化学物质英文命名规律全概要
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:862.50 KB
- 文档页数:59

有机化合物的英文命名官能团决定着有机化合物的性质,所以按照官能团来对有机化合物进行分类是有机化学常用的一种分类方法。
根据不同的官能团,有机化合物主要可分为:烃(hydrocarbon )、醇( alcohol )、醚( ether )、醛( aldehyde )、酮( ketone )、羧酸(carboxylic acid )、酯(ester )、胺(amine)、酰胺( amide)、氨基酸(amino acid )和氰( nitrile )等。
现在国际上通常用( 当然也是英文书籍、期刊中经常使用)的是国际纯粹与应用化学联合会系统命名法 , 简称 IUPAC 系统命名法。
同时, 出于历史、习惯或简便原因, 也使用一些普通名(common name)或俗名 ( trivial name ) ,甚至缩略名( abbreviatedname ,如TNT和DDT 等)。
除特别说明外, 本文讲的命名法为IUPAC 系统命名法。
Advanced Chemistry Development 公司的网站上找到,学生全部的IUPAC命名法也可以在也可以在需要的时候查询,具体地址为/iupac/nomenclature/一、烃的命名1.烷烃Alkanes烷烃的英文命名 :有关词头+–ane从第5个成员戊烷(pentane)开始,烷烃的命名根据其含碳数由希腊数字派生,如果希腊数字末尾带字幕–a, 命名对应的烷烃时直接在其后加– ne.例如:甲烷:methane 乙烷: ethane 丙烷:propane丁烷:butane 戊烷:pentane 己烷: hexane 庚烷:heptane 辛烷: octane 壬烷: nonane 癸gui 烷: decane 十一烷:undecane十二烷:dodecane 十五烷:pentadecane 十六烷:hexadecane烷烃消去一个氢原子之后就变成烷基(alkyl radical ), 烷基的英文名称将对应的烷烃词尾 -ane 改为 –yl例如:甲基: methyl 乙基: ethyl 正丙基; n-propyl异丙基: isopropyl正丁基: n-butyl( 普通命名 )1-butyl(系统命名)新戊基: neopentyl正戊基 n-pentyl异戊基: isopentyl上表中的“ n ”即“ normal ” , 相当于中文的“正” , 表示烃基中无支链 ; “ iso ”相当于中 文的“异” , 通常指烷基的一端有 (CH ) 2 CH - 结构 ; “ sec ”、“ tert ”即“ secondary ”、3“tertiary ” , 相当于中文的“仲”和“叔” , 分别表示该基团以其中的“仲”和“叔”碳原子和别的基团相连接。


化学物质的英文命名法
甲烷methane乙烷ethane丙烷propane 丁烷butane戊烷pentane己烷hexane 庚烷heptane辛烷octane
烷烃-ane 烯烃-ene 环烃-cyclo- 甲基methyl 乙基ethyl 二甲基dimethyl 二乙基diethyl 三。
tri- 氯chrolo 溴bromo 碘iodo 顺cis- 反trans-
二氯二甲基丙烷2-Chrolo-2-methylpropane 一溴一甲基环己烷1-Bromo-1-methylcyclohexane summary:首个字母大写,基团按字母表顺序,首字母在前的先写。
若有两个或三个重复的,di-,tri-不参与排列。
次序:bromo,chrolo,ethyl,methyl
一氯环己烯1-Methylcyclohexene 顺1,2二溴环戊烷trans-1,2-Dibromocyclopentane summary:cis-,trans-不为官能团,不用遵循首个字母大写。
异丁烯2-Methylpropene (普通命名Iso butyl ene) 二甲基一,三丁二烯2-Methyl-1,3-butadiene (普通命名Iso pr ene) 2,2-二甲基-3-乙基-3-庚烯3-Ethyl-2,2-dimethyl-3-heptene。

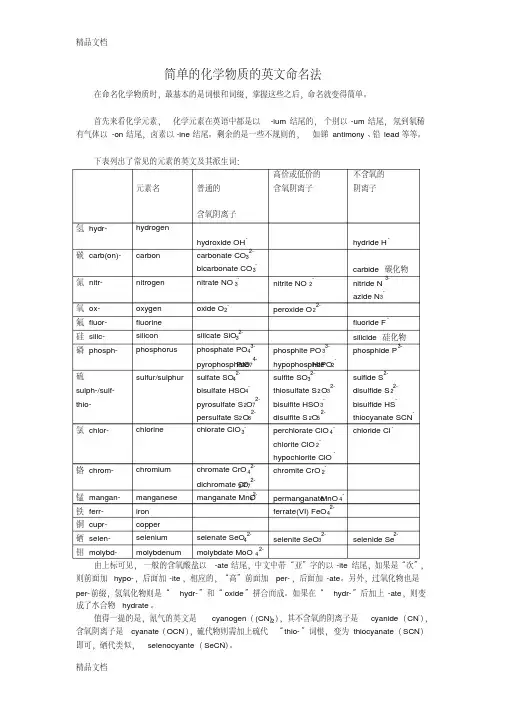
Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds无机化合物的命名(Prefix词头,前缀Suffix词尾,后缀Stem词根)1.Trivial Names俗名H2O water不说dihydrogen oxideNH3 ammonia不说nitrogen trihydrideCaO quicklimeCaCO3 limestone2.Systematic Nomenclature系统命名1)Oxide氧化物——先命名非氧元素ZnOzinc oxideCaO calcium oxideCO carbon oxideNa2O2 sodium peroxideH2O2hydrogen peroxide 注:peroxide过氧化物2)Hydroxide氢氧化物(base碱)Ba(OH)2 barium hydroxideKOH potassium hydroxide3)Acid酸Hydro acid氢酸General formula通式:HnX 命名:hydro- + stem of X + -ic acid H2S hydrosulfuric acid(英) hydrosulphuric(美) 氢硫酸S:sulfur(英)、sulphur(美) HBr 氢溴酸hydrobromic acidBr: bromine HCl 氢氯酸(盐酸)hydrochloric acidCl: chlorine HF 氢氟酸hydrofluoric acidF: fluorineOxoacid or Oxyacid含氧酸General formula通式:HnXOm 命名:Stem of X + -ic acid 注:oxo- (oxy-) 含氧, 氧代H2SO4 sulfuric acid(英) sulphuric acid(美)H2CO3 carbonic acidH3PO4 phosphoric acid P: phosphorus H3BO3 boric acid B: boron HNO3 nitric acid N: nitrogen If X has two oxidation states:-ic:the higher oxidation state-ous:the lower oxidation stateH2SO4 sulfuric acidH2SO3 sulfurous acid1/5HNO3 nitric acidHNO2 nitrous acidIf X (such as halogens) has more than two oxidation states:halogen卤素per- (过,高) + -ic:the still higher oxidation statehypo- (次,在…下) + -ous:the still lower oxidation stateHClO3 chloric acidHClO2 chlorous acidHClO4 perchloric acidHClO hypochlorous acidHIO hypoiodous acid4)Salt盐General formula通式:MnXm 命名:Name of M stem of X + -ide(-ide…化物)Oxide、chloride、nitride、hydrideKI potassium iodideAl2S3 aluminum sulfideLiH lithium hydrideOxysalt含氧酸盐Name the metal ion first and then the anionNaming anions:-ate anions derived from the -ic acid(the higher oxidation state of X)-ite anions derived from the -ous acid (the lower oxidation state of X)HNO3 nitric acidNaNO3 sodium nitrateHNO2 nitrous acidNaNO2 sodium nitriteSO42- sulfateSO32- sulfiteAgClO4 silver perchlorateNaIO3 sodium iodateKClO2 potassium chloriteKBrO potassium hypobromiteMnO42- manganateMnO4- permanganateAcid salt 酸式盐Using “hydrogen” to specify “H”NaHSO4 sodium hydrogen sulfateNaH2PO4 sodium dihydrogen phosphateNa2HPO4 disodium hydrogen phosphate P: phosphorus phosphate磷酸盐(根) Using prefix bi- + name of anion if only one acid salt existsNaHSO4 sodium bisulfateNaHSO3 sodium bisulfiteKHCO3 potassium bicarbonate5)Metals(M)with more than one oxidation state2/5Two methods:①后缀法: 早期使用stem of M + -ic the higher oxidation state of Mstem of M + -ous the lower oxidation state of MHgI2 mercuric iodideHg2I2 mercurous iodide Hg:mercury Cr2+ chromousCr3+ chromic Cr: chromium注:In most cases, Latin stem is used if the metal has symbol derived from itsLatin name.(mercury is an exception)Cu:cuprum (拉丁),copper (英)Cu+ cuprousCu2+ cupricCuI cuprous iodideCuS cupric sulfideSn:stannum (拉丁), tin (英)SnCl2 stannous chlorideSnO2 stannic oxideFe:ferrum (拉丁), iron (英)Fe(OH)2 ferrous hydroxideFeBr3 ferric bromide②IUPAC Rule 1957年开始使用English name of metal(Roman numeral)CuBr copper(I) bromideCuF2 copper(II) fluorideSnO tin(II) oxideSnS2 tin(IV) sulfideFe(NO3)2 iron(II) nitrateFe2(SO4)3 iron(III) sulfateUse Greek prefixes希腊文前缀Mon(o)一di二tri三tetr(a)四pent(a)五hex(a)六hepta七octa八nona九1.to specify the number of each atom in the chemical formula.NO2 nitrogen dioxidePCl5 phosphorus pentachlorideCO2 carbon dioxide2.to specify the number of identical central atoms in condensed acids and their corresponding anions.condensed acid缩酸H3PO4 (mono)phosphoric acidH4P2O7 diphosphoric acid3/5H2SO4 sulfuric acidH2S3O10 trisulfuric acidCrO42- 铬酸盐(根) chromateCr2O72- 重铬酸盐(根)dichromate3. to indicate extent of substitutionPO43- phosphatePS2O23- dithiophosphate thio-硫代…,硫的,含硫的注:The prefixes ortho- and meta- have been used to distinguish acids differingin the “content of water.”ortho- [希腊词头] 正、原(无机酸用)邻(位)(有机化合物命名)meta- [希腊词头] 偏(无机酸用)间(位)(有机化合物命名)ortho-acid 原酸;meta-acid 偏酸H3BO3 orthoboric acid(or boric acid)(原)硼酸(HBO3)n metaboric acid偏硼酸H4SiO4 orthosilicic acid(or silicic acid)原硅酸H2SiO3 metasilicic acid 硅酸(习惯上不叫偏硅酸)H3PO4 orthophosphoric acid (or phosphoric acid)(正)磷酸(HPO3)n metaphosphoric acid 偏磷酸。


有机化合物的英文命名官能团决定着有机化合物的性质,所以按照官能团来对有机化合物进展分类是有机化学常用的一种分类方法。
根据不同的官能团,有机化合物主要可分为:烃〔hydrocarbon〕、醇〔alcohol〕、醚〔ether〕、醛〔aldehyde〕、酮〔ketone〕、羧酸〔carboxylic acid〕、酯〔ester〕、胺〔amine〕、酰胺〔amide〕、氨基酸〔amino acid〕和氰〔nitrile〕等。
现在国际上通常用(当然也是英文书籍、期刊中经常使用) 的是国际纯粹与应用化学联合会系统命名法,简称IUPAC 系统命名法。
同时,出于历史、习惯或简便原因,也使用一些普通名(mon name)或俗名( trivial name ) , 甚至缩略名( abbreviatedname ,如TNT 和DDT 等) 。
除特别说明外,本文讲的命名法为IUPAC 系统命名法。
全部的IUPAC命名法也可以在 Advanced Chemistry Development 公司的上找到,学生也可以在需要的时候查询,具体地址为.acdlabs./iupac/nomenclature/一、烃的命名1. 烷烃 Alkanes烷烃的英文命名: 有关词头+ –ane 从第5个成员戊烷〔pentane〕开始,烷烃的命名根据其含碳数由希腊数字派生,如果希腊数字末尾带字幕–a,命名对应的烷烃时直接在其后加–ne.例如:甲烷: methane 乙烷:ethane 丙烷: propane丁烷: butane 戊烷: pentane 己烷:hexane庚烷: heptane 辛烷:octane 壬烷:nonane癸gui烷:decane 十一烷: undecane十二烷:dodecane 十五烷: pentadecane十六烷: hexadecane烷烃消去一个氢原子之后就变成烷基〔alkyl radical〕,烷基的英文名称将对应的烷烃词尾-ane 改为–yl例如:甲基:methyl 乙基:ethyl 正丙基;n-propyl异丙基:isopropyl正丁基:n-butyl(普通命名)1-butyl 〔系统命名〕新戊基: neopentyl 正戊基n-pentyl 异戊基:isopentyl上表中的“n〞即“normal〞,相当于中文的“正〞,表示烃基中无支链;“iso〞相当于中文的“异〞,通常指烷基的一端有(CH3 ) 2 CH - 结构;“sec〞、“tert〞即“secondary〞、“tertiary〞,相当于中文的“仲〞和“叔〞,分别表示该基团以其中的“仲〞和“叔〞碳原子和别的基团相连接。


中学化学物质的英⽂命名化合物的英⽂命名(Nomenclature of compounds)I ⽆机物的命名(Inorganic compounds)1 元素与单质的命名“元素”和“单质”的英⽂意思都是“element”,有时为了区别,在强调“单质”时可⽤“free element”。
因此,单质的英⽂名称与元素的英⽂名称是⼀样的。
下⾯给出的既是元素的名称,同时⼜是单质的名称。
S-block ElementIA IIAH Hydrogen Be BerylliumLi Lithium Mg MagnesiumNa Sodium Ca CalciumK Potassium Sr StrontiumRb Rubidium Ba BariumCs CesiumFr Francium Ra RadiumP-block ElementIIIA IV A V AB BoronC Carbon N NitrogenAl Aluminium Si Silicon P PhosphorusGa Gallium Ge Germanium As ArsenicIn Indium Sn Tin Sb AntimonyTl Thallium Pb Lead Bi BismuthVIA VIIA 0He Helium O Oxygen F Fluorine Ne NeonS Sulfur Cl Chlorine Ar ArgonSe Selenium Br Bromine Kr KryptonTe Tellurium I Iodine Xe XenonPo Polonium At Astatine Rn Radon Common Transition ElememtFe : iron Mn : manganeseCu: copper Zn: zincHg: mercury Ag: silverAu: gold2化合物的命名(4)tetra –,(5)penta- (6)hexa-,(7)hepta-,(8)octa-,(9)nona-,(10)deca-,但是在不会引起歧义时,这些前缀都尽可能被省去。

无机化合物的英文命名1. 金属氧化物,碱和盐的命名:原则:先说正离子名(对于有变价的金属后面要有价态标志,如I、II、III等),后说负离子名即可。
负离子的命名:(按照负离子的组成分为三类)1) All monoatomic anions have names ending with “ide” for example, F-(fluoride), Cl-(chloride), Br- (bromide), S2- (sulfide) and P3- (phosphide).2) Two polyatomic anions which also have names ending with “ide” are OH-(hydroxide) and CN- (cyanide).3) Many polyatomic anions contain oxygen in addition to another element. The number of oxygen atoms in such oxyanions is denoted by the use of suffixes “ite” and “ate”, meaning fewer and more oxyen atoms, respectively. In cases where it is necessary to denote more than two oxyanions of the same element, the prefixes “hypo” and “per”, meaning still fewer and still more ox ygen atoms, respectively, may be used.许多的多原子阴离子(polyatomic anion)除了氧原子之外还有另外一种元素。
这类含氧阴离子(oxyanion)中所含氧的数目由后缀“ite” 和“ate”来表示,分别意味着较多的氧原子和较少的氧原子。

有机化合物的英文命名官能团决定着有机化合物的性质,所以按照官能团来对有机化合物进行分类是有机化学常用的一种分类方法。
根据不同的官能团,有机化合物主要可分为:烃(hydrocarbon)、醇(alcohol)、醚(ether)、醛(aldehyde)、酮(ketone)、羧酸(carboxylic acid)、酯(ester)、胺(amine)、酰胺(amide)、氨基酸(amino acid)和氰(nitrile)等。
现在国际上通常用(当然也是英文书籍、期刊中经常使用) 的是国际纯粹与应用化学联合会系统命名法,简称IUPAC 系统命名法。
同时,出于历史、习惯或简便原因,也使用一些普通名(common name)或俗名( trivial name ) , 甚至缩略名( abbreviatedname ,如TNT 和DDT 等) 。
除特别说明外,本文讲的命名法为IUPAC 系统命名法。
全部的IUPAC命名法也可以在 Advanced Chemistry Development 公司的上找到,学生也可以在需要的时候查询,具体地址为.acdlabs./iupac/nomenclature/一、烃的命名1. 烷烃 Alkanes烷烃的英文命名: 有关词头+ –ane 从第5个成员戊烷(pentane)开始,烷烃的命名根据其含碳数由希腊数字派生,如果希腊数字末尾带字幕–a,命名对应的烷烃时直接在其后加–ne.例如:甲烷: methane 乙烷:ethane 丙烷: propane丁烷: butane 戊烷: pentane 己烷:hexane庚烷: heptane 辛烷:octane 壬烷:nonane癸gui烷:decane 十一烷: undecane十二烷:dodecane 十五烷: pentadecane十六烷: hexadecane烷烃消去一个氢原子之后就变成烷基(alkyl radical),烷基的英文名称将对应的烷烃词尾-ane 改为–yl例如:甲基:methyl 乙基:ethyl 正丙基;n-propyl异丙基:isopropyl正丁基:n-butyl(普通命名)1-butyl (系统命名)新戊基: neopentyl 正戊基n-pentyl 异戊基:isopentyl上表中的“n”即“normal”,相当于中文的“正”,表示烃基中无支链;“iso”相当于中文的“异”,通常指烷基的一端有(CH3 ) 2 CH - 结构;“sec”、“tert”即“secondary”、“tertiary”,相当于中文的“仲”和“叔”,分别表示该基团以其中的“仲”和“叔”碳原子和别的基团相连接。
有机化合物的英文命名官能团决定着有机化合物的性质,所以按照官能团来对有机化合物进行分类是有机化学常用的一种分类方法。
根据不同的官能团,有机化合物主要可分为:烃(hydrocarbon)、醇(alcohol)、醚(ether)、醛(aldehyde)、酮(ketone)、羧酸(carboxylic acid)、酯(ester)、胺(amine)、酰胺(amide)、氨基酸(amino acid)和氰(nitrile)等。
现在国际上通常用(当然也是英文书籍、期刊中经常使用) 的是国际纯粹与应用化学联合会系统命名法,简称IUPAC 系统命名法。
同时,出于历史、习惯或简便原因,也使用一些普通名(common name)或俗名( trivial name ) , 甚至缩略名( abbreviatedname ,如TNT 和DDT 等) 。
除特别说明外,本文讲的命名法为IUPAC 系统命名法。
全部的IUPAC命名法也可以在 Advanced Chemistry Development 公司的网站上找到,学生也可以在需要的时候查询,具体地址为/iupac/nomenclature/一、烃的命名1. 烷烃 Alkanes烷烃的英文命名: 有关词头+ –ane 从第5个成员戊烷(pentane)开始,烷烃的命名根据其含碳数由希腊数字派生,如果希腊数字末尾带字幕–a,命名对应的烷烃时直接在其后加–ne.例如:甲烷: methane 乙烷:ethane 丙烷: propane丁烷: butane 戊烷: pentane 己烷:hexane庚烷: heptane 辛烷:octane 壬烷:nonane癸gui烷:decane 十一烷: undecane十二烷:dodecane 十五烷: pentadecane十六烷: hexadecane烷烃消去一个氢原子之后就变成烷基(alkyl radical),烷基的英文名称将对应的烷烃词尾-ane 改为–yl例如:甲基:methyl 乙基:ethyl 正丙基;n-propyl异丙基:isopropyl正丁基:n-butyl(普通命名)1-butyl (系统命名)新戊基: neopentyl 正戊基n-pentyl 异戊基:isopentyl上表中的“n”即“normal”,相当于中文的“正”,表示烃基中无支链;“iso”相当于中文的“异”,通常指烷基的一端有(CH3 ) 2 CH - 结构;“sec”、“tert”即“secondary”、“tertiary”,相当于中文的“仲”和“叔”,分别表示该基团以其中的“仲”和“叔”碳原子和别的基团相连接。
有机化合物英文命名法
有机化合物英文命名法主要分为以下几种:
1. 烷基命名法:对于链状和支链状化合物,以主链为基础,用烷基来修饰分支部分。
2. 双键位置编号法:对于双键存在的化合物,以主链为基础,通过给双键编号来表示双键的位置。
3. 双键立体异构体命名法:对于含有双键的不对称化合物,根据E、Z规则来区分双键两侧基团的位置关系。
4. 羟基官能团命名法:对于含有羟基(-OH)的化合物,以主链为基础,通过在名称中加入“ol”来表示羟基的存在。
5. 醛、酮官能团命名法:对于含有醛(-CHO)或酮(-CO-)官能团的化合物,以主链为基础,在名称中加入相应的前缀或后缀来表示其存在。
6. 氨基官能团命名法:对于含有氨基(-NH2)的化合物,以主链为基础,在名称中加入“amine”来表示氨基的存在。
以上是常见的有机化合物英文命名法,需要根据具体情况选择适当的命名方法。