AB DF1串口通讯协议API接口
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:125.50 KB
- 文档页数:6
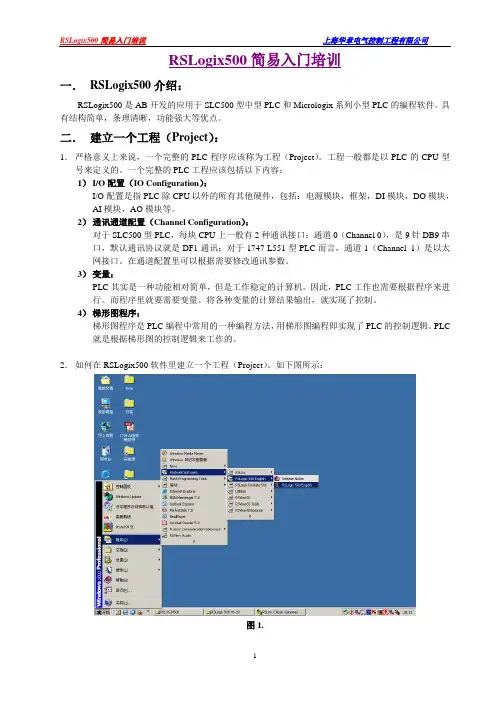
RSLogix500简易入门培训一.RSLogix500介绍:RSLogix500是AB开发的应用于SLC500型中型PLC和Micrologix系列小型PLC的编程软件。
具有结构简单,条理清晰,功能强大等优点。
二.建立一个工程(Project):1.严格意义上来说,一个完整的PLC程序应该称为工程(Project)。
工程一般都是以PLC的CPU型号来定义的。
一个完整的PLC工程应该包括以下内容:1)I/O配置(IO Configuration):I/O配置是指PLC除CPU以外的所有其他硬件,包括:电源模块,框架,DI模块,DO模块,AI模块,AO模块等。
2)通讯通道配置(Channel Configuration):对于SLC500型PLC,每块CPU上一般有2种通讯接口:通道0(Channel 0),是9针DB9串口,默认通讯协议就是DF1通讯;对于1747-L551型PLC而言,通道1(Channel 1)是以太网接口。
在通道配置里可以根据需要修改通讯参数。
3)变量:PLC其实是一种功能相对简单,但是工作稳定的计算机。
因此,PLC工作也需要根据程序来进行。
而程序里就要需要变量。
将各种变量的计算结果输出,就实现了控制。
4)梯形图程序:梯形图程序是PLC编程中常用的一种编程方法,用梯形图编程即实现了PLC的控制逻辑。
PLC 就是根据梯形图的控制逻辑来工作的。
2.如何在RSLogix500软件里建立一个工程(Project)。
如下图所示:图1.点击左上角的新建工程(New)图标,启动后弹出新的窗口,如下图所示:图3.入图3所示,Porcessor Name就是整个工程的名字,可以根据需要编辑。
下拉菜单里是RSLogix500软件支持的所有PLC的CPU类型。
我们根据实际情况选择CPU的类型。
点击OK按钮,即完成了一个工程总体框架的建立。
进入到下一个步骤,如下图所示:图4.三.如何配置I/O(IO Configuration):点击左侧下拉菜单里的“IO Configuration”选项,弹出I/O配置窗口,如下图所示:可以通过本地扩展电缆(1746-C9)扩展3个机架共30个模块,因此有Rack1,2,3共3个清单。

ABPLC协议AB PLC协议是一种常用的工业自动化设备通信协议,主要用于控制系统中的可编程逻辑控制器(PLC)的通信。
AB PLC(Allen-Bradley Programmable Logic Controller)是一种常见的商用PLC品牌,由Rockwell Automation公司制造。
1. 通信协议:AB PLC使用的通信协议主要有DF1、DH-485和EtherNet/IP。
其中,DF1是一种串行通信协议,支持RS-232和RS-485接口;DH-485是一种多节点串行通信协议,用于在PLC网络中连接多个PLC;EtherNet/IP是一种基于以太网的协议,用于实现PLC与其他设备的通信。
2. 数据传输方式:AB PLC协议支持不同的数据传输方式,如点对点(Point-to-Point)和多播(Multicast)。
点对点传输方式用于单个PLC与其他设备之间的通信,而多播传输方式用于多个设备之间的通信。
3.数据格式:ABPLC协议支持多种数据格式,包括位数据、字节数据、整数、浮点数等。
根据不同的数据类型,可以选择不同的数据编码方式,如ASCII码、BCD码等。
4.报文结构:ABPLC协议的报文结构包括报文头、命令字、数据和校验等部分。
报文头用于标识报文的起始,命令字指示数据传输的操作,数据部分包含实际传输的数据,校验用于确保传输的数据的完整性。
ABPLC协议的应用广泛,常用于工业自动化领域中的控制系统。
它可以和其他设备(如人机界面、传感器、执行机构等)进行通信,实现设备之间的数据交换和控制操作。
同时,ABPLC协议也可以用于PLC之间的通信,通过建立PLC网络,实现分布式控制和集中监控。
在实际应用中,ABPLC协议还可以与其他通信协议(如MODBUS、OPC 等)结合使用,实现更复杂的控制系统。
例如,可以通过ABPLC协议与远程监控系统进行通信,实现远程监控和远程操作。
总的来说,ABPLC协议是一种常用的工业自动化设备通信协议,具有通信协议选择多样、数据传输方式灵活、支持多种数据格式和通信功能等特点。

串口通讯协议串口通讯协议是一种用于在计算机和外部设备之间进行数据传输的通信协议。
它是通过串行通信接口(串口)将数据以逐位的方式传输。
串口通讯协议通常用于连接计算机和各种外设,如打印机、调制解调器、传感器等。
1. 什么是串口通讯协议?串口通讯协议是一种规定了数据传输格式和通信规则的协议。
它定义了数据帧的结构、数据的编码和解码方式、数据的传输速率等。
串口通讯协议通常由硬件和软件两部分组成。
硬件部分包括串口接口的物理连接、电气特性以及数据线的连接方式。
串口通常包括发送线(TX)、接收线(RX)和地线(GND)。
这些线路通过串口线连接计算机和外设。
软件部分涉及到数据的传输和解析。
在串口通讯中,数据被分为连续的字节,并通过串行方式逐个传输。
发送方将字节一位一位地发送到接收方,接收方则按照事先约定好的规则解析和处理数据。
2. 常见的串口通讯协议2.1 RS-232RS-232是一种常见的串口通讯协议,它定义了串口的物理接口和电气特性。
RS-232通常使用DB9或DB25连接器,并且规定了数据线的连接方式、电平范围等。
2.2 UARTUART(Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter)是一种通用的异步收发器。
它是实现串口通讯的重要组件,负责将数据从并行格式转换为串行格式,并在发送和接收之间进行时序控制。
UART可以通过调整参数来适应不同的通信需求,如波特率、数据位、停止位和校验位等。
2.3 SPISPI(Serial Peripheral Interface)是一种同步串行通信协议,常用于连接微控制器和外部设备。
SPI使用4条线进行通信,包括时钟线、数据线、主从选择线和片选线。
SPI具有高速传输和多设备连接的优势。
2.4 I2CI2C(Inter-Integrated Circuit)是一种串行通信协议,用于连接集成电路芯片之间的通信。
I2C使用两条线进行通信,一条是时钟线(SCL),另一条是数据线(SDA)。

组态王通过DF1通讯协议与AB PLC通讯配置参考文档此文档由北京亚控公司提供,仅作为组态王与罗克韦尔PLC通讯配置的使用参考,北京亚控公司不对此文档涉及的PLC硬件配置部分承担任何使用责任, PLC硬件的详细说明请参考厂家提供的使用说明,关于PLC硬件配置过程中的疑问请致电厂家技术支持工程师。
目录一、简介 (3)二、软硬件环境 (3)三、软硬件安装与接线: (3)1、软件安装要求 (3)2、连接电缆选择 (3)四、半双工协议配置与测试 (3)1、DF1半双工协议配置 (3)2、通讯参数检测 (5)3、注意事项 (5)五、组态王驱动的定义与变量配置: (6)1、组态王中设备定义 (6)2组态王变量的定义 (6)3、注意事项 (7)图表图4.1 上传PLC参数 (4)图4.2 PLC的参数列表 (4)图4.3 PLC通讯参数配置项 (4)图4.4 PLC参数下传 (5)图4.5 RSLinx 驱动配置 (5)图4.6 RSLinx 驱动配置验证 (5)图5.1 组态王软件设备定义 (6)图5.2 设备地址设备 (6)图5.3 寄存器列表 (7)一、简介目前组态王支持DF1通讯方式或OPC方式与罗克韦尔公司的PLC进行通信。
罗克韦尔公司部分ControlLogix、MicroLogix、SLC及PLC-X系列PLC都支持DF1协议通讯,DF1通讯协议分为全双工和半双工两种。
此协议采用串行通讯,需要使用计算机中的串口进行通讯。
当用户选用DF1通讯方式与AB PLC通讯时,需要安装RSLogix500、RSlinx软件对PLC 的通讯参数进行配置。
本文主要以SLC 500为例讲解组态王的DF1半双工通信协议通信的详细配置说明。
二、软硬件环境Window XP(SP2)操作系统Kingview6.5(组态王)Version 65.20.2002Rslogix500 PLC编程软件Rslinx(测试软件)Version 2.4.2SLC500 PLC及其附件三、软硬件安装与接线:1、软件安装要求Rslogx500和Rslinx软件可以安装于任一台计算机,并不要求需要和组态王软件安装在一起,因为组态王软件是直接和PLC的DF1通讯协议直接进行通讯。
常见通信协议的接口调试方法版本号:1.0.1发布时间:2012-2-41. ModbusModbus是一种工业领域通信协议标准,并且现在是工业电子设备之间相当常用的连接方式。
Modbus协议是一个Master/Slave架构的协议。
有一个节点是Master 节点,其他使用Modbus协议参与通信的节点是Slave 节点。
Master节点类似Client/Server架构中的Client,Slave则类似Server。
工业上Modbus协议的常见架构如下图所示。
1.1. 应用场合Modbus协议主要用于测风塔数据实时读取、风机数据实时读取。
将来有可能用于集控系统中,读取各类数据和进行远程控制。
在清三营、长风风电场,莱维赛尔的测风塔使用Modbus RTU协议与功率预测系统通信。
在向阳风电场,明阳的SCADA服务器通过Modbus TCP协议向功率预测系统提供各风机的实时运行数据。
在乌力吉、浩日格吐、马力、前后查台等风电场,赛风的测风塔使用Modbus RTU over TCP协议与功率预测系统通信。
1.2. Modbus数据模型在Slave和Master进行通信时,Slave会将其提供的变量映射到四张不同的表上,Master从表中相应位置读/写变量,就完成了数据获取或命令下达。
这四张不同的表,称作Modbus数据模型(Modbus Data Model)。
为了理解方便,这里将四张表分别称作1位只读表、1位可读可写表、16位只读表、16位可读可写表。
(类似电力通信国标中的遥信、遥控、遥测、遥调。
)1位表用来映射单比特数据类型的变量,通常是布尔型变量;16位表用来映射双字节数据类型的变量,如int16、float16等,如果希望映射int32、float32等四字节变量,可以通过一次使用16位表中的两个位置来实现。
只读表用来映射Master只能读取的变量;可读可写表用来映射Master既可读取、又可改写的变量。

VC串口通讯,API函数介绍介绍工业控制领域利用串口和外围设备进行通讯。
正文前言:总所周之,利用串口进行数据通讯在在通讯通讯领域重占有着重要的地位。
利用RS232-RS485进行数据信号的采集和传递是VC编程的又一大热点。
串口通讯在通讯软件重有着十分广泛的应用。
如电话、传真、视频和各种控制等。
在各种开发工具中间,VC由于功能强大和灵活,同时也得到了Microsoft的最大支持,所以在一般进行涉及硬件操作的通讯编程中,大都推荐使用VC作为开发工具。
然而工业控制串口通讯这个又不同于一般的串口通讯程序,因为控制外围设备传送的大都是十六进制数据(BYTE类型),所以,为了提高程序的运行稳定性,我们在编写程序进行通讯时可以不考虑传送BYTE类型数据的工作。
串口通讯目前流行的方法大概有两种:一是利用Microsoft提供的CMSCOMM 控件进行通讯,不过现在很多程序员都觉应该放弃这种方式。
二是利用WINAPI 函数进行编程,这种编程的难度最高,要求你要掌握很多的API函数。
三是利用现在网络上面提供的一些串口通讯控件进行编写,比如CSerial类等。
程序实现:我在经过许多的项目的开发和实践中发现,采用WIN API函数进行串口的开发能够给程序员很大的空间,并且程序运也很稳定。
所以我将与串口接触的函数进行封装,然后在各个工程中进行调用,效果还是比较好的,现将各个函数和调用方法列举出来,希望对各位有所帮助。
一、设置串口相关工作#define MAXBLOCK 2048#define XON 0x11#define XOFF 0x13BOOL SetCom(HANDLE &m_hCom, const char *m_sPort, int BaudRate, int Databit, CString parity, CString stopbit){COMMTIMEOUTS TimeOuts; ///串口输出时间超时设置DCB dcb; ///与端口匹配的设备m_hCom=CreateFile(m_sPort, GENERIC_READ | GENERIC_WRITE, 0, NULL, OPEN_EXISTING, FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL | FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED, NULL); // 以重叠方式打开串口if(m_hCom==INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE){AfxMessageBox("设置串口部分,串口打开失败"); /////重叠方式异步通信(INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)函数失败。

串口标准协议一、数据传输格式串口数据传输通常采用异步方式,即数据传输速率与时钟频率无关,每个数据位后面都有一个特定的位作为起始位和停止位。
常见的数据格式有:7E1、7O1、8E1、8O1等。
其中,7E1表示7个数据位,1个起始位,1个奇校验位和1个停止位;8E1表示8个数据位,1个起始位,1个偶校验位和1个停止位。
二、数据传输速率串口数据传输速率通常以波特率表示,即每秒传输的位数。
常见的波特率有:9600、19200、38400、57600、115200等。
波特率的选择应根据实际需求和通信距离进行选择。
三、数据流控制串口数据流控制是为了防止数据丢失或溢出而采取的措施。
常用的数据流控制方式有硬件流控制和软件流控制两种。
硬件流控制是通过RTS/CTS线进行控制,软件流控制则是通过XON/XOFF字符进行控制。
四、错误检测与纠正串口通信过程中可能会出现数据传输错误的情况,因此需要进行错误检测与纠正。
常见的错误检测方式有奇偶校验和CRC校验等。
奇偶校验是在数据位后面添加一个校验位,使得整个数据位的1的个数为偶数或奇数;CRC校验则是通过模2除法运算对数据进行校验。
纠正则是通过反向散列运算对数据进行纠正。
五、设备识别与通信规则在串口通信中,需要确定主设备和从设备之间的通信规则,包括设备地址、命令格式、响应格式等。
设备地址用于标识不同的设备,命令格式用于发送指令,响应格式用于接收响应。
六、命令与响应模式串口通信中的命令与响应模式是一种约定,规定了主设备和从设备之间的数据交互方式。
命令由主设备发送给从设备,从设备根据命令执行相应的操作,并将结果以响应的形式返回给主设备。
七、电源管理在串口通信中,电源管理也是需要考虑的一个重要方面。
为了降低功耗,可以采用空闲模式和休眠模式等电源管理模式,以及使用低功耗器件和电路设计等技术手段。
八、接口电气特性串口通信接口的电气特性包括信号线数、信号极性、信号电平、信号驱动能力等。

df1协议引言DF1协议是一种用于工业自动化领域的通信协议,通常用于PLC(可编程逻辑控制器)和其他设备之间的数据交换。
本文将介绍DF1协议的基本概念、通信方式以及应用场景。
概述DF1协议是由美国罗克韦尔自动化(Rockwell Automation)公司开发的一种串行通信协议。
它是一种半双工、基于字符的协议,使用RS-232或RS-485接口进行通信。
DF1协议通过命令和应答的方式进行数据交换,支持点对点和多点通信。
通信方式点对点通信在点对点通信中,DF1协议通过主站和从站之间建立一条直接的连接。
主站负责发送请求命令,从站收到命令后执行相应的操作,并将结果返回给主站。
主站和从站之间的通信可以是单向的,也可以是双向的。
多点通信在多点通信中,DF1协议使用一个中继站来实现多个从站之间的数据交换。
中继站负责接收从站的请求命令,并将其转发给相应的主站。
主站收到请求后执行相应的操作,并将结果返回给中继站。
中继站再将结果转发给请求数据的从站。
数据帧格式DF1协议使用特定的数据帧格式来进行信息交换。
数据帧由起始字符、地址、命令、数据和校验码组成。
以下是一个典型的DF1数据帧的示例::<STX><ADDR><CMD><DATA><CHK><ETX>其中,<STX>是起始字符,用于标识数据帧的开始;<ADDR>是设备地址,用于标识数据帧的目标设备;<CMD>是命令,用于指示设备执行相应的操作;<DATA>是数据,用于传输需要交换的信息;<CHK>是校验码,用于检测数据帧的完整性;<ETX>是结束字符,用于标识数据帧的结束。
应用场景DF1协议广泛应用于工业自动化领域,特别是在PLC和其他控制设备之间的数据交换中。
它可以用于实时监控和控制生产线上的设备,以及收集和处理生产数据。

串口及通讯协议范文串口是计算机与外部设备进行数据传输的重要接口,常用于计算机与单片机、传感器、打印机等设备之间的通信。
串口通信协议则是规定了数据传输的格式、传输速率、校验方式等规则,以保证数据的正确传输。
串口通信采用的是串行传输方式,即按位传输数据。
比较常见的串口通信标准有RS232、RS485、RS422等。
RS232是最早用于串口通信的标准,它采用单线传输数据的方式,并且定义了数据传输的起始位、数据位、停止位等格式。
在串口通信中,数据是以字节的形式进行传输的。
通常情况下,一个字节由8个位组成,其中最高位是起始位,最低位是停止位,其他位用来传输数据。
在传输开始之前,发送端先发送起始位,接收端检测到起始位后开始接收数据,然后再接收数据位,最后接收停止位,以此确认数据的传输完整性。
为了确保数据的正确传输,串口通信协议还规定了数据的校验方式。
常用的校验方式有奇偶校验和循环冗余检验(CRC)。
奇偶校验是通过对数据位进行奇偶校验来检测数据传输的错误,如果数据位的个数是奇数,则校验位设为1,否则设为0。
而CRC是通过在数据传输过程中增加校验码来检测数据的出错情况,接收端收到数据后计算CRC值并与发送端发送的CRC值进行比对,如果不一致则说明数据传输出错。
除了数据格式和校验方式,串口通信协议还规定了数据的传输速率、数据流控制方式等。
传输速率通常以波特率(baud rate)表示,表示每秒传输的比特数。
数据流控制方式用于控制数据的流向和流量,常见的流控方式有硬件流控和软件流控。
硬件流控通过控制RTS(请求发送)和CTS(清除发送)信号来实现,软件流控则通过发送特定的控制字符来实现。
总之,串口及通信协议是计算机与外部设备进行数据传输的重要手段。
通过定义数据格式、校验方式、传输速率和数据流控制等规则,可以保证数据的正确传输和稳定性。
在实际应用中,根据具体的设备和通信需求选择合适的串口标准和通信协议,以满足数据传输的要求。

串口通讯协议
串口通讯协议是指在串行通讯中,设备之间进行数据交换时所遵循的规则和约定。
在现代计算机和嵌入式系统中,串口通讯协议被广泛应用于各种设备之间的数据传输,如传感器、显示器、打印机等。
本文将介绍串口通讯协议的基本概念、常见协议类型和应用场景。
首先,串口通讯协议可以分为同步和异步两种类型。
同步传输是指发送端和接
收端通过时钟信号来同步数据传输,而异步传输则是通过起始位、停止位和数据位来进行同步。
在实际应用中,异步传输更为常见,因为它具有灵活性高、成本低的优点。
而同步传输则通常用于高速数据传输和长距离通讯。
其次,串口通讯协议还包括多种标准,如RS-232、RS-485、UART等。
RS-
232是最早的串口通讯标准之一,它定义了串口通讯的物理接口和信号电平。
RS-485则是一种多点通讯标准,适用于多个设备之间的数据传输。
而UART则是通用异步收发传输器,它是实现串口通讯的芯片级别的实现。
在实际应用中,串口通讯协议被广泛用于各种领域。
比如在工业控制系统中,
各种传感器和执行器通过串口通讯协议与主控制器进行数据交换,实现自动化生产。
在嵌入式系统中,串口通讯协议也被用于外围设备和主控制器之间的数据传输。
此外,在通讯设备中,如调制解调器、路由器等,串口通讯协议也扮演着重要的角色。
总之,串口通讯协议作为设备之间数据交换的规则和约定,在现代计算机和嵌
入式系统中扮演着重要的角色。
通过了解串口通讯协议的基本概念、常见类型和应用场景,我们可以更好地理解和应用串口通讯技术,为各种设备之间的数据传输提供可靠的基础。
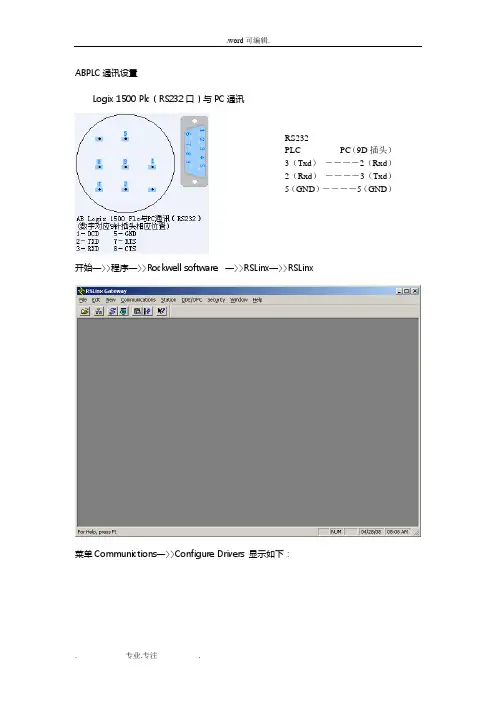
ABPLC通讯设置Logix 1500 Plc(RS232口)与PC通讯RS232PLC PC(9D插头)3(Txd)――――2(Rxd)2(Rxd)――――3(Txd)5(GND)――――5(GND)开始—〉〉程序—〉〉Rockwell software —〉〉RSLinx—〉〉RSLinx菜单Communictions—〉〉Configure Drivers 显示如下:创建新设置,“RS-232 DF1 devices”选择“AB_DF1-1”设置串口,及Device,鼠标点击“自动配置”测试成功后界面PLC以太网模块通讯设置下一步输入模块IP地址(出厂默认192.168.1.254)RSLinx—〉communictions—〉RSWho,打开PLC编程软件,开始—〉〉程序—〉〉Rockwell software —〉〉RSLinx—〉〉RSLlogix 500English新建配置PLC的CPU型号双击“IO Configuration”,添加PL其他模块双击“Channel Configuration”检查通讯设置界面1界面2界面3界面4PLC在线测试测试成功画面VB于ABPLC之间的DDE设置判断RSLinx是否运行开始—〉〉程序—〉〉Rockwell software —〉〉RSLinx—〉〉RSLinx打开的界面查看PLC寄存器的值:菜单Communictions—〉〉RSWho 显示如下:鼠标右键点击“01,SLC-5/04,UNTITLED”,再点“Data Monitor”,显示显示PLC内N7寄存器的实时值(事先要定义N7地址)建立DDE连接:鼠标右键点击“01,SLC-5/04,UNTITLED”,再点“Configure New DDE/OPC”,显示更改DDE默认名称“UNTITLED”为VB程序引用的实际名字。
VB程序设置:<1>先判断“RSLINX.EXE”是否运行On Error GoTo ErrFlagAppActivate "RSLinx"Exit SubErrFlag:Call Shell("C:\Program Files\Rockwell Software\RSLINX\RSLINX.EXE", vbHide) <2>建立DDE连接Label1.LinkTopic = "RSLINX|UNTITLED" ‘DDE名字Label1.LinkItem = "N7:0" ‘ N7寄存器地址Label1.LinkMode = 1 ‘1:Automatic。
串口通讯协议书范本甲方(提供方):_______________________地址:_________________________________联系电话:_____________________________法定代表人(或授权代表):_____________乙方(接收方):_______________________地址:_________________________________联系电话:_____________________________法定代表人(或授权代表):_____________鉴于甲方拥有串口通讯技术及相关设备,乙方需要使用该技术进行数据传输,双方本着平等互利的原则,经友好协商,就串口通讯技术的使用达成如下协议:第一条定义1.1 串口通讯:指通过串行接口进行数据传输的一种通讯方式。
1.2 通讯协议:指双方约定的用于规范数据传输格式和流程的规则。
第二条协议目的2.1 本协议旨在明确双方在串口通讯技术使用过程中的权利、义务和责任,确保数据传输的安全性、准确性和效率。
第三条技术提供3.1 甲方负责提供符合本协议约定的串口通讯技术及相关设备,并保证其正常运行。
3.2 甲方应向乙方提供必要的技术支持和培训,确保乙方能够正确使用串口通讯技术。
第四条技术使用4.1 乙方应按照甲方提供的通讯协议进行数据传输,不得擅自更改通讯协议或使用非授权的通讯方式。
4.2 乙方应确保其传输的数据内容合法、准确,不得传输违法或侵权信息。
第五条保密条款5.1 双方应对在本协议执行过程中知悉的对方商业秘密和技术秘密负有保密义务,未经对方书面同意,不得向第三方披露。
5.2 保密义务在本协议终止后仍然有效。
第六条违约责任6.1 如一方违反本协议约定,应承担违约责任,并赔偿对方因此遭受的损失。
6.2 因不可抗力导致任何一方不能履行或完全履行本协议的,该方应及时通知对方,并提供相应的证明,双方应协商解决。
DF1协议概述ZPMC OPC Server支持与ABCompactLogix系列PLC通过RS232串行进行通讯,将使用您的计算机中的串口。
通讯方式的设置是通过PLC的RSLogix5000软件和RSLinx软件来完成的,相关内容请参考硬件配置与连接。
ZPMC OPC Server通过计算机串口与1769-L35E CompactLogix控制器RS-232串口连接。
本驱动支持的通讯协议为DF1协议,支持的硬件型号为1769-L35E。
支持的运行环境:硬件:CPU: 至少Pentium III 733MHz以上内存:至少128M以上硬盘:至少100M以上显卡:256VGA图形适配卡,最小分辨率800x600网卡:10/100M自适应网卡PLC型号:1769 CompactLogix 控制器PLC通讯模块:1769 CompactLogix 控制器RS-232软件:Windows2000Pro或更高版本;RSLogix5000RSLinx硬件配置与连接连接图:PC与PLC的连接图1.选择合适的电缆1756-CP3电缆把控制器直接连接到RS-232设备上。
如果用户使用自制的电缆,该电缆必须屏蔽而且屏蔽端必须连接到电缆终端的金属外壳上。
用户也可以使用1747-CP3电缆,这种电缆的直角型连接器比1756-CP3电缆的大。
2.将合适的电缆连接到串行口3.工作站通过串行链路直接连接到CompactLogix控制器上。
PLC通讯方式的软件配置一.RSLogix5000 配置1.在RSLogix 5000编程软件中,选择Edit菜单,编辑Controllerfolder(控制器文件夹)。
2.在Serial Port(串行口)选项卡,指定合适的串行通讯信息。
3.在System Protocol(系统协议)选项卡中,选择合适的DF1通讯模式(全双工或半双工),指定串行口特性。
4.在RSLinx软件中,选择Communication菜单下Configure Driver项。
DF1协议常⽤命令PCCC:Programmable Controller Communication Commands.AB PLC常⽤指令The best commands for SLC5/MicroLogix controllers are:Protected Typed Logical Read with 3-Address Fields (Cmd=0x0F, SubFnc=0xA2)Protected Typed Logical Write with 3-Address Fields (Cmd=0x0F, SubFnc=0xAA)Protected Typed Logical Masked-Write with 3-Address Fields (Cmd=0x0F, SubFnc=0xAB)Protected Typed Logical Read with 2-Address Fields (Cmd=0x0F, SubFnc=0xA1)Protected Typed Logical Write with 2-Address Fields (Cmd=0x0F, SubFnc=0xA9)Only the first two (0xA2/AA) are documented in the official DF1 protocol specification. The third (0xAB) is not documented but is commonly used by OPC servers; In fact a Rockwell engineer formally sent me details of it when I asked; it is not considered "secret".The last two (0xA1/A9) are only of value if you're creating a slave driver since a few of Rockwell's software tools assume these are supported. While they are not documented in the DF1 specification, RSLogix5000 outlines support for them as part of its legacy support for PCCC messages. But there is no reason for an OPC server or master to use 0xA1/A9 since support by slaves is not universal. Using SubFnc 0xA1 instead of 0xA2 just drops one unrequired NULL byte from the command, so is of modest value. For example, to read N7:1 your Read command would include the 6 bytes "A2 02 07 89 01 00" for the 3-Address Fields form and only the 5 bytes "A1 02 07 89 01" for the 2-Address Fields form. Big deal, eh? Well, yes - a big deal if you try to use 0xA1 with a slave that doesn't understand 0xA1.怎样单独写⼀位:How do I write single bits on a SLC5/MicroLogix?use the undocumented (but well supported) Cmd=0x0F SubFnc=0xAB Masked WriteThe command looks much like the documented Protected Typed Logical Write with 3-Address Fields (Cmd=0x0F, SubFnc=0xAA) except you'll find an added 16-bit word of data. So here are examples of each:0xAA 02 03 85 00 00 01 000xAB 02 03 85 00 00 01 00 01 000xAB 04 03 85 00 00 01 00 01 00 00 00The first command (0xAA) in effect clears bits B3:0/1 to B3:0/15 and sets bit B3:0/0. So the entire first word of the B3 table is changed -often not the desired action. In contrast, the second command (0xAB) just sets B3:0/0 to 1 without affecting the other 15 bits of B3:0.Notice that the 16-bit "mask" is not included in the byte count of 2. The third command (0xAB) shows that more than one data word can be sent, but there is always just a single 16-bit mask. The third command would set B3:0/0 to "1" and clear B3:1/0 to "0". If you - for example - desire to set both bits B3:0/0 and B3:1/6 to "1", then you'd need to issue two separate commands since they don't share the same 16-bit mask. AB PLC常⽤指令--具体A2指令--protected typed logical read with three address fieldsReads data from a logical address in a SLC 500 module读取N7:1⼀个字(2bytes)request: 10 02 01 00 0F 00 36 0D A2 02 07 89 01 00 10 03 80 D8reply: 10 06 10 02 00 01 4F 00 36 0D E8 03 10 03 75 65读取N7:0五个字(10bytes)request: 10 02 01 00 0F 00 08 52 A2 0A 07 89 00 00 10 03 8D 4Dreply: 10 06 10 02 00 01 4F 00 08 52 D0 07 E8 03 00 00 00 00 00 00 10 03 5F E2AA指令--protected typed logical write with three address fieldsWrites data to a logical address in a SLC processor写B3:0request: 10 02 01 00 0F 00 08 54 AA 04 03 85 00 00 03 00 01 00 10 03 DB B2 reply: 10 06 10 02 00 01 4F 00 08 54 10 03 AB 1C 10 05 10 05 10 05 10 05⽰例⼀组PLC数据定义:DF1协议DF1协议控制字符DF1协议传输标志DF1协议链路协议帧Half-duplexFull-duplexDF1协议应⽤帧。
Fax: 1-703-709-0985 Allen-Bradley DF1 Serial Communication Interface APIThe DASTEC Corporation Allen-Bradley DF1 Serial Communication Interface API allows the user to implement bi-directional serial communications to exchange data between applications running on a Windows/WinCE-based system with other devices supporting the Allen-Bradley DF1 full-duplex serial protocol. The devices can be AB devices, other host computers or even other system applications using the API.The Allen-Bradley DF1 Serial Communication Interface API enables a system to acts as a client device to other Allen-Bradley peer devices, initiating read and write operations on behalf of the system applications. The API also allows the system to emulate an Allen-Bradley PLC to respond to read and write requests and thus acts as a “virtual PLC” to other AB peers. The API is available for different Windows/WinCE-based systems/platforms and can be used with C/C++ or Visual Basic.The API consists of two component functionalities, client side and server side. The client side functionality is implemented with a single API DLL. Server side functionality is implemented with a DLL/executable pair. Together these components manage all aspects of the protocol and data exchange including responding to peers with proper acknowledgements, error/success codes and protocol data byte ordering. The system application need only to deal with the data values exchanged in native byte order. The user can employ either the API’s client, server or both functionalities with minimal code implementation.Fax: 1-703-709-0985 Client API FunctionalityTo exchange data with Allen-Bradley peers, a system application can initiate read and/or write operation(s) to the devices by simply calling the client DLL functions. The functions include the ability to configure the communication serial port(s), create handle(s) for the device(s) and then using those handle(s) to call DLL read and write functions. Operation results are returned directly to the calling application, as is data in the case of read operations.Client API Supports• One or more serial communication ports with configurable communication parameters. • Defining of multiple device(s) representing Allen-Bradley devices.• PLC types supported: PLC5, SLC 500, SLC 5/01, SLC 5/02, SLC 5/03, SLC 5/04, SLC 5/05, MicroLogix and CompactLogix.• Functions to read data from and write file data to defined device(s).• File types supported: Output, Input, Status, Bit, Timer, Counter, Control, Integer, Float, ASCII and String.• Data can be read/written as 16-bit, 32-bit or ASCII string values. • Global addressing for write requests.• Multiple user applications can use the client API simultaneously.Fax: 1-703-709-0985 Server API FunctionalityUsing the server executable program provided as part of the API, a system can appear as an Allen-Bradley peer (Allen-Bradley PLC) on the network. By managing all DF1 serial communication operations, the server executable receives and responds to both read and write requests from peer devices. Data written by peers is stored into separate databases maintained by the server executable for each Allen-Bradley file type (Output, Input, Status, Bit, Timer, Counter, Control, Integer, Float, ASCII and String). The data received is stored in the byte order appropriate for the system’s processor. The data for read requests received from peers is retrieved and returned from these databases as well.No user programming is required for the system to act in this server mode. Peers can read and write to the system as if it were an Allen-Bradley PLC with no user application programs running. Applications have access to the server’s databases indirectly through specific API DLL functions calls or directly via shared memory access. In this way, the user applications obtain data written from peers and can update the system’s “virtual PLC’s” database so that peers can retrieve it.Server API Supports:• One serial communication port with configurable communication parameters. • Define PLC type (PLC5 or SLC 5/04) for which the server will emulate.• File types supported: Output, Input, Status, Bit, Timer, Counter, Control, Integer, Float, ASCII and String.• Maximum 100 files with a separate adjustable database maintained for each file. • Access to databases via function calls and/or through shared memory. • Multiple user applications can access the server databases simultaneously.Fax: 1-703-709-0985 Specifications:• Supported Platform:o Any computer running Windows 98/NT/2000/XP operating system o WinCEIntelligent Instrumentation EDAS CE and LANpoint CE• Supported serial communication ports: 1 – 32• Supported protocol: Allen-Bradley DF1 full-duplex• Supports multiple, multi-thread user applications simultaneously • Client API Supportso One or more serial communication ports with configurable communication parameters.o Defining of multiple device(s) representing Allen-Bradley devices.o PLC types supported: PLC5, SLC 500, SLC 5/01, SLC 5/02, SLC 5/03, SLC 5/04, SLC 5/05, MicroLogix and CompactLogix.o Functions to read data from and write file data to defined device(s).o File types supported: Output, Input, Status, Bit, Timer, Counter, Control, Integer, Float, ASCII and String.o Data can be read/written as 16-bit, 32-bit or ASCII string values. o Global addressing for write requests.o Multiple user applications can use the client API simultaneously. o Allen-Bradley DF1 protocol commands:PLC5• Word Range Write (Command 0F, Function 00) • Word Range Read (Command 0F, Function 01)• Read Modify-Write (Write Bit) (Command 0F, Function 26) SLC/MicroLogix/CompactLogix• Protected Typed Logical Read (with 3 Address Fields) (Command 0F, Function A2)• Protected Typed Logical Write (with 3 Address Fields) (Command 0F, Function AA)• Protected Typed Logical Write with Mask (Write Bit) (Command 0F, Function AB) (not supported by SLC 500, SLC 5/01 or SLC 5/02)Fax: 1-703-709-0985 • Server API Supports:o One serial communication port with configurable communication parameters. o Define PLC type (PLC5 or SLC 5/04) for which the server will emulate.o File types supported: Output, Input, Status, Bit, Timer, Counter, Control, Integer, Float, ASCII and String.o Maximum 100 files with a separate adjustable database maintained for each file. o Access to databases via function calls and/or through shared memory. o Multiple user applications can access the server databases simultaneously. o Allen-Bradley DF1 protocol commands:PLC5• Read Diagnostic Counters (Command 06, Function 01) • Read Diagnostic Status (Command 06, Function 03) • Word Range Write (Command 0F, Function 00) • Word Range Read (Command 0F, Function 01)• Read Modify-Write (Write Bit) (Command 0F, Function 26) • Read Section Size (Command 0F, Function 29) • Type Write (Command 0F, Function 67) • Type Read (Command 0F, Function 68) SLC 5/04• Read Diagnostic Counters (Command 06, Function 01) • Read Diagnostic Status (Command 06, Function 03) • Read File Info (Command 0F, Function 94)• Protected Typed Logical Read (with 2 Address Fields) (Command 0F, Function A1)• Protected Typed Logical Write (with 2 Address Fields) (Command 0F, Function A9)• Protected Typed Logical Read (with 3 Address Fields) (Command 0F, Function A2)• Protected Typed Logical Write (with 3 Address Fields) (Command 0F, Function AA)• Protected Typed Logical Write with Mask (Write Bit) (Command 0F, Function AB)Fax: 1-703-709-0985 Ordering Information:Product Name: Allen-Bradley DF1 Serial Communication Interface API Platform Part Numbers:• Computer running Windows 98/NT/2000/XP Part No: WinPC-ABDF1API • WinCEo Intelligent Instrumentation EDAS CE and LANpoint CE Part No: IIIWinCE-ABDF1APISoftware package includes 3-1/2" diskette and User's manual (electronic image)Contact DASTEC about other supported platforms or to inquire about supporting other platforms.Copyright and Trademark notices: 2003 DASTEC Corporation, Inc.WinCE, Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows XP and Windows Explorer are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.Pentium and Pentium Pro are trademarks of Intel Corporation.PLC-5, SLC, SLC 500, SLC 5/01, SLC 5/02, SLC 5/03, SLC 5/04, SLC5/05, MicroLogix and CompactLogix are trademarks of Allen-Bradley Company, Inc.EDAS CE and LANpoint CE are registered trademarks of Intelligent Instrumentation, Inc.。
各PLC通讯协议简介(2015-05-11 16:34:51)分类:自从第一台PLC在GM公司汽车生产线上首次应用成功以来,PLC凭借其方便性、可靠性以及低廉的价格得到了广泛的应用。
但PLC毕竟是一个黑盒子,不能实时直观地观察控制过程,与DCS相比存在比较大的差距。
计算机技术的发展和普及,为PLC又提供了新的技术手段,通过计算机可以实施监测PLC的控制过程和结果,让PLC如虎添翼。
但是各PLC通讯介质和通讯协议各不相同,下面将简单介绍主要PLC的通讯介质和协议内容。
??美系厂家?RockwellAB?Rockwell的PLC主要是包括PLC2、PLC3、PLC5、SLC500、ControlLogix等型号,PLC2和PLC3是早期型号,现在用的比较多的小型PLC是SLC500,中型的一般是ControlLogix,大型的用PLC5系列。
?DF1协议是Rockwell各PLC都支持的通讯协议,DF1协议可以通过232或422等串口介质进行数据传输,也可以通过DH、DH+、DH485、ControlNet等网络介质来传输。
DF1协议的具体内容可以在AB的资料库中下载。
?AB的plc也提供了OPC和DDE,其集成的软件中RSLogix中就包含DDE和OPC SERVER,可以通过上述软件来进行数据通讯。
?AB的中高档的PLC还提供了高级语言编程功能,用户还可以通过编程实现自己的通讯协议。
??GE?GE现在在国内用的比较多的主要是90-70和90-30系列plc,这两款PLC都支持SNP协议,SNP协议在其PLC 手册中有协议的具体内容。
?现在GE的PLC也可以通过以太网链接,GE的以太网协议内容不对外公开,但GE提供了一个SDK开发包,可以基于该开发包通讯。
??欧洲系列?西门子?西门子系列PLC主要包括其早期的S5和现在的S7-200、S7-300、S7-400等各型号PLC,早期的S5PLC支持的是3964R协议,但是因为现在在国内应用较少,除极个别改造项目外,很少有与其进行数据通讯的。
AI系列仪表V5.0串行通讯接口协议说明AI系列人工智能调节器/多路巡检仪/流量积算仪的AI通讯接口协议,具备 16位的求和校正码,通讯可靠,支持1200,2400,4800,9600,19200等多种波特率,并且将上位机访问一台仪表的平均时间缩短到0.1秒以下.仪表允许在一个RS485通讯接口上连接多达101台仪表(为保证通讯可靠,仪表数量大于60台时需要加一个RS485中继器)。
一、接口规格AI系列仪表使用异步串行通讯接口,接口电平符合RS232C或RS485标准中的规定。
数据格式为1个起始位,8位数据,无校验位,一个或2个停止位。
通讯传输数据的波特率可调为1200--19200 bit/S(波特率为19200时需配界高速光耦的通讯模块。
AI仪表采用多机通讯协议,如果采用RS485通讯接口,则可将1—101台的仪表同时连接在一个通讯接口上。
采用RS232C通讯接口时,一个通讯接口只能联接一台仪表。
RS485通讯接口通讯距离长达1KM以上,只需两根线就能使多台AI仪表与计算机进行通讯,优于RS232通讯接口。
为使用普通个人计算机PC能作上位机,可使用RS232C/RS485型通讯接口转换器,将计算机上的RS232C通讯口转为RS485通讯口。
宇光电子技术有限公司所为此专门开发了新型RS232/RS485转换器,与其他公司同类产品相比,具备体积小,无需初始化而可适应任何软件,无需外接电源,具有抗雷击等优点.按RS485接口的规定,RS485通讯接口可在一条通讯线路上连接最多32台仪表或计算机。
需要联接更多的仪表时需要中继器,也可选择采用75LBC184或MAX487芯片的通讯接口,则最多可连接100台AI仪表在一条通讯线路上,目前生产的AI仪表通讯接口模块通常采用75LBC184,这种芯片具备一定的防雷和防静电功能,且无需中继器即可连接约60台仪表。
AI仪表的RS232C及RS485通讯接口采用光电隔离技术将通讯接口与仪表的其他部分线路隔离,当通讯线路上的某台仪表损坏或故障时,并不会对其它仪表产生影响。
Fax: 1-703-709-0985 Allen-Bradley DF1 Serial Communication Interface APIThe DASTEC Corporation Allen-Bradley DF1 Serial Communication Interface API allows the user to implement bi-directional serial communications to exchange data between applications running on a Windows/WinCE-based system with other devices supporting the Allen-Bradley DF1 full-duplex serial protocol. The devices can be AB devices, other host computers or even other system applications using the API.The Allen-Bradley DF1 Serial Communication Interface API enables a system to acts as a client device to other Allen-Bradley peer devices, initiating read and write operations on behalf of the system applications. The API also allows the system to emulate an Allen-Bradley PLC to respond to read and write requests and thus acts as a “virtual PLC” to other AB peers. The API is available for different Windows/WinCE-based systems/platforms and can be used with C/C++ or Visual Basic.The API consists of two component functionalities, client side and server side. The client side functionality is implemented with a single API DLL. Server side functionality is implemented with a DLL/executable pair. Together these components manage all aspects of the protocol and data exchange including responding to peers with proper acknowledgements, error/success codes and protocol data byte ordering. The system application need only to deal with the data values exchanged in native byte order. The user can employ either the API’s client, server or both functionalities with minimal code implementation.Fax: 1-703-709-0985 Client API FunctionalityTo exchange data with Allen-Bradley peers, a system application can initiate read and/or write operation(s) to the devices by simply calling the client DLL functions. The functions include the ability to configure the communication serial port(s), create handle(s) for the device(s) and then using those handle(s) to call DLL read and write functions. Operation results are returned directly to the calling application, as is data in the case of read operations.Client API Supports• One or more serial communication ports with configurable communication parameters. • Defining of multiple device(s) representing Allen-Bradley devices.• PLC types supported: PLC5, SLC 500, SLC 5/01, SLC 5/02, SLC 5/03, SLC 5/04, SLC 5/05, MicroLogix and CompactLogix.• Functions to read data from and write file data to defined device(s).• File types supported: Output, Input, Status, Bit, Timer, Counter, Control, Integer, Float, ASCII and String.• Data can be read/written as 16-bit, 32-bit or ASCII string values. • Global addressing for write requests.• Multiple user applications can use the client API simultaneously.Fax: 1-703-709-0985 Server API FunctionalityUsing the server executable program provided as part of the API, a system can appear as an Allen-Bradley peer (Allen-Bradley PLC) on the network. By managing all DF1 serial communication operations, the server executable receives and responds to both read and write requests from peer devices. Data written by peers is stored into separate databases maintained by the server executable for each Allen-Bradley file type (Output, Input, Status, Bit, Timer, Counter, Control, Integer, Float, ASCII and String). The data received is stored in the byte order appropriate for the system’s processor. The data for read requests received from peers is retrieved and returned from these databases as well.No user programming is required for the system to act in this server mode. Peers can read and write to the system as if it were an Allen-Bradley PLC with no user application programs running. Applications have access to the server’s databases indirectly through specific API DLL functions calls or directly via shared memory access. In this way, the user applications obtain data written from peers and can update the system’s “virtual PLC’s” database so that peers can retrieve it.Server API Supports:• One serial communication port with configurable communication parameters. • Define PLC type (PLC5 or SLC 5/04) for which the server will emulate.• File types supported: Output, Input, Status, Bit, Timer, Counter, Control, Integer, Float, ASCII and String.• Maximum 100 files with a separate adjustable database maintained for each file. • Access to databases via function calls and/or through shared memory. • Multiple user applications can access the server databases simultaneously.Fax: 1-703-709-0985 Specifications:• Supported Platform:o Any computer running Windows 98/NT/2000/XP operating system o WinCEIntelligent Instrumentation EDAS CE and LANpoint CE• Supported serial communication ports: 1 – 32• Supported protocol: Allen-Bradley DF1 full-duplex• Supports multiple, multi-thread user applications simultaneously • Client API Supportso One or more serial communication ports with configurable communication parameters.o Defining of multiple device(s) representing Allen-Bradley devices.o PLC types supported: PLC5, SLC 500, SLC 5/01, SLC 5/02, SLC 5/03, SLC 5/04, SLC 5/05, MicroLogix and CompactLogix.o Functions to read data from and write file data to defined device(s).o File types supported: Output, Input, Status, Bit, Timer, Counter, Control, Integer, Float, ASCII and String.o Data can be read/written as 16-bit, 32-bit or ASCII string values. o Global addressing for write requests.o Multiple user applications can use the client API simultaneously. o Allen-Bradley DF1 protocol commands:PLC5• Word Range Write (Command 0F, Function 00) • Word Range Read (Command 0F, Function 01)• Read Modify-Write (Write Bit) (Command 0F, Function 26) SLC/MicroLogix/CompactLogix• Protected Typed Logical Read (with 3 Address Fields) (Command 0F, Function A2)• Protected Typed Logical Write (with 3 Address Fields) (Command 0F, Function AA)• Protected Typed Logical Write with Mask (Write Bit) (Command 0F, Function AB) (not supported by SLC 500, SLC 5/01 or SLC 5/02)Fax: 1-703-709-0985 • Server API Supports:o One serial communication port with configurable communication parameters. o Define PLC type (PLC5 or SLC 5/04) for which the server will emulate.o File types supported: Output, Input, Status, Bit, Timer, Counter, Control, Integer, Float, ASCII and String.o Maximum 100 files with a separate adjustable database maintained for each file. o Access to databases via function calls and/or through shared memory. o Multiple user applications can access the server databases simultaneously. o Allen-Bradley DF1 protocol commands:PLC5• Read Diagnostic Counters (Command 06, Function 01) • Read Diagnostic Status (Command 06, Function 03) • Word Range Write (Command 0F, Function 00) • Word Range Read (Command 0F, Function 01)• Read Modify-Write (Write Bit) (Command 0F, Function 26) • Read Section Size (Command 0F, Function 29) • Type Write (Command 0F, Function 67) • Type Read (Command 0F, Function 68) SLC 5/04• Read Diagnostic Counters (Command 06, Function 01) • Read Diagnostic Status (Command 06, Function 03) • Read File Info (Command 0F, Function 94)• Protected Typed Logical Read (with 2 Address Fields) (Command 0F, Function A1)• Protected Typed Logical Write (with 2 Address Fields) (Command 0F, Function A9)• Protected Typed Logical Read (with 3 Address Fields) (Command 0F, Function A2)• Protected Typed Logical Write (with 3 Address Fields) (Command 0F, Function AA)• Protected Typed Logical Write with Mask (Write Bit) (Command 0F, Function AB)Fax: 1-703-709-0985 Ordering Information:Product Name: Allen-Bradley DF1 Serial Communication Interface API Platform Part Numbers:• Computer running Windows 98/NT/2000/XP Part No: WinPC-ABDF1API • WinCEo Intelligent Instrumentation EDAS CE and LANpoint CE Part No: IIIWinCE-ABDF1APISoftware package includes 3-1/2" diskette and User's manual (electronic image)Contact DASTEC about other supported platforms or to inquire about supporting other platforms.Copyright and Trademark notices: 2003 DASTEC Corporation, Inc.WinCE, Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows XP and Windows Explorer are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.Pentium and Pentium Pro are trademarks of Intel Corporation.PLC-5, SLC, SLC 500, SLC 5/01, SLC 5/02, SLC 5/03, SLC 5/04, SLC5/05, MicroLogix and CompactLogix are trademarks of Allen-Bradley Company, Inc.EDAS CE and LANpoint CE are registered trademarks of Intelligent Instrumentation, Inc.。