C语言日期时函数
- 格式:doc
- 大小:113.00 KB
- 文档页数:5

C语言中如何获取时间?精度如何?1 使用time_t time( time_t * timer ) 精确到秒2 使用clock_t clock() 得到的是CPU时间精确到1/CLOCKS_PER_SEC秒3 计算时间差使用double difftime( time_t timer1, time_t timer0 )4 使用DWORD GetTickCount() 精确到毫秒5 如果使用MFC的CTime类,可以用CTime::GetCurrentTime() 精确到秒6 要获取高精度时间,可以使用BOOL QueryPerformanceFrequency(LARGE_INTEGER *lpFrequency)获取系统的计数器的频率BOOL QueryPerformanceCounter(LARGE_INTEGER *lpPerformanceCount)获取计数器的值然后用两次计数器的差除以Frequency就得到时间。
7 Multimedia Timer FunctionsThe following functions are used with multimedia timers.timeBeginPeriod/timeEndPeriod/timeGetDevCaps/timeGetSystemTime//*********************************************************************//用标准C实现获取当前系统时间的函数一.time()函数time(&rawtime)函数获取当前时间距1970年1月1日的秒数,以秒计数单位,存于rawtime 中。
#include "time.h"void main (){time_t rawtime;struct tm * timeinfo;time ( &rawtime );timeinfo = localtime ( &rawtime );printf ( "\007The current date/time is: %s", asctime (timeinfo) );exit(0);}=================#include -- 必须的时间函数头文件time_t -- 时间类型(time.h 定义是typedef long time_t; 追根溯源,time_t是long)struct tm -- 时间结构,time.h 定义如下:int tm_sec;int tm_min;int tm_hour;int tm_mday;int tm_mon;int tm_year;int tm_wday;int tm_yday;int tm_isdst;time ( &rawtime ); -- 获取时间,以秒计,从1970年1月一日起算,存于rawtimelocaltime ( &rawtime ); -- 转为当地时间,tm 时间结构asctime ()-- 转为标准ASCII时间格式:星期月日时:分:秒年-----------------------------------------------------------------------------二.clock()函数,用clock()函数,得到系统启动以后的毫秒级时间,然后除以CLOCKS_PER_SEC,就可以换成“秒”,标准c函数。

c语言函数库目录第一章(C标准库) ............................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
1. <>:诊断............................................................................. 错误!未定义书签。
2. <>:字符类别测试 ............................................................ 错误!未定义书签。
3. <>:错误处理..................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
4. <>:整型常量..................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
5. <>:地域环境..................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
6. <>:数学函数..................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
7. <>:非局部跳转................................................................. 错误!未定义书签。
8. <>:信号............................................................................. 错误!未定义书签。
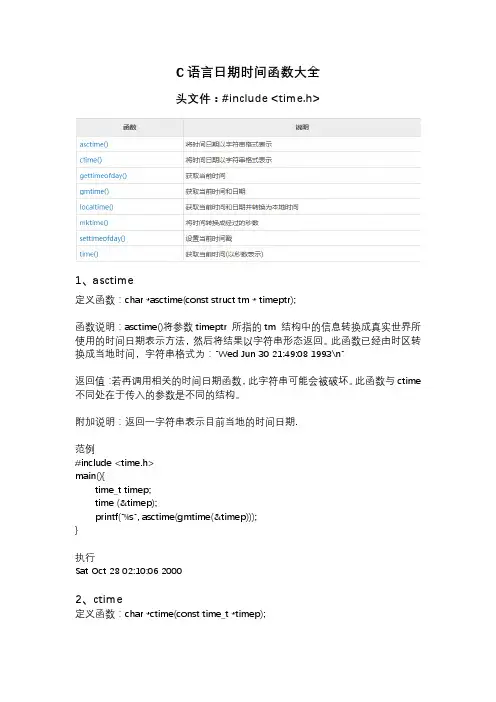
C语言日期时间函数大全头文件:#include <time.h>1、asctime定义函数:char *asctime(const struct tm * timeptr);函数说明:asctime()将参数timeptr 所指的tm 结构中的信息转换成真实世界所使用的时间日期表示方法,然后将结果以字符串形态返回。
此函数已经由时区转换成当地时间,字符串格式为:"Wed Jun 30 21:49:08 1993\n"返回值:若再调用相关的时间日期函数,此字符串可能会被破坏。
此函数与ctime 不同处在于传入的参数是不同的结构。
附加说明:返回一字符串表示目前当地的时间日期.范例#include <time.h>main(){time_t timep;time (&timep);printf("%s", asctime(gmtime(&timep)));}执行Sat Oct 28 02:10:06 20002、ctime定义函数:char *ctime(const time_t *timep);函数说明:ctime()将参数timep 所指的time_t 结构中的信息转换成真实世界所使用的时间日期表示方法,然后将结果以字符串形态返回。
此函数已经由时区转换成当地时间,字符串格式为"Wed Jun 30 21 :49 :08 1993\n"。
注意:若再调用相关的时间日期函数,此字符串可能会被破坏。
返回值:返回一字符串表示目前当地的时间日期。
范例#include <time.h>main(){time_t timep;time (&timep);printf("%s", ctime(&timep));}执行Sat Oct 28 10 : 12 : 05 20003、gettimeofday头文件:#include <sys/time.h> #include <unistd.h>定义函数:int gettimeofday (struct timeval * tv, struct timezone * tz);函数说明:gettimeofday()会把目前的时间有tv 所指的结构返回,当地时区的信息则放到tz 所指的结构中。

C语言时间函数的应用C语言时间函数的应用C语言程序,常涉及时间的获取和计算,例如获取当前时间,倒计时计算,时间差计算。
C/C++语言提供了一些库函数,可用于此目的。
下面以VC++ 6.0 编译器为例,叙述C语言时间函数的应用,调用时间函数需头文件time.h。
(1)获取现在时间并打印C语言提供函数 time(),可以获取现在时间。
函数原型是time_t time ( time_t *t);你可以通过实参获取时间,也可以通过返回值获取时间。
例如:time_t now;now = time(NULL);或 time(&now);得到的time_t型数值是从1970年1月1日起到现在的秒数。
用C语言提供的函数 ctime 转换成字符串形式,打印出年月日时分秒。
见下面程序里的 print_current_time() 子程序。
(2)获取现在时间并转换成整数年月日时分秒形式C语言提供的函数localtime(), 可以把 time_t 数值转换成 tm 结构,tm结构里含年月日时分秒和是否是闰年等信息,结构里的年加1900是真实的年,结构里的月加1是真实的月。
见子程序 get_current_YMD().(3)输入年月日计算这天是该年的第几天当我们要绘制某年度的统计数据时,常以天做横座标按比例绘图,这时就需要把月日换算为天。
把日加上前几个月的天数就可得结果。
只要注意该年是平年还是闰年,闰年的2月份多一天。
闰年的判断是:if ((Y%4==0)&&(Y%100!=0)||(Y%400==0) {printf("闰年");}见子程序 YMD_2_JD();(4)输入年月日计算这天是星期几公元计年从1年1月1日开始,这天是星期一。
平年一年有365天,365除7取余数为1。
也就是说平年的星期几等于上一年的星期几加1。
闰年的星期几等于上一年的星期几加2。
所以,若知年份,就可以推算出这年元旦推移了多少天,变星期几,再调用YMD_2_JD(),算出某月某日推移了多少天,就算得这天是星期几。

c语言中time函数的用法c语言中的time函数是一个非常常用的函数,它主要用于获取当前系统的时间和日期。
在本文中,我将为您详细介绍time函数的用法及其在实际项目中的应用。
首先,让我们来了解一下time函数的基本用法。
在c语言中,time函数的原型如下所示:ctime_t time(time_t *seconds);该函数的返回值是一个time_t类型的值,表示从1970年1月1日00:00:00到当前时间经过了多少秒。
如果参数seconds不为空指针(NULL),则该参数指向的变量将被设置为与time_t类型的返回值相同的值。
接下来,我们将一步一步回答关于time函数的常见问题。
1. time函数如何获取当前系统的时间?time函数是通过系统调用来获取当前系统时间的。
它使用计算机内部的时钟来计算从1970年1月1日00:00:00到当前时间经过了多少秒。
这种以秒为单位的计时方式被称为Unix时间戳,是一种广泛使用的时间表示方式。
2. 如何将time_t类型的值转换为可读的时间格式?time函数返回的time_t类型的值表示的是从1970年1月1日00:00:00到当前时间经过的秒数。
要将它转换为可读的时间格式,可以使用ctime 函数或localtime函数。
ctime函数的原型如下:cchar *ctime(const time_t *time);它接受一个time_t类型的指针作为参数,并返回一个指向包含可打印的时间字符串的静态内存缓冲区的指针。
localtime函数的原型如下:cstruct tm *localtime(const time_t *time);它也接受一个time_t类型的指针作为参数,并返回一个指向tm结构的指针,其中包含了年、月、日、时、分、秒等各个时间字段的值。
下面是一个示例代码,演示了如何使用ctime函数将time_t类型的值转换为可读的时间字符串:c#include <stdio.h>#include <time.h>int main() {time_t now;time(&now);printf("Current time: s", ctime(&now));return 0;}3. 如何将可读的时间字符串转换为time_t类型的值?如果我们有一个可读的时间字符串,想将它转换为time_t类型的值,可以使用mktime函数。

C语言函数大全函数名:abort功能: 异常终止一个进程用法: void abort(void)函数名: abs功能: 求整数的绝对值用法: int abs(int i)函数名: absread, abswirte功能: 绝对磁盘扇区读、写数据用法: int absread(int drive, int nsects, int sectno, void *buffer)int abswrite(int drive, int nsects, in tsectno, void *buffer函数名: access功能: 确定文件的访问权限用法: int access(const char *filename, int amode)函数名: acos功能:反余弦函数用法: double acos(double x)函数名: allocmem功能: 分配DOS存储段用法:int allocmem(unsigned size, unsigned *seg)函数名: arc功能: 画一弧线用法:void far arc(int x, int y, int stangle, int endangle, int radius)函数名: asctime功能: 转换日期和时间为ASCII码用法:char *asctime(const struct tm *tblock)函数名: asin功能:反正弦函数用法: double asin(double x)函数名: assert功能: 测试一个条件并可能使程序终止用法:void assert(int test)函数名: atan功能: 反正切函数用法: double atan(double x)函数名: atan2功能: 计算Y/X的反正切值用法: double atan2(double y, double x)函数名:atexit功能: 注册终止函数用法: int atexit(atexit_t func)函数名: atof功能: 把字符串转换成浮点数用法:double atof(const char *nptr)函数名: atoi功能: 把字符串转换成长整型数用法: int atoi(const char *nptr)函数名: atol功能: 把字符串转换成长整型数用法: long atol(const char *nptr)函数名: bar功能: 画一个二维条形图用法: void far bar(int left, int top, int right, int bottom)函数名: bar3d功能: 画一个三维条形图用法:void far bar3d(int left, int top, int right, int bottom,int depth, int topflag)函数名: bdos功能: DOS系统调用用法: int bdos(int dosfun, unsigned dosdx, unsigned dosal)函数名:bdosptr功能:DOS系统调用用法: int bdosptr(int dosfun, void*argument, unsigned dosal)函数名:bioscom功能: 串行I/O通信用法:int bioscom(int cmd, char abyte, int port)函数名:biosdisk功能: 软硬盘I/O用法:int biosdisk(int cmd, int drive, int head, int track, int sectorint nsects, void *buffer)函数名:biosequip功能: 检查设备用法:int biosequip(void)函数名:bioskey功能: 直接使用BIOS服务的键盘接口用法:int bioskey(int cmd)函数名:biosmemory功能: 返回存储块大小用法:int biosmemory(void)函数名:biosprint功能: 直接使用BIOS服务的打印机I/O用法:int biosprint(int cmd, int byte, int port)函数名:biostime功能: 读取或设置BIOS时间用法: long biostime(int cmd, long newtime)函数名: brk功能: 改变数据段空间分配用法:int brk(void *endds)函数名:bsearch功能: 二分法搜索用法:void *bsearch(const void *key, const void *base, size_t *nelem,size_t width, int(*fcmp)(const void *, const *))函数名: cabs功能: 计算复数的绝对值用法: double cabs(struct complex z);函数名:calloc功能:分配主存储器用法:void *calloc(size_t nelem, size_t elsize);函数名: ceil功能: 向上舍入用法: double ceil(double x);函数名: cgets功能: 从控制台读字符串用法: char *cgets(char *str)函数名:chdir功能: 改变工作目录用法: int chdir(const char *path);函数名:_chmod, chmod功能: 改变文件的访问方式用法: int chmod(const char *filename, int permiss);函数名:chsize功能: 改变文件大小用法: int chsize(int handle, long size);函数名: circle功能: 在给定半径以(x, y)为圆心画圆用法: void far circle(int x, int y, int radius);函数名: cleardevice功能: 清除图形屏幕用法: void far cleardevice(void);函数名:clearerr功能: 复位错误标志用法:void clearerr(FILE *stream);函数名: clearviewport功能: 清除图形视区用法: void far clearviewport(void);函数名:_close, close功能: 关闭文件句柄用法:int close(int handle);函数名: clock功能:确定处理器时间用法: clock_t clock(void);函数名:closegraph功能: 关闭图形系统用法: void far closegraph(void);函数名:clreol功能: 在文本窗口中清除字符到行末用法:void clreol(void)函数名:clrscr功能: 清除文本模式窗口用法:void clrscr(void);函数名: coreleft功能: 返回未使用内存的大小用法:unsigned coreleft(void);函数名: cos功能: 余弦函数用法:double cos(double x);函数名:cosh功能: 双曲余弦函数用法: dluble cosh(double x);函数名: country功能: 返回与国家有关的信息用法: struct COUNTRY *country(int countrycode, struct country *country); 函数名: cprintf功能: 送格式化输出至屏幕用法:int cprintf(const char *format[, argument, ...]);函数名: cputs功能: 写字符到屏幕用法: void cputs(const char *string);函数名: _creat creat功能: 创建一个新文件或重写一个已存在的文件用法: int creat (const char *filename, int permiss)函数名:creatnew功能: 创建一个新文件用法:int creatnew(const char *filename, int attrib);函数名: cscanf功能: 从控制台执行格式化输入用法:int cscanf(char*format[,argument, ...]);函数名: ctime功能: 把日期和时间转换为字符串用法:char *ctime(const time_t *time);函数名: ctrlbrk功能: 设置Ctrl-Break处理程序用法: void ctrlbrk(*fptr)(void);函数名: delay功能: 将程序的执行暂停一段时间(毫秒)用法: void delay(unsigned milliseconds); 函数名: delline功能: 在文本窗口中删去一行用法: void delline(void);函数名:detectgraph功能: 通过检测硬件确定图形驱动程序和模式用法: void far detectgraph(int far*graphdriver, int far *graphmode);函数名: difftime功能: 计算两个时刻之间的时间差用法: double difftime(time_t time2, time_t time1);函数名: disable功能: 屏蔽中断用法:void disable(void);函数名: div功能: 将两个整数相除, 返回商和余数用法:div_t (int number, int denom);函数名: dosexterr功能: 获取扩展DOS错误信息用法:int dosexterr(struct DOSERR *dblkp); 函数名: dostounix功能: 转换日期和时间为UNIX时间格式用法: long dostounix(struct date *dateptr, struct time *timeptr);函数名: drawpoly功能: 画多边形用法: void far drawpoly(int numpoints, int far *polypoints);函数名:dup功能: 复制一个文件句柄用法: int dup(int handle);函数名:dup2功能: 复制文件句柄用法: int dup2(int oldhandle, int newhandle);函数名: ecvt功能: 把一个浮点数转换为字符串用法: char ecvt(double value, int ndigit, int *decpt, int *sign);函数名: ellipse功能: 画一椭圆用法:void far ellipse(int x, int y, int stangle, int endangle,int xradius, int yradius);函数名: enable功能: 开放硬件中断用法: void enable(void);函数名: eof功能: 检测文件结束用法: int eof(int *handle);函数名: exec...功能: 装入并运行其它程序的函数用法: int execl(char *pathname, char *arg0, arg1, ..., argn, NULL);int execle(char *pathname, char *arg0,arg1, ..., argn, NULL,char *envp[]);int execlp(char *pathname, char *arg0,arg1, .., NULL);int execple(char *pathname, char *arg0,arg1, ..., NULL,char *envp[]);int execv(char *pathname, char *argv[]);int execve(char *pathname, char *argv[], char *envp[]);int execvp(char *pathname, char *argv[]); int execvpe(char *pathname, char *argv[], char *envp[]);函数名:exit功能: 终止程序用法: void exit(int status);函数名: exp功能: 指数函数用法: double exp(double x);函数名: gcvt功能: 把浮点数转换成字符串用法: char *gcvt(double value, int ndigit, char *buf);函数名: geninterrupt功能: 产生一个软中断用法: void geninterrupt(int intr_num);函数名: getarccoords功能: 取得最后一次调用arc的坐标用法: void far getarccoords(struct arccoordstype far *arccoords);函数名: getaspectratio功能: 返回当前图形模式的纵横比用法: void far getaspectratio(int far *xasp, int far *yasp);函数名: getbkcolor功能: 返回当前背景颜色用法: int far getbkcolor(void);函数名: getc功能: 从流中取字符用法: int getc(FILE *stream);函数名: getcbrk功能: 获取Control_break设置用法: int getcbrk(void);函数名: getch功能: 从控制台无回显地取一个字符用法: int getch(void);函数名: getchar功能: 从stdin流中读字符用法: int getchar(void);函数名: getche功能: 从控制台取字符(带回显)用法: int getche(void);函数名: getcolor功能: 返回当前画线颜色用法: int far getcolor(void);函数名: getcurdir功能: 取指定驱动器的当前目录用法: int getcurdir(int drive, char *direc); 函数名: getcwd功能: 取当前工作目录用法: char *getcwd(char *buf, int n);函数名: getdate功能: 取DOS日期用法: void getdate(struct *dateblk);函数名: getdefaultpalette功能: 返回调色板定义结构用法: struct palettetype *far getdefaultpalette(void);函数名: getdisk功能: 取当前磁盘驱动器号用法: int getdisk(void);函数名: getdrivername功能: 返回指向包含当前图形驱动程序名字的字符串指针用法: char *getdrivename(void);函数名: getdta功能: 取磁盘传输地址用法: char far *getdta(void);函数名: getenv功能: 从环境中取字符串用法: char *getenv(char *envvar);函数名: getfat, getfatd功能: 取文件分配表信息用法: void getfat(int drive, struct fatinfo *fatblkp);函数名: getfillpattern功能: 将用户定义的填充模式拷贝到内存中用法: void far getfillpattern(char far*upattern);函数名: getfillsettings功能: 取得有关当前填充模式和填充颜色的信息用法: void far getfillsettings(struct fillsettingstype far *fillinfo);函数名: getftime功能: 取文件日期和时间用法: int getftime(int handle, struct ftime *ftimep);函数名: getgraphmode功能: 返回当前图形模式用法: int far getgraphmode(void);函数名: getftime功能: 取文件日期和时间用法: int getftime(int handle, struct ftime *ftimep);函数名: getgraphmode功能: 返回当前图形模式用法: int far getgraphmode(void);函数名: getimage功能: 将指定区域的一个位图存到主存中用法: void far getimage(int left, int top, int right, int bottom,void far *bitmap);函数名: getlinesettings功能: 取当前线型、模式和宽度用法: void far getlinesettings(struct linesettingstype far *lininfo):函数名: getmaxx功能: 返回屏幕的最大x坐标用法: int far getmaxx(void);函数名: getmaxy功能: 返回屏幕的最大y坐标用法: int far getmaxy(void);函数名: getmodename功能: 返回含有指定图形模式名的字符串指针用法: char *far getmodename(intmode_name);函数名: getmoderange功能: 取给定图形驱动程序的模式范围用法: void far getmoderange(int graphdriver, int far *lomode,int far *himode);函数名: getpalette功能: 返回有关当前调色板的信息用法: void far getpalette(struct palettetype far *palette);函数名: getpass功能: 读一个口令用法: char *getpass(char *prompt);函数名: getpixel功能: 取得指定像素的颜色用法: int far getpixel(int x, int y);函数名: gets功能: 从流中取一字符串用法: char *gets(char *string);函数名: gettext功能: 将文本方式屏幕上的文本拷贝到存储区用法: int gettext(int left, int top, int right, int bottom, void *destin);函数名: gettextinfo功能: 取得文本模式的显示信息用法: void gettextinfo(struct text_info*inforec);函数名: gettextsettings功能: 返回有关当前图形文本字体的信息用法: void far gettextsettings(struct textsettingstype far *textinfo);函数名: gettime功能: 取得系统时间用法: void gettime(struct time *timep);函数名: getvect功能: 取得中断向量入口用法: void interrupt(*getvect(intintr_num));函数名: getverify功能: 返回DOS校验标志状态用法: int getverify(void);函数名: getviewsetting功能: 返回有关当前视区的信息用法: void far getviewsettings(struct viewporttype far *viewport);函数名: getw功能: 从流中取一整数用法: int getw(FILE *strem);函数名: getx功能: 返回当前图形位置的x坐标用法: int far getx(void);函数名: gety功能: 返回当前图形位置的y坐标用法: int far gety(void);函数名: gmtime功能: 把日期和时间转换为格林尼治标准时间(GMT)用法: struct tm *gmtime(long *clock);函数名: gotoxy功能: 在文本窗口中设置光标用法: void gotoxy(int x, int y);函数名: gotoxy功能: 在文本窗口中设置光标用法: void gotoxy(int x, int y);函数名: graphdefaults功能: 将所有图形设置复位为它们的缺省值用法: void far graphdefaults(void);函数名: grapherrormsg功能: 返回一个错误信息串的指针用法: char *far grapherrormsg(int errorcode);函数名: graphresult功能: 返回最后一次不成功的图形操作的错误代码用法: int far graphresult(void);函数名: _graphfreemem功能: 用户可修改的图形存储区释放函数用法: void far _graphfreemem(void far *ptr, unsigned size);函数名: _graphgetmem功能: 用户可修改的图形存储区分配函数用法: void far *far_graphgetmem(unsigned size);函数名: harderr功能: 建立一个硬件错误处理程序用法: void harderr(int (*fptr)());函数名: hardresume功能: 硬件错误处理函数用法: void hardresume(int rescode);函数名: highvideo功能: 选择高亮度文本字符用法: void highvideo(void);函数名: hypot功能: 计算直角三角形的斜边长用法: double hypot(double x, double y);函数名: imagesize功能: 返回保存位图像所需的字节数用法: unsigned far imagesize(int left, int top, int right, int bottom);函数名: initgraph功能: 初始化图形系统用法: void far initgraph(int far *graphdriver, int far *graphmode函数名: inport功能: 从硬件端口中输入用法: int inp(int protid);函数名: insline功能: 在文本窗口中插入一个空行用法: void insline(void);函数名: installuserdriver功能: 安装设备驱动程序到BGI设备驱动程序表中用法: int far installuserdriver(char far*name, int (*detect)(void));函数名: installuserfont功能: 安装未嵌入BGI系统的字体文件(CHR) 用法: int far installuserfont(char far*name);函数名: int86功能: 通用8086软中断接口用法: int int86(int intr_num, union REGS *inregs, union REGS *outregs)函数名: int86x功能: 通用8086软中断接口用法: int int86x(int intr_num, union REGS *insegs, union REGS *outregs,函数名: intdos功能: 通用DOS接口用法: int intdos(union REGS *inregs, union REGS *outregs);函数名: intdosx功能: 通用DOS中断接口用法: int intdosx(union REGS *inregs, union REGS *outregs,struct SREGS *segregs);函数名: intr功能: 改变软中断接口用法: void intr(int intr_num, struct REGPACK *preg);函数名: ioctl功能: 控制I/O设备用法: int ioctl(int handle, int cmd[,int*argdx, int argcx]);函数名: isatty功能: 检查设备类型用法: int isatty(int handle);函数名: itoa功能: 把一整数转换为字符串用法: char *itoa(int value, char *string, int radix);函数名: kbhit功能: 检查当前按下的键用法: int kbhit(void);函数名: keep功能: 退出并继续驻留用法: void keep(int status, int size);函数名: kbhit功能: 检查当前按下的键用法: int kbhit(void);函数名: keep功能: 退出并继续驻留用法: void keep(int status, int size);函数名: labs用法: long labs(long n);函数名: ldexp功能: 计算value*2的幂用法: double ldexp(double value, int exp); 函数名: ldiv功能: 两个长整型数相除, 返回商和余数用法: ldiv_t ldiv(long lnumer, long ldenom);函数名: lfind功能: 执行线性搜索用法: void *lfind(void *key, void *base, int *nelem, int width,int (*fcmp)());函数名: line功能: 在指定两点间画一直线用法: void far line(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1);函数名: linerel功能: 从当前位置点(CP)到与CP有一给定相对距离的点画一直线用法: void far linerel(int dx, int dy);函数名: localtime功能: 把日期和时间转变为结构用法: struct tm *localtime(long *clock);函数名: lock功能: 设置文件共享锁用法: int lock(int handle, long offset, long length);函数名: log功能: 对数函数ln(x)用法: double log(double x);函数名: log10功能: 对数函数log用法: double log10(double x);函数名: longjump功能: 执行非局部转移用法: void longjump(jmp_buf env, int val); 函数名: lowvideo功能: 选择低亮度字符用法: void lowvideo(void);函数名: lrotl, _lrotl功能: 将无符号长整型数向左循环移位用法: unsigned long lrotl(unsigned long lvalue, int count);unsigned long _lrotl(unsigned long lvalue, int count);函数名: lsearch功能: 线性搜索用法: void *lsearch(const void *key, void *base, size_t *nelem,size_t width, int (*fcmp)(const void *, const void *));函数名: lseek功能: 移动文件读/写指针用法: long lseek(int handle, long offset, int fromwhere);main()主函数每一C 程序都必须有一main() 函数, 可以根据自己的爱好把它放在程序的某个地方。


C语言库函数手册目录A. 分类函数[函数库为ctype.h] (1)B. 数学函数[函数库为math.h、stdlib.h、string.h、float.h] (2)C. 目录函数[函数库为dir.h、dos.h] (3)D. 进程函数[函数库为stdlib.h、process.h] (4)E. 转换子程序[函数库为math.h、stdlib.h、ctype.h、float.h] (6)F. 诊断函数[函数库为assert.h、math.h] (6)G. 输入输出子程序[函数库为io.h、conio.h、stat.h、dos.h、stdio.h、signal.h] (7)H. 接口子程序[函数库为dos.h、bios.h] (13)I. 操作函数[函数库为string.h、mem.h] (21)J. 存贮分配子程序[函数库为dos.h、alloc.h、malloc.h、stdlib.h、process.h] (23)K. 时间日期函数[函数库为time.h、dos.h] (24)int isalpha(int ch) 若ch是字母('A'-'Z','a'-'z')返回非0值,否则返回0int isalnum(int ch) 若ch是字母('A'-'Z','a'-'z')或数字('0'-'9')返回非0值,否则返回0int isascii(int ch) 若ch是字符(ASCII码中的0-127)返回非0值,否则返回0int iscntrl(int ch) 若ch是作废字符(0x7F)或普通控制字符(0x00-0x1F)返回非0值,否则返回0int isdigit(int ch) 若ch是数字('0'-'9')返回非0值,否则返回0int isgraph(int ch) 若ch是可打印字符(不含空格)(0x21-0x7E)返回非0值,否则返回0int islower(int ch) 若ch是小写字母('a'-'z')返回非0值,否则返回0int isprint(int ch) 若ch是可打印字符(含空格)(0x20-0x7E)返回非0值,否则返回0int ispunct(int ch) 若ch是标点字符(0x00-0x1F)返回非0值,否则返回0int isspace(int ch) 若ch是空格(' '),水平制表符('\t'),回车符('\r'),走纸换行('\f'),垂直制表符('\v'),换行符('\n')返回非0值,否则返回0int isupper(int ch) 若ch是大写字母('A'-'Z')返回非0值,否则返回0int isxdigit(int ch) 若ch是16进制数('0'-'9','A'-'F','a'-'f')返回非0值,否则返回0int tolower(int ch) 若ch是大写字母('A'-'Z')返回相应的小写字母('a'-'z')int toupper(int ch) 若ch是小写字母('a'-'z')返回相应的大写字母('A'-'Z')int abs(int i) 返回整型参数i的绝对值double cabs(struct complex znum) 返回复数znum的绝对值double fabs(double x) 返回双精度参数x的绝对值long labs(long n) 返回长整型参数n的绝对值double exp(double x) 返回指数函数e^x的值double frexp(double value,int *eptr) 返回value=x*2n中x的值,n存贮在eptr中double ldexp(double value,int exp); 返回value*2exp的值double log(double x) 返回ln(x)的值double log10(double x) 返回log10(x)的值double pow(double x,double y) 返回x^y的值double pow10(int p) 返回10^p的值double sqrt(double x) 返回x的正平方根double acos(double x) 返回x的反余弦cos-1(x)值,x为弧度double asin(double x) 返回x的反正弦sin-1(x)值,x为弧度double atan(double x) 返回x的反正切tan-1(x)值,x为弧度double atan2(double y,double x) 返回y/x的反正切tan-1(x)值,y的x为弧度double cos(double x) 返回x的余弦cos(x)值,x为弧度double sin(double x) 返回x的正弦sin(x)值,x为弧度double tan(double x) 返回x的正切tan(x)值,x为弧度double cosh(double x) 返回x的双曲余弦cosh(x)值,x为弧度double sinh(double x) 返回x的双曲正弦sinh(x)值,x为弧度double tanh(double x) 返回x的双曲正切tanh(x)值,x为弧度double hypot(double x,double y) 返回直角三角形斜边的长度(z),x和y为直角边的长度,z2=x2+y2double ceil(double x) 返回不小于x的最小整数double floor(double x) 返回不大于x的最大整数void srand(unsigned seed) 初始化随机数发生器int rand() 产生一个随机数并返回这个数double poly(double x,int n,double c[])从参数产生一个多项式double modf(double value,double *iptr)将双精度数value分解成尾数和阶double fmod(double x,double y) 返回x/y的余数double frexp(double value,int *eptr) 将双精度数value分成尾数和阶double atof(char *nptr) 将字符串nptr转换成浮点数并返回这个浮点数double atoi(char *nptr) 将字符串nptr转换成整数并返回这个整数double atol(char *nptr) 将字符串nptr转换成长整数并返回这个整数char *ecvt(double value,int ndigit,int *decpt,int *sign)将浮点数value转换成字符串并返回该字符串char *fcvt(double value,int ndigit,int *decpt,int *sign)将浮点数value转换成字符串并返回该字符串char *gcvt(double value,int ndigit,char *buf)将数value转换成字符串并存于buf中,并返回buf的指针char *ultoa(unsigned long value,char *string,int radix)将无符号整型数value转换成字符串并返回该字符串,radix为转换时所用基数char *ltoa(long value,char *string,int radix)将长整型数value转换成字符串并返回该字符串,radix为转换时所用基数char *itoa(int value,char *string,int radix)将整数value转换成字符串存入string,radix为转换时所用基数double atof(char *nptr) 将字符串nptr转换成双精度数,并返回这个数,错误返回0int atoi(char *nptr) 将字符串nptr转换成整型数, 并返回这个数,错误返回0long atol(char *nptr) 将字符串nptr转换成长整型数,并返回这个数,错误返回0double strtod(char *str,char **endptr)将字符串str转换成双精度数,并返回这个数,long strtol(char *str,char **endptr,int base)将字符串str转换成长整型数,并返回这个数, int matherr(struct exception *e)用户修改数学错误返回信息函数(没有必要使用)double _matherr(_mexcep why,char *fun,double *arg1p,double *arg2p,double retval) 用户修改数学错误返回信息函数(没有必要使用)unsigned int _clear87() 清除浮点状态字并返回原来的浮点状态void _fpreset() 重新初使化浮点数学程序包unsigned int _status87() 返回浮点状态字int chdir(char *path) 使指定的目录path(如:"C:\\WPS")变成当前的工作目录,成功返回0int findfirst(char *pathname,struct ffblk *ffblk,int attrib)查找指定的文件,成功int findnext(struct ffblk *ffblk) 取匹配finddirst的文件,成功返回0 void fumerge(char *path,char *drive,char *dir,char *name,char *ext) 此函数通过盘符drive(C:、A:等),路径dir(\TC、\BC\LIB等),文件名name(TC、WPS等),扩展名ext(.EXE、.COM等)组成一个文件名存与path中.int fnsplit(char *path,char *drive,char *dir,char *name,char *ext) 此函数将文件名path分解成盘符drive(C:、A:等),路径dir(\TC、\BC\LIB等), 文件名name(TC、WPS等),扩展名ext(.EXE、.COM等),并分别存入相应的变量中. int getcurdir(int drive,char *direc) 此函数返回指定驱动器的当前工作目录名称 drive 指定的驱动器(0=当前,1=A,2=B,3=C等)direc 保存指定驱动器当前工作路径的变量成功返回0char *getcwd(char *buf,iint n) 此函数取当前工作目录并存入buf中,直到n个字节长为为止.错误返回NULLint getdisk() 取当前正在使用的驱动器,返回一个整数(0=A,1=B,2=C等)int setdisk(int drive) 设置要使用的驱动器drive(0=A,1=B,2=C等), 返回可使用驱动器总数int mkdir(char *pathname) 建立一个新的目录pathname,成功返回0int rmdir(char *pathname) 删除一个目录pathname,成功返回0char *mktemp(char *template) 构造一个当前目录上没有的文件名并存于template中char *searchpath(char *pathname) 利用MSDOS找出文件filename所在路径,,此函数使用DOS的PATH变量,未找到文件返回NULLD. 进程函数[函数库为stdlib.h、process.h]void abort() 此函数通过调用具有出口代码3的_exit写一个终止信息于stderr,并异常终止程序。

c语言时间函数时间是我们生活中一个非常重要的概念,我们总是需要知道时间的流逝,以便安排我们的日常活动和计划。
在计算机编程领域,时间同样也非常重要。
C语言提供了一些函数来帮助我们获取和操作时间,这些函数被称为时间函数。
1. time()函数time()函数是C语言中最常用的时间函数之一。
它返回自1970年1月1日以来经过的秒数。
通常情况下,我们使用time()函数来获取当前的时间戳。
2. localtime()函数localtime()函数将一个时间戳转换为本地时间。
它接受time()函数返回的时间戳作为参数,并返回一个指向tm结构体的指针,该结构体包含了年、月、日、时、分、秒等信息。
3. strftime()函数strftime()函数可以将时间格式化为字符串。
它接受一个格式化字符串作为参数,并根据这个格式化字符串将时间转换为指定的格式。
例如,我们可以使用"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"来将时间格式化为"年-月-日时:分:秒"的形式。
4. mktime()函数mktime()函数与localtime()函数相反,它将一个tm结构体转换为时间戳。
我们可以使用mktime()函数将一个包含年、月、日、时、分、秒等信息的tm结构体转换为一个表示时间的秒数。
5. difftime()函数difftime()函数可以计算两个时间之间的差值。
它接受两个时间戳作为参数,并返回它们之间的差值,单位为秒。
6. clock()函数clock()函数用于测量程序运行的时间。
它返回程序运行的时钟周期数,单位为毫秒。
通过测量程序开始和结束之间的时钟周期数差值,我们可以计算出程序的运行时间。
7. sleep()函数sleep()函数用于让程序暂停执行一段时间。
它接受一个整数作为参数,表示暂停的秒数。
通过调用sleep()函数,我们可以让程序在执行到某个地方时暂停一段时间,然后再继续执行。

time函数c语言time()函数1. time()函数的用途time_t time(time_t *t);函数说明:此函数会返回从公元1970年1月1日的UTC时间从0时0分0秒算起到现在所经过的秒数(即格林尼治时间1970年1月1日00:00:00到当前时刻的时长,时长单位是秒)。
如果t并非空指针的话,此函数也会将返回值存在t指针所指的内存。
返回值:成功则返回秒数,失败则返回((time_t)-1)值,错误原因存于error 中。
从声明中可以看出,time()函数返回值的数据类型是time_t。
传递给time()函数的参数是指向time_t数据类型的指针。
2. time()函数的头文件要使用time(),必须在程序中包含##include <time.h> 头文件。
3. time()函数返回的数据类型下面是从<time.h>文件中找到的函数声明:time_t time(time_t *t)time(time_t *t)从声明中可以看出,time()函数返回值的数据类型是time_t 。
传递给time()函数的参数是指向time_t数据类型的指针。
4. time()函数使用示例time()函数有两种使用方式:(1) t1=time(NULL)或t1=time(0)将空指针传递给time()函数,并将time()返回值赋给变量t1(2) time(&t2);将变量t2的地址作为实参传递给time()函数,函数自动把结果传递给t2,不需要额外的赋值语句。
示例代码:#include <stdio.h>#include <time.h>int main(){time_t t1,t2; //分别声明两种使用方式的赋值对象t1=time(0); //第一种使用方式time(&t2); //第二种使用方式printf("t1=%ld\n",t1);printf("t2=%ld",t2);return 0;}localtime函数struct tm* localtime(const time_t *timep);函数说明:localtime()将参数timep所指的time_t结构中的信息转换成真实世界所使用的时间日期表示方法,然后将结果由结构tm返回。
C语言中的时间日期函数在C语言中,时间和日期是非常重要的概念,我们经常需要处理时间和日期相关的操作。
为了方便对时间和日期进行处理,C语言提供了一系列的时间日期函数。
本文将介绍C语言中常用的时间日期函数,并提供一些示例代码来说明它们的使用方法。
1. time函数time函数用于获取当前的系统时间,返回从1970年1月1日零时开始经过的秒数。
其函数原型如下:```ctime_t time(time_t *timer);```参数`timer`为一个time_t类型的指针,可以用于获取系统时间。
示例如下:```c#include <stdio.h>#include <time.h>int main() {time_t currentTime;time(¤tTime);printf("当前时间:%ld\n", currentTime);return 0;}```上述代码将输出当前系统时间对应的秒数。
2. localtime函数localtime函数用于将一个时间戳转换为本地时间,返回一个tm结构体,其中包含了详细的年、月、日、时、分、秒等信息。
其函数原型如下:```cstruct tm *localtime(const time_t *timer);```示例代码:```c#include <stdio.h>#include <time.h>int main() {time_t currentTime;struct tm *localTime;time(¤tTime);localTime = localtime(¤tTime);printf("当前时间:%d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d\n", localTime->tm_year + 1900, localTime->tm_mon + 1, localTime->tm_mday,localTime->tm_hour, localTime->tm_min, localTime->tm_sec);return 0;}```上述代码将输出当前系统时间对应的年、月、日、时、分、秒。
c语言函数库目录第一章(C标准库) (4)1. <>:诊断 (4)2. <>:字符类别测试 (5)3. <>:错误处理 (5)4. <>:整型常量 (6)5. <>:地域环境 (6)6. <>:数学函数 (7)7. <>:非局部跳转 (8)8. <>:信号 (9)9. <>:可变参数表 (11)10. <>:公共定义 (11)11. <>:输入输出 (12)12. <>:实用函数 (13)13. <>:日期与时间函数 (13)第二章(IO函数) (14)clearerr:复位错误标志函数 (18)feof:检测文件结束符函数 (18)ferror:检测流上的错误函数 (19)fflush:清除文件缓冲区函数 (20)fgetc:从流中读取字符函数 (22)fgetpos:取得当前文件的句柄函数 (23)fgets:从流中读取字符串函数 (24)fopen、fclose:文件的打开与关闭函数 (24)fprintf:格式化输出函数 (26)fputc:向流中输出字符函数 (27)fputs:向流中输出字符串函数 (28)fread:从流中读取字符串函数 (28)freopen:替换文件中数据流函数 (29)fscanf:格式化输入函数 (30)fseek:文件指针定位函数 (31)fsetpos:定位流上的文件指针函数 (32)ftell:返回当前文件指针位置函数 (33)fwrite:向文件写入数据函数 (34)getc:从流中读取字符函数 (35)getchar:从标准输入文件中读取字符函数 (36)gets:从标准输入文件中读取字符串函数 (36)perror:打印系统错误信息函数 (37)printf:产生格式化输出的函数 (38)putc:向指定流中输出字符函数 (38)putchar:向标准输出文件上输出字符 (39)remove:删除文件函数 (40)rename:重命名文件函数 (41)rewind:重置文件指针函数 (42)scanf:格式化输入函数 (43)setbuf、setvbuf:指定文件流的缓冲区函数 (43)sprintf:向字符串写入格式化数据函数 (45)sscanf:从缓冲区中读格式化字符串函数 (45)tmpfile:创建临时文件函数 (46)tmpnam:创建临时文件名函数 (47)ungetc:把字符退回到输入流函数 (47)第三章(字符处理函数) (49)isalnum:检查字符是否是字母或数字 (52)isalpha:检查字符是否是字母 (53)isascii:检查字符是否是ASCII码 (54)iscntrl:检查字符是否是控制字符 (54)isdigit:检查字符是否是数字字符 (55)isgraph:检查字符是否是可打印字符(不含空格) (56)islower:检查字符是否是小写字母 (56)isprint:检查字符是否是可打印字符(含空格) (57)ispunct:检查字符是否是标点字符 (58)isspace:检查字符是否是空格符 (58)isupper:检查字符是否是大写字母 (59)isxdigit:检查字符是否是十六进制数字字符 (60)toascii:将字符转换为ASCII码 (60)tolower:将大写字母转换为小写字母 (61)toupper:将小写字母转换为大写字母 (62)第四章(字符串函数) (62)atof:字符串转浮点型函数 (66)atoi:字符串转整型函数 (67)atol:字符串转长整型函数 (67)memchr:字符搜索函数 (68)memcmp:字符串比较函数 (68)memcpy:字符串拷贝函数 (70)memmove:字块移动函数 (71)memset:字符加载函数 (72)strcat:字符串连接函数 (73)strchr:字符串中字符首次匹配函数 (73)strcmp:字符串比较函数 (74)strcpy:字符串拷贝函数 (75)strcspn:字符集逆匹配函数 (76)strdup:字符串新建拷贝函数 (77)strerror:字符串错误信息函数 (78)strlen:计算字符串长度函数 (79)strncat:字符串连接函数 (80)strncmp:字符串子串比较函数 (81)strncpy:字符串子串拷贝函数 (82)strpbrk:字符集字符匹配函数 (83)strrchr:字符串中字符末次匹配函数 (84)strrev:字符串倒转函数 (85)strset:字符串设定函数 (86)strspn:字符集匹配函数 (87)strstr:字符串匹配函数 (88)strtod:字符串转换成双精度函数 (89)strtok:字符串分隔函数 (90)strtol:字符串转换成长整型函数 (91)strtoul:字符串转换成无符号长整型函数 (92)strupr:字符串大写转换函数 (93)strupr:字符串大写转换函数 (94)第五章(数学函数) (94)abs、labs、fabs:求绝对值函数 (98)acos:反余弦函数 (99)asin:反正弦函数 (99)atan:反正切函数 (100)atan2:反正切函数2 (100)ceil:向上舍入函数 (101)cos :余弦函数 (101)cosh:双曲余弦函数 (102)div、ldiv:除法函数 (102)exp:求e的x次幂函数 (104)floor:向下舍入函数 (104)fmod:求模函数 (105)frexp:分解浮点数函数 (105)hypot:求直角三角形斜边长函数 (106)ldexp:装载浮点数函数 (106)log、log10:对数函数 (107)modf:分解双精度数函数 (108)pow、pow10:指数函数 (108)rand:产生随机整数函数 (109)sin:正弦函数 (109)sinh:双曲正弦函数 (110)sqrt:开平方函数 (110)srand:设置随机时间的种子函数 (111)tan:正切函数 (112)tanh:双曲正切函数 (112)第六章(时间和日期函数) (113)asctime:日期和时间转换函数 (116)clock:测定运行时间函数 (117)ctime:时间转换函数 (118)difftime:计算时间差函数 (119)gmtime:将日历时间转换为GMT (119)localtime:把日期和时间转变为结构 (120)mktime:时间类型转换函数 (121)time:获取系统时间函数 (122)第七章(其它函数) (123)abort:异常终止进程函数 (126)atexit:注册终止函数 (127)bsearch:二分搜索函数 (127)calloc:分配主存储器函数 (129)exit:正常终止进程函数 (130)free:释放内存函数 (131)getenv:获取环境变量 (132)malloc:动态分配内存函数 (132)qsort:快速排序函数 (133)realloc:重新分配主存函数 (134)第一章(C标准库)1. <>:诊断2. <>:字符类别测试3. <>:错误处理4. <>:整型常量5. <>:地域环境6. <>:数学函数7. <>:非局部跳转8. <>:信号9. <>:可变参数表10. <>:公共定义11. <>:输入输出12. <>:实用函数13. <>:日期与时间函数1. <>:诊断<>中只定义了一个带参的宏assert,其定义形式如下:void assert (int 表达式)assert宏用于为程序增加诊断功能,它可以测试一个条件并可能使程序终止。
附录C C语言常用的库函数
库函数并不是C语言的一部分,它是由编译系统根据一般用户的需要编制并提供给用户使用的一组程序。
每一种C编译系统都提供了一批库函数,不同的编译系统所提供的库函数的数目和函数名以及函数功能是不完全相同的。
ANSIC标准提出了一批建议提供的标准库函数。
它包括了目前多数C编译系统所提供的库函数,但也有一些是某些C编译系统未曾实现的。
考虑到通用性,本附录列出ANSIC建议的常用库函数。
由于C库函数的种类和数目很多,例如还有屏幕和图形函数、时间日期函数、与系统有关的函数等,每一类函数又包括各种功能的函数,限于篇幅,本附录不能全部介绍,只从教学需要的角度列出最基本的。
读者在编写C程序时可根据需要,查阅有关系统的函数使用手册。
1.数学函数
使用数学函数时,应该在源文件中使用预编译命令:
2.字符函数
在使用字符函数时,应该在源文件中使用预编译命令:
3.字符串函数
使用字符串中函数时,应该在源文件中使用预编译命令:
4.输入输出函数
在使用输入输出函数时,应该在源文件中使用预编译命令:
5.动态存储分配函数
在使用动态存储分配函数时,应该在源文件中使用预编译命令:
6.其他函数
有些函数由于不便归入某一类,所以单独列出。
使用这些函数时,应该在源文件中使用预编译命令:。
C语言中的时间和日期处理时间和日期是计算机程序中常用的数据类型,而C语言作为一种通用的编程语言,提供了许多用于处理时间和日期的函数和库。
本文将详细介绍C语言中的时间和日期处理,包括日期和时间的表示、标准库中的时间函数以及常见的时间和日期操作等。
一、日期和时间的表示在C语言中,日期和时间可以使用多种方式进行表示。
最常见的方式是使用结构体tm来表示日期和时间。
结构体tm定义在C标准库的<time.h>头文件中,其成员包括秒(tm_sec)、分(tm_min)、时(tm_hour)、天(tm_mday)、月(tm_mon)、年(tm_year)等,分别表示时间的各个单位。
另一种表示日期和时间的方式是使用整数表示。
UNIX时间戳(Unix timestamp)是指从1970年1月1日0时0分0秒开始经过的秒数,可以表示绝大多数现代操作系统所支持的日期和时间范围。
C语言中的time_t类型可以用来保存时间戳,通常使用time函数获取当前时间的时间戳。
二、标准库中的时间函数C标准库提供了一些常用的时间函数,可以用于获取当前时间、日期和执行时间和日期的各种操作。
1. time函数time函数用于获取当前系统时间的时间戳。
其函数原型如下:```time_t time(time_t *timer);```其中,timer参数可以用来保存获取到的时间戳,如果不需要保存,可以将其设置为NULL。
示例代码:```c#include <stdio.h>#include <time.h>int main() {time_t now;time(&now);printf("当前时间的时间戳:%lld\n", now);return 0;}```2. localtime和gmtime函数这两个函数用于将时间戳转换为结构体tm的形式,分别表示本地时间和协调世界时(UTC)。
c语言中time.h用法详解2008年07月22日12:53:11 作者:meizhe143本文从介绍基础概念入手,探讨了在C/C++中对日期和时间操作所用到的数据结构和函数,并对计时、时间的获取、时间的计算和显示格式等方面进行了阐述。
本文还通过大量的实例向你展示了time.h头文件中声明的各种函数和数据结构的详细使用方法。
关键字:UTC(世界标准时间),Calendar Time(日历时间),epoch(时间点),clock tick(时钟计时单元)1.概念在C/C++中,对字符串的操作有很多值得注意的问题,同样,C/C++对时间的操作也有许多值得大家注意的地方。
最近,在技术群中有很多网友也多次问到过C++语言中对时间的操作、获取和显示等等的问题。
下面,在这篇文章中,笔者将主要介绍在C/C++中时间和日期的使用方法.通过学习许多C/C++库,你可以有很多操作、使用时间的方法。
但在这之前你需要了解一些“时间”和“日期”的概念,主要有以下几个:Coordinated Universal Time(UTC):协调世界时,又称为世界标准时间,也就是大家所熟知的格林威治标准时间(Greenwich Mean Time,GMT)。
比如,中国内地的时间与UTC的时差为+8,也就是UTC+8。
美国是UTC-5。
Calendar Time:日历时间,是用“从一个标准时间点到此时的时间经过的秒数”来表示的时间。
这个标准时间点对不同的编译器来说会有所不同,但对一个编译系统来说,这个标准时间点是不变的,该编译系统中的时间对应的日历时间都通过该标准时间点来衡量,所以可以说日历时间是“相对时间”,但是无论你在哪一个时区,在同一时刻对同一个标准时间点来说,日历时间都是一样的。
epoch:时间点。
时间点在标准C/C++中是一个整数,它用此时的时间和标准时间点相差的秒数(即日历时间)来表示。
clock tick:时钟计时单元(而不把它叫做时钟滴答次数),一个时钟计时单元的时间长短是由CPU控制的。
asctime(将时间和日期以字符串格式表示)相关函数:time,ctime,gmtime,localtime表头文件:#include<time.h>定义函数:char * asctime(const struct tm * timeptr);函数说明:asctime()将参数timeptr所指的tm结构中的信息转换成真实世界所使用的时间日期表示方法,然后将结果以字符串形态返回。
此函数已经由时区转换成当地时间,字符串格式为:“Wed Jun 30 21:49:08 1993\n”返回值:若再调用相关的时间日期函数,此字符串可能会被破坏。
此函数与ctime不同处在于传入的参数是不同的结构。
附加说明:返回一字符串表示目前当地的时间日期。
范例:1#include <time.h>2main() {3 time_t timep;4 time (&timep);5printf(“%s”,asctime(gmtime(&timep)));6}执行结果:Sat Oct 28 02:10:06 2000ctime(将时间和日期以字符串格式表示)相关函数:time,asctime,gmtime,localtime表头文件:#include<time.h>定义函数:char *ctime(const time_t *timep);函数说明:ctime()将参数timep所指的time_t结构中的信息转换成真实世界所使用的时间日期表示方法,然后将结果以字符串形态返回。
此函数已经由时区转换成当地时间,字符串格式为“Wed Jun 30 21 :49 :08 1993\n”。
若再调用相关的时间日期函数,此字符串可能会被破坏。
返回值:返回一字符串表示目前当地的时间日期。
范例:1#include<time.h>2main(){3 time_t timep;4 time (&timep);5printf(“%s”,ctime(&timep));6}执行结果:Sat Oct 28 10 : 12 : 05 2000gettimeofday(取得目前的时间)相关函数:time,ctime,ftime,settimeofday表头文件:#include <sys/time.h>#include <unistd.h>定义函数:int gettimeofday ( struct timeval * tv , struct timezone * tz ) 函数说明:gettimeofday()会把目前的时间有tv所指的结构返回,当地时区的信息则放到tz所指的结构中。
timeval结构定义为:1struct timeval{2long tv_sec; /*秒*/3long tv_usec; /*微秒*/4};timezone 结构定义为:1struct timezone{2int tz_minuteswest; /*和Greenwich 时间差了多少分钟*/3int tz_dsttime; /*日光节约时间的状态*/4};上述两个结构都定义在/usr/include/sys/time.h。
tz_dsttime 所代表的状态如下DST_NONE /*不使用*/DST_USA /*美国*/DST_AUST /*澳洲*/DST_WET /*西欧*/DST_MET /*中欧*/DST_EET /*东欧*/DST_CAN /*加拿大*/DST_GB /*大不列颠*/DST_RUM /*罗马尼亚*/DST_TUR /*土耳其*/DST_AUSTALT /*澳洲(1986年以后)*/返回值:成功则返回0,失败返回-1,错误代码存于errno。
附加说明EFAULT指针tv和tz所指的内存空间超出存取权限。
范例:1#include<sys/time.h>2#include<unistd.h>3main(){4struct timeval tv;5struct timezone tz;6 gettimeofday (&tv , &tz);7printf(“tv_sec; %d\n”, t v,.tv_sec) ;8printf(“tv_usec; %d\n”,_usec);9printf(“tz_minuteswest; %d\n”, tz.tz_minuteswest);10printf(“tz_dsttime, %d\n”,tz.tz_dsttime);11}执行结果:tv_sec: 974857339tv_usec:136996tz_minuteswest:-540tz_dsttime:0gmtime(取得目前时间和日期)相关函数:time,asctime,ctime,localtime表头文件:#include<time.h>定义函数:struct tm*gmtime(const time_t*timep);函数说明:gmtime()将参数timep 所指的time_t 结构中的信息转换成真实世界所使用的时间日期表示方法,然后将结果由结构tm返回。
结构tm的定义为1struct tm {2int tm_sec;3int tm_min;4int tm_hour;5int tm_mday;6int tm_mon;7int tm_year;8int tm_wday;9int tm_yday;10int tm_isdst;11};int tm_sec 代表目前秒数,正常范围为0-59,但允许至61秒int tm_min 代表目前分数,范围0-59int tm_hour 从午夜算起的时数,范围为0-23int tm_mday 目前月份的日数,范围01-31int tm_mon 代表目前月份,从一月算起,范围从0-11int tm_year 从1900 年算起至今的年数int tm_wday 一星期的日数,从星期一算起,范围为0-6int tm_yday 从今年1月1日算起至今的天数,范围为0-365int tm_isdst 日光节约时间的旗标此函数返回的时间日期未经时区转换,而是UTC时间。
返回值:返回结构tm代表目前UTC 时间范例:1#include <time.h>2main(){3char *wday[]={"Sun","Mon","Tue","Wed","Thu","Fri","Sat"};4time_t timep;5struct tm *p;6time(&timep);7p=gmtime(&timep);8printf(“%d%d%d”,(1900+p->tm_year), (1+p->tm_mon),p->tm_mday);9printf(“%s%d;%d;%d\n”, wday[p->tm_wday], p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, p->tm_sec);10}执行结果:2000/10/28 Sat 8:15:38localtime(取得当地目前时间和日期)相关函数:time, asctime, ctime, gmtime表头文件:#include<time.h>定义函数:struct tm *localtime(const time_t * timep);函数说明:localtime()将参数timep所指的time_t结构中的信息转换成真实世界所使用的时间日期表示方法,然后将结果由结构tm返回。
结构tm的定义请参考gmtime()。
此函数返回的时间日期已经转换成当地时区。
返回值:返回结构tm代表目前的当地时间。
范例:1#include<time.h>2main(){3char *wday[]={“Sun”,”Mon”,”Tue”,”Wed”,”Thu”,”Fri”,”Sat”};4time_t timep;5struct tm *p;6time(&timep);7p=localtime(&timep); /*取得当地时间*/8printf (“%d%d%d ”, (1900+p->tm_year),( l+p->tm_mon), p->tm_mday);9p rintf(“%s%d:%d:%d\n”, wday[p->tm_wday],p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, p->tm_sec);10}执行结果:2000/10/28 Sat 11:12:22mktime(将时间结构数据转换成经过的秒数)相关函数:time,asctime,gmtime,localtime表头文件:#include<time.h>定义函数:time_t mktime(strcut tm * timeptr);函数说明:mktime()用来将参数timeptr所指的tm结构数据转换成从公元1970年1月1日0时0分0 秒算起至今的UTC时间所经过的秒数。
返回值:返回经过的秒数。
范例:1/* 用time()取得时间(秒数),利用localtime()2转换成struct tm 再利用mktine()将struct tm转换成原来的秒数*/3#include<time.h>4main() {5time_t timep;6strcut tm *p;7time(&timep);8printf(“time() : %d \n”,timep);9p=localtime(&timep);10timep = mktime(p);11printf(“time()->localtime()->mktime():%d\n”,timep);12}执行结果:time():974943297time()->localtime()->mktime():974943297settimeofday(设置目前时间)相关函数:time,ctime,ftime,gettimeofday表头文件:#include<sys/time.h>#include<unistd.h>定义函数:int settimeofday ( const struct timeval *tv,const struct timezone *tz);函数说明:settimeofday()会把目前时间设成由tv所指的结构信息,当地时区信息则设成tz所指的结构。