body modification
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:5.28 MB
- 文档页数:75

Ergonomic Evaluation and CustomizedDesign of Toothbrush HandleVibha Bhatia,Amit Bhatia,Parveen Kalra,Jagjit Singhand Rahul DattaAbstract Toothbrush handles available in the market are classified in adult,junior and baby sizes.As per IS3387:2004,the length of the handle for these variants is specified.However,the width and thickness of the handle is not specified.As per the standard“The width and thickness of the handle may vary according to the individual design”.The focus of the current work is to design an ergonomic toothbrush handle based on hand anthropometry.This would improve the grip of the handle(user comfort)and enhance oral hygiene.A commercially available toothbrush was taken as reference tofind out the optimal parameters of toothbrush handle.Hand anthropometric data of volunteers was collected.The comfort rating of these volunteers was related to the normalized handle sizes.The resulting regression equation was used tofind out the optimal handle dimensions.Contact area was measured using both commercially available toothbrush handle and the same toothbrushes with different fabricated handle sleeves.Electromyography activity was recorded for muscle fatigue.The plaque index was also obtained before and after two weeks of using customized toothbrush handle.It was observed that the customized toothbrush handle was comparatively more purposeful.Relevance to Industry.From the results of this study,tooth brush designers,researchers and manufacturers can obtain guidelines for maximising grip comfort based on the hand sizes of users.The results also shows that optimal handle diameter will result in V.Bhatia(&)ÁA.BhatiaÁP.KalraÁJ.SinghPEC University of Technology,Chandigarh,Indiae-mail:vibhavansh@A.Bhatiae-mail:amit.bhatia1991@P.Kalrae-mail:parveenkalra@pec.ac.inJ.Singhe-mail:jagjitsingh@pec.ac.inR.DattaCoE I&PD,PEC University of Technology,Chandigarh,Indiae-mail:docdatta@©Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.2017205 A.Chakrabarti and D.Chakrabarti(eds.),Research into Designfor Communities,Volume1,Smart Innovation,Systemsand Technologies65,DOI10.1007/978-981-10-3518-0_18206V.Bhatia et al. increasing the subjective comfort rating which will further increase the user per-formance and will lower the risk of muscle fatigue.Keywords Toothbrush handleÁDistal oblique gripÁNHSÁEMGÁGrip forceÁSubjective comfort ratingÁErgonomicsÁAnthropometryÁPlaque indexÁMuscle fatigueÁRPT1IntroductionA toothbrush is a fundamental product used to maintain the oral hygiene of an individual.If teeth are not properly cleaned,bacteria interact with the food particles present.This releases an acid and causes tooth decay.Dental Plaque is sticky transparent bacterial mass accumulated on our teeth.Built up plaque gets converted into Tartar which is difficult to remove by normal brushing.Survey by Dental Council of India says that89.6%of periodontal disease occurs in the age group of35–44years.Also,according to a recent study held in Australia, adults over35are prone to lose more teeth due to gum diseases than from cavities. Gingiva is a soft tissue lining surrounding the teeth which provides a seal around them.Some individuals face a problem of gingival recession(receding gums)which leads to exposure of roots of teeth due to loss in gum tissues.Gingival recession commonly occurs in individuals over40years of age,but it may also occur in teenagers,around the10–12years of age.To get rid of this problem,the pressure on the toothbrush handle must not be excessive.Excessive pressure would further lead to receding gums.Ergonomics,a science behind making products more efficient,can be used to improve toothbrush handle design.As per IS3387:2004,the length and size of the head of the brush is specified,but nothing is mentioned about the width and thickness of toothbrush handle.While brushing teeth some peoplefind it difficult to grip the toothbrush properly due to the sleek design of toothbrush handle.The brush may also slip from the hand in such a case.Therefore,excessive force is required to grip the toothbrush in between thefingers resulting in hand muscle fatigue.Kong and Lowe have stated that the maximal voluntary contraction(MVC)force offinger depends on handle diameter.Therefore,the variability in handle sizes should be in accordance with hand andfinger sizes[1].The authors also suggested that for smaller handles the ringfinger’s contribution to grip force is higher than that of the indexfinger and vice versa.According to the authors,there is increase in the contribution of the middlefinger when the handle diameter is increased up to 40mm.Some researchers used electromyography and force sensors to define the optimal diameters of the cylindrical handle,consideringfinger forces and muscle activity[2].Ergonomic Evaluation and Customized Design of Toothbrush Handle207 In some cases,where the toothbrushes are not ergonomically designed,it may not be effective in plaque removal.Ergonomically designed toothbrush handle ensures a relaxed grip and reduces pressure on both teeth and gums enhancing plaque removal.Though there arefive methods of holding a toothbrush,distal oblique is most commonly used and is considered here for experimentation.In real world,it is very difficult to analyze the grasping of any object and is dependent on the comfort ratings of the user[3].In this work the author has observed a strong correlation between perceived subjective comfort and user performance and has suggested incorporation of this aspect during the design phase[4].Gregor Harih and Bojan Dolšak have suggested that developing the digital human hand model with the use of Magnetic Resonance Imaging(MRI)and subsequent3D printing of the optimal diameter tool handle using the anthropometric data will give an anatomical shape to the tool handle[5].This would increase the perceived level of comfort.The focus of the current work is tofind the optimal handle size that would result in increased contact area,reduced muscle fatigue and increased user comfort rating [5].The aim is to develop an approach that wouldfinally give optimal size for a range of hand sizes in accordance with design for human variability.The paper is organized along the following lines:Sect.2describes the methods used in current investigation;Results and discussion are given in Sect.3whereas conclusions are given in Sect.4.2Methods2.1SubjectsThe study showed that the urban population of Ludhiana is more prone to peri-odontitis than rural population(periodontitis is the medical terminology equivalent to gingival recession)[6],so volunteers considered for study were mostly urban. Majumdar[7]studied that in different regions of India wefind different Indian population,so North Indians were focused as the target user population.Forty right handed University students volunteered in the study,twenty of both genders within the age group of22–28years.In the Handgrip strength test performed,the best of three trials for the grip strength for males varied between32–62kg and for females it was16–26kg.Further,these volunteers had no prior complaint to muscle fati-gue.Participants were informed about the study and their willingness was recorded on the consent to participate form.The averages of their ringfinger length(from hand crease),population height and hand width were171.5±20.5mm, 1780±42.0mm and81.5±13.5mm respectively.The study was approved by the ethics committee,COE-I&PD of PEC University of Technology,Chandigarh, India.2.2EquipmentVernier caliper .Vernier calliper with least count of 1/20mm =0.05mm was used to measure the hand anthropometric data of the volunteers for the design purpose.Hand length was measured from the crease of the hand to the tip of the finger considered in design.Electromyographic measuring system .The electromyographic activity of the Extensor Digitorium (ED)muscle was acquired at a sampling frequency of 1000Hz.EMG is used in the experimentation to detect the muscle fatigue while gripping the toothbrush.Surface electrodes,used to extract the EMG activity of muscle,were positioned over the Extensor Digitorium muscle parallel to the lon-gitudinal axis of the muscle fibers [8].2.3Experimental DesignThe handle shape of a commercially available toothbrush (Thermoseal)having circumference 34mm (ring finger location)was selected as a reference for evalu-ation out of all the reputed brands of toothbrushes.The other four 3D printed handle sleeves having circumferences 42,51,55,59mm were considered in study.Here standard toothbrush with same bristle length,softness,sharpness and material was used prior and after the change in circumference.This toothbrush is shown in Fig.1(Fig.2).The main aim of study is to find out the handle diameter according to individ-ual ’s hand anthropometric factors considered.Procedure for experimentation is shown in Fig.3.Before the experiments,all volunteers were asked about illnesses or injuries of their upper extremities by which the results could be affected.Brief Fig.1Toothbrushes usedwhile taking subjectiveratings (thinner one beingcommercially availabletoothbrush)208V.Bhatia et al.purposes and procedures of the experiment were discussed with the volunteers.Experiment has been conducted in two phases as given below:Phase 1.Five different circumferences (34,42,51,55,and 59mm)of handle at location of ring finger were used in experimentation.Each subject was asked torate Fig.2Customized toothbrushes according to handanthropometryFig.3Procedure of experimentationErgonomic Evaluation and Customized Design of Toothbrush Handle 209all toothbrushes with variable circumferences on the Semantic scale of1–7(1—Very uncomfortable,2—Moderately Uncomfortable,3—Somewhat Uncomfortable, 4—Neutral,5—Somewhat Comfortable,6—Moderately Comfortable and7—Very Comfortable).As the ratings for various brushes were taken in random order, therefore,it was a balanced design.Hand Anthropometric measurements of the volunteers were assessed.All vol-unteers were asked to grip the toothbrush of various circumferences in their right hand and subjective comfort ratings were collected.For smaller handles,ringfinger has higher contribution while gripping from indexfinger[1].Phase2.The volunteers were provided with the toothbrush of optimized handle design and were asked to grip in their hand.The EMG muscle activity was recorded and analyzed to check the muscle fatigue.In surface EMG,for the assessment of muscle fatigue,Mean Frequency(MNF)and Median Frequency(MDF)are most useful frequency domain features[9].The optimal variables(i.e.MNF and MDF features)which are extracted from EMG are used to identify the muscle fatigue [10].Extensor Digitorium muscle was chosen tofind out the Median Frequency (MDF)of the EMG activity.These muscles stabilize the wrist during gripping motions.The stronger the grip,the stronger the muscle(extensor digitorium)gets activated.The contact area signifies the comfort level of any object.For handles,more the contact area more will be the comfort in gripping the handle[5].Paint was used on the handles during the experimentation and the volunteers were asked to grip the handle and trace it on the A4size blank paper.The contact area was compared for the commercially available and the customized handle and the results were assessed.Dental indices are used for recording oral diseases in individuals.According to Russel AL,Index of plaque is basically a defined graduated scale having upper and lower limits,with scores on the scale which correspond to specific criteria and is designed to facilitate comparison with other population.Oral Hygiene Index(OHI), developed in1960,was used in the research work.OHI is simple and sensitive method used for assessing individual oral hygiene.Debris Index used in the study is scored between1–3scale,which signifies‘0’—no debris or stain present,‘1’—soft debris or extrinsic strains covering not more than1/3rd the tooth surface,‘2’—soft debris covering more than1/3rd but not more than2/3rd of the exposed tooth surface and‘3’—soft debris covering more than2/3rd of the exposed tooth surface. Rating scores for Oral Hygiene Index(OHI)indicates‘0’for excellent,‘0.1–1.7’for good,‘1.8–3.4’for fair,and‘3.5–5.0’for poor.On the basis of above theory, plaque score of all individuals were assessed,as in Eq.(1).Plaque Score of an individual¼Total ScoreNumber of teeth examinedð1ÞThe plaque index before and after the use of customized toothbrush was com-pared.The improvement in the plaque index will signify an improved design. 210V.Bhatia et al.3Results and Discussion3.1Experimentation—Phase1NHS is expressed as a function of handle size and key hand anthropometric dimensions related to the grasping.NHS is taken as the ratio of Handle Circumference(HC)at location of ring/middlefinger to hand length(HL)at ring/middlefinger.NHS(Normalized Handle Size)was defined in a manner similar to that given by Kong,2001and is calculated as:NHS ij;k¼HC jHL iÃ100ð2Þwhere HC is the handle circumference(mm)of handle j,HL is the Hand Length (mm)of volunteer i,i is the subject,j is the handle,k is the subject number,NHS i is the Normalized Handle Size based on hand length measured at ringfinger,NHS j is the Normalized Handle Size based on hand length measured at middlefinger.These parameters are shown in Fig.4a,b.Subjective comfort rating for the gripping task was assessed and relation between NHS and subjective comfort rating was evaluated using Minitab®17.1.0. Software.There were total hundred experiments.The regression model was used for the relationship between NHS and the subjective comfort ratings.It was further used to derive the NHS that maximizes the subjective comfort ratings for handle.The effect of bothfingers(middle and ringfinger)in gripping the handle was found out using Minitab®17.1.0.The various types of regressions i.e.Linear Regression,Quadratic Regression and Cubic Regression were undergone. Regression data is given in Table1.For Linear Regression,the R2value was9.60%,which is very low and hence was not considered for design purpose.Likewise,for Cubic Regression,the p values for both thefingers were0.187and0.227respectively,which were insignificant.The result was significant for Quadratic Regression with R2value 68.9%.Moreover,the NHS based on the ringfinger shows the p value(p<0.014) significant than that based on the middlefinger for this regression model.This shows that while gripping the toothbrush,the ringfinger contributes more as compared to middlefinger.Therefore,the NHS based on ringfinger was considered for the design purpose.The variation of comfort rating with NHS based on hand length measured at ringfinger is shown in Fig.4.The relation between comfort rating and NHS works out to be: Subjective comfort rating¼À0:03783ÃðNHSÞ2þ2:166ÃðNHSÞÀ25:94ð3ÞThe optimal value NHS obtained byfirst derivative of the Eq.(3)works out to be28.63%,[NHS%=2.166/(2*0.03783)].As ringfinger came out to be the most significant factor,taking ringfinger hand length as a reference,handle Ergonomic Evaluation and Customized Design of Toothbrush Handle211circumference(optimal)[i.e.Handle Circumference Optimal =user ’s hand length *NHS Optimal ]was found out for all the forty volunteers based on their ring finger hand lengths.Further,experimentation was done on four representatives out of forty.The customized handles were fabricated using Rapid Prototyping Technology (RPT)for a subset of the volunteers (Table 2).Fig.4a Hand length measurements for ring and middle finger.b Cross section showing handle circumference (HC)of tooth brushTable 1Regression analysis dataRegressionR-square (%)p-value Signi ficant factor Ring finger Middle finger Linear9.60.0330.015–Quadratic68.90.0140.995Ring finger Cubic 71.890.2770.187–212V.Bhatia et al.3.2Experimentation —Phase 2Plaque score was found out for 4representatives based on the Oral Hygiene Index (OHI).The normal plaque score of all the representatives were 1.33,1.5,1.33and1.5respectively.The representatives were provided with the optimallydesigned Fig.5The relationship between subjective comfort rating and NHSTable 2Recommended handle diameters of 4representatives for maximizing subjective comfort VolunteersHand length (mm)Handle width (mm)Handle depth (mm)Recommended handle diameters (mm)117817.910.718.2218018.110.818.4315616.109.716.4416717.210.217.4Table 3Plaque index scores before and after brushing with optimally designed toothbrush Volunteers Plaque indexAt start of experimentationAfter brushing with optimally designed toothbrush for 2weeks 1 1.331.22 1.51.33 1.331.141.5 1.3Ergonomic Evaluation and Customized Design of Toothbrush Handle 213214V.Bhatia et al.toothbrush handle and were asked to use the designed toothbrush handle while brushing for two weeks.The improvement in plaque score was noticed after the use of the designed toothbrush handle by all4representatives.Plaque Index scores before and after brushing with optimally designed toothbrush is given in Table3.Median Frequency is considered for the assessment of muscle fatigue.Muscle fatigue was detected in static contraction as the EMG signals during short-time intervals may be assumed to be stationary.The EMG Activity during grasping of commercially available and the designed toothbrush handle were extracted and the graph between their Median Frequencies is plotted for all the 4representatives,as shown in the Fig.6.It was observed that the fatigue occurred earlier for the commercially available handle as compared to the designed handle for all representatives.The contact area of both the handles was assessed.The handles were painted and the representatives were asked to grip the handles one by one.After gripping,hand impressions on blank paper for both handles were obtained.Areas were found by Meshing/Triangulation method.The results were compared for the hand impres-sions for both handles.It was seen that the contact area for the designed handle was more as compared to the commercially available handle.The contact areas obtained on the blank sheets for both the handles are shown in Fig.7.LEFT SIDE Impression —Using Commercially Available toothbrushes.RIGHT SIDE Impression —Using Ergonomically designed toothbrushes (Table 4).Fig.7Hand prints taken to measure contact area for both type of handles of all the four representativesTable 4Contacts areas of toothbrushesVolunteersAreas (cm 2)Commercially available toothbrush Optimally designed toothbrush 124.8032.70227.1037.70320.8028.60421.3030.17Ergonomic Evaluation and Customized Design of Toothbrush Handle 215216V.Bhatia et al. 4ConclusionExperimentation shows that brushing with the customized handle results in increase of perceived comfort and reduction of muscle fatigue.Brushing with this tooth-brush also results in reduction of plaque index.A toothbrush handle should therefore be designed on the basis of suitable hand anthropometric parameters.This would include the hand length measured at ringfinger.In future,effort would be made to consider different sections and designs of toothbrush handle and inclusion of additional anthropometric parameters for evaluation of dependent design parameters.5Future ScopeThe study is limited to manual brushes only and hence the concept of motorized brushes was kept out of scope for time being and was kept for future evaluation(as results of fatigue/plaque index in motorized brushes will depend on other param-eters like motor performance,bristle movement and vibration etc.).The future study will take the survey feedback forfive different types of brush holding techniques which was avoided in the current study to maintain the simplicity of the problem at initial stages of research.Also,the static EMG analysis was done as a part of initial study,so dynamic analysis and evaluation will be done in further experimentations to serve the real life problem in design.DfHv approach will be considered for designing the toothbrush handles for the ranges of hand sizes where we can design it for different segments like baby,junior sizes etc.References1.Kong,Y.,Lowe,B.:Optimal cylindrical handle diameter for grip force tasks.Int.J.Ind.Ergon.35,495–507(2005)2.Grant,K.A.,Habes,D.J.,Steward,L.L.:An analysis of handle designs for reducing manualefforts:the influence of grip diameter.Int.J.Ind.Ergon.10,199–206(1992)3.De Looze,M.,Kuijt-Evers,L.,Van Dieën,J.:Sitting comfort and discomfort and therelationship with objective measures.TERG Ergon.46,985–997(2003)4.Kuijt-Evers,L.F.M.,Vink,P.,de Looze,M.P.:Comfort predictores for different kinds of handtools:differences and similarities.Int.J.Ind.Ergon.37,73–84(2007)5.Harih,Gregor,Dolšak,Bojan:Tool-handle design based on a digital human hand model.Int.J.Ind.Ergon.43(4),288–295(2013)6.Singh,G.P.,Soni,B.J.:Prevalence of periodontal diseases in urban and rural areas ofLudhiana.Punjab.Indian J Community Med.30,128–129(2005)7.Majumdar,D.N.:Races&Cultures of India.Universal Publishers,Lucknow(1951)8.Zipp,P.:Recommendations for the standardization of lead positions in surface electromyo-graphy.Eur.J.Appl.Physiol.50,41–54(1982)Ergonomic Evaluation and Customized Design of Toothbrush Handle217 9.Phinyomark,A.,Limsakul,C.,Phukpattaranont,P.:A novel feature extraction for robustEMG pattern put.1(1),71–80(2009).ISSN2151-961710.Phinyomark,A.,Limsakul,C.,Phukpattaranont,P.:Feature reduction and selection for EMGsignal classification.Expert Syst.Appl.39(8),7420–7431(2012).ISSN0957-4174。


生物电阻抗身体成分检测仪测算的相位角在超重和肥胖预测中的应用余凤1,马依拉·买买提2,赵效国1,张世瑶2,李蓉蓉2,李莉21 新疆医科大学公共卫生学院,乌鲁木齐830011;2 新疆医科大学第一附属医院临床营养科摘要:目的 观察基于生物电阻抗身体成分检测仪测算的相位角(PhA )在超重和肥胖预测中的应用效果。
方法 663例营养科就诊患者,其中体质量指数BMI≤23.9 kg /m 2(正常组)161例、24 kg /m 2≤BMI<28 kg /m 2(超重组)179例、BMI≥28 kg /m 2(肥胖组)323例,采用InBody 770多频分段生物电阻抗身体成分检测仪检测三组PhA 、体脂肪相关指标、人体肌肉质量相关指标及人体水分相关指标。
采用Pearson 相关性分析法分析PhA 与超重和肥胖患者体脂肪相关指标、人体肌肉质量相关指标及人体水分相关指标的相关性,采用多元线性逐步回归分析法分析肥胖和超重患者PhA 的影响因素,绘制受试者工作特征曲线(ROC )分析PhA 对超重和肥胖的预测效能。
结果 与正常组比较,超重组PhA 水平高、体脂肪相关指标、人体肌肉质量相关指标及人体水分相关指标水平高;与超重组比较,肥胖组PhA 水平高、体脂肪相关指标水平高、人体肌肉质量相关指标及人体水分相关指标水平高(P <0.01)。
PhA 与超重和肥胖患者细胞内水分(ICW )、肌肉量(SMM )、骨骼肌指数(SMI )呈正相关(r 分别为0.305,0.305,0.394;P 均<0.05);与细胞外水分(ECW )/ICW 、ECW /全身水分(TBW )呈负相关(r 分别为-0.825,-0.827;P 均<0.05)。
ICW 、ECW /TBW 、内脏脂肪面积(VFA )、腰臀脂肪比(WHR )和SMI 是超重和肥胖患者PhA 的影响因素。
当PhA 为5.05°时,ROC 曲线下面积为0.704(95% CI 为0.661~0.748),PhA 预测超重和肥胖的灵敏度62.0%、特异度67.7%。

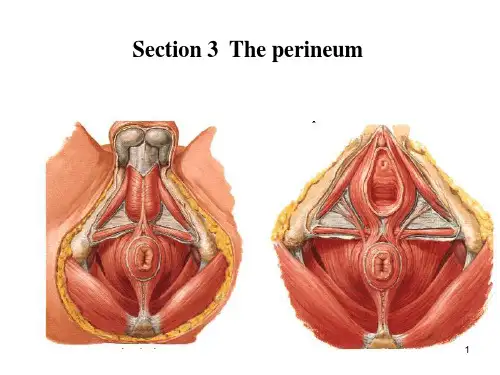
牙龈形态学词汇中英对照为大家整理了牙龈形态学词汇中英对照,希望对你有帮助哦牙龈形态学词汇中英对照:牙龈形态学gingival morphology牙槽嵴形态学alveolar ridge morphology研究模型study model模型分析model analysis侧貌分析profile analysis美学诊断蜡型aesthetic diagnostic wax-up绘图模拟paint simulation蜡模拟wax simulation切平面in cisal pla ne凸出切平面convex in cisal pla ne鸥翼切平面gull wing in cisal pla ne混合型切平面comb in ati on in cisal pla ne龈平面gingival plane切端轮廓in cisal silhouette 又称“切缘轮廓”。
切端外展隙in cisal embrasure 又称“切端楔状隙”。
切端暴露in cisal display水平对称horizontal symmetry放射对称radiation symmetry切龈融合incisal-gingival blend侧影显露profile emerge nee龈缘突gingival convexity龈下外形subgi ngival eon tour龈曲gingival curvature龈线gingival line微笑美学smile aesthetics微笑构成components of smile微笑分析smile analysis高位微笑high smile微笑时显露100%的上前牙与部分牙龈。
低位微笑low smile微笑时上前牙面积显露小于75%.中位微笑median smile微笑时上前牙面积显露在75% 100%之间,少见牙龈乳头。
露龈笑gummy smile直线笑straight smile扁平微笑曲线flat smile curve反笑线reverse smile line牙齿可见度tooth visibility牙齿暴露量tooth display牙齿大小tooth size牙牙比例tooth-to-tooth proport ion牙齿排歹卩tooth arrangement牙齿光泽tooth gloss牙龈点彩gingival stippling龈缘高度gingival height龈缘高点gingival zenith牙龈孚L头gingival papilla金瓷修复体metal ceramic prosthesis, ceramometal prosthesis 又称“金属烤瓷修复体(porcela nin-fused-to-metal prosthesis) ”。

诊断学教案第一篇常见症状了解以下概念症状、体征、症状学症状(symptom):患者主观感受到不适或痛苦的异常感觉或病态表现体征:(sign)医师或其他人能客观检查到的改变症状学(symptomatology):研究症状的识别、发生机制、临床表现特点及其在诊断中的作用根据诊断学研究所集体备课要求,我们讲授10个常见症状。
第一节发热(fever)正常体温的调控正常体温: 36--37℃24小时波动<1℃发热机体在致热源作用下或各种原因引起体温调节中枢功能障碍时,体温升高超过正常范围,为发热发生机制1. 致热源(pyrogen)分外源性致热源|:如微生物病原体及其产物、炎症渗出物、无菌性坏死组织、抗原抗体复合物等,不能直接作用于体温调节中枢。
因为大分子物质不能通过血脑屏障。
内源性致热源:有称白细胞致热源。
通过血脑屏障直接作用于体温调节中枢,1)通过垂体内分泌因素,使代谢增加;2)通过运动神经使骨骼肌阵缩,是产热增加;3)通过交感神经,使皮肤血管及竖毛肌收缩,散热减少。
2. 非致热源(nonpyrogen)病因分类------- 1.感染性发热(infective fever)2.非感染性发热(noninfective)①无菌性坏死物质的吸收②抗原抗体反应③内分泌代谢障碍④皮肤散热少⑤体温调节中枢功能障碍⑥自主神经功能紊乱发热分度低热37.3--38℃中等热度38.1--39℃高热39.1--41℃超高热41℃以上发热的临床过程及特点分三阶段-------体温上升期包括两种方式高热期体温下降期两种方式热型—(用图讲解) 本节的重点,要掌握各种热型的特点及临床意义。
1.稽留热(continued fever):体温恒定在39~40℃以上达数天或数周,24小时内体温波动范围不超过1℃,常见于大叶肺炎、斑疹伤寒及伤寒高热期。
2.驰张热(remittent fever):有称败血症热型。
体温常在39℃以上,24小时波动范围大于2℃,但都在正常范围以上。



Aabdomen 腹部abdominal 腹部的abiotic 非生物的abnormal 反常的,变态的abscisic 脱落酸abscission 脱落absorb 吸收(水、热、光等) absorption spectrum 吸收光谱,吸收谱absorption 吸收作用abut 连接accelerate 加速,加快acceptable 可接受的acceptor 受体acetate 醋酸盐;醋酸根acetone 丙酮acetyl 乙酰基acorn 橡树子acquire[o’kwaio)uJ.获得,取得 .actin 肌动蛋白actinomycinD 放线菌素D activation 活化;激活activationenergy 活化能active site 活性中心active 主动的;活性的adapt 使适应,改编 适应adaptin 衔接蛋白adaptive radiation 适应辐射adenine 腺嘌呤adenosine 腺嘌呤核苷adenosyl 腺苷的adenovirus 腺病毒adhering junctings 粘着连接adhesion 粘着;附着adipose 脂肪多的adjacent 毗邻的adjust 调节,调整;校正admit 让……进入adolescent 青少年adrenal肾上腺的, 肾上腺adulthood 成年affinity 亲和;吸引agar 琼脂,洋菜agarose 琼脂糖agency 媒介agent 剂aggregate 聚合体Agrobacterium tumefaciens根癌农杆菌airborne 空气传播的alanine 丙氨酸albino 白化体albumin 白蛋白,清蛋白aldosterone 醛固酮,醛甾酮allcviate 减轻;缓和allelc 等位基因allele 等位基因 突变遗传因子allosteric modification 别构修饰allosteric 别构的aloft 向上Alzheimer’s disease阿尔茨海默氏病amino 氨基的 ~acid氨基酸aminocyclopropylcarboxylic氨基环丙烷羧酸aminopeptidase 氨基肽酶amnion 羊膜amoeboid 阿米巴样的amphibian 两栖动物amphipathic 两亲的 两性的amphiploid 双倍体amplify 扩增amylase 淀粉酶anaerobic 厌氧的anal 肛门的,臀的analogous 机能相似的, 同功的analysis 分析,分解analyze 分析anaphase (细胞分裂的)后期anaphase—promoting complex,APC 促后期复合物anarogen 雄激素anatomy 解剖学ancestor 祖先ancient 古老(的生物) 古老的anemia 贫血(症) 局部缺血angiosperm 被子植物anionic 阴离子的antagonistic 对抗性的antagonize 对抗;中和antennae 触角anterior 前的anther 花药anticodon 反密码子antidiuretiC 抗利尿的 抗利尿anus 肛门anus 肛门aorta 主动脉apex (复)apices 顶,顶点apparatus 体;器官;装置appendicitis 阑尾炎appendix 阑尾appetlte 食欲,胃口appreciable 可估计的appropriate 适当的approximately 近似地,大约archaebacteria 古细菌archaic 古代的arterial 动脉的arteriole 小动脉artery 动脉arthritis 关节炎artificial chromosome 人工染色体aspartic 天冬氨酸astrocyte 星形(神经胶质),细胞asymmetric 不对称的atmosphere 大气层,大气圈atrium 心房autocatalytic 自动催化的autonomic neuron 自主神经元autonomously replicatingsequence A RS自主复制起序列autophagy 自噬作用axon 轴突axoplasm 轴浆Bbacillus 杆菌bacteria 细菌bacterial artificialchromosome, B AC 细菌人工染色体bacteriophage 噬菌体bacterium 细菌basal cell carcinoma 基层细胞癌base 碱基basement membrane 基膜bicarbonate 碳酸氢盐bilateral symmetry 两侧对称bilayer 双层binal 双重的,两倍的,孪生的binding 结合位点binomial 双名的biochemical 生物化学的biogeography 生物地理学biology 生物学biotechnology 生物技术biotic 生物的bipedal 两足动物的bipolar 双极的blastocoele 囊胚腔blastoderm 胚盘blastomere 卵裂球blastula 囊胚blister水疱,疱blood pressure 血压blood-clotting 凝血boron 硼botanist 植物学家botanist 植物学家boulder 巨砾,圆石bounce 跳起breeze 微风bryophytes 苔藓类植物bud 芽buffer 缓冲,缓冲剂bulb 鳞茎bulky 泡状bumble 犯大错bump 碰,撞bundle 维管束bunting 巫鸟buoyancy 浮力buoyant 有浮力的butanol 丁醇Ccaecilian 无足类caffeine 咖啡因cambium 形成层Cambrian 寒武纪cancerous 癌的capillary bed 毛细血管床capillary 毛细血管capsid (病毒)衣壳carbohydrate 碳水化合物,糖类carbonate 碳酸盐carboxy 羧基carboxylation 羧化作用carboxypeptidase 羧肽酶carcinogen 致癌剂carcinoma 癌cardiovascular 心血管的carotenoid 类胡萝卜素carotid 颈动脉的carpel 心皮catalyze 催化catecholamine 儿茶酚胺cateract 白内障cell secretion细胞分泌cell wall 细胞壁cellulose 纤维素,植物纤维物质Cenozoic 新生代centiped 少足类central dogma 中心法则central vacuole 中央液泡centrifuge 离心机centriole 中心粒centromere 着丝粒,着丝点centromeric sequence C EN着丝粒序列cephalization 头部形成cerebellum 小脑cerebral 大脑的champion 拥护者channel通道,管道chemotaxis 趋化性chlorine 氯,氯气chlorofluorocarbon 含氯氟烃chlorophyll 叶绿素chlorophyllase 叶绿素酶chloroplast 叶绿体chloroquine 氯奎choke 窒息,噎cholesterol 胆固醇chordate 脊索动物chorion 绒毛膜chromatid 染色单体chromatin 染色质chromatography 层析chromosome 染色体chylomicron 乳糜小滴chyme 食糜chymotripisn 糜蛋白酶chysophyte 金藻chytrids 壶菌cicada 蝉ciliated 具纤毛的Ciliophora 纤毛门circadian 全天的circulate 循环,环流circumstance 环境cis-acting element 顺式作用元件cis-G olgi network, C GN高尔基内侧网络cistron 顺反子citric 柠檬的clathrin-coated vesicle 披网格蛋白小泡cleavage 卵裂,细胞分裂cleave 分开clone 克隆,无性系clot 凝块cloverleaf 三叶草club fungi珊瑚菌担子菌(B asidiomycetes)coccus 球菌coccyx 尾骶骨的 尾骨code 密码coelom 体腔coenzyme 辅酶coexist 共存coherent 粘着的,连贯的coil 卷,盘绕coincidence 巧合coleoptile 胚芽鞘collagen 骨胶原,成胶质collateral 侧支collenchyma 厚角组织commensalisms 共栖,共生competitive inhibitor 竞争性抵制剂complementary 互补的,补充的concentration 浓度connective tissue 结缔组织constitutive enzyme 组成酶Constitutive secretory pathway 组成型分泌途径contaminant 沾染物contour 轮廓,外形contractile 可收缩的contraction 收缩convulsion 惊厥coolant 冷却剂C O P II coated vesicles C O P II 被膜小泡C O P I coated vesicles C O P I被膜小泡copulate 交配cord 索cork 皮层,木栓cornea 角膜cortex 皮质corticosteroid 皮质甾类cortisol 肾上腺皮质索cotyledon 子叶cotyledonary 子叶的counterpart 副本,复本covalence 共价covalent bond 共价键covalent 共价covering 覆盖cranial nerves 脑神经cranial 脑的crawl 蠕动creature 生物crenate 圆齿状的crest 达到顶点cretaceous 白垩纪的crevice 裂缝crispnsee 脆,鲜嫩cristae 嵴 (拉)crossing over 遗传物质的交换cross—linked 交联的crustacea 浮游甲壳动物crustacean 甲壳动物crystalline 结晶的culture 培养,栽培cushione 缓冲 缓和cuticle 表皮,角质层cutin 角质cyanobacteria 蓝细菌cyclin 细胞周期蛋白cyclin-dependent proteinkinases, CD K 细胞周期依赖性蛋白激酶cytochrome 细胞色素cytokinin 细胞分裂素cytomembrane systeme 膜系统cytoplasm 细胞质cytosine 胞嘧啶cytoskeleton 细胞骨架cytosol 胞液,细胞溶质Ddaughter chromosome 子染色体debris 碎片decipher 破译decomposer 分解者degenerate 变性degrade 使降解deletion 染色体的缺失denaturation 变性dendrite 树突deoxyribonucleic acid 脱氧核糖核酸deoxyribonucleic脱氧核糖核酸的deoxyribose 脱氧核糖deposition 沉积作用deprive 剥夺deprive 夺去derevative 衍生物desensitization脱敏现象,减感作用detergent 去垢剂deuterostome 后口动物development 发育,发展dextran 葡聚糖dialysis 透析,渗析diaphragm 横隔膜diastolic 心脏舒张的diatom 硅藻differential centrifugation差速离心differentiation 分化diffraction 衍射diffusion 扩散,渗滤digestive tract 消化道dihybrid 双因子杂种dilute 稀释dimensional 维,度,元dimer 二聚体dioxide 二氧化物dip 浸,蘸dipeptide 二肽diploid 二倍体的distort 变形,扭曲distortion 畸变,变形,失真divergence 分歧diverse vesicle 消化泡diversity 多样性,差异Docking protein, DP 停泊蛋白dodecyl 十二烷基dominant 显性的,显性性状donor 供体dormant 休眠的dorsal 背面的dorsal root ganglion背根神经节dorsal 背部的double helix 双螺旋duodenum 十二指肠duplicate 复制dynamic 动力学的,动态的dyneins 动力蛋白dysentery 痢疾Eearlobe 耳垂earthworm 蚯蚓echinoderm 棘皮动物ecological 生态学的ecosystem 生态系统ectoderm 外胚层ectotherm 冷血动物edoplasmic reticulum 内质网effector 效应器efferent 传出的egg 蛋,卵egg-laying mammals 卵生哺乳动物egret 白鹭,冠毛eject 排斥,逐出elaborate 精细制作的,复杂的elastic connective tissue 弹力结缔组织elastin 弹性蛋白electron 电子electrophoresis 电泳embryo 胚,胚胎embryogenesis 胚胎发生embryology 胚胎学embryonic 胚胎的emulsion 乳状液encephalitis 脑炎encode 编码endocrine 内分泌endocytic 细胞内吞作用endocytosis 胞吞作用endoderm 内胚层endomembrane systems内膜系统endoplasmic 内质的endoplasmic reticulum内质网endosome 内体endosperm胚乳endosymbiosis 内共生endothelial 内皮的endotherm 热血动物enucleate 去…。

模具专业术语(专业人士一定要收藏)模具工程常用词汇die 模具figure file, chart file图档cutting die, blanking die冲裁模progressive die, follow (-on)die 连续模compound die复合模punched hole冲孔panel board镶块to cutedges=side cut=side scrap切边to bending折弯to pull, to stretch拉伸Line streching, line pulling线拉伸engraving, to engrave刻印upsiding down edges翻边to stake铆合designing, to design设计design modification设计变化die block模块folded block折弯块sliding block滑块location pin定位销lifting pin顶料销die plate, front board模板padding block垫块stepping bar垫条upper die base上模座lower die base下模座upper supporting blank上承板upper padding plate blank上垫板spare dies模具备品spring 弹簧bolt螺栓plain die简易模pierce die冲孔模forming die成型模progressive die连续模gang dies复合模shearing die剪边模riveting die铆合模pierce冲孔forming成型(抽凸,冲凸)draw hole抽孔bending折弯trim切边emboss凸点dome凸圆semi-shearing半剪stamp mark冲记号deburr or coin压毛边punch riveting冲压铆合side stretch侧冲压平reel stretch卷圆压平groove压线blanking下料stamp letter冲字(料号) shearing剪断tick-mark nearside正面压印tick-mark farside反面压印冲压名称类stamping, press冲压punch press, dieing out press冲床uncoiler & strainghtener整平机feeder送料机rack, shelf, stack料架cylinder油缸robot机械手taker取料机conveyer belt输送带transmission rack输送架top stop上死点bottom stop下死点one stroke一行程inch寸动to continue, cont.连动to grip(material)吸料location lump, locating piece, block stop 定位块reset复位smoothly顺利dent压痕scratch刮伤deformation变形filings铁削to draw holes抽孔inquiry, search for查寻to stock, storage, in stock库存receive领取approval examine and verify审核processing, to process加工delivery, to deliver 交货to return delivenry to.to send delinery backto retrn of goods退货registration登记registration card登记卡to control管制to put forward and hand in提报safe stock安全库存acceptance = receive验收to notice通知application form for purchase请购单consume, consumption消耗to fill in填写abrasion磨损reverse angle = chamfer倒角character die字模to collect, to gather收集failure, trouble故障statistics统计demand and supply需求career card履历卡to take apart a die卸下模具to load a die装上模具to tight a bolt拧紧螺栓to looser a bolt拧松螺栓to move away a die plate移走模板easily damaged parts易损件standard parts标准件breaking.(be)broken,(be)cracked 断裂to lubricate润滑common vocabulary for die engineering extension dwg展开图procedure dwg工程图die structure dwg模具结构图material材质material thickness料片厚度factor系数upward向上downward向下press specification冲床规格die height range适用模高die height闭模高度burr毛边gap间隙weight重量total wt.总重量punch wt.上模重量五金零件类inner guiding post内导柱inner hexagon screw内六角螺钉dowel pin固定销coil spring弹簧lifter pin顶料销eq-height sleeves=spool等高套筒pin销lifter guide pin浮升导料销guide pin导正销wire spring圆线弹簧outer guiding post外导柱stop screw止付螺丝located pin定位销outer bush外导套模板类top plate上托板(顶板)top block上垫脚punch set上模座punch pad上垫板punch holder上夹板stripper pad脱料背板up stripper上脱料板male die公模(凸模)feature die公母模female die母模(凹模)upper plate上模板lower plate下模板die pad下垫板die holder下夹板die set下模座bottom block下垫脚bottom plate下托板(底板) stripping plate内外打(脱料板) outer stripper外脱料板inner stripper内脱料板lower stripper下脱料板零件类punch冲头insert入块(嵌入件)deburring punch压毛边冲子groove punch压线冲子stamped punch字模冲子round punch圆冲子special shape punch异形冲子bending block折刀roller滚轴baffle plate挡块located block定位块supporting block for location定位支承块air cushion plate气垫板air-cushion eject-rod气垫顶杆trimming punch切边冲子stiffening rib punch = stinger 加强筋冲子ribbon punch压筋冲子reel-stretch punch卷圆压平冲子guide plate定位板sliding block滑块sliding dowel block滑块固定块active plate活动板lower sliding plate下滑块板upper holder block上压块upper mid plate上中间板spring box弹簧箱spring-box eject-rod弹簧箱顶杆spring-box eject-plate弹簧箱顶板bushing bolck衬套cover plate盖板guide pad导料块塑件&模具相关英文compre sion molding压缩成型flash mold溢流式模具plsitive mold挤压式模具split mold分割式模具cavity型控母模core模心公模taper锥拔leather cloak仿皮革shiver饰纹flow mark流痕welding mark溶合痕post screw insert螺纹套筒埋值self tapping screw自攻螺丝striper plate脱料板piston活塞cylinder汽缸套chip细碎物handle mold手持式模具encapsulation molding低压封装成型two plate两极式(模具)well type蓄料井insulated runner绝缘浇道方式hot runner热浇道runner plat浇道模块valve gate阀门浇口band heater环带状的电热器spindle阀针spear head刨尖头slag well冷料井cold slag冷料渣air vent排气道h=0.02~0.05mmw=3.2mmL=3~5mmwelding line熔合痕eject pin顶出针knock pin顶出销return pin回位销反顶针sleave套筒stripper plate脱料板insert core放置入子runner stripper plate浇道脱料板guide pin导销eject rod (bar)(成型机)顶业捧subzero深冷处理three plate三极式模具runner system浇道系统stress crack应力电裂orientation定向sprue gate射料浇口,直浇口nozzle射嘴sprue lock pin料头钩销(拉料杆) slag well冷料井side gate侧浇口edge gate侧缘浇口tab gate搭接浇口film gate薄膜浇口flash gate闸门浇口slit gate缝隙浇口fan gate扇形浇口dish gate因盘形浇口H=F=1/2t~1/5tT=2.5~3.5mmdiaphragm gate隔膜浇口ring gate环形浇口subarine gate潜入式浇口tunnel gate隧道式浇口pin gate针点浇口Φ0.8~1.0mmRunner less无浇道(sprue less)无射料管方式long nozzle延长喷嘴方式sprue浇口;溶渣accurate die casting 精密压铸powder forming 粉末成形calendaring molding 压延成形powder metal forging 粉末锻造cold chamber die casting 冷式压铸precision forging 精密锻造cold forging 冷锻press forging 冲锻compacting molding 粉末压出成形rocking die forging 摇动锻造compound molding 复合成形rotary forging 回转锻造compression molding 压缩成形rotational molding 离心成形dip mold 浸渍成形rubber molding 橡胶成形encapsulation molding 注入成形sand mold casting 砂模铸造extrusion molding 挤出成形 shell casting 壳模铸造foam forming 发泡成形sinter forging 烧结锻造forging roll 轧锻six sidesforging 六面锻造gravity casting 重力铸造slush molding 凝塑成形hollow(blow) molding 中空(吹出)成形squeeze casting 高压铸造hot chamber die casting 热室压铸swaging 挤锻hot forging 热锻transfermolding 转送成形injection molding 射出成形warm forging 温锻investment casting 精密铸造matched die method 对模成形法laminating method 被覆淋膜成形low pressure casting 低压铸造lost wax casting 脱蜡铸造matched mould thermal forming 对模热成形模各式模具分类用语bismuth mold 铋铸模landed plungermold 有肩柱塞式模具burnishing die 挤光模 landed positivemold 有肩全压式模具button die 镶入式圆形凹模loading shoemold 料套式模具center-gated mold 中心浇口式模具loose detail mold 活零件模具chill mold 冷硬用铸模loose mold 活动式模具clod hobbing 冷挤压制模louveringdie 百叶窗冲切模composite dies 复合模具manifold die 分歧管模具counter punch 反凸模modular mold 组合式模具double stack mold 双层模具multi-cavity mold 多模穴模具electroformed mold 电铸成形模multi-gate mold 复式浇口模具expander die 扩径模offswt bendingdie 双折冷弯模具extrusion die 挤出模palletizing die叠层模family mold 反套制品模具plaster mold 石膏模blank through dies 漏件式落料模porous mold 通气性模具duplicated cavity plate 复板模positive mold 全压式模具fantail die 扇尾形模具pressure die 压紧模fishtail die 鱼尾形模具profile die 轮廓模flash mold 溢料式模具progressive die顺序模gypsum mold 石膏铸模protable mold 手提式模具hot-runner mold 热流道模具prototype mold 雏形试验模具ingot mold 钢锭模punching die 落料模lancing die 切口模raising(embossing)压花起伏成形re-entrant mold 倒角式模具sectional die 拼合模runless injection mold 无流道冷料模具sectional die 对合模具segment mold 组合模semi-positive mold 半全压式模具shaper 定型模套single cavitymold 单腔模具solid forging die 整体锻模split forging die 拼合锻模split mold 双并式模具sprueless mold 无注道残料模具squeezing die 挤压模stretch formdie 拉伸成形模sweeping mold 平刮铸模swing die 振动模具three plates mold 三片式模具trimming die 切边模unit mold 单元式模具universal mold 通用模具unscrewing mold 退扣式模具yoke type die 轭型模模具厂常用之标准零配件air vent vale 通气阀anchor pin 锚梢angular pin 角梢baffle 调节阻板angular pin 倾斜梢baffle plate 折流档板ball button 球塞套ball plunger 定位球塞ball slider 球塞滑块binder plate 压板blank holder 防皱压板blanking die 落料冲头bolster 上下模板bottom board 浇注底板bolster 垫板bottom plate 下固定板bracket 托架bumper block 缓冲块buster 堵口casting ladle 浇注包casting lug 铸耳cavity 模穴(模仁)cavity retainer plate 模穴托板center pin 中心梢clamping block 锁定块coil spring 螺旋弹簧cold punched nut 冷冲螺母cooling spiral 螺旋冷却栓core 心型core pin 心型梢cotter 开口梢cross 十字接头cushion pin 缓冲梢diaphragm gate 盘形浇口die approach 模头料道die bed 型底die block 块形模体die body 铸模座die bush 合模衬套die button 冲模母模die clamper 夹模器die fastener 模具固定用零件die holder 母模固定板die lip 模唇die plate 冲模板die set 冲压模座direct gate 直接浇口dog chuck 爪牙夹头dowel 定位梢dowel hole 导套孔dowel pin 合模梢dozzle 辅助浇口dowel pin 定位梢draft 拔模锥度draw bead 张力调整杆drive bearing 传动轴承ejection pad 顶出衬垫ejector 脱模器ejector guide pin 顶出导梢ejector leader busher 顶出导梢衬套ejector pad 顶出垫ejector pin 顶出梢ejector plate 顶出板ejector rod 顶出杆ejector sleeve 顶出衬套ejector valve 顶出阀eye bolt 环首螺栓filling core 椿入蕊film gate 薄膜形浇口finger pin 指形梢finish machined plate 角形模板finish machined round plate 圆形模板fixed bolster plate 固定侧模板flanged pin 带凸缘销flash gate 毛边形浇口flask 上箱floating punch 浮动冲头gate 浇口gate land 浇口面gib 凹形拉紧?goose neck 鹅颈管guide bushing 引导衬套guide pin 导梢guide post 引导柱guide plate 导板guide rail 导轨head punch 顶冲头headless punch 直柄冲头heavily tapered solid 整体模蕊盒hose nippler 管接头impact damper 缓冲器injection ram 压射柱塞inlay busher 嵌入衬套inner plunger 内柱塞inner punch 内冲头insert 嵌件insert pin 嵌件梢king pin 转向梢king pin bush 主梢衬套knockout bar 脱模杵land 合模平坦面land area 合模面leader busher 导梢衬套lifting pin 起模顶?lining 内衬locating centerpunch 定位中心冲头locating pilot pin 定位导梢locating ring 定位环lock block 压块locking block 定位块locking plate 定位板loose bush 活动衬套making die 打印冲子manifold block 歧管档块master plate 靠模样板match plate 分型板mold base 塑胶模座mold clamp 铸模紧固夹mold platen 模用板parallel block 平行垫块paring line 分模线parting lock set 合模定位器pass guide 穴型导板peened head punch 镶入式冲头pilot pin 导杆pin gate 针尖浇口plate 衬板pre extrusion punch 顶挤冲头punch 冲头puncher 推杆pusher pin 衬套梢rack 机架rapping rod 起模杆re-entrant mold 凹入模retainer pin 嵌件梢retainer plate 托料板return pin 回位梢riding stripper 浮动脱模器ring gate 环型浇口roller 滚筒runner 流道runner ejector set 流道顶出器runner lock pin 流道拉梢screw plug 头塞set screw 固定螺丝shedder 脱模装置shim 分隔片shoe 模座之上下模板shoot 流道shoulder bolt 肩部螺丝skeleton 骨架slag riser 冒渣口slide(slidecore) 滑块slip joint 滑配接头spacer block 间隔块spacer ring 间隔环spider 模蕊支架spindle 主轴sprue 注道sprue bushing 注道衬套sprue bushingguide 注道导套sprue lock bushing 注道定位衬套sprue puller 注道拉料spue line 合模线square key 方键square nut 方螺帽square thread 方螺纹stop collar 限位套stop pin 止动梢stop ring 止动环stopper 定位停止梢straight pin 圆柱销stripper bolt 脱料螺栓stripper bushing 脱模衬套stripper plate 剥料板stroke end block 行程止梢submarine gate 潜入式浇口support pillar 支撑支柱/顶出支柱support pin 支撑梢supporting plate 托板sweep templete 造模刮板tab gate 辅助浇口taper key 推拔键taper pin 拔锥梢/锥形梢teeming 浇注three start screw 三条螺纹thrust pin 推力销tie bar 拉杵tunnel gate 隧道形浇口vent 通气孔wortle plate 拉丝模板。

•血液净化护理专题•【摘要】 目的 对国内外用于评估血液透析患者皮肤瘙痒的工具进行范围综述,为临床护理工作者选择筛查血液透析患者皮肤瘙痒的评估工具提供参考。
方法 系统、全面地检索8个中英文数据库,检索时限为建库至2023年3月30日。
提取文献中血液透析患者皮肤瘙痒评估工具相关内容进行系统分析,并采用范围综述的方法对检索结果进行规范化报告。
结果 纳入25篇符合标准的文献,其中16篇关于评估工具的开发,9篇关于评估工具的运用。
结论 国内外关于血液透析患者皮肤瘙痒评估工具较缺乏,特别是适合本国血液透析患者皮肤瘙痒评估工具还需进一步开发。
【关键词】 血液透析;皮肤瘙痒;评估工具;范围综述;护理中图分类号R47 文献标识码A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-9676.2023.17.005血液透析患者皮肤瘙痒评估工具的范围综述基金项目:2022年度湖南省中医药科研计划项目(编号:D202203) ;2021年度湖南省中医药科研计划项目(编号:2021006);2020年湖南省学位与研究生教育改革研究项目(编号:2020JGZX011)作者单位:410208 湖南省长沙市,湖南中医药大学(徐玉娇,李铃佳),湖南中医药大学第一附属医院(陈青,吴秀丽),当代护士杂志社有限公司(曾维轲),湖南中医药高等专科学校(倪娟)第一作者:徐玉娇,本科(硕士在读)通信作者:吴秀丽,硕士徐玉娇 陈青 曾维轲 倪娟 李铃佳 吴秀丽Review of the scope of itchy skin assessment tools for haemodialysis patients XU Yujiao, CHEN Qing, ZENG Weike, NI Juan, LI Lingjia, WU Xiuli (Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Changsha, 410208, China)【Abstract 】 Objective To provide a scoping review of domestic and international tools for assessing skin itch in haemodialysis patients, and to provide a reference for clinical caregivers to select assessment tools for screening skin itch in haemodialysis patients. Methods Eight Chinese and English databases were systematically and comprehensively searched, with a time frame of 30 March 2023 for the construction of the databases. Literature related to assessment tools for itchy skin in haemodialysis patients was extracted for systematic analysis, and the search results were standardised and reported using a scoping review. Results 25 literature articles that met the criteria were included, of which 16 were on the development of assessment tools and 9 were on the use of assessment tools. Conclusion There is a lack of national and international assessment tools on skin itching in haemodialysis patients, and further development of skin itching assessment tools, especially those suitable for haemodialysis patients is needed.【Key words 】 Haemodialysis; Itchy skin; Assessment tools; Scope review; Nursing血液透析(hemodialysis,HD)是终末期肾脏疾病患者重要的治疗手段之一[1],患者在接受治疗过程中会出现各种并发症[2],瘙痒就是其中一种,它是一种皮肤或者黏膜的激惹症状[3-4],会导致患者产生负性情绪(焦虑、抑郁、激动)、疲劳以及睡眠障碍[5],严重影响患者的生存质量[6-7]。
•论著•超声引导下收肌管联合ipAck神经阻滞在膝关节置换术后镇痛中的应用研究*刘宇权,乌卩文伟,王军,曾志文,廖亿舞(梅州市人民医院麻醉科,广东梅州514031)[摘要]目的探讨超'引导下收肌管联合ipAck神经阻滞用于膝关节置换术后镇痛的临床效果$方法选取该院2018年2月至2019年12月该院收治的行膝关节置换术患者90例,随机分为对照组(45例)和观察组(45例),分别采用超'引导下收肌管阻滞和超'引导下收肌管联合ipAck神经阻滞方案行术后镇痛$比较两组术后48h疼痛数字评分法11(NRS)静态/动态评分曲线下面积(AUC)、麻醉药物使用情况[舒芬太尼使用量、静脉自控镇痛泵(PCIA)按压率)下床最多活动步数及主动屈膝最大角度$结果观察组术后48h NRS静态/动态评分AUC均显著低于对照组;舒芬太尼用量显著少于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)两组PCIA按压率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)观察组术后48h下床最多活动步数和主动屈膝最大角度均显著多于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)结论超'引导下收肌管联合ipAck神经阻滞用于膝关节置换术后镇痛可有效缓解患者术后疼痛程度,减少麻醉药物用量,并有助于改善患者早期活动功能$[关键词]超'&收肌管阻滞;ipAck神经阻滞;膝关节置换术;镇痛DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.202109.008中图法分类号:R614.3;R614.4文章编号:1009-5519(2021)09-1465-03文献标识码:AStudy on the application of adductor tube combined with ipAck nerve block under ultrasoundguidance in analgesia after knee arthroplasty*LIU Yuquan,WU Wenzvei,WANG Jun ZENG Zhixven LIAO Yiling(.Department of Anesthesiology^Meizhou People'Hospital■,Meizhou,Guangdong514031China') [Abstract]Objective To explore the clinical effect of adductor tube combined with ipAck nerve block under ultrasound guidance in analgesia after knee arthroplasty.Methods A total of90patients undergoing knee arthroplasty in the hospital from February2018to December2019were selected and randomly divided into control group(45cases)and observation group(45cases). AdduGtortubebloGkunderultrasoundguidanGeandadduGtortubeGombinedwithipAGknervebloGkultrasound-guidedwereadopt-ed for postoperative analgesia respectively.The Area under the curve(AUC)of static/dynamic score of numerical pain score11 (NRS),the use of anesthetics[the usage of sufentanil,the compression rate of intravenous patient-controlled analgesia pump(PICA)],the maximum number of steps to get out of bed,and the maximum angle of active knee flexion at48hours after the operation were compared between the two groups.Results The AUC of static/dynamic score of NRS at48h after operation in the observation group was significantly lower than that in the control group;the dosage of sufentanil in the observation group was significantly less than that in the control group,and the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).There was no significant di f erence in the compression rate of PCIA between the two groups(P>005)/The maximum number of steps to get out of bed and the maximum angle of active knee flexion in the observation group were significantly more than those in the control group at 48h after operation,and the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).Conclusion The use of adductor tube combined wihipAcknerveblockunderulrasoundguidanceforposDoperaDiveanalgesiaafDerkneearDhroplasDycane f ecivelyrelieveposDop-eraDivepainreduceDheamounDofanesDheicsandhelpimproveDhepaDienD'searly mobiliDy.[Key words]Ultrasound;Adductor tube block;ipAck nerve block;Knee replacement;Analgesia既往研究表明,股神经联合坐骨神经阻滞的术后镇痛效果良好,但对股四头肌肌力影响显著)12&收肌管阻滞尽管可提供与上述方法相似镇痛效果且不影响股四头肌肌力,但无法满足膝关节后方镇痛需求3&近年来,ipAck神经阻滞开始被用于解决膝关节后方疼痛,主要针对支配膝关节后方终末感觉支,主要包括腓总神经、胫神经和闭孔神经关节支,不影响腓总神经功能[45]&本研究以本院收治的行膝关节基金项目:广东省梅州市科技局科技计划项目(2018B017)&作者简介:刘宇权(1985—),本科,主治医师,主要从事心脏麻醉、区域神经阻滞等方面研究&置换术患者90例作为研究对象,分别采用超声引导下收肌管阻滞和超声引导下收肌管联合ipAck神经阻滞方案行术后镇痛,探讨超声引导下收肌管联合ipAck神经阻滞用于膝关节置换术后镇痛的临床效果,现报道如下&1资料与方法1.1一般资料选取本院2018年2月至2019年12月收治的行膝关节置换术患者90例,随机分为对照组和观察组,每组45例&纳入标准:(1)符合膝关节置换术指征[6];(2)美国麻醉医师协会(ASA)分级1〜/级;(3)单侧膝关节病变;(4)首次手术。
1、The earliest known native language of England is ________.1. Celtic2. Scottish3. Saxon4. Anglian2、In the 19th century, gold was first ________ in California.1. incovered2. recovered3. uncovered4. discovered3、Which of the following word is NOT a compound?()1. darkroom2. wet day3. small talk4. hot dog4、“ex-” in ex-husband reads ________ and means ________.1./Iks/, “former”2./eks/, “former”3./Iks/, “out”4./eks/, “out”5、My sister lives 1000 miles away from us, so I only got to see her ________.1. once in a blue moon2. one time in a blue moon3. one time in a moon4. once in a moon6、In the Early Modern English Period, ________ exerted the greatest influence(s) on English.1. Chinese2. Latin and Greek3. German4. French7、— Does Tom smoke?— No. He is a _______.1. unsmoker2. nonsmoker3. dissmoker4. insmoker8、Words such as priest, bishop, monk, nun, candle, etc. are of ________ origin.1. Russian2. Indian3. Latin4. Greek9、Which of the following words has gone through the semantic change of pejoration?()1. queen2. nice3. vulgar4. picture10、Which one of the following abbreviations means “and so on”?()1. e.g.2. i.e.3. viz.4. etc.11、I’ll never buy a car, for it will only be a _________ to me.1. hatched egg2. fly in the ointment3. white elephant4. sleeping dog12、We’ve all experienced unpleasant moments at which we have to _______.1. chew the bullet2. bite the bullet3. bite bullets4. munch the bullet13、My husband is extremely ________, while I am extremely ________.1. long-sighted, short-sighted2. long-sight, short-sight3. long-sights, shot-sights4. long-sighting, short-sighting14、I will take this $260 for now. ________.1. D. A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush2. A bird in the hand is worth two in the wood3. A bird in the hand is worth two in the jungles4. A bird in hand is worth two birds in forest15、If they _______ our offer, we will ________ their goods.1. refuse, reject2. reject, refuse3. reject, reject4. refuse, refuse16、In “Tom’s family keep a good table”, the word table means ________.1. food and drinks served at meals2. none of the above3. people assembled around a table, as at meals4. the piece of furniture with a flat horizontal surface supported by one or more vertical legs 17、It is in the ________ that English became regularized and standardized.1. Late Modern English Period2. Middle English Period3. borrowing processes of Greek element4. Early Modern English Period18、The antonym of “fresh” in “fresh bread” is ________.1. faded2. stale3. tired4. stuffy19、American women were ________ the right to vote until 1920 after many years of hard struggle.1. refused2. ignored3. neglected4. denied20、Contrary ________ public opinion, this area has long been a heaven for all forms of insect life.1. for2. with3. to4. at21、John turns his nose ________ Ann, which hurt her a lot.1. up at2. at3. on4. upon22、It is its ________ that makes Old English fundamentally different from Modern English.1. pronunciation2. spelling3. meaning4. grammar23、Mrs. Smith is afraid that she and her husband don’t see ________ on New Year Resolutions.1. eye to eye2. heart to heart3. face to face4. back to back24、John complained that there were several pages ________.1. missing2. leaking3. losing4. dropping25、We saw a(n) ________ of how to revive a person who has been almost drowned.1. F. demonstration2. spectacle3. exhibition4. show判断题26、Old English is a non-inflectional language.1. A.√2. B.×27、There is no possibility for the word over to be used as a noun.1. A.√2. B.×28、Conceptual meaning of a word is generally context sensitive.1. A.√2. B.×29、The word nice has gone through a semantic change called “generalization”.1. A.√2. B.×30、Connotative meaning of a word is relatively stable and insensitive to the change of context.1. A.√2. B.×31、AmE and BrE shares all grammatical rules.1. A.√2. B.×32、Comparatively speaking, ask is more formal than interrogate.1. A.√2. B.×33、“Pragmatic meaning”can also be referred to as “contextual meaning”.1. A.√2. B.×34、In the sentence, “More hands are needed on the farm”, metonymy is employed.1. A.√2. B.×35、The word safe means the same in The child is safe and The beach is safe.1. A.√2. B.×36、Lexical semantics is not only a subset of lexicology, but also a subset of semantics.1. A.√2. B.×37、Answering the question “Will you marry me?”with “Yes, I will”, the speaker is using substitution.1. A.√2. B.×38、In the English vocabulary, foreign elements made up a much bigger part in number than the native elemen1. A.√2. B.×39、-ed in short-sighted is an inflectional morpheme.1. A.√2. B.×40、Among the four words accepting, accepted, acceptance and acceptable, the first two are derived from deriva1. A.√2. B.×41、The vocabulary of any language never remains stable; it is constantly changing.1. A.√2. B.×42、Hyperbole has the effect of weakening the meaning of words.1. A.√2. B.×43、According to cognitive semantics, our mind can be explored via the study of linguistic meanings.1. A.√2. B.×44、de-urbanization is a word composed of 5 morphemes, all of which are bound ones.1. A.√2. B.×45、For an English word, the shift of stress may indicate a change of part of speech; export is a perfect exampl1. A.√2. B.×主观题46、type参考答案:Type is the general kind of a word as listed in a dictionary. For example, “A boy saw a cat fight with a dog yesterday”may b based on type, according to the definition of which, “a”is used three times as the definite article and thus should be counted to which, each appearance of “a”should be recognized as a word.47、blending参考答案:Blending refers to process of making a new word by combining parts of two or more words. For example, the word “brunc48、meronymy参考答案:Meronymy refers to the part-whole sense relationship. For example, the word “body”and “head”, “arm”, “leg”, etc. have a “meronymy”.49、context of situation参考答案:Context of situation refers to the immediate environment of the text.50、specialization参考答案:Specialization refers to process where by a word of wide meaning acquires a narrow or specialized sense. For example, “bre means “the type of food made from flour, water and yeast mixed together and baked.”51、generalization参考答案:Generalization refers to the extension of the word range, or the widening of the semantic scope. For example, “manuscript semantic scope has been widened to be “a copy of a book, a piece of music,etc. before it has been printed”.52、polysemy参考答案:Polysemy refers to semantic phenomenon where a single word or phrase has several meanings. For example, “show” means noun and it means quite differently when it is used as a verb.53、dictionary meaning参考答案:dictionary meaning: Dictionary meaning is also called “inherent meaning”. It refers to the meaning of words out of context, its dictionary meaning of “adult”, “unmarried”and “male”. In contrast, other related meanings related to unmarried man, su not dictionary meaning of bachelor, thus, are not listed as its meanings in dictionaries.54、What is the structural invariability of idioms? Are there any variants for this characteristics?参考答案:An English idiom has the established form, one that has been accepted by traditional usage. The words in idiomatic expressi synonymous words, or put in a different order, without affecting or destroying the figurative meaning. The following examp idioms. The structural invariability can be observed by the following two examples:See the structural invariability with a comparison between the following two sentences:*I expected him to kick the bucket and kick it he did.I asked him to write a letter to my aunt, but not to write it in English.To sum up, the structural invariability of an English idiom is at least two-fold in sense. In the first place, it implies that Engl are reproduced in speech as ready-made units; secondly, unlike free phrases which may vary according to the needs of comm reproduced as a single unchangeable collocation.But, idioms do have seven types of variants:1) Variants differing in inflection: Inflectional information for English idioms is identical to that of non-idiomatic or lexical Verbal idioms can occur in a variety of tenses, e.g. Royal housekeeper spills the beans.Nouns involved in idioms may be either singular or plural, e.g. There is an inherent fear that inflation is going to rear its h2) Open slots: Some idioms have open slots into which any noun phrase (NP) can be inserted to meet the requirements of the.g. see NP through: to understand, realize the true nature of …We saw through his superficial charm: he was obviously a liar.3) Modification: parts of some English idioms are syntactically modifiable,e.g. call the shots: to decide on the course of action, to be in chargeWhy do you have to call all the shots? Do what you’re told. It is up to the boss to call the final shots.4) Passive: many idioms can appear separated from each other in passive constructionse.g. to turn the table on sb.: to suddenly take a position of strength or advantage that was formerly held by someone else5) Topicalization: The topic is the part of the proposition that is being talked about or predicated. Topicalization refers to thee.g. to pull strings: to use one’s influen ce over important people in order to get something or to help someoneThose strings, he wouldn’t pull for you.6) Distribution over several clauses: parts of some English idioms can be spread over a main clause and a subordinate clausee.g. a mold that badly need breakingthe United States is trying to regain face that was lost when President Clinton backed down last year.7) Incomplete idioms: Some English idioms can be recognized even when only parts of them are present.e.g. Count one’s chi ckens before they are hatched.55、What is a word?参考答案:A word can be simple defined as the minimal meaningful free unit of language. This definition is to be understood in the fro1) A word is the sound unit of language.(1) A word is a sound unit (or unit of speech) for the purpose of communication. In this sense, a word sound in nature and Even the first word uttered by a baby is for communication.(2) A word is a sound cluster conventionally sequenced. In this sense, the order of sound elements in a word is fixed and a word /ɡəu/, the sequence /ɡ/must precede /əu /, otherwise, it is not the word “go” at all.(3) A word is a combination of sound and meaning according to the conventions of specific languages. For example, the so Chinese.2) A word is the smallest free form of language.(1) Words are free forms of a language, i.e., forms that can be moved without destroying the grammaticality of the sentenc “Bill” can all move freely and each sentence is grammatically correct.(2) In contrast, the letters that form a word are fixed with rigid sequential order. A word is the smallest free form of langua or even its status as a word. For example, only “John”is a boy’s name, but not “Jonh”, “Jhon”, “Jhno”or “Joan”.3) A word is the building block for phrase and sentence.When separated from the phrase, sentence or passage, a word will be difficult to understand since it is no more than a “dead passages are contexts for the interpretation of words. In sum, words are the building blocks out of which phrases and senten56、Brave it out, no matter how difficult it is.参考答案:无论那有多困难,你都应勇敢面对。
第42卷第6期2021年11月Vol.42No.6November2021中山大学学报(医学科学版)JOURNAL OF SUN YAT⁃SEN UNIVERSITY(MEDICAL SCIENCES)中国南方地区亨廷顿患者不同运动分型的临床特征林丽山1,苏凤娟1,吴腾腾2,曾译萱3,尤桦菁1,陈定邦1,李洵桦1,裴中1(1.中山大学附属第一医院神经科,广东广州510080;2.复旦大学附属中山医院神经内科,上海200032;3.深圳市第二人民医院神经内科,广东深圳518035)摘要:【目的】探讨中国南方地区亨廷顿病患者不同运动分型的临床特征,便于个体化精准治疗。
【方法】纳入自2014年3月至2021年5月在中国亨廷顿病协作网广州中心登记的亨廷顿病患者58例,利用亨廷顿舞蹈症整体评估量表对患者进行运动分型,精神状态、认知功能以及全面生活能力测试,最后利用Kruskal-Wallis H检验方法对不同分型患者各组临床特征进行分析。
【结果】中国南方地区亨廷顿患者运动分型以混合型为主,共42例,占比72.41%。
不同分型临床特征不同,运动机能减退-僵硬为主型患者全面生活能力低于舞蹈症状为主型患者[8.00(4.00~11.00)vs13.00(11.00~13.00);P=0.037]。
【结论】中国南方地区亨廷顿患者运动症状复杂。
精准的运动分型,对药物治疗与预后评估有一定的意义。
关键词:亨廷顿病;运动分型;药物治疗;预后评估中图分类号:R441文献标志码:A文章编号:1672-3554(2021)06-0944-06DOI:10.13471/ki.j.sun.yat-sen.univ(med.sci).2021.0618Clinical Characteristics of Different Motor Phenotypes in Patients with Huntington’sDisease in Southern ChinaLIN Li-shan1,SU Feng-juan1,WU Teng-teng2,ZENG Yi-xuan3,YOU Hua-jing1,CHEN Ding-bang1,LI Xun-hua1,PEI Zhong1(1.Department of Neurology,The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University,Guangzhou510080,China;2.De⁃partment of Neurology,Zhongshan Hospital of Fudan University,Shanghai200032,China;3.Department of Neurology,Shenzhen Second People's Hospital,Shenzhen518035,China)Correspondence to:PEI Zhong;E-mail:peizhong@Abstract:【Objective】To explore clinical characteristics of different motor phenotypes in patients with Huntington’s disease in southern China for individualized precise treatment.【Method】A total of58Huntington’s disease(HD)patients were enrolled from Guangzhou Center of Chinese Huntington’s Disease Network(CHDN)from March2014to May2021.United Huntington’s Disease Rating Scale(UHDRS)was used to assess patients’motor function,mental state,cognition and total functional capacity(TFC).The differences of clinical characteristics among different motor phenotypes were ana⁃lyzed by Kruskal-Wallis test.【Results】In southern China,HD patients showed a predominant mixed-motor phenotype,with72.41%(42/58)of all cases.The clinical characteristics among different motor phenotypes were different,and the TFC score in hypokinetic-rigidity phenotype was lower than that in choreatic motor phenotype[8.00(4.00~11.00)vs13.00(11.00~13.00),P=0.037].【Conclusion】The symptoms of movement disorders in HD patients in southern Chinaare complex.The precise classification of motor phenotype is helpful for the treatment and prognosis of HD.Key words:Huntington’s disease;motor phenotype;treatment;prognosis[J SUN Yat⁃sen Univ(Med Sci),2021,42(6):944-949]·临床研究·收稿日期:2021-07-12基金项目:国家重点研发计划项目(2017YFA0105104);广州市民生科技攻关计划项目(201803010092)作者简介:林丽山,学士,硕士生,研究方向:神经退行性疾病的临床与基础研究,E-mail:linlsh6@;苏凤娟,共同第一作者,学士,护理师,研究方向:神经退行性疾病的临床研究,E-mail:jisufengjuan@;裴中,通信作者,博士,研究员,研究方向:神经退行性疾病的临床与基础研究,E-mail:peizhong@第6期林丽山,等.中国南方地区亨廷顿患者不同运动分型的临床特征亨廷顿病(Huntington’s disease,HD)是一种常染色体显性遗传的神经退行性疾病,发病率极低,亚洲人群中发病率约为百万分之五[1]。