorder to assure the Congress of the expenditure of publicfunds in accordance with its directives and the law.3.IRS agents perform compliance audits to enforce the federaltax laws as defined by Congress, interpreted by the courts,and regulated by the IRS.4.Internal auditors perform compliance or operational auditsin order to assure management or the board of directors thatcontrols and policies are properly and consistentlydeveloped, applied and evaluated.1-12 The four parts of the Uniform CPA Examination are: Auditing and Attestation, Financial Accounting and Reporting, Regulation, and Business Environment and Concepts.1-13 It is important for CPAs to be knowledgeable about e-commerce technologies because more of their clients are rapidly expanding their use of e-commerce. Examples of commonly used e-commerce technologies include purchases and sales of goods through the Internet, automatic inventory reordering via direct connection to inventory suppliers, and online banking. CPAs who perform audits or provide other assurance services about information generated with these technologies need a basic knowledge and understanding of information technology and e-commerce in order to identify and respond to risks in the financial and other information generated by these technologies.Multiple Choice Questions From CPA Examinations1-14 a. (3) b. (2) c. (2) d. (3)1-15 a. (2) b. (3) c. (4) d. (3)Discussion Questions And Problems1-16 a. The relationship among audit services, attestation services and assurance services is reflected in Figure 1-3 on page 13of the text. Audit services are a form of attestationservice, and attestation services are a form of assuranceservice. In a diagram, audit services are located within theattestation service area, and attestation services arelocated within the assurance service area.b. 1. (1) Audit of historical financial statements2.(2) An attestation service other than an auditservice; or(3) An assurance service that is not an attestationservice (WebTrust developed from the AICPASpecial Committee on Assurance Services, but theservice meets the criteria for an attestationservice.)3.(2) An attestation service other than an auditservice4.(2) An attestation service other than an auditservice5.(2) An attestation service other than an auditservice6.(2) An attestation service that is not an auditservice (Review services are a form ofattestation, but are performed according toStatements on Standards for Accounting andReview Services.)7.(2) An attestation service other than an auditservice8.(2) An attestation service other than an auditservice9.(3) An assurance service that is not an attestationservice1-17 a. The interest rate for the loan that requires a review report is lower than the loan that did not require a review becauseof lower information risk. A review report provides moderateassurance to financial statement users, which lowersinformation risk. An audit report provides further assuranceand lower information risk. As a result of reduced information risk, the interest rate is lowest for the loan with the audit report.b.Given these circumstances, Vial-tek should select the loanfrom City First Bank that requires an annual audit. In this situation, the additional cost of the audit is less than the reduction in interest due to lower information risk. The following is the calculation of total costs for each loan:1-17 (continued)c. Vial-tek may desire to have an audit because of the manyother positive benefits that an audit provides. The auditwill provide Vial-tek’s management with assurance aboutannual financial information used for decision-makingpurposes. The audit may detect errors or fraud, and providemanagement with information about the effectiveness ofcontrols. In addition, the audit may result inrecommendations to management that will improve efficiencyor effectiveness.d. Under a strategic systems audit approach, the auditor musthave a thorough understanding of the client and itsenvironment, including the client’s e-commerce technologies,industry, regulatory and operating environment, suppliers,customers, creditors, and business strategies and processes.This thorough analysis helps the auditor identify risksassociated with the client’s strategies that may affectwhether the financial statements are fairly stated. Whenapplying the strategic systems audit approach, the auditoroften discovers ways to help the client improve businessoperations, thereby providing added value to the auditfunction.1-18 a. The services provided by Consumers Union are very similar to assurance services provided by CPA firms. The servicesprovided by Consumers Union and assurance services providedby CPA firms are designed to improve the quality ofinformation for decision makers. CPAs are valued for theirindependence, and the reports provided by Consumers Union are valued because Consumers Union is independent of the products tested.b.The concepts of information risk for the buyer of anautomobile and for the user of financial statements are essentially the same. They are both concerned with the problem of unreliable information being provided. In the case of the auditor, the user is concerned about unreliable information being provided in the financial statements. The buyer of an automobile is likely to be concerned about the manufacturer or dealer providing unreliable information.c.The four causes of information risk are essentially the samefor a buyer of an automobile and a user of financial statements:(1)Remoteness of information It is difficult for a userto obtain much information about either an automobilemanufacturer or the automobile itself withoutincurring considerable cost. The automobile buyer doeshave the advantage of possibly knowing other users whoare satisfied or dissatisfied with a similarautomobile.(2)Biases and motives of provider There is a conflictbetween the automobile buyer and the manufacturer. Thebuyer wants to buy a high quality product at minimumcost whereas the seller wants to maximize the sellingprice and quantity sold.(3)Voluminous data There is a large amount of availableinformation about automobiles that users might like tohave in order to evaluate an automobile. Either that information is not available or too costly to obtain.1-18 (continued)(4)Complex exchange transactions The acquisition of anautomobile is expensive and certainly a complexdecision because of all the components that go intomaking a good automobile and choosing between a largenumber of alternatives.d.The three ways users of financial statements and buyers ofautomobiles reduce information risk are also similar:(1)User verifies information him or herself That can beobtained by driving different automobiles, examiningthe specifications of the automobiles, talking toother users and doing research in various magazines.(2)User shares information risk with management Themanufacturer of a product has a responsibility to meetits warranties and to provide a reasonable product.The buyer of an automobile can return the automobilefor correction of defects. In some cases a refund maybe obtained.(3)Examine the information prepared by Consumer ReportsThis is similar to an audit in the sense thatindependent information is provided by an independentparty. The information provided by Consumer Reports iscomparable to that provided by a CPA firm that auditedfinancial statements.1-19 a. The following parts of the definition of auditing are related to the narrative:(1)Virms is being asked to issue a report aboutqualitative and quantitative information for trucks.The trucks are therefore the information with which the auditor is concerned.(2)There are four established criteria which must beevaluated and reported by Virms: existence of the trucks on the night of June 30, 2005, ownership of each truck by Regional Delivery Service, physical condition of each truck and fair market value of each truck.(3)Susan Virms will accumulate and evaluate four types ofevidence:(a)Count the trucks to determine their existence.(b)Use registrations documents held by Oatley forcomparison to the serial number on each truck todetermine ownership.(c)Examine the trucks to determine each truck'sphysical condition.(d)Examine the blue book to determine the fairmarket value of each truck.(4)Susan Virms, CPA, appears qualified, as a competent,independent person. She is a CPA, and she spends most of her time auditing used automobile and truck dealerships and has extensive specialized knowledge about used trucks that is consistent with the nature of the engagement.1-19(continued)(5)The report results are to include:(a)which of the 35 trucks are parked in Regional'sparking lot the night of June 30.(b)whether all of the trucks are owned by RegionalDelivery Service.(c)the condition of each truck, using establishedguidelines.(d)fair market value of each truck using thecurrent blue book for trucks.b.The only parts of the audit that will be difficult for Virmsare:(1)Evaluating the condition, using the guidelines of poor,good, and excellent. It is highly subjective to do so.If she uses a different criterion than the "bluebook," the fair market value will not be meaningful.Her experience will be essential in using thisguideline.(2)Determining the fair market value, unless it isclearly defined in the blue book for each condition.1-20 a. The major advantages and disadvantages of a career as an IRS agent, CPA, GAO auditor, or an internal auditor are:1-20 (continued)EMPLOYMENT ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGESINTERNAL AUDITOR 1.Extensive exposure to allsegments of theenterprise with whichemployed.2.Constant exposure to oneindustry presentingopportunity for expertisein that industry.3.Likely to have exposureto compliance, financialand operational auditing.1.Little exposure totaxation and the auditthereof.2.Experience is limited toone enterprise, usuallywithin one or a limitednumber of industries.(b)Other auditing careers that are available are:Auditors within many of the branches of the federalgovernment ., Atomic Energy Commission)Auditors for many state and local government units .,state insurance or bank auditors)1-21 The most likely type of auditor and the type of audit for each of the examples are:1-22 a. The conglomerate should either engage the management advisory services division of a CPA firm or its own internalauditors to conduct the operational audit.b.The auditors will encounter problems in establishingcriteria for evaluating the actual quantitative events andin setting the scope to include all operations in whichsignificant inefficiencies might exist. In writing thereport, the auditors must choose proper wording to state that no financial audit was performed, that the procedures were limited in scope and that the results reported do not necessarily include all the inefficiencies that might exist.1-23 a. The CPA firm for the Internet company described in this problem could address these customer concerns by performinga WebTrust attestation engagement. The WebTrust assuranceservice was created by the profession to respond to thegrowing need for assurance resulting from the growth ofbusiness transacted over the Internet.b.The appropriate WebTrust principle for each of the customerconcerns noted in the problem is as follows:1.Accuracy of product descriptions and adherence tostated return policies: (3) Processing Integrity.2.Credit card and other personal information: (1) OnlinePrivacy and (2) Security.3.Selling information to other companies: (1) OnlinePrivacy and (2) Security.4.System failure: (4) Availability.Internet Problem Solution: Assurance Services1-1 This problem requires students to work with the AICPA assurance services Web site.1.Considering the assurance needs of customers and thecapabilities of CPAs, the Special Committee on AssuranceServices developed business plans for six assurance services.Chapter 1 of the textbook discussed several of theseservices. Go to the service description for the assuranceservice that most interests you (any one of the six). Whatare the major aspects or sections of the associated businessplan ., does the plan address market potential, competition,etc.)Answer: Each business plan provides background information,describes the service, assesses market potential, discussesissues such as competition and why CPAs should offer theservice, identifies practice tools available and steps thatCPAs must take to begin offering the services.2.The Special Committee's report on Assurance Servicesdiscusses competencies needed by assurance providers todayand in the coming decade. Briefly describe the 5 generalcompetencies needed in the next decade (Hint: See the“About Assurance Services” link. Then follow the“Assurance Services and Academia” link.)Answer:The Committee identified the following five majorimperatives regarding future competencies, each of whichimplies increasing emphasis on the competencies noted:1-1 (continued)Customer focus.Assurance service providers need tounderstand user decision processes and how informationshould enter into those processes. Increased emphasis isneeded on: understanding user needs, communication skills,relationship management, responsiveness and timeliness.Migration to higher value-added information activities. To provide more value to client/decision makers and others, assurance service providers need to focus less on activities involved in the conversion of business events into information ., collecting, classifying, and summarizing activities) and more on activities involved in the transformation of information into knowledge ., analyzing, interpreting, and evaluating activities) that effectively drives decision processes. This will require: analytical skills, business advisory skills, business knowledge, model building (including sensitivity analysis), understanding the client’s business processes, measurement theory (development of operational definitions of concepts, design of appropriate measurement techniques, etc.).Information technology (IT).Assurance services deal in information. Hence, the profound changes occurring in information technology will shape virtually all aspects of assurance services. As information specialists, assurance service providers need to embrace information technology in all of its complex dimensions. Embracing IT means understanding how it is transforming all aspects of business. It also means learning how to effectively use new developments in hardware, software, communications, memory, encryption, etc., in everything assurance service providers do as information specialists, not only in dealing with clients, but also in dealing with each other as individuals,teams, firms, state societies, and national professionalorganizations.Pace of change and complexity. Assurance services will takeplace in an environment of rapid change and increasingcomplexity. Assurance service providers need to investheavily in life-long learning in order to maintain up-to-date knowledge and skills. They will require: intellectualcapability, learning and rejuvenation.Competition.Growth in new assurance services will dependless on franchise/regulation and more on market forces.Assurance service providers need to develop their marketingskills —the ability to see clients’ latent informationand assurance needs and rapidly design and deploy cost-effective services to meet those needs —in order toeffectively compete for market-driven assurance services.Required skills include: marketing and selling,understanding customer needs, designing and deployingeffective solutions.1-1 (continued)(Note: Internet problems address current issues using Internet sources. Because Internet sites are subject to change, Internet problems and solutions are subject to change. Current information on Internet problems is available at。

第1章市场营销与市场营销学(1)(一)单项选择题(在下列每小题中,选择一个最适合的答案。
)1、市场是一个由消费者决定并由推动的过程。
A.生产者B.中间商C.政府D.零售商2、市场营销的核心是_________。
A.生产B.分配C.交换D.促销3、从市场营销的角度看,市场就是。
A.买卖的场所B.商品交换关系的总和C.交换过程本身D.具有购买欲望和支付能力的消费者4、在交换双方中,如果一方比另一方更主动、更积极地寻求交换,我们就将前者称之为_________,后者称为潜在顾客。
A.厂商B.市场营销者C.推销者D.顾客5、市场营销学作为一门独立的经营管理学科诞生于20世纪初的_________。
A.欧洲B.日本C.美国D.中国6、市场营销学第二次“革命”的标志是提出了_________的观念。
A.以消费者为中心B.以生产者为中心C.市场营销组合D.网络营销7、站在经营者角度,人们常常把卖方称之为_________,而将买方称之为市场。
A.企业B.厂商C.供货者D.行业8、从营销理论的角度而言,企业市场营销的最终目标是_________。
A.满足消费者的需求和欲望B.获取利润C.求得生存和发展D.把商品推销给消费者9、消费者未能得到满足的感受状态称为。
A.欲望B.需要C.需求D.愿望10、与顾客建立长期合作关系是_________的核心内容。
A.关系营销B.绿色营销C.公共关系D.相互市场营销11、当买卖双方都表现积极时,我们就把双方都称为_________,并将这种情况称为相互市场营销。
A.市场营销者B.相互市场营销者C.生产者D.推销者12、在20世纪30年代以前,市场营销的研究领域还主要局限于_________,真正的市场营销观念尚未形成。
第01章市场营销与市场营销学.2.A.生产领域B.流通领域C.交换领域D.消费领域13、营销理论的基础是_________和价值实现论。
A.价值来源论B.生产目的论C.交换目的论D.消费者主权论14、我国现存最早的市场营销学教材,是由丁馨伯教授编译、复旦大学1933年出版的_________。

SOLUTIONS TO TEXT PROBLEMS:Quick Quizzes1. The four principles of economic decisionmaking are: (1) people face tradeoffs; (2) the cost ofsomething is what you give up to get it; (3) rational people think at the margin; and (4) peoplerespond to incentives. People face tradeoffs because to get one thing that they like, they usually have to give up another thing that they like. The cost of something is what you give up to get it, not just in terms of monetary costs but all opportunity costs. Rational people think at the margin by taking an action if and only if the marginal benefits exceed the marginal costs. Peoplerespond to incentives because as they compare benefits to costs, a change in incentives maycause their behavior to change.2. The three principles concerning economic interactions are: (1) trade can make everyone betteroff; (2) markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity; and (3) governments cansometimes improve market outcomes. Trade can make everyone better off because it allowscountries to specialize in what they do best and to enjoy a wider variety of goods and services.Markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity because the invisible hand leadsmarkets to desirable outcomes. Governments can so metimes improve market outcomes because sometimes markets fail to allocate resources efficiently because of an externality or market power.3. The three principles that describe how the economy as a whole works are: (1) a country’sstandard of living depends on its ability to produce goods and services; (2) prices rise when thegovernment prints too much money; and (3) society faces a short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. A country’s standard of living depends on its ability to produce g oods andservices, which in turn depends on its productivity, which is a function of the education ofworkers and the access workers have to the necessary tools and technology. Prices rise whenthe government prints too much money because more money in circulation reduces the value of money, causing inflation. Society faces a short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment that is only temporary and policymakers have some ability to exploit this relationship usingvarious policy instruments.Questions for Review1. Examples of tradeoffs include time tradeoffs (such as studying one subject over another, orstudying at all compared to engaging in social activities) and spending tradeoffs (such as whether to use your last ten dollars on pizza or on a study guide for that tough economics course).2. The opportunity cost of seeing a movie includes the monetary cost of admission plus the timecost of going to the theater and attending the show. The time cost depends on what else youmight do with that time; if it's staying home and watching TV, the time cost may be small, but if it's working an extra three hours at your job, the time cost is the money you could have earned. 3. The marginal benefit of a glass of water depends on your circumstances. If you've just run amarathon, or you've been walking in the desert sun for three hours, the marginal benefit is veryhigh. But if you've been drinking a lot of liquids recently, the marginal benefit is quite low. Thepoint is that even the necessities of life, like water, don't always have large marginal benefits.4. Policymakers need to think about incentives so they can understand how people will respond tothe policies they put in place. The text's example of seat belts shows that policy actions canhave quite unintended consequences. If incentives matter a lot, they may lead to a very2 Chapter 1/Ten Principles of Economicsdifferent type of policy; for example, some economists have suggested putting knives in steeringcolumns so that people will drive much more carefully! While this suggestion is silly, it highlights the importance of incentives.5. Trade among countries isn't a game with some losers and some winners because trade can makeeveryone better off. By allowing specialization, trade between people and trade betweencountries can improve everyone's welfare.6. The "invisible hand" of the marketplace represents the idea that even though individuals andfirms are all acting in their own self-interest, prices and the marketplace guide them to do what is good for society as a whole.7. The two main causes of market failure are externalities and market power. An externality is theimpact of one person’s actions on the well-being of a bystander, such as from pollution or thecreation of knowledge. Market power refers to the ability of a single person (or small group ofpeople) to unduly influence market prices, such as in a town with only one well or only one cable television company. In addition, a market economy also leads to an unequal distribution ofincome.8. Productivity is important because a country's standard of living depends on its ability to producegoods and services. The greater a country's productivity (the amount of goods and servicesproduced from each hour of a worker's time), the greater will be its standard of living.9. Inflation is an increase in the overall level of prices in the economy. Inflation is caused byincreases in the quantity of a nation's money.10. Inflation and unemployment are negatively related in the short run. Reducing inflation entailscosts to society in the form of higher unemployment in the short run.Problems and Applications1. a. A family deciding whether to buy a new car faces a tradeoff between the cost of the carand other things they might want to buy. For example, buyi ng the car might mean theymust give up going on vacation for the next two years. So the real cost of the car is thefamily's opportunity cost in terms of what they must give up.b. For a member of Congress deciding whether to increase spending on national parks, thetradeoff is between parks and other spending items or tax cuts. If more money goesinto the park system, that may mean less spending on national defense or on the policeforce. Or, instead of spending more money on the park system, taxes could be reduced.c. When a company president decides whether to open a new factory, the decision is basedon whether the new factory will increase the firm's profits compared to other alternatives.For example, the company could upgrade existing equipment or expand existing factories.The bottom line is: Which method of expanding production will increase profit the most?d. In deciding how much to prepare for class, a professor faces a tradeoff between thevalue of improving the quality of the lecture compared to other things she could do withher time, such as working on additional research.2. When the benefits of something are psychological, such as going on a vacation, it isn't easy tocompare benefits to costs to determine if it's worth doing. But there are two ways to think aboutChapter 1/Ten Principles of Economics 3 the benefits. One is to compare the vacation with what you would do in its place. If you didn'tgo on vacation, would you buy something like a new set of golf clubs? Then you can decide ifyou'd rather have the new clubs or the vacation. A second way is to think about how much work you had to do to earn the money to pay for the vacation; then you can decide if thepsychological benefits of the vacation were worth the psychological cost of working.3. If you are thinking of going skiing instead of working at your part-time job, the cost of skiingincludes its monetary and time costs, which includes the opportunity cost of the wages you aregiving up by not working. If the choice is between skiing and going to the library to study, then the cost of skiing is its monetary and time costs including the cost to you of getting a lower grade in your course.4. If you spend $100 now instead of saving it for a year and earning 5 percent interest, you aregiving up the opportunity to spend $105 a year from now. The idea that money has a time value is the basis for the field of finance, the subfield of economics that has to do with prices offinancial instruments like stocks and bonds.5. The fact that you've already sunk $5 million isn't relevant to your decision anymore, since thatmoney is gone. What matters now is the chance to earn profits at the margin. If you spendanother $1 million and can generate sales of $3 million, you'll earn $2 million in marginal profit,so you should do so. You are right to think that the project has lost a total of $3 million ($6million in costs and only $3 million in revenue) and you shouldn't have started it. That's true, but if you don't spend the additional $1 million, you won't have any sales and your losses will be $5million. So what matters is not the total profit, but the profit you can earn at the margin. In fact, you'd pay up to $3 million to complete development; any more than that, and you won't beincreasing profit at the margin.6. Harry suggests looking at whether productivity would rise or fall. Productivity is certainlyimportant, since the more productive workers are, the lower the cost per gallon of potion. Ronwants to look at average cost. But both Harry and Ron are missing the other side of theequation−revenue. A firm wants to maximize its profits, so it needs to examine both costs andrevenues. Thus, Hermione is right−it’s best to examine whether the extra revenue wouldexceed the extra costs. Hermione is the only one who is thinking at the margin.7. a. The provision of Social Security benefits lowers an individual’s incentive to save forretirement. The benefits provide some level of income to the individual when he or sheretires. This means that the individual is not entirely dependent on savings to supportconsumption through the years in retirement.b. Since a person gets fewer after-tax Social Security benefits the greater is his or herearnings, there is an incentive not to work (or not work as much) a fter age 65. Themore you work, the lower your after-tax Social Security benefits will be. Thus thetaxation of Social Security benefits discourages work effort after age 65.8. a. When welfare recipients who are able to work have their benefits cut off after two years,they have greater incentive to find jobs than if their benefits were to last forever.b. The loss of benefits means that someone who can't find a job will get no income at all,so the distribution of income will become less equal. But the economy will be moreefficient, since welfare recipients have a greater incentive to find jobs. Thus the changein the law is one that increases efficiency but reduces equity.9. By specializing in each task, you and your roommate can finish the chores more quickly. If you4 Chapter 1/Ten Principles of Economicsdivided each task equally, it would take you more time to cook than it would take your roommate, and it would take him more time to clean than it would take you. By specializing, you reduce the total time spent on chores.Similarly, countries can specialize and trade, making both better off. For example, suppose ittakes Spanish workers less time to make clothes than French workers, and French workers canmake wine more efficiently than Spanish workers. Then Spain and France can both benefit ifSpanish workers produce all the clothes and French workers produce all the wine, and theyexchange some wine for some clothes.10. a. Being a central planner is tough! To produce the right number of CDs by the right artistsand deliver them to the right people requires an enormous amount of information. Youneed to know about production techniques and costs in the CD industry. You need toknow each person's musical tastes and which artists they want to hear. If you make thewrong decisions, you'll be producing too many CDs by artists that people don't want tohear, and not enough by others.b. Your decisions about how many CDs to produce carry over to other decisions. You haveto make the right number of CD players for people to use. If you make too many CDsand not enough cassette tapes, people with cassette players will be stuck with CDs theycan't play. The probability of making mistakes is very high. You will also be faced withtough choices about the music industry compared to other parts of the economy. If youproduce more sports equipment, you'll have fewer resources for making CDs. So alldecisions about the economy influence your decisions about CD production.11. a. Efficiency: The market failure comes from the monopol y by the cable TV firm.b. Equityc. Efficiency: An externality arises because secondhand smoke harms nonsmokers.d. Efficiency: The market failure occurs because of Standard Oil's monopoly power.e. Equityf. Efficiency: There is an externality because of accidents caused by drunk drivers.12. a. If everyone were guaranteed the best health care possible, much more of our nation'soutput would be devoted to medical care than is now the case. Would that be efficient?If you think that currently doctors form a monopoly and restrict health care to keep theirincomes high, you might think efficiency would increase by providing more health care.But more likely, if the government mandated increased spending on health care, theeconomy would be less efficient because it would give people more health care than theywould choose to pay for. From the point of view of equity, if poor people are less likelyto have adequate health care, providing more health care would represent animprovement. Each person would have a more even slice of the economic pie, thoughthe pie would consist of more health care and less of other goods.b. When workers are laid off, equity considerations argue for the unemployment benefitssystem to provide them with some income until they can find new jobs. After all, no oneplans to be laid off, so unemployment benefits are a form of insurance. But there’s anefficiency problem why work if you can get income for doing nothing? The economyisn’t operating efficiently if p eople remain unemployed for a long time, andunemployment benefits encourage unemployment. Thus, there’s a tradeoff betweenequity and efficiency. The more generous are unemployment benefits, the less income islost by an unemployed person, but the more that person is encouraged to remainunemployed. So greater equity reduces efficiency.Chapter 1/Ten Principles of Economics 5 13. Since average income in the United States has roughly doubled every 35 years, we are likely tohave a better standard of living than our parents, and a much better s tandard of living than our grandparents. This is mainly the result of increased productivity, so that an hour of workproduces more goods and services than it used to. Thus incomes have continuously risen overtime, as has the standard of living.14. If Americans save more and it leads to more spending on factories, there will be an increase inproduction and productivity, since the same number of workers will have more equipment towork with. The benefits from higher productivity will go to both the workers, who will get paidmore since they're producing more, and the factory owners, who will get a return on theirinvestments. There is no such thing as a free lunch, however, because when people save more, they are giving up spending. They get higher incomes at the cost of buying fewer goods.15. a. If people have more money, they are probably going to spend more on goods andservices.b. If prices are sticky, and people spend more on goods and services, then output mayincrease, as producers increase output to meet the higher demand rather than raisingprices.c. If prices can adjust, then the higher spending of consumers will be matched withincreased prices and output won't rise.16. To make an intelligent decision about whether to reduce inflation, a policymaker would need toknow what causes inflation and unemployment, as well as what determines the tradeoff between them. Any attempt to reduce inflation will likely lead to higher unemployment in the short run. A policymaker thus faces a tradeoff between the benefits of lower inflation compared to the cost of higher unemployment.。
Chapter 1Introduction to Corporate Finance Multiple Choice Questions1. Conflicts between shareholders and managers are usually resolvedA) by arbitration.B) in favor of shareholders.C) in favor of managers.D) by rules of first priority.E) None of the above.Answer: B Difficulty: Easy Page: 12. Firms issue securities or financial instruments (or claims) to raise capital. These claims areclassified asA) stocks or bonds.B) debt or equity.C) contingent claims on the value of the firm.D) All of the above.E) None of the above.Answer: D Difficulty: Medium Page: 23. The balance sheet is made up of what five key components?A) Fixed assets, current liabilities, long term debt, tangible current assets and shareholders equityB) Intangible fixed assets, current liabilities, long-term debt, net income and current assetsC) Fixed assets, long-term debt, current assets, current liabilities and shareholders equityD) Current assets, fixed assets, long term debt, shareholders equity and retained earningsE) None of the above.Answer: C Difficulty: Medium Page: 34. In terms of the balance sheet model of the firm, the value of the firm in financial markets is equal toA) tangible fixed assets plus intangible fixed assets.B) sales minus costs.C) cash inflow minus cash outflow.D) the value of the debt plus the value of the equity.E) the value of the debt minus the value of the equity.Answer: D Difficulty: Easy Page: 35. Inventory is a(n) ________ account.A) current assetB) current liabilityC) equityD) fixed assetE) long-term liabilityAnswer: A Difficulty: Easy Page: 36. Capital structure is defined as the major financing of the firm. The capital structure is dividedA) between debtholders and creditors.B) creditors and shareholders.C) assets and liabilities.D) All of the above.E) None of the above.Answer: B Difficulty: Medium Page: 47. Using the balance sheet model of the firm, finance may be thought of as analysis of three primarysubject areas. Which of the following groups correctly lists these three areas?A) Capital budgeting, capital structure, net working capitalB) Capital budgeting, capital structure, security marketingC) Capital budgeting, net working capital, tax analysisD) Capital budgeting, tax analysis, security marketingE) Net working capital, tax analysis, security marketingAnswer: A Difficulty: Easy Page: 48. Which of the following is not considered one of the basic questions of corporate finance?A) What long-lived assets should the firm invest?B) How much inventory should the firm hold?C) How can the firm raise cash for required capital expenditures?D) How should the short-term operating cash flows be managed?E) All of the above.Answer: B Difficulty: Medium Page: 49. The need to manage net working capital arises becauseA) financial management is naturally broken into those areas.B) shareholders want to ensure they receive dividend payments.C) there is a mismatch between the timing of cash inflows and cash outflows.D) the sum of current assets and current liabilities usually is zero.E) the capital structure pie is limited in size.Answer: C Difficulty: Easy Page: 410. In the managerial structure of the corporation the two officers and their responsibilities that reportdirectly to the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) areA) the credit manager who handles accounts receivable and the tax manager who minimizes taxpayments.B) the personnel manager who manages salaries and compensation, and the production operationsmanager who manages facility operations.C) the treasurer who is responsible handling cash flow and making financial decisions and the taxmanager who minimizes tax payments.D) the controller who manages the accounting function and the treasurer who is responsiblehandling cash flow and making financial decisions.E) None of the above.Answer: D Difficulty: Easy Page: 5-611. Value is created and recognized over time ifA) cash raised is invested in the investment activities of the firm.B) funds are raised in the capital markets.C) cash paid to investors, shareholders and bondholders, is greater than cash raised in the financialmarkets.D) management pursues activities to reduce taxes to zero.E) All of the above.Answer: C Difficulty: Medium Page: 712. Generally accepted accounting principles may recognize and record a saleA) before a customer pays assuming they will pay soon.B) only after the company receives payment in full.C) when the company receives at least 50% of the total revenue from the customer.D) All of the above.E) None of the above.Answer: A Difficulty: Medium Page: 713. Time preference refers to the fact thatA) corporations match current assets with current liabilities to minimize the chance of bankruptcy.B) corporations match both current and long-term assets with current and long-term liabilities tominimize the change of bankruptcy.C) investors prefer current cash flows to future cash flows.D) investors seek to time cash flows to minimize tax liabilities.E) None of the above.Answer: C Difficulty: Medium Page: 814. Finance determines the value to the firm is based onA) the cash flows of the firm.B) the timing and risk of the cash flows.C) the profits earned under GAAP.D) Both A and C.E) Both A and B.Answer: E Difficulty: Medium Page: 8-915. A corporate security can be viewed as a contingent claim on the firm. This means thatA) debtholders will receive their payoff from the firm based on their fixed claim or the firm cashflows if less than the fixed claim.B) debtholders will receive the maximum of the firm cash flows or the fixed claim.C) no payoff will be made unless the firm makes more than the fixed claim of the debt.D) no debt payoff will be made unless there is an equity payoff.E) None of the above.Answer: A Difficulty: Medium Page: 916. If a firm has debt outstanding the contingent claim of a shareholder isA) equal to the payment to the debtholders.B) equal to the firm cash flows minus the fixed debt payment if the residual cash flows arepositive.C) equal to the firm cash flows minus the fixed debt payment whether positive or negative.D) equal to the debt payment plus the residual cash flow of the firm.E) None of the above.Answer: B Difficulty: Medium Page: 1017. The Simple Corporation has outstanding obligation to the Complex Corporation of $250. It isyear-end and the total cash flow of Simple from all sources is $325. The contingent payoff to the debtholders and the shareholders isA) $250; $325B) $75; $250C) $250; $75D) $325; $250E) None of the above.Answer: C Difficulty: Medium Page: 1018. Sole proprietorships are predominantly started becauseA) they are easily and cheaply setup.B) the proprietorship life is limited to the business owner's life.C) all business taxes are paid as individual tax.D) All of the above.E) None of the above.Answer: D Difficulty: Easy Page: 1119. Which of the following is a true statement concerning partnerships?A) Limited partners are responsible for all debts of the partnership.B) Limited partners generally manage the partnership.C) The income of the general partner is taxed at the corporate income tax rate.D) Partnerships are never terminated and they have infinite life.E) None of the above.Answer: E Difficulty: Easy Page: 1120. The general partner(s) in a general partnership agree to share work, costs, profits, and losses. EachpartnerA) has liability only up to the amount of their investment.B) has liability for the debts of the partnership.C) has liability only if it is formally documented.D) never has any liability but the limited partners do.E) None of the above.Answer: B Difficulty: Medium Page: 1121. In the large corporation, the separation of management and ownership provides the followingadvantage(s)A) it must have a limited life.B) ease of share ownership transfer.C) unlimited shareholder liability.D) Both A and B.E) Both B and C.Answer: B Difficulty: Medium Page: 11-1222. Businesses that are good candidates for incorporation haveA) low taxable income.B) low marginal corporate tax rates.C) low marginal personal tax rates among potential shareholders.D) All of the above.E) None of the above.Answer: D Difficulty: Hard Page: 1423. The Splitz Corporation has borrowed $5 million in debt with a promise to repay $5.5 million in oneyear. The corporation had 10 million shares outstanding worth $2 each at the time of the borrowing.Splitz's net income was earns $6 million during the year. What is the debtholder's contingent claim;how much do the debtholders receive; and, how much do the shareholders receive?A) $5,500,000; $6,000,000; $20,000,000B) $5,000,000; $5,500,000; $0C) $5,000,000; $5,500,000; $20,000,000D) $5,500,000; $5,500,000; $500,000E) $5,000,000; $5,000,000; $1,000,000Answer: D Difficulty: Medium Page: 9-10Rationale:Earnings - Debt Claim = Shareholder Residual or Debt Shortfall = $6,000,000 - $5,500,000 =$500,000; debtholders receive $5,500,000; stockholders receive $500,000.24. The Splitz Corporation has borrowed $5 million in debt with a promise to repay $5.5 million in oneyear. The corporation had 10 million shares outstanding worth $2 each at the time of the borrowing.Splitz earns $5 million during the year. What is the debtholder's contingent claim; how much does the debtholder receive; and, how much do the shareholders receive?A) $5,000,000; $5,500,000; $20,000,000B) $5,500,000; $5,000,000; $0C) $5,000,000; -$500,000; $20,000,000D) -$500,000; $5,000,000; $0.E) $5,000,000; 5,500,000; -$500,000Answer: B Difficulty: Medium Page: 9-10Rationale:Earnings - Debt Claim = Shareholder Residual or Debt Shortfall = $5,000,000 - $5,500,000 =-500,000; debtholders receive $5,000,000; stockholders receive $0.25. Corporate securities are contingent claims becauseA) they don't represent a direct claim on the firm.B) the firm may be bought out.C) the securities value is derived from the value of the firm.D) book value can be negative.E) None of the above.Answer: C Difficulty: Hard Page: 9-1026. Agency costs surrounding the conflict of interest between managers and shareholders areA) the monitoring costs of the shareholders and the residual loss of wealth due to divergentmanagement behavior.B) the costs of implementing control devices and the monitoring costs of the shareholders.C) the costs of implementing control devices and the residual loss of wealth due to divergentmanagement behavior.D) the set-of-contracts needed to structure the firm and residual wealth.E) None of the above.Answer: B Difficulty: Hard Page: 1527. Residual losses surrounding the conflict of interest between shareholders and management arecalledA) reduction in shareholder wealth due to competitors' behaviors.B) a gain to shareholder wealth if the manager does not own stock in the company.C) lost wealth of the shareholders due to divergent behavior of managers.D) Both A and C.E) None of the above.Answer: C Difficulty: Hard Page: 1528. From a finance perspective, what is the primary goal of the corporation?A) Maximize the pay and compensation of employees and managers of the firm.B) Maximize the value of the stockholders because they are the owners of the corporation.C) Maximize the wealth of all stakeholders if the firm wants to continue to exist.D) Maximize the societal value to minimize governmental interference.E) None of the above.Answer: B Difficulty: Easy Page: 1529. Shareholders attempt to control managerial behavior byA) electing the board of directors who select management.B) the threat of a takeover by another firm.C) setting compensation contracts and tying compensation to corporate success.D) Both A and B.E) All of the above.Answer: E Difficulty: Medium Page: 1630. Financial markets are composed ofA) capital markets and equity markets.B) capital markets and debt markets.C) capital markets and money markets.D) equity markets and money markets.Answer: C Difficulty: Easy Page: 1731. The primary market is defined as theA) market for insured securities.B) market for new issues.C) market for securities of the largest firms.D) over-the-counter market.E.) None of the above.Answer: B Difficulty: Easy Page: 1732. Registration of a public issue of new securities with the Securities and Exchange Commission(SEC) requiresA) the use of an underwriter.B) disclosure of all material information in a registration statement.C) the sale of the securities by private negotiation.D) All of the above.E) None of the above.Answer: B Page: 1733. The NYSE and NASDAQ are bothA) primary markets.B) dealer markets.C) secondary markets.D) All of the above.E) None of the above.Answer: C Difficulty: Medium Page: 1834. Which of the following statements concerning registration of publicly available corporatesecurities is false?A) The securities must be registered at the SEC.B) Registration involves the disclosure of relevant information.C) The costs of preparing the registration statement are negligible.D) Private placement of securities avoids registering with the SEC.E) None of the above.Answer: C Difficulty: Easy Page: 1735. The NYSE listing requirements for non-U.S. companies areA) more flexible than those for U.S. companies.B) more stringent than those for U.S. companies.C) the same as those for U.S. companies.D) irrelevant since non U.S. companies cannot list on the NYSE.E) None of the above.Answer: B Difficulty: Medium Page: 1836. In order to list on the NYSE, a firm must haveA) net tangible assets of at least $40 million.B) a market value for publicly held shares of at least $40 million.C) at least 3,000 holders of 100 shares of stock or more.D) Both A and B.E) All of the above.Answer: D Difficulty: Hard Page: 1837. In a limited partnershipA) each partner's liability is limited to his net worth.B) each partner's liability is limited to the amount he put into the partnership.C) each partner's liability is limited to his annual salary.D) there is no limitation on liability; only a limitation on what the partner can earn.E) None of the above.Answer: B Difficulty: Easy Page: 11Essay Questions38. Flea Fall Inc., a maker of dog flea collars, paid $125,000 cash for inventory on January 1, 2004. OnDecember 31, 2004, the company's sales total $147,000 of which $117,000 has been collected. If inventory represents Flea Falls only cost, calculate the firms accounting profit as well as its cash flow as of December 31, 2004.Difficulty: Medium Page: 7-8Answer:Accounting Profit = Sales - Cost [$147,000 - $125,000 = $22,000]Cash Flow = Cash Inflow-Cash Outflow [$117,000 - $125,000 = $-8,000]39. The Harlow Corporation has promised to pay its debtholders an amount of $2,700 over the nextyear. The firm's shareholders hold claim to whatever is left after the debtholders' claims have been satisfied. Calculate Harlow's debt and equity level if its assets total $1,100 at the end of the year.Recalculate for asset levels of $2,200 and $6,000.Difficulty: Medium Page: 9-10Answer:If assets = $1,100: Value of Debt = $1,100; Value of Equity =$0If assets = $2,200: Value of Debt = $2,200; Value of Equity =$0If assets = $6,000: Value of Debt = $2,700; Value of Equity = $3,30040. A financial manager's most important job is to create value from capital budgeting, financing, andliquidity activities. Explain how financial managers create value.Difficulty: Medium Page: 6Answer:∙ Buy assets that generate more than their cost.∙ Sell financial securities that raise more cash than they cost.∙ Minimize cash payouts to non-investors, i.e., taxes to governments.41. The decision to incorporate must consider the fact that earnings will be taxed at both the corporateand personal levels. Since this is disadvantageous, provide three reasons why one may want to incorporate.Difficulty: Hard Page: 12-14Answer:∙ Easier access to capital markets.∙ Retention of funds for reinvestment opportunities.∙ Market pricing and trading of securities.∙ Ownership can be more readily transferred∙ Corporations have unlimited life.∙ Shareholders' liability is limited to the amount invested.42. How can shareholders attempt to control managerial behavior to match shareholder interest?Difficulty: Hard Page: 16Answer:∙ Vote for directors with shareholder's interest to select management.∙ Provide incentive contracts; performance shares or options.∙ Outside threat of takeover.∙ Competition in managerial labor market.。
Chapter 1Managerial Accounting and the Business Environment Solutions to Questions1-1 A strategy is a game plan that enables a company to attract customers by distinguishing itself from competitors. The focal point of a company’s strategy should be its target customers.1-2Customer value propositions fall into three broad categories—customer intimacy, operational excellence, and product leadership.A company with a customer intimacy strategy attempts to better understand and respond to its customers’ individual needs than its competitors. A company that adopts an operational excellence strategy attempts to deliver products faster, more conveniently, and at a lower price than its competitors. A company that has a product leadership strategy attempts to offer higher quality products than its competitors.1-3 A person in a line position is directly involved in achieving the basic objectives of the organization. A person in a staff position provides services and assistance to other parts of the organization, but is not directly involved in achieving the basic objectives of the organization.1-4The Chief Financial Officer is responsible for providing timely and relevant data to support planning and control activities and for preparing financial statements for external users.1-5The three main categories of inventories in a manufacturing company are raw materials, work in process, and finished goods.1-6The five steps in the lean thinking model are: (1) identify value in specific products and services; (2) identify the business process that delivers value; (3) organize work arrangements around the flow of the business process; (4) create a pull system that responds to customer orders; and (5) continuously pursue perfectionin the business process.1-7Successful implementation of the lean thinking model should result in lower inventories, fewer defects, less wasted effort, and quicker customer response times.1-8In a pull production system, production is not initiated until a customer order is received. Inventories are reduced to a minimum by purchasing raw materials and producing products only as needed to meet customer demand.1-9Some benefits from improvement efforts come from cost reductions, but the primary benefit is often an increase in capacity. At non-constraints, increases in capacity just add to the already-existing excess capacity. Therefore, im-provement efforts should ordinarily focus on the constraint.1-10 Six Sigma is a process improvement method that relies on customer feedback and fact-based data gathering and analysis techniques to drive process improvement. The goal is to reduce defect rates below 3.4 defects per million.1-11 The five stages in the Six Sigma DMAIC Framework are (1) Define; (2) Measure; (3) Analyze; (4) Improve; and (5) Control. The goals for the define stage are to establish the scope and purpose of the project, to diagram the flow of the current process, and to establish the customer’s requirements for the process.© The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2010. All rights reserved.The goals for the measure stage are to gather baseline performance data related to the existing process and to narrow the scope of the project to the most important problems. The goal in the analyze stage is to identify the root causes of the problems identified in the measure stage. The goal in the improve stage is to develop, evaluate, and implement solutions to the problems. The goals in the control stage are to ensure the problems remain fixed and to seek to improve the new methods over time.1-12If people generally did not act ethically in business, no one would trust anyone else and people would be reluctant to enter into business transactions. The result would be less funds raised in capital markets, fewer goods and services available for sale, lower quality, and higher prices. 1-13Corporate governance is the system by which a company is directed and controlled. If properly implemented, the corporate governance system should provide incentives for the board of directors and top management to pursue objectives that are in the best interests of the company’s owners and it should provide for effective monitoring of performance.1-14Enterprise risk management is a process used by a company to proactively identify the risks that it faces and to manage those risks.1-15The stakeholder groups include customers, suppliers, stockholders, employees, communities, and environmental and human rights advocates.© The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2010. All rights reserved.1. Line2. Organization chart3. Staff4. Decentralization5. Controller6. Chief Financial Officer© The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2010. All rights reserved.1. strategy2. Six Sigma3. business process4. corporate governance5. enterprise risk management6. manufacturing cell7. stakeholders8. constraint9. nonconstraint10. value chain11. Corporate social responsibility12. supply chain management13. lean thinking model; pulls14. customer value proposition15. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 200216. non-value-added activity17. Theory of Constraints© The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2010. All rights reserved.If cashiers routinely shortchanged customers whenever the opportunity presented itself, most of us would be careful to count our change before leaving the counter. Imagine what effect this would have on the line at your favorite fast-food restaurant. How would you like to wait in line while each and every customer laboriously counts out his or her change? Additionally, if you can’t trust the cashiers to give honest change, can you trust the cooks to take the time to follow health precautions such as washing their hands? If you can’t trust anyone at the restaurant would you even want to eat out?Generally, when we buy goods and services in the free market, we assume we are buying from people who have a certain level of ethical standards. If we could not trust people to maintain those standards, we would be reluctant to buy. The net result of widespread dishonesty would be a shrunken economy with a lower growth rate and fewer goods and services for sale at a lower overall level of quality.© The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2010. All rights reserved.1. Failure to report the obsolete nature of the inventory would violate theIMA’s Statement of Ethical Professional Practice as follows:Competence• Perform duties in accordance with relevant technical standards.Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) require the write-down of obsolete inventory.• Prepare decision support information that is accurate.Integrity• Mitigate actual conflicts of interest and avoid apparent conflicts ofinterest.• Refrain from engaging in any conduct that would prejudice carrying out duties ethically.• Abstain from activities that would discredit the profession.Members of the management team, of which Perlman is a part, are responsible for both operations and recording the results of operations.Because the team will benefit from a bonus, increasing earnings by ignoring the obsolete inventory is clearly a conflict of interest.Furthermore, such behavior is a discredit to the profession.© The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2010. All rights reserved.Credibility• Communicate information fairly and objectively.• Disclose all relevant information.• Hiding the obsolete inventory impairs the objectivity and relevance of financial statements.(Unofficial CMA solution) 2. As discussed above, the ethical course of action would be for Perlman toinsist on writing down the obsolete inventory. This would not, however, be an easy thing to do. Apart from adversely affecting her owncompensation, the ethical action may anger her colleagues and make her very unpopular. Taking the ethical action would require considerable courage and self-assurance.© The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2010. All rights reserved.1. See the organization chart on the following page.2. Line positions include the university president, academic vice-president,the deans of the four colleges, and the dean of the law school. Inaddition, the department heads (as well as the faculty) are in linepositions. The reason is that their positions are directly related to the basic purpose of the university, which is education. (Line positions are shaded on the organization chart.)All other positions on the organization chart are staff positions. The reason is that these positions are indirectly related to the educational process, and exist only to provide service or support to the line positions.3. All positions would have need for accounting information of some type.For example, the manager of central purchasing would need to know the level of current inventories and budgeted allowances in variousareas before doing any purchasing; the vice-president for admissions and records would need to know the status of scholarship funds asstudents are admitted to the university; the dean of the business college would need to know his/her budget allowances in various areas, as well as information on cost per student credit hour; and so forth.© The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2010. All rights reserved.1. No, Charlie would not be justified in ignoring the situation. First, theStatement of Ethical Professional Practice states that the management accountant must “Regularly communicate with business associates to avoid apparent conflicts of interest. Advise all parties of any potential conflicts.” If J.B. insists on continuing the relationship with A-1, Charlie has a responsibility to advise both the corporate counsel and WIW’s Board of Directors.Second, as the company’s controller, Charlie has a responsibility toensure that the JIT approach is properly implemented. From the data given in the problem, it does not appear that A-1 Warehouse Sales is the best or most dependable supplier available. Orders are late and not complete, and there is no way to ensure proper quality because nearly all orders are shipped directly from the manufacturer. The presentarrangement with A-1 negates most of the benefits that can accrue from JIT.2. Charlie’s first step should be to verify the accuracy of his information.He states that A-1’s markup is 30%, but he does not indicate how he obtained this figure. Also, the adverse financial impact on WIW isdependent in part on the price it would have to pay directly to themanufacturers as compared to the price being paid to A-1. That is, can WIW purchase directly from the manufacturers for the same price as given to jobbers, who handle huge volumes of goods? If not, then the adverse financial impact of buying through A-1 may, in fact, be very small because WIW may have to pay about the same price either way.Charlie’s second step should be to discuss the potential legalramifications on a confidential basis with WIW’s corporate counsel.Before meeting with the corporate counsel, Charlie may wish todiscretely determine if Tony, the purchasing agent, and J.B., thepresident, worked together in their prior employment. (Remember that both have been with WIW for five years.) Armed with the information obtained from the discussion with counsel, Charlie should review the situation again with J.B., explaining more directly his concerns about the apparent conflict of interest and ask that the Board of Directors approve the continued use of A-1 as a supplier.© The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2010. All rights reserved.If J.B. refuses to follow this course of action, Charlie’s only alternative is to submit a memorandum to the Board of Directors. J.B. should be notified of this action in advance. The memorandum should present only the facts. If the Board approves the continued relationship with A-1, Charlie may possibly conclude that his concerns about an apparent conflict of interest do not represent an actual conflict. This presumes that legal counsel has advised the Board that the arrangement with A-1 does not violate any laws and that the company has made adequate disclosures in its public filings. Only Charlie can make the decision as to whether or not he can continue at WIW under these circumstances.1. If all automotive service shops routinely tried to sell parts and servicesto customers that they didn’t really need, most customers wouldeventually figure this out. They would then be reluctant to accept the word of the service representative that a particular problem needs to be corrected—even when a real problem exists. Either the work would not be done, or customers would learn to diagnose and repair problemsthemselves, or customers would hire an independent expert to verify that the work is really needed. All three of these alternatives impose costs and hassles on customers.2. As argued above, if customers could not trust their servicerepresentatives, they would be reluctant to follow the servicerepresentative’s advice. They would be inclined not to authorize work even when it is really necessary. And, more customers would learn to do automotive repairs and maintenance themselves. Moreover, customers would be unwilling to pay as much for work that is done becausecustomers would have reason to believe that the work may beunnecessary. These two effects would reduce demand for automotive repair services. The reduced demand would reduce employment in the industry and would lead to lower overall profits.1. Line authority is directly related to the achievement of an organization’sbasic objectives. Line managers have formal authority to directoperations.Staff assists line management in the achievement of an organization’s basic objectives. Persons with staff authority provide support services.Staff managers typically have advisory authority because of theirparticular expertise.2. Mark Johnson’s responsibility for maintaining the production scheduleinvolves line authority. Johnson would be directly concerned withmeeting the company’s primary objective of producing metal parts.Johnson’s responsibility to consult with production supervisors is a staff role because he apparently cannot order changes in those consultations, he can only advise. Johnson’s supervision of new alloy testing and his role regarding the use of new alloys in product development is basicallya staff function as well. He has limited authority regarding the use ofnew alloys because his authority applies only to product development and not to production.3. Mark Johnson may experience several conflicts because he has beengiven both line and staff authority.First, Johnson may initially find it difficult to communicate with theproduction supervisors because he operates out of a staff position.Second, a conflict could easily develop if the supervisors lack a clear understanding of Johnson’s responsibilities and authorities. Thesupervisors could resent apparent staff interference and refuse todiscuss their problems with Johnson, making the meetings fruitless. The supervisors working on the new contract may fail to perceive Johnson’s line authority and refuse to follow his orders.Third, Johnson might have difficulty in understanding the nature of his position and job. Johnson might also find it difficult to distinguishbetween his staff capacity and line capacity. For instance, Johnsonmight have difficulty in remaining objective if any production problems develop in the alloys he tested.(Unofficial CMA Solution, adapted)Research and Application 1-91.Whole Foods Market succeeds first and foremost because of its productleadership customer value proposition. The first boldface heading in the company’s Declaration of Interdependence says “We Sell the Highest Quality Natural and Organic Products Available.” Page 4 of the 10-K/A indicates that the real source of the company’s product leadershipposition centers on perishable products (e.g., produce, dairy, meat,seafood, bakery, and prepared foods). Perishable product sales account for about 67% of total retail sales. Customers choose Whole FoodsMarket primarily because they are able to buy better natural and organic foods and higher-quality perishable products than in conventionalsupermarkets.Customer service is also an important part of Whole Foods Market’ssuccess, but it is secondary in importance to product quality.2. Whole Foods Market faces numerous business risks as described inpages 11-15 of the 10-K/A. Here are four of the more prominent risks with suggested control activities:∙Risk: Customers will defect to conventional supermarkets that are beginning to stock more natural and organic foods. Control activities: Whole Foods Market can expand its selection of product offerings,particularly perishables, and continue to invest heavily in employeetraining and retention so that it offers market-leading levels of informed customer service.∙Risk: Growth targets will not be realized due to failed new store openings. Control activities: Implement formal reviews of the sightselection, construction, and new employee hiring and training processes. ∙Risk: Adverse economic conditions could reduce consumer spending at retail locations. Control activities: Continue to develop private labelproduct categories, such as the 365 Everyday Value category mentioned on page 8 of the 10-K/A, which are less expensive but meet rigorous quality standards.Risk: Extended power outages could cause severe inventory losses because of the company’s emphasis on perishable products. Control activities: Implement a contingency plan that specifies responses in the event of a power outage.3. There are no absolute right and wrong answers to this question becausethe information available in the annual report is piecemeal. Nonetheless, students could make the following observations based on availableinformation. First, the CEO (John P. Mackey) has a layer of seniormanagers that report to him including two Co-Presidents/ChiefOperating Officers, and three Executive Vice Presidents. Second, there are ten Regional Presidents. In the organization chart shown below, we assume that the Regional Presidents report to the Chief OperatingOfficers. Third, each Regional President has a layer of management that reports to him or her. For example, the Global All-Stars include David Schwartz, who is the Vice President of the Midwest Region. He would report to the President of the Midwest Region. John Simrell is theDirector of Finance for the South Region and he would report to the South Region President. Robin Graf is the Team Member ServicesDirector for the Southern Pacific Region. She would report to thePresident of the Southern Pacific Region.Fourth, each region has a manager/coordinator for each productcategory. For example, Theo Weening is the Meat Category Manager for the Mid-Atlantic Region and Bobby Turner is the Bakery Coordinator for the Midwest Region. In the organization chart shown below, we assume that these regional managers/coordinators report to a Vice-President at the regional level. Fifth, each region has Store Team Leaders for each retail location within the region. For example, John Robertson is the Store Team Leader in Charlottesville, Va. We have assumed that the store team leaders report to the regional vice-president level. Finally, each store location has various team leaders that report to the store team leader. For example, Rolando Alas is the Produce Team Leader at the Mill Valley Store location.Based on insights such as these, students should be able to prepare an organization chart that resembles the one shown at the end of thissolution.The Global All-Stars include numerous line and staff employees. Three staff employees are Roberta Lang, General Counsel, Chris Pine, VicePresident of Real Estate, and Jennifer McFarlin, Payroll Benefit Specialist, Madison. Three line employees are Rocco Terrazano, Meat Team Leader, Yorkville, Don Hosfeld, Grocery Team Leader, Ft. Lauderdale, and Joel Leonard, Prepared Foods Team Leader, Fresh Pond.4. Both documents emphasize that the respective companies serve a broadrange of stakeholders (e.g., customers, employees, suppliers,communities, and stockholders). Both companies mention that theirmost important stakeholder is the customer. The first sentence of the Johnson & Johnson Credo says “We believe our first responsibility is to the doctors, nurses, and patients, to mothers and fathers and all others who use our products and services.” Whole Foods Market says “Ourcustomers are the most important stakeholder in our business.Therefore, we go to extraordinary lengths to satisfy and delight ourcustomers.”The Whole Foods Market Declaration of Interdependence explicitlyrecognizes that satisfying all stakeholders’ interests will require balance and making trade-offs. In fact, the company says “One of the mostimportant responsibilities of Whole Foods Market’s leadership is to make sure the interests, desires and needs of our various stakeholders arekept in balance… Any conflicts must be mediated and win-win solutions found.” The Johnson & Johnson Credo does not explicitly acknowledge the need to strike a balance when managing the needs of its variousstakeholders.5. Whole Foods Market’s mission statement differs from its Code ofConduct and Ethics in three important respects. First, the missionstatement sets forth goals that the company strives to achieve. The tone of the document is positive because it focuses on goals thecompany hopes to achieve. The Code of Conduct and Ethics defines prohibited conduct. The tone of the document is appropriately negative because it describes those behaviors that are “out of bounds.”Second, the mission statement refers to a broader set of stakeholders(e.g., suppliers, customers, and communities) than the Code of Conductand Ethics, which pertains primarily to Whole Foods Market TeamMembers and Directors. Third, the mission statement is values-based. It reflects a vision of what the company stands for. The Code of Conduct and Ethics is rule-based. The majority of the code is based on the rules of governing bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the Nasdaq stock exchange, and the Financial AccountingStandards Board (FASB).Research and Application 1-9 (continued)。
Ch011. 对于信息的功能特征,它的____________ 在于维持和强化世界的有序性动态性。
2.对于信息的功能特征,它的 ___________ 表现为维系社会的生存、促进人类文明的进步和自身的发展。
3.信息技术主要分为感测与识别技术、 ____________ 、信息处理与再生技术、信息的施用技术等四大类。
4.信息系统是指基于计算机技术和网络通信技术的系统,是人、_______________ 、数据库、硬件和软件等各种设备、工具的有机集合。
5.在信息安全领域,重点关注的是与 ___________ 相关的各个环节。
6.信息化社会发展三要素是物质、能源和 ____________ 。
7.信息安全的基本目标应该是保护信息的机密性、_____________ 、可用性、可控性和不可抵赖性。
8._________ 指保证信息不被非授权访问,即使非授权用户得到信息也无法知晓信息的内容,因而不能使用。
9._________ 指维护信息的一致性,即在信息生成、传输、存储和使用过程中不应发生人为或非人为的非授权篡改。
10._________ 指授权用户在需要时能不受其他因素的影响,方便地使用所需信息。
这一目标是对信息系统的总体可靠性要求。
11. _________ 指信息在整个生命周期内都可由合法拥有者加以安全的控制。
12._________ 指保障用户无法在事后否认曾经对信息进行的生成、签发、接收等行为。
13.PDRR 模型,即“信息保障”模型,作为信息安全的目标,是由信息的保护技术、信息使用中的检测技术、信息受影响或攻击时的响应技术和受损后的__________________ 组成的。
14.当前信息安全的整体解决方案是PDRR 模型和 ______________ 的整合应用。
15.为了避免给信息的所有者造成损失,信息_____________ 往往是有范围(区域上、时间上)和有条件的。
16.信息技术IT 简单地说就是3C,即Compute(r 计算机)、Communication(通信)和 ___17.数据链路层要负责建立、维持和释放____________ 的连接。
引例沃尔玛借助管理信息系统登上世界企业500强之首在美国《财富》杂志评选的2001年美国企业500强中,零售业巨人沃尔玛连锁店将埃克森·美孚石油公司拉下马来,以2 198.12亿美元的营业收入总额坐上了美国乃至世界企业的龙头宝座。
而沃尔玛的主席罗伯逊·沃尔玛超过微软公司董事长比尔·盖茨成为全球首富。
沃尔玛在全球拥有4 600多家连锁店,雇员120多万人。
如此庞大的队伍,确实可称得上企业帝国。
这个企业帝国的成功秘诀是其管理信息系统。
沃尔玛的全球采购战略、配送系统、商品管理、电子数据系统、天天平价战略在业界都是经典。
其成功建立在利用信息技术整合优势资源、信息技术战略与零售业整合的基础之上。
沃尔玛在全球的4 600多家连锁店通过它的网络可在1小时之内对每种商品的库存、上架、销售量全部盘点一遍。
公司的创始人山姆·沃尔玛特别重视信息的沟通和信息系统的建设。
在20世纪60年代中期,他只拥有几家商店时,就已经认识到管理人员必须能够随时随地获得所需要的数据。
某种商品在沃尔玛的商店里一共有多少?订购了多少商品?上周的销售量、订购量呢?昨天呢?去年呢?订购的商品什么时候可以到达?在管理信息系统应用之前,必须通过大量的人工计算与处理才能得到。
要在现有的基础上扩大经营规模,只有不断应用先进的管理信息系统。
在管理信息系统的支持下,沃尔玛能够以最优质的服务、最低的成本、最快速的反应进行全球运作。
1974年,公司开始在其分销中心和各家连锁店运用计算机进行库存控制管理。
1983年,沃尔玛用上条码扫描系统。
1984年,沃尔玛开发了一套市场营销管理软件系统,这可以使每家连锁店按照自身的市场环境和销售类型制定出相应的营销产品组合。
在1985—1987年,沃尔玛安装了公司专用的卫星通信系统,使总部、分销中心和各连锁店之间可以实现双向的声音和数据传输,全球各家分店也都能够通过自己的终端与总部进行实时的通信联系。
通过采用最新的信息技术,员工能更有效地做好工作,更好地做出决策,以提高生产率和降低成本。
20世纪80年代,沃尔玛开始利用电子数据交换系统(EDI)与供应商建立自动订货系统。
到1990年,沃尔玛已与它的5 000余家供应商中的1 800家实现了电子数据交换,成为EDI技术在全美国的最大用户。
沃尔玛的配送管理是其管理信息系统中最重要的一环。
20世纪90年代沃尔玛提出了新的零售业配送理论,即各连锁店由集中管理的配送中心提供货源,而不是直接将货品运送到连锁店。
沃尔玛的配送系统由高效率的配送中心、快速的运输系统和先进的卫星通信网络组成。
这种独特的配送体系,大大降低了成本,加速了存货周转,形成了沃尔玛的核心竞争力。
管理信息系统的应用使沃尔玛有关各方可以迅速得到所需的货品层面数据,观察销售趋势、存货水平和订购信息甚至更多。
根据产品外部需求订单,广泛应用信息系统推算原料需求量及交货时间,以最大限度减少资金占用,减少库存,降低生产成本。
沃尔玛的信息系统是最先进的,其主要特点是:功能全、速度快、智能化和全球联网化。
沃尔玛在管理信息系统的投资不遗余力,负责软件设计的工程师有2 000多名。
20世纪90年代以后,互联网逐渐普及,为沃尔玛公司提供了以更少的费用建设高效的信息系统的可能。
对于山姆·沃尔玛来说,他最关心的就是每天如何提供低价的商品,为用户提供满意的服务。
技术在沃尔玛的发展中所起的作用主要遵循一个原则,即在供应商和沃尔玛之间的配送渠道方面,沃尔玛必须控制商品的变动情况。
它需掌握从商品所在位置到货品抵达时间的所有信息,这样相关人员就能确定时间,并准确地把货品送到商店,保证货品存储量达到最优。
沃尔玛努力避开一切中间环节,直接从工厂进货,其雄厚的经济实力使之具有强大的议价能力,管理信息系统则成为实现这一理想的重要手段。
沃尔玛的网络系统连接着上万个供货商和合作伙伴。
沃尔玛将传统的网络变成了一个高效的基于Internet的系统,让供货商更加方便。
无论这个供货商在世界的任何地方,只需要使用浏览器就可以进入这套系统,可以从沃尔玛的网站上得到多媒体格式的商品描述。
管理信息系统帮助沃尔玛与供应商建立了友好的协作关系,沃尔玛给予供应商的优惠远远超过同行。
沃尔玛对供应商品的付款期平均仅为29天,而美国第三大零售商凯马特平均为45天。
这激发了供应商与沃尔玛积极建立业务,从而保证了沃尔玛商品的最优进价。
如此高效率的财务结算,只有有了其全球化的高宽带管理信息系统网络才可能实现。
资料来源:尹涛. 管理信息系统. 北京:高等教育出版社,2005:29~31。
问题:(1) 随着经营规模的不断扩张,沃尔玛是如何逐渐利用信息系统支持运作的?(2) 在建立和使用信息系统时,管理上会面临哪些挑战?(3) 随着经济全球化和企业竞争的加剧,沃尔玛的管理者是如何利用信息技术提升企业的竞争力的?思考与讨论思考题1.当代企业面临的商务环境有何特点与趋势?试举例说明。
2.什么是知识经济?与工业经济相比,知识经济有哪些显著特征?3.当代商务环境的变化给企业带来的挑战主要有哪些?试举例说明。
4.企业在建立、运行和维护信息系统过程中,管理所面临的主要挑战有哪些?5.什么是信息化体系?查阅信息系统的参考书,比较不同作者所介绍的信息化体系结构有什么异同?6.什么是知识?什么是知识工作?7.成为一名精通信息的知识工作者的主要职责是什么?8.什么是知识工作者计算化?为什么它对我们非常重要?9.信息系统能引起管理变革吗?试举例说明。
讨论题1.有人说“当计算机变得更快更便宜时,信息系统给我们带来的大多数问题将消失”,请就这一说法进行讨论。
2.结合一个具体的企业,讨论其在建设和运用信息系统过程中遇到的问题与挑战有哪些。
若你是企业管理人员,你将采取哪些措施来应对这些问题与挑战。
3.知识工作者主宰当今的企业环境,然而,很多行业仍需要那些不属于知识工作者范畴的人。
哪些行业仍需要那些属于非知识工作者的技术工人呢?能否预见这些工作将由知识工作者取代的时间?“春发”借助信息技术发展企业天津春发香精香料有限公司是一家专门生产食品添加剂的民营企业。
春发的起家可以说是中国民营企业发展史的一个缩影。
1992年在邓小平同志南巡以后,“发展是硬道理”极大地鼓舞了渴望发展的中国人民。
一批民营中小企业在全国像雨后春笋一样发展起来。
春发的创始人就是在那时从几千块钱起步,如今已发展成为一个对整个中国食品工业有重要影响的企业。
目前,春发的年产值1亿元,虽然相比整个中国食品工业的10 000亿元年产值显得微不足道,但对于整个食品加工产业链来说,春发占据着一个举足轻重的地位,像华龙、统一、双汇、雀巢这样的著名企业都是天津春发的客户。
也就是说当消费者在享用各种休闲食品、快速食品和方便食品时,背后都有春发人的贡献。
按照西方国家经济发展的规律,人均GDP超过1 000美元后食品工业将大规模发展,而目前我国的肉类加工率只有7%~8%,这里蕴涵着巨大的发展空间。
春发在多年的生产经营中,形成了自己的核心技术,一直保持较高的生产率和利润率。
但是同许多发展中的企业一样,成长的肌体也会出现各种疾病,春发在发展中也出现了一些问题。
由于春发对客户信用控制力度不够,造成应收账款过多,资金占用的额度过于庞大,又由于欠款催收不及时造成了大量呆坏账;由于对外分销货物监控的力度不够,春发无法对经销商库存的产品进行预先的保质期预警,造成外放产品过期退货、库存物料报废损失;在采购方面,对供应商、自制半成品、产成品生产的物料需求和计划控制的信息不准确,造成生产过程中库存储备不均衡、采购批量不合理、浪费和占用流动资金较多;在生产方面,由于不能及时跟踪各批次产品实际成本和不合理损耗,对成本控制不能做到及时考核,使生产过程浪费很多,造成产品成本上升。
春发虽然已经成为食品添加剂行业排头兵,不过目前这一行业的集中度很低,春发面对的主要竞争对手是一批规模小,甚至非法的作坊式香精厂。
食品工业的未来发展对于春发来说既意味着巨大的机遇,也蕴藏着巨大的挑战。
随着食品行业的资源逐渐集中,香精香料工业也必然会紧随其后出现高度垄断的局面,到时候春发面对的就不是几个小作坊了。
日本前十名香料企业已经有3个进入了中国,美国国际香料集团也即将进入中国,虽然春发有着更熟悉中国消费者口味的本土化优势,但拥有雄厚资本的跨国企业完全可以通过收购解决这个问题。
虽然今天的春发活得很好,但是如果带着这些“管理弊病”,又如何能够适应国际化市场竞争的要求呢?对春发来说,面对国际强手的进入,不进则退。
春发董事会给自己制定了5年之内做到4个亿的打算,也就是意味着春发要进入更多咸味香精的细分市场和国际市场,并且要成为更多大型食品企业的供货商。
春发面临着发展的机遇,同时也遭遇到成长的烦恼和问题的困扰。
没有退路只有前进,适者生存是竞争的法则,只有应用信息技术方能适应信息时代的企业竞争,走企业信息化的道路是企业决策层经过深思熟虑以后的战略选择。
春发人选择了利用信息技术进行精细化管理,从而提升企业竞争力的方案。
从2003年初他们开始实施ERP,经过近一年的艰苦努力,取得了显著的实效。
仅原材料成本占用流动资金的减少就带来了一笔不小的收益,单位成本下降了5%,从3 000多万元的原材料资金中省下了100多万元。
从无形效益方面来讲,带来了管理的提升和全员整体素质的提高。
没用ERP时,五六个会计人员结账工作每月就要忙活十多天,核算成为他们的主要工作;有了ERP之后,财务人员用于核算的时间只有一两天,把剩下的大量时间转向了财务分析和管理。
春发的张总深有体会地说:“通过实施ERP,我们认识到,以信息化和标准化为手段的全过程的精细化管理,既是国外先进企业的现实状况,也是未来中国企业成功的必经之路,春发的信息化之路只是取得了良好的开端,好戏还在后头。
”现在,张总每天必做的事情是登录ERP,查看销售、回款、库存、成本数据,问题能够在第一时间发现,在问题的源头发现,从而使决策更加及时、准确。
春发从信息技术的应用中已经尝到了甜头,下一步春发公司准备把ERP的应用扩展到上游的客户以及下游的供应商,期望通过应用信息技术提高销售预测的准确度,规范对供应商的送货、结算管理。
资料来源:宋玉贤. 企业信息化管理. 北京:北京大学出版社,2005:34~37。
问题:(1) 许多企业都会遭遇到像春发那样的成长烦恼和发展困惑。
你认为春发利用信息技术解决发展中的问题是否正确?决策的依据是什么?(2) 如果你是春发的老总,面对这些问题,你会做出怎样的决策?(3) 随着企业竞争的加剧,企业管理者常常会感叹,信息时代,身在信息包围之中,却不知如何利用信息,甚至信息多得都“爆炸”了,却抓不住有用的信息。