遥感影像数据产品级别
- 格式:docx
- 大小:18.93 KB
- 文档页数:3

北京揽宇方圆信息技术有限公司常见国产卫星遥感影像数据的简介本文介绍了常见国产卫星数据的简介、数据时间、传感器类型、分辨率等情况。
中国资源卫星应用中心产品级别说明◆1A级和1C级产品均为相对辐射校正产品,只是不同卫星选用的生产参数不同。
◆2级,2A级和2C级产品均为系统几何校正产品,只是不同卫星选用的生产参数不同。
其中:■GF-1卫星和ZY3卫星归档产品为1A级,ZY1-02C卫星数据归档产品级别为1C级,其他卫星归档级别为2级!◆归档产品是指:该类产品已经存在于系统中,仅需要从存储系统中迁移出来.即可供用户下载的数据。
◆生产产品是指:该类产品不是已经存在的产品,需要对原始数据产品进行生产,然后再提供给用户下载的数据。
■当用户需要的产品级别是上述归档的级别,直接选择相应的产品级别,然后查询即可!■当用户需要的产品级别不是上述归档的级别,就需要进行生产.本系统提供GF-1卫星和ZY3卫星2A级的生产产品,ZY1-02C卫星2C级的生产产品,在选择需要的级别查询后,无论有没有数据,在查询结果页上方有一个“查询0级景”按钮,点击此按钮后,进行数据查询,如果有数据,选择需要的产品直接订购,即可选择需要的产品级别。
国产卫星一、GF-3(高分3号)1.简介2016年8月10日6时55分,高分三号卫星在太原卫星发射中心用长征四号丙运载火箭成功发射升空。
高分三号卫星是中国高分专项工程的一颗遥感卫星,为1米分辨率雷达遥感卫星,也是中国首颗分辨率达到1米的C频段多极化合成孔径雷达(SAR)成像卫星,由中国航天科技集团公司研制。
2.数据时间2016年8月10日-现在3.传感器SAR:1米二、ZY3-02(资源三号02星)1.简介资源三号02星(ZY3-02)于2016年5月30日11时17分,在我国在太原卫星发射中心用长征四号乙运载火箭成功将资源三号02星发射升空。
这将是我国首次实现自主民用立体测绘双星组网运行,形成业务观测星座,缩短重访周期和覆盖周期,充分发挥双星效能,长期、连续、稳定、快速地获取覆盖全国乃至全球高分辨率立体影像和多光谱影像。
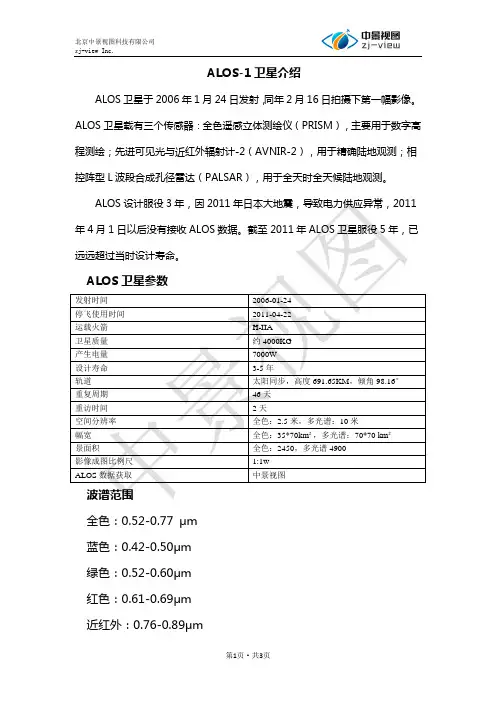
ALOS-1卫星介绍ALOS卫星于2006年1月24日发射,同年2月16日拍摄下第一幅影像。
ALOS卫星载有三个传感器:全色遥感立体测绘仪(PRISM),主要用于数字高程测绘;先进可见光与近红外辐射计-2(AVNIR-2),用于精确陆地观测;相控阵型L波段合成孔径雷达(PALSAR),用于全天时全天候陆地观测。
全色:0.52-0.77 μm蓝色:0.42-0.50μm绿色:0.52-0.60μm红色:0.61-0.69μm近红外:0.76-0.89μmALOS数据产品级别一、PRISM 数据产品Leve1 1A :原始数据分别附带独立的辐射定标和几何定标参数文件。
Leve1 1B1 :对1A数据做辐射校正,增加了绝对定标系数。
Leve1 1B2 :经过辐射与几何校正的产品。
提供地理编码数据和地理参考数据两种选择。
二、AVNIR-2 数据产品Leve1 1A :原始数据附带辐射校正和几何纠正参数。
Leve1 1B1 :对1A数据做辐射校正,增加了绝对定标系数。
Leve1 1B 2:经辐射与几何校正的产品。
提供地理编码数据、地理参考数据和DEM粗纠正数据(限日本区域)三种选择。
三、PALSAR 数据产品Leve1 1.0 :未经处理的原始信号产品,附带辐射与几何纠正参数。
Leve1 1.1 :经过距离向和方位向压缩,斜距产品,单视复数数据。
Leve1 1.5 :经过多视处理及地图投影,未采用DEM高程数据进行几何纠正。
提供地理编码或地理参考数据两种选择,投影方式可选,数据采样间隔根据观测模式可选。
中景视图全色存档数据库中景视图多光谱存档数据库。

1007-4619(2013)03-0566-12Journal of Remote Sensing㊀遥感学报Classification and gradation rule for remotesensing satellite data productsWANG Jinnian ,GU Xingfa ,MING Tao ,ZHOU XiangInstitute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth of Chinese Academy of Sciences ,Beijing 100101,ChinaAbstract :Remote sensing information products utilizing the multi -source,multi -scale,multi -temporal,multi -type remote sensingsatellite data and ground observation data become important research topics.The various classification and gradation rules of data products from different remote sensing satellites in different countries have difficulty in meeting the requirements of the integration of multi -source and multi -type geographic information.The main products series as well as the classification and gradation rules for both domestic and abroad usage were investigated in this paper.A new classification and gradation rule for remote sensing satellite data products in China was provided following the principles of efficiency,science,integrality compatibility,maneuver -ability,and extendibility.The classification rule was based on the spectral character and data acquisition method,whereas the gradation rule was based on the processing level of remote satellite data.The uniform classification and gradation rule was built.The rule could keep up with the correlative international standards that is still on progress.The rule included major remote sensing satellite data products at present and could conveniently build a mapping mechanism with other classification and gradation rules.Its scalability can meet the requirements of classification and gradation for new products in the future.The rule provided the basis for research on the indicator system of classification and gradation and for the development of correlative national standards.Key words :remote sensing satellite data products,classification,gradation,indicator system,standardization CLC number :TP701㊀㊀㊀Document code :ACitation format :Wang J N ,Gu X F ,Ming T and Zhou X.2013.Classification and gradation rule for remote sensing satellite dataproducts.Journal of Remote Sensing ,17(3):000-000Received :2012-11-21;Accepted :2012-10-09Foundation :National satellite application high -tech industrialization special project Research on autonomous remote sensing satellite data products and serv -ices technical standards and development of support system high -tech industrialization demonstration projectFirst author biography :WANG Jinnian (1966 ㊀),male,professor.His research interests are hyperspectral remote sensing,comprehensive application tech -nology on RS,GIS and GPS.E -mail:jwang@1㊀THE INTEGRATION OF MULTI-SOURCE NEEDS A UNIFORM CLASSIFICATION AND GRADATION RULEThe remote sensing satellite application in China started towards the end of 1970s.Remote sensing data depend on imported sources because of the absence of an autonomous remote sensing data source.The earth observation technology and application in China have greatly progressed recently.China already have autonomous remote sensing satellites now,such as Fengyun (FY )meteorological satellite series,ocean satellite series,China -Brazil Earth Resources Satellite (CBERS)series,Huanjing series,Beijing -1,and Tianhui,but also obtained a large amount of optical and microwave data.More advanced high -resolution earth observation satellites and marine -land observation satellites have been included in planning.Two kinds of commonly used data resources have been recently formed.In the foreseeable future,autonomous remote sensing data will gradually become the main data source and the international cooperation in the global earth observing system has increasingly expanded.The remote sensing satellite application in China has devel -oped from experimental to business and industrial operations inmany application domains.With the rapid increase in data acqui -sition capacity and the constant expansion of application domain,the need for sharing and integrating applications for remote sens -ing satellite data resources has increased.The requirement of global massive multi -source seamless database as a technical support for global observation and global scientific research,creates a new challenge to the existing model of data integration.In addition,the development of spatial information industry chain has made a higher demand for data production processing ability,especially in standardization and scale processing capacity.The integration of multi -source,multi -temporal,multi -scale,and multi -type remote sensing data,the integrated utilization of multi -type remote sensing data,ground observation information,and the further utilization of remote sensing data products with large -scale production capacity have become the important and urgent development direction.The uniform classification and gradation rule for remote sensing satellite data products is the foundation of exchange,integration,and integrated application of multi -resource data.The inconsistency among existing classification and gradation rules of different series of remote sensing satellite data products leads to the inconsistency between product specifications and testing methods.This inconsistency has not only influenced the网络出版时间:2013-03-27 11:04网络出版地址:/kcms/detail/11.3841.TP.20130327.1104.004.htmlWANG Jinnian,et al.:Classification and gradation rule for remote sensing satellite data products567㊀utilization by integration of multi-source,multi-scale,multi-temporal,multi-type remote sensing satellite data,as well as deep exploitation and utilization of remote sensing information prod-ucts,but also influenced the effective evaluation of users on the performance and quality of data products from different sources. The absence of uniform classification and gradation rule for remote sensing satellite data products has caused increasing obstacles in large-scale production and application of data prod-ucts in the development of spatial information industry.International organizations,such as International Organization for Standardization(ISO),are accelerating the development of relevant standards to meet the challenges in this technology. Some international geographic information standards such as ISO/TS19101-2Geographic information-Reference model-Part 2:Imagery,ISO/TS19130Geographic information-Sensor and data model for imagery and gridded data,ISO/DIS19144-1 Geographic information-Classification systems-Part1:Classification system structure,ISO/RS19124Geographic information-Imagery and gridded data components,and ISO19115 Geographic Information-Metadata standardize the classification of remote sensing sensors,imagery data format,classification system,and production of data products,et al.They laid the foundation for the creation of the uniform classification and gradation rule.2㊀THE MAJOR EXISTING CLASSIFICATION AND GRADATION RULE FOR REMOTE SENSING SATELLITE DATA PRODUCTS ㊀㊀Several classification and gradation rules exist for remote sensing satellite data products domestic and abroad.These rules are mainly based on satellite observation objects,observation models,and application goals.The ocean and meteorological satellites with low spatial resolution are types of satellites wherein observation objects are dynamic phenomena in larger areas.The data product character-istics of these satellites are low spatial resolution,high temporal resolution,and emphasis on spectral applications.The rules for these data products are relatively uniform.Radiometric correction and system geometric correction are finished in level1,whereas the production of parameter inversion is in level2and in higher levels.The data products include FY-2C/2D/2E[1],HY-1(State Oceanic Administration People s Republic of China,2004), MODIS[2-4],and ASTER[5-6],et al.In recent years,the applica-tions of meteorological and ocean satellites have gradually progressed beyond the traditional professional scope.They are increasingly used in environmental protection,traffic management,city structures,and several other fields.The original classification and gradation rules for data products were unable to meet the need for data integration and sharing.The land satellite is another type of satellite wherein the observation objects are land surfaces.The observation area is small and the required precision is high.The data product char-acteristics of this type of satellite include high spatial resolution and low temporal resolution.The existing classification and gra-dation rules for land satellites data products were created mainly according to the satellite series.The gradation rules for panchro-matic and multispectral data products are comparative maturity. The system geometric correction,relative radiometric calibration, and absolute radiometric calibration are usually finished in level 1or level2.Advance data products are produced in level3or higher.The typical rules include CBERS(State Commission of Science and Technology for National Defense Industry,2007), HJ1A/1B(Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People s Republic of China,2011),BJ-1[7],LandSat[8],WorldView[9], GeoEye[10],and SPOT(SPOT Image,2003),et al.The application of hyperspectral remote sensing has recently started and the gradation rules of hyperspectral data products refer to the multi-spectral data products.The gradation rules of microwave satellite data products are clearer.The typical gradation rules include EnviSat(ESA,2007)and RadarSat(European Space Agenly, 2009).[1]Fengyun satellite remote sensing data service web.Data Overview.http:// /PortalSite/Ord/DataOverview.aspx[2]USGS.MODIS OverView.[2012-03-22]/products /modis_overview[3]National Aeronautics and Space Administration.MODIS DATA PROD-UCTS.[2012-03-26]/data/[4]The Resources and Environment Remote Sensing Database.MODIS Data Description.[2012-03-20]/ modisintruduction.asp[5]Earth Remote Sensing Data Analysis Center.ASTER Standard and Semi-Standard Products.[2012-03-28]http://www.gds.aster.Ersdac.or.jp/gds_ www2002/exhibition_e/a_products_e/a_product2_e.html[6]Jet Propulsion Laboratory.ASTER Data Products.[2012-03-28]http:// /data_products.asp[7]BLMIT.Product Type.[2012-03-05]/document/ chanpinfuwu.jsp[8]National Aeronautics and Space ndsat Science Data Us-ers Handbook.[2012-03-25]/ [9]Digital Globe.DigitalGlobe_Core_Imagery_Products_Guide.[2012-03-25]/downloads/DigitalGlobe_Core_Imagery_ Products_Guide.pdf[10]GeoEye.Product Specifications.[2012-04-02]/ CorpSite/products-and-services/imagery-collection/satellite-imagery-products/ product-specifications.aspxAlthough great differences exist among classification and gradation rules for different types of remote sensing satellite data products,the rules have basic common aspects and compatibility because of the systematized remote sensing science and the common points in data processing flow.The classification of data products is according to the observation model of sensor.Data products are divided into optical and microwave data products, and can be further subdivided.The gradation of data products is according to processing level.The basic processes of optical or microwave products include geometric correction and radiometric calibration.Therefore,a systematic,scientific,and highly compatible rule that can unify the gradation rule could be made based on the processing levels of geometric correction and radiometric calibration.3㊀THE FORMULATING PRINCIPLE OF CLAS-SIFICATION AND GRADATION RULE㊀㊀The consensus on the classification of data products in remote sensing application area and gradation of data products in568㊀Journal of Remote Sensing㊀遥感学报㊀2013,17(3)Table1㊀Typical gradation rules of remote sensing data productsData Product Level DescriptionMODIS Level0Row dataset received from satellite without any processingLevel1Data rebuilt from row data with time registration and auxiliary annotation including L1A and L1BLevel2Derived geophysical variables at the same resolution and location as level1source data(swath products)Level3Gridded variables in derived spatial and/or temporal resolutionsLevel4Model output or results from analyses of lower-level dataHY-1A Data Product Level0COCTS:row data after data detaching cocts.L0Level1CCD:row data after data detaching cocts.L0Level1L1A and L1B data by cloud detection,geographic positioning and radiometric calibrationLevel2COCTS:six leaving radiance data products(412,443,490,510,555,and670band),three atmospheric aerosol radiation data products(670,750,and865band),aerosol radiation by band7to band8,aerosol optical depth(865band),chlorophyll-αdistri-bution,surface temperature distribution,suspended sediments distribution,diffuse attenuation coefficient LANDSAT-7Level1Radiometric calibration date product without geometric correctionLevel2Radiometric calibration and geometric correction data products have been mapped to map projection.Level3Radiometric calibration and geometric correction data products with Ground Control Points(GCPs),called precise geometric correc-tion productsLevel4Systematic geometric correction product,radiometric and precise geometric correction products using Digital Terrain Model(DTM) for terrain parallax correction.CBERS-01/02/02B Level0Raw data:frame synchronized and decommutated computer compatible data.Level1Radiometric correction product,radiometrically corrected and geometrically raw dataLevel2Systematically geometric correction product,radiometrically and geometrically corrected using systematic model without Ground Con-trol Points(GCPs).Level3Precise geometric correction product,radiometrically and geometrically corrected using GCPs.Level4DTM-based correction product,radiometrically and geometrically corrected using GCPs and Digital Terrain Model(DTM)for terrain parallax correction.Level5Standard mosaic image product,seamless mosaic image based on Level4image.EnviSat Data Product Row data data received directly from satellite and stored in high density tapeLevel0Data reformatted from row data and stored by time sequenceLevel1b Geographical location data products,conversion to project unit,dividing auxiliary data from measuring data,radiometrically selectiveLevel2Geographical location geophysical parameters productsdifferent data provider lays the foundation for making uniform classification and gradation rule.The following principles were used to create the classification and gradation rule.(1)System and science:The rule should follow the laws of remote sensing science and applied science.The theory and tech-nology of data acquisition and data processing should be taken as the foundation of classification and gradation.The systems science as the design guide of classification and gradation archi-tecture and the requirements of applied science to remote sensing are the basis on the design of the classification and gradation index system.(2)Integrity:Several different data products exist in the spatial information industry in China,including domestic and abroad usage.Thus,the formulation of classification and gradation rule should cover all kinds of existing data products, reflect the situation of different application direction,and meet future requirements.(3)Operability:Several existing classification and gradation rules are encountered by expert users that bring difficult to common users.Thus,the rule should focus on the development of spatial information industry and meet the requirements of data processing by data providers and data users.The rule should be concise,highly versatile,convenient to operate,and acceptable.(4)Compatibility:The rule should refer to existing kinds of related standards,specifications,classifications,and gradation rules.The formulation of the rule should based on existing achievement,maintain maximum compatibility with existing rules,and conveniently establish mapping with existing rules.(5)Expandability:The classification and gradation architec-ture should be expandable.The rule should meet the special application requirement and distinctive data products by expanding into subclasses and sublevels.The rule should also maintain the capacity to accept future data products.4㊀THE CLASSIFICATION OF REMOTE SENS-ING SATELLITE DATA PRODUCTS㊀㊀In remote sensing applications,the understanding on the classification of remote sensing satellite data products is uniform. The classification of data products is based on the type of sensor. In ISO/TS19101-2Geographic information-Reference model-Part2:Imagery,the sensors are divided into optical sensor, microwave sensor,laser radar,and sonar,et al.The optical and microwave sensors are further divided.Optical sensors areWANG Jinnian,et al.:Classification and gradation rule for remote sensing satellite data products569㊀divided into panchromatic,multispectral,and hyperspectral sensors,et al.Microwave sensors are divided into active micro-wave,and passive microwave sensors,among others.The indica-ted principles of classification are generally accepted.According to the principles,the classification could adopt the structure of class-division-section. The class could be created according to the type of sensor.Based on the international standard,the data products are divided into four classes including optical data product,microwave data product, laser data product,and other data products.The class is divided into divisions according to four aspects, such as detection wave band range,spectral resolution,character-istic of detection object,and detection mode.The satellite finishes remote sensing by electromagnetic radiation measurement.Different sensors are sensitive to specific electro-magnetic radiation bands.Thus,the band is an import factor in dividing the class.The division of wave bands according to the practical application of optical and microwave wave bands based on the International Lighting V ocabulary(1987,CIE)and IEEE Standard Letter Designations for Radar-Frequency Bands(2002, IEEE).The multispectral and hyperspectral wave bands both include visible light and infrared.The difference is the quantity of bands.Thus,spectral resolution could be used as the factor to differentiate between multispectral data product and hyperspectral data product(Tong,et al.,2006).Different sensors detect different physical quantities.The characteristics of the detection object could also be used to classify data products. Therefore,the users could select the appropriate data products to meet the application requirement.The detection mode can have an important effect on the application direction and data quality. For example,hyperspectral data products have more abundant and accurate spectral information than multispectral data products. They also have better description and reflection of the characteris-tics of the surface features.Thus,detection mode is also a main factor in showing the application value of data products.According to the discussed factors,optical and microwave data products are divided into several divisions.Optical data products are divided into panchromatic,multispectral,hyperspec-tral,and thermal infrared data products.Microwave data products are divided into active and passive microwave data products.A division can be divided into several sections according to the application direction by the data provider or application user. The scheme of the divisions and sections of remote sensing satel-lite data products is shown in Table2.Table2㊀The scheme of classes and divisions of remote satellite data productsData product Class Division Detection waveband range/μmSpectralresolution/nmCharacteristic ofdetection object Detection modeOptical data productPanchromatic0.4 0.7 Reflectance Detecting surface luminance of object by single-channel detector Multispectral0.36 2.5100Reflectance Detecting surface luminance and spectrum information of object bymulti-channel detectorHyperspectral0.36 2.510Reflectance Achieving continuous spectrum in high spectral resolution by ima-ging spectrometerThermal infrared3 1.0ˑ103 Radiant temperature,emissivity Detecting radiation energy by thermal detectorsMicrowave Active100 3.0ˑ105 Backscatteringcoefficient Detecting and ranging by emitting microwavePassive 3.0ˑ105 Brightnesstemperature Detecting and surveying microwave irradiation emitted by objectLaser data product0.1 1.0ˑ103 Range,Backscatteringcoefficient Getting range information by emitting laser and information pro-cessingOther data product Other remote sensing except for three detecting modes above,suchas gravity and magnetic field5㊀THE GRADATION OF REMOTE SENSING SATELLITE DATA PRODUCTS5.1㊀The level of remote sensing satellite data prod-ucts㊀㊀Two schemes exist in gradation of remote sensing data products.The first scheme emphasizes on the geometric correction and radiometric calibration as the main basis with5 8levels,as represented by the land observation satellite.Another scheme emphasizes on the order in producing retrieval products with less than five levels,as represented by ocean and meteoro-logical satellites.The application trend of ocean and meteorologi-cal satellite data products and the application requirements of land observation are closer.The quantitative and testing require-ments of data products increasingly become higher.Thus,the gradation scheme of the land observation satellite is selected as the uniform gradation scheme while considering the compatibility with other schemes.In this scheme,the products are divided into eight levels,which include row data,level0, primary data products(levels1and2),and advance data products (levels3 6).This scheme can not only coordinate with the scheme of the land observation satellite and maintain compatibility with the scheme of ocean and meteorological satel-lites.5.2㊀The establishment of sublevelIn remote satelliate applications,the produced methods of data products are divided into geometric correction,radiometric570㊀Journal of Remote Sensing㊀遥感学报㊀2013,17(3)correction,imagery fusion,and parameter inversion,et al., according to the produced targets.Among these methods,the geometric correction and radiometric calibration are considered the necessary and basic methods.Each level of data product can be divided into four sublevels according to the produced meth-ods.(1)Radiometric calibration sublevelAccording to the different processing stages,the radiometric calibration of data product is divided into four stages,which includes relative radiometric calibration,absolute radiometric calibration,atmospheric correction,and topographic radiometric correction.These stages correspond with the primary data products and advance data products from level1to level4.(2)Geometric correction and representation sublevelThe geometric correction processing is divided into system geometric correction,geometric accurate correction,and ortho correction,et al.They correspond with the primary and advance data products from level1to level4.With the development of information integration requirement,the geometric representation does not only include imagery but also includes more geographic information to enhance the information on the representation of features.Thus,navigation and positioning information,funda-mental geographic information,and three-dimensional represen-tation are additional requirements to distinguish level5and level 6data products.(3)Imagery fusion sublevelThe imagery fusion includes the pixel,feature,and decision level fusions in ISO/TS19101-2Geographic information-Refer-ence model-Part2:Imagery.The difference in the imagery fusion of different data product classes are fully considered in this scheme.The imagery fusion is divided into four levels,including pixel level fusion between data products of the same class,pixel level fusion between data products of different classes,feature level fusion,and decision level fusion.These sublevels correspond with the advance data products from level3to level6.(4)Parameter inversion sublevelParameter inversion data products have progressed from experimental to business operation and applied in many applica-tion fields.However,the degree of the scale and standardization of the production of parameter inversion data products are not high.The precision of many parameter inversion data products maintain a certain distance from the requirement of application. The scale and standardization of production should be enhanced and the product quality inspection should be emphasized to meet the application requirement.In this scheme,the parameter inver-sion data products are divided into three sublevels,including data products without quality inspection,data products with contrasting verification by other remote satellite data products, and data products by ground validation according to the quality inspection level.These sublevels correspond with the advance data products from level3to level5.5.3㊀The gradation architecture of remote satellitedata products㊀㊀According to the discussed rule,each level data product is defined as below:Row data are data received directly from satellite without processing.Level0data products are products with dislodgement format as well as decompression and distribution by stripe or scene.Primary data products are products by radiometric calibration and geometric correction.Primary data products are divided into level1and level2data products.Each level is divided into radiometric calibration sublevels as well as geometric correction and representation sublevels.Advance data products are primary data products that underwent further processing.They are divided into levels3 6. Each level can be divided into four sublevels,including radio-metric calibration sublevel,geometric correction and representation sublevel,imagery fusion sublevel,and parameter inversion sublevel.The remote satellite data products in the gradation rule of levels1 6are shown as below.Table3㊀Levels1 6schemeLevelRadiometriccalibrationsublevelGeometriccorrection andrepresentationsublevelImagery fusionsublevelParameterinversionsublevel Level1Relative radio-metric calibra-tion㊀㊀ ㊀㊀ ㊀㊀㊀ Level2Absolute radio-metric calibra-tionSystem geom-etric correction㊀㊀ ㊀㊀㊀Level3AtmosphericcorrectionGeometric accu-rate correctionPixel level fus-ion between dataproducts in thesame classData products with-out quality inspec-tion Level4TopographicradiometriccorrectionOrtho correctionPixel level fusionbetween dataproducts in dif-ferent classesData products withcontrastive verifi-cation by other re-mote satellite dataproducts㊀Level5㊀㊀Add navigationand positioninginformation,fundamental ge-ographic infor-mationFeaturelevel fusionData products byground validation Level6㊀㊀three-dimen-sional represen-tationDecisionlevel fusion㊀㊀㊀6㊀CONCLUSIONThe universal classification and gradation rule for remote sensing satellite data products is not yet available in the produc-tion and application of remote satellite data products for domestic and abroad usage.With the rapid development of remote satellite application industry in China,a complete,systematic,and highly operational classification and gradation rule for remote sensing satellite data products is urgently needed.A new classification and gradation rule is proposed for all kinds of existing classification and gradation rules for remote satellite data products.This rule follows the law of remote science and the consensus on classification and gradation for data。

中国科学院中国遥感卫星地面站卫星数据产品价目表(2003年7月)SPOT-2/4卫星数据产品价目表ENVISAT数据产品价格LANDSAT-7卫星数字产品价目表LANDSAT-5卫星数字产品价目表RESOURCESAT-1(IRS-P6)卫星数据价格表RADARSAT卫星存档数据价目表RADARSAT卫星编程数据价目表快鸟卫星数据中国市场统一价目表QuickBird卫星立体像对数据产品价目表照相产品(激光输出产品)价目表ERS卫星存档数据产品ASTER数据产品及价目SPOT-2/4卫星数据产品价目表(人民币:元)(2006年4月1日)一、中国遥感卫星地面站接收的数据价格全景子区多光谱数据PAN数据多光谱数据PAN数据产品级别1A2000元4900元------2A2000元4900元---1000km2/1500元1.8元/ km2二、法国Spotimage接收的数据价格全景多光谱数据PAN数据产品级别1A900090002A90009000三、台湾及其他地面站接收的数据价格全景多光谱数据PAN数据产品级别1A14800148002A1480014800四、卫星编程费:7000元/景ENVISAT数据产品的价格(不包括申请费):Image Mode 和Wide Swath Mode :3000元/景Alternating Polarisation Mode :4000元/景我站ENVISAT数据编程申请的收费标准如下:a.提前14 天以上的编程申请为普通编程,不收申请费用;b.7-14 天编程申请为加急编程,每一数据段用户需付申请费3000元;c.2-7天编程申请为特急编程,每一数据段用户需付申请费8000元;(注:编程申请最少需要提前两天提交。
)LANDSAT-7卫星数字产品价目表(2003年7月1日执行)单位:人民币元全景1/2景1/4景融合/景面积范围级别1-8波段1-7波段PAN波段1-8波段1-7波段PAN波段1-8波段1-7波段PAN波段PAN&多光谱元/平方公里1级500380200280230150150120110---------------2级50038020028023015015012011045000.33级7006004004804503503503203106000--------4级8007005005805504504504204107000---------LANDSAT-5卫星数字产品价目表(2003年7月1日执行)单位:人民币元产品级别全景1/2景1/4景面积(km²)1级3800230012002级3800230012000.33级6000450032004级700055004200产品级别说明中国遥感卫星地面站提供的Landsat-5和Landsat-7数据产品的处理级别包括Level 1、Level 2、Level 3和Level 4。
全国土地利用分类遥感数据
北京揽宇方圆信息技术有限公司全国土地利用数据产品是指基于Landsat TM数字影像,采用全数字化人机交互遥感快速提取方法,同时参照国内外现有的土地利用/土地覆盖分类体系,以及遥感信息源的实际情况,将全国土地利用类型划分为6个一级分类,25个二级分类以及部分三级分类的土地利用/土地覆盖数据产品
土地利用数据产品,其中包括6个一级类和25个二级类,二级类分为水田、旱地、有林地、灌木林、疏林地、其他林地、高覆盖度草地、中覆盖度草地、低覆盖度草地、河渠、湖泊、水库坑塘、永久性冰川雪地、滩涂、滩地、城镇用地、农村居民点、其他建设用地、沙地、戈壁、盐碱地、沼泽地、裸土地、裸岩石砾地、其他等土地利用/覆盖类型。


SPOT-4卫星于1998年3月发射,是法国SPOT卫星的第四颗卫星,SPOT-4卫星属于第二代卫星,它的有效载荷和定位能力与第一代卫星相比有一定提高。
SPOT-4卫星增加了一个短波红外波段(158-1.75pm);把原
0.61-0.68um的红波段改为0.49-0.73um包含“红”的波段,并替代原全色波段,可以产生分辨率10m的全色影像和分辨率20m的多光谱影像。
SPOT-4卫星增加了一个多角度遥感仪器,即宽视域植被探测仪Vegetation(VGT),用于全球和区域两个层次上,对自然植被和农作物进行连续监测,对大范围的环境变化、气象、海洋等应用研究很有意义。
SPOT-4卫星VGT被设计为垂直方向的空间分辨率1.15km,扫描宽度2250km,可见光一短波红外波段0.43-1.75um共5个波段。
它们为蓝波段0.43-0.47um、绿波段0.50-0.59um、红波段0.61-0.68um,近红外波段0.79-0.89um、短波红外波段1.58-1.75um。
SPOT-4中的
VGT和HRVs将使同一区域有可能同时获得较大范围的粗分辨率数据和小范围的细分辨率数据。
SPOT4卫星参数
SPOT-4卫星数据级别划分
注:目前全部提供1A级别影像SPOT-4卫星传感器。

4D数据什么是4D(DRG、DLG、DOM、DEM)数据一.DOM (数字正射影像图):利用数字高程模型对扫描处理的数字化的航空相片、遥感影像,经逐个像元纠正,按图幅范围裁切生成的影像数据,它的信息比较直观,具有良好的可判读性和可量测性,从中可直接提取自然地理和社会经济信息。
在SAR图像处理中,往往需借助DEM数据来解决RD定位导致的斜距成像几何失真。
因此,求解X,Y,Z考虑了三个方程。
即距离公式、多普勒频率公式和地球坐标公式。
也就是说DOM是需要DEM进行二次加工的,也是4D产品中最为高级的产品。
DEM (数字高程模型) :通过等高线、或航空航天影像建立以表达地面高程起伏形态的数字集合。
目前可得到的有90m的SRTM,和30m的Aster GDTM数据。
前者采用InSAR技术获取,后者则是高分辨率立体摄影测量技术。
两者相似之处都需要两幅图像,而且精确配准。
需要有一定的基线长度,需在一定范围内取值。
不同之处,前者是利用波的相干性原理求得,后者则是光直线传播所产生的共线方程。
DEM数据为基础数据。
DRG (数字栅格地图) :数字栅格地图是纸制地形图的栅格形式的数字化产品,可与DOM、DEM 集成派生出新的可视信息。
该类型数据主要是将已有的纸质地图进行栅格化,然后配准,目前这类图很少用到,多用高分辨率的影像来取代,或者就是将主要地物进行矢量化表征和存储,目前大多数的GIS软件都支持这一功能。
DLG (数字线划地图) :利用航空航天影像通过对影像进行识别和矢量化,建立基础地理要素分层存储的矢量数据集,既包括空间信息也包括属性信息,可用于各专业信息系统的空间定位基础。
这个图是目前Google map, 和百度地图,以及搜狗地图等网络上留下的电子地图主要表现形式。
Google Map做的最好,因为其有强大的栅格影像数据,而且是高分辨率的。
因此叠加矢量数据后,反映的地图形象更加直观、清晰和准确。
二.数字高程模型(Digital Elevation Model,缩写DEM)是在某一投影平面(如高斯投影平面)上规则格网点的平面坐标(X,Y)及高程(Z)的数据集。
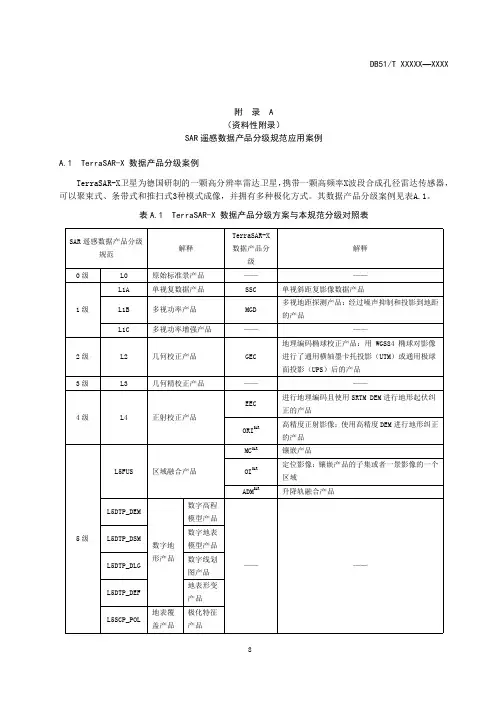
附录A(资料性附录)SAR遥感数据产品分级规范应用案例A.1TerraSAR-X数据产品分级案例TerraSAR-X卫星为德国研制的一颗高分辨率雷达卫星,携带一颗高频率X波段合成孔径雷达传感器,可以聚束式、条带式和推扫式3种模式成像,并拥有多种极化方式。
其数据产品分级案例见表A.1。
表A.1TerraSAR-X数据产品分级方案与本规范分级对照表SAR遥感数据产品分级规范解释TerraSAR-X数据产品分级解释0级L0原始标准景产品————1级L1A单视复数据产品SSC单视斜距复影像数据产品L1B多视功率产品MGD多视地距探测产品:经过噪声抑制和投影到地距的产品L1C多视功率增强产品————2级L2几何校正产品GEC 地理编码椭球校正产品:用WGS84椭球对影像进行了通用横轴墨卡托投影(UTM)或通用极球面投影(UPS)后的产品3级L3几何精校正产品————4级L4正射校正产品EEC进行地理编码且使用SRTM DEM进行地形起伏纠正的产品ORI SAR高精度正射影像:使用高精度DEM进行地形纠正的产品5级L5FUS区域融合产品MC SAR镶嵌产品OI SAR定位影像:镶嵌产品的子集或者一景影像的一个区域ADM SAR升降轨融合产品L5DTP_DEM数字地形产品数字高程模型产品————L5DTP_DSM数字地表模型产品L5DTP_DLG数字线划图产品L5DTP_DEF地表形变产品L5SCP_POL地表覆盖产品极化特征产品表A.1(续)SAR遥感数据产品分级规范解释TerraSAR-X数据产品分级解释5级L5SCP_CLA 地表覆盖产品地物分类产品————6级L6专题产品OM SAR正射图:具有地图结构和图例的正射制图产品CDM SAR变化监测图SUB SAR地表沉陷图A.2COSMO-SkyMed数据产品分级案例COSMO-SkyMed系统是一个由意大利航天局和意大利国防部共同研发的4颗雷达卫星组成的星座,工作于X波段,提供了具有全球覆盖能力、适应各种气候的日夜获取能力及高分辨率、高精度、高干涉极化测量能力的高效便利的产品服务。

hy1c数据l1级别格式
HY-1C通常指的是中国的海洋一号C卫星,该卫星用于海洋环境监测,包括海洋水色、水温、海冰、海岸带等方面的观测。
L1级别的数据通常指的是经过初步处理后的遥感数据,这些数据已经进行了辐射定标和几何校正,但未进行大气校正或更高级别的处理。
对于HY-1C卫星的L1级别数据格式,具体的信息可能会因数据提供商或处理流程的不同而有所差异。
但一般来说,这类数据可能包含以下信息:
1.元数据(Metadata):描述数据本身的信息,如卫星轨道参数、传感器参数、数据获取
时间、地理定位信息等。
2.辐射定标数据:将原始的传感器读数转换为物理量(如辐亮度或反射率)的过程。
L1
级别的数据通常会提供经过辐射定标后的图像数据。
3.几何校正数据:对图像进行几何校正,以消除由于传感器姿态、地球曲率、大气折射等
因素引起的图像畸变。
这些数据通常以特定的文件格式存储,如HDF(Hierarchical Data Format)、GeoTIFF(带有地理信息的TIFF格式)或其他遥感数据格式。
为了读取和处理这些数据,你可能需要使用专门的遥感数据处理软件,如ENVI、ERDAS Imagine、ArcGIS等。
常见遥感卫星基本参数大全1、CBERS-1 中巴资源卫星CBERS-1 中巴资源卫星由中国与巴西于1999年10月14日合作发射,是我国的第一颗数字传输型资源卫星卫星参数:太阳同步轨道轨道高度:778公里,倾角:98.5o 重复周期:26天平均降交点地方时为上午10:30 相邻轨道间隔时间为 4 天扫描带宽度:185公里星上搭载了CCD传感器、IRMSS红外扫描仪、广角成像仪,由于提供了从20米-256米分辨率的11个波段不同幅宽的遥感数据,成为资源卫星系列中有特色的一员。
红外多光谱扫描仪:波段数:4波谱范围:B6:0.50 –1.10(um)B7:1.55 – 1.75(um)B8:2.08 – 2.35(um)B9:10.4 –12.5(um)覆盖宽度:119.50公里空间分辨率:B6 –B8:77.8米B9:156米CCD 相机:波段数:5波谱范围:B1:0.45 –0.52(um)B2:0.52 –0.59(um)B3:0.63 –0.69(um)B4:0.77 –0.89(um)B5:0.51 –0.73(um)覆盖宽度:113公里空间分辨率:19.5米(天底点)侧视能力:-32 士32广角成像仪:波段数:2波谱范围:B10:0.63 –0.69(um)B11:0.77 –0.89(um)覆盖宽度:890公里空间分辨率:256米CBERS-1卫星于1999年10月14日发射成功后,截止到2001年10月14日为止,它在太空中己运行2年,围绕地球旋转10475圈,向地面发送了大量的遥感图像数据,已存档218201景0级数据产品。
CBERS-1卫星的设计寿命是2年,但据航天专家测定CBERS-1卫星在轨道上运行正常。
有效载荷除巴西研制的宽视场成像仪于2000年5月9日因电源系统故障失效外,其余均工作正常,而且目前星上的所有设备均工作在主份状态,备份设备还未启用,星上燃料绰绰有余。
因此,虽然卫星设计寿命是2年,但航天专家设计时对各个器件都打有超期服役的余量,从CBERS-1卫星目前的运行情况来,其寿命肯定要远远大于2年。
遥感数字图像处理复习理论习题一、名词解释:1.遥感数字图像;遥感数字图像(digital image)是以数字形式表述的遥感图像。
不同的地物能够反射或辐射不同波长的电磁波,利用这种特性,遥感系统可以产生不同的遥感数字图像。
2.像素;数字图像最根本的单位是像素,像素是A/D转换中的取样点,是计算机图像处理的最小单元;每个像素具有特定的空间位置与属性特征。
3.遥感数字图像处理;遥感数字图像处理是通过计算机图像处理系统对遥感图像中的像素进展的系列操作过程。
4.电磁波谱;将各种电磁波按其波长〔或频率〕的大小依次排列所构成的图谱。
5.辐射分辨率;辐射分辨率是传感器区分反射或发射的电磁波辐射强度差异的能力6.空间分辨率;是指遥感图像上能够详细区分的最小单元的尺寸或大小,即传感器能把两个目标物作为清晰的实体记录下来的两个目标物之间最小的距离。
7.直方图;对于数字图像来说,直方图实际就是图像灰度值的概率密度函数的离散化图形。
8.累积直方图;以横轴表示灰度级,以纵轴表示每一级灰度级及其以下灰度级所具有的像素数或此像素所占总像素数的比值,做出的直方图即为累积直方图。
9.窗口;对于图像中的任一像素〔x,y〕,以此为中心,按上下左右对称所设定的像素范围,称为窗口。
10.邻域处理〔运算〕;对于中心像素〔x,y〕,其值用ƒ〔x,y〕表示,可按照相邻性规那么通过计算产生。
11.伪彩色合成;是把单波段灰度图像中的不同灰度级按特定的函数关系变换成彩色,然后进展彩色图像显示的方法。
12.真彩色合成;如果彩色合成中选择的波段的波长及红绿蓝的波长一样或近似,那么得到的图像的颜色及真彩色近似,这种合成方式称为真彩色合成。
13.密度分割法;是对单波段遥感图像按灰度分级,对每级赋予不同的色彩,使之变为一幅彩色图像。
14.辐射误差;传感器所得到的目标测量值及目标的光谱反射率或光谱辐亮度等物理量之间的差值称为辐射误差。
15.几何精纠正;又称为几何配准〔registration〕,是把不同传感器具有几何精度的图像、地图或数据集中的一样地物元素准确地彼此匹配、叠加在一起的过程。
什么是4D(DRG、DLG、DOM、DEM)数据1,DOM ,利⽤数字⾼程模型对扫描处理的数字化的航空相⽚、遥感影像抄,经逐个像元纠正,按图幅范围裁切⽣成的影像数据。
百DOM 是需要DEM进⾏⼆次加⼯的,也是4D产品中最为⾼级的产品。
2,DEM ,通过等⾼线、或航空航天影像建⽴以表达地⾯⾼程起伏形态的数字集合。
DEM数据为基础数据。
3,DRG,是纸制地形图的栅格形式的数字化产品,可与DOM、DEM集成派⽣出新的可视信息。
4,DLG,利⽤航空航天影像通过对影像进⾏识别和⽮度量化,建⽴基础地理要素分层存储的⽮量数据集,既包括空间信息也包括属性信息,可⽤于各专业信息系统的空间定位基础。
⼀、 DOM (图):利⽤数字⾼程模型对扫描处理的数字化的航空相⽚、,经逐个像元纠正,按图幅范围裁切⽣成的影像数据,它的信息⽐较直观,具有良好的可判读性和可量测性,从中可直接提取⾃然地理和社会经济信息。
在SAR图像处理中,往往需借助DEM数据来解决RD定位导致的斜距成像⼏何失真。
因此,求解X,Y,Z考虑了三个⽅程。
即距离公式、多普勒频率公式和地球坐标公式。
也就是说DOM是需要DEM 进⾏⼆次加⼯的,也是4D产品中最为⾼级的产品。
DEM (数字⾼程模型) :通过等⾼线、或影像建⽴以表达地⾯⾼程起伏形态的数字集合。
⽬前可得到的有90m的SRTM,和30m的Aster GDTM数据。
前者采⽤InSAR技术获取,后者则是⾼分辨率⽴体摄影测量技术。
两者相似之处都需要两幅图像,⽽且精确配准。
需要有⼀定的基线长度,需在⼀定范围内取值。
不同之处,前者是利⽤波的相⼲性原理求得,后者则是光直线传播所产⽣的共线⽅程。
DEM数据为基础数据。
DRG (数字栅格地图) :数字栅格地图是纸制地形图的栅格形式的数字化产品,可与DOM、DEM集成派⽣出新的可视信息。
该类型数据主要是将已有的纸质地图进⾏栅格化,然后配准,⽬前这类图很少⽤到,多⽤⾼分辨率的影像来取代,或者就是将主要地物进⾏⽮量化表征和存储,⽬前⼤多数的都⽀持这⼀功能。
高分辨率卫星价格单片产品单位:元/平方公里产品类型存档S级编程/90天内编程S+级编程Worldview-30.3米真彩色330 550 640 0.3米全色+4个多光谱Worldview-3 0.3米全色+8个多光谱420 690 800Geoeye Worldview-2 Wordview-30.4米真彩色220 244 360 0.4米全色+4个多光谱Worldview-2Worldview-30.4米全色+8个多光谱330 380 430Geoeye Worldview-2 Wordview-30.5米真彩色195 220 330 0.5米全色+4个多光谱Worldview-2Worldview-30.5米全色+8个多光谱310 340 400 Worldview-1 0.5米全色146 179 280Quickbird(快鸟)0.6米真彩色195 220 330 0.6米全色+4个多光谱ikonos0.8米真彩色130 190 300 0.8米全色+4个多光谱pleiades0.5米真彩色195 195 220 0.5米全色+4个多光谱rapideye 5米多光谱12 12 15 资源三号 2.1米全+5.8米多光谱4000高分一号2米全色+8米多光谱4000高分二号0.8米全色+3.2米多光谱20000锁眼卫星全色6000默认的数据产品级别是:没有经过地形校正的产品,只经过了辐射校正、传感器和卫星平台引起的误差校正,具有地图投影。
用户可以直接通过相关专业软件结合自己的DEM、RPC参考模型、亚米级精度的地面控制点来做正射校正。
立体产品单位:元/平方公里产品类型存档S级编程/90天内编程S+级编程全色340 440 8404波段540 640 11528波段890 990 1511 IKONOS 410 510 1020 Pleiades-1 540 640 840立体相对100平方公里起订。
名词解释:1.图像:是对客观对象一种相似性的描述或写真,它包含了被描述物体或写真对象的信息,是人们最主要的信息源。
2.数字图像:指用计算机存储和处理的图像,是一种空间坐标和灰度均不连续、以离散数学原理表达的图像。
3.遥感系统:是一个从地面到空中乃至整个空间,从信息收集、存储、传输、处理到分析、判读、应用的技术体系,主要包括遥感试验、信息获取(传感器、遥感平台)、信息传输、信息处理、信息应用等5个部分。
4.传感器:又称为遥感器(remote sensor),是收集和记录电磁辐射能量信息的装置,是信息获取的核心部件,如航空摄影机、多光谱扫描仪、成像仪等。
传感器搭载在遥感平台上,通过传感器获取遥感数字图像数据。
5.元数据(meta data):是关于图像数据特征的表达,是关于数据的数据。
6.直方图规范化:又称为直方图匹配,这种方法经常作为图像镶嵌或应用遥感图像进行动态变化研究的预处理工作。
通过直方图匹配可以部分消除由于太阳高度角或大气影像造成的相邻图像的色调差异,从而可以降低目视解译的错误。
7.辐射校正:消除图像数据中依附在辐亮度中的各种失真的过程成为辐射量校正(radiometric calibration),简称辐射校正。
8.辐射通亮:单位时间内通过某一表面的辐射能量称为辐射通量(radiant flux),单位为W。
9.辐照度:指单位时间内单位面积上接受的辐射通量,单位为W/m^2。
10.辐亮度:和辐射度两个概念的含义相同,指的是沿辐射方向、单位面积、单位立体角上的辐射通量,单位为W/(m2.sr)。
11.反射率:是反射能量与入射能量的比值。
12.吸收率:是吸收能量与入射能量的比值。
13.透射率:是透射能量与入射能量的比值。
在介质内部,反射率吸收率和透射率的和为1。
14.反照率:不同于反射率,指的是界面反射的辐照度与内部的反射的辐照度之和与入射的辐照度的比值。
15.几何精纠正:又称为几何配准(registration),是把不同传感器具有几何精度的图像、地图或数据集中的相同地物元素精确地彼此匹配、叠加在一起的过程。
遥感影像数据产品级别
卫星数据服务商北揽宇方圆信息技术有限公司是国内规模最大、服务最稳定、服务质量最高的卫星影像数据综合应用服务企业,一直致力于为用户提供全球中、高分辨率卫星影像数据及基于遥感数据的应用服务。
多颗国际领先的高分辨率遥感卫星数据资源,这些卫星群能够以极快地速度为用户提供全球各地的超高分辨率影像。
0级:经数据重构,未进行任何处理的原始数据;所有的通信信息(比如:同步帧、通信头和重复数据)被移除。
1A级:经数据重构,具有时间参考、辅助信息(包括辐射、几何校正系数等)以及地理坐标参数等(如:平台星历等,并没有应用于0级产品)的未进行任何处理的原始数据。
1B级:在1A级产品的基础上处理至传感器单元(并不是所有数据都有L1B级数据)。
2级: 与1级数据具有相同分辨率和位置的地球物理参量数据产品。
3级: 投影至统一时空格网尺度,通常具有一定完整性和一致性的数据产品。
4级: 模型输出结果或从低级数据分析得到的结果。
该分级体系的一个重要方面是它的每一级是积累的,新的一个级别是由其下一级别生成同时它也是上一级产品的输入数据。
0级数据基本上是原始的、未经任何处理的仪器和传感器数据。
虽然它是基本的数据级别,但我们通常不会使用它,对传感器本身准确性和敏感性比较感兴趣的人将会是它的用户。
0级数据的主要作用是作为数据处理链中的原始数据被用来生成更高级别的数据产品。
1级数据可以恢复为0级,同时1级数据也是生成更高级别数据的基础。
2级数据可直接用于大多数的科学研究。
相对于1级数据来说,2级数据可能由于某些原因(比如:在空间尺度或光谱范围等方面做了缩减)要小一些。
3级产品可能会更小,以便其更容易被使用,同时规则的空间和时间组织使得这些数据更容易与不同数据源的数据结合使用。
一般地,随着处理技术的改进,数据集本身将会变得更小,但其在科学应用中的价值和效用将会变的更大。
对于遥感影像预处理类型和程度来说,采用统一的处理级别体系来描述其优
点变得清晰。
这种方法似乎已经发展到被普遍采用,尽管有许多不同情况存在。
通常情况下,可使用下述定义来描述不同数据级别:
0级:传感器收集到的原始数据。
0级数据并不是十分有用,除非你的兴趣点或研究内容是传感器本身。
1A级:均衡化辐射校正的数据产品。
通过不同检测器的均衡功能对影响传感器的变化进行校正。
包括了将DN值装换为辐射亮度值的绝对校正系数。
1B级:该步主要用于对一些传感器的几何畸变进行校正。
对没有几何畸变的传感器来说,这一步是不需要的。
同时,需要注意的是,1B级数据不可恢复为0级数据。
2A级:经过系统几何校正的数据。
该级别数据名义上具有地理参考,但其精度并不高。
2B级:为了提高影像的空间位置精度,需要考虑到用户输入信息,借助具有准确位置信息的地面控制点来对影像进行位置校准。
经过该处理的影像是具有原始空间分辨率且空间位置准确的数据产品(局部地形起伏较大的区域除外)。
3级:经正射校正的数据产品。
对于具有大量地势起伏(比如:多山区域)的地区,要获取更准确的空间位置,需要进一步的校正来消除由于地形起伏、传感器倾斜等导致的几何误差。
对同一传感器来说,其3级数据是同一尺度的,适用于大范围的栅格尺度,比如:镶嵌。
值得注意的是,由于各种原因,不同的系统具有不同的侧重点,被赋予不同的任务,因而具有不同的数据产品级别。
比如:Landsat7采用校正至传感器单元的L1G级别作为其产品分发级别;DG公司则采用一种扩展系统来对产品级别进行分类,从"基础"级1B开始,到"标准"2A级,再到3F级(具有1:5000地图精度的正射校正影像)和Stereo OR2A(Ortho-ready Standard)级(立体像对,用户可以根据自己的需求和流程进行正射校正)。
中国资源卫星应用中心公布的卫星标准数据产品级别如下:
卫星标准数据产品根据处理程度不同,分为1A级、1C级、2级、2A级和2C 级产品,各级产品主要说明如下:
1A级(预处理级辐射校正影像产品):经数据解析、均一化辐射校正、去噪、MTFC、CCD拼接、波段配准等处理的影像数据;并提供卫星直传姿轨数据生产的RPC文件。
1C级(高精度预处理级辐射校正影像产品):经数据解析、均一化辐射校正、去噪、MTFC、CCD拼接、波段配准等处理的影像数据;并提供整轨精化的姿轨数据生产的RPC文件。
2级(系统级几何校正影像产品):经相对辐射校正、系统级几何校正后的影像产品。
2A级(预处理级几何校正影像产品):1A级数据经几何校正、地图投影生成的影像产品。
2C级(高精度预处理级几何校正影像产品):1C级数据经几何校正、地图投影生成的影像产品。