ADC0832中文资料及汇编程序
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:132.04 KB
- 文档页数:4


ADC0832设计模块1、ADC0832的主要技术指标:(1)8位分辨率,逐次逼近型。
(2)5V电源供电时,基准电压为5V,输入模拟电压范围为0~5V。
(3)输入和输出电平与TTL和CMOS兼容。
(4)有两个可供选择的模拟输入通道。
(5)在250KHz时钟频率时,转换时间为32µs。
(6)一般功耗仅为15mW。
2、ADC0832引脚说明(1)/CS片选使能,低电平有效。
(2)CHO模拟通道0,差分输入时,作为IN+或IN-使用。
(3)CH1模拟输入通道1,差分输入时,作为IN+或IN-使用。
(4)GND 电源地。
(5)DI数据信号输出,选择通道控制。
(6)DO数据信号输出,转换数据输出。
(7)Vcc/Vre电源输入及参考电压输入(复用)。
(8)CLK芯片时钟信号3、ADC0832时序图4、运用ADC0832设计一个0-5V的数字电压表电路如图所示:设计要求:五位数码管动态显示,第一位显示通道状态(0、1)第二位显示C,第三位是个数,第三位和第四位数码管分别显示十分位和百分位;按键SW1选择通道0,按键SW2选择通道1,并且蜂鸣器和短时间鸣叫;调节滑动变阻器数码管的示数能在0.00~5.00之间变化。
C程序:/************************************************CAUCyeyongan*************************************************/#include <reg52.h>#include <intrins.h>#define uchar unsigned charsbit CS=P3^5;sbit Clk=P1^6; //时钟sbit DO=P3^7; //ADC0832输出引脚sbit DI=P3^6; //ADC0832输入引脚sbit key=P3^3; //按键bit keydownflg; //操作位的定义bit adc_flg;uchar dat,channel;uchar key_buffer;uchar P2_buffer;uchar Beep_cnt;uchar disp_cnt;uchar count4ms;uchar disp_buff[5]; //数码管显示缓存uchar code Tab1[]={0xC0,0xF9,0xA4,0xB0,0x99,0x92,0x82,0xF8,0x80,0x90,0x88,0x83,0xA7,0 xA1,0x86,0x8E}; //共阳数码表uchar code Tab[5]={0x7f,0xbf,0xdf,0xef,0xf7}; //数码管位选表uchar A_D(uchar CH) //AD函数{uchar i,adval,test; //定义局部变量并初始化adval=0x00;test=0x00;Clk=0; //clk低电平DI=1; //DI初始高电平在第一个时钟脉冲的下降沿前保持高电平,表示启动信号_nop_();CS=0; //片选_nop_();Clk=1; //clk上升沿,起始位写入_nop_();if(CH==0x00) //选择通道0{Clk=0; //clk低电平DI=1;_nop_();Clk=1; //clk上升沿,通道0的第一位写入_nop_();Clk=0;DI=0;_nop_();Clk=1; //clk上升沿,通道0的第二位写入_nop_();}else{Clk=0;DI=1;_nop_();Clk=1; //clk上升沿,通道1的第一位写入_nop_();Clk=0;DI=1;_nop_(); //clk上升沿,通道1的第二位写入Clk=1;_nop_();}Clk=0;DI=1;for(i=0;i<8;i++) //从高位向低位读取八位AD值{_nop_();adval<<=1;Clk=1;_nop_();Clk=0;if(DO)adval|=0x01;elseadval|=0x00;}for(i=0;i<8;i++){test>>=1; //从低位向高位读取八位AD值if(DO)test|=0x80;elsetest|=0x00;_nop_();Clk=1;_nop_();Clk=0;}if(adval==test) dat=test; //判断两个读取值是否相等相等就把读取的数赋值给DAT_nop_();CS=1;DO=1;Clk=1;return dat;}void FillDispBuffer(void) //数码管显示缓存函数{disp_buff[0]=channel; //显示通道disp_buff[1]=12; //显示"C"disp_buff[2]=dat/51; //显示个位disp_buff[3]=dat%51*10/51; //显示十分位disp_buff[4]=((dat%51)*10%51)*10/51; //显示百分位}void dealkey(void) //按键处理{if(keydownflg) return; //keydownflg控制位为1,不对按键进行处理key_buffer=P2;if((key_buffer&0x80)!=0x80) channel=0; //选择通道0if((key_buffer&0x40)!=0x40) channel=1; //选择通道1FillDispBuffer(); //数码管显示缓存Beep_cnt=0;keydownflg=1; //keydownflg控制位置1 }void main(void) //主函数{P0=0xff; //初始化P2=0xff;dat=0x00;disp_cnt=0;count4ms=0;channel=0;TMOD=0x10;TH0=(65535-4000)/256;TL0=(65535-4000)%256;EA=1;TR0=1;ET0=1;while(1){if(adc_flg) //ADC转换控制位,防止输入与输出产生冲突{adc_flg=0;A_D(channel); //ADC函数FillDispBuffer(); //数码管显示缓存}if(!key) //按键dealkey();}}void T0_service(void) interrupt 1 //定时器0中断子函数{TH0=(65535-4000)/256;TL0=(65535-4000)%256;P2_buffer=Tab[disp_cnt]; //查表,数码管的位选择if(keydownflg) //蜂鸣器0.4s的短时间鸣叫{P2_buffer=P2_buffer&0xfe;Beep_cnt++;if(Beep_cnt==100) keydownflg=0;}P2=P2_buffer; //数码管显示数字符号if(disp_cnt==2) //第三位数码管显示小数点P0=Tab1[disp_buff[disp_cnt]]&0x7f;elseP0=Tab1[disp_buff[disp_cnt]];disp_cnt++; //if(disp_cnt==5) disp_cnt=0;count4ms++;if(count4ms==50) //0.2s ADC转换一次{adc_flg=1;count4ms=0;}}。

ADC0831/ADC0832/ADC0834/ADC08388-Bit Serial I/O A/D Converters with Multiplexer OptionsGeneral DescriptionThe ADC0831series are 8-bit successive approximation A/D converters with a serial I/O and configurable input multiplex-ers with up to 8channels.The serial I/O is configured to comply with the NSC MICROWIRE ™serial data exchange standard for easy interface to the COPS ™family of proces-sors,and can interface with standard shift registers or µPs.The 2-,4-or 8-channel multiplexers are software configured for single-ended or differential inputs as well as channel as-signment.The differential analog voltage input allows increasing the common-mode rejection and offsetting the analog zero input voltage value.In addition,the voltage reference input can be adjusted to allow encoding any smaller analog voltage span to the full 8bits of resolution.Featuresn NSC MICROWIRE compatible —direct interface to COPS family processorsn Easy interface to all microprocessors,or operates “stand-alone”n Operates ratiometrically or with 5V DC voltage referencen No zero or full-scale adjust requiredn 2-,4-or 8-channel multiplexer options with address logic n Shunt regulator allows operation with high voltage suppliesn 0V to 5V input range with single 5V power supply n Remote operation with serial digital data link n TTL/MOS input/output compatiblen 0.3"standard width,8-,14-or 20-pin DIP package n 20Pin Molded Chip Carrier Package (ADC0838only)n Surface-Mount PackageKey Specificationsn Resolution8Bitsn Total Unadjusted Error ±1⁄2LSB and ±1LSBn Single Supply 5V DC n Low Power15mW nConversion Time32µsTypical ApplicationTRI-STATE ®is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.COPS ™and MICROWIRE ™are trademarks of National Semiconductor Corporation.DS005583-1August 1999ADC0831/ADC0832/ADC0834/ADC08388-Bit Serial I/O A/D Converters with Multiplexer Options©1999National Semiconductor Corporation Connection DiagramsADC08388-Channel MuxSmall Outline/Dual-In-Line Package(WM and N)DS005583-8Top ViewADC08344-Channel MUXSmall Outline/Dual-In-Line Package(WM and N)DS005583-30COM internally connected to A GND Top ViewTop ViewADC08322-Channel MUX Dual-In-Line Package (N)DS005583-31COM internally connected to GND.V REF internally connected to V CC .Top ViewTop ViewADC08322-Channel MUX Small Outline Package (WM)DS005583-41Top ViewADC0831Single Differential Input Dual-In-Line Package (N)DS005583-32Top ViewADC0831Single Differential Input Small Outline Package (WM)DS005583-42Top ViewADC08388-Channel MUX Molded Chip Carrier (PCC)Package (V)DS005583-33 2Ordering InformationPart Number Analog Input Total Package TemperatureChannels Unadjusted Error RangeADC0831CCN1±1Molded(N)0˚C to+70˚CADC0831CCWM SO(M)0˚C to+70˚CADC0832CIWM2±1SO(M)−40˚C to+85˚CADC0832CCN Molded(N)0˚C to+70˚CADC0832CCWM SO(M)0˚C to+70˚CADC0834BCN4±1⁄2Molded(N)0˚C to+70˚CADC0834CCN±1Molded(N)0˚C to+70˚CADC0834CCWM SO(M)0˚C to+70˚CADC0838BCV8±1⁄2PCC(V)0˚C to+70˚CADC0838CCV±1PCC(V)0˚C to+70˚CADC0838CCN Molded(N)0˚C to+70˚CADC0838CIWM SO(M)−40˚C to+85˚CADC0838CCWM SO(M)0˚C to+70˚CSee NS Package Number M14B,M20B,N08E,N14A,N20A or V20A3Absolute Maximum Ratings(Notes1,2) If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/ Distributors for availability and specifications.Current into V+(Note3)15mA Supply Voltage,V CC(Note3) 6.5V VoltageLogic Inputs−0.3V to V CC+0.3V Analog Inputs−0.3V to V CC+0.3V Input Current per Pin(Note4)±5mA Package±20mA Storage Temperature−65˚C to+150˚C Package Dissipationat T A=25˚C(Board Mount)0.8W Lead Temperature(Soldering10sec.)Dual-In-Line Package(Plastic)260˚C Molded Chip Carrier PackageVapor Phase(60sec.)215˚C Infrared(15sec.)220˚C ESD Susceptibility(Note5)2000V Operating Ratings(Notes1,2)Supply Voltage,V CC 4.5V DC to6.3V DC Temperature Range T MIN≤T A≤T MAX ADC0832/8CIWM−40˚C to+85˚C ADC0834BCN,ADC0838BCV,ADC0831/2/4/8CCN,ADC0838CCV,ADC0831/2/4/8CCWM0˚C to+70˚CConverter and Multiplexer Electrical Characteristics The following specifications apply for V CC=V+=V REF=5V,V REF≤V CC+0.1V,T A=T j=25˚C,and f CLK=250kHz unless otherwise specified.Boldface limits apply from T MIN to T MAX.Parameter Conditions CIWM Devices BCV,CCV,CCWM,BCNand CCN DevicesTyp Tested Design Typ Tested Design Units (Note12)Limit Limit(Note12)Limit Limit(Note13)(Note14)(Note13)(Note14)CONVERTER AND MULTIPLEXER CHARACTERISTICSTotal Unadjusted Error V REF=5.00VADC0838BCV(Note6)±1⁄2±1⁄2ADC0834BCN±1⁄2±1⁄2LSB(Max) ADC0838CCV±1±1ADC0831/2/4/8CCN±1±1ADC0831/2/4/8CCWM±1±1ADC0832/8CIWM±1Minimum Reference 3.5 1.3 3.5 1.3 1.3kΩInput Resistance(Note7)Maximum Reference 3.5 5.9 3.5 5.4 5.9kΩInput Resistance(Note7)Maximum Common-ModeInput Range(Note8)V CC+0.05V CC+0.05V CC+0.05VMinimum Common-ModeInput Range(Note8)GND−0.05GND−0.05GND−0.05V DC Common-Mode Error±1/16±1⁄4±1/16±1⁄4±1⁄4LSB Change in zero15mA into V+error from V CC=5V V CC=N.C.to internal zener V REF=5Voperation(Note3)111LSB V Z,internal MIN15mA into V+ 6.3 6.3 6.3diode breakdown MAX8.58.58.5V (at V+)(Note3)Power Supply Sensitivity V CC=5V±5%±1/16±1⁄4±1⁄4±1/16±1⁄4±1⁄4LSBI OFF,Off Channel Leakage On Channel=5V,−0.2−0.2−1µACurrent(Note9)Off Channel=0V−1On Channel=0V,+0.2+0.2+1µAOff Channel=5V+14Converter and Multiplexer Electrical Characteristics The following specifications apply for V CC=V+=V REF=5V,V REF≤V CC+0.1V,T A=T j=25˚C,and f CLK=250kHz unless otherwise specified.Boldface limits apply from T MIN to T MAX.(Continued)Parameter Conditions CIWM Devices BCV,CCV,CCWM,BCNand CCN DevicesTyp Tested Design Typ Tested Design Units (Note12)Limit Limit(Note12)Limit Limit(Note13)(Note14)(Note13)(Note14)CONVERTER AND MULTIPLEXER CHARACTERISTICSI ON,On Channel Leakage On Channel=0V,−0.2−0.2−1µA Current(Note9)Off Channel=5V−1On Channel=5V,+0.2+0.2+1µAOff Channel=0V+1DIGITAL AND DC CHARACTERISTICSV IN(1),Logical“1”Input V CC=5.25V 2.0 2.0 2.0V Voltage(Min)V IN(0),Logical“0”Input V CC=4.75V0.80.80.8V Voltage(Max)I IN(1),Logical“1”Input V IN=5.0V0.00510.00511µA Current(Max)I IN(0),Logical“0”Input V IN=0V−0.005−1−0.005−1−1µA Current(Max)V OUT(1),Logical“1”Output V CC=4.75VVoltage(Min)I OUT=−360µA 2.4 2.4 2.4VI OUT=−10µA 4.5 4.5 4.5VV OUT(0),Logical“0”Output V CC=4.75V0.40.40.4V Voltage(Max)I OUT=1.6mAI OUT,TRI-STATE Output V OUT=0V−0.1−3−0.1−3−3µA Current(Max)V OUT=5V0.130.1+3+3µAI SOURCE,Output Source V OUT=0V−14−6.5−14−7.5−6.5mA Current(Min)I SINK,Output Sink Current(Min)V OUT=V CC168.0169.08.0mAI CC,Supply Current(Max)ADC0831,ADC0834,0.9 2.50.9 2.5 2.5mA ADC0838ADC0832Includes Ladder 2.3 6.5 2.3 6.5 6.5mACurrentAC CharacteristicsThe following specifications apply for V CC=5V,t r=t f=20ns and25˚C unless otherwise specified.Typ Tested Design Limit Parameter Conditions(Note12)Limit Limit Units(Note13)(Note14)f CLK,Clock Frequency Min10kHzMax400kHzt C,Conversion Time Not including MUX Addressing Time81/f CLK Clock Duty Cycle Min40% (Note10)Max60%t SET-UP,CS Falling Edge or250ns Data Input Valid to CLKRising Edget HOLD,Data Input Valid90ns after CLK Rising Edge5AC Characteristics(Continued)The following specifications apply for V CC =5V,t r =t f =20ns and 25˚C unless otherwise specified.TypTested Design Limit ParameterConditions(Note 12)Limit Limit Units(Note 13)(Note 14)t pd1,t pd0—CLK Falling C L =100pF Edge to Output Data Valid Data MSB First 6501500ns (Note 11)Data LSB First 250600ns t 1H ,t 0H ,—Rising Edge of C L =10pF,R L =10k125250ns CS to Data Output and (see TRI-STATE ®Test Circuits)SARS Hi–ZC L =100pf,R L =2k500ns C IN ,Capacitance of Logic 5pF InputC OUT ,Capacitance of Logic 5pFOutputsNote 1:Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur.DC and AC electrical specifications do not apply when operating the device beyond its specified operating conditions.Note 2:All voltages are measured with respect to the ground plugs.Note 3:Internal zener diodes (6.3to 8.5V)are connected from V+to GND and V CC to GND.The zener at V+can operate as a shunt regulator and is connected to V CC via a conventional diode.Since the zener voltage equals the A/D’s breakdown voltage,the diode insures that V CC will be below breakdown when the device is powered from V+.Functionality is therefore guaranteed for V+operation even though the resultant voltage at V CC may exceed the specified Absolute Max of 6.5V.It is recommended that a resistor be used to limit the max current into V+.(See Figure 3in Functional Description Section 6.0)Note 4:When the input voltage (V IN )at any pin exceeds the power supply rails (V IN <V −or V IN >V +)the absolute value of current at that pin should be limited to 5mA or less.The 20mA package input current limits the number of pins that can exceed the power supply boundaries with a 5mA current limit to four.Note 5:Human body model,100pF discharged through a 1.5k Ωresistor.Note 6:Total unadjusted error includes offset,full-scale,linearity,and multiplexer errors.Note 7:Cannot be tested for ADC0832.Note 8:For V IN (−)≥V IN (+)the digital output code will be 00000000.Two on-chip diodes are tied to each analog input (see Block Diagram)which will forward conduct for analog input voltages one diode drop below ground or one diode drop greater than the V CC supply.Be careful,during testing at low V CC levels (4.5V),as high level analog inputs (5V)can cause this input diode to conduct —especially at elevated temperatures,and cause errors for analog inputs near full-scale.The spec allows 50mV forward bias of either diode.This means that as long as the analog V IN or V REF does not exceed the supply voltage by more than 50mV,the output code will be correct.To achieve an absolute 0V DC to 5V DC input voltage range will therefore require a minimum supply voltage of 4.950V DC over temperature varia-tions,initial tolerance and loading.Note 9:Leakage current is measured with the clock not switching.Note 10:A 40%to 60%clock duty cycle range insures proper operation at all clock frequencies.In the case that an available clock has a duty cycle outside of these limits,the minimum,time the clock is high or the minimum time the clock is low must be at least 1µs.The maximum time the clock can be high is 60µs.The clock can be stopped when low so long as the analog input voltage remains stable.Note 11:Since data,MSB first,is the output of the comparator used in the successive approximation loop,an additional delay is built in (see Block Diagram)to allow for comparator response time.Note 12:Typicals are at 25˚C and represent most likely parametric norm.Note 13:Tested limits are guaranteed to National’s AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level).Note 14:Guaranteed but not 100%production tested.These limits are not used to calculate outgoing quality levels.Typical Performance CharacteristicsUnadjusted Offset Error vs V REF VoltageDS005583-43Linearity Error vs V REF VoltageDS005583-44Linearity Error vs TemperatureDS005583-45 6Typical Performance Characteristics(Continued)Leakage Current Test CircuitLinearity Error vs f CLKDS005583-46Power Supply Current vs Temperature (ADC0838,ADC0831,ADC0834)DS005583-47Note:For ADC0832add I REF .Output Current vs TemperatureDS005583-48Power Supply Current vs f CLKDS005583-29DS005583-37TRI-STATE Test Circuits and WaveformsTiming Diagramst 1HDS005583-49t 0HDS005583-50t 1H DS005583-51t 0HDS005583-52Data Input TimingDS005583-24Data Output TimingDS005583-25ADC0831Start Conversion TimingDS005583-26 8Timing Diagrams(Continued)ADC0831TimingDS005583-27*LSB first output not available on ADC0831.ADC0832TimingDS005583-28ADC0834TimingDS005583-59Timing Diagrams(Continued)A D C 0838T i m i n gD S 005583-6*M a k e s u r e c l o c k e d g e #18c l o c k s i n t h e L S B b e f o r e S E i s t a k e n l o w10ADC0838Functional Block DiagramD S 005583-7*S o m e o f t h e s e f u n c t i o n s /p i n s a r e n o t a v a i l a b l e w i t h o t h e r o p t i o n s .N o t e 1:F o r t h e A D C 0834,D 1i s i n p u t d i r e c t l y t o t h e D i n p u t o f S E L E C T 1.S E L E C T 0i s f o r c e d t o a “1”.F o r t h e A D C 0832,D I i s i n p u t d i r e c t l y t o t h e D I i n p u t o f O D D /S I G N .S E L E C T 0i s f o r c e d t o a “0”a n d S E L E C T 1i s f o r c e d t o a “1”.11Functional Description 1.0MULTIPLEXER ADDRESSINGThe design of these converters utilizes a sample-data com-parator structure which provides for a differential analog in-put to be converted by a successive approximation routine. The actual voltage converted is always the difference be-tween an assigned“+”input terminal and a“−”input terminal. The polarity of each input terminal of the pair being con-verted indicates which line the converter expects to be the most positive.If the assigned“+”input is less than the“−”in-put the converter responds with an all zeros output code.A unique input multiplexing scheme has been utilized to pro-vide multiple analog channels with software-configurable single-ended,differential,or a new pseudo-differential option which will convert the difference between the voltage at any analog input and a common terminal.The analog signal con-ditioning required in transducer-based data acquisition sys-tems is significantly simplified with this type of input flexibility. One converter package can now handle ground referenced inputs and true differential inputs as well as signals with some arbitrary reference voltage.A particular input configuration is assigned during the MUX addressing sequence,prior to the start of a conversion.The MUX address selects which of the analog inputs are to be enabled and whether this input is single-ended or differential.In the differential case,it also assigns the polarity of the channels.Differential inputs are restricted to adjacent chan-nel pairs.For example channel0and channel1may be se-lected as a different pair but channel0or1cannot act differ-entially with any other channel.In addition to selecting differential mode the sign may also be selected.Channel0 may be selected as the positive input and channel1as the negative input or vice versa.This programmability is best il-lustrated by the MUX addressing codes shown in the follow-ing tables for the various product options.The MUX address is shifted into the converter via the DI line. Because the ADC0831contains only one differential input channel with a fixed polarity assignment,it does not require addressing.The common input line on the ADC0838can be used as a pseudo-differential input.In this mode,the voltage on this pin is treated as the“−”input for any of the other input channels. This voltage does not have to be analog ground;it can be any reference potential which is common to all of the inputs. This feature is most useful in single-supply application where the analog circuitry may be biased up to a potential other than ground and the output signals are all referred to this potential.TABLE1.Multiplexer/Package OptionsPart Number of Analog Channels Number ofNumber Single-Ended Differential Package PinsADC0831118ADC0832218ADC08344214ADC08388420 12Functional Description(Continued)TABLE2.MUX Addressing:ADC0838Single-Ended MUX ModeMUX Address Analog Single-Ended Channel#SGL/ODD/SELECT01234567COMDIF SIGN101000+−1001+−1010+−1011+−1100+−1101+−1110+−1111+−TABLE3.MUX Addressing:ADC0838Differential MUX ModeMUX Address Analog Differential Channel-Pair#SGL/ODD/SELECT0123DIF SIGN10012345670000+−0001+−0010+−0011+−0100−+0101−+0110−+0111−+TABLE4.MUX Addressing:ADC0834Single-Ended MUX ModeMUX Address Channel#SGL/ODD/SELECTDIF SIGN10123100+101+110+111+COM is internally tied to A GNDTABLE5.MUX Addressing:ADC0834Differential MUX ModeMUX Address Channel#SGL/ODD/SELECTDIF SIGN10123000+−001+−010−+011−+13Functional Description(Continued)TABLE6.MUX Addressing:ADC0832Single-Ended MUX ModeMUX Address Channel#SGL/ODD/01DIF SIGN10+11+COM is internally tied to A GNDTABLE7.MUX Addressing:ADC0832Differential MUX ModeMUX Address Channel#SGL/ODD/01DIF SIGN00+−01−+Since the input configuration is under software control,it can be modified,as required,at each conversion.A channel can be treated as a single-ended,ground referenced input for one conversion;then it can be reconfigured as part of a dif-ferential channel for another conversion.Figure1illustrates the input flexibility which can be achieved.The analog input voltages for each channel can range from 50mV below ground to50mV above V CC(typically5V)with-out degrading conversion accuracy.2.0THE DIGITAL INTERFACEA most important characteristic of these converters is their serial data link with the controlling ing a serial communication format offers two very significant system im-provements;it allows more function to be included in the converter package with no increase in package size and it can eliminate the transmission of low level analog signals by locating the converter right at the analog sensor;transmitting highly noise immune digital data back to the host processor. To understand the operation of these converters it is best to refer to the Timing Diagrams and Functional Block Diagram and to follow a complete conversion sequence.For clarity a separate diagram is shown of each device.1.A conversion is initiated by first pulling the CS(chip select) line low.This line must be held low for the entire conversion. The converter is now waiting for a start bit and its MUX as-signment word.2.A clock is then generated by the processor(if not provided continuously)and output to the A/D clock input.14Functional Description(Continued)3.On each rising edge of the clock the status of the data in (DI)line is clocked into the MUX address shift register.The start bit is the first logic “1”that appears on this line (all lead-ing zeros are ignored).Following the start bit the converter expects the next 2to 4bits to be the MUX assignment word.4.When the start bit has been shifted into the start location of the MUX register,the input channel has been assigned and a conversion is about to begin.An interval of 1⁄2clock pe-riod (where nothing happens)is automatically inserted to al-low the selected MUX channel to settle.The SAR status line goes high at this time to signal that a conversion is now in progress and the DI line is disabled (it no longer accepts data).5.The data out (DO)line now comes out of TRI-STATE and provides a leading zero for this one clock period of MUX set-tling time.6.When the conversion begins,the output of the SAR com-parator,which indicates whether the analog input is greater than (high)or less than (low)each successive voltage from the internal resistor ladder,appears at the DO line on each falling edge of the clock.This data is the result of the conver-sion being shifted out (with the MSB coming first)and can be read by the processor immediately.7.After 8clock periods the conversion is completed.The SAR status line returns low to indicate this 1⁄2clock cycle later.8.If the programmer prefers,the data can be provided in an LSB first format [this makes use of the shift enable (SE)con-trol line].All 8bits of the result are stored in an output shift register.On devices which do not include the SE control line,the data,LSB first,is automatically shifted out the DO line,after the MSB first data stream.The DO line then goes low and stays low until CS is returned high.On the ADC0838the SE line is brought out and if held high,the value of the LSB remains valid on the DO line.When SE is forced low,the data is then clocked out LSB first.The ADC0831is an excep-tion in that its data is only output in MSB first format.9.All internal registers are cleared when the CS line is high.If another conversion is desired,CS must make a high to low transition followed by address information.The DI and DO lines can be tied together and controlled through a bidirectional processor I/O bit with one wire.This is possible because the DI input is only “looked-at”during the MUX addressing interval while the DO line is still in a high impedance state.8Single-EndedDS005583-538Pseudo-DifferentialDS005583-544Differential DS005583-55Mixed ModeDS005583-56FIGURE 1.Analog Input Multiplexer Options for the ADC083815Functional Description(Continued)3.0REFERENCE CONSIDERATIONSThe voltage applied to the reference input to these convert-ers defines the voltage span of the analog input (the differ-ence between V IN(MAX)and V IN(MIN))over which the 256possible output codes apply.The devices can be used in ei-ther ratiometric applications or in systems requiring absolute accuracy.The reference pin must be connected to a voltage source capable of driving the reference input resistance of typically 3.5k Ω.This pin is the top of a resistor divider string used for the successive approximation conversion.In a ratiometric system,the analog input voltage is propor-tional to the voltage used for the A/D reference.This voltage is typically the system power supply,so the V REF pin can be tied to V CC (done internally on the ADC0832).This technique relaxes the stability requirements of the system reference as the analog input and A/D reference move together maintain-ing the same output code for a given input condition.For absolute accuracy,where the analog input varies be-tween very specific voltage limits,the reference pin can be biased with a time and temperature stable voltage source.The LM385and LM336reference diodes are good low cur-rent devices to use with these converters.The maximum value of the reference is limited to the V CC supply voltage.The minimum value,however,can be quite small (see Typical Performance Characteristics)to allow di-rect conversions of transducer outputs providing less than a 5V output span.Particular care must be taken with regard to noise pickup,circuit layout and system error voltage sources when operating with a reduced span due to the increased sensitivity of the converter (1LSB equals V REF /256).4.0THE ANALOG INPUTSThe most important feature of these converters is that they can be located right at the analog signal source and through just a few wires can communicate with a controlling proces-sor with a highly noise immune serial bit stream.This in itself greatly minimizes circuitry to maintain analog signal accu-racy which otherwise is most susceptible to noise pickup.However,a few words are in order with regard to the analog inputs should the input be noisy to begin with or possibly riding on a large common-mode voltage.The differential input of these converters actually reduces the effects of common-mode input noise,a signal common to both selected “+”and “−”inputs for a conversion (60Hz is most typical).The time interval between sampling the “+”in-put and then the “−”input is 1⁄2of a clock period.The change in the common-mode voltage during this short time interval can cause conversion errors.For a sinusoidal common-mode signal this error is:where f CM is the frequency of the common-mode signal,V PEAK is its peak voltage valueand f CLK ,is the A/D clock frequency.For a 60Hz common-mode signal to generate a 1⁄4LSB error (≈5mV)with the converter running at 250kHz,its peak value would have to be 6.63V which would be larger than allowed as it exceeds the maximum analog input limits.Due to the sampling nature of the analog inputs short spikes of current enter the “+”input and exit the “−”input at the clock edges during the actual conversion.These currents decay rapidly and do not cause errors as the internal com-parator is strobed at the end of a clock period.Bypass ca-pacitors at the inputs will average these currents and cause an effective DC current to flow through the output resistance of the analog signal source.Bypass capacitors should not be used if the source resistance is greater than 1k Ω.This source resistance limitation is important with regard to the DC leakage currents of input multiplexer as well.The worst-case leakage current of ±1µA over temperature will create a 1mV input error with a 1k Ωsource resistance.An op amp RC active low pass filter can provide both imped-ance buffering and noise filtering should a high impedance signal source be required.DS005583-57a)Ratiometric DS005583-58b)Absolute with a reduced SpanFIGURE 2.Reference Examples16Functional Description(Continued)5.0OPTIONAL ADJUSTMENTS5.1Zero ErrorThe zero of the A/D does not require adjustment.If the mini-mum analog input voltage value,V IN(MIN),is not ground a zero offset can be done.The converter can be made to out-put00000000digital code for this minimum input voltage by biasing any V IN(−)input at this V IN(MIN)value.This utilizes the differential mode operation of the A/D.The zero error of the A/D converter relates to the location of the first riser of the transfer function and can be measured by grounding the V IN(−)input and applying a small magnitude positive voltage to the V IN(+)input.Zero error is the differ-ence between the actual DC input voltage which is neces-sary to just cause an output digital code transition from0000 0000to00000001and the ideal1⁄2LSB value(1⁄2LSB=9.8 mV for V REF=5.000V DC).5.2Full-ScaleThe full-scale adjustment can be made by applying a differ-ential input voltage which is11⁄2LSB down from the desired analog full-scale voltage range and then adjusting the mag-nitude of the V REF input(or V CC for the ADC0832)for a digi-tal output code which is just changing from11111110to1111 1111.5.3Adjusting for an Arbitrary Analog Input Voltage RangeIf the analog zero voltage of the A/D is shifted away from ground(for example,to accommodate an analog input signal which does not go to ground),this new zero reference should be properly adjusted first.A V IN(+)voltage which equals this desired zero reference plus1⁄2LSB(where the LSB is calculated for the desired analog span,using1LSB= analog span/256)is applied to selected“+”input and the zero reference voltage at the corresponding“−”input should then be adjusted to just obtain the00HEX to01HEX code tran-sition.The full-scale adjustment should be made[with the proper V IN(−)voltage applied]by forcing a voltage to the V IN(+)in-put which is given by:where:V MAX=the high end of the analog input rangeandV MIN=the low end(the offset zero)of the analog range.(Both are ground referenced.)The V REF(or V CC)voltage is then adjusted to provide a code change from FE HEX to FF HEX.This completes the adjust-ment procedure.6.0POWER SUPPLYA unique feature of the ADC0838and ADC0834is the inclu-sion of a zener diode connected from the V+terminal to ground which also connects to the V CC terminal(which is the actual converter supply)through a silicon diode,as shown in Figure3.(Note3)This zener is intended for use as a shunt voltage regulator toeliminate the need for any additional regulating components.This is most desirable if the converter is to be remotely lo-cated from the system power source.Figure4and Figure5il-lustrate two useful applications of this on-board zener whenan external transistor can be afforded.An important use of the interconnecting diode between V+and V CC is shown in Figure6and Figure7.Here,this diodeis used as a rectifier to allow the V CC supply for the converterto be derived from the clock.The low current requirements ofthe A/D and the relatively high clock frequencies used(typi-cally in the range of10k–400kHz)allows using the smallvalue filter capacitor shown to keep the ripple on the V CC lineto well under1⁄4of an LSB.The shunt zener regulator canalso be used in this mode.This requires a clock voltageswing which is in excess of V Z.A current limit for the zener isneeded,either built into the clock generator or a resistor canbe used from the CLK pin to the V+pin.DS005583-11FIGURE3.An On-Chip Shunt Regulator Diode 17。

单片机驱动ADC0832模数转换程序ADC0832是美国国家半导体公司生产的一种8位分辨率、双通道A/D转换芯片。
ADC0832具有以下特点:8位分辨率;双通道A/D转换;输入输出电平与TTL/CMOS相兼容;5V电源供电时输入电压在0~5V之间;工作频率为250KHZ,转换时间为32μS;一般功耗仅为15mW;8P、14P—DIP(双列直插)、PICC多种封装;商用级芯片温宽为0°C to +70°C?,工业级芯片温宽为40℃ to +85℃模数转换芯片是用来模拟信号转为数字信号以便电脑处理的,可以用来对传感器的数据进行收集分析。
本来想买ADC0809的,它可以对8个模拟量进行采集,假如是一个脚用三个压力传感器,那就正好够用了。
这个ADC0832是跟单片机开发板一个淘宝店买的,因为那个淘宝店没有ADC0809。
网上搜了个ADC0832的转换函数,拼了个程序在开发板的四位数码管上显示转换过来的数据,要注意的是那个显示函数是调一次只显示四位数码管的一位的,所以不能转换显示转换显示这样,要转换,显示一次二次三次四次,转换,显示一次二次三次四次这样。
ADC0832引脚及代码如下:(一晚没睡,等下准备回家过清明扫墓去。
归去来兮!问西楼禁烟何处好?绿野晴天道。
马穿杨柳嘶,人倚秋千笑,探莺花总教春醉倒。
)//头文件: #include ; #include ;//变量定义:unsigned char ly_dis[4];//定义显示缓冲区code unsigned chartable[]={0xc0,0xf9,0xa4,0xb0,0x99,0x92,0x82,0xf8, 0x80,0x90};//表:共阳数码管 0-9unsigned char l_posit=0; //显示位置//引脚定义:sbit SMG_q = P3^4; //定义数码管阳级控制脚(千位)sbit SMG_b = P3^5; //定义数码管阳级控制脚(百位)sbit SMG_s = P3^7; //定义数码管阳级控制脚(十位)sbit SMG_g = P3^6; //定义数码管阳级控制脚(个位) sbit CS= P0^5;sbit Clk = P0^6;sbit DATI = P0^4;sbit DATO = P0^4;unsigned char dat = 0x00;//AD值unsigned char count = 0x00;//定时器计数unsigned char CH;//通道变量//函数声明:void display(void);//显示函数,显示缓冲区内容void delay(void);//unsigned char GetValue0832(bit Channel); unsigned char adc0832(unsigned char CH);//主函数,C语言的入口函数:void main(){unsigned int i=0;int ltemp;while(1){if(i==100){ltemp=adc0832(1);//隔时取模数转换(0~255对应0.00-5.00的电压) ly_dis[0]=ltemp/100;//显示百位值ltemp=ltemp%100;ly_dis[1]=ltemp/10; //显示十位值ltemp=ltemp%10;ly_dis[2]=ltemp/1; //显示个位值ly_dis[3]=0; //显示小数点后一位0}i++;if(i==3000)i=0;display(); //调用显示调一次只显示一位轮流显示四位delay();}}//显示函数,参数为显示内容void display(){P0=0XFF;//switch(l_posit){case 0: //选择千位数码管,关闭其它位SMG_q=0;SMG_b=1;SMG_g=1;P0=table[ly_dis[0]]; //输出显示内容 break;case 1: //选择百位数码管,关闭其它位 SMG_q=1;SMG_b=0;SMG_s=1;SMG_g=1;P0=table[ly_dis[1]];break;case 2: //选择十位数码管,关闭其它位 SMG_q=1;SMG_b=1;SMG_s=0;SMG_g=1;P0=table[ly_dis[2]]&0x7f;break;case 3: //选择个位数码管,关闭其它位 SMG_q=1;SMG_b=1;SMG_s=1;P0=table[ly_dis[3]];break;}l_posit++; //每调用一次将轮流显示一位if(l_posit>;3)l_posit=0;}//延时子函数,短暂延时void delay(void){unsigned char i=10;while(i--);}/************************************************ ****************************函数功能:AD转换子程序入口参数:CH出口参数:dat************************************************* ***************************/unsigned char adc0832(unsigned char CH) {unsigned char i,test,adval;adval = 0x00;test = 0x00;Clk = 0;//初始化DATI = 1;_nop_();CS = 0;_nop_();Clk = 1;_nop_();if ( CH == 0x00 )//通道选择{Clk = 0;DATI = 1;//通道0的第一位_nop_();Clk = 1;_nop_();Clk = 0;DATI = 0;//通道0的第二位 _nop_();Clk = 1;_nop_();}else{Clk = 0;DATI = 1;//通道1的第一位 _nop_();Clk = 1;_nop_();Clk = 0;DATI = 1;//通道1的第二位_nop_();Clk = 1;_nop_();}Clk = 0;DATI = 1;for( i = 0;i ;>;= 1; if (DATO)test |= 0x80;elsetest |= 0x00;_nop_();Clk = 1;_nop_();Clk = 0;}if (adval == test)//比较前8位与后8位的值,如果不相同舍去。

1.ADC0832驱动子程序#include <REGX51.H>#include <intrins.h> //常用汇编指令引用。
unsigned char tab[]={0xc0,0xf9,0xa4,0xb0,0x99,0x92,0x83,0xf8,0x80,0x98}; //共阳代码//接口电路sbit AD0832_CS = P3^5ﻩ; //片选信号sbit AD0832_CLK = P3^6; //时钟接口sbit AD0832_DI = P3^7; //数据接口void main( void){unsigned char i=0 , x =0 , y = 0 ;unsigned int temp=0;while(1){//时钟12Mhz, 整个转换时间为224us//使用芯片准备(参考PDF时序图)ﻩAD0832_CLK = 0 ; //时钟置低平ﻩ AD0832_DI = 1 ; //开始信号为高电平ﻩ AD0832_CS = 0;//片选信号置低,启动AD转换芯片//输入开始信号(构成一个正脉冲)_nop_();ﻩAD0832_CLK = 1 ; //时钟上升沿,输入开始信号_nop_();ﻩ AD0832_CLK = 0 ; //时钟下降沿//模拟信号输入模式选择(1:单模信号,0:双模差分信号)AD0832_DI = 1 ;ﻩ _nop_();ﻩ AD0832_CLK = 1 ; //时钟上升沿,输入开始信号ﻩ _nop_();AD0832_CLK = 0 ; //时钟下降沿//模拟信号输入通道选择(1:通道CH1,0:通道CH0)AD0832_DI = 0 ; //选择通道0_nop_();ﻩAD0832_CLK = 1 ; //时钟上升沿,输入开始信号_nop_();ﻩ AD0832_CLK = 0 ; //时钟下降沿///////////////////////////////////////////AD0832_DI = 1; //数据线置高,准备接收数据for(i = 0 ; i<8 ; i++)ﻩ //从高位移入数据{ﻩ AD0832_CLK = 1 ;_nop_();AD0832_CLK = 0 ; //时钟下降沿,AD0832输出数据,高位(MSB)先x = x<<1;ﻩﻩﻩ//数据左移位,补0if(AD0832_DI ==1)ﻩx = x | 0x01; //如果数据为“1”,移入1,} ﻩﻩﻩﻩ //如果数据为“0”,移入0,for(i = 0 ; i<8 ; i++)ﻩ //从低位移入数据ﻩ{y = y>>1; ﻩ//数据左移位,补0if(AD0832_DI==1)ﻩy =y| 0x80;ﻩ //如果数据为“1”,移入1,ﻩﻩﻩ//如果数据为“0”,移入0ﻩ AD0832_CLK = 1 ;_nop_();ﻩAD0832_CLK = 0 ; //时钟下降沿,AD0832输出数据,高位(MSB)先}//数据线置高,释放总线,完成一次转换AD0832_CLK = 1 ;ﻩ AD0832_DI = 1 ;AD0832_CS = 1 ;ﻩﻩ if(x==y) //输出{ﻩ temp = x *2 ; //(参考电压为5V,8位。

ADC08328位串行A/D 转换器ADC08321.功能特点ADC0832是NS(National Semiconductor)公司生产的串行接口8位A/D转换器,通过三线接口与单片机连接,功耗低,性能价格比较高,适宜在袖珍式的智能仪器仪表中使用。
ADC0832为8位分辨率A/D转换芯片,其最高分辨可达256级,可以适应一般的模拟量转换要求。
芯片具有双数据输出可作为数据校验,以减少数据误差,转换速度快且稳定性能强。
独立的芯片使能输入,使多器件连接和处理器控制变得更加方便。
通过DI 数据输入端,可以轻易的实现通道功能的选择。
其主要特点如下:●8位分辨率,逐次逼近型,基准电压为5V;●5V 单电源供电;●输入模拟信号电压范围为0~5V;●输入和输出电平与TTL 和CMOS 兼容;●在250KHZ 时钟频率时,转换时间为32us;●具有两个可供选择的模拟输入通道;●功耗低,15mW。
2.外部引脚及其说明ADC0832有DIP 和SOIC 两种封装,DIP 封装的ADC0832引脚排列如图6.21所示。
各引脚说明如下:●CS——片选端,低电平有效。
●CH0,CH1——两路模拟信号输入端。
●DI——两路模拟输入选择输入端。
●DO——模数转换结果串行输出端。
●CLK——串行时钟输入端。
●Vcc/REF——正电源端和基准电压输入端。
●GND——电源地。
3.单片机对ADC0832的控制原理一般情况下ADC0832与单片机的接口应为4条数据线,分别是CS、CLK、DO、DI。
但由于DO端与DI端在通信时并未同时有效并与单片机的接口是双向的,所以电路设计时可以将DO 和DI 并联在一根数据线上使用。
当ADC0832未工作时其CS输入端应为高电平,此时芯片禁用,CLK 和DO/DI 的电平可任意。
当要进行A/D转换时,须先将CS端置于低电平并且保持低电平直到转换完全结束。
此时芯片开始转换工作,同时由处理器向芯片时钟输入端CLK提供时钟脉冲,DO/DI端则使用DI端输入通道功能选择的数据信号。

adc0832模块程序/* ADC0832差分00工作方式*/#include#include"adc0832.h"#include"1602.h"sbit ADC_CS =P2^0;sbit ADC_CLK=P2^1;sbit ADC_DO =P2^2;sbit ADC_DI =P2^3;unsigned char adval;unsigned char ReadADC(void) //把模拟电压值转换成8位二进制数并返回{unsigned char i,ch,bb,cc,dd;ch=0;ADC_CS=0;ADC_DO=0;//片选,DO为高阻态for(i=0;i<10;i++){;}ADC_CLK=0;delay(2);ADC_DI=1;ADC_CLK=1;delay(2); //第一个脉冲,起始位ADC_CLK=0;delay(2);ADC_DI=1;ADC_CLK=1;delay(2); //第二个脉冲,DI=1表示双通道单极性输入ADC_CLK=0;delay(2);ADC_DI=1;ADC_CLK=1;delay(2); //第三个脉冲,DI=1表示选择通道1(CH2)ADC_DI=0;ADC_DO=1;//DI转为高阻态,DO脱离高阻态为输出数据作准备ADC_CLK=1;delay(2);ADC_CLK=0;delay(2);//经实验,这里加一个脉冲AD便能正确读出数据,//不加的话读出的数据少一位(最低位d0读不出?for(i=0;i<8;i++){ADC_CLK=1;delay(2);ADC_CLK=0;delay(2);ch=(ch<<1)|ADC_DO;//在每个脉冲的下降沿DO输出一位数据,最终ch为8位二进制数}ADC_CS=1;//取消片选,一个转换周期结束adval=ch;returnadval;}。

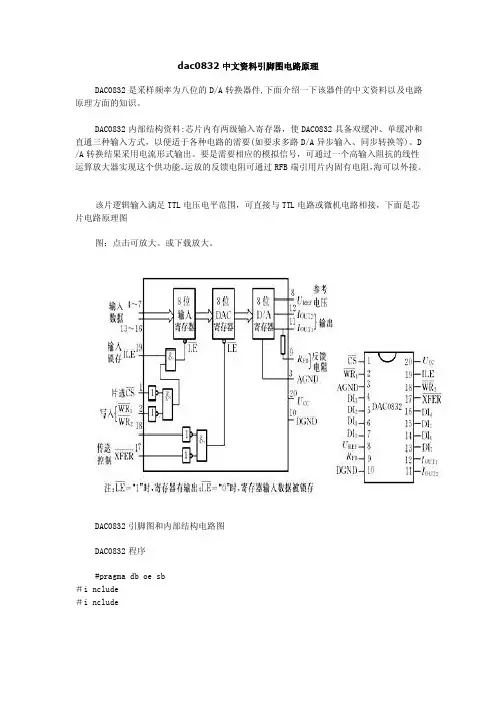
dac0832中文资料引脚图电路原理DAC0832是采样频率为八位的D/A转换器件,下面介绍一下该器件的中文资料以及电路原理方面的知识。
DAC0832内部结构资料:芯片内有两级输入寄存器,使DAC0832具备双缓冲、单缓冲和直通三种输入方式,以便适于各种电路的需要(如要求多路D/A异步输入、同步转换等)。
D /A转换结果采用电流形式输出。
要是需要相应的模拟信号,可通过一个高输入阻抗的线性运算放大器实现这个供功能。
运放的反馈电阻可通过RFB端引用片内固有电阻,海可以外接。
该片逻辑输入满足TTL电压电平范围,可直接与TTL电路或微机电路相接,下面是芯片电路原理图图:点击可放大。
或下载放大。
DAC0832引脚图和内部结构电路图DAC0832程序#pragma db oe sb#i nclude#i nclude#define DAC0832 XBYTE[0x7fff] /* 定义端口地址 */ #define uchar unsigned charvoid delay(uchar t) { /* 延时函数 */while(t--);}void saw(void) { /* 锯齿波发生函数 */uchar i;for (i=0;i<255;i++) {DAC0832=i;}}void square(void) { /* 方波发生函数 */DAC0832=0x00;delay(0x10);DAC0832=0xff;delay(0x10);}void main(void) { /* DAC0832主程序*/uchar i,j;i=j=0xff;while(i--) {saw(); /* 产生一段锯齿波 */}while(j--) {square(); /* 产生一段方波 */}。


//******************adc0832****************************// sbit CS=P1^0; //使能。
sbit CLK=P1^1;//时钟sbit Do=P1^2; // 数据输出sbit Di=P1^2;//数据输入unsigned char CH=0x02;//通道的选择:0x02就是单通道0;0x03就是单通道1;//0x00就是双通道ch0=“+”;ch0=“-”//0x01就是双通道ch0=“-”;ch0=“+”//*****************************************************// unsigned char ADconv(void){unsigned char i;unsigned int data_f=0,data_c=0;Di=1;CS=1;_nop_();CS=0;Di=1; ;//芯片使能之前的初始化。
第一个下降沿CLK=1;_nop_();_nop_();/****************************************/CLK=0; // 确定通道模式、第2个下降沿_nop_();_nop_();CLK=1;Di=(bit)(0x02&CH); //设定通道初始化_nop_();CLK=0;_nop_();_nop_();CLK=1;Di=(bit)(0x01&CH); //设定通道初始化 .第3个下降沿_nop_();_nop_();CLK=0; //AD转化的初始化完成。
Di=1;CLK=1;_nop_();_nop_();CLK=0;_nop_();CLK=1;for(i=8;i>0;i--)//得到一个正常排序的8位数据{data_f|=Do;data_f<<=1;CLK=1;_nop_();_nop_();CLK=0;_nop_();}for(i=8;i>0;i--)//得到一个反序排列的8位数据{data_c<<=1;data_c|=Do;_nop_();CLK=1;_nop_();_nop_();CLK=0;_nop_();CLK=0;_nop_();_nop_();CLK=1;_nop_();_nop_();CLK=0;_nop_();_nop_();CLK=1;_nop_();CS=1;_nop_();_nop_();return data_f;}void main(void){ unsigned int data_temp=0; while(1){ data_temp=ADconv();xs_int(196*data_temp,1);}}//***********************led.h*******************************************// //******************led1602**********/#include<intrins.h>#include<math.h>#define DD P2sbit Rs=P3^0;sbit Rw=P3^1;sbit E=P3^2;sbit busy_p=ACC^7;//********************************//void delay_1ms(unsigned char i) //最小延时1ms{ unsigned char j;while(i--)for(j=0;j<125; j++);}void delay_10ns(unsigned char i) //最小延时10ns{ unsigned char j;for(j=0;j<10; j++);}/*void rd_busy(void) //读忙。